Generic Genome Browser: General Help
These are general instructions for using the Generic Genome Browser.
This page should be customized by the administrator of this resource
to describe site-specific features.
 To select a region of the genome to view, enter its name in the text
field labeled "Landmark or Region". Recognized types of names are
under the control of the administrator, but usually the following
names are accepted:
To select a region of the genome to view, enter its name in the text
field labeled "Landmark or Region". Recognized types of names are
under the control of the administrator, but usually the following
names are accepted:
- a chromosome name
- For genomes that have been assembled into chromosome-length
segments, you can enter the name of the chromosome. The
chromosome name follows the conventional nomenclature for the
species. For example, C. elegans chromosomes are
indicated using roman numerals, such as III,
D. melanogaster uses chromosome arms such as 2L and 2R,
while H. sapiens uses arabic numbers such as 9.
- a gene name
- You can enter the name of a gene using the standard nomenclature
for that species.
- a contig or clone name
- You can enter the name of a structural landmark such as a
cosmid, BAC or contig.
- an accession number
- You can enter a GenBank or EMBL accession number.
- protein names, primer names, ORF IDs, author names...
- At the discretion of the administrator of the database, other
identifiers can be entered. See the examples listed at the
top of the browser page for hints.
The Overview and Detail Panels
If the landmark is found in the database, the browser will display the
region of the genome it occupies. The region is displayed in two
graphical panels:
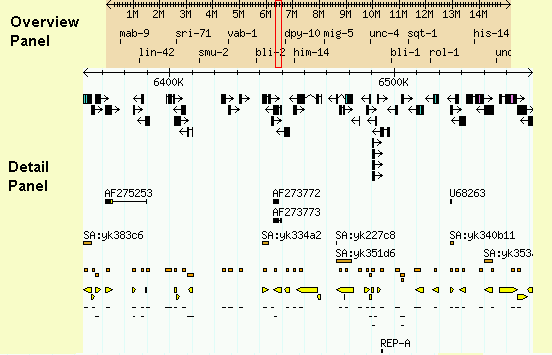
- overview panel
- This panel displays the genomic context, typically an entire
assembled chromosome or a large portion of the sequence
assembly such as a scaffold or contig. At the administrators'
discretion, certain important landmarks, such as a well-known
genetic markers or cytogenetic bands can be placed in this view.
A red rectangle indicates the region of the genome that is
displayed in the detail panel. This rectangle may appear as
a single line if the detailed region is relatively small.
- detail panel
- This panel displays a zoomed-in view of the genome corresponding
to the overview's red rectangle. The detail panel consists of
one or more tracks showing annotations and other features that
have been placed on the genome. The detail panel is described
at length later.
If the requested landmark is not found, the browser will display a
message to this effect.
Specifying the Landmark Class
At the administrator's option, some kinds of landmarks may have to be
qualified with their "class" using the format class:landmark.
For example, to look up the PCR product sjj_K08A8.1 in the
C. elegans database, you will search for
PCR_Product:sjj_K08A8.1.
In the case of clashes between names, such as a contig and a gene both
named c23, you can use the name class to specify which landmark you
mean.
- "name
- CDS
- Gene
- GMap
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|1357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1539|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2210|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|735nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000001|aap-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000002|aat-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000003|aat-2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000003|aat-2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000003|aat-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000003|aat-2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000003|aat-2|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=756|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000004|aat-3|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000004|aat-3|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000004|aat-3|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2003|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000004|aat-3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000004|aat-3|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000005|aat-4|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000005|aat-4|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000005|aat-4|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=587|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000005|aat-4|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000006|aat-5|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00000007|aat-6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000008|aat-7|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000009|aat-8|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000009|aat-8|574nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000009|aat-8|578nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000009|aat-8|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000009|aat-8|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00000010|aat-9|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000010|aat-9|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000010|aat-9|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=736|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000010|aat-9|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000010|aat-9|469nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000012|abf-1|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000012|abf-1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=216|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000013|abf-2|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000013|abf-2|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000013|abf-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000013|abf-2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1134|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000013|abf-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000013|abf-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000013|abf-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000014|abf-3|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00000014|abf-3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00000015|abf-4|1429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000015|abf-4|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000016|abf-5|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000016|abf-5|1410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000016|abf-5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=662|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000016|abf-5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1069|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000016|abf-5|840nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000017|abf-6|1148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000017|abf-6|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000017|abf-6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000017|abf-6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1275|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000017|abf-6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000017|abf-6|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000018|abl-1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000018|abl-1|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000018|abl-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1095|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000018|abl-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000018|abl-1|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000019|abt-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000019|abt-1|223nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000019|abt-1|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000019|abt-1|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=782|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000020|abt-2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000022|abt-4|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000022|abt-4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000022|abt-4|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000022|abt-4|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000023|abt-5|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000023|abt-5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000023|abt-5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2784|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000024|abu-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000025|abu-2|1149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000025|abu-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000026|abu-3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000027|abu-4|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000027|abu-4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000028|abu-5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000029|abu-6|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000029|abu-6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1457|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000029|abu-6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000030|abu-7|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000030|abu-7|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1144|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000030|abu-7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000031|abu-8|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000031|abu-8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000031|abu-8|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000031|abu-8|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000031|abu-8|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2540|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000031|abu-8|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|1069nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|1245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|1500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=771|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000032|abu-9|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000033|abu-10|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2108|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000033|abu-10|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000033|abu-10|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=99|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000033|abu-10|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000033|abu-10|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000033|abu-10|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000033|abu-10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000034|abu-11|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000034|abu-11|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000034|abu-11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000034|abu-11|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1186|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000034|abu-11|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1366|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000034|abu-11|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000034|abu-11|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000035|ace-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000035|ace-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000035|ace-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000035|ace-1|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000035|ace-1|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000035|ace-1|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000035|ace-1|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000036|ace-2|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000036|ace-2|840nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=744|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000036|ace-2|844nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000036|ace-2|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000036|ace-2|939nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000036|ace-2|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000037|ace-3|294nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000037|ace-3|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000037|ace-3|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000037|ace-3|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000037|ace-3|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000037|ace-3|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000038|ace-4|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=677|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000039|acn-1|409nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5508|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000040|aco-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|1504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2711|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13999|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=797|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000041|aco-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|1395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2113|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=398|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|964nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000042|acr-2|966nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=364|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=191|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000043|acr-3|47nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000044|acr-5|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000044|acr-5|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000045|acr-6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000045|acr-6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000046|acr-7|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000046|acr-7|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000047|acr-8|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000047|acr-8|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000048|acr-9|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000049|acr-10|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000049|acr-10|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000049|acr-10|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000049|acr-10|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000050|acr-11|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000050|acr-11|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000050|acr-11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000050|acr-11|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000050|acr-11|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=525|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2890|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000051|acr-12|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000053|acr-14|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000053|acr-14|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000053|acr-14|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000053|acr-14|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000053|acr-14|801nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000053|acr-14|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000053|acr-14|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1368|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000054|acr-15|1052nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000054|acr-15|1058nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000054|acr-15|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2649|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000055|acr-16|240nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000055|acr-16|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000055|acr-16|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000055|acr-16|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1144|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00000055|acr-16|351nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000055|acr-16|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000056|acr-17|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000056|acr-17|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000056|acr-17|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000056|acr-17|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000057|acr-18|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000057|acr-18|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000057|acr-18|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000057|acr-18|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=847|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000057|acr-18|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000058|acr-19|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000058|acr-19|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000058|acr-19|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000058|acr-19|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000058|acr-19|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000058|acr-19|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000058|acr-19|764nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000059|acr-20|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000059|acr-20|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000060|acr-21|961nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000060|acr-21|963nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000060|acr-21|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000060|acr-21|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000061|lgc-11|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000062|acr-23|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00000062|acr-23|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1056|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=403|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1563|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40658|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24038|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1988|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000063|act-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13066|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33944|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=304|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12838|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=383|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=513|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|719nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000064|act-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|1184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=617|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2141|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4976|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17733|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222001|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8840|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|463nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|495nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000066|act-4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11554|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21263|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000067|act-5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|206nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1400|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000068|acy-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000069|acy-2|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=518|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000069|acy-2|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000069|acy-2|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000069|acy-2|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000069|acy-2|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000069|acy-2|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000069|acy-2|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=388|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000070|acy-3|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000070|acy-3|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000070|acy-3|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=329|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000070|acy-3|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=363|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000071|acy-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000072|add-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000072|add-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000072|add-1|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000072|add-1|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=482|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000072|add-1|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000072|add-1|343nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000073|add-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000073|add-2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000073|add-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1888|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|181nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=955|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=646|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000074|adm-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=330|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|449nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|452nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|454nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|456nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000075|adm-4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1658|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=848|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|241nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000079|adr-1|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5144|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000080|adr-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000081|ads-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4338|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000081|ads-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000081|ads-1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000083|adt-2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000083|adt-2|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=618|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000083|adt-2|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000083|adt-2|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000083|adt-2|616nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000083|adt-2|620nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000083|adt-2|622nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000084|aex-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000084|aex-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000084|aex-1|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000084|aex-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000084|aex-1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000085|aex-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000085|aex-2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=958|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000085|aex-2|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000085|aex-2|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000085|aex-2|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|1334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|152nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|160nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1690|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000086|aex-3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000088|aex-5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|1364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|1367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=309|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|256nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|259nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1370|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1391|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000089|aex-6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1314|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000090|age-1|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|316nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=584|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|344nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|353nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11025|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000092|ags-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=657|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|741nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000093|agt-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=766|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2036|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=941|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=376|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000094|agt-2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1148|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|658nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000095|aha-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000096|ahr-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000096|ahr-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000096|ahr-1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000096|ahr-1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=766|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000096|ahr-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000096|ahr-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000096|ahr-1|759nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3136|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154602|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=927|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|630nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000097|aip-1|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=302|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7267|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|389nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000098|air-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1841|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000099|air-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|1461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=381|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|287nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|294nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1146|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=410|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1013|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000100|ajm-1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|1063nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|1252nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1234|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4662|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|766nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000101|aka-1|814nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|172nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=187|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|179nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|186nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|395nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8399|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|433nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|438nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|442nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000102|akt-1|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|403nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|405nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|409nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1357|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000103|akt-2|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|1216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|1318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|1551nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2064|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|1559nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000105|alg-1|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|1406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|1409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|1412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=916|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000106|alg-2|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=474|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|135nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|137nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|145nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|148nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|1519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|151nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|155nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|561nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|566nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|569nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1855|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2875|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000107|alh-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=309|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000108|alh-2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000108|alh-2|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|1271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2318|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000109|alh-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=957|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000110|alh-4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7440|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000111|alh-5|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000111|alh-5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000111|alh-5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000111|alh-5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000111|alh-5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000112|alh-6|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000112|alh-6|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5048|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000112|alh-6|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000112|alh-6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000112|alh-6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000112|alh-6|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000113|alh-7|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000113|alh-7|1290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000113|alh-7|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000113|alh-7|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000113|alh-7|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000113|alh-7|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1067|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12095|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7489|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8950|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4264|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000114|alh-8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|1165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|1176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3280|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=649|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000115|alh-9|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000116|alh-10|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000116|alh-10|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000116|alh-10|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1195|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00000116|alh-10|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000117|alh-11|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000117|alh-11|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2803|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000117|alh-11|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=682|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000117|alh-11|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000117|alh-11|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=777|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=707|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000118|alh-12|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000120|aly-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000120|aly-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000120|aly-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000120|aly-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1538|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00000120|aly-1|875nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000120|aly-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1121|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000120|aly-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=465|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2324|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000121|aly-2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7621|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|194nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4408|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7687|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=591|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000122|aly-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8021|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|657nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=147|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|660nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000123|ama-1|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000133|amt-1|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=150|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000134|amt-2|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=568|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000135|amt-3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000135|amt-3|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=920|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000135|amt-3|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=935|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|378nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000136|amt-4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000137|amx-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000137|amx-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000137|amx-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000137|amx-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000138|amx-2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=866|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|41nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=268|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000139|amx-3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000140|anc-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000140|anc-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000140|anc-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000140|anc-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000140|anc-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3324|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000140|anc-1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000140|anc-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=550|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4109|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000142|aos-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000143|apc-2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000143|apc-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000143|apc-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000143|apc-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000143|apc-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000143|apc-2|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1156|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000144|apc-10|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000144|apc-10|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000144|apc-10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000144|apc-10|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000144|apc-10|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2839|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00000144|apc-10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000144|apc-10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|101nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1267|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|105nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=68|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=852|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|199nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|951nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000145|apc-11|95nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=356|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|409nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4862|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000146|ape-1|422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=977|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00000147|aph-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000147|aph-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000147|aph-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000147|aph-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2923|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000147|aph-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000147|aph-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3393|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000148|aph-2|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3350|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=610|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|526nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|529nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|532nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|535nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1218|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1980|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15000|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=672|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1095|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=830|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|690nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000149|apl-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|302nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1283|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000150|apm-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2205|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000151|apn-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000155|app-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000155|app-1|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6822|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000155|app-1|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000155|app-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000155|app-1|534nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1802|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000156|apr-1|393nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=640|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1317|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1394|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|173nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000157|aps-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|1196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|435nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1027|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1049|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000158|apg-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=809|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3690|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|146nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|149nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000159|aps-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=271|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2886|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000160|apb-1|910nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|471nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3392|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|474nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|477nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|496nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=316|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|505nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|509nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|517nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|549nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|553nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000161|apa-2|927nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=629|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000162|apd-3|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1153|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2716|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000163|apb-3|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|1097nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3938|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|289nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|294nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000164|apm-3|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|884nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|888nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=313|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|891nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1959|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|895nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|943nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|951nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|968nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|972nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000165|aps-3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=326|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1380|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|349nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000166|apt-9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1472|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=860|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000168|apx-1|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000169|aqp-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=552|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6863|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=620|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|320nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=132|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000170|aqp-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000171|aqp-3|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000171|aqp-3|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00000171|aqp-3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000172|aqp-4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1190|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000172|aqp-4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000172|aqp-4|1288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000173|aqp-5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00000173|aqp-5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000173|aqp-5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000174|aqp-6|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=230|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1405|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34517|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=511|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3913|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000175|aqp-7|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1036nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1040nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1044nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=262|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1057nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1060nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1064nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=844|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=802|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|965nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000176|aqp-8|967nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=301|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|680nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000177|aqp-9|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1419|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1332|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000178|aqp-10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000179|aqp-11|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000179|aqp-11|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000179|aqp-11|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=630|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000179|aqp-11|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1776|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000179|aqp-11|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000180|arc-1|676nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000180|arc-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000180|arc-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1636|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000180|arc-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000180|arc-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4222|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5600|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=497|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000181|ard-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2112|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=506|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11272|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1641|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2163|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000182|arf-1.2|706nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2600|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|381nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2191|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|385nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2177|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8785|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|399nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6310|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|473nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000183|arf-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=697|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|505nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=761|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|511nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=547|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|516nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000184|arf-6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|386nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|391nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1259|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|395nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|399nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000186|ark-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|1384nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|358nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|360nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|366nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=233|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|374nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|377nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|382nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|386nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|390nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|408nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|418nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3370|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|424nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000187|arl-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|1595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7968|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000188|arl-3|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|1056nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|1063nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|1070nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|1074nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|1079nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|1086nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|1119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1518|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=189|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|955nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|979nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1134|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000189|arl-5|991nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000190|arf-1.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000190|arf-1.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000190|arf-1.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000190|arf-1.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3333|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000190|arf-1.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000190|arf-1.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=592|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000190|arf-1.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|1021nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=501|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6140|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=877|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1810|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|479nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=218|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|483nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|491nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|493nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000192|arl-8|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000193|arl-6|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000193|arl-6|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000193|arl-6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000193|arl-6|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000193|arl-6|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000195|arr-1|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2256|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000195|arr-1|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000195|arr-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000195|arr-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=779|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000196|aars-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=468|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12722|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000197|aars-2|474nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17172|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=669|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000198|art-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|309nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5404|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|326nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000199|arx-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=492|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1009|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=169|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3322|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1683|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000200|arx-2|836nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=471|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=690|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=578|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=608|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3551|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000201|arx-3|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|1028nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|1030nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=615|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|1035nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|1038nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=839|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|1046nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000202|exos-4.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=637|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=330|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1087|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=662|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|885nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|889nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000203|arx-5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3969|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000204|arx-6|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2965|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000205|arx-7|684nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12907|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1486|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000206|asb-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=936|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3263|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1083|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=391|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8828|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3795|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000207|asb-2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000208|asc-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000208|asc-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000208|asc-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5274|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000208|asc-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|71nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18148|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=792|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000209|asg-1|87nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=769|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3850|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=413|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000210|asg-2|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1319|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00000211|asm-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000211|asm-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000211|asm-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000211|asm-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000211|asm-1|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000212|asm-2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000212|asm-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000212|asm-2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000212|asm-2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000212|asm-2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000213|asm-3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000213|asm-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=803|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000213|asm-3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48432|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30850|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1904|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1088|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000214|asp-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|1376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1951|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19867|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2511|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=305|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000215|asp-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=453|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=703|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17759|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19504|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6699|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1815|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000216|asp-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3702|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=749|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=659|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000217|asp-4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22422|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23172|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=861|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000218|asp-5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5042|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16746|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29444|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8320|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3118|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000219|asp-6|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000220|atf-2|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000220|atf-2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000220|atf-2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00000220|atf-2|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=852|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000220|atf-2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000220|atf-2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=240|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12810|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=527|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000221|atf-5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000222|atf-6|1139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000222|atf-6|624nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00000222|atf-6|629nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=211|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000222|atf-6|632nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=469|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000222|atf-6|638nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=187|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000222|atf-6|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1002nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1015nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1024nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5408|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3495|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|1574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|833nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|840nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|852nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1814|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000223|atf-7|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8987|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=492|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000224|atgp-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000225|atgp-2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000225|atgp-2|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000225|atgp-2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000225|atgp-2|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000225|atgp-2|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1662|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000225|atgp-2|455nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000225|atgp-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000226|atl-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2701|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000226|atl-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000226|atl-1|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000226|atl-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000226|atl-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000227|atm-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000227|atm-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000227|atm-1|429nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000227|atm-1|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000227|atm-1|442nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000227|atm-1|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000227|atm-1|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2428|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2325|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000228|atn-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1132|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1424|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20810|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19302|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=948|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6128|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37699|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|311nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|320nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11259|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11233|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1175|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000229|atp-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|1364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|1500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37957|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1567|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=555|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000230|atp-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8305|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1496|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000231|atx-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|1280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|1493nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|1495nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2135|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1457|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|987nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|989nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000232|avr-14|994nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=537|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=859|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000233|avr-15|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|1105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|1124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|1483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=577|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17596|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3825|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000235|baf-1|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|1327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|149nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=43|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1638|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1380|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000236|bag-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000237|bam-2|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1131|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000237|bam-2|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000237|bam-2|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000237|bam-2|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000238|bar-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000238|bar-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000238|bar-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000238|bar-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1878|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000239|bas-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000240|pah-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000240|pah-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3271|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000240|pah-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000240|pah-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000240|pah-1|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=328|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000241|bbs-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000242|bbs-2|20nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000242|bbs-2|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000242|bbs-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000242|bbs-2|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000242|bbs-2|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=786|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2050|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000244|bbs-8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=177|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2664|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=184|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=273|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000245|bca-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000246|bcc-1|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000246|bcc-1|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000246|bcc-1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000246|bcc-1|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000246|bcc-1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000246|bcc-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2460|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000247|bec-1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=525|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=369|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|631nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1072|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|638nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1954|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|640nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1707|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|643nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=279|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|645nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000248|ben-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1243|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=982|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6849|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000249|bir-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3016|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000250|bir-2|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1572|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00000250|bir-2|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000250|bir-2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=797|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00000250|bir-2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000251|bli-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00000251|bli-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=938|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000251|bli-1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=319|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4793|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=232|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000252|bli-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000253|bli-3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000253|bli-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000253|bli-3|1384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000253|bli-3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=422|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000253|bli-3|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000253|bli-3|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000253|bli-3|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1165|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1119|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|221nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1943|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|225nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=815|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|790nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000254|bli-4|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|1429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|1438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000255|bli-5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12994|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=296|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=731|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8159|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000256|bli-6|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000257|bmk-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000257|bmk-1|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000257|bmk-1|510nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000257|bmk-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000257|bmk-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2165|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1046|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=908|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000259|bpl-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2237|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000262|bra-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|1195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|1198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50658|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2669|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=376|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000263|F23H11.5.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=469|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|253nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|256nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000264|brc-1|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000265|brd-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000265|brd-1|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000265|brd-1|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000265|brd-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2578|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000265|brd-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000266|bre-1|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4737|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00000266|bre-1|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000266|bre-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000266|bre-1|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000266|bre-1|454nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000267|bre-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000267|bre-2|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000267|bre-2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000267|bre-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000267|bre-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000267|bre-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|530nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|694nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|696nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|705nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3978|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000268|bre-3|710nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000269|bre-4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000269|bre-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000269|bre-4|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000269|bre-4|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000269|bre-4|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000269|bre-4|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=417|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|60nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=941|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000270|bre-5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=690|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=438|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|316nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|363nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000271|brf-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000272|bro-1|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00000272|bro-1|627nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20145|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000273|brp-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000274|btf-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000274|btf-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000274|btf-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1062|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000274|btf-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000274|btf-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000275|bub-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000275|bub-1|1536nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000275|bub-1|1562nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000275|bub-1|1586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000275|bub-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000275|bub-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3549|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000275|bub-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000276|byn-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000276|byn-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000276|byn-1|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6693|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000276|byn-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000276|byn-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000276|byn-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=404|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|1176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=424|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=864|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1333|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3372|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3439|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1595|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=873|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|550nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6275|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|559nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|635nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|644nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|646nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|654nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|664nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39019|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|667nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1351|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|672nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|793nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=550|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000277|cab-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=355|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=970|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=377|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000279|cah-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3528|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000280|cah-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7968|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000281|cah-3|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1940|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=312|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5741|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000282|cah-4|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000283|cah-5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1353|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000283|cah-5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000283|cah-5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000283|cah-5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=648|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2405|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000284|cah-6|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=432|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000285|cal-1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|1221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|1572nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|1580nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2759|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2598|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000286|cal-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000287|cal-3|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000287|cal-3|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000287|cal-3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2030|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4607|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000288|cal-4|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000289|cam-1|487nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000289|cam-1|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2302|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000289|cam-1|499nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000289|cam-1|668nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6971|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=917|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|353nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|357nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|361nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|365nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|373nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000292|cap-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|1113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|1116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|1120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|1128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2286|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1808|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|402nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|413nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=310|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|416nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|615nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|617nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|623nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000293|cap-2|910nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16867|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000294|cas-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|197nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1587|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000295|cat-1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000296|cat-2|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000298|cat-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4848|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000301|cav-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000302|cav-2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000302|cav-2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000302|cav-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=566|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000302|cav-2|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|783nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=549|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2822|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000366|cbp-1|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|540nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=664|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|542nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=719|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|545nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=285|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00000367|cca-1|547nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000368|ccb-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=648|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000368|ccb-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000368|ccb-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=901|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|345nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3850|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000369|ccf-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5134|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10389|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=577|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000370|ccg-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1574|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2018|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3357|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1621|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|340nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8937|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=491|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1557|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30815|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000371|cco-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5669|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000372|cyp-13A7|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000372|cyp-13A7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000373|cyp-14A5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000373|cyp-14A5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000373|cyp-14A5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=657|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1261|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=574|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000375|cyp-44A1|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=436|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3996|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|1225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=456|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|957nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000376|ccr-4|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|142nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=131|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|1470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|149nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=215|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|153nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|158nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1172|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16540|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000377|cct-1|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|1293nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|1299nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|1322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=156|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22218|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3863|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|347nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|358nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000378|cct-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|216nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17301|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=945|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|238nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|242nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000379|cct-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|256nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41429|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000380|cct-5|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|1041nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|1086nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|1128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|1218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|1428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17134|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000381|cct-6|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000382|cdc-6|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000382|cdc-6|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=827|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000382|cdc-6|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2044|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000382|cdc-6|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000382|cdc-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000382|cdc-6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=514|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3894|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=680|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1312|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000383|cdc-14|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|420nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|422nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|427nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4192|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|429nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|431nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000386|cdc-25.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000387|cdc-25.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000387|cdc-25.2|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000387|cdc-25.2|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000387|cdc-25.2|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000387|cdc-25.2|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000388|cdc-25.3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000388|cdc-25.3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000388|cdc-25.3|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000388|cdc-25.3|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000388|cdc-25.3|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000389|cdc-25.4|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000389|cdc-25.4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000389|cdc-25.4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|758nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12794|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|766nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=988|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|769nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|775nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|777nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000390|cdc-42|794nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000391|cdd-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000391|cdd-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000391|cdd-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000392|cdd-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000392|cdd-2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1291|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000392|cdd-2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13742|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000392|cdd-2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000392|cdd-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000392|cdd-2|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|1443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1397|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000393|cdf-1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000395|cdh-3|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000395|cdh-3|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000395|cdh-3|1429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000395|cdh-3|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000395|cdh-3|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000395|cdh-3|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1878|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|686nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|691nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|809nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000396|cdh-4|816nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000397|cdh-5|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000397|cdh-5|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000397|cdh-5|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000397|cdh-5|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000397|cdh-5|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000397|cdh-5|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000399|cdh-7|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000399|cdh-7|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000399|cdh-7|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000399|cdh-7|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000399|cdh-7|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000401|cdh-9|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000401|cdh-9|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000402|cdh-10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000402|cdh-10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|1001nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1383|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|259nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|268nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|273nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|275nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|278nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|333nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64468|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1020|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000403|casy-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000405|cdk-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2782|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000405|cdk-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5370|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000405|cdk-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4754|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000405|cdk-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000405|cdk-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000406|cdk-4|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000406|cdk-4|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000406|cdk-4|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=695|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000406|cdk-4|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000406|cdk-4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5549|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|300nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|316nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|321nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|324nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=766|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000407|cdk-5|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2921|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1690|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000408|cdk-7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1538|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1035|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000409|cdk-8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000410|cdk-9|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000410|cdk-9|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2508|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000410|cdk-9|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000410|cdk-9|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|297nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|301nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|303nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|309nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|312nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|394nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6015|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000411|cdl-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000412|cdr-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000413|cdt-1|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000413|cdt-1|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=826|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000413|cdt-1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000413|cdt-1|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000413|cdt-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|14nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3797|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1264|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=841|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000414|cec-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=517|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1320|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=471|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000415|ced-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000416|ced-2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000416|ced-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000416|ced-2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000416|ced-2|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000416|ced-2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3370|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000416|ced-2|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000416|ced-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|875nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|878nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|936nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000417|ced-3|957nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000418|ced-4|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|307nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|320nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|404nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|505nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|564nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|584nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|629nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|633nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000419|ced-5|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1271|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000420|ced-6|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=645|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2141|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000421|ced-7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|935nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000422|ced-8|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|457nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1016|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|461nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=846|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000423|ced-9|770nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1046nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1052nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|1340nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=655|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=781|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000424|ced-10|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=614|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000425|ced-11|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000425|ced-11|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2772|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000426|ced-12|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000427|ced-13|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000428|ceh-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000428|ceh-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000428|ceh-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000428|ceh-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000428|ceh-1|347nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000429|ceh-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000429|ceh-2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000429|ceh-2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000429|ceh-2|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=161|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000429|ceh-2|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000429|ceh-2|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000429|ceh-2|983nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000430|ceh-5|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000430|ceh-5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|304nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=541|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000431|ceh-6|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000432|ceh-7|1153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000432|ceh-7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1601|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|1483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|1486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|412nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|419nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|422nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000433|ceh-8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2130|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1714|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=413|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|282nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000434|ceh-9|287nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000435|ceh-10|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000435|ceh-10|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000435|ceh-10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000435|ceh-10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000435|ceh-10|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000435|ceh-10|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000435|ceh-10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000436|ceh-12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000436|ceh-12|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1220|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000436|ceh-12|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000436|ceh-12|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000436|ceh-12|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000436|ceh-12|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000436|ceh-12|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|1425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|1446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|1496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|1504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|1532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|1537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=394|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000437|ceh-13|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|759nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|788nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|856nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000438|ceh-14|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000439|ceh-16|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000439|ceh-16|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000439|ceh-16|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000439|ceh-16|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000440|ceh-17|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000440|ceh-17|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1163|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000440|ceh-17|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000440|ceh-17|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000441|ceh-18|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000441|ceh-18|853nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1695|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000441|ceh-18|856nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000441|ceh-18|859nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000442|ceh-19|114nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=503|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000442|ceh-19|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000442|ceh-19|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000442|ceh-19|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000442|ceh-19|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000442|ceh-19|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000442|ceh-19|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|1383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|1396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|1403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2080|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|1405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|1410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|1478nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000443|ceh-20|562nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000444|ceh-21|1271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000444|ceh-21|1274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000444|ceh-21|422nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=737|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000445|ceh-22|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=211|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=605|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|259nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000446|ceh-23|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000447|ceh-24|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000447|ceh-24|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1551|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000447|ceh-24|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000447|ceh-24|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|1014nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000448|pros-1|945nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|121nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3225|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000449|ceh-27|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000450|ceh-28|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000450|ceh-28|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000451|ceh-30|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000451|ceh-30|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000451|ceh-30|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00000451|ceh-30|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|1249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|1287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2987|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000452|ceh-31|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=601|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=849|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|571nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000453|ceh-32|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|1187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|930nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|932nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000454|ceh-33|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|1128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2543|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1645|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000455|ceh-34|447nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000457|ceh-36|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000457|ceh-36|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000457|ceh-36|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000457|ceh-36|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000458|ceh-37|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000458|ceh-37|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000458|ceh-37|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000458|ceh-37|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=809|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000458|ceh-37|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000458|ceh-37|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000458|ceh-37|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=531|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2698|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00000459|ceh-38|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000460|ceh-39|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000460|ceh-39|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000460|ceh-39|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000460|ceh-39|533nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=701|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000461|ceh-40|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000461|ceh-40|133nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000461|ceh-40|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000461|ceh-40|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00000462|ceh-41|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000462|ceh-41|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000462|ceh-41|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000462|ceh-41|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000462|ceh-41|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000462|ceh-41|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000463|ceh-43|1379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000463|ceh-43|1381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000463|ceh-43|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000463|ceh-43|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=430|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000463|ceh-43|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=469|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=279|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1623|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=509|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|625nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000464|ceh-44|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36387|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|424nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|677nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|947nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000465|cpg-1|953nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|1540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3678|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000466|cel-1|979nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000467|cep-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1856|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000467|cep-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000467|cep-1|1555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000467|cep-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000467|cep-1|399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000467|cep-1|643nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000467|cep-1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000468|ces-1|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000469|ces-2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00000469|ces-2|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|1101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|1103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|1513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|1515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=535|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=704|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=545|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=962|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=558|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20008|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1028|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=553|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5548|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9154|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|648nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|652nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|656nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|660nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|676nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|678nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000472|cey-1|969nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|142nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|152nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=436|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|155nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=446|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63128|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=383|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000473|cey-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7378|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17131|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=610|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2871|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1151|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=324|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000474|cey-3|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=431|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27481|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4116|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000475|cey-4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|832nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|872nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000476|cfi-1|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000477|cft-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000477|cft-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000478|cfz-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000478|cfz-2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000478|cfz-2|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=415|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=432|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=407|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|934nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|938nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67106|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|947nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|960nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=371|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000479|cgh-1|998nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2118|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|1361nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=537|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4666|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2392|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|313nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|460nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|525nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|600nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000480|cgp-1|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=780|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2241|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|271nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|344nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|353nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000481|cha-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000482|chd-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000482|chd-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000482|chd-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2842|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000482|chd-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000482|chd-3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000482|chd-3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000482|chd-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000483|che-1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000483|che-1|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000484|che-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000484|che-2|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000484|che-2|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000484|che-2|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00000484|che-2|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000484|che-2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000485|che-3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000485|che-3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000485|che-3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000485|che-3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000485|che-3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00000487|che-6|1096nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000488|che-7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000490|che-11|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000490|che-11|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000490|che-11|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=230|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00000491|che-12|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2129|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000492|che-13|20nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000492|che-13|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000492|che-13|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000492|che-13|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=947|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000492|che-13|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000492|che-13|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000493|che-14|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000493|che-14|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000493|che-14|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000493|che-14|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000493|che-14|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00000493|che-14|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000493|che-14|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=973|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2734|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|157nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|164nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000496|chs-1|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000497|chs-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000497|chs-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000497|chs-2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000497|chs-2|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000497|chs-2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000497|chs-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2270|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000498|chk-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=769|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1087nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1353nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|1382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000499|chk-2|987nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|1083nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|1094nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6308|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000500|chn-1|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|1469nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|1477nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=844|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=538|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4333|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109069|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21796|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2236|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|689nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|692nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000501|cho-1|723nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=321|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11424|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=301|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=573|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000502|chp-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=508|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1147|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000503|cht-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000506|cic-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000506|cic-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4200|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00000506|cic-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000506|cic-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|544nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|549nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1558|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|552nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|554nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|559nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000507|cit-1.1|630nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|1172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1990|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|941nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|944nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000508|cit-1.2|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000509|cka-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000509|cka-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000509|cka-1|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1655|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000509|cka-1|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6226|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000510|cka-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000511|ckb-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000511|ckb-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000511|ckb-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000511|ckb-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000511|ckb-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1033|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000511|ckb-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000511|ckb-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000512|ckb-2|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1143|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000512|ckb-2|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000513|ckb-3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000513|ckb-3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000514|ckb-4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=658|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000514|ckb-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000514|ckb-4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000514|ckb-4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2603|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1634|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|1367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000515|ckc-1|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000516|cki-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000516|cki-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000516|cki-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000516|cki-1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000516|cki-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000516|cki-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1427|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=460|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|583nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000517|cki-2|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|280nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=975|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|320nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000518|ckk-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000519|cku-70|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000519|cku-70|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000519|cku-70|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1171|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000519|cku-70|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=888|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1231|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=205|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000520|cku-80|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000521|cky-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000521|cky-1|250nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1290|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=305|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2134|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=568|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1169|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=721|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000522|clc-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000523|clc-2|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000523|clc-2|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=252|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000523|clc-2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000523|clc-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=821|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=931|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000524|clc-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000525|clc-4|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000525|clc-4|219nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000525|clc-4|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000526|clc-5|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=458|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=793|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1540|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=911|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4692|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=429|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5236|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1100|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000527|cle-1|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1098|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|923nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000528|clh-1|929nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1149|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000529|clh-2|49nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000530|clh-3|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000530|clh-3|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000530|clh-3|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000531|clh-4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|1293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|607nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|612nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000532|clh-5|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|269nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=909|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|272nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|276nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|279nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|385nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000533|clh-6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4526|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57215|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4769|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|587nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|616nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=380|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000534|cpi-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=494|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31541|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1584|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000535|cpi-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|183nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3766|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000536|clk-1|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000537|clk-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000537|clk-2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000537|clk-2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=788|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00000537|clk-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1365|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000537|clk-2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000537|clk-2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000539|cln-3.1|1198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000539|cln-3.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000539|cln-3.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000539|cln-3.1|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=388|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000539|cln-3.1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000539|cln-3.1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=714|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|746nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000540|cln-3.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000541|cln-3.3|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000541|cln-3.3|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=357|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000541|cln-3.3|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000541|cln-3.3|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000541|cln-3.3|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000541|cln-3.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000541|cln-3.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10450|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4642|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=329|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000542|clp-1|390nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000543|clp-2|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1693|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000543|clp-2|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000544|clp-3|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|1083nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4778|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=574|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|214nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|710nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000545|clp-4|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000546|clp-6|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000546|clp-6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000546|clp-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000547|clp-7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000547|clp-7|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000547|clp-7|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2783|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000547|clp-7|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000547|clp-7|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|413nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|420nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2040|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000548|clr-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000549|cls-2|1438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000549|cls-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1274|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000549|cls-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4248|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000549|cls-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000549|cls-2|619nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000549|cls-2|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|1109nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|477nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|483nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|632nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|634nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7001|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00000550|clu-1|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000551|clx-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|1042nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1680|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|1515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=311|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2755|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|435nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=359|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|459nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|525nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|708nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|950nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|959nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1729|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|964nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1527|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|971nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|981nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13046|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000552|cmd-1|988nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|431nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|433nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|439nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=211|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|443nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|450nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1304|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|455nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2714|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=474|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|630nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|645nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|649nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000553|cmk-1|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=432|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=506|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|353nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|363nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2824|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|368nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|370nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|390nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=633|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1447|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|407nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1329|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|441nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000554|cnb-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000555|cnc-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000555|cnc-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000555|cnc-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000555|cnc-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000556|cnc-2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2302|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00000556|cnc-2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000557|cnc-3|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=511|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000557|cnc-3|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1449|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000557|cnc-3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000557|cnc-3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3772|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=377|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000558|cnc-4|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000559|cnc-5|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000560|cnc-6|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000560|cnc-6|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000560|cnc-6|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000561|cnd-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000561|cnd-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000561|cnd-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000561|cnd-1|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000562|cng-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000562|cng-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000562|cng-1|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000562|cng-1|592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000562|cng-1|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000562|cng-1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000563|cng-3|1039nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1574|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|737nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000564|cnk-1|901nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000565|cnt-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1872|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000565|cnt-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000565|cnt-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|332nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|340nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|345nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1435|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000566|cnt-2|498nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|17nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4642|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|25nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000567|cnx-1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6436|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2571|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1315|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000583|cof-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000584|cog-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000584|cog-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000584|cog-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=657|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000584|cog-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3759|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000585|cogc-2|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1012nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1015nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1018nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=490|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|1138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000591|coh-1|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000592|coh-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000592|coh-3|240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1367|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000592|coh-3|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000592|coh-3|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000592|coh-3|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000593|col-2|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000593|col-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000593|col-2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4278|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000593|col-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|113nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|1539nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9799|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53075|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=838|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000594|col-3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000596|col-7|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000596|col-7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1491|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000596|col-7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3308|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000596|col-7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000596|col-7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000596|col-7|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000596|col-7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8948|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19603|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8997|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000597|col-8|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000598|col-9|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39569|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000599|col-10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10244|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|75nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|79nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=3097|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|81nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1265|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|84nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|89nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|92nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000601|col-12|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000602|col-13|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5468|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10622|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000603|col-14|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5389|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=979|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000606|col-17|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=435|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37675|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000608|col-19|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=743|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44332|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23579|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4843|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=699|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000609|col-20|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000610|col-33|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000610|col-33|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=629|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000611|col-34|1501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1766|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000611|col-34|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000611|col-34|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000611|col-34|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000611|col-34|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4127|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000611|col-34|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000612|col-35|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000612|col-35|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000612|col-35|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1416|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000612|col-35|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000612|col-35|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9613|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000613|col-36|472nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29915|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|80nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000615|col-38|83nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|1529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=852|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1824|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10234|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1013|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000616|col-39|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000617|col-40|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2577|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000617|col-40|113nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000617|col-40|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000617|col-40|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000617|col-40|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000617|col-40|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000618|col-41|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2116|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000618|col-41|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1025|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10556|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000620|col-43|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000621|col-44|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000621|col-44|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1734|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000621|col-44|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000621|col-44|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000622|col-45|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2578|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000622|col-45|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000622|col-45|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000622|col-45|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000623|col-46|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000623|col-46|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000623|col-46|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000623|col-46|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000624|col-47|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00000624|col-47|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000624|col-47|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000624|col-47|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000625|col-48|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2523|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000625|col-48|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000625|col-48|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000625|col-48|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000625|col-48|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000625|col-48|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000626|col-49|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10171|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000626|col-49|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000626|col-49|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000626|col-49|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000626|col-49|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000627|col-50|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3101|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000627|col-50|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=704|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000627|col-50|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000627|col-50|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|42nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2237|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000628|col-51|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000629|col-52|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000629|col-52|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000630|col-53|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000630|col-53|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00000630|col-53|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=281|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000630|col-53|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000631|col-54|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000631|col-54|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000631|col-54|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000631|col-54|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000631|col-54|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000631|col-54|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000632|col-55|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000632|col-55|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000632|col-55|624nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000633|col-56|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000633|col-56|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000633|col-56|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000634|col-58|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=922|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|178nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2029|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000636|col-60|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000637|col-61|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000637|col-61|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000637|col-61|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000637|col-61|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000637|col-61|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1711|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000637|col-61|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1627|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3286|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000638|col-62|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000639|col-63|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000639|col-63|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000639|col-63|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000639|col-63|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5783|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000639|col-63|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2379|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00000639|col-63|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000640|col-64|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000640|col-64|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=299|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=152|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=444|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4580|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00000641|col-65|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000644|col-68|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000644|col-68|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=219|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000644|col-68|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000644|col-68|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000644|col-68|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000645|col-69|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000645|col-69|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000645|col-69|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000646|H17B01.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000646|H17B01.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000646|H17B01.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000647|col-71|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000647|col-71|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000647|col-71|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13086|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000647|col-71|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000648|col-72|1543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000648|col-72|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000648|col-72|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|102nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=617|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5187|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2158|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000649|col-73|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000650|col-74|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000650|col-74|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000650|col-74|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000650|col-74|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000651|col-75|100nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000651|col-75|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000651|col-75|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000651|col-75|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000652|col-76|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000652|col-76|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1233|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000652|col-76|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000652|col-76|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000652|col-76|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000652|col-76|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21792|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000653|col-77|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000654|col-78|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00000654|col-78|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00000655|col-79|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000655|col-79|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000655|col-79|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000655|col-79|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2660|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000655|col-79|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000655|col-79|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11558|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000656|col-80|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20201|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2959|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000657|col-81|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18282|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000658|col-83|1464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000658|col-83|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000658|col-83|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000659|col-84|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000659|col-84|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000659|col-84|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000660|col-85|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3380|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000660|col-85|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1897|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00000660|col-85|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000660|col-85|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000660|col-85|180nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000660|col-85|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000660|col-85|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000661|col-86|1402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|234nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000662|col-87|876nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000663|col-88|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1947|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000663|col-88|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000663|col-88|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000663|col-88|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000663|col-88|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000663|col-88|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|1014nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|1021nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2050|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|1023nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|1028nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|1096nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4809|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=658|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000664|col-89|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=248|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|1212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|257nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|68nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=663|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=382|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1008|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000665|col-90|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1816|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3962|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000666|col-91|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000667|col-92|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000667|col-92|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000667|col-92|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000667|col-92|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000667|col-92|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000667|col-92|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28808|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00000667|col-92|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=484|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|1552nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54262|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1059|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000668|col-93|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31126|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000669|col-94|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6251|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13379|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000670|col-95|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000671|col-96|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000671|col-96|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000671|col-96|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1814|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000671|col-96|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000671|col-96|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000671|col-96|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000671|col-96|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7315|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=450|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000672|col-97|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=418|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21026|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2398|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3996|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=971|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000673|col-98|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000674|col-99|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000674|col-99|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000674|col-99|793nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=950|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40188|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4818|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000675|col-101|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000676|col-102|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000676|col-102|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1165|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000676|col-102|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26647|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=921|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000677|col-103|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1399|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000678|col-104|48nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000679|col-105|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000680|col-106|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000680|col-106|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000680|col-106|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63481|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000680|col-106|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1745|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000680|col-106|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000680|col-106|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000680|col-106|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000681|col-107|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000681|col-107|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000681|col-107|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000681|col-107|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15430|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000681|col-107|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14095|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000681|col-107|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=988|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000682|col-108|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1909|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000682|col-108|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8741|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|333nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000683|col-109|389nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|192nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=851|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000684|col-110|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|1104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2001|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=659|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000685|col-111|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=812|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=524|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000687|col-113|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000688|col-114|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000688|col-114|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000688|col-114|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000688|col-114|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1018|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000688|col-114|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1165|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000688|col-114|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000688|col-114|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000689|col-115|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000689|col-115|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=242|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000689|col-115|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000689|col-115|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000689|col-115|241nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=21|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000689|col-115|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000689|col-115|411nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000690|col-116|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000690|col-116|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000692|col-118|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000692|col-118|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000692|col-118|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000692|col-118|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=917|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000692|col-118|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4672|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00000692|col-118|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000692|col-118|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35177|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=329|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=279|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=567|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=872|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000693|col-119|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000694|col-120|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000694|col-120|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=567|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000694|col-120|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5918|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000694|col-120|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000694|col-120|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000694|col-120|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000695|col-121|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000695|col-121|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000695|col-121|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000695|col-121|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|374nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53319|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1049|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|532nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|89nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=541|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|97nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000696|col-122|99nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000697|col-123|457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000697|col-123|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1315|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000697|col-123|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=278|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000697|col-123|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000697|col-123|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000697|col-123|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=511|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1075|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108170|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6464|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000698|col-124|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5146|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49158|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2776|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000699|col-125|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000701|col-127|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000701|col-127|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000701|col-127|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000701|col-127|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3989|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000701|col-127|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000701|col-127|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000702|col-128|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000702|col-128|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000702|col-128|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28986|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|80nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|87nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000703|col-129|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000704|col-130|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000704|col-130|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000704|col-130|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000704|col-130|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10654|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000704|col-130|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1543|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000704|col-130|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000704|col-130|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000705|col-131|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000705|col-131|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000706|col-132|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000706|col-132|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|1044nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11907|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000707|col-133|832nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000708|col-135|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000708|col-135|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000708|col-135|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000708|col-135|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000708|col-135|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000708|col-135|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1651|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000710|col-137|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000710|col-137|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000710|col-137|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000710|col-137|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000710|col-137|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000710|col-137|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000711|col-138|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000711|col-138|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000711|col-138|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000711|col-138|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7115|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|1562nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31388|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=604|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000712|col-139|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42467|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86021|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8161|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000713|col-140|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000714|col-141|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000714|col-141|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000714|col-141|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20308|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000715|col-142|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1068|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86795|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4128|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=561|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000716|col-143|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=540|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1076|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31363|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000717|col-144|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8162|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000718|col-145|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10490|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000719|col-146|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=501|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7927|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1292|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000720|col-147|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000721|col-148|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4435|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|51nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|55nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000722|col-149|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000723|col-150|1483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000723|col-150|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000723|col-150|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000723|col-150|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000723|col-150|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4726|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000724|col-151|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000724|col-151|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=352|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000724|col-151|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000725|col-152|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000725|col-152|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000725|col-152|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=777|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=435|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000726|col-153|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6270|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000727|col-154|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000728|col-155|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000728|col-155|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000728|col-155|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000728|col-155|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9752|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000728|col-155|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000728|col-155|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000729|col-156|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000729|col-156|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000729|col-156|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2922|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000729|col-156|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000729|col-156|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000729|col-156|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2236|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2348|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000730|col-157|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6161|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=610|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000731|col-158|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000732|col-159|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27301|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72862|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000733|col-160|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000734|col-161|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000734|col-161|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000734|col-161|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000734|col-161|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16995|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000734|col-161|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000734|col-161|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000734|col-161|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000735|col-162|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000735|col-162|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11077|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000735|col-162|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000736|col-163|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000737|col-164|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2198|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000737|col-164|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000737|col-164|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000737|col-164|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000738|col-165|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000738|col-165|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000738|col-165|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=257|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4035|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1125|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000739|col-166|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16610|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1152|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=444|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13298|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5486|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7591|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000740|col-167|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000741|col-168|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000741|col-168|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000741|col-168|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000741|col-168|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=655|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000741|col-168|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7081|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000741|col-168|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1023|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000741|col-168|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000742|col-169|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000742|col-169|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000742|col-169|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000742|col-169|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5039|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000742|col-169|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000742|col-169|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000742|col-169|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000743|col-170|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000743|col-170|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000743|col-170|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=680|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00000743|col-170|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4066|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000743|col-170|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000743|col-170|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000745|col-172|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000745|col-172|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000745|col-172|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000745|col-172|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000746|col-173|1252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000746|col-173|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=303|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000747|col-174|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000747|col-174|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000747|col-174|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5167|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13836|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000748|col-175|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=570|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15783|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=722|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1488|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=502|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000749|col-176|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=259|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000750|col-177|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000750|col-177|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000750|col-177|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000750|col-177|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=747|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94874|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58880|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1256|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000751|col-178|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=957|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000752|col-179|1534nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000752|col-179|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000752|col-179|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000752|col-179|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1104|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000752|col-179|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13018|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000752|col-179|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000752|col-179|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4967|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1185|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000753|col-180|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20832|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=882|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2133|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=166|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115369|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000754|col-181|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2698|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000755|col-182|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000755|col-182|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1376|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000755|col-182|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000756|col-183|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2447|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000756|col-183|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63522|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3071|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000757|col-184|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000758|col-185|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000758|col-185|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4596|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000758|col-185|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000758|col-185|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000758|col-185|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000759|col-186|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000759|col-186|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=454|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000759|col-186|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000759|col-186|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00000759|col-186|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000760|col-187|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000761|coq-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000761|coq-1|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2426|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000761|coq-1|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=609|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=753|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=523|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000762|coq-2|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000763|coq-3|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2293|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00000763|coq-3|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=861|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000763|coq-3|1283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000763|coq-3|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000763|coq-3|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=310|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000764|coq-4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000764|coq-4|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000764|coq-4|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=357|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000764|coq-4|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=259|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000764|coq-4|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000764|coq-4|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=575|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000764|coq-4|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000765|coq-5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000765|coq-5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1769|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000765|coq-5|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000765|coq-5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000765|coq-5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000765|coq-5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000765|coq-5|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000767|coq-8|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000767|coq-8|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000767|coq-8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000767|coq-8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000767|coq-8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2307|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000767|coq-8|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000768|cor-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=589|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000768|cor-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000768|cor-1|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000770|cpb-1|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000770|cpb-1|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000770|cpb-1|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1512|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000770|cpb-1|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000771|cpb-2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000771|cpb-2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000771|cpb-2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000771|cpb-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000771|cpb-2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000772|cpb-3|453nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000772|cpb-3|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000772|cpb-3|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2021|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000772|cpb-3|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=904|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000772|cpb-3|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2237|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000773|cpf-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000774|cpf-2|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000774|cpf-2|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=270|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000774|cpf-2|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000774|cpf-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000774|cpf-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1976|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000774|cpf-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000774|cpf-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000775|cpin-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=600|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000775|cpin-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000775|cpin-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000775|cpin-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000775|cpin-1|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000775|cpin-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5814|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91701|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1684|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000776|cpl-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19213|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000777|cpn-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000778|cpn-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=706|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00000778|cpn-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000778|cpn-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000778|cpn-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000778|cpn-2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000778|cpn-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000778|cpn-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3392|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28069|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90970|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1629|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=530|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000779|cpn-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000780|cpn-4|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8244|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000780|cpn-4|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000780|cpn-4|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000780|cpn-4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17519|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000781|cpr-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000782|cpr-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000782|cpr-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=959|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00000782|cpr-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000782|cpr-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000782|cpr-2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=346|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=675|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1061|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=635|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000783|cpr-3|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4173|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14396|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000784|cpr-4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21887|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=554|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000785|cpr-5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4287|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26443|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35623|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=921|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000786|cpr-6|87nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|361nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000787|cps-6|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3272|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32923|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000788|cpz-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000789|cpz-2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000789|cpz-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000789|cpz-2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000789|cpz-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5622|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000792|crb-1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000792|crb-1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000792|crb-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000792|crb-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000792|crb-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1096nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1537nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1541nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1545nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=215|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=326|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|1580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000793|crh-1|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000794|crn-1|119nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000794|crn-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000794|crn-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000794|crn-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000794|crn-1|69nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000794|crn-1|73nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000794|crn-1|79nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1811|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|158nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|160nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|165nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|177nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=166|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|839nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=415|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1290|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000795|crn-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000796|crn-3|103nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000796|crn-3|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000796|crn-3|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2588|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000797|crn-4|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=590|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00000797|crn-4|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000798|crn-5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000798|crn-5|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000798|crn-5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000798|crn-5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2186|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000799|crn-6|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|1543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=534|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6411|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000800|cars-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=288|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1025|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60616|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1221|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000802|crt-1|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000803|csb-1|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000803|csb-1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000803|csb-1|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=800|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=881|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=624|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|224nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=753|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000804|csc-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2336|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|732nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|736nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000812|csk-1|816nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000813|csn-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000813|csn-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3085|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000813|csn-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3409|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000814|csn-2|79nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000815|csn-3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000815|csn-3|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000815|csn-3|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=348|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000815|csn-3|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1705|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00000815|csn-3|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000815|csn-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2115|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=476|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000816|csn-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|137nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|142nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=60|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|144nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|236nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|685nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2998|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000817|csn-5|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=204|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2206|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2318|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000818|csn-6|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000819|csp-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000819|csp-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000819|csp-1|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000819|csp-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000819|csp-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000819|csp-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000820|csp-2|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000820|csp-2|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000821|csp-3|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7768|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000822|csq-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000830|ctl-1|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000830|ctl-1|104nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000830|ctl-1|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000830|ctl-1|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000830|ctl-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000830|ctl-1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2284|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000830|ctl-1|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=760|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1134|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|43nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000831|ctl-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000832|ctn-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000832|ctn-1|126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000832|ctn-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000832|ctn-1|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000832|ctn-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000832|ctn-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000832|ctn-1|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2250|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33653|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3437|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=421|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4856|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000833|cts-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1189|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2342|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000834|cua-1|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6004|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3535|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2095|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000835|cuc-1|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1894|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1781|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|339nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|343nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000836|cul-1|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|479nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|488nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5045|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000837|cul-2|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|586nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2855|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|588nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|646nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=553|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|649nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|682nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000838|cul-3|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1532|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000839|cul-4|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=759|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2986|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|287nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|292nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000840|cul-5|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000841|cul-6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000841|cul-6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000841|cul-6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000841|cul-6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000841|cul-6|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10964|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|399nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000843|cup-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31615|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=702|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=615|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|665nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000845|cup-4|864nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000846|cup-5|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3267|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000846|cup-5|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000846|cup-5|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000851|cut-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00000851|cut-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00000851|cut-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000851|cut-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000853|cut-6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000853|cut-6|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000853|cut-6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000854|cux-7|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3229|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000854|cux-7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000857|cwn-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000857|cwn-1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000857|cwn-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2342|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000857|cwn-1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000857|cwn-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000857|cwn-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000857|cwn-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|239nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|243nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|251nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4027|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000858|cwn-2|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000859|cwp-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000859|cwp-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000859|cwp-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000859|cwp-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000859|cwp-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000860|cwp-2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000860|cwp-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1016|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000860|cwp-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000860|cwp-2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000861|cwp-3|1233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000861|cwp-3|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000861|cwp-3|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1232|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000862|cwp-4|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000863|cya-1|572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000864|cya-2|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1108|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1526|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2095|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=684|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2240|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=812|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|413nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=709|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|424nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2323|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|429nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000865|cyb-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|1579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|238nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1057|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1034|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1939|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000866|cyb-2.1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|1572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|224nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|239nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1551|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=962|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|298nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=1652|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000867|cyb-2.2|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2573|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12809|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000868|cyb-3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=255|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1555|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2144|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1715|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|576nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5241|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|583nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|589nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|591nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000869|cyc-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000870|cyd-1|559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00000870|cyd-1|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000870|cyd-1|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000870|cyd-1|572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000870|cyd-1|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000870|cyd-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000871|cye-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000871|cye-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000871|cye-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000871|cye-1|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000871|cye-1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=374|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000871|cye-1|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3615|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000871|cye-1|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000872|cyk-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000872|cyk-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3479|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000872|cyk-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000872|cyk-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000874|cyk-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000874|cyk-3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000874|cyk-3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2112|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000874|cyk-3|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000874|cyk-3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=651|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1889|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=937|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000875|cyk-4|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000876|cyl-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000876|cyl-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1715|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000876|cyl-1|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=593|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000876|cyl-1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=845|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000876|cyl-1|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000876|cyl-1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000876|cyl-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=840|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000877|cyn-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1324|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1359|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000878|cyn-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8929|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|496nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|540nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|716nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000879|cyn-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15607|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1048|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=511|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000880|cyn-4|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5492|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11441|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4184|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=374|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=666|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1896|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000881|cyn-5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000882|cyn-6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000882|cyn-6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000882|cyn-6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000882|cyn-6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4469|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000882|cyn-6|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188440|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4231|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2827|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000883|cyn-7|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33982|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000884|cyn-8|1159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000884|cyn-8|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000884|cyn-8|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000884|cyn-8|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000884|cyn-8|436nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2339|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000884|cyn-8|546nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000884|cyn-8|549nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1241|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000885|cyn-9|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=898|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|115nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=651|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000886|cyn-10|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000887|cyn-11|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000887|cyn-11|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3386|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000887|cyn-11|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000888|cyn-12|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000888|cyn-12|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000888|cyn-12|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000888|cyn-12|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12476|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000888|cyn-12|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=294|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000889|cyn-13|1209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000889|cyn-13|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000889|cyn-13|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1215|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000889|cyn-13|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4503|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000889|cyn-13|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=687|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3041|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000890|sig-7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=611|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=910|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000891|cyn-15|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|1078nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|1101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|1313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|643nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|697nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=579|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|938nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000892|cyn-16|945nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000893|cyn-17|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000893|cyn-17|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000893|cyn-17|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000893|cyn-17|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000893|cyn-17|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000893|cyn-17|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|522nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11795|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|530nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|532nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000894|dab-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000895|dac-1|1187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000895|dac-1|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000895|dac-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000895|dac-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000895|dac-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1143|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000895|dac-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000896|dad-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000896|dad-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000896|dad-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000896|dad-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12261|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000896|dad-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000896|dad-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000896|dad-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000897|daf-1|418nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000897|daf-1|423nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000897|daf-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000897|daf-1|447nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000897|daf-1|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000897|daf-1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00000897|daf-1|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1365nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1376nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1378nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1881|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|1414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000898|daf-2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000899|daf-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000899|daf-3|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000899|daf-3|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2055|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000899|daf-3|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000899|daf-3|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000899|daf-3|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000899|daf-3|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1332|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000900|daf-4|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|621nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4089|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|626nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=524|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00000901|daf-5|629nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000902|daf-6|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000902|daf-6|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|471nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|473nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|477nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|480nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1359|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|483nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30814|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7928|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7563|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000903|daf-7|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000904|daf-8|1234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=822|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000904|daf-8|1239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000904|daf-8|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000905|daf-9|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000906|daf-10|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00000906|daf-10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000907|daf-11|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=537|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=650|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|1401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000908|daf-12|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1363|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000910|daf-14|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|391nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|410nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|416nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|422nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000911|daf-15|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|1259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1939|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|1302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|766nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|769nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|773nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|995nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000912|daf-16|998nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|1096nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=590|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4229|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|406nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|408nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|416nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=282|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|418nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|424nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000913|daf-18|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|120nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|393nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=755|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=513|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|757nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|760nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000914|daf-19|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2342|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78791|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52427|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1722|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000915|daf-21|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000917|daf-25|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000917|daf-25|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1428|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000917|daf-25|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=748|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000917|daf-25|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000917|daf-25|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000917|daf-25|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6679|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5511|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=776|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|336nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000920|daf-28|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000923|daf-31|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000923|daf-31|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000923|daf-31|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000923|daf-31|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000923|daf-31|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4631|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000923|daf-31|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000923|daf-31|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2212|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1437|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000928|dao-2|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=237|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000929|dao-3|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000929|dao-3|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=997|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000929|dao-3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000929|dao-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=901|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000929|dao-3|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000929|dao-3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000929|dao-3|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000930|dao-4|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2469|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=518|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10582|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000931|dao-5|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000932|dao-6|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000932|dao-6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000932|dao-6|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1534|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000932|dao-6|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000932|dao-6|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000932|dao-6|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=463|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=538|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=611|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|1558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|1565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|1573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000933|dap-3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000934|dat-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000934|dat-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000934|dat-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000934|dat-1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000934|dat-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|427nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3275|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9551|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=741|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000935|daz-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|475nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|480nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=950|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=301|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|488nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|889nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000936|dbl-1|895nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000937|dbr-1|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000937|dbr-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000937|dbr-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1274|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1259|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1858|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1532nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|1535nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000938|dcp-66|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|1200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2395|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000939|dcr-1|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000940|dcs-1|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1936|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000940|dcs-1|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|155nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000941|ddp-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4557|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|1581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000942|deb-1|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2650|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=593|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000950|deg-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000951|deg-3|1180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000951|deg-3|1185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000951|deg-3|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=639|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000951|deg-3|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000952|del-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1851|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000952|del-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000952|del-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=266|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000953|del-2|411nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000955|des-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000955|des-2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1424|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000955|des-2|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000955|des-2|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|1324nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|477nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1096|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000958|dgk-1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|308nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2614|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=362|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000959|dgk-2|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|70nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000960|dgk-3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1179|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=333|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000961|dgn-1|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1399|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9278|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=956|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|212nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000962|dhc-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000963|dhp-1|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000963|dhp-1|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000963|dhp-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000963|dhp-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000963|dhp-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000964|dhp-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000964|dhp-2|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000964|dhp-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000964|dhp-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000964|dhp-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1815|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1486|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|293nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|296nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|298nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|307nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000965|dhs-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000966|dhs-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000966|dhs-2|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000966|dhs-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000966|dhs-2|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000966|dhs-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000966|dhs-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000966|dhs-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000967|dhs-3|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000967|dhs-3|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000967|dhs-3|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6946|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000967|dhs-3|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000967|dhs-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000968|dhs-4|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000968|dhs-4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000968|dhs-4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000968|dhs-4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00000968|dhs-4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000968|dhs-4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000969|dhs-5|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000969|dhs-5|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000969|dhs-5|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=583|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000969|dhs-5|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000969|dhs-5|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000969|dhs-5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3515|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=312|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000970|dhs-6|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000971|dhs-7|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000971|dhs-7|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000971|dhs-7|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=238|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000971|dhs-7|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000972|dhs-8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=993|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2890|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000973|dhs-9|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000974|dhs-11|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1338|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00000975|dhs-12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000975|dhs-12|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000975|dhs-12|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000975|dhs-12|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1560|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000975|dhs-12|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|517nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2091|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|525nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=487|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|527nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1441|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=394|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|546nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000976|dhs-13|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2036|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000977|dhs-14|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000978|dhs-15|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000978|dhs-15|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000979|dhs-16|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000979|dhs-16|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000979|dhs-16|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00000979|dhs-16|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000979|dhs-16|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000980|dhs-17|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000980|dhs-17|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000980|dhs-17|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3697|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000980|dhs-17|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000980|dhs-17|313nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000980|dhs-17|320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000980|dhs-17|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=124|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2225|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1211|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000981|dhs-18|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5048|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000982|dhs-19|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000983|dhs-20|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000983|dhs-20|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000983|dhs-20|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000983|dhs-20|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000983|dhs-20|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000984|dhs-21|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000984|dhs-21|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000984|dhs-21|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7546|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000984|dhs-21|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000984|dhs-21|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|145nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000985|dhs-22|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000986|dhs-23|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000986|dhs-23|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000986|dhs-23|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000987|dhs-24|729nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1854|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000987|dhs-24|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9205|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1670|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000988|dhs-25|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000989|dhs-26|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000990|dhs-27|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000990|dhs-27|457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000990|dhs-27|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000990|dhs-27|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=395|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000990|dhs-27|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=745|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4213|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000991|dhs-28|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=615|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|1541nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=152|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000992|dhs-29|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000993|dhs-30|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1711|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000993|dhs-30|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00000993|dhs-30|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000993|dhs-30|149nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000993|dhs-30|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2360|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=573|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000994|dic-1|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|764nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=309|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|768nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|801nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1143|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|804nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000995|die-1|810nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2794|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=869|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=959|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00000996|dif-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8458|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00000998|dig-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1542|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13245|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=793|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|268nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1297|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|343nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|348nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|352nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=305|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|359nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=524|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1719|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|536nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|541nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=704|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001000|dim-1|548nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=319|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2538|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001001|dis-3|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1643|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001002|div-1|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11197|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=593|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=982|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5010|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16484|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8272|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1419|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001005|dlc-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001006|dlg-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001006|dlg-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001006|dlg-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001006|dlg-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001006|dlg-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001006|dlg-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=677|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2506|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=762|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1850|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4678|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=659|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=423|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=475|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001007|dli-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|212nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|223nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1916|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001008|dlk-1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001016|dna-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001016|dna-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001016|dna-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001016|dna-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001016|dna-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1007|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001016|dna-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=648|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=518|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3023|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001017|dnc-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001018|dnc-2|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3948|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001018|dnc-2|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=757|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001018|dnc-2|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001018|dnc-2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001018|dnc-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001018|dnc-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1300|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2613|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001019|dnj-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|249nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2319|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001020|dnj-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001021|dnj-3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001021|dnj-3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=835|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001021|dnj-3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001021|dnj-3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001021|dnj-3|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=928|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|739nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001022|dnj-4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2803|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4018|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001023|dnj-5|97nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2657|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001025|dnj-7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|1139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|1165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|294nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2679|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001026|dnj-8|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=717|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=275|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001028|dnj-10|307nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=473|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3751|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2163|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001029|dnj-11|665nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11642|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4013|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001030|dnj-12|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8590|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2610|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|408nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001031|dnj-13|413nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|369nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|459nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|461nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|467nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001032|dnj-14|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001033|dnj-15|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001033|dnj-15|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001033|dnj-15|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2314|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001033|dnj-15|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001033|dnj-15|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=458|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1061nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1944|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1212nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1402|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1217nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=148|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1289nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1814|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3916|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|831nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|839nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=208|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001034|dnj-16|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001035|dnj-17|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001035|dnj-17|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001035|dnj-17|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001035|dnj-17|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001035|dnj-17|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=684|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001035|dnj-17|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1469|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001036|dnj-18|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1670|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14776|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1037|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001037|dnj-19|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9412|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5739|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|1228nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|266nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|345nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|482nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|485nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|960nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001038|dnj-20|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|1070nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3502|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001039|dnj-21|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|1338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1266|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001040|dnj-22|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6386|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001041|dnj-23|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001042|dnj-24|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001042|dnj-24|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001042|dnj-24|549nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001042|dnj-24|552nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1741|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001042|dnj-24|557nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=209|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001042|dnj-24|635nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001042|dnj-24|680nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3024|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001043|dnj-25|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001044|dnj-26|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00001044|dnj-26|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00001045|dnj-27|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00001045|dnj-27|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001045|dnj-27|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001046|dnj-28|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=799|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001046|dnj-28|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001046|dnj-28|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00001046|dnj-28|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001046|dnj-28|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001046|dnj-28|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|1323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=880|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3848|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|377nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|565nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|571nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001047|dnj-29|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2358|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|640nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001048|dnj-30|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001049|dog-1|1158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001049|dog-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001049|dog-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001049|dog-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1089|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001050|dom-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001050|dom-3|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001050|dom-3|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001050|dom-3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001050|dom-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=774|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001050|dom-3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001050|dom-3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|360nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2802|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9222|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|429nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001051|cks-1|431nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001052|dop-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001052|dop-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001052|dop-1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001053|dop-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001053|dop-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001053|dop-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1358|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001053|dop-2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001053|dop-2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001054|dpf-1|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001054|dpf-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001054|dpf-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00001054|dpf-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001054|dpf-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001054|dpf-1|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|350nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|385nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|394nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1274|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001055|dpf-2|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2073|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3781|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001056|dpf-3|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1195|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001057|dpf-4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4913|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2685|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001058|dpf-5|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001059|dpf-6|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001059|dpf-6|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001059|dpf-6|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001059|dpf-6|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001059|dpf-6|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001059|dpf-6|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001059|dpf-6|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=500|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1478|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|904nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|907nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001060|dpf-7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=835|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3293|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=472|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00001061|dpl-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001062|dpr-1|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001063|dpy-1|1352nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001063|dpy-1|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001063|dpy-1|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001064|dpy-2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001064|dpy-2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001064|dpy-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001064|dpy-2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001064|dpy-2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=783|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001065|dpy-3|1314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001065|dpy-3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001065|dpy-3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=651|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001065|dpy-3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001066|dpy-4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001066|dpy-4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001066|dpy-4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001066|dpy-4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38549|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001066|dpy-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=815|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001066|dpy-4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001066|dpy-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9418|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001067|dpy-5|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001068|dpy-6|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00001068|dpy-6|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001068|dpy-6|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001068|dpy-6|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001068|dpy-6|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001068|dpy-6|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001068|dpy-6|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001069|dpy-7|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1192|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001069|dpy-7|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001069|dpy-7|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001069|dpy-7|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001069|dpy-7|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2801|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001070|dpy-8|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=549|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=646|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001071|dpy-9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001072|dpy-10|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|1210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=717|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6569|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001073|dpy-11|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35992|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001074|dpy-13|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001075|dpy-14|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001075|dpy-14|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1703|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001076|dpy-17|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1655|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001076|dpy-17|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001077|dpy-18|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001077|dpy-18|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001077|dpy-18|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3965|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001078|dpy-19|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001078|dpy-19|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001078|dpy-19|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001078|dpy-19|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=738|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|1020nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|1023nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5386|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3534|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1210|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|363nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|369nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|381nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001079|dpy-20|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|539nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|546nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2974|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|548nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|551nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001080|dpy-21|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001081|dpy-22|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001081|dpy-22|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001081|dpy-22|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001081|dpy-22|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1829|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001081|dpy-22|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001081|dpy-22|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|600nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|609nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|614nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|618nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|634nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2099|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001082|dpy-23|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=475|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1377|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001085|dpy-26|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|1167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=539|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|608nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001086|dpy-27|899nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00001087|dpy-28|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001087|dpy-28|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001087|dpy-28|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001087|dpy-28|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1656|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001087|dpy-28|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001087|dpy-28|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1194|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001087|dpy-28|437nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1217|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6592|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6123|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=892|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001088|dpy-30|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001089|dre-1|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2359|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00001089|dre-1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001090|drh-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001090|drh-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001090|drh-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1136|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001092|dro-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001092|dro-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001092|dro-1|390nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001092|dro-1|392nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2168|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001092|dro-1|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001092|dro-1|404nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001092|dro-1|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1910|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2046|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001093|drp-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|1023nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1136|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26159|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=977|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=691|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|230nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001094|dars-1|984nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001095|dars-2|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=708|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001095|dars-2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001095|dars-2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001095|dars-2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001095|dars-2|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001096|dsc-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001096|dsc-1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001096|dsc-1|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001096|dsc-1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001099|dsc-4|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001099|dsc-4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001099|dsc-4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001099|dsc-4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1091|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001099|dsc-4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1467|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001099|dsc-4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2430|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001101|dsh-1|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001102|dsh-2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1196|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001102|dsh-2|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001102|dsh-2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001102|dsh-2|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001102|dsh-2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001103|dsl-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001103|dsl-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001103|dsl-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001104|dsl-2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001104|dsl-2|836nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001104|dsl-2|950nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001105|dsl-3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001107|dsl-5|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001107|dsl-5|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00001107|dsl-5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00001107|dsl-5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001107|dsl-5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001108|dsl-6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001109|dsl-7|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00001109|dsl-7|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00001110|duo-1|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=884|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001110|duo-1|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001110|duo-1|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001112|duo-3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001112|duo-3|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1530|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00001112|duo-3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001112|duo-3|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001112|duo-3|314nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001112|duo-3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1495|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|380nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|396nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|398nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|415nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001113|dur-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=308|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=340|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001115|dyb-1|975nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|494nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|497nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|500nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|504nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1142|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|576nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001116|dyc-1|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|1021nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|1024nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=886|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001117|dyf-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001118|dyf-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001118|dyf-2|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001118|dyf-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=782|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001118|dyf-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001119|dyf-3|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001119|dyf-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001119|dyf-3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001119|dyf-3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1124|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001119|dyf-3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001119|dyf-3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001119|dyf-3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|307nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|316nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|478nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001121|dyf-5|751nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001122|dyf-6|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1532|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001122|dyf-6|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001122|dyf-6|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|1500nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|497nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|503nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=686|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|508nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|511nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|543nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|548nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=424|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|550nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001123|dyf-7|555nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|423nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|597nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|604nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001127|dyf-11|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001129|dyf-13|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001129|dyf-13|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1264|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001129|dyf-13|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|1013nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|348nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|353nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|506nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|509nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=340|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1430|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|745nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3593|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|753nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001130|dyn-1|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=424|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1030|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001131|dys-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|138nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=249|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|140nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=121|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|143nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1952|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001132|alp-1|607nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001133|eat-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001133|eat-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001133|eat-2|949nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00001133|eat-2|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|375nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=3448|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|380nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=604|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|383nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=250|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=442|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001134|eat-3|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001135|eat-4|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001135|eat-4|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001135|eat-4|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2541|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001135|eat-4|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001135|eat-4|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001135|eat-4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001135|eat-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001136|eat-5|1006nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001136|eat-5|1048nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001136|eat-5|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001136|eat-5|1114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00001136|eat-5|988nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3846|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35630|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13797|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1568|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001137|eat-6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|730nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|732nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|739nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|773nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5655|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|874nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|877nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001145|eat-16|978nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|730nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001148|eat-20|735nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|435nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|576nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5511|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1968|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001149|bcat-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001150|ech-1.1|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001150|ech-1.1|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001150|ech-1.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001150|ech-1.1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001150|ech-1.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001150|ech-1.1|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00001150|ech-1.1|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|1560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2390|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001151|ech-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001152|ech-3|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001152|ech-3|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001152|ech-3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001152|ech-3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001152|ech-3|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1902|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=530|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=406|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001153|ech-4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001154|ech-5|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001154|ech-5|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1802|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001154|ech-5|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001154|ech-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001154|ech-5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17509|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2594|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|257nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|259nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=621|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001155|ech-6|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1922|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001156|ech-7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001157|ech-8|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00001157|ech-8|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001157|ech-8|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001157|ech-8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|1341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001158|ech-9|337nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001159|eff-1|1196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001159|eff-1|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001159|eff-1|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3495|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001160|efk-1|912nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001161|efl-1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001161|efl-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001161|efl-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001161|efl-1|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001161|efl-1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=982|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001161|efl-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001161|efl-1|375nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=271|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001162|efl-2|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|1181nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|1461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|1483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1294|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001163|efn-2|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001164|efn-3|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001164|efn-3|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001164|efn-3|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001164|efn-3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001164|efn-3|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001164|efn-3|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001165|efn-4|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=960|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001165|efn-4|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|1002nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|1034nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|1040nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2162|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2695|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001166|eftu-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4301|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52741|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8419|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=407|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101575|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4289|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001167|eef-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=419|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12698|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17727|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001169|eef-1A.2|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001170|egl-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=809|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001170|egl-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001171|egl-2|1236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=790|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001171|egl-2|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001171|egl-2|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001171|egl-2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|1046nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|1337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|1339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|1371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4937|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=984|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|349nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=380|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|353nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=705|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|355nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=1733|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|357nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=390|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|359nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=267|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|361nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|363nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=374|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|369nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|413nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|418nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|425nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16797|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=784|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=330|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1772|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|627nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|635nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|640nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|643nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001172|egl-3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|641nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|646nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1809|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|649nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7922|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|652nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1267|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|656nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|659nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|665nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001173|egl-4|669nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001174|egl-5|800nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001174|egl-5|810nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=577|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001175|egl-6|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001175|egl-6|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001175|egl-6|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|510nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=576|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|516nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|518nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|520nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|525nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1244|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|529nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=662|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|531nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|533nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001177|egl-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|1498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|346nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4206|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|538nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|827nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|834nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001178|egl-9|938nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|1218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|1224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3951|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|1229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|1275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|845nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|873nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|963nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001179|egl-10|982nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001182|egl-13|667nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=589|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001182|egl-13|670nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001182|egl-13|673nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|1286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001184|egl-15|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001185|egl-17|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|427nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|478nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=453|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|483nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1384|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001186|egl-18|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1774|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001187|egl-19|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001188|egl-20|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001188|egl-20|781nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=484|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001188|egl-20|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001188|egl-20|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00001188|egl-20|823nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001188|egl-20|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|1418nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=998|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74030|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36922|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2164|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001189|egl-21|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001190|egl-23|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001190|egl-23|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001190|egl-23|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1781|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001190|egl-23|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001190|egl-23|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001193|egl-26|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001193|egl-26|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001193|egl-26|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001193|egl-26|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001193|egl-26|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=904|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001193|egl-26|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001193|egl-26|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|589nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|593nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|595nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2454|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|599nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|602nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|605nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001194|egl-27|610nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1187|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1042nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=648|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1049nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17066|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1052nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=4376|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1072nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1243|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1077nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|1081nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|314nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|480nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|611nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001196|egl-30|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001202|egl-36|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1127|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00001202|egl-36|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001202|egl-36|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001202|egl-36|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001202|egl-36|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001202|egl-36|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001202|egl-36|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|599nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001204|egl-38|630nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=30|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|1322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|830nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|866nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|870nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|874nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|877nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|889nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001207|egl-43|893nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|582nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|584nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|588nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2296|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|595nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|597nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001208|egl-44|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9209|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001209|egl-45|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1119|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001210|egl-46|606nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001211|egl-47|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=776|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=896|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=226|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=556|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001214|ego-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|433nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1751|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|445nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001215|ego-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001223|ehn-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001223|ehn-3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001223|ehn-3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2914|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001224|ehs-1|369nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|1513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|335nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|338nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=213|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|342nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5107|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|347nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=390|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=647|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=458|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|426nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001225|eif-3.B|629nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|1240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8304|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=458|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001226|eif-3.C|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=831|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6376|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00001227|eif-3.D|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=458|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4822|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001228|eif-3.E|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|255nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|261nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|265nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|301nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11321|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|312nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1474|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=288|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=739|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001229|eif-3.F|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001230|eif-3.G|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001230|eif-3.G|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001230|eif-3.G|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001230|eif-3.G|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001230|eif-3.G|271nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6662|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001230|eif-3.G|275nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001230|eif-3.G|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1190|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1767|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1251|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|344nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|361nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001231|eif-3.H|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001232|eif-3.I|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=478|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001232|eif-3.I|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4437|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00001232|eif-3.I|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001232|eif-3.I|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001232|eif-3.I|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001232|eif-3.I|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001233|eif-3.K|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1187|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001233|eif-3.K|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7559|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00001233|eif-3.K|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001233|eif-3.K|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001233|eif-3.K|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=352|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3245|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001234|eif-6|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2416|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001235|elb-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=877|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001235|elb-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3083|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001235|elb-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001235|elb-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001235|elb-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3820|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1488nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1551nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1560nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|1563nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|339nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|526nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|746nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001236|elc-1|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001237|elc-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001237|elc-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001237|elc-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001237|elc-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2044|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001237|elc-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001237|elc-2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001237|elc-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=637|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7423|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=760|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1671|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1418|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001239|elo-1|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|1182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|1207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|1211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5736|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1771|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001240|elo-2|56nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|1233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|549nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|555nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3152|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|562nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=578|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|595nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1311|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|597nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|809nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|980nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|983nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001241|elo-3|985nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001242|elo-4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001242|elo-4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001242|elo-4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001242|elo-4|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=681|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5222|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3107|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001243|elo-5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=629|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1839|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1115|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001244|elo-6|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10426|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001245|elo-7|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001245|elo-7|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001245|elo-7|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001246|elo-8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=781|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001247|elo-9|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00001247|elo-9|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001247|elo-9|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001247|elo-9|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001247|elo-9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001248|elp-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=741|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001248|elp-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001248|elp-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001248|elp-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001248|elp-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001248|elp-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=588|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001249|elt-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001250|elt-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001250|elt-2|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001250|elt-2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001250|elt-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001250|elt-2|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|490nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=401|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|494nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|523nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001251|elt-3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001252|elt-4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001252|elt-4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001252|elt-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001252|elt-4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001253|elt-6|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001253|elt-6|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=679|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001253|elt-6|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001253|elt-6|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3057|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001258|emb-4|573nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=663|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5944|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001259|emb-5|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5801|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001262|emb-8|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5453|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6533|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|980nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|983nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001263|emb-9|985nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001281|emb-27|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001281|emb-27|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2295|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001281|emb-27|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2267|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001284|emb-30|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4675|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3072|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19725|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=682|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001303|emo-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001309|emr-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001309|emr-1|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5265|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001309|emr-1|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001309|emr-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001310|end-1|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001310|end-1|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001310|end-1|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001310|end-1|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00001311|end-3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001311|end-3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001311|end-3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001311|end-3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=983|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2522|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001320|ent-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1141|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001324|eor-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001325|eor-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001325|eor-2|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001325|eor-2|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001325|eor-2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=888|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001325|eor-2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001328|epi-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001328|epi-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001328|epi-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3796|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001328|epi-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001328|epi-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|177nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=184|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|187nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|479nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|488nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|491nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4995|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=694|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|724nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=824|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001329|epn-1|849nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=278|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=713|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|323nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|328nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|332nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001330|eps-8|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|346nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=758|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|350nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17239|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5470|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=156|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|366nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|368nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|372nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|376nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|380nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|689nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|976nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001331|erd-2|978nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001332|eri-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001332|eri-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001332|eri-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1301|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001332|eri-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001332|eri-1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1309|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001332|eri-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001332|eri-1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1265|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|529nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|537nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4785|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|539nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2662|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|544nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=982|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|548nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|556nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|562nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|565nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|574nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001333|erm-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4546|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=755|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001334|ero-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2092|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1728|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001335|erp-1|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5588|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=321|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001336|qars-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|1129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7318|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001337|ears-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001338|ears-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001338|ears-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001338|ears-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001338|ears-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001338|ears-2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1473|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001338|ears-2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001338|ears-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|404nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|850nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=594|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001340|etr-1|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1165|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|220nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|223nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|228nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|372nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=950|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|375nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=350|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|378nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=174|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1435|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=609|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|491nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001345|fos-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001352|evl-14|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001352|evl-14|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001352|evl-14|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2348|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001352|evl-14|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001352|evl-14|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2451|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001358|evl-20|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001365|exc-4|1225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001365|exc-4|1229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1133|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001365|exc-4|1233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001365|exc-4|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001365|exc-4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001366|exc-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001366|exc-5|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001366|exc-5|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001366|exc-5|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001366|exc-5|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3163|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001368|exc-7|915nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001371|exl-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001371|exl-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2955|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001371|exl-1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001371|exl-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001371|exl-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001372|exo-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1923|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=954|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001373|exp-1|984nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1679|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|1275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|1306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|1309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|306nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|324nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=808|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001374|exp-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001377|eya-1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001377|eya-1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=928|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00001377|eya-1|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001377|eya-1|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001377|eya-1|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001377|eya-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95505|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=470|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|714nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11144|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16610|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001385|far-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=380|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=998|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318920|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2247|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1018|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001386|far-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8969|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001387|far-3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001388|far-4|1474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001388|far-4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001388|far-4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001389|far-5|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001389|far-5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=718|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001389|far-5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001389|far-5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|114nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2318|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=913|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001390|far-6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001391|far-7|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001391|far-7|61nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001391|far-7|64nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001391|far-7|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001391|far-7|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=810|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001391|far-7|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001391|far-7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001392|far-8|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001392|far-8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001392|far-8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001392|far-8|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2500|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001392|far-8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001392|far-8|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1982|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9160|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=782|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001393|fat-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16516|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1420|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|945nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001394|fat-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001395|fat-3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10537|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001395|fat-3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001395|fat-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7781|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5103|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1595|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001396|fat-4|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001397|fat-5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001397|fat-5|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4243|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001397|fat-5|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=620|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001397|fat-5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001397|fat-5|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2899|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16245|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=188|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001398|fat-6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=649|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001399|fat-7|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=537|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001400|fax-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001401|fbf-1|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=265|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00001401|fbf-1|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001401|fbf-1|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001401|fbf-1|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001401|fbf-1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=613|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001402|fbf-2|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001402|fbf-2|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001402|fbf-2|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=671|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001402|fbf-2|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001402|fbf-2|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001402|fbf-2|277nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=777|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001402|fbf-2|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001403|fbl-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001403|fbl-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001403|fbl-1|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001403|fbl-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001403|fbl-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3009|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2261|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1733|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001404|fbp-1|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001405|fce-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001405|fce-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001405|fce-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3501|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001405|fce-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001405|fce-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001405|fce-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001405|fce-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001406|fce-2|229nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001406|fce-2|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001406|fce-2|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001406|fce-2|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=844|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001406|fce-2|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001410|feh-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001410|feh-1|265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1342|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001410|feh-1|279nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001410|feh-1|281nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=890|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001410|feh-1|284nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001411|fem-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001411|fem-1|171nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001411|fem-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001411|fem-1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3307|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001411|fem-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001411|fem-1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001412|fem-2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001412|fem-2|383nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001412|fem-2|389nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3998|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001412|fem-2|393nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001412|fem-2|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001412|fem-2|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001412|fem-2|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|1155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=568|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001413|fem-3|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001414|fer-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001414|fer-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001414|fer-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36636|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3771|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001423|fib-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001424|fis-1|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001424|fis-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001424|fis-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001425|fis-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001425|fis-2|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001425|fis-2|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2125|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001425|fis-2|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1745|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001425|fis-2|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001425|fis-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001425|fis-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|1056nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=601|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|1065nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|1067nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3076|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=306|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=780|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|550nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|553nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|690nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|699nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|710nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=775|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001426|fkb-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37563|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=540|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=840|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001427|fkb-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=644|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001428|fkb-3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001429|fkb-4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001429|fkb-4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001429|fkb-4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001429|fkb-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1307|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001429|fkb-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001429|fkb-4|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001429|fkb-4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4666|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=957|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001430|fkb-5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|1189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12855|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|921nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001431|fkb-6|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|267nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|276nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001432|fkb-7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001433|fkb-8|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001434|fkh-2|1455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001434|fkh-2|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001434|fkh-2|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001434|fkh-2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001435|fkh-3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001435|fkh-3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001436|fkh-4|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001436|fkh-4|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001436|fkh-4|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001436|fkh-4|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00001436|fkh-4|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001436|fkh-4|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001437|fkh-5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|280nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=540|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|489nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|497nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001438|fkh-6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001439|fkh-7|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001439|fkh-7|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001439|fkh-7|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001439|fkh-7|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001439|fkh-7|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001439|fkh-7|733nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001439|fkh-7|740nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1419|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1375|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=293|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=124|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001440|fkh-8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001441|fkh-9|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001441|fkh-9|1099nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001441|fkh-9|1101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2997|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001441|fkh-9|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001441|fkh-9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001441|fkh-9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=865|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001442|fkh-10|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=530|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1358|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|791nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=326|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|795nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001443|fli-1|797nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2567|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1029|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=834|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=198325|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62944|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|1554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1716|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|1585nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|162nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1408|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=345|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=939|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=651|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=548|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001444|flp-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=572|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=454|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15684|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=643|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001445|flp-2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4875|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001446|flp-3|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|193nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4775|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|201nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2016|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|208nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|279nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|281nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001447|flp-4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100308|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5953|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=676|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1714|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=775|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15527|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4008|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=750|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|279nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|297nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|306nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001448|flp-5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|223nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9353|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|227nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=766|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=342|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|303nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=231|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|326nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001449|flp-6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001450|flp-7|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001450|flp-7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001450|flp-7|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001450|flp-7|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001450|flp-7|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001450|flp-7|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3190|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79092|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001451|flp-8|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9061|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1027|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6859|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5383|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488185|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1223|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1063|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=481|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=348|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|330nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2054|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26599|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=680|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|348nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10308|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3254|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001452|flp-9|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|257nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4605|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=766|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1117|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001453|flp-10|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|1325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|1330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2573|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76766|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69001|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=465|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001454|flp-11|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1364|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|1197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3479|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4574|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4042|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1843|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2183|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408502|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=372|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=862|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14596|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=441|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|276nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|280nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001455|flp-12|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14669|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|283nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=273|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|418nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|422nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001456|flp-13|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=350|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|171nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|174nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54213|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2628|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|31nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|434nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|487nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001457|flp-14|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9019|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7118|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9599|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11357|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001458|flp-15|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7747|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|333nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|336nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=539|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|342nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1694|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|345nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|350nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|410nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|415nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|443nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|705nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001459|flp-16|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4015|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|392nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|400nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001460|flp-17|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=350|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14553|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8012|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=262|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001461|flp-18|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119342|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3223|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=498|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001462|flp-19|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3278|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001463|flp-20|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4263|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1346|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001464|flp-21|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001465|flr-1|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001465|flr-1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001465|flr-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001465|flr-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|1533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|328nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2556|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|462nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|465nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1218|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001466|flr-2|797nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001468|flr-4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001468|flr-4|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001468|flr-4|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001468|flr-4|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|249nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=189|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1023|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001470|baz-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001475|fmi-1|225nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001475|fmi-1|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001475|fmi-1|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001475|fmi-1|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001475|fmi-1|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001475|fmi-1|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001476|fmo-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001476|fmo-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001476|fmo-1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001476|fmo-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001476|fmo-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=719|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001476|fmo-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|1533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|1557nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=647|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001477|fmo-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001478|fmo-3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1545|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001478|fmo-3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001478|fmo-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001478|fmo-3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2472|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001479|fmo-4|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2534|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2477|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001480|fmo-5|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=701|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001481|fog-1|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=602|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|37nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001482|fog-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|510nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|518nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9285|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|521nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7890|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|528nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=284|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001483|fog-3|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|453nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|458nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|461nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|466nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3754|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|747nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|938nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|944nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|952nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|954nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001484|fox-1|963nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001485|fre-1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1116|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001485|fre-1|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=371|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001485|fre-1|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=711|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=754|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=185|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|436nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001486|frh-1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001487|frk-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001487|frk-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|385nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|554nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=807|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|559nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=940|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|562nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=373|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|567nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=776|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|573nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14015|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|582nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1076|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|646nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|652nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|654nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001488|frm-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001489|frm-2|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001489|frm-2|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1276|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001489|frm-2|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|866nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=560|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|869nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|871nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001490|frm-3|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|1243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|398nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|405nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=396|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4345|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=642|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001491|frm-4|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001492|frm-5.1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001492|frm-5.1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001492|frm-5.1|424nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001492|frm-5.1|429nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001492|frm-5.1|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001492|frm-5.1|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001492|frm-5.1|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00001493|frm-7|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001493|frm-7|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001493|frm-7|630nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2961|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001493|frm-7|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001493|frm-7|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001493|frm-7|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001493|frm-7|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001494|frm-8|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001494|frm-8|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001494|frm-8|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2878|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001494|frm-8|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001494|frm-8|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001494|frm-8|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001494|frm-8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001495|frm-9|337nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001495|frm-9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001495|frm-9|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001495|frm-9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=988|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001495|frm-9|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001495|frm-9|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|1367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|139nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23199|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1041|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001496|frm-10|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4989|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=401|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001497|fars-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3465|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1797|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|412nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001498|fars-3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001499|fsn-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001499|fsn-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001499|fsn-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001499|fsn-1|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5396|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001499|fsn-1|318nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2485|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001499|fsn-1|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001499|fsn-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001500|ftn-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001500|ftn-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001500|ftn-1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001500|ftn-1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=403|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001500|ftn-1|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=854|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00001500|ftn-1|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29014|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4896|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001501|ftn-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1033|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9432|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=285|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9358|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39067|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|392nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|445nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=279|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001502|ftt-2|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|155nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22847|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1290|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001503|fum-1|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001505|fut-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001505|fut-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=752|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001506|fut-2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001506|fut-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001506|fut-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001507|fut-4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|225nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=802|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|322nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00001508|fut-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3127|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001509|fzo-1|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|793nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|808nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|815nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|819nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=708|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|827nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|831nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|835nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=800|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|837nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1264|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|850nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001510|fzr-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1893|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=778|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=871|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|696nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|872nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001511|fzy-1|882nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001512|gab-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001512|gab-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=984|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001512|gab-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001512|gab-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2230|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=543|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|464nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001513|gad-1|468nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001514|xnd-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001514|xnd-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=879|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001514|xnd-1|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001514|xnd-1|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001514|xnd-1|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=829|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001514|xnd-1|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001514|xnd-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001515|gap-1|1173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1061|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001515|gap-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001516|gap-2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001516|gap-2|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001516|gap-2|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001516|gap-2|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=811|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001516|gap-2|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001516|gap-2|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001517|gar-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=801|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001517|gar-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=601|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001517|gar-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001517|gar-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4377|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001518|gar-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|244nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|250nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=864|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|253nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|256nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|260nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|293nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|313nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001519|gar-3|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=882|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2364|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1012|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001520|gas-1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001522|gbh-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001522|gbh-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001522|gbh-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001522|gbh-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1222|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001522|gbh-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=961|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001523|gbh-2|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|869nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|874nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2999|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|883nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001526|gck-1|890nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001527|gcs-1|1020nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001527|gcs-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001527|gcs-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001527|gcs-1|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1084|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001527|gcs-1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3553|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00001527|gcs-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001530|gcy-3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001531|gcy-4|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001532|gcy-5|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001532|gcy-5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001533|gcy-6|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001533|gcy-6|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001533|gcy-6|1344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001533|gcy-6|1555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001534|gcy-7|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001534|gcy-7|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001535|gcy-8|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001535|gcy-8|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001536|gcy-9|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|441nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=619|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3112|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001537|gcy-11|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001538|gcy-12|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001538|gcy-12|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001538|gcy-12|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001538|gcy-12|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3039|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001538|gcy-12|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001539|gcy-13|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001540|gcy-14|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001540|gcy-14|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001541|gcy-15|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001541|gcy-15|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2074|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001541|gcy-15|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001541|gcy-15|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001541|gcy-15|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001542|gcy-17|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001543|gcy-18|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001543|gcy-18|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001543|gcy-18|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001544|gcy-19|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001544|gcy-19|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001545|gcy-20|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001546|gcy-21|676nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00001546|gcy-21|685nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00001547|gcy-22|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001547|gcy-22|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1825|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001547|gcy-22|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001547|gcy-22|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001547|gcy-22|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001547|gcy-22|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001547|gcy-22|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001548|gcy-23|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=451|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001548|gcy-23|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001549|gcy-25|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001549|gcy-25|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001550|gcy-27|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00001550|gcy-27|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00001551|gcy-31|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001551|gcy-31|510nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001551|gcy-31|512nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001552|gcy-32|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001552|gcy-32|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001552|gcy-32|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001552|gcy-32|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001552|gcy-32|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001552|gcy-32|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1128|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4216|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1453|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001553|gcy-33|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001554|gcy-34|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001554|gcy-34|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001555|gcy-35|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001555|gcy-35|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001555|gcy-35|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001556|gcy-36|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001556|gcy-36|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001556|gcy-36|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001556|gcy-36|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00001557|gcy-37|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001557|gcy-37|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001557|gcy-37|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=834|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=470|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|321nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28311|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001558|gdi-1|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001559|gei-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=555|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|1086nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|1089nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|1093nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|1098nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|1107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3750|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001560|gei-3|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|500nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|627nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4656|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001561|gei-4|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|1067nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|1089nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|618nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001562|lin-66|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001563|gei-6|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001563|gei-6|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001563|gei-6|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=968|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001563|gei-6|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=598|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001563|gei-6|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001564|icl-1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001564|icl-1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9503|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001564|icl-1|1101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001564|icl-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1092|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001564|icl-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2630|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001565|gei-8|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001565|gei-8|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001565|gei-8|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001565|gei-8|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001565|gei-8|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1175|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00001565|gei-8|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|1095nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1903|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|935nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|948nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|955nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001566|acdh-13|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3805|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001568|snpc-4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001569|meg-3|189nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=893|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001569|meg-3|192nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001569|meg-3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001569|meg-3|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001569|meg-3|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001569|meg-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|687nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=195|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|689nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|850nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|863nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|868nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001570|gei-13|870nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001571|gei-14|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=839|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001571|gei-14|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001571|gei-14|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001571|gei-14|237nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001571|gei-14|239nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=652|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=520|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001572|gei-15|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2265|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|328nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=514|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|330nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3242|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=171|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001574|gei-17|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001575|gei-18|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=403|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1805|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001577|gem-4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001578|ges-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001578|ges-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001578|ges-1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=749|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1237|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001579|gex-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001580|gex-3|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001580|gex-3|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1920|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001580|gex-3|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001581|gfi-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001581|gfi-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001581|gfi-1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001581|gfi-1|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=694|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|665nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|669nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|673nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=442|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|680nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2202|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001582|gfi-2|685nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=984|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001583|gfi-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|1307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|1312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001584|nrde-4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1926|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001585|gfl-1|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001585|gfl-1|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1347|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001585|gfl-1|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1194|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001585|gfl-1|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001586|ggr-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001586|ggr-1|1580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001586|ggr-1|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001586|ggr-1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001586|ggr-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001586|ggr-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1350|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001586|ggr-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001587|ggr-2|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001587|ggr-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001587|ggr-2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1164|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001587|ggr-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001587|ggr-2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001588|ggr-3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001588|ggr-3|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1394|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001588|ggr-3|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001589|gip-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001589|gip-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1414|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001589|gip-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001589|gip-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001589|gip-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001590|C45G3.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001590|C45G3.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001590|C45G3.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1304|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001590|C45G3.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|1322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|582nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|584nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=642|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001591|glc-1|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001592|glc-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001592|glc-2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001592|glc-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00001592|glc-2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001592|glc-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001593|glc-3|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001593|glc-3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=683|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00001593|glc-3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001594|glc-4|1462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001594|glc-4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001594|glc-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1208|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001594|glc-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|207nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|797nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|800nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|807nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9394|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5349|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|826nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001595|gld-1|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1081nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1088nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1092nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3922|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|1176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|512nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|521nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001596|gld-2|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3091|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=618|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|62nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|643nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|655nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2458|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|659nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|665nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|668nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001597|gld-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=953|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15592|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2307|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=504|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=196|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001598|glh-1|776nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=655|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1378|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1646|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001599|glh-2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=639|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|258nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001600|glh-3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1027|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=296|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=284|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|282nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=419|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001601|glh-4|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1226|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001602|gln-1|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001603|gln-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001603|gln-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001603|gln-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=975|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001603|gln-2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11622|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001604|gln-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1008|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25875|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001606|gln-5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=539|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=184|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=939|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1080|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=864|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=498|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2675|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=389|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2545|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|753nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001607|gln-6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001608|R07B1.8|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00001608|R07B1.8|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001608|R07B1.8|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001608|R07B1.8|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001608|R07B1.8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001609|glp-1|1477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001609|glp-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001609|glp-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001609|glp-1|364nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=846|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00001609|glp-1|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=503|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001609|glp-1|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001609|glp-1|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001612|glr-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2051|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001612|glr-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001612|glr-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001612|glr-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001612|glr-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001613|glr-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001613|glr-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1334|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001613|glr-2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1521|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00001613|glr-2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001614|glr-3|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001614|glr-3|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001614|glr-3|1474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001614|glr-3|1501nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001614|glr-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001614|glr-3|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2444|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001615|glr-4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001615|glr-4|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=974|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001615|glr-4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001615|glr-4|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001615|glr-4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001615|glr-4|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001615|glr-4|678nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|145nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=65|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|163nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2853|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=484|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|413nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|419nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=202|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001616|glr-5|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001617|glr-6|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001617|glr-6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001617|glr-6|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1401|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001617|glr-6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001617|glr-6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001617|glr-6|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001618|glr-7|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001618|glr-7|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001618|glr-7|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001619|glr-8|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001619|glr-8|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001619|glr-8|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001619|glr-8|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001619|glr-8|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001619|glr-8|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001619|glr-8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001620|glt-1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001620|glt-1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8441|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001620|glt-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001620|glt-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001621|glt-3|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=245|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1014nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|1593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|634nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|656nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001622|glt-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001623|glt-5|304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001623|glt-5|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001623|glt-5|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|1130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001624|glt-6|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001625|glt-7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001625|glt-7|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001626|gly-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001626|gly-1|55nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001626|gly-1|59nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=83|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001626|gly-1|64nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=40|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001628|gly-3|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001628|gly-3|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001628|gly-3|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2976|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001628|gly-3|455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001628|gly-3|457nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001628|gly-3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001629|gly-4|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001629|gly-4|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001629|gly-4|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2312|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3333|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001630|gly-5|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001631|gly-6|1330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001631|gly-6|499nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001631|gly-6|504nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=746|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00001631|gly-6|507nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001631|gly-6|511nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001631|gly-6|534nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001632|gly-7|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001632|gly-7|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001632|gly-7|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001632|gly-7|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2409|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001632|gly-7|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001632|gly-7|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001633|gly-8|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1506|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001635|gly-10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001636|gly-11|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00001636|gly-11|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001636|gly-11|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001636|gly-11|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001636|gly-11|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001636|gly-11|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001636|gly-11|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|710nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|712nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|715nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|720nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|787nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|790nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1764|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|795nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|798nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001637|gly-12|801nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001638|gly-13|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001638|gly-13|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001638|gly-13|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=968|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001638|gly-13|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001638|gly-13|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001638|gly-13|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001639|gly-14|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001639|gly-14|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001640|gly-15|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001640|gly-15|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001643|gly-18|1087nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001643|gly-18|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001643|gly-18|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001644|gly-19|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3901|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|380nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|382nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001645|gly-20|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001646|gna-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001646|gna-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=776|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00001646|gna-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001646|gna-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001646|gna-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001646|gna-1|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001647|gna-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001647|gna-2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3853|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001647|gna-2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3741|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001647|gna-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|1000nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|1378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|1409nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|1561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|416nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|501nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|856nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3728|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|860nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11819|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|864nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=857|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|869nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001648|goa-1|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001649|gob-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001649|gob-1|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001649|gob-1|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001649|gob-1|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001649|gob-1|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1781|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|1216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|859nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1707|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|864nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001650|gon-1|866nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001651|gon-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001651|gon-2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001651|gon-2|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001651|gon-2|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=796|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001651|gon-2|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001651|gon-2|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001651|gon-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|65nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|71nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1221|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001653|gon-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|1477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|1502nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|1527nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|1532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|1535nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|1538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=912|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001660|gop-1|987nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001661|gop-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3032|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00001661|gop-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00001661|gop-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001661|gop-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001661|gop-2|916nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001661|gop-2|960nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001662|gop-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001662|gop-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001662|gop-3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001662|gop-3|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5493|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00001662|gop-3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001662|gop-3|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001663|gpa-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001663|gpa-1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001663|gpa-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=541|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001664|gpa-2|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001665|gpa-3|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001665|gpa-3|1151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001665|gpa-3|1154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001665|gpa-3|1156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001665|gpa-3|1159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001665|gpa-3|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|543nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|546nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|885nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|888nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|891nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001666|gpa-4|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001667|gpa-5|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001667|gpa-5|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001668|gpa-6|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001668|gpa-6|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001668|gpa-6|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001668|gpa-6|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001668|gpa-6|433nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00001668|gpa-6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|469nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|478nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1543|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|484nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=406|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|486nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001669|gpa-7|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001670|gpa-8|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001670|gpa-8|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001670|gpa-8|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001670|gpa-8|1146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001670|gpa-8|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001670|gpa-8|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001670|gpa-8|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001671|gpa-9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001671|gpa-9|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001671|gpa-9|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001671|gpa-9|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=249|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|1031nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001672|gpa-10|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001673|gpa-11|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=185|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001673|gpa-11|282nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001673|gpa-11|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001673|gpa-11|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001674|gpa-12|187nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=502|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001674|gpa-12|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|798nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001676|gpa-14|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=277|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001677|gpa-15|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1612|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|1540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001678|gpa-16|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1042nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1067nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1092nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12282|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3714|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|517nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|519nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|521nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=240|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|525nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|528nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|530nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|654nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|961nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|965nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=706|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|967nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001679|gpb-1|971nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1085|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=597|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=869|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001680|gpb-2|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|1286nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|1498nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|1506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|166nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=394|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|409nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1499|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=335|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|425nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=607|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|427nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|478nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001681|gpc-1|486nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=276|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=446|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24584|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1449|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=529|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1578|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001682|gpc-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001683|gpd-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001683|gpd-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001683|gpd-1|1433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001683|gpd-1|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15146|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001683|gpd-1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=233|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001683|gpd-1|962nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001683|gpd-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2504|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=427|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110499|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2197|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001684|gpd-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24211|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21239|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12339|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=891|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001685|gpd-3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001686|gpd-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10220|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001686|gpd-4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001686|gpd-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001687|gpn-1|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=201|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001688|gpr-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001688|gpr-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=563|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001689|gpr-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001689|gpr-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001689|gpr-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001689|gpr-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=848|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001689|gpr-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001690|grd-1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001690|grd-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00001690|grd-1|59nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001690|grd-1|62nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001690|grd-1|64nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|193nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|201nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001691|grd-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1845|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6051|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001692|grd-3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6400|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|70nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|73nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1660|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001693|grd-4|88nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16025|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|293nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001694|grd-5|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001695|grd-6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1148|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=167|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001696|grd-7|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001697|grd-8|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001698|grd-9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001698|grd-9|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001698|grd-9|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5821|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=565|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=469|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001699|grd-10|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001700|grd-11|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00001700|grd-11|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00001700|grd-11|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00001700|grd-11|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00001701|grd-12|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001701|grd-12|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001702|grd-13|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001702|grd-13|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001702|grd-13|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001702|grd-13|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2117|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001703|grd-14|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001703|grd-14|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5811|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001703|grd-14|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001703|grd-14|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001704|grd-15|32nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001704|grd-15|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001704|grd-15|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001704|grd-15|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001705|grd-16|1216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001705|grd-16|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001707|grh-1|1241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001707|grh-1|1260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001707|grh-1|1280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001707|grh-1|1288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001707|grh-1|1290nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=209|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001707|grh-1|1292nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|314nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3330|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|764nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|767nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001708|grk-1|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|629nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|639nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|642nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001709|grk-2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001710|grl-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001711|grl-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001711|grl-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001711|grl-2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001711|grl-2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001711|grl-2|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|295nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001712|grl-3|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4432|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1256|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|71nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001714|grl-5|74nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001715|grl-6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001716|grl-7|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001716|grl-7|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1151|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001716|grl-7|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001716|grl-7|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001716|grl-7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=442|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001716|grl-7|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001716|grl-7|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001717|grl-8|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001717|grl-8|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001717|grl-8|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2724|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001717|grl-8|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001717|grl-8|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1087|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001718|grl-9|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|1328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|1333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=577|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1230|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001719|grl-10|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001720|grl-11|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=312|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001721|grl-12|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001722|grl-13|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001723|grl-14|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001723|grl-14|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001723|grl-14|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001724|grl-15|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001724|grl-15|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001724|grl-15|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001724|grl-15|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001724|grl-15|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2860|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8403|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001725|grl-16|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001726|grl-17|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001726|grl-17|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001726|grl-17|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001727|grl-18|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001727|grl-18|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001727|grl-18|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1157|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001728|grl-19|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001729|grl-20|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001729|grl-20|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001729|grl-20|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4467|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001729|grl-20|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001729|grl-20|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4031|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=442|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001730|grl-21|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001731|grl-22|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001731|grl-22|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001731|grl-22|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001731|grl-22|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001732|grl-23|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001732|grl-23|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001732|grl-23|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001733|grl-24|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001733|grl-24|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001733|grl-24|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001733|grl-24|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001733|grl-24|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001733|grl-24|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001734|grl-25|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001734|grl-25|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001735|grl-26|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001735|grl-26|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001735|grl-26|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001736|grl-27|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=920|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001736|grl-27|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001736|grl-27|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001736|grl-27|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001739|grl-30|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=649|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001740|gro-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|1149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=683|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9809|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|569nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=535|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001743|grp-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7622|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=435|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001744|gars-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|1464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|691nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|801nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|810nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001745|gsa-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|632nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|656nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|931nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|935nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|944nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9321|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001746|gsk-3|947nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|654nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12892|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|664nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=970|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|738nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|765nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001747|gsp-1|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|1590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2727|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=658|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10858|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001748|gsp-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8977|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001749|gst-1|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23454|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001750|gst-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001750|gst-2|897nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001750|gst-2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001751|gst-3|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001751|gst-3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001751|gst-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001751|gst-3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|1200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3233|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001752|gst-4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|20nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1134|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39969|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001753|gst-5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001754|gst-6|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1337|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001754|gst-6|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001754|gst-6|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001754|gst-6|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001754|gst-6|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001754|gst-6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001754|gst-6|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=407|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=540|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35397|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2803|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001755|gst-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001756|gst-8|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001756|gst-8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001756|gst-8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001756|gst-8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001756|gst-8|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001757|gst-9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001757|gst-9|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001757|gst-9|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001757|gst-9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001757|gst-9|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8761|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001758|gst-10|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|1536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=248|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1005|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=426|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001759|gst-11|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001760|gst-12|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2438|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001761|gst-13|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001761|gst-13|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001761|gst-13|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001761|gst-13|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8116|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001761|gst-13|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001761|gst-13|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001761|gst-13|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001762|gst-14|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001762|gst-14|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001762|gst-14|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001763|gst-15|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001763|gst-15|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001763|gst-15|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001764|gst-16|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001764|gst-16|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=557|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001764|gst-16|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2359|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001764|gst-16|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001765|gst-17|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001765|gst-17|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001766|gst-18|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001767|gst-19|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001767|gst-19|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001767|gst-19|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001767|gst-19|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=531|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10565|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001768|gst-20|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001769|gst-21|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001769|gst-21|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001769|gst-21|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001769|gst-21|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001769|gst-21|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001769|gst-21|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001769|gst-21|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001770|gst-22|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001770|gst-22|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001770|gst-22|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001770|gst-22|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001771|gst-23|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001771|gst-23|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1190|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6977|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001772|gst-24|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001773|gst-25|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00001773|gst-25|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00001774|gst-26|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001774|gst-26|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1159|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001774|gst-26|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1067|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001775|gst-27|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001775|gst-27|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=722|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00001775|gst-27|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2988|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001775|gst-27|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=662|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=373|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=750|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001776|gst-28|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001777|gst-29|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001777|gst-29|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001777|gst-29|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001777|gst-29|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001777|gst-29|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001778|gst-30|119nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001778|gst-30|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001778|gst-30|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001779|gst-31|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001779|gst-31|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001779|gst-31|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001780|gst-32|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001781|gst-33|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001781|gst-33|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=282|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001781|gst-33|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001782|gst-34|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001783|gst-35|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00001783|gst-35|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001783|gst-35|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001784|gst-36|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001784|gst-36|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=773|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001784|gst-36|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3755|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001784|gst-36|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001784|gst-36|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001784|gst-36|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001784|gst-36|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001786|gst-38|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001786|gst-38|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001786|gst-38|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001786|gst-38|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=835|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001787|gst-39|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001787|gst-39|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001787|gst-39|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=628|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00001787|gst-39|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001787|gst-39|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=989|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001787|gst-39|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1096|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1216|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001788|gst-40|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001789|gst-41|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001789|gst-41|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00001789|gst-41|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|1403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1571|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001790|gst-42|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001791|gst-43|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001791|gst-43|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001791|gst-43|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001791|gst-43|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001791|gst-43|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001792|gst-44|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001792|gst-44|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00001792|gst-44|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=721|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001793|gsy-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3822|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5712|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4521|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1324|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=255|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001794|gta-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=666|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001795|gtl-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001796|gtl-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001796|gtl-2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001803|lite-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001803|lite-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7849|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001803|lite-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001803|lite-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001803|lite-1|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001803|lite-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|129nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001804|gur-3|603nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001805|gur-4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001805|gur-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001805|gur-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00001805|gur-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001805|gur-4|74nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=261|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001805|gur-4|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001805|gur-4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001806|gur-5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00001806|gur-5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00001806|gur-5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00001806|gur-5|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=513|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=260|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001808|gut-2|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8384|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001811|haf-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001811|haf-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001811|haf-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5527|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001812|haf-2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=610|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3203|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|238nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|241nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|248nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001813|haf-3|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2125|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001814|haf-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2101|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001815|hmt-1|703nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001816|haf-6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001816|haf-6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001816|haf-6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1005|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1337|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001817|haf-7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|1060nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|1095nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1108|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001819|haf-9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001820|ham-1|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001820|ham-1|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001820|ham-1|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=451|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00001820|ham-1|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001820|ham-1|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001820|ham-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001821|ham-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001821|ham-2|587nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001821|ham-2|592nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001821|ham-2|594nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=252|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=533|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=393|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001823|hap-1|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=396|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00001824|hbl-1|1376nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001824|hbl-1|1379nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001824|hbl-1|1387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001824|hbl-1|1393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00001824|hbl-1|1397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4249|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=876|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|548nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|686nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|697nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|700nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001827|hcf-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001828|hch-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001828|hch-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5515|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001829|hcp-1|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1811|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|1169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001830|hcp-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001831|hcp-3|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2653|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00001831|hcp-3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001831|hcp-3|146nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001831|hcp-3|150nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2167|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001832|hcp-4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001833|hcp-6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1459|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001833|hcp-6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001833|hcp-6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001833|hcp-6|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001833|hcp-6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001833|hcp-6|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001833|hcp-6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10403|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001834|hda-1|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=895|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001835|hda-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001836|hda-3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001836|hda-3|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001836|hda-3|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2796|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00001836|hda-3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|1006nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1508|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|660nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|665nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|668nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001837|hda-4|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001838|hda-10|1126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001838|hda-10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001838|hda-10|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001838|hda-10|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001838|hda-10|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=811|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001839|hdl-1|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001839|hdl-1|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001839|hdl-1|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001839|hdl-1|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8819|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5321|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|454nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|458nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001840|hel-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001841|hen-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001842|her-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001842|her-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001842|her-1|402nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001842|her-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001842|her-1|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001842|her-1|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00001842|her-1|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001843|hgo-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001843|hgo-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001843|hgo-1|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001843|hgo-1|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001843|hgo-1|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6883|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001843|hgo-1|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001843|hgo-1|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001844|hid-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001844|hid-1|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001844|hid-1|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=547|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00001844|hid-1|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=468|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001844|hid-1|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001844|hid-1|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001844|hid-1|293nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|301nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|303nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|399nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13976|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|402nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=340|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|408nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001851|hif-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=491|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001852|hil-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001852|hil-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1501|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2081|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2149|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2144|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1537|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26966|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=674|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001853|hil-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=612|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9616|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001854|hil-3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2892|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|1545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13834|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=277|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8865|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001855|hil-4|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1850|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15059|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001856|hil-5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001857|hil-6|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001857|hil-6|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2394|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=395|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001858|hil-7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001860|him-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001860|him-1|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=770|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001860|him-1|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3615|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001860|him-1|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001860|him-1|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001860|him-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2858|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=880|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|256nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001862|him-3|265nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001863|him-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001863|him-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001863|him-4|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001863|him-4|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1001|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001863|him-4|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=324|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001863|him-4|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001864|him-5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001864|him-5|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001864|him-5|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001864|him-5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001864|him-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|1290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1194|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001865|him-6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001867|him-8|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001867|him-8|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1380|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00001867|him-8|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1187|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001869|him-10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=516|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001872|him-14|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001874|him-17|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3157|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001874|him-17|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001874|him-17|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001874|him-17|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001881|his-7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001881|his-7|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001881|his-7|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001881|his-7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001881|his-7|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001881|his-7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00001882|his-8|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001882|his-8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001882|his-8|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001882|his-8|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001882|his-8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001882|his-8|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001882|his-8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=841|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|855nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|861nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|863nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3417|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|871nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|873nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001888|his-14|876nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3208|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17214|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001898|his-24|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001903|his-29|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001908|his-34|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001908|his-34|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001908|his-34|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3424|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25801|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1632|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|1303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=841|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1737|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1606|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|194nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|210nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|230nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001909|his-35|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|1223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|1259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|1269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|1587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|845nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|850nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|853nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4358|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|862nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238971|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|869nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10883|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|895nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|901nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|905nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|908nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1070|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|910nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1152|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|914nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34709|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|947nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|954nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|998nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001910|C50F4.6|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001912|his-38|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001912|his-38|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=619|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001912|his-38|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001912|his-38|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001912|his-38|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001914|his-40|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001914|his-40|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001914|his-40|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229388|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22465|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=474|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=422|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001915|his-41|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001928|his-54|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001928|his-54|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001928|his-54|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00001928|his-54|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001928|his-54|1297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00001929|his-55|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001929|his-55|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001929|his-55|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1279|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001929|his-55|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=715|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001929|his-55|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001929|his-55|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=416|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001929|his-55|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001930|his-56|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001930|his-56|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001930|his-56|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001931|his-57|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001931|his-57|765nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001931|his-57|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001931|his-57|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001931|his-57|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001932|his-58|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001933|his-59|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001934|his-60|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001934|his-60|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|1087nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|771nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|773nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001936|his-62|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00001941|his-67|1004nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001941|his-67|1453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001941|his-67|1457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001941|his-67|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001941|his-67|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001941|his-67|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001941|his-67|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001943|his-69|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001943|his-69|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001943|his-69|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00001944|his-70|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=392|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00001944|his-70|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=836|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001944|his-70|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001944|his-70|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001945|his-71|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001945|his-71|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001945|his-71|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6581|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001945|his-71|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001945|his-71|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001945|his-71|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001945|his-71|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1737|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40398|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2539|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001946|his-72|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001947|his-73|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001947|his-73|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001947|his-73|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001948|hlh-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001948|hlh-1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001948|hlh-1|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001948|hlh-1|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|379nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|383nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=230|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|386nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=568|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|390nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|413nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=260|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001949|hlh-2|724nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001950|hlh-3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001950|hlh-3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001950|hlh-3|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001950|hlh-3|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001950|hlh-3|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001950|hlh-3|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001951|hlh-4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=879|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001951|hlh-4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001952|hlh-6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001952|hlh-6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001952|hlh-6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001952|hlh-6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|1234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=455|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=217|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001953|hlh-8|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001954|hlh-10|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001954|hlh-10|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001954|hlh-10|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001954|hlh-10|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001954|hlh-10|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|1574nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=325|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=385|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|608nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4000|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=972|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|686nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|692nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|695nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|766nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001955|hlh-11|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|491nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001956|hlh-12|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00001957|hlh-13|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001957|hlh-13|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001957|hlh-13|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2266|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001957|hlh-13|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001957|hlh-13|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001957|hlh-13|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001957|hlh-13|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001958|hlh-14|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001958|hlh-14|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001958|hlh-14|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001959|hlh-15|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001959|hlh-15|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001959|hlh-15|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001959|hlh-15|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00001960|hlh-16|1593nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001960|hlh-16|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001960|hlh-16|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=557|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3331|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001961|hlh-17|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001962|hlh-19|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001963|btb-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001964|hlh-25|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001966|hlh-27|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001967|hlh-28|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00001968|hlh-29|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001968|hlh-29|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5421|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35776|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001971|hmg-1.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|242nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|383nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|386nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|390nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=449|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|397nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11203|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1066|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4253|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|500nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|502nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=712|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|507nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001972|hmg-1.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001973|hmg-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001973|hmg-3|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001973|hmg-3|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001973|hmg-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001973|hmg-3|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001973|hmg-3|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001973|hmg-3|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001974|hmg-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001974|hmg-4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1764|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001974|hmg-4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001974|hmg-4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001974|hmg-4|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001974|hmg-4|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2972|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001975|hmg-5|244nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001976|hmg-11|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001976|hmg-11|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001976|hmg-11|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001976|hmg-11|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5495|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00001976|hmg-11|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1460|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001976|hmg-11|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001976|hmg-11|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9357|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=673|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1778|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|230nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001977|hmg-12|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3932|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=421|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001978|hmp-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=960|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=575|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001979|hmp-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|612nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14473|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|617nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|622nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001980|hmr-1|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001981|hnd-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001981|hnd-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001981|hnd-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001981|hnd-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001983|hoe-1|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001983|hoe-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1200|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001983|hoe-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1110|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001983|hoe-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001984|hog-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001984|hog-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=414|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001984|hog-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001984|hog-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001984|hog-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001984|hog-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001984|hog-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001985|hop-1|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001985|hop-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001985|hop-1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=987|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3023|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=780|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|415nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|417nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001986|hot-1|930nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=383|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001987|hot-2|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001988|hot-3|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001988|hot-3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001988|hot-3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|727nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001989|hot-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001990|hot-5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=335|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001990|hot-5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20120|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001990|hot-5|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001990|hot-5|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001990|hot-5|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001990|hot-5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|1586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1494|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001991|hot-6|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|1096nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1501|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001992|hot-7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001993|hpd-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001993|hpd-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001993|hpd-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001993|hpd-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001993|hpd-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2732|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001993|hpd-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3789|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001993|hpd-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1087nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1091nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=649|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1096nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4137|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|1144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|644nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|670nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|793nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001994|hpk-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001995|hpl-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001995|hpl-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001995|hpl-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001995|hpl-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001995|hpl-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001995|hpl-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1821|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1478|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=711|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001996|hpl-2|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001997|hpr-9|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001997|hpr-9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001997|hpr-9|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001997|hpr-9|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001997|hpr-9|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00001997|hpr-9|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00001997|hpr-9|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=195|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001998|hpr-17|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001998|hpr-17|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001998|hpr-17|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=724|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|1226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|1316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=413|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=570|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4426|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9461|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=867|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23845|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4903|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00001999|hrp-1|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|406nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3269|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6387|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002000|hrp-2|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=407|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3272|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3536|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002001|hars-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|802nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|805nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|808nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=266|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|813nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|817nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2945|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2067|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|875nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|931nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002002|hsb-1|933nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002003|hse-5|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00002003|hse-5|1076nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002003|hse-5|1087nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1460|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002003|hse-5|1091nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002003|hse-5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002003|hse-5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1096|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3023|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002004|hsf-1|736nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4401|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79385|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8430|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|289nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|435nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002005|hsp-1|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1776|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31234|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5118|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=514|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|471nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|478nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002007|hsp-3|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20834|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2383|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002008|hsp-4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9069|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2507|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|492nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|497nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002010|hsp-6|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002011|hsp-12.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002011|hsp-12.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002011|hsp-12.2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002011|hsp-12.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1621|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002011|hsp-12.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2348|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002011|hsp-12.2|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002011|hsp-12.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002012|hsp-12.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002012|hsp-12.3|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4913|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002012|hsp-12.3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002012|hsp-12.3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002012|hsp-12.3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002013|hsp-12.6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=314|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2936|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=415|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1051|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=342|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|664nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|680nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|760nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|768nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=654|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|774nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|781nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=239|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21700|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002015|hsp-16.1|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1328|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1944914|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3512|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=926|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|1423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=580|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1303|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105512|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1104|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3140|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=601|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10215|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5850|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21012|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=602|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|819nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|850nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|861nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68619|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2287|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002016|hsp-16.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13309|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28791|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=432|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1626|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1215|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|1244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=983|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373459|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29089|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=870|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|1522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=885|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=576|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=449|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=656|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9913|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62367|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=402807|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1563811|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1110307|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19278|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002017|hsp-16.11|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20110|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1689|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95932|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|1081nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1093381|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332601|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31922|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|1207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24156|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=500|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|1512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=724|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=427|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9393|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10557|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|609nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|629nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|647nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6801|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=736|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|791nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1425|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|843nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=583|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=404|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|949nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|952nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|961nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002018|hsp-16.41|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|520nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|525nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|527nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|736nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=345|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|819nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=516|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|834nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002019|hsp-16.48|837nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=473|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6922|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=423|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1129|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=377|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2863|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13044|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5943434|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2012596|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13955|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|665nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6732|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=621|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=767|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002020|hsp-16.49|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2047|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=279|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00002021|hsp-17|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1071|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11158|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1321|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=412|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=315|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2084|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|386nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|667nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1597|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002023|hsp-25|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|1166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|1376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3669|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002024|hsp-43|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|388nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|390nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2026|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10067|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|400nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|403nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|406nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|763nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|820nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002025|hsp-60|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2610|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1375|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|1195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=482|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|259nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|316nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|351nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|488nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|574nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|667nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=503|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1399|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37810|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8526|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213782|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9154|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002026|hsp-70|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15984|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|1504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|1565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|479nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1425|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|482nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1539|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=723|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|494nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2546|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|878nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|956nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002027|hsr-9|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=911|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002028|hst-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002029|hst-2|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00002029|hst-2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00002029|hst-2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002029|hst-2|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=589|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002029|hst-2|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002029|hst-2|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002030|hst-3.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002030|hst-3.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002031|hst-6|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002031|hst-6|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=732|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002031|hst-6|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1652|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1997|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002032|htp-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002033|htp-2|1066nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002033|htp-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002033|htp-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1499|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002033|htp-2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002033|htp-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002033|htp-2|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1089|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|413nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|721nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002034|htp-3|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002035|hum-1|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002035|hum-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002035|hum-1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002035|hum-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1731|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002035|hum-1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002035|hum-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002035|hum-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|1054nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4832|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=779|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|372nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|375nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002036|hum-2|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002037|hum-4|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7036|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=602|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002038|hum-5|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002039|hum-6|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002039|hum-6|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=305|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002039|hum-6|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002039|hum-6|547nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002040|hum-7|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002040|hum-7|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=389|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002040|hum-7|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002041|hum-8|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002041|hum-8|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1563|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002041|hum-8|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002042|hus-1|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002042|hus-1|402nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002042|hus-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002042|hus-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002042|hus-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1601|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002042|hus-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002042|hus-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1420|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002043|hyl-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3475|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1067|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002044|hyl-2|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14117|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10458|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=412|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26190|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7791|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1048|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12973|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1360|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002045|icd-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=845|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2808|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1722|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002046|icln-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1530|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1134|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002047|icp-1|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|1010nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=490|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|210nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|213nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31873|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|405nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|407nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002048|ida-1|883nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002050|ifa-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002050|ifa-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002051|ifa-3|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1047|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=561|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|308nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002052|ifa-4|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=898|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5542|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|457nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002053|ifb-1|462nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6650|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002054|ifb-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002055|ifc-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002055|ifc-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=872|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002055|ifc-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3784|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2253|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=761|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|573nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|576nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|579nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002056|ifc-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002057|ifd-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002057|ifd-1|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002057|ifd-1|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=420|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002057|ifd-1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=239|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002057|ifd-1|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002057|ifd-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002057|ifd-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002058|ifd-2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002058|ifd-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002058|ifd-2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6842|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7635|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=793|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002059|ife-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=889|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1627|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002060|ife-2|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1269|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1166|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|349nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3995|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|352nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=780|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002061|ife-3|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|1150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11440|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|1183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1050|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002062|ife-4|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002063|ife-5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=691|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002063|ife-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002064|iff-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002064|iff-1|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002064|iff-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002064|iff-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002064|iff-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002064|iff-1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50291|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002064|iff-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1335|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2282|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22837|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|403nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|407nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2300|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|409nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3102|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|421nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3477|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002065|iff-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1018nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1021nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7296|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=688|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2172|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|247nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|253nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=196|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=181|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002066|ifg-1|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002067|ifp-1|114nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002067|ifp-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=801|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002067|ifp-1|271nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002067|ifp-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002067|ifp-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002067|ifp-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002067|ifp-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2930|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4004|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1644|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=248|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=291|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2046|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002068|ify-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|1437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|1447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|1453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=518|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002069|ikb-1|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|131nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3687|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2513|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=873|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1192|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002070|ile-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2658|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002071|ile-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2661|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002072|ima-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3133|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9079|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1812|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=387|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|204nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|206nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002073|ima-2|975nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1041nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1047nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3984|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1054nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7631|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1093nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1097nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=242|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|1099nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002074|ima-3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3541|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|690nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|694nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|704nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002075|imb-1|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002076|imb-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002076|imb-2|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002076|imb-2|519nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002076|imb-2|523nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002076|imb-2|525nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5140|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002076|imb-2|534nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=451|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|421nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15364|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|423nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3021|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002077|imb-3|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3292|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1368|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3655|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2715|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1344|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|777nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|782nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|788nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1413|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002078|xpo-1|790nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3510|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|377nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002079|xpo-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|524nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|526nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|528nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1218|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|542nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|546nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=707|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002080|xpo-3|574nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002081|ina-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002081|ina-1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002081|ina-1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1320|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002081|ina-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002081|ina-1|328nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002081|ina-1|336nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|1339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|1347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|1534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=168|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18335|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8149|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|330nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=565|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1001|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002083|inf-1|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002084|ins-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002084|ins-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002084|ins-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002084|ins-1|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002084|ins-1|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002084|ins-1|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3196|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002084|ins-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002085|ins-2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002085|ins-2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=381|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002085|ins-2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57388|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002086|ins-3|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2889|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|460nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002087|ins-4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002088|ins-5|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002088|ins-5|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2153|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002088|ins-5|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002088|ins-5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9856|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17689|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35784|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3963|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|1467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|1474nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|1476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1516|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002089|ins-6|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002090|ins-7|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002090|ins-7|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002090|ins-7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=652|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002090|ins-7|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1488|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1489|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7044|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002092|ins-9|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002093|ins-10|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002093|ins-10|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002093|ins-10|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002093|ins-10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002093|ins-10|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8269|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002093|ins-10|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002093|ins-10|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2431|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=249|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002094|ins-11|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002095|ins-12|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002095|ins-12|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002096|ins-13|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002096|ins-13|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002096|ins-13|594nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002096|ins-13|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002096|ins-13|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002096|ins-13|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7157|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|769nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|771nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002097|ins-14|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002098|ins-15|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002098|ins-15|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=924|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002098|ins-15|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002098|ins-15|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002099|ins-16|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002099|ins-16|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|1119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|1312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1068|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13367|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3754|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4021|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1507|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|722nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|912nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|942nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002100|ins-17|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2356|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|486nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=143|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002101|ins-18|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002102|ins-19|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=753|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002103|ins-20|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002103|ins-20|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002103|ins-20|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002104|ins-21|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002104|ins-21|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002104|ins-21|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002104|ins-21|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002104|ins-21|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002104|ins-21|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=753|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1694|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3686|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002105|ins-22|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002106|ins-23|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002106|ins-23|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3125|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002106|ins-23|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002106|ins-23|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=678|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6163|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002107|ins-24|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2549|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002108|ins-25|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=995|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17004|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56937|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=922|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=998|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=372|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=357|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002109|ins-26|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002110|ins-27|1371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002110|ins-27|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002110|ins-27|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1726|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002110|ins-27|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002110|ins-27|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1155|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=282|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1366|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36699|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002111|ins-28|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9768|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1901|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17907|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002112|ins-29|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=606|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=391|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18057|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002113|ins-30|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002114|ins-31|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1532|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1691|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1961|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002115|ins-32|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002116|ins-33|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3838|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002116|ins-33|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002117|ins-34|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002117|ins-34|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002117|ins-34|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002117|ins-34|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002118|ins-35|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002118|ins-35|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002118|ins-35|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002119|ins-36|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002119|ins-36|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002119|ins-36|648nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002119|ins-36|655nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002119|ins-36|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=965|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002120|ins-37|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1932|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|1060nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|1063nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|556nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|560nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002123|inx-1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1017|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002124|inx-2|728nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002125|inx-3|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002125|inx-3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002125|inx-3|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002125|inx-3|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002125|inx-3|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00002125|inx-3|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1215|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002125|inx-3|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002127|inx-5|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002127|inx-5|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1087|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002127|inx-5|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002127|inx-5|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002128|inx-6|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002128|inx-6|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=682|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002129|inx-7|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5095|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=608|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002130|inx-8|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|132nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|140nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002131|inx-9|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|224nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=393|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002132|inx-10|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002133|inx-11|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1677|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2278|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002134|inx-12|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002135|inx-13|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002135|inx-13|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002135|inx-13|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002135|inx-13|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3864|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002135|inx-13|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002135|inx-13|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002135|inx-13|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|1357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1275|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5229|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002136|inx-14|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002137|inx-15|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002137|inx-15|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002137|inx-15|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002137|inx-15|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002137|inx-15|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002138|inx-16|588nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002138|inx-16|591nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002138|inx-16|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002138|inx-16|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002138|inx-16|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1146|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002138|inx-16|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002139|inx-17|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002140|inx-18|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=886|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002140|inx-18|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002141|inx-19|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00002141|inx-19|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002141|inx-19|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002141|inx-19|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00002142|inx-20|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002142|inx-20|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002142|inx-20|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002142|inx-20|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002142|inx-20|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00002143|inx-21|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002143|inx-21|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002143|inx-21|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00002143|inx-21|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002143|inx-21|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002143|inx-21|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1224|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002143|inx-21|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3009|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002144|inx-22|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|448nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=265|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|451nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|453nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|455nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|468nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|474nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|478nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=390|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|483nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|554nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|573nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|576nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002146|ipp-5|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2062|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002147|ire-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|304nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|343nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=638|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|353nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|385nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|390nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=275|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|393nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|489nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|493nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002148|gon-14|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002149|irk-1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002149|irk-1|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002149|irk-1|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002149|irk-1|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002149|irk-1|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002149|irk-1|636nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|504nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002150|irk-2|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=936|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=595|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002151|irk-3|757nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|1340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|1390nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7739|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002152|iars-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|1059nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|1062nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|1536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|588nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|595nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1029|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|669nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=321|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|672nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002153|iars-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23029|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1876|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4249|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002162|isp-1|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002163|ist-1|396nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=702|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002163|ist-1|399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002163|ist-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002169|isw-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002169|isw-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002169|isw-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002169|isw-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8503|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00002169|isw-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002169|isw-1|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002169|isw-1|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|1035nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|1045nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|1060nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1682|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|495nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002173|itr-1|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002174|itx-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002174|itx-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=749|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002174|itx-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002174|itx-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=807|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1122|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002175|jac-1|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002176|jip-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002176|jip-1|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002176|jip-1|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3167|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|162nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|166nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1439|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1158|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002177|jkk-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002178|jnk-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3774|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002178|jnk-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002178|jnk-1|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002178|jnk-1|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002178|jnk-1|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002178|jnk-1|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|1423nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|502nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|505nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|512nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=509|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3178|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002179|jph-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002180|jtr-1|1180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002180|jtr-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002180|jtr-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=737|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002180|jtr-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002180|jtr-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002181|kal-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002181|kal-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002181|kal-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002181|kal-1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1382|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002181|kal-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002181|kal-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002182|kap-1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002182|kap-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002182|kap-1|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002182|kap-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002182|kap-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=783|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002182|kap-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1067|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002182|kap-1|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4334|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3282|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=737|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|1212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002183|kat-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002184|kel-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1044|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002184|kel-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002184|kel-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002185|kel-3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2672|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002186|kel-10|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=854|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00002186|kel-10|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=777|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=347|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=913|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002187|kgb-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002188|kgb-2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002188|kgb-2|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|1475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|1575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|469nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|478nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4109|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|803nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|894nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002189|kin-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1000nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1007nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=845|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1011nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1041nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1052nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16955|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|1529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|416nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|418nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|468nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|471nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|991nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002190|kin-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|355nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3609|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|357nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7432|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1741|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|376nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2111|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002191|kin-3|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|344nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=279|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3393|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|418nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=462|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002192|kin-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002193|kin-5|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=387|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002193|kin-5|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002194|kin-6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00002194|kin-6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00002194|kin-6|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00002195|kin-9|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=205|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|1082nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|223nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4111|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3415|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8369|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=653|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11450|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002196|kin-10|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002198|kin-14|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=678|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002198|kin-14|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=920|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002198|kin-14|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002198|kin-14|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002198|kin-14|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002199|kin-15|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=549|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002199|kin-15|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002200|kin-16|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002200|kin-16|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002200|kin-16|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1054|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|273nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1306|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|456nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|560nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|889nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002201|kin-18|897nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|1275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|1281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|1296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|281nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|284nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|666nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9423|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|669nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|783nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|788nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3425|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002202|kin-19|790nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|1044nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1163|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|1048nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|978nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002203|kin-20|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002204|kin-21|1205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002204|kin-21|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002204|kin-21|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002205|kin-23|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002205|kin-23|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002206|kin-24|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002206|kin-24|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002206|kin-24|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002206|kin-24|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|1163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|1167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|317nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=503|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|323nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=727|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|329nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=101|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|337nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|534nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002207|sid-3|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002208|kin-26|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002208|kin-26|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|16nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|890nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3361|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|892nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|895nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|899nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002210|kin-29|932nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002211|kin-30|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002211|kin-30|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002211|kin-30|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00002213|kin-32|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002213|kin-32|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002213|kin-32|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002213|kin-32|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002213|kin-32|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002213|kin-32|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=742|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2542|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002214|klc-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1536|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=736|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2690|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002215|klc-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=816|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=563|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002216|klp-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002217|klp-4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002217|klp-4|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=550|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002217|klp-4|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3652|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002217|klp-4|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=906|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002217|klp-4|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002218|klp-6|234nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002218|klp-6|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002218|klp-6|611nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1248nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1262nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1409nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1479nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=86|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1491nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|1518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8244|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002219|klp-7|253nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002220|gcc-1|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002220|gcc-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002220|gcc-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1161|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002220|gcc-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002220|gcc-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002222|klp-11|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002222|klp-11|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002222|klp-11|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002222|klp-11|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002222|klp-11|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=864|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3781|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002223|klp-12|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002224|klp-13|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002224|klp-13|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00002224|klp-13|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002224|klp-13|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002224|klp-13|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002224|klp-13|721nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002225|klp-15|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002225|klp-15|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002225|klp-15|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002225|klp-15|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3237|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002225|klp-15|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002225|klp-15|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002225|klp-15|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9141|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|549nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|555nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|563nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002226|klp-16|984nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002227|klp-17|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00002227|klp-17|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2752|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002228|klp-18|767nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1511|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1553|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002229|klp-19|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002230|klp-20|1249nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=538|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002230|klp-20|1252nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002230|klp-20|1254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002230|klp-20|1280nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002230|klp-20|1288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002231|knl-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002231|knl-1|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=934|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002231|knl-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=842|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002231|knl-1|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002231|knl-1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002231|knl-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002231|knl-1|380nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=806|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1957|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002232|kpc-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002233|kqt-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002233|kqt-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002233|kqt-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002233|kqt-1|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00002233|kqt-1|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002233|kqt-1|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002234|kqt-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002234|kqt-2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=528|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002234|kqt-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002234|kqt-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002234|kqt-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002235|kqt-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002235|kqt-3|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002235|kqt-3|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2143|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=197|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9115|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002238|kars-1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|245nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=861|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002239|ksr-1|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|546nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2434|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|549nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|552nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002240|ksr-2|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002241|kup-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002241|kup-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002241|kup-1|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3025|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002241|kup-1|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|227nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=997|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|433nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002242|kvs-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002243|lad-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002243|lad-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002243|lad-2|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=579|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00002243|lad-2|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=823|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002243|lad-2|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1053nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1064nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1471nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1473nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=354|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4861|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|1505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|232nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|341nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|867nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002244|laf-1|887nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3883|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002245|lag-1|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002246|lag-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002246|lag-2|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002247|lam-1|1152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002247|lam-1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002247|lam-1|524nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4582|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002247|lam-1|529nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002247|lam-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002247|lam-1|570nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002248|lam-3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=438|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2491|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2267|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1802|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002249|lap-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2946|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13485|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|466nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=612|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|472nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002250|lap-2|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|337nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2351|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|548nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|556nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|564nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002251|lat-1|837nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002252|lat-2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002252|lat-2|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=518|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00002252|lat-2|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002252|lat-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12477|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|1475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=471|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=558|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14508|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002253|lbp-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15559|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1681|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3037|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34477|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4801|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002254|lbp-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002255|lbp-3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6113|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002255|lbp-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002255|lbp-3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002256|lbp-4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2914|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00002257|lbp-5|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002257|lbp-5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002257|lbp-5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002257|lbp-5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002257|lbp-5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002257|lbp-5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=824|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002257|lbp-5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1911|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5369|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2556|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|1233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|126nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3415|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=832|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=510|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002258|lbp-6|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002259|lbp-7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2347|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002259|lbp-7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002259|lbp-7|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002260|lbp-8|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002260|lbp-8|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002260|lbp-8|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002260|lbp-8|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|1041nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|324nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|627nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|646nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1526|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1412|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002261|ldb-1|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23481|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=525|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002262|ldh-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2000|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|263nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2763|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=720|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3065|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002263|lea-1|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3219|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51218|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1818|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=371|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002264|lec-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|262nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|264nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=327|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|267nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=555|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2203|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16725|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|689nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|730nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002265|lec-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|1291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=859|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13116|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2636|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|989nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002266|lec-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21374|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|1109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=517|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002267|lec-4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002268|lec-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002268|lec-5|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002268|lec-5|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002268|lec-5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9563|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002268|lec-5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9213|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13088|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002269|lec-6|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|58nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=615|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002270|lec-7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=594|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26685|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002271|lec-8|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3122|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=671|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26887|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002272|lec-9|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3333|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|504nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|685nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12075|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3625|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002273|lec-10|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=481|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2101|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=774|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002274|lec-11|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002275|lem-2|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002275|lem-2|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002275|lem-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002275|lem-2|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002275|lem-2|920nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002275|lem-2|924nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1639|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002275|lem-2|956nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002276|lem-3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002276|lem-3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002276|lem-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1536|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002276|lem-3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00002276|lem-3|526nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=240|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=930|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8144|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2064|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4425|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1195|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002280|let-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|1350nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|1550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002282|let-4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|1404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|572nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|575nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|578nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=442|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002295|let-19|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|544nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|554nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1216|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=239|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002297|ect-2|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002299|let-23|1594nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002299|let-23|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002299|let-23|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=859|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002324|let-49|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002324|let-49|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1466|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00002324|let-49|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=337|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002324|let-49|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002324|let-49|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002324|let-49|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=288|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|1067nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=372|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|812nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|820nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3801|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|823nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1545|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|826nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|829nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002335|let-60|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|1074nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|1084nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1674|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2309|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=943|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66082|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1963|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002344|let-70|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|1038nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=316|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002348|myo-1|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=611|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|390nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|453nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2934|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12177|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|764nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|766nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002363|let-92|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=480|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2360|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002368|let-99|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002393|lpr-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002393|lpr-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1222|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002497|let-268|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=387|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002497|let-268|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=925|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002497|let-268|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|429nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|431nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=286|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|434nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8972|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|441nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=734|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|444nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002583|let-363|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|504nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002601|let-381|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002632|let-413|1048nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002632|let-413|1061nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1336|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002632|let-413|1067nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002632|let-413|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002632|let-413|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002632|let-413|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2575|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1401|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=669|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002637|let-418|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=985|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1320|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|733nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|738nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|745nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=728|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002694|let-502|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=570|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2418|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002696|let-504|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|643nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|653nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|655nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|659nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|661nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|721nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|774nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|781nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2508|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|784nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2900|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|788nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3376|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|791nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|819nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002717|let-526|918nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1024|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=916|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=704|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=365|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|704nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|712nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4293|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|715nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|773nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|779nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|784nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002783|let-607|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002804|let-630|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1356|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002804|let-630|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002804|let-630|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002804|let-630|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1111|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002827|let-653|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002827|let-653|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002827|let-653|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1043nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1068nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1070nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1073nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7206|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1797|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002845|let-711|978nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1785|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1236|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=689|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002850|let-716|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1276nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1554|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5663|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=209|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|924nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002855|let-721|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1122|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4406|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002879|let-754|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002881|let-756|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=716|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002881|let-756|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002881|let-756|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002889|let-765|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002889|let-765|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002889|let-765|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1462|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002889|let-765|734nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1832|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002889|let-765|739nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1107|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002889|let-765|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002889|let-765|813nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002891|let-767|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002891|let-767|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002891|let-767|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002891|let-767|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002891|let-767|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9011|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00002891|let-767|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2797|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002915|let-805|390nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1980|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002915|let-805|392nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002915|let-805|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15063|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8082|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4795|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=590|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=879|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=651|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|328nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|366nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|374nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|400nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=643|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002957|let-858|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3119|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002974|lev-1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002974|lev-1|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002974|lev-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=354|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002974|lev-1|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002974|lev-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=234|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002975|lev-8|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002976|lev-9|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002976|lev-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2776|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002977|lev-10|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6622|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2087|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71746|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4725|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9688|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5412|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=432|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=831|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002978|lev-11|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002979|lfe-2|199nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002979|lfe-2|225nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002979|lfe-2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002979|lfe-2|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002979|lfe-2|390nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1485|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002979|lfe-2|395nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002979|lfe-2|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|1184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41091|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32056|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|314nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=252|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002980|lgg-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|1304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|1325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|1384nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|242nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|256nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13599|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002981|lgg-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1642|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002982|lgg-3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002983|lgx-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002983|lgx-1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002983|lgx-1|291nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002983|lgx-1|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002983|lgx-1|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=743|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|1172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|1337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|1456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|1471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|1494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002985|lig-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1516|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002986|lig-4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002986|lig-4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1651|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002986|lig-4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002986|lig-4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002986|lig-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002986|lig-4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00002986|lig-4|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|1529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4150|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002987|lim-4|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002988|lim-6|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002988|lim-6|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1132|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002988|lim-6|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002988|lim-6|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|361nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|447nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|458nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1459|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002989|lim-7|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002990|lin-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002990|lin-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002990|lin-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002990|lin-1|411nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=711|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002990|lin-1|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002990|lin-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002990|lin-1|884nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002991|lin-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002991|lin-2|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002991|lin-2|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002991|lin-2|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002991|lin-2|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1753|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002991|lin-2|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002991|lin-2|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=411|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|409nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|411nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|413nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|417nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|425nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|428nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002992|lin-3|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002994|lin-5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002994|lin-5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002994|lin-5|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=149|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002994|lin-5|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6840|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002994|lin-5|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002994|lin-5|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|1240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|1309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=813|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|1332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=754|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|1341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|1363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002996|lin-7|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002997|lin-8|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002997|lin-8|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002997|lin-8|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1025|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002997|lin-8|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002998|lin-9|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002998|lin-9|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002998|lin-9|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002998|lin-9|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1742|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002998|lin-9|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002998|lin-9|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4130|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00002999|lin-10|928nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|1176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|258nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8523|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=278|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|266nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|393nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003000|lin-11|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|1013nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|475nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|480nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003001|lin-12|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=413|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1885|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1079|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1574|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=914|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|50nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003002|lin-13|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003003|lin-14|1601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2480|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003006|lin-17|1406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003006|lin-17|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003006|lin-17|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003006|lin-17|692nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003006|lin-17|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=797|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003007|lin-18|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003008|lin-22|1121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003008|lin-22|1232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|1476nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|620nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|636nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5495|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|638nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|641nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|856nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|863nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003009|lin-23|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003010|lin-24|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003010|lin-24|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003010|lin-24|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6864|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003010|lin-24|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=696|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003011|lin-25|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2025|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003012|lin-26|583nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|1012nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|406nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|410nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=307|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1932|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003014|lin-28|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|689nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|696nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|698nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=615|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|702nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|746nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003015|lin-29|749nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003017|lin-31|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003017|lin-31|482nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003017|lin-31|487nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003017|lin-31|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003017|lin-31|562nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003018|lin-32|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00003018|lin-32|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00003018|lin-32|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|1581nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1504|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1713|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003019|lin-33|885nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|303nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|307nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1988|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|309nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=483|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003020|lin-35|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2181|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003021|lin-36|553nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1536|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=289|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003022|lin-37|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1383|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=543|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003024|lin-39|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2508|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=655|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|335nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003025|lin-40|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2100|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|1164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2404|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003026|lin-41|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003029|lin-44|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003029|lin-44|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003029|lin-44|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00003029|lin-44|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003029|lin-44|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|682nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|687nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|700nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3199|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|703nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=310|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003030|lin-45|708nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|1076nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|1112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|1116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|1193nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|1202nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|1234nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|1250nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003031|lin-46|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003033|lin-48|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003033|lin-48|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|1450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1601|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|514nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003034|lin-49|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|1347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2287|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2906|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003035|lin-52|861nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7234|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003036|lin-53|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003037|lin-54|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003037|lin-54|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003037|lin-54|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003037|lin-54|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=657|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003037|lin-54|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003038|lin-56|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003038|lin-56|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003038|lin-56|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=863|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003038|lin-56|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1169|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003038|lin-56|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|633nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=181|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|635nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1304|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|639nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1979|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003040|lin-59|645nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=474|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2814|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003041|lin-61|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|710nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|712nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=531|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|718nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|720nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|845nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003043|lip-1|851nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003044|lir-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003044|lir-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003044|lir-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=625|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003044|lir-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2428|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003044|lir-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003044|lir-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003044|lir-1|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003045|lir-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003045|lir-2|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003045|lir-2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4450|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003045|lir-2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=711|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003045|lir-2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003045|lir-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003045|lir-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003046|lir-3|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003046|lir-3|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003046|lir-3|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003046|lir-3|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=348|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003046|lir-3|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|445nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=375|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|488nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2286|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|490nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4169|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=387|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|494nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003047|lis-1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|553nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|556nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|602nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|606nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|609nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=597|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|614nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|617nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|620nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|922nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|931nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|939nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5025|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003048|lit-1|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|1258nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=580|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14212|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003052|lmn-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14298|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003053|lmp-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|1266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|1351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|1355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00003055|lon-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1545|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003056|lon-2|787nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003057|lon-3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003057|lon-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003057|lon-3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003057|lon-3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003057|lon-3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7133|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003057|lon-3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003057|lon-3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003058|lov-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003059|lpd-2|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|181nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=324|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=502|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1440|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003060|lpd-3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003061|lpd-5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003061|lpd-5|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=454|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003061|lpd-5|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3619|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003061|lpd-5|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=853|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003061|lpd-5|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003062|lpd-6|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003062|lpd-6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003062|lpd-6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2490|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003062|lpd-6|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003062|lpd-6|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003062|lpd-6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003062|lpd-6|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003063|lpd-7|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003063|lpd-7|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6226|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00003063|lpd-7|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1084|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003063|lpd-7|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003063|lpd-7|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003063|lpd-7|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=295|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=271|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=336|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=422|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2406|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003064|lpd-8|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3284|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=486|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3889|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003065|lpd-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1237|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|1467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|1470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|1475nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003066|lpl-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|1018nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=927|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|390nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|739nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|903nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003068|lrk-1|905nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1606|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003071|lrp-1|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|1487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1481|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|650nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003072|lrp-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003073|lars-1|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7092|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003073|lars-1|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=706|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003073|lars-1|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003073|lars-1|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003073|lars-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003074|lars-2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=451|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003074|lars-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=938|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003074|lars-2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003074|lars-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003075|lrx-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003075|lrx-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003075|lrx-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003075|lrx-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003076|lsm-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003076|lsm-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003076|lsm-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3268|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003076|lsm-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=292|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003076|lsm-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1411|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8716|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003077|lsm-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003078|lsm-4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003078|lsm-4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003078|lsm-4|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003078|lsm-4|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5883|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003078|lsm-4|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003078|lsm-4|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003078|lsm-4|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=358|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=438|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8081|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3327|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003079|lsm-5|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003080|lsm-6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4117|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00003080|lsm-6|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003080|lsm-6|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=166|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3639|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=302|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003081|lsm-7|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|1443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|1455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4372|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003082|lsm-8|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|1534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1189|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2318|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003083|lst-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|626nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|631nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=556|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|634nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003084|lst-2|640nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|1353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|1539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|423nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|430nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|432nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|450nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|462nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|464nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|846nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|852nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|857nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|864nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|867nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|879nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|881nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003085|lst-3|891nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=710|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|361nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3128|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=718|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=190|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003086|lst-4|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=664|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2112|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003087|lsy-2|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003089|ltd-1|1306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003089|ltd-1|1309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003089|ltd-1|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003089|ltd-1|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003089|ltd-1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003089|ltd-1|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|1346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16622|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1130|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003090|lys-1|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|1335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|1340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|1434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|1475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26903|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003091|lys-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003092|lys-3|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00003092|lys-3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003092|lys-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003092|lys-3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003092|lys-3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003092|lys-3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003092|lys-3|969nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5491|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10650|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003093|lys-4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003094|lys-5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003094|lys-5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00003094|lys-5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003095|lys-6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003095|lys-6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003095|lys-6|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003095|lys-6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003095|lys-6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=798|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2595|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003096|lys-7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3943|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003097|lys-8|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|1313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|1318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|1320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=601|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|1350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=436|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003099|lys-10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003100|mab-3|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003102|mab-5|805nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003104|mab-7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003104|mab-7|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003104|mab-7|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003104|mab-7|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1349|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003104|mab-7|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003106|mab-9|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003106|mab-9|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003106|mab-9|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=901|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003106|mab-9|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003106|mab-9|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|689nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=690|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|872nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003107|mab-10|884nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|1119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|1281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7869|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003111|mab-20|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003112|mab-21|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003112|mab-21|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003112|mab-21|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003112|mab-21|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2333|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003112|mab-21|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003112|mab-21|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003112|mab-21|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003114|mab-23|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003114|mab-23|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1512|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003119|mac-1|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003123|mag-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15933|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003123|mag-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003123|mag-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003123|mag-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003123|mag-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003123|mag-1|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3135|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=433|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1770|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003124|mai-1|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003129|map-1|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003129|map-1|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003129|map-1|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003129|map-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3244|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003129|map-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3741|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|648nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003130|map-2|960nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|173nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|175nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2385|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=900|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003132|mat-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003133|mat-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003133|mat-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003133|mat-2|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003133|mat-2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003133|mat-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2594|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003133|mat-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003133|mat-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003134|mat-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003134|mat-3|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003134|mat-3|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=739|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003134|mat-3|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=699|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003134|mat-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=882|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=402|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003136|mau-2|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=879|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003142|mau-8|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003143|max-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003143|max-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003143|max-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003143|max-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2378|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003143|max-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003143|max-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1030nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=989|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1034nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1038nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1797|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1042nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1060nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|1548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|807nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|964nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=297|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1798|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003144|max-2|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|1206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|1224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|1284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|1448nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42935|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1315|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003148|mbf-1|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003149|mbk-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003149|mbk-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1809|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003149|mbk-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003149|mbk-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003149|mbk-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1012|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=924|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2719|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=711|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1214nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1218nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|407nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|414nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=575|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|602nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|604nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|608nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|905nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|957nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|967nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|984nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5551|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003150|mbk-2|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|608nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1865|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003151|mca-1|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|1591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|1596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|1598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|305nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4269|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|698nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7892|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|713nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|717nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003153|mca-3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003154|mcm-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10530|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003154|mcm-2|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003154|mcm-2|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003154|mcm-2|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003155|mcm-3|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003155|mcm-3|244nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5438|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003155|mcm-3|248nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003155|mcm-3|763nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003155|mcm-3|768nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003155|mcm-3|772nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4813|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=558|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003156|mcm-4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003157|mcm-5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003157|mcm-5|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003157|mcm-5|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4282|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003157|mcm-5|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003157|mcm-5|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003157|mcm-5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003157|mcm-5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|1472nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=226|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3736|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2979|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|340nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003158|mcm-6|471nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003159|mcm-7|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003159|mcm-7|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003159|mcm-7|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003159|mcm-7|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003159|mcm-7|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1968|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003159|mcm-7|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2282|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003159|mcm-7|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003160|mdf-1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003160|mdf-1|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003160|mdf-1|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2454|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003160|mdf-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003160|mdf-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003160|mdf-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4088|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003161|mdf-2|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|1467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|1470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1139|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=790|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2572|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|282nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18137|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4554|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=377|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=790|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|455nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003162|mdh-2|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19028|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2219|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003163|mdl-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2319|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=271|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003164|mdt-6|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=583|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1061|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003165|mec-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=831|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|353nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|512nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|514nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|517nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1009|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|524nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1014|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|528nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003166|mec-2|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=473|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003167|mec-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003168|mec-4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003169|mec-5|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1263|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003169|mec-5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003169|mec-5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|288nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|291nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|296nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003170|mec-6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27766|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=427|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003171|mec-7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|963nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2382|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003172|mec-8|971nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003173|mec-9|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003173|mec-9|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003173|mec-9|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003173|mec-9|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003173|mec-9|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=544|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003173|mec-9|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|1106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|293nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|74nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003174|mec-10|959nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1246|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150991|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1249|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|20nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=480|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|555nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|559nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003175|mec-12|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003176|mec-14|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003176|mec-14|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003176|mec-14|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3078|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|782nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003177|mec-15|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|1014nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1526|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3992|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5676|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77629|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9701|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=610|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=864|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=611|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003178|mec-17|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003179|mec-18|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003179|mec-18|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003179|mec-18|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003179|mec-18|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003179|mec-18|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2399|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003179|mec-18|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003179|mec-18|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003180|med-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003180|med-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00003180|med-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|1371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|1377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003181|med-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|1562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|535nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|575nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|582nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|794nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|804nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2230|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|811nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003182|mef-2|820nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1037|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1294|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1416|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|308nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003183|mei-1|426nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003184|mei-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003184|mei-2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003184|mei-2|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4533|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003184|mei-2|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003184|mei-2|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003184|mei-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003184|mei-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=594|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4470|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003185|mek-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|107nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1892|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1011|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003186|mek-2|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|242nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1792|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|486nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|493nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003196|mel-11|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|505nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|507nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|513nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5122|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|522nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003209|mel-26|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=645|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3204|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003210|mel-28|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16804|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=877|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=309|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003214|mel-32|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003218|mep-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003218|mep-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003218|mep-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003218|mep-1|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2574|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003218|mep-1|439nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3074|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00003218|mep-1|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003219|mes-1|480nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=776|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003219|mes-1|483nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003219|mes-1|527nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003219|mes-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1476|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003220|mes-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|751nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|805nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|809nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|811nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2202|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|816nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=916|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003221|mes-3|819nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003222|mes-4|365nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=853|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003222|mes-4|371nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003222|mes-4|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003222|mes-4|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003222|mes-4|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003222|mes-4|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003222|mes-4|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|171nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=147|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=741|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10188|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003225|mev-1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|402nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|412nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|415nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003228|mex-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|693nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14641|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003229|mex-3|695nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|1210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2148|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|562nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11548|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1084|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003230|mex-5|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2929|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4054|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003231|mex-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=209|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=230|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=249|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003232|mgl-1|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|1140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|268nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3023|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003234|mif-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4158|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=465|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003235|mif-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1862|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003236|mif-3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003237|mif-4|170nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003237|mif-4|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2381|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003237|mif-4|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003238|mig-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003238|mig-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3444|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003238|mig-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003238|mig-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003238|mig-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003238|mig-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003238|mig-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|1511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|428nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|433nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=209|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|438nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|442nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=719|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|693nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|799nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|801nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003239|mig-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2199|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003241|mig-5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2705|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17466|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=760|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9513|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003242|mig-6|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1775|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=658|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003243|mig-10|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003245|mig-13|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003245|mig-13|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003245|mig-13|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00003245|mig-13|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003245|mig-13|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003246|mig-14|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003246|mig-14|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003246|mig-14|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=913|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003246|mig-14|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003246|mig-14|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1570|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003247|mig-15|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003248|mig-17|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003248|mig-17|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00003248|mig-17|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003248|mig-17|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003248|mig-17|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003249|mig-18|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003252|mig-21|1020nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00003252|mig-21|1024nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003252|mig-21|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003252|mig-21|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2112|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1380|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003253|mig-22|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003254|mig-23|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003254|mig-23|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=611|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003254|mig-23|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|589nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=963|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003258|cogc-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1336|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=652|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003367|mix-1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=382|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3907|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|632nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|634nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|647nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003368|mkk-4|652nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|1246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30609|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3424|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|630nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003369|mlc-1|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53041|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4008|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1591|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1542|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5043|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003370|mlc-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20203|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18708|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|343nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=387|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|345nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3019|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33902|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7359|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1151|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|438nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2700|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003371|mlc-3|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22607|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3862|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003372|mlc-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003373|mlh-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=784|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003373|mlh-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003373|mlh-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003373|mlh-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003373|mlh-1|889nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003374|mlk-1|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003374|mlk-1|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003374|mlk-1|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1384|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003374|mlk-1|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003374|mlk-1|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13663|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003375|mlp-1|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003376|mls-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003376|mls-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003376|mls-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003377|mls-2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|289nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|291nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|296nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=499|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|302nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|305nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003378|mml-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003380|mnm-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003380|mnm-2|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00003380|mnm-2|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003384|moc-1|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=586|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00003384|moc-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003385|moc-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003385|moc-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003385|moc-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003385|moc-2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003385|moc-2|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003385|moc-2|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2669|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003385|moc-2|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003386|mod-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003386|mod-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003386|mod-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003386|mod-1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1266|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00003386|mod-1|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=141|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003386|mod-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|1223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|1244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|1249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|481nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|488nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|493nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|496nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|498nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|514nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|517nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|521nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003387|mod-5|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003388|moe-3|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1490|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00003388|moe-3|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003388|moe-3|404nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003388|moe-3|411nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003388|moe-3|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003388|moe-3|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003389|mog-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003389|mog-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003389|mog-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1968|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00003389|mog-1|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003389|mog-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3153|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=669|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003390|mog-2|774nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003391|mog-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5618|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003392|mog-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003392|mog-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003392|mog-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003392|mog-4|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003392|mog-4|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00003392|mog-4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003392|mog-4|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003393|mog-5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2248|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003393|mog-5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003393|mog-5|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003393|mog-5|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003393|mog-5|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003393|mog-5|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003393|mog-5|416nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003394|mom-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003394|mom-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003394|mom-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=480|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003394|mom-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003394|mom-1|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003394|mom-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1212|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2109|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003395|mom-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=486|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=463|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|289nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2084|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|293nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=354|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|297nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|361nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|364nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|819nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003396|mom-4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|697nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|703nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2371|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|706nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|710nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|807nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003397|mom-5|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003400|dapk-1|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003400|dapk-1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|496nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|512nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|515nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|622nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|630nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2396|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|637nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10771|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|639nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|641nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003401|mpk-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003402|mpk-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003402|mpk-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003402|mpk-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003402|mpk-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003402|mpk-2|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003402|mpk-2|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00003402|mpk-2|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=700|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=994|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|220nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003403|mps-1|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4430|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003404|mpz-1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=360|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=442|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1000|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003405|mre-11|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1274|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4439|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003406|mrg-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003407|mrp-1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003407|mrp-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003407|mrp-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1418|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003407|mrp-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003407|mrp-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003407|mrp-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003407|mrp-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003408|mrp-2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3864|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003408|mrp-2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003408|mrp-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003409|mrp-3|1370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003409|mrp-3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003409|mrp-3|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=591|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003409|mrp-3|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003409|mrp-3|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1236|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1714|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003410|mrp-4|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003411|mrp-5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003411|mrp-5|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003411|mrp-5|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003411|mrp-5|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003411|mrp-5|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2271|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003412|mrp-6|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003412|mrp-6|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003412|mrp-6|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003412|mrp-6|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003413|mrp-7|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5103|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003413|mrp-7|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003413|mrp-7|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003413|mrp-7|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003413|mrp-7|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003414|mrp-8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003414|mrp-8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|1115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|1228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|1231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|1243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|1249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7764|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003415|mars-1|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003417|mrt-2|1455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003417|mrt-2|1569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003417|mrt-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003417|mrt-2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=704|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003417|mrt-2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003417|mrt-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003417|mrt-2|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003418|msh-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003418|msh-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1887|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003418|msh-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003418|msh-2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003418|msh-2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003421|msh-5|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=850|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003421|msh-5|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=501|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4051|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003422|msh-6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|1038nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|1046nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5074|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|1051nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|1055nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003423|msi-1|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003424|msp-3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003424|msp-3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9375|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003424|msp-3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|1346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11542|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003431|msp-33|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003434|msp-38|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003434|msp-38|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003434|msp-38|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4212|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003434|msp-38|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2302|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003434|msp-38|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003442|msp-49|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003442|msp-49|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003442|msp-49|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003442|msp-49|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003442|msp-49|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7515|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003442|msp-49|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=651|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003446|msp-53|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003446|msp-53|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003446|msp-53|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003446|msp-53|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8637|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003446|msp-53|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2322|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003446|msp-53|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15480|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1785|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00003450|msp-57|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003451|msp-58|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003451|msp-58|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003451|msp-58|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4184|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003451|msp-58|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003451|msp-58|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003456|msp-63|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003456|msp-63|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003462|msp-74|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003462|msp-74|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003463|msp-76|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003463|msp-76|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4240|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003463|msp-76|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3581|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003463|msp-76|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003464|msp-77|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003464|msp-77|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003464|msp-77|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5353|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003464|msp-77|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003464|msp-77|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003464|msp-77|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003464|msp-77|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003465|msp-78|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003465|msp-78|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003465|msp-78|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6429|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003465|msp-78|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003466|msp-79|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003466|msp-79|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003466|msp-79|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003466|msp-79|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003466|msp-79|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003470|msp-152|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003470|msp-152|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003470|msp-152|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003470|msp-152|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003470|msp-152|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13438|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003470|msp-152|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1511|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=226|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|131nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003471|mtd-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3390|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=770|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003472|mtk-1|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13213|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003473|mtl-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10859|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003474|mtl-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5961|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00003475|mtm-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003475|mtm-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1360|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003475|mtm-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003475|mtm-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003475|mtm-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|624nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10674|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003476|mtm-3|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003477|mtm-5|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003477|mtm-5|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1571|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1143|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003478|mtm-6|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=946|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=378|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003479|mtm-9|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003480|klf-3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003480|klf-3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003480|klf-3|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=852|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2062|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2153|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|275nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=547|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|820nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003482|mua-3|875nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003485|mua-6|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003485|mua-6|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=392|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003485|mua-6|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1220|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00003485|mua-6|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3006|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003485|mua-6|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003485|mua-6|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003485|mua-6|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=417|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7562|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5334|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1108|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5450|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003495|mup-2|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|1209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|189nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|196nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|333nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2818|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003497|mup-4|844nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003499|mut-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003504|mut-7|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1010|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003504|mut-7|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003507|mut-14|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=661|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003507|mut-14|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003507|mut-14|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003507|mut-14|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003507|mut-14|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003507|mut-14|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003507|mut-14|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1643|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=811|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|561nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|569nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|791nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|795nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003508|mut-16|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003509|mxl-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003509|mxl-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003509|mxl-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003509|mxl-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003509|mxl-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3051|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003509|mxl-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003510|mxl-2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003510|mxl-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003510|mxl-2|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=184|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003510|mxl-2|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2574|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003510|mxl-2|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003510|mxl-2|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003510|mxl-2|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=835|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1256|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003511|mxl-3|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1527|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2433|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003514|myo-2|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=782|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=563|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4308|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=981|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003515|myo-3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003516|nab-1|651nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003517|nac-1|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003517|nac-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003517|nac-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003517|nac-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003517|nac-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003517|nac-1|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003517|nac-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003518|nac-2|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003518|nac-2|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=403|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|1149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|1152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|1179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|1182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|432nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1061|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|435nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|439nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11692|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003519|nac-3|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003520|nas-1|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003520|nas-1|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=456|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003520|nas-1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003520|nas-1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003520|nas-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003522|nas-3|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003522|nas-3|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003523|nas-4|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003523|nas-4|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003523|nas-4|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003523|nas-4|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00003523|nas-4|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003523|nas-4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003524|nas-5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003524|nas-5|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003524|nas-5|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003524|nas-5|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003525|nas-6|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00003525|nas-6|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00003526|nas-7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003526|nas-7|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003527|nas-8|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003527|nas-8|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003527|nas-8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003528|nas-9|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1141|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003529|nas-10|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003530|nas-11|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003530|nas-11|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003530|nas-11|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=416|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003530|nas-11|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003530|nas-11|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003530|nas-11|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003530|nas-11|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003531|nas-12|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003531|nas-12|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003531|nas-12|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003532|nas-13|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003532|nas-13|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003532|nas-13|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003532|nas-13|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003533|nas-14|487nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003533|nas-14|489nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003533|nas-14|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003533|nas-14|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003534|nas-15|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003534|nas-15|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003534|nas-15|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003534|nas-15|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003534|nas-15|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003537|nas-18|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003537|nas-18|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003537|nas-18|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=772|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=646|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003539|nas-20|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003540|nas-21|20nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003540|nas-21|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003541|nas-22|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003541|nas-22|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003541|nas-22|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003541|nas-22|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003541|nas-22|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003541|nas-22|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00003542|nas-23|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003542|nas-23|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003542|nas-23|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003543|nas-24|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003544|nas-25|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003544|nas-25|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003544|nas-25|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003545|nas-27|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003545|nas-27|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003546|nas-28|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003546|nas-28|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003547|nas-29|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003547|nas-29|179nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003547|nas-29|188nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003548|nas-30|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003548|nas-30|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003548|nas-30|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003549|nas-31|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003549|nas-31|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003550|nas-32|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003550|nas-32|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003551|nas-33|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003552|nas-36|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003553|nas-37|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003553|nas-37|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003553|nas-37|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003553|nas-37|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=720|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003554|nas-38|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003554|nas-38|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003555|nas-39|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003555|nas-39|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003555|nas-39|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=525|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003555|nas-39|489nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003558|nca-2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003558|nca-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=660|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003558|nca-2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00003558|nca-2|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003558|nca-2|574nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003558|nca-2|581nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|1229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|1231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|1280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|1355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5144|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|1359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|1371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003559|ncl-1|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|1491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1796|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003561|ncr-1|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003562|ncr-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003562|ncr-2|1132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003562|ncr-2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003562|ncr-2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003562|ncr-2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003562|ncr-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003563|ncs-1|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003563|ncs-1|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003563|ncs-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003563|ncs-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003563|ncs-1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=136|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00003563|ncs-1|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=293|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003563|ncs-1|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|1338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|614nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|617nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|619nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|621nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|724nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|733nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|744nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15699|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003564|ncs-2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|1133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=513|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003565|ncs-3|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1673|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003566|ncx-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2935|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|817nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|820nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003567|ncx-2|826nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003568|ncx-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003568|ncx-3|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003568|ncx-3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=976|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003568|ncx-3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003568|ncx-3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003569|ncx-4|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003569|ncx-4|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003569|ncx-4|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003569|ncx-4|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1142|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003569|ncx-4|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=871|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003569|ncx-4|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003570|ncx-5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003570|ncx-5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003570|ncx-5|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003570|ncx-5|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003570|ncx-5|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003571|ncx-6|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003571|ncx-6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003571|ncx-6|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003572|ncx-7|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003572|ncx-7|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003573|ncx-8|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003573|ncx-8|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003573|ncx-8|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003573|ncx-8|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003573|ncx-8|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003574|ncx-9|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003574|ncx-9|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003574|ncx-9|776nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=485|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00003575|ncx-10|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003575|ncx-10|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1276|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=518|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003576|ndc-80|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=670|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=300|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003577|ndg-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003578|ndx-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003578|ndx-1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003578|ndx-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003578|ndx-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1857|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003578|ndx-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003578|ndx-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003579|ndx-2|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003579|ndx-2|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003579|ndx-2|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003579|ndx-2|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=561|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003579|ndx-2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003579|ndx-2|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003579|ndx-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|1373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|1524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|1541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=189|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003580|ndx-3|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=397|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=252|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003581|ndx-4|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2208|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|199nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1654|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003582|dcap-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003583|ndx-6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003583|ndx-6|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=421|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003583|ndx-6|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2066|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003584|ndx-7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003584|ndx-7|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003584|ndx-7|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=906|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003584|ndx-7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=985|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00003584|ndx-7|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003584|ndx-7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003584|ndx-7|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003585|ndx-8|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003585|ndx-8|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003585|ndx-8|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003585|ndx-8|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|166nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=307|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=448|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=451|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003586|ndx-9|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=325|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16715|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003587|ned-8|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23612|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003588|nex-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|1101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|1105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=587|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|458nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|462nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|469nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|471nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|501nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=224|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|510nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|567nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1015|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00003589|nex-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003590|nex-3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003590|nex-3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003590|nex-3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00003590|nex-3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003590|nex-3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003590|nex-3|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00003590|nex-3|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1047|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=964|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003591|nex-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=757|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003592|nfi-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003592|nfi-1|467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1725|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003592|nfi-1|470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003592|nfi-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003592|nfi-1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=604|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|697nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|877nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|881nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|884nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003593|nfm-1|908nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003594|nft-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003594|nft-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1286|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003594|nft-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003595|ngn-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003596|ngp-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003596|ngp-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003596|ngp-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003596|ngp-1|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4791|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003596|ngp-1|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003596|ngp-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003597|nhl-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003597|nhl-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003597|nhl-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003597|nhl-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003597|nhl-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1043nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3947|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|1506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|522nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|543nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|649nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|664nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003598|nhl-2|670nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|1216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=256|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003599|nhl-3|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|1044nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|1589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|1595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|1598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|291nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1130|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|298nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=390|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|697nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|699nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|716nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|722nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|811nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|813nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|937nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2197|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|939nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003600|nhr-1|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003601|nhr-2|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003601|nhr-2|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003601|nhr-2|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1517|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003602|nhr-3|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003603|nhr-4|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003603|nhr-4|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00003603|nhr-4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003603|nhr-4|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=638|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003603|nhr-4|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003603|nhr-4|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003603|nhr-4|252nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003604|nhr-5|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003604|nhr-5|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003604|nhr-5|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003605|nhr-6|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003605|nhr-6|373nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003605|nhr-6|377nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003605|nhr-6|383nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=380|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003605|nhr-6|385nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003605|nhr-6|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003605|nhr-6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003606|nhr-7|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003606|nhr-7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=756|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003607|nhr-8|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003608|nhr-9|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003608|nhr-9|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003609|nhr-10|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003609|nhr-10|344nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003609|nhr-10|351nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1272|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003610|nhr-11|1151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003610|nhr-11|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003610|nhr-11|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00003610|nhr-11|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003610|nhr-11|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00003610|nhr-11|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003610|nhr-11|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003611|nhr-12|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1121|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003611|nhr-12|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003611|nhr-12|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003611|nhr-12|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003611|nhr-12|1480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003612|nhr-13|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003612|nhr-13|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003612|nhr-13|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|349nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|352nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|356nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|542nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|544nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=838|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|546nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|549nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003613|nhr-14|552nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003614|nhr-15|15nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=918|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003614|nhr-15|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003614|nhr-15|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003615|nhr-16|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003615|nhr-16|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003615|nhr-16|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003615|nhr-16|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00003615|nhr-16|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=463|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=292|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|428nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|431nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003616|nhr-17|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003617|nhr-18|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003617|nhr-18|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00003617|nhr-18|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|1044nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|295nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1119|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|733nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003618|nhr-19|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=478|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2009|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=643|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003619|nhr-20|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003620|nhr-21|1172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003620|nhr-21|1246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003620|nhr-21|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003620|nhr-21|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1514|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003620|nhr-21|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=310|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003621|nhr-22|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|869nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|875nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=649|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003622|nhr-23|877nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003623|nhr-25|750nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00003623|nhr-25|803nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|347nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003624|nhr-28|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|177nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|425nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|563nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|566nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=339|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|569nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|571nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|576nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=548|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1565|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003625|nhr-31|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=529|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003626|nhr-32|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003627|nhr-34|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=536|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003627|nhr-34|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=488|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003627|nhr-34|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003628|nhr-35|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003629|nhr-38|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003629|nhr-38|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003629|nhr-38|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003629|nhr-38|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|107nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|122nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|448nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|453nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|465nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4362|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|468nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003630|nhr-40|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=307|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|17nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=328|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=703|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003632|nhr-42|62nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003633|nhr-43|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003634|nhr-44|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=490|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003634|nhr-44|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003634|nhr-44|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003634|nhr-44|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003634|nhr-44|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003634|nhr-44|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|435nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|441nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|443nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|450nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1966|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003635|nhr-45|452nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003636|nhr-46|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=757|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003636|nhr-46|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1689|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=394|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5771|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003637|nhr-47|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|439nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|443nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|445nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=700|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003638|nhr-48|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|467nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|469nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=207|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|475nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|477nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|497nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|500nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|503nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|505nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1791|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|508nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|510nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=891|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|515nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=742|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003639|nhr-49|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=976|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003640|nhr-50|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00003641|nhr-51|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003641|nhr-51|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003642|nhr-52|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003642|nhr-52|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003642|nhr-52|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003642|nhr-52|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003643|nhr-53|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003644|nhr-54|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003644|nhr-54|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003644|nhr-54|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003645|nhr-55|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003645|nhr-55|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003645|nhr-55|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=787|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00003645|nhr-55|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003645|nhr-55|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003645|nhr-55|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003645|nhr-55|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003646|nhr-56|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003646|nhr-56|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003646|nhr-56|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003646|nhr-56|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1166|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003646|nhr-56|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003646|nhr-56|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003646|nhr-56|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=260|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=602|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003647|nhr-57|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003648|nhr-58|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003648|nhr-58|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003648|nhr-58|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=628|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00003648|nhr-58|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003649|nhr-59|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003649|nhr-59|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003649|nhr-59|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003649|nhr-59|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003649|nhr-59|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003649|nhr-59|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003649|nhr-59|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003650|nhr-60|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003650|nhr-60|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|1378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|1524nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=814|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003651|nhr-61|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003652|nhr-62|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=991|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003652|nhr-62|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003652|nhr-62|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003653|nhr-63|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003653|nhr-63|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003653|nhr-63|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003653|nhr-63|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003654|nhr-64|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003654|nhr-64|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=399|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003654|nhr-64|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=288|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003654|nhr-64|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003654|nhr-64|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003654|nhr-64|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003655|nhr-65|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003655|nhr-65|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003655|nhr-65|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003655|nhr-65|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003655|nhr-65|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|403nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|407nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1475|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|410nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003656|nhr-66|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5892|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1661|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003657|nhr-67|585nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1658|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003658|nhr-68|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003659|nhr-69|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003660|nhr-70|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003660|nhr-70|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003660|nhr-70|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00003660|nhr-70|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003661|nhr-71|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003661|nhr-71|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003661|nhr-71|332nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003661|nhr-71|427nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1732|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003661|nhr-71|661nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003662|nhr-72|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003663|nhr-73|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003664|nhr-74|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003665|nhr-75|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003668|nhr-78|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003668|nhr-78|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003668|nhr-78|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1653|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003668|nhr-78|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003668|nhr-78|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003669|nhr-79|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003669|nhr-79|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003669|nhr-79|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003670|nhr-80|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=928|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003671|nhr-81|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=787|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|1547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003674|nhr-84|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003675|nhr-85|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003675|nhr-85|952nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=260|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003675|nhr-85|956nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003675|nhr-85|993nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003676|nhr-86|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003676|nhr-86|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003676|nhr-86|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003676|nhr-86|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003676|nhr-86|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003677|nhr-87|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003677|nhr-87|27nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003677|nhr-87|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003677|nhr-87|32nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003677|nhr-87|41nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=394|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003677|nhr-87|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|1009nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|1099nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2513|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|1103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|1106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|763nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003678|nhr-88|988nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003680|nhr-90|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=679|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00003680|nhr-90|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003680|nhr-90|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003680|nhr-90|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003681|nhr-91|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003681|nhr-91|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003681|nhr-91|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003681|nhr-91|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003681|nhr-91|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=354|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003681|nhr-91|435nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003681|nhr-91|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003682|nhr-92|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003684|nhr-94|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003684|nhr-94|456nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003684|nhr-94|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=167|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1110|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003685|nhr-95|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3052|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00003686|nhr-96|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003686|nhr-96|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003686|nhr-96|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003686|nhr-96|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|820nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|834nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|843nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|848nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=465|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|870nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3268|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|944nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|948nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003687|nhr-97|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003688|nhr-98|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003688|nhr-98|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003688|nhr-98|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003688|nhr-98|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003688|nhr-98|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003688|nhr-98|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003688|nhr-98|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003689|nhr-99|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00003689|nhr-99|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00003690|nhr-100|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003690|nhr-100|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003690|nhr-100|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4281|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00003690|nhr-100|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|1053nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|1116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|1118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=329|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003691|nhr-101|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003692|nhr-102|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00003692|nhr-102|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003692|nhr-102|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003692|nhr-102|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003692|nhr-102|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003693|nhr-103|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=300|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003693|nhr-103|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003694|nhr-104|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003694|nhr-104|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1043|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003694|nhr-104|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003694|nhr-104|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003695|nhr-105|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003695|nhr-105|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1774|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003695|nhr-105|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1179|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003696|nhr-106|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003696|nhr-106|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003696|nhr-106|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003697|nhr-107|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003697|nhr-107|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003697|nhr-107|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003697|nhr-107|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003697|nhr-107|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003698|nhr-108|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003699|nhr-109|14nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003699|nhr-109|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00003699|nhr-109|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003700|nhr-110|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003702|nhr-112|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003702|nhr-112|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003702|nhr-112|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003702|nhr-112|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003702|nhr-112|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003702|nhr-112|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003702|nhr-112|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003703|nhr-113|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003703|nhr-113|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003703|nhr-113|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003703|nhr-113|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003703|nhr-113|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003703|nhr-113|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003704|nhr-114|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=972|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003704|nhr-114|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003704|nhr-114|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003704|nhr-114|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003704|nhr-114|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003704|nhr-114|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003704|nhr-114|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003705|nhr-115|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003705|nhr-115|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003705|nhr-115|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003705|nhr-115|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003705|nhr-115|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003706|nhr-116|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003706|nhr-116|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003707|nhr-117|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|1072nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|1074nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|1077nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|1181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|1228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|1274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003709|nhr-119|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003710|nhr-120|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003710|nhr-120|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003710|nhr-120|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003711|nhr-121|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003711|nhr-121|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003711|nhr-121|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00003711|nhr-121|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003711|nhr-121|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003711|nhr-121|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003712|nhr-122|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=458|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00003712|nhr-122|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003712|nhr-122|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003712|nhr-122|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003712|nhr-122|700nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003713|nhr-123|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00003713|nhr-123|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00003713|nhr-123|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003713|nhr-123|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003714|nhr-124|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003714|nhr-124|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003714|nhr-124|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003714|nhr-124|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003716|nhr-126|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003716|nhr-126|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003716|nhr-126|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003717|nhr-127|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00003717|nhr-127|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00003718|nhr-128|738nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003718|nhr-128|743nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003719|nhr-129|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003719|nhr-129|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003720|nhr-130|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003720|nhr-130|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003720|nhr-130|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003720|nhr-130|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003720|nhr-130|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003720|nhr-130|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003721|nhr-131|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003721|nhr-131|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003721|nhr-131|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003722|nhr-132|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003722|nhr-132|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=514|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00003722|nhr-132|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003722|nhr-132|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003723|nhr-133|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003723|nhr-133|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003723|nhr-133|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1127|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003723|nhr-133|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003724|nhr-134|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003724|nhr-134|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=638|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003725|nhr-135|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1018|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003725|nhr-135|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003726|nhr-136|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003726|nhr-136|119nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003726|nhr-136|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003726|nhr-136|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003726|nhr-136|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003726|nhr-136|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003727|nhr-137|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003727|nhr-137|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=509|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003727|nhr-137|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003727|nhr-137|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003727|nhr-137|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003727|nhr-137|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003727|nhr-137|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003728|nhr-138|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003728|nhr-138|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003728|nhr-138|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003728|nhr-138|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1360|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003728|nhr-138|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003728|nhr-138|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003728|nhr-138|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003729|nhx-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003729|nhx-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003729|nhx-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1223|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|651nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003730|nhx-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003731|nhx-3|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003731|nhx-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003731|nhx-3|317nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003731|nhx-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003731|nhx-3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003731|nhx-3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003731|nhx-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003732|nhx-4|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003732|nhx-4|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003732|nhx-4|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003732|nhx-4|660nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003732|nhx-4|663nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003732|nhx-4|710nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1538|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1391|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|407nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|585nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|897nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003733|nhx-5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003734|nhx-6|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003735|nhx-8|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003735|nhx-8|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003735|nhx-8|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003736|nhx-9|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003736|nhx-9|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003736|nhx-9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003736|nhx-9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003738|nid-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003738|nid-1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003738|nid-1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003738|nid-1|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1931|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003738|nid-1|241nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003738|nid-1|243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003738|nid-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3172|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1771|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1123|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=510|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003739|nlp-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003740|nlp-2|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2015|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003740|nlp-2|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2660|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3253|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2983|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003741|nlp-3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|932nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003742|nlp-4|938nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003743|nlp-5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003743|nlp-5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003743|nlp-5|621nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003743|nlp-5|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1543|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003743|nlp-5|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003743|nlp-5|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|1007nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13437|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5453|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1691|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|910nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8187|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|969nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003744|nlp-6|973nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=236|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003745|nlp-7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003745|nlp-7|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3123|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003745|nlp-7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003745|nlp-7|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003745|nlp-7|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003745|nlp-7|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6237|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|333nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|370nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003746|nlp-8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6151|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9311|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|341nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|352nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=301|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|384nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003747|nlp-9|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=466|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4669|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1728|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=953|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003748|nlp-10|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8768|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3002|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7604|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7148|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1191|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1046|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|240nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1534|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003749|nlp-11|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10932|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=610|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003750|nlp-12|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|124nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|307nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6619|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1041|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1632|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8048|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003751|nlp-13|849nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=344|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11064|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003752|nlp-14|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|1146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=596|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=398|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135477|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=863|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|387nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|426nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|512nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003753|nlp-15|539nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003754|nlp-16|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003754|nlp-16|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003754|nlp-16|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2328|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003754|nlp-16|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003754|nlp-16|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003754|nlp-16|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16989|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1628|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3347|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003755|nlp-17|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=887|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3714|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=807|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28760|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3302|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2135|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67304|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2507|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=855|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|369nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003756|nlp-18|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003757|nlp-19|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003757|nlp-19|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=639|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003757|nlp-19|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19313|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16594|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003758|nlp-20|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|1211nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=478|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|753nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=639|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160013|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141988|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27238|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|765nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|785nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|788nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|791nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|794nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|796nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|802nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|805nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003759|nlp-21|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003760|nlp-22|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003760|nlp-22|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003761|nlp-23|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003762|nlp-24|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003762|nlp-24|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003762|nlp-24|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8323|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003762|nlp-24|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003762|nlp-24|562nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003763|nlp-25|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003763|nlp-25|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003763|nlp-25|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00003763|nlp-25|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=657|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2635|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003764|nlp-26|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003765|nlp-27|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003765|nlp-27|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003765|nlp-27|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46316|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003765|nlp-27|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3107|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003765|nlp-27|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003765|nlp-27|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003766|nlp-28|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6739|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003766|nlp-28|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003766|nlp-28|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003766|nlp-28|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003766|nlp-28|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003766|nlp-28|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13044|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1428|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003767|nlp-29|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2067|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1897|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=712|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003768|nlp-30|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9425|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=524|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=983|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003769|nlp-31|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6408|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003770|nlp-32|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003770|nlp-32|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003770|nlp-32|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003770|nlp-32|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003770|nlp-32|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003770|nlp-32|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=819|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46285|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6064|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=227|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|891nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003771|nlp-33|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2598|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003772|nlr-1|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5229|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1938|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1265|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003773|nlt-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003774|nmr-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003774|nmr-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003774|nmr-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003774|nmr-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003774|nmr-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|1571nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1680|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=361|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003775|nmr-2|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=794|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|486nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4707|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|497nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=447|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|500nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=174|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|503nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003776|nmy-1|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1010|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7208|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|416nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=138|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=483|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1032|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=793|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|472nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003777|nmy-2|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003778|nnt-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00003778|nnt-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003778|nnt-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003779|nob-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003779|nob-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003779|nob-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003779|nob-1|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003783|nos-1|1519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003783|nos-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003783|nos-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003783|nos-1|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003783|nos-1|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003783|nos-1|299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1133|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|263nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|268nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=429|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|272nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=300|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|289nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=347|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|292nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003784|nos-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|1360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|578nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|585nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6390|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|589nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=386|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|591nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=479|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003785|nos-3|596nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1997|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1226|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=539|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4587|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003786|npa-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3929|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003787|npp-1|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2457|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003788|npp-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3578|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1370|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|169nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|172nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=612|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003789|npp-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=887|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2964|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003790|npp-4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003791|npp-5|1517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003791|npp-5|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=995|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00003791|npp-5|1582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003791|npp-5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1188|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003791|npp-5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003791|npp-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=590|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3242|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=202|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003792|npp-6|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|810nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5172|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=527|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|823nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|830nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|914nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003793|npp-7|917nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|394nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5004|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003794|npp-8|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12903|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=663|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003795|npp-9|410nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1429|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1006|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3718|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1528|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|302nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|306nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003796|npp-10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003797|npp-11|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3757|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003797|npp-11|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=563|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003797|npp-11|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003797|npp-11|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003797|npp-11|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003798|npp-12|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003798|npp-12|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003798|npp-12|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4021|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00003798|npp-12|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003798|npp-12|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003798|npp-12|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003798|npp-12|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003799|npp-13|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4702|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003799|npp-13|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1101|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003799|npp-13|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003799|npp-13|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003799|npp-13|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003799|npp-13|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2637|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=498|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003800|npp-14|960nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|1432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|1436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|1445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3359|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003801|npp-15|926nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=551|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=895|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|119nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3437|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|122nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=435|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|135nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|137nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1391nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|1584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=917|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003802|npp-16|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|312nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|315nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2529|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003803|rae-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=911|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=781|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003804|npp-18|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|1512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|1522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|1524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|1533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|1536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=915|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4579|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003805|npp-19|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3325|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=749|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003806|npp-20|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003807|npr-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003807|npr-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003807|npr-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003807|npr-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003807|npr-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003807|npr-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3763|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003808|npr-2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003812|nrf-5|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003812|nrf-5|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003812|nrf-5|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003812|nrf-5|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003812|nrf-5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2263|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003812|nrf-5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003813|nrf-6|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2682|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003813|nrf-6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003813|nrf-6|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003813|nrf-6|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|1005nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1230|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|1433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5548|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=924|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=982|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1016|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=433|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|511nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|611nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003815|nars-1|956nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003816|asns-1|348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003816|asns-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=478|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003816|asns-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003816|asns-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4996|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3607|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003818|nsf-1|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4785|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003821|nst-1|996nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003822|nsy-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003822|nsy-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003822|nsy-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003822|nsy-1|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003822|nsy-1|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003822|nsy-1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=854|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003822|nsy-1|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=286|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10344|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5206|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003825|ntl-2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1973|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=815|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|511nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2272|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|560nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|570nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|576nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|584nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003826|ntl-3|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|919nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4252|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003827|ntl-4|925nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|193nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4081|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003828|nuc-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003829|nud-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003829|nud-1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003829|nud-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2648|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003829|nud-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1471|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003829|nud-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003829|nud-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003829|nud-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|328nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1119|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|334nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003830|num-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=263|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1565|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1965|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1423|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003831|nuo-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5574|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|1000nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|1004nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|1006nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|1010nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|817nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4966|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003834|nxf-1|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=637|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003835|nxf-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003836|nxt-1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12504|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003836|nxt-1|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=575|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003836|nxt-1|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003836|nxt-1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003837|oat-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003837|oat-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003837|oat-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003837|oat-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00003838|ocr-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00003838|ocr-1|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003838|ocr-1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003838|ocr-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003839|ocr-2|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003839|ocr-2|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003839|ocr-2|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003839|ocr-2|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003840|ocr-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003841|ocr-4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003841|ocr-4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003841|ocr-4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003842|oct-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003842|oct-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003842|oct-1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003842|oct-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003842|oct-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003842|oct-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1178|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003843|oct-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003843|oct-2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=658|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003844|odc-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003844|odc-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3097|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003844|odc-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003845|odd-1|363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003845|odd-1|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003845|odd-1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003846|odd-2|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003846|odd-2|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003846|odd-2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003847|blmp-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003847|blmp-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003847|blmp-1|918nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003847|blmp-1|926nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=501|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003847|blmp-1|928nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003847|blmp-1|931nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|1165nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|908nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|911nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|917nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003848|odr-1|929nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1157|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17149|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=996|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=528|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=661|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|74nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003849|odr-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|1453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003850|odr-3|709nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003851|odr-4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003851|odr-4|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003851|odr-4|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003851|odr-4|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3814|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003851|odr-4|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003851|odr-4|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003854|odr-7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003856|odr-10|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003856|odr-10|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003856|odr-10|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003856|odr-10|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1158|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00003856|odr-10|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003856|odr-10|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003856|odr-10|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|1574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5014|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|670nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|672nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|678nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003858|ogt-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003859|oig-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003859|oig-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003859|oig-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5740|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00003859|oig-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003859|oig-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003859|oig-1|834nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003860|oig-2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4138|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003860|oig-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=901|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003861|oig-3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003862|old-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003862|old-1|19nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003863|old-2|18nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=720|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1016|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9826|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=431|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003864|oma-1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|1025nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|260nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=555|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9359|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003865|oma-2|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003868|ooc-3|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3047|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003868|ooc-3|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003868|ooc-3|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003868|ooc-3|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003868|ooc-3|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003868|ooc-3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=727|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1607|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003870|ooc-5|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003876|pept-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003876|pept-2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1181|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00003876|pept-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003877|pept-1|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003877|pept-1|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003877|pept-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003877|pept-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2494|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003877|pept-1|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003878|pept-3|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003878|pept-3|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003878|pept-3|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003878|pept-3|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=663|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003878|pept-3|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003878|pept-3|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003879|ora-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003879|ora-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003879|ora-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003879|ora-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1783|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003879|ora-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003879|ora-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003879|ora-1|1522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|1072nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|1457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|372nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1484|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|379nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=802|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003882|orc-2|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003883|osm-1|548nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003883|osm-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003883|osm-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003883|osm-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003883|osm-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003884|osm-3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003884|osm-3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003884|osm-3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=679|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003884|osm-3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003884|osm-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003885|osm-5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003886|osm-6|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1333|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003886|osm-6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003887|osm-7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=376|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00003887|osm-7|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00003888|osm-8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003888|osm-8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003888|osm-8|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003888|osm-8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003889|osm-9|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003889|osm-9|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003889|osm-9|631nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003889|osm-9|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003889|osm-9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7065|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003890|osm-10|859nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=635|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1745|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2857|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23325|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5157|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003891|osm-11|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003892|osm-12|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003892|osm-12|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003892|osm-12|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=400|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=355|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=984|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10080|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17348|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1638|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=672|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003893|ost-1|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|1387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|1417nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=899|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=952|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003898|oxi-1|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16713|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1328|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=697|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=845|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003901|paa-1|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6670|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7098|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99891|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1410|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1578|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003902|pab-1|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=518|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=921|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|910nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|930nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|934nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=400|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|936nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1174|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|942nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6098|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|947nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|956nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=412|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003903|pab-2|962nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3812|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1648|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003904|pabp-2|598nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3632|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003905|pad-1|787nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003906|paf-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003906|paf-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003906|paf-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003906|paf-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003906|paf-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003907|paf-2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003907|paf-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003907|paf-2|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003907|paf-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003907|paf-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1493|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003909|pag-3|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003909|pag-3|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003909|pag-3|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|1392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1599|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003911|pak-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=149|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|491nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|494nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|498nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=267|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2248|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=358|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|508nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|511nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003912|pal-1|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16669|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2069|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2330|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=605|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003914|pam-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|28nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|31nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11315|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2789|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|823nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003915|pan-1|828nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|752nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|758nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|763nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7024|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|766nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2983|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|771nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|774nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003916|par-1|947nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|273nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|276nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=319|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|279nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1271|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|281nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=328|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|286nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=554|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003917|par-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|282nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|329nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1199|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|341nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3396|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|399nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|402nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003918|par-3|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|1163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1994|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|1173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003919|par-4|986nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|419nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=783|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|424nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=480|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34641|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56652|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|761nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003920|par-5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003921|par-6|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2823|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003921|par-6|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|199nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12617|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|210nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4506|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|215nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=832|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|217nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=267|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|301nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=425|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003922|pas-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13588|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003923|pas-2|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|1340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|1367nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13916|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003924|pas-3|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12365|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|165nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=240|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|167nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|169nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|174nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003925|pas-4|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14885|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|1055nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|1563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003926|pas-5|991nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|1152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13595|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1869|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=711|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003927|pas-6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=547|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6561|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6372|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|567nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003928|pas-7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003929|pat-2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2981|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|399nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2918|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|404nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=445|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003930|pat-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1341|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003931|pat-4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2721|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|1272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|1280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003932|pat-6|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|669nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003933|pat-9|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=457|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1524|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17043|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80726|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85178|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4449|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1852|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=531|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003934|pat-10|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|1576nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|1581nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3220|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003936|pat-12|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003938|pax-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00003938|pax-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003938|pax-2|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003938|pax-2|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003938|pax-2|723nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003938|pax-2|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003939|pax-3|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003939|pax-3|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003939|pax-3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3245|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003941|pbo-1|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|333nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003943|pbo-4|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13749|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|1198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003947|pbs-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=607|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=213|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12858|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003948|pbs-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6982|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3508|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=778|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003949|pbs-3|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|1112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=394|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10805|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3176|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3066|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=487|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=490|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003950|pbs-4|890nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27433|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1316|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=644|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1448|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003951|pbs-5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13564|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2186|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|1297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|1392nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|1395nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|1483nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|840nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003952|pbs-6|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=263|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003953|pbs-7|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003953|pbs-7|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003953|pbs-7|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003953|pbs-7|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003953|pbs-7|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4496|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003953|pbs-7|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15205|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003953|pbs-7|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23839|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=267|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=275|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=490|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003954|pcm-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13134|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=947|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003955|pcn-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2769|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=804|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003956|pcp-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1417|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003957|pcp-2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1248|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003958|pcp-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003959|pcp-4|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003959|pcp-4|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=647|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003959|pcp-4|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003959|pcp-4|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003960|pcs-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|343nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3409|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|721nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003961|pct-1|884nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3074|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10544|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=379|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|1237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|1251nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|1286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|1291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|938nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|941nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003962|pdi-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|1140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78613|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40134|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=734|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003963|pdi-2|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37448|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3891|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003964|pdi-3|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|491nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=587|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|496nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003965|pdk-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|1085nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3588|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=549|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|767nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003966|pdl-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003967|pdr-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2613|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003967|pdr-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003967|pdr-1|1550nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003967|pdr-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003967|pdr-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003967|pdr-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003967|pdr-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003968|peb-1|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003968|peb-1|881nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003968|peb-1|886nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003969|pef-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003969|pef-1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003969|pef-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003969|pef-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003969|pef-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003969|pef-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003969|pef-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003970|pek-1|1107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003970|pek-1|390nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003970|pek-1|396nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1115|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003970|pek-1|770nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003970|pek-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003970|pek-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003975|pen-2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4035|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003975|pen-2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1898|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003975|pen-2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1244|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003975|pen-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003975|pen-2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003975|pen-2|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003976|pes-1|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003976|pes-1|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|1467nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|1524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|1578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|358nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|360nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=422|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|710nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003978|pes-4|712nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003979|pes-5|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003979|pes-5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=381|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003979|pes-5|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003980|pes-7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003980|pes-7|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003980|pes-7|852nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003980|pes-7|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1338|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003980|pes-7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2745|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3097|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003981|pes-8|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3736|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=707|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=189|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003982|pes-9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003983|pes-10|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1504|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=619|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=432|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|695nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003986|mct-4|716nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003987|pes-23|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3328|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39187|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003989|pfn-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|425nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4958|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|428nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6292|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|431nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|434nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1039|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1778|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|491nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003990|pfn-2|495nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00003991|pfn-3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=537|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003991|pfn-3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003991|pfn-3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003991|pfn-3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003991|pfn-3|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00003991|pfn-3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2451|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5449|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1076|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|191nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|196nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|200nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|204nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|206nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|210nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|212nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003992|pgl-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003993|pgl-2|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003993|pgl-2|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=288|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003993|pgl-2|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=573|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003993|pgl-2|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=299|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003993|pgl-2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003993|pgl-2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4034|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003994|pgl-3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003995|pgp-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=584|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003995|pgp-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003995|pgp-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003996|pgp-2|1459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00003996|pgp-2|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003996|pgp-2|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00003996|pgp-2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2042|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003996|pgp-2|464nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003997|pgp-3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00003997|pgp-3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00003997|pgp-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00003998|pgp-4|139nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=57|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003998|pgp-4|144nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=650|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00003998|pgp-4|146nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003998|pgp-4|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00003999|pgp-5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00003999|pgp-5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00003999|pgp-5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1163|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00003999|pgp-5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1843|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004000|pgp-6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|774nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004001|pgp-7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004002|pgp-8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004002|pgp-8|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004002|pgp-8|1286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004002|pgp-8|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004002|pgp-8|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004002|pgp-8|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004003|pgp-9|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004003|pgp-9|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004003|pgp-9|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004004|pgp-10|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00004004|pgp-10|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004004|pgp-10|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004004|pgp-10|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004005|pgp-11|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004006|pgp-12|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004006|pgp-12|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004006|pgp-12|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004007|pgp-13|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004007|pgp-13|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=996|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004008|pgp-14|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004010|pha-1|706nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=507|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004010|pha-1|710nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004010|pha-1|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004010|pha-1|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004010|pha-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004010|pha-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004010|pha-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004011|pha-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00004011|pha-2|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00004011|pha-2|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00004013|pha-4|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004013|pha-4|634nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=516|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9791|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1983|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3708|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=198|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004014|phb-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=475|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1116|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=798|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6369|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=552|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=282|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=501|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|377nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004015|phb-2|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004016|phf-5|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004016|phf-5|750nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5412|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004016|phf-5|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004017|phg-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004017|phg-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=772|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004017|phg-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004017|phg-1|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1456|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1114|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004020|pho-1|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004023|pho-4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004023|pho-4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004023|pho-4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004024|php-3|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004024|php-3|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004024|php-3|494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004024|php-3|498nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004024|php-3|504nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004025|phy-2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1447|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004025|phy-2|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004025|phy-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004025|phy-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004026|phy-3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004026|phy-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004026|phy-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1025|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004027|pie-1|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=626|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004028|pif-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=539|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004028|pif-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004028|pif-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004029|pik-1|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004029|pik-1|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004029|pik-1|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004029|pik-1|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004029|pik-1|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004029|pik-1|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004030|pin-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004030|pin-2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004030|pin-2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004031|pis-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004031|pis-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1591|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|1064nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|1069nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4896|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|1076nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1849|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|1080nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1081|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|394nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|538nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004032|pkc-1|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=307|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|185nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|189nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1200|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3106|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|326nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|329nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|857nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1207|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|860nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004033|pkc-2|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1947|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004034|pkc-3|548nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=245|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004035|pkd-2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|1601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|230nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|234nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|237nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|245nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=779|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1037|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004036|plc-1|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=411|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|63nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004037|plc-2|73nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004038|plc-3|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=596|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=889|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=353|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|958nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004039|plc-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1344|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004040|pld-1|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2388|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|1470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3804|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004042|plk-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2233|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|235nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|239nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=111|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|248nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|572nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004043|plk-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=129|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=516|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3282|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=469|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004044|plk-3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004045|pll-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004045|pll-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1824|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004045|pll-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004045|pll-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004046|plp-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004046|plp-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004046|plp-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19215|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004046|plp-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004046|plp-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2126|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004046|plp-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004046|plp-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004047|plx-1|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004047|plx-1|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1020|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004047|plx-1|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004048|plx-2|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1142|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004048|plx-2|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004048|plx-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004048|plx-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004048|plx-2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004048|plx-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=184|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3735|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004049|parp-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1666|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=979|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004050|parp-2|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2990|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004051|parg-1|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1664|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004052|parg-2|453nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004053|tank-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2679|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004053|tank-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004053|tank-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|1090nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|510nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|516nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|518nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=553|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|525nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=224|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|532nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=694|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|536nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004055|pmk-1|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004056|pmk-2|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004056|pmk-2|308nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004056|pmk-2|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=748|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004056|pmk-2|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1646|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004056|pmk-2|321nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004057|pmk-3|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2661|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004057|pmk-3|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1877|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004057|pmk-3|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004058|pmp-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004058|pmp-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1020|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004058|pmp-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004059|pmp-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004059|pmp-2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004059|pmp-2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=840|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004059|pmp-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004059|pmp-2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004059|pmp-2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004059|pmp-2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|555nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|560nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=575|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|565nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=262|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|572nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1592|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004060|pmp-3|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004061|pmp-4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004061|pmp-4|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004061|pmp-4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004061|pmp-4|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=601|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004061|pmp-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004061|pmp-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004061|pmp-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|286nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3297|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|69nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1616|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|74nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=709|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|87nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004062|pmp-5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|307nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2364|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1387|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004063|pmr-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004064|pms-2|1394nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004064|pms-2|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004064|pms-2|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004064|pms-2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004064|pms-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1543|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004064|pms-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4148|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3124|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004068|pnk-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9794|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|592nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|599nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004075|pod-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|101nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1642|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3815|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6698|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004076|pod-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004077|pop-1|1229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=926|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004077|pop-1|1235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004077|pop-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004077|pop-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3640|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1914|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19872|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004078|pos-1|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004083|pph-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004083|pph-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004083|pph-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004083|pph-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004083|pph-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004083|pph-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1608|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004083|pph-1|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004084|pph-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1045|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|525nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004085|pph-4.1|899nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|306nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1564|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004086|pph-4.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1019nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1024nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5839|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1095nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1098nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|1100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|682nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004087|ppk-1|843nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004088|ppk-2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004088|ppk-2|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3922|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004088|ppk-2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3594|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004088|ppk-2|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004088|ppk-2|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004089|ppk-3|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004089|ppk-3|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004089|ppk-3|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=547|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004089|ppk-3|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=559|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004089|ppk-3|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004090|ppp-1|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1408|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004090|ppp-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=612|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004090|ppp-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004090|ppp-1|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004090|ppp-1|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=698|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4931|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9137|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004091|pps-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004092|ppt-1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004092|ppt-1|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004092|ppt-1|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|149nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1571|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1879|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1385|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004093|ppw-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004094|ppw-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004094|ppw-2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004094|ppw-2|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3801|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004094|ppw-2|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004094|ppw-2|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|264nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4804|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|377nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004095|pqe-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=260|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=388|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|259nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004096|pqm-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1501|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004098|pqn-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004099|abu-15|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004099|abu-15|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004099|abu-15|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1447|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004099|abu-15|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004100|pqn-8|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004100|pqn-8|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004100|pqn-8|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004100|pqn-8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004100|pqn-8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|290nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2778|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=751|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004101|hgrs-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004102|pqn-10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004102|pqn-10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004103|pqn-11|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004104|pqn-13|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004104|pqn-13|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004104|pqn-13|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=511|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004105|szy-20|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004105|szy-20|279nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=4234|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004105|szy-20|282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004105|szy-20|287nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004105|szy-20|374nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004106|pqn-15|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|1076nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|1078nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004107|pqn-16|861nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|537nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|713nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004108|pqn-18|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|413nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2314|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|417nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1896|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3846|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|425nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|427nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|473nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|476nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004109|stam-1|965nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|1134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|921nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|923nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1920|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|925nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|929nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004110|pqn-20|931nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=844|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004111|pqn-21|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2060|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1816|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1190|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|288nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=488|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|290nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|309nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004112|pqn-22|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004113|pqn-24|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004113|pqn-24|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004113|pqn-24|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004113|pqn-24|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00004113|pqn-24|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004114|pqn-25|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004114|pqn-25|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004114|pqn-25|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004115|pqn-26|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004115|pqn-26|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004115|pqn-26|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004115|pqn-26|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004115|pqn-26|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2475|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=291|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004116|pqn-27|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3737|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|183nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004117|sin-3|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004118|pqn-29|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004118|pqn-29|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004118|pqn-29|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004118|pqn-29|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004119|pqn-31|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004119|pqn-31|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004119|pqn-31|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004119|pqn-31|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=915|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004119|pqn-31|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004119|pqn-31|87nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004119|pqn-31|92nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004120|pqn-32|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1714|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004121|ptrn-1|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00004122|pqn-35|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1552|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004122|pqn-35|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004122|pqn-35|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004123|pqn-36|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00004123|pqn-36|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004123|pqn-36|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004123|pqn-36|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004123|pqn-36|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004123|pqn-36|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004124|pqn-37|1559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004124|pqn-37|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1009|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=580|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004125|mdt-30|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=288|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004126|pqn-39|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1725|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004127|abu-12|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004127|abu-12|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004127|abu-12|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=238|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00004127|abu-12|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004127|abu-12|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004127|abu-12|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004127|abu-12|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6725|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1217|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004128|pqn-41|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004129|pqn-42|487nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004129|pqn-42|494nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00004129|pqn-42|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004130|ketn-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004130|ketn-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004130|ketn-1|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004130|ketn-1|894nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5434|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|1081nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=360|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=507|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|350nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|352nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3043|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|539nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74649|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1271|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5784|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|844nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=809|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004131|pqn-44|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1010nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1013nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1018nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=955|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1021nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=839|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1024nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5088|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1029nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6721|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1033nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|667nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|669nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|981nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004132|ifet-1|983nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004133|abu-13|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00004133|abu-13|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004133|abu-13|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004133|abu-13|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004133|abu-13|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004133|abu-13|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|664nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|799nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|805nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3805|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|839nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|841nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|848nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004134|myrf-1|988nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2483|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004135|pqn-48|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|357nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2718|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|360nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|366nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1550|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9509|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=292|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004136|pqn-51|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6910|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4009|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004138|pqn-53|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2411|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004139|pqn-54|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1016|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004140|ebax-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2680|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8289|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4083|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004143|pqn-59|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2813|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1234|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004144|pqn-60|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004145|pqn-62|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004145|pqn-62|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004145|pqn-62|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004145|pqn-62|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004145|pqn-62|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004146|pqn-63|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004146|pqn-63|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|629nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4047|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|635nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2606|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|638nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|729nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|734nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004147|larp-5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4279|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|220nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|913nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004148|pqn-65|915nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004150|pqn-67|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00004150|pqn-67|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00004151|pqn-68|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004151|pqn-68|1600nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004151|pqn-68|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004151|pqn-68|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1891|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10495|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=836|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=398|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|345nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004152|pqn-70|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004153|pqn-71|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004153|pqn-71|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004153|pqn-71|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00004153|pqn-71|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00004154|pqn-72|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004154|pqn-72|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004154|pqn-72|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004154|pqn-72|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004154|pqn-72|558nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004154|pqn-72|571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004154|pqn-72|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004155|pqn-73|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004155|pqn-73|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004155|pqn-73|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004156|pqn-74|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3327|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004156|pqn-74|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1173|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004156|pqn-74|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004156|pqn-74|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004156|pqn-74|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004156|pqn-74|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004157|pqn-75|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004157|pqn-75|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00004157|pqn-75|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004157|pqn-75|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004158|pqn-76|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004158|pqn-76|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004159|pqn-78|186nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004159|pqn-78|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004159|pqn-78|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00004159|pqn-78|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004159|pqn-78|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004161|pqn-80|1151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004161|pqn-80|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004161|pqn-80|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004161|pqn-80|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004161|pqn-80|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004163|pqn-82|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004163|pqn-82|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004163|pqn-82|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004163|pqn-82|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004163|pqn-82|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004163|pqn-82|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=875|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2645|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|271nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=222|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004164|pqn-83|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004165|pqn-84|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004165|pqn-84|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1835|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004166|pqn-85|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|119nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|1590nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9898|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1615|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|491nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|494nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|496nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|588nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|594nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004167|pqn-87|598nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004168|pqn-88|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=688|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004168|pqn-88|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1014|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004168|pqn-88|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|174nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1619|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004169|pqn-89|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004170|pqn-90|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00004170|pqn-90|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00004171|pqn-91|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00004171|pqn-91|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00004172|pqn-92|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004172|pqn-92|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1351|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004172|pqn-92|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|1219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|1271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|1273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|1275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1540|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004173|pqn-94|705nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3862|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=817|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004174|abu-14|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004175|pqn-96|1162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004175|pqn-96|365nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1504|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004175|pqn-96|372nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00004175|pqn-96|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004176|pqn-97|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004176|pqn-97|786nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004176|pqn-97|788nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004176|pqn-97|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004176|pqn-97|796nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004177|pqn-98|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|1533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6984|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004178|prg-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=491|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|1361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|1365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5173|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004179|prg-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004180|pri-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004180|pri-1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004180|pri-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1452|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004180|pri-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004180|pri-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004180|pri-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004180|pri-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=523|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|789nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1907|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004181|pri-2|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004182|prk-1|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004182|prk-1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1059|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004182|prk-1|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004182|prk-1|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004182|prk-1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004182|prk-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|664nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|683nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|687nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|724nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004183|prk-2|729nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3162|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=814|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1736|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|604nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|715nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|719nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|723nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|726nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004184|T19D2.2.2|731nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|106nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=837|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1677|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|1181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|1187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|384nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004185|pro-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1385|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1803|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004186|prpf-4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|367nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9670|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=714|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=597|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004187|prp-8|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004188|prp-21|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004188|prp-21|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1642|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004188|prp-21|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004189|pars-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004189|pars-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004189|pars-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004189|pars-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004189|pars-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004189|pars-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004189|pars-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004190|pars-2|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004190|pars-2|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004190|pars-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004190|pars-2|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004190|pars-2|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1931|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004190|pars-2|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004191|prx-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=739|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004191|prx-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004191|prx-1|837nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004192|prx-2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004192|prx-2|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004192|prx-2|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004192|prx-2|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004192|prx-2|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=227|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004193|prx-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004194|prx-5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=584|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004195|prx-6|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004195|prx-6|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004195|prx-6|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|890nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004196|prx-11|892nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004197|prx-12|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004197|prx-12|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004197|prx-12|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00004197|prx-12|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004197|prx-12|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004198|prx-13|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004198|prx-13|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004198|prx-13|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004198|prx-13|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=319|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004198|prx-13|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|173nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|177nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|179nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3476|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=530|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004199|prx-14|770nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|251nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4240|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|55nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004201|prx-19|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004202|pry-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|473nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|476nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|677nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2524|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1179|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004203|swsn-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|317nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|323nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|325nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|329nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5448|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|343nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004204|swsn-4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|1221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1693|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|1488nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=267|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004205|psr-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004206|pst-1|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004206|pst-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004206|pst-1|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004206|pst-1|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004206|pst-1|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00004206|pst-1|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1531|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004206|pst-1|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2314|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|564nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|617nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|620nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004207|ptb-1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|297nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=246|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1099|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|794nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|797nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2208|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|800nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13128|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|804nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|806nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|808nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=863|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004208|ptc-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1022|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004210|ptc-3|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004211|ptd-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004211|ptd-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004211|ptd-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00004211|ptd-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004212|ptl-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=605|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004212|ptl-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1419|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004212|ptl-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004212|ptl-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004212|ptl-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004212|ptl-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004212|ptl-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|358nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|411nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2270|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|599nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|633nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004213|ptp-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1781|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004214|ptp-2|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|1087nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|1358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|464nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=370|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|466nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2667|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|471nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1217|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|692nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|696nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|700nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004215|ptp-3|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004216|ptr-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004216|ptr-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1056nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1061nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1067nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2806|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=532|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004217|ptr-2|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004218|ptr-3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004218|ptr-3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004219|ptr-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004219|ptr-4|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004219|ptr-4|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00004219|ptr-4|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004219|ptr-4|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004219|ptr-4|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|1038nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|266nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|546nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1500|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|568nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|570nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|609nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=312|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004220|ptr-5|954nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004221|ptr-6|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004221|ptr-6|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004221|ptr-6|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004222|ptr-8|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004222|ptr-8|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004222|ptr-8|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004222|ptr-8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004223|ptr-9|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004223|ptr-9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004224|ptr-10|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004224|ptr-10|105nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=181|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004224|ptr-10|108nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=20|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004224|ptr-10|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004224|ptr-10|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004224|ptr-10|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004225|ptr-11|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004225|ptr-11|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004225|ptr-11|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004225|ptr-11|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004226|ptr-12|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=824|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004226|ptr-12|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004226|ptr-12|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004226|ptr-12|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004226|ptr-12|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004226|ptr-12|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004227|ptr-13|698nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004227|ptr-13|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004227|ptr-13|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004227|ptr-13|707nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004228|ptr-14|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004228|ptr-14|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004228|ptr-14|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004228|ptr-14|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004229|ptr-15|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004230|ptr-16|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004230|ptr-16|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004230|ptr-16|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004230|ptr-16|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004230|ptr-16|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004230|ptr-16|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004230|ptr-16|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004231|ptr-17|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004231|ptr-17|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004231|ptr-17|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004231|ptr-17|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004232|ptr-18|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004232|ptr-18|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004233|ptr-19|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004234|ptr-20|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004234|ptr-20|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004234|ptr-20|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004235|ptr-21|556nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004235|ptr-21|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004235|ptr-21|611nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004235|ptr-21|620nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1603|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004235|ptr-21|623nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00004235|ptr-21|629nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004236|ptr-22|1298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004236|ptr-22|1422nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004236|ptr-22|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004237|ptr-23|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004238|ptr-24|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004238|ptr-24|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004238|ptr-24|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1302|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00004238|ptr-24|267nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4049|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3746|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004239|puf-3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|1074nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|1083nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|1102nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|1130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11269|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|358nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004241|puf-5|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|1590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|378nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|381nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|387nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=226|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|394nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=768|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|400nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004242|puf-6|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4773|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|364nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|576nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|585nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|590nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=710|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|592nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|598nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004243|puf-7|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004244|puf-8|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004244|puf-8|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4357|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004244|puf-8|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004244|puf-8|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004244|puf-8|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004244|puf-8|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1043nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=413|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1100|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|1412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|867nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004245|puf-9|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1541|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004248|pus-1|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004249|pvf-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=978|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004249|pvf-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004249|pvf-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004249|pvf-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2560|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|477nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004254|pxf-1|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004255|epac-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004255|epac-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004255|epac-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004255|epac-1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=849|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=520|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004256|pxn-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004257|pxn-2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004257|pxn-2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004257|pxn-2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004257|pxn-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004257|pxn-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004258|pyc-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004258|pyc-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004258|pyc-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004258|pyc-1|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5045|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00004258|pyc-1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004258|pyc-1|372nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004258|pyc-1|389nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3373|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004259|pyr-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004264|qua-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004264|qua-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=706|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004264|qua-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004265|qui-1|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=504|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004265|qui-1|1098nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004265|qui-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004265|qui-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004265|qui-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004265|qui-1|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=516|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|1595nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=529|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4412|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16029|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2399|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004266|rab-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8102|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1840|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004267|rab-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|1342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|1346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|234nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|239nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11180|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4729|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004268|rab-5|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4773|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=108|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=208|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|253nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004269|rab-6.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1315|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004270|rab-6.2|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1645|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|430nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|432nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=944|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|434nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8481|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=478|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|444nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|446nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|448nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|452nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|456nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004271|rab-7|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|1416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6546|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=519|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004272|rab-8|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14944|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=966|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004273|rab-10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|499nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|501nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|505nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|516nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=382|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14340|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11739|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1446|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004274|rab-11.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004275|rab-11.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004275|rab-11.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|1563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|223nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|229nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|493nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|495nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|534nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3063|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|537nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|646nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=259|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|650nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|653nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004276|rab-14|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|1231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|1445nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|1475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|1529nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|1543nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3393|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|1548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|221nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=621|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004277|rab-18|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004278|rab-19|1042nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004278|rab-19|1283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004278|rab-19|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004278|rab-19|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9476|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004278|rab-19|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9683|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004278|rab-19|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004279|rab-21|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004279|rab-21|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004279|rab-21|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2007|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004279|rab-21|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004279|rab-21|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004281|rab-28|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004281|rab-28|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=500|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004281|rab-28|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004281|rab-28|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004281|rab-28|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004281|rab-28|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004282|rab-30|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004282|rab-30|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004282|rab-30|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004282|rab-30|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1336|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004282|rab-30|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004283|rab-33|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1995|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|416nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|454nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|845nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|854nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|873nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004284|rab-35|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|705nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|710nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=557|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|882nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|884nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|886nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004285|rab-37|890nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004286|rab-39|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004286|rab-39|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2861|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004286|rab-39|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004286|rab-39|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004286|rab-39|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004286|rab-39|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1742|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=948|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004296|rad-50|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=674|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1507|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=476|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=169|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004297|rad-51|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004298|rad-54|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28851|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|909nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004300|ram-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004301|ram-5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004301|ram-5|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004301|ram-5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00004301|ram-5|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=950|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|1064nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1934|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29738|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1328|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|229nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2035|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|233nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4378|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1073|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2969|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17103|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1992|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=523|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=530|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004302|ran-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|1281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|1283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|279nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|285nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|288nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2149|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004303|ran-2|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|1203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|1213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7395|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004304|ran-3|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|1010nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|1013nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8065|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=543|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004305|ran-4|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=871|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=266|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2360|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004306|ran-5|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10737|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|643nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|651nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=340|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|657nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004307|rap-1|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004308|rap-2|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004308|rap-2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=716|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004308|rap-2|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1537|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00004308|rap-2|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004308|rap-2|408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004308|rap-2|412nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=284|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004308|rap-2|419nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004309|rap-3|67nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|1006nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1138|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|931nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|933nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004310|ras-1|935nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004311|ras-2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7785|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5047|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|1217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|582nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|646nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|648nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|650nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004312|rba-1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|338nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|340nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|343nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1628|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004313|rbc-1|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=315|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=928|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=459|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|453nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|958nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004314|rbc-2|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004315|rbd-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004315|rbd-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004315|rbd-1|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=385|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004315|rbd-1|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1103|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=913|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=685|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1312|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=982|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004316|rbf-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004317|rbg-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004317|rbg-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1005|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004317|rbg-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004317|rbg-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004317|rbg-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1159|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004318|rbg-2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|562nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|567nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2032|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|613nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004319|rbr-2|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=189|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=225|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|258nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12469|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004320|rbx-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|1523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=127|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3665|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004321|rcn-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|1248nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|1251nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|1291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|1297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|1438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=718|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004322|rcq-5|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004323|rde-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004323|rde-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1711|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004323|rde-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004323|rde-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004323|rde-1|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004323|rde-1|964nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004324|rde-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=728|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004324|rde-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=536|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004324|rde-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=426|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004324|rde-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004324|rde-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3755|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1053|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004326|rde-4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004328|rdy-2|1124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004328|rdy-2|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004328|rdy-2|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004328|rdy-2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004328|rdy-2|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=481|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=604|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=318|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|1326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|652nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|654nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|657nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004333|rec-8|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004334|ref-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004334|ref-1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004334|ref-1|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004335|ref-2|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2834|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=385|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=275|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|403nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1720|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|405nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22392|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|411nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10822|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=447|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|759nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004336|ret-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2380|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2812|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004337|rfc-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004338|rfc-2|1550nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004338|rfc-2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=442|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004338|rfc-2|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=473|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004338|rfc-2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|61nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1943|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|63nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1131|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|66nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=83|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004339|rfc-3|69nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2795|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2266|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1783|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004340|rfc-4|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004341|rfl-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004341|rfl-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004341|rfl-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004341|rfl-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1004|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00004341|rfl-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2286|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004341|rfl-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004342|rfs-1|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004342|rfs-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004343|rgr-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004343|rgr-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004343|rgr-1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004343|rgr-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004344|rgs-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004344|rgs-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004344|rgs-1|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3067|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004344|rgs-1|407nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004344|rgs-1|411nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004344|rgs-1|414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|1000nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6648|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|821nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004345|rgs-2|827nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|1265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=263|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3756|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=731|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|392nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|394nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|427nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004346|rgs-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|1178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|1236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|694nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|786nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|790nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1382|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|794nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=564|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|799nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004347|rgs-4|802nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=714|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|260nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|262nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004348|rgs-5|521nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=380|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|1574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|379nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=895|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004349|rgs-6|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=541|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|413nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|420nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|430nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|433nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1233|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1686|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|440nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=499|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004350|rgs-7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|154nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=638|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|157nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|161nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=165|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004352|rgs-9|163nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=84|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004353|rgs-10|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004353|rgs-10|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004353|rgs-10|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004353|rgs-10|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004353|rgs-10|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004354|rgs-11|1059nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=391|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004354|rgs-11|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004354|rgs-11|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004354|rgs-11|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004354|rgs-11|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004355|rha-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2410|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2795|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1348|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004356|rhi-1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17032|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3708|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|1415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|405nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=447|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|451nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|454nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|595nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|729nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|750nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|791nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004357|rho-1|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|203nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6713|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004358|rhr-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004359|rhr-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004359|rhr-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004359|rhr-2|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004359|rhr-2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|1043nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|1059nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|1067nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1105|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|509nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004360|rib-1|519nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=595|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|1207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|1527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004361|rib-2|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|1054nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1520|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|61nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=83|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|63nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=46|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004363|ric-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|303nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=918|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=367|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1039|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|330nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=219|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|337nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1432|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13977|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=731|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004364|ric-4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=911|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|617nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|624nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004367|ric-8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3740|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3697|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004368|ric-19|820nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004369|rig-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004369|rig-1|393nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1210|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004369|rig-1|399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004369|rig-1|404nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004369|rig-1|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3339|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004370|rig-3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004371|rig-4|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004371|rig-4|442nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004371|rig-4|446nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2153|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004371|rig-4|449nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004371|rig-4|454nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004372|rig-5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2452|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004372|rig-5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004372|rig-5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17719|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|407nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=282|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|415nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|421nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004373|rme-1|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004374|rme-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004374|rme-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004374|rme-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004374|rme-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5767|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004374|rme-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1993|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004374|rme-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004374|rme-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1902|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004375|rme-4|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004377|rme-6|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004377|rme-6|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004377|rme-6|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1261|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004377|rme-6|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004377|rme-6|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004377|rme-6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|490nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1401|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|493nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1677|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004378|rme-8|604nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004380|rnf-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004380|rnf-1|1067nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004380|rnf-1|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004380|rnf-1|1240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004380|rnf-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004380|rnf-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004380|rnf-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2072|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004381|rnf-5|1403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004381|rnf-5|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004381|rnf-5|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004381|rnf-5|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004381|rnf-5|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004381|rnf-5|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3376|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004381|rnf-5|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1031|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1280|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=869|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1071|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|762nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|765nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004382|rnh-1.0|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004383|rnh-2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2026|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004383|rnh-2|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004383|rnh-2|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004383|rnh-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004383|rnh-2|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004383|rnh-2|863nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4182|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|285nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|287nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004384|rnp-1|290nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1130|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1140|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004385|rnp-2|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004386|rnp-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7444|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004386|rnp-3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004386|rnp-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7246|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1831|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004387|rnp-4|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004388|rnp-5|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5049|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004388|rnp-5|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004388|rnp-5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004388|rnp-5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|1596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2786|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=556|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004389|rnp-6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4260|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6576|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=547|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004390|rnp-7|736nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6047|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1133|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004391|rnr-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=506|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2265|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=292|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7332|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1334|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004392|rnr-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|567nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|585nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004393|rnt-1|617nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|1022nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|1042nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9570|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|920nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004394|rol-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004395|rol-3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004395|rol-3|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004395|rol-3|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004397|rol-6|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004397|rol-6|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004397|rol-6|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004397|rol-6|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004397|rol-6|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004397|rol-6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4832|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004397|rol-6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|124nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3542|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18644|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=935|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004398|rol-8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004400|rom-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=360|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004400|rom-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004400|rom-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004400|rom-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004400|rom-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004400|rom-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004400|rom-1|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004402|rom-3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004403|rom-4|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|383nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|394nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004404|rom-5|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|1387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18155|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=465|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2517|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004405|rop-1|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=617|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=357072|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=615|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=307|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=579|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004408|rla-0|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4426|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350477|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1653|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|54nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|62nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|69nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004409|rla-1|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8247|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1048|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193096|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004410|rla-2|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004411|rpc-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004411|rpc-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1944|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004411|rpc-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=543|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00004411|rpc-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004411|rpc-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004411|rpc-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004411|rpc-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004412|rpl-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004412|rpl-1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004412|rpl-1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98044|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004412|rpl-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22616|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004412|rpl-1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1297|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81750|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1264|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004413|rpl-2|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130206|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24391|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|581nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004414|rpl-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5234|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=463|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|25nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|30nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32364|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55916|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14084|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=714|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2619|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=321|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=240|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=326|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004415|rpl-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=284|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|1428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8990|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=149838|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5588|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004416|rpl-5|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8477|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11055|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1175|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90379|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004417|rpl-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=93245|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4090|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=663|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2249|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004418|rpl-7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=513|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124300|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1532|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004419|rpl-7A|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1039|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=99448|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25299|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004420|rpl-9|80nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=179|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126629|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21043|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2602|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004421|rpl-10|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61576|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2514|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=287|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|516nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5171|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004422|rpl-11.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=620|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|260nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60044|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=567|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=661|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3636|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004423|rpl-11.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=873|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269176|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17982|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1248|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3695|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13177|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126333|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1253|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004424|rpl-12|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=449|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65336|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70139|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1492|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3757|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|62nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|73nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|77nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|80nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|85nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|90nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|92nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=507|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004425|rpl-13|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|1418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74173|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2906|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2408|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1242|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004426|rpl-14|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=496|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1749|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=442|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56805|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14579|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3263|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004427|rpl-15|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4988|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82838|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14879|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004428|rpl-16|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|124nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=138909|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2550|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004429|rpl-17|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|1444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6905|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80818|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31893|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2268|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004430|rpl-18|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99582|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134910|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6753|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004431|rpl-19|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|391nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5338|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110655|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10770|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=326|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|969nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004432|rpl-20|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|21nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1651|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75941|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72635|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4590|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=314|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=815|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004433|rpl-21|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100574|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004434|rpl-22|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=165877|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1875|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22697|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=370|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004435|rpl-23|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1583|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147842|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004436|rpl-24.1|88nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004437|rpl-24.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004437|rpl-24.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004437|rpl-24.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004437|rpl-24.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004437|rpl-24.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004437|rpl-24.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3167|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004437|rpl-24.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1980|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004438|rpl-25.1|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004438|rpl-25.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004438|rpl-25.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004438|rpl-25.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28848|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004438|rpl-25.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1198|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50616|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9776|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004439|rpl-25.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|1094nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131106|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1123|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|88nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004440|rpl-26|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3925|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138331|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5915|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1393|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|620nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|644nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004441|rpl-27|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=601|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1120|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40381|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6739|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=589|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004442|rpl-28|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|29nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=117563|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4740|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=403|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2532|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=682|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|856nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004443|rpl-29|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|1351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2506|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39654|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43171|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14021|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004444|rpl-30|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52181|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5197|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17652|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22018|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004445|rpl-31|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2548|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=121360|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4199|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1497|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=600|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=943|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004446|rpl-32|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116139|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1456|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004447|rpl-33|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=347|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36388|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48793|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3886|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|56nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|59nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004448|rpl-34|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=250|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|581nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26613|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53823|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=979|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004449|rpl-35|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=420|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=201279|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1133|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004450|rpl-36|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2396|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83606|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41586|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004452|rpl-38|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1476|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243060|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=557|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004453|rpl-39|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=431|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272305|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1224|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4287|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=299|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004454|rpl-41|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004455|rpl-42|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004455|rpl-42|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004455|rpl-42|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=818|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3511|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108045|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9277|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004456|rpl-43|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=424|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|806nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004457|rpm-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|1360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|1546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|1570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1410|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12205|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=579|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004458|rpn-1|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7319|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2887|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=226|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004459|rpn-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|1344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1508|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7463|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=474|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=661|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=394|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4369|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=987|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004460|rpn-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11327|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=542|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|216nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|219nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|344nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004461|rpn-5|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|1094nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11326|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1509|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|948nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004462|rpn-6.1|987nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8957|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|1466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3731|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=271|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|392nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|397nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|599nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|601nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004463|rpn-7|604nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=897|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8356|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=364|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|224nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004464|rpn-8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27577|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1081|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=492|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004465|rpn-9|600nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12589|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1493|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1606|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=913|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004466|rpn-10|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21064|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=518|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|485nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004467|rpn-11|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7176|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004468|rpn-12|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2602|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|1032nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|1039nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2022|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|1041nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|1046nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50792|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103604|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=645|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004469|rps-0|98nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=279|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|1480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=129550|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=707|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2134|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=860|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=458|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004470|rps-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=263|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17918|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9163|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|138nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|150nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1806|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52525|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1305|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|543nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=950|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=693|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|72nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|75nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|79nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=176|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004471|rps-2|90nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|1150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|1153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|1158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1439|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1441|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1708|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111871|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1124|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004472|rps-3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004473|rps-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=872|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004473|rps-4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004473|rps-4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004473|rps-4|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199528|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00004473|rps-4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004473|rps-4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004473|rps-4|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=687|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58142|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=97388|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4314|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1519|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004474|rps-5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|306nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|360nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2893|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119494|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=621|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004475|rps-6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|102nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1245|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121820|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17337|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6040|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|83nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|883nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|92nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004476|rps-7|97nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=422|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=646|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|56nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13065|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|59nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=88591|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|61nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6992|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|68nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|70nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|73nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004477|rps-8|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|101nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|107nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1575|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9138|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126227|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46069|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39313|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=538|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=329|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|94nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004478|rps-9|98nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=782|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1121|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=770|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69922|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3525|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18874|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004479|rps-10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1242|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65840|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17533|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=450|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004480|rps-11|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179266|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8889|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004481|rps-12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91252|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4554|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004482|rps-13|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55212|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187286|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24604|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|476nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1305|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004483|rps-14|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|1039nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|107nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43968|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68877|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23652|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=428|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|97nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004484|rps-15|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187911|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2924|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1624|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1760|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1451|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=286|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004485|rps-16|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167047|total_reads(99.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004486|rps-17|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1188|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3673|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|173nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129751|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7045|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004487|rps-18|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2568|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56190|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=698|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2710|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|503nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35745|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7049|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|73nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|76nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|94nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004488|rps-19|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1284|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1096|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72730|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21446|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004489|rps-20|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96317|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=385|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=696|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2267|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=440|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004490|rps-21|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004491|rps-22|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004491|rps-22|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3780|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004491|rps-22|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20247|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004491|rps-22|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42957|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004491|rps-22|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3833|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004491|rps-22|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|107nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=102|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|112nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=85|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|115nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|119nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42537|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11251|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1977|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61477|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20190|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5723|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004492|rps-23|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=365|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1375|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75201|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20380|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004493|rps-24|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|1017nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=525|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|1083nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|1428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|1578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|1594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115926|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15487|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=501|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004494|rps-25|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2521|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4860|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1291|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=504|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|1236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118643|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5498|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5240|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5527|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4408|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004495|rps-26|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1821|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|1220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|1225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|1228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=772|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78000|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|72nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=244|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=63073|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|806nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004496|rps-27|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9547|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|1061nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87861|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004497|rps-28|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11928|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1078|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1363|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67413|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19392|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004498|rps-29|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=997|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3115|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107754|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14537|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004499|rps-30|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4764|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13642|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|210nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=649|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|213nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=321|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=405|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004501|rpt-1|848nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11844|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|1559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004502|rpt-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004503|rpt-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10253|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004503|rpt-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=930|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004503|rpt-3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004503|rpt-3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004503|rpt-3|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004503|rpt-3|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7740|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|155nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=237|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=379|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=461|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004504|rpt-4|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2768|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004505|rpt-5|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9290|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004505|rpt-5|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004505|rpt-5|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|13nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1924|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6546|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004506|rpt-6|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1863|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1072|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004507|rpy-1|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|1040nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|1145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|1147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1141|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004508|rrf-1|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|1240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|1543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=834|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004509|rrf-2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004510|rrf-3|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1339|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004510|rrf-3|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004510|rrf-3|159nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004510|rrf-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1330|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=905|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2650|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1441|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004679|rars-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004680|rars-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004680|rars-2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004680|rars-2|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1550|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004680|rars-2|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004680|rars-2|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004680|rars-2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004680|rars-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004681|rsd-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004681|rsd-2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4188|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004681|rsd-2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004681|rsd-2|1488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004681|rsd-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1793|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004682|rsd-3|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|1281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|467nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=475|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|471nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3503|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|473nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004684|rsd-6|475nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|1023nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5455|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|179nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=986|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=321|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=251|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004698|rsp-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|1082nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|1320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6124|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004699|rsp-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19470|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2065|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|767nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|775nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1744|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004700|rsp-3|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5847|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2837|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004701|rsp-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5173|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1649|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=819|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004702|rsp-5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5230|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=543|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9538|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004703|rsp-6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004704|rsp-7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004704|rsp-7|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004704|rsp-7|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3488|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=411|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8351|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|277nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|367nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|369nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|382nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004705|rsp-8|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1618|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=504|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|26nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004706|rsr-1|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=341|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|534nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1258|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1349|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|539nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=239|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|545nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|573nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004719|sad-1|578nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004721|san-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004721|san-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004721|san-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004721|san-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=617|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004721|san-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=793|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004721|san-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5306|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=540|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004723|sap-49|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004726|sas-4|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1127|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1084|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004727|sax-1|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1007|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1027|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004728|sax-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|584nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004729|sax-3|601nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|1005nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|1202nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|1214nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|1255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|1259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|1265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3917|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|869nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|872nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|878nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|882nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4394|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004732|sax-7|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|21nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=368|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004735|sbp-1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1021nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1037nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1040nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=568|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1046nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17526|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1049nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3023|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1051nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1131|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1055nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1088nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|1492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9353|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=590|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|443nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|928nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|930nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004736|sca-1|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004737|scc-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1009|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004737|scc-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004737|scc-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3577|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1313|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004738|scc-3|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2243|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004739|scd-1|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004740|scd-2|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2002|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004740|scd-2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004740|scd-2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004742|scl-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004742|scl-1|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=478|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1663|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3104|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=601|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004743|scm-1|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|1317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32018|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004744|scp-1|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004745|sdc-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=400|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004745|sdc-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004745|sdc-1|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004745|sdc-1|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=241|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004745|sdc-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004745|sdc-1|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004745|sdc-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004746|sdc-2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004746|sdc-2|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004746|sdc-2|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004746|sdc-2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004747|sdc-3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004747|sdc-3|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004747|sdc-3|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004747|sdc-3|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=351|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004747|sdc-3|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004747|sdc-3|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004748|sdf-9|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00004748|sdf-9|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004748|sdf-9|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00004748|sdf-9|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|223nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|229nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|561nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|570nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=334|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|572nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|575nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=458|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004749|sdn-1|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004750|sea-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004750|sea-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004750|sea-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004750|sea-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004750|sea-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004750|sea-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|589nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|594nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4029|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|606nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|697nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004751|sea-2|983nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004752|sec-5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1148|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004752|sec-5|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=906|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|230nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|249nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004753|sec-8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4777|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1297|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=411|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004754|sec-23|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5244|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004755|sec-24.1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|390nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1115|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|397nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|400nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|403nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|407nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=601|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=616|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|640nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|663nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004756|sec-24.2|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|692nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|711nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|730nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|978nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1598|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=738|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004758|sek-1|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|277nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3619|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004759|sel-1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2458|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1386|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=419|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004760|sel-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=804|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|306nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1923|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|460nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|729nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|755nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|766nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|804nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|914nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004762|sel-5|919nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004764|sel-7|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004764|sel-7|825nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004764|sel-7|830nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=923|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1009|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004765|sel-8|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|116nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=249|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|118nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=471|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|1217nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1195|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4032|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=300|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004766|sel-9|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|421nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|427nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=621|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2754|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=505|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004767|sel-10|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004768|sel-11|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004768|sel-11|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004768|sel-11|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6217|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004768|sel-11|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004769|sel-12|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=558|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004769|sel-12|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00004769|sel-12|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004769|sel-12|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004771|sem-2|709nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004771|sem-2|770nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=502|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004771|sem-2|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004773|sem-4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004773|sem-4|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004773|sem-4|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004773|sem-4|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3777|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004773|sem-4|605nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|752nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|756nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|759nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1397|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|761nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=676|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004774|sem-5|764nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=169|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004775|sep-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004775|sep-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004775|sep-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1960|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004775|sep-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004775|sep-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004776|ser-1|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004776|ser-1|561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1113|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004776|ser-1|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004776|ser-1|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1629|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1098|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|363nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004777|ser-2|799nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00004778|ser-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004779|ser-4|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=685|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004779|ser-4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1033|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004779|ser-4|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004779|ser-4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004779|ser-4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004779|ser-4|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1107|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1372|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=868|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|769nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|775nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004780|ser-7|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|1253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|1298nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=442|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2160|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004781|set-1|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004782|set-2|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004782|set-2|568nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1064|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004782|set-2|575nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=166|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004782|set-2|578nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004782|set-2|581nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|1340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|217nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4606|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004783|seu-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|294nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=361|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004786|sex-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004787|sft-1|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004787|sft-1|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=771|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=535|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6505|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1032|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004788|sft-4|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004789|sgk-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004789|sgk-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=541|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004789|sgk-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00004789|sgk-1|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|17nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|20nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|23nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=420|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004790|sgn-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004793|shw-3|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004793|shw-3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1090|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00004793|shw-3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004793|shw-3|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004793|shw-3|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2007|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004795|sid-1|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004796|sid-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004796|sid-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004796|sid-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004796|sid-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004796|sid-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004796|sid-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|1470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1005|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4283|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6688|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112364|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004798|sip-1|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1410|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1705|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004800|sir-2.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004801|sir-2.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004801|sir-2.2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004801|sir-2.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1225|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004801|sir-2.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004801|sir-2.2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004801|sir-2.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004801|sir-2.2|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004802|sir-2.3|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004803|sir-2.4|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1494|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004803|sir-2.4|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004803|sir-2.4|542nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004803|sir-2.4|578nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004803|sir-2.4|625nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|1426nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|678nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12736|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=923|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=899|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|692nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=509|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004804|skn-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2040|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004806|skp-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2583|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=887|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1505|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3644|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3367|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55786|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16241|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=549|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|418nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|420nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|519nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004807|skr-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|1094nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|1153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3682|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5497|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004808|skr-2|808nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=291|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4212|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004809|skr-3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=529|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004810|skr-4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004811|skr-5|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004811|skr-5|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=542|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004811|skr-5|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004811|skr-5|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004811|skr-5|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004811|skr-5|92nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004813|skr-7|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004813|skr-7|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004813|skr-7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1388|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004813|skr-7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004813|skr-7|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004814|skr-8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004814|skr-8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004814|skr-8|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004815|skr-9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004815|skr-9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=416|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004815|skr-9|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004816|skr-10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=654|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004818|skr-12|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=764|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004818|skr-12|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004818|skr-12|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004819|skr-13|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004819|skr-13|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004819|skr-13|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004820|skr-14|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004820|skr-14|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1277|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004820|skr-14|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004821|skr-15|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004821|skr-15|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004821|skr-15|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004822|skr-16|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004822|skr-16|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004822|skr-16|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004822|skr-16|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004822|skr-16|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1645|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004822|skr-16|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004823|skr-17|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004823|skr-17|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004823|skr-17|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004823|skr-17|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1855|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004823|skr-17|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004823|skr-17|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004824|F56B3.4b|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004824|F56B3.4c|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1422|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004824|F56B3.4c|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|489nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1259|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004825|skr-19|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1612|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004826|skr-20|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004827|skr-21|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004827|skr-21|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=634|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004827|skr-21|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004827|skr-21|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|391nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|393nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|400nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1637|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004829|sli-1|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004830|slo-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004830|slo-1|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004830|slo-1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=335|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3602|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004831|slo-2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004854|slt-1|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004854|slt-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004854|slt-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004854|slt-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004854|slt-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|399nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2867|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3406|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004855|sma-1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004856|sma-2|190nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004856|sma-2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004856|sma-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004856|sma-2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004856|sma-2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004856|sma-2|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004857|sma-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004857|sma-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=369|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004857|sma-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004858|sma-4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004858|sma-4|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004858|sma-4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=451|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004858|sma-4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=944|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004858|sma-4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004858|sma-4|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004859|sma-5|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004860|sma-6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004860|sma-6|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004860|sma-6|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004860|sma-6|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004860|sma-6|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1941|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|583nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=483|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|585nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=998|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|589nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|592nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|594nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|892nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004862|sma-9|895nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|304nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|312nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1993|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|315nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00004873|smc-3|971nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|155nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|159nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6713|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004874|smc-4|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=638|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6396|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004875|smd-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004876|smf-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004876|smf-1|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004876|smf-1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=504|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004876|smf-1|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004877|smf-2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004877|smf-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004878|smf-3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004878|smf-3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004878|smf-3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004878|smf-3|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004879|smg-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004879|smg-1|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004879|smg-1|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2623|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004879|smg-1|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004879|smg-1|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3082|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|1472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|1476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|1498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004880|smg-2|897nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004881|smg-3|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=590|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2004|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004882|smg-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004883|smg-5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004883|smg-5|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=612|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004883|smg-5|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004883|smg-5|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1199|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=491|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1018|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004884|smg-6|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004885|smg-7|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004885|smg-7|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=746|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004885|smg-7|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004885|smg-7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004885|smg-7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004885|smg-7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004886|smi-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1776|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=267|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=600|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|367nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4741|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004887|smn-1|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3053|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1125|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=346|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23708|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1060|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|265nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004888|smo-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|377nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|387nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=460|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|835nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004889|smp-1|881nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004890|smp-2|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004890|smp-2|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004890|smp-2|637nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=960|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00004890|smp-2|641nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004891|smr-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004891|smr-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004891|smr-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3401|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004891|smr-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=764|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004891|smr-1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3329|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004892|sms-1|805nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|408nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|416nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|418nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=440|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004893|sms-2|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004894|sms-3|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1174|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004894|sms-3|320nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|197nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5223|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004895|smu-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004896|smu-2|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004896|smu-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004896|smu-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004896|smu-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3147|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004896|smu-2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004896|smu-2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004896|smu-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9077|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14200|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=798|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|534nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004897|snb-1|829nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1137|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004898|snb-2|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004899|snb-5|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004899|snb-5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004899|snb-5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004899|snb-5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004899|snb-5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004899|snb-5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004900|snf-1|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004900|snf-1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2810|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004900|snf-1|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004901|snf-2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004901|snf-2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4394|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004902|snf-3|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004904|snf-5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004904|snf-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=640|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004904|snf-5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004904|snf-5|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004905|snf-6|1502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004905|snf-6|1504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004905|snf-6|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004905|snf-6|1566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004905|snf-6|1576nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004905|snf-6|1578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004906|snf-7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004906|snf-7|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004906|snf-7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|24nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1024|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004908|snf-9|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004909|snf-10|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004909|snf-10|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00004909|snf-10|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004909|snf-10|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004910|snf-11|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004910|snf-11|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004910|snf-11|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004910|snf-11|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004911|snf-12|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=537|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004912|sng-1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2609|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004913|snn-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004913|snn-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004913|snn-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004913|snn-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1936|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004913|snn-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004913|snn-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004913|snn-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1182|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13794|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|825nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004914|snr-1|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|1174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|1176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28506|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11754|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2892|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004915|snr-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|1334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10008|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004916|snr-3|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004917|snr-4|164nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004917|snr-4|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14361|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004917|snr-4|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5191|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004917|snr-4|174nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004917|snr-4|176nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=396|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004917|snr-4|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004917|snr-4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8626|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1718|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004918|snr-5|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77254|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=876|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004919|snr-6|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|1147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=472|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14415|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004920|snr-7|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2087|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3464|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=826|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|478nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|486nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|488nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004921|snt-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004922|snt-2|1022nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004922|snt-2|490nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004922|snt-2|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1832|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004922|snt-2|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004922|snt-2|665nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004922|snt-2|732nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1887|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1202|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004923|snt-3|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=648|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3781|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13929|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44703|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=504|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|612nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004924|snt-4|964nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004925|snt-5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004925|snt-5|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=331|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004925|snt-5|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1466|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00004925|snt-5|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004926|snt-6|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2480|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00004926|snt-6|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1564|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004926|snt-6|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1408|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=706|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|308nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=385|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004927|snx-1|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004928|soc-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004928|soc-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004928|soc-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004928|soc-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004928|soc-1|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004928|soc-1|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|1019nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|1062nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|349nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=295|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|358nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=829|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2273|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004929|soc-2|945nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=539|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16707|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004930|sod-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004931|sod-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004931|sod-2|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004931|sod-2|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6287|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004931|sod-2|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004931|sod-2|304nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1284|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004932|sod-3|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|126nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=284|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6792|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004933|sod-4|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|1033nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3118|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004944|sol-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|385nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=642|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|389nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004945|sop-2|397nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004946|sop-3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004946|sop-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004946|sop-3|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004946|sop-3|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004946|sop-3|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1747|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004946|sop-3|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004946|sop-3|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|514nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1366|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004947|sos-1|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004949|sox-2|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004949|sox-2|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004949|sox-2|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004949|sox-2|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004949|sox-2|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=900|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004949|sox-2|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00004950|sox-3|1392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004950|sox-3|1405nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004950|sox-3|1410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004950|sox-3|1412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004950|sox-3|1416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004950|sox-3|1419nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004950|sox-3|1423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2806|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|480nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|484nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=389|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|487nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14991|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004951|spc-1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=434|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2015|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=316|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004952|spd-1|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3357|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004953|spd-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004954|spd-3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004954|spd-3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004954|spd-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004954|spd-3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004954|spd-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3220|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1154|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004955|spd-5|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|1160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004958|spe-4|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|1206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|1209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2478|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004959|spe-5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004960|spe-6|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004960|spe-6|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004960|spe-6|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004962|spe-8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004962|spe-8|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004962|spe-8|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004962|spe-8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004962|spe-8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004962|spe-8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004963|spe-9|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004963|spe-9|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004963|spe-9|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004963|spe-9|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004963|spe-9|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004964|spe-10|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00004964|spe-10|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=298|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004964|spe-10|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004964|spe-10|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004965|spe-11|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004965|spe-11|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004965|spe-11|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004965|spe-11|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004965|spe-11|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004966|spe-12|1082nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004966|spe-12|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004966|spe-12|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004966|spe-12|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004969|spe-15|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004969|spe-15|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2366|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004969|spe-15|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004971|spe-17|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004971|spe-17|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004971|spe-17|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004972|spe-26|1314nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004972|spe-26|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004972|spe-26|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=335|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004972|spe-26|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004972|spe-26|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004972|spe-26|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004972|spe-26|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004973|spe-27|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004973|spe-27|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1733|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004973|spe-27|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00004973|spe-27|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004973|spe-27|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004973|spe-27|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004974|spe-29|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004974|spe-29|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004974|spe-29|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004974|spe-29|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004974|spe-29|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004974|spe-29|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004974|spe-29|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004975|spe-39|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004975|spe-39|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004975|spe-39|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2217|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004975|spe-39|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004975|spe-39|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004976|spe-41|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004976|spe-41|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00004976|spe-41|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2582|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004978|spg-7|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004979|sph-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004979|sph-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004979|sph-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004979|sph-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1416|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00004979|sph-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004979|sph-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|1292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|192nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|201nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1440|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7987|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|721nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|741nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|745nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1653|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|750nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=477|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|753nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|850nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004980|spk-1|966nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004981|spl-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004981|spl-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=718|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004981|spl-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004981|spl-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004981|spl-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004981|spl-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2171|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004981|spl-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|462nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|465nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=394|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10386|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|471nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=193|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004984|spn-4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1282|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004985|spo-11|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004986|spp-1|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004986|spp-1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10066|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004986|spp-1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004986|spp-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00004986|spp-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004986|spp-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004986|spp-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3595|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1161|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2567|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1079|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004987|spp-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14776|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004988|spp-3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=461|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=629|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1490|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004989|spp-4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=589|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49411|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=882|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004990|spp-5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004991|spp-6|1099nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00004991|spp-6|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004991|spp-6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004992|spp-7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004992|spp-7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004992|spp-7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00004993|spp-8|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004993|spp-8|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00004993|spp-8|277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004993|spp-8|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004993|spp-8|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3818|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004993|spp-8|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004993|spp-8|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004994|spp-9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004994|spp-9|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004994|spp-9|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00004994|spp-9|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4279|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3630|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1278|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=854|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3073|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004995|spp-10|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004996|spp-11|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004996|spp-11|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004997|spp-12|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004997|spp-12|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004997|spp-12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004997|spp-12|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2680|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004998|spp-13|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=509|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27677|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00004999|spp-14|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3590|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2675|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1099|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1580|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005000|spp-15|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|108nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|113nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1294|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|34nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2612|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005001|spp-16|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005002|spp-17|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005002|spp-17|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005002|spp-17|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005002|spp-17|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19699|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005002|spp-17|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005002|spp-17|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=413|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=976|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3599|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=371|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=870|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005003|spp-18|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005004|spp-19|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005004|spp-19|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005004|spp-19|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005004|spp-19|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005004|spp-19|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005005|spp-20|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=890|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005006|spr-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005007|spr-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005007|spr-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005007|spr-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005007|spr-2|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005007|spr-2|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6395|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005007|spr-2|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005007|spr-2|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005008|spr-3|1578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005008|spr-3|1589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005008|spr-3|431nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=239|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005008|spr-3|438nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=411|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|1058nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|1145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|279nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|283nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1355|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|287nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|291nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|827nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005009|spr-4|839nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005010|spr-5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005010|spr-5|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=471|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005010|spr-5|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2539|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005010|spr-5|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005010|spr-5|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005011|F26F4.8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005011|F26F4.8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005011|F26F4.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1807|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005011|F26F4.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005011|F26F4.8|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005011|F26F4.8|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005011|F26F4.8|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|259nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1826|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|530nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005012|F26F4.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005013|jmjd-1.1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005013|jmjd-1.1|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005013|jmjd-1.1|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005014|spt-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005014|spt-4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005014|spt-4|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4286|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005014|spt-4|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005014|spt-4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005014|spt-4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005014|spt-4|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=694|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2822|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=364|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=176|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=368|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005015|spt-5|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=387|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14081|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=917|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005016|sqt-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=349|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|470nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4802|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|894nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|929nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|931nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|939nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|964nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005017|sqt-2|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29532|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005018|sqt-3|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|328nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1196|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|330nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2091|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|415nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|418nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|421nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005019|sqv-1|423nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=422|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1426|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005020|sqv-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=534|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005021|sqv-3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=868|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1096|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3582|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=442|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|1554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005022|sqv-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|413nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4664|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|673nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|677nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|680nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005023|sqv-5|685nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005024|sqv-6|1302nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1328|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00005024|sqv-6|1304nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=452|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005024|sqv-6|1325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005024|sqv-6|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005024|sqv-6|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005024|sqv-6|532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=281|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4504|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=390|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005025|sqv-7|466nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005026|sqv-8|1272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005026|sqv-8|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1993|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005026|sqv-8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005026|sqv-8|1502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005026|sqv-8|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005027|sra-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005027|sra-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005029|sra-3|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005029|sra-3|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005029|sra-3|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005029|sra-3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005029|sra-3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005029|sra-3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005030|sra-4|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005030|sra-4|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005030|sra-4|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005030|sra-4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005030|sra-4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005032|sra-6|1599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005032|sra-6|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005033|sra-7|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005033|sra-7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005035|sra-9|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005036|sra-10|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005036|sra-10|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005036|sra-10|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005036|sra-10|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005036|sra-10|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005037|sra-11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005037|sra-11|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005037|sra-11|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005037|sra-11|991nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005038|sra-12|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005038|sra-12|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005039|sra-13|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005039|sra-13|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005039|sra-13|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005039|sra-13|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005039|sra-13|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005039|sra-13|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005039|sra-13|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005040|sra-14|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005040|sra-14|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005043|sra-17|1265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005043|sra-17|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005043|sra-17|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005043|sra-17|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005044|sra-18|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005046|sra-20|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00005046|sra-20|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00005047|sra-21|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005047|sra-21|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005050|sra-24|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005051|sra-25|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005051|sra-25|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005051|sra-25|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00005052|sra-26|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005053|sra-27|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005053|sra-27|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005053|sra-27|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005053|sra-27|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005053|sra-27|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005053|sra-27|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005054|sra-28|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005057|sra-31|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005057|sra-31|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005057|sra-31|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005058|sra-32|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005058|sra-32|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005059|sra-33|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005060|sra-34|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005060|sra-34|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005061|sra-35|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005062|sra-36|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005063|sra-37|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005063|sra-37|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005063|sra-37|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005063|sra-37|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005063|sra-37|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005063|sra-37|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005064|sra-38|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005064|sra-38|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005065|sra-39|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005065|sra-39|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005066|srb-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005067|srb-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005067|srb-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005067|srb-2|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005067|srb-2|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00005068|srb-3|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005068|srb-3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005068|srb-3|1460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005068|srb-3|1465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00005068|srb-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005068|srb-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005068|srb-3|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005071|srb-6|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00005071|srb-6|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|631nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|641nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005072|srb-7|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005073|srb-8|1096nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005076|srb-11|1016nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005076|srb-11|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005076|srb-11|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005076|srb-11|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005076|srb-11|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005077|src-1|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005077|src-1|917nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=299|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005077|src-1|924nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1845|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005077|src-1|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005077|src-1|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005078|src-2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005078|src-2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005079|srd-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005079|srd-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005079|srd-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00005080|srd-2|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005081|srd-3|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005082|srd-4|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005083|srd-5|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00005083|srd-5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005083|srd-5|1574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00005083|srd-5|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00005083|srd-5|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005083|srd-5|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005083|srd-5|881nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005085|srd-7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005085|srd-7|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005085|srd-7|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005085|srd-7|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005087|srd-9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005087|srd-9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005087|srd-9|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005088|srd-10|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005088|srd-10|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005088|srd-10|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005088|srd-10|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005089|srd-11|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005090|srd-12|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005091|srd-13|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00005091|srd-13|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005091|srd-13|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005093|srd-15|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005094|srd-16|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005094|srd-16|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005095|srd-17|1425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005095|srd-17|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005095|srd-17|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005096|srd-18|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005096|srd-18|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005096|srd-18|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=420|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005096|srd-18|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005096|srd-18|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005096|srd-18|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005096|srd-18|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005097|srd-19|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005097|srd-19|716nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005097|srd-19|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00005098|srd-20|655nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005098|srd-20|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005098|srd-20|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005101|srd-23|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005101|srd-23|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005101|srd-23|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005101|srd-23|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005101|srd-23|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005104|srd-26|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005104|srd-26|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005104|srd-26|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005104|srd-26|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005104|srd-26|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005104|srd-26|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=817|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6772|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3288|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005105|srd-27|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005106|srd-28|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005106|srd-28|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005106|srd-28|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005106|srd-28|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1415|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005106|srd-28|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005110|srd-32|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005110|srd-32|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=889|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005110|srd-32|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=939|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005110|srd-32|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005110|srd-32|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005110|srd-32|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005111|srd-33|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005111|srd-33|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005111|srd-33|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005111|srd-33|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005112|srd-34|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005112|srd-34|772nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005113|srd-35|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005113|srd-35|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005113|srd-35|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005113|srd-35|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005113|srd-35|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005114|srd-36|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005114|srd-36|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005114|srd-36|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005114|srd-36|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005114|srd-36|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005117|srd-39|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005117|srd-39|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005118|srd-40|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005118|srd-40|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005119|srd-41|1263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005119|srd-41|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005120|srd-42|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005120|srd-42|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005120|srd-42|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005120|srd-42|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=592|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005120|srd-42|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005121|srd-43|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005121|srd-43|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005121|srd-43|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00005121|srd-43|965nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005123|srd-45|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005123|srd-45|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005123|srd-45|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005123|srd-45|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005124|srd-46|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005125|srd-47|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005126|srd-48|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00005126|srd-48|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005126|srd-48|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005127|srd-49|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005127|srd-49|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005127|srd-49|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005127|srd-49|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005128|srd-50|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005128|srd-50|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005128|srd-50|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|433nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00005129|srd-51|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005131|srd-53|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005131|srd-53|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005131|srd-53|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005131|srd-53|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005131|srd-53|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005131|srd-53|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005131|srd-53|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00005132|srd-54|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005132|srd-54|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005133|srd-55|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005134|srd-56|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005135|srd-58|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005135|srd-58|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005136|srd-59|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005136|srd-59|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005136|srd-59|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00005136|srd-59|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005136|srd-59|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005136|srd-59|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005136|srd-59|263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005137|srd-60|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00005137|srd-60|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005137|srd-60|710nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005137|srd-60|713nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005137|srd-60|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005137|srd-60|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005140|srd-63|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005140|srd-63|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005141|srd-64|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005142|srd-65|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=211|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00005142|srd-65|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00005144|srd-67|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005144|srd-67|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005144|srd-67|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005144|srd-67|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005144|srd-67|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005145|srd-68|1147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005145|srd-68|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005147|srd-70|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005147|srd-70|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005147|srd-70|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005148|srd-71|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005148|srd-71|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00005148|srd-71|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005148|srd-71|345nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005149|sre-1|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00005149|sre-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00005150|sre-2|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005153|srf-3|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=742|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005153|srf-3|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005153|srf-3|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005153|srf-3|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005153|srf-3|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005153|srf-3|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005159|srg-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005159|srg-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005159|srg-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005159|srg-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005159|srg-1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005160|srg-2|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005161|srg-3|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005162|srg-4|1359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005162|srg-4|1392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005162|srg-4|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005163|srg-5|1026nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005163|srg-5|1537nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005163|srg-5|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005164|srg-6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005164|srg-6|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005165|srg-7|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00005165|srg-7|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005165|srg-7|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005166|srg-8|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005167|srg-9|1365nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005167|srg-9|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005167|srg-9|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005167|srg-9|194nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005167|srg-9|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005167|srg-9|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005168|srg-10|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005168|srg-10|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00005168|srg-10|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005169|srg-11|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005169|srg-11|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005169|srg-11|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005169|srg-11|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005169|srg-11|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005169|srg-11|902nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005169|srg-11|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005170|srg-13|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005170|srg-13|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005170|srg-13|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005171|srg-14|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=249|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005172|srg-15|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005173|srg-16|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005174|srg-17|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005174|srg-17|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005177|srg-20|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005177|srg-20|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005177|srg-20|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005178|srg-21|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005178|srg-21|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005178|srg-21|849nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005178|srg-21|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005178|srg-21|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005178|srg-21|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005179|srg-22|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005180|srg-23|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005182|srg-25|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005182|srg-25|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005182|srg-25|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005184|srg-27|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005184|srg-27|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005184|srg-27|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005186|srg-29|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005186|srg-29|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005186|srg-29|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005186|srg-29|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=511|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005186|srg-29|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005186|srg-29|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005187|srg-30|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005188|srg-31|741nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005188|srg-31|749nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005189|srg-32|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005189|srg-32|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005189|srg-32|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00005189|srg-32|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005190|srg-33|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005191|srg-34|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005193|srg-36|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005193|srg-36|803nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005193|srg-36|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005195|srg-38|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005196|srg-39|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005196|srg-39|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005197|srg-40|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005197|srg-40|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005197|srg-40|233nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005197|srg-40|250nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005197|srg-40|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005198|srg-41|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005198|srg-41|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005198|srg-41|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005198|srg-41|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005198|srg-41|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00005198|srg-41|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005199|srg-42|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005199|srg-42|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005199|srg-42|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005201|srg-44|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005202|srg-45|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005203|srg-46|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005204|srg-47|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005204|srg-47|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005204|srg-47|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005204|srg-47|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005204|srg-47|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005205|srg-48|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005205|srg-48|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005205|srg-48|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005207|srg-50|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005207|srg-50|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005207|srg-50|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005207|srg-50|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005208|srg-51|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005208|srg-51|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005208|srg-51|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005208|srg-51|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005210|srg-53|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005210|srg-53|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005210|srg-53|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005213|srg-56|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005213|srg-56|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005213|srg-56|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005215|srg-58|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005218|srg-61|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005218|srg-61|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005218|srg-61|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005218|srg-61|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005219|srg-62|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|1146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|1323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|1523nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|1540nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|1550nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=961|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005221|srg-64|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005222|srg-65|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005223|srg-66|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005223|srg-66|855nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005226|srg-69|1418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005226|srg-69|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005226|srg-69|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005226|srg-69|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005227|srh-1|1143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005227|srh-1|1146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005228|srh-2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005228|srh-2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005229|srh-3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005231|srh-5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005233|srh-7|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005234|srh-8|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005234|srh-8|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005236|srh-10|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005237|srh-11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005237|srh-11|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005237|srh-11|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005237|srh-11|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00005240|srh-15|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1878|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005240|srh-15|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005240|srh-15|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005240|srh-15|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005240|srh-15|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|486nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005241|srh-16|489nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005242|srh-17|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005242|srh-17|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005242|srh-17|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005243|srh-18|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005243|srh-18|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005243|srh-18|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=506|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005243|srh-18|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005243|srh-18|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005245|srh-20|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005245|srh-20|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005245|srh-20|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005246|srh-21|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005246|srh-21|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005246|srh-21|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005247|srh-22|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005249|srh-25|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005249|srh-25|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00005249|srh-25|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005250|srh-27|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005250|srh-27|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005251|srh-28|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005251|srh-28|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005251|srh-28|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005251|srh-28|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005253|srh-30|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005253|srh-30|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005253|srh-30|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00005253|srh-30|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005253|srh-30|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005253|srh-30|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005253|srh-30|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005255|srh-32|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005255|srh-32|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005258|srh-35|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005259|srh-36|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005260|srh-37|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005261|srh-38|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005261|srh-38|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005262|srh-39|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005262|srh-39|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00005262|srh-39|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005262|srh-39|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005262|srh-39|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005262|srh-39|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005262|srh-39|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005264|srh-41|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005265|srh-42|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005265|srh-42|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005267|srh-44|1377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005267|srh-44|1382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005267|srh-44|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005267|srh-44|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005268|srh-45|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005269|srh-46|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005269|srh-46|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005269|srh-46|887nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005270|srh-47|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005270|srh-47|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005271|srh-48|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005271|srh-48|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005273|srh-50|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005274|srh-51|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005279|srh-56|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005279|srh-56|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005281|srh-59|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005281|srh-59|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005281|srh-59|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005282|srh-60|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005283|srh-61|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005283|srh-61|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005288|srh-67|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005289|srh-68|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005289|srh-68|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005290|srh-69|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005290|srh-69|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005290|srh-69|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005291|srh-70|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00005291|srh-70|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005291|srh-70|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005292|srh-71|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005295|srh-74|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005295|srh-74|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005295|srh-74|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005295|srh-74|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005295|srh-74|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005295|srh-74|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005295|srh-74|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005296|srh-75|23nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005296|srh-75|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005296|srh-75|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1096nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|1477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|742nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|746nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=261|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|750nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005297|srh-76|752nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005299|srh-78|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005299|srh-78|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005299|srh-78|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005299|srh-78|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005301|srh-80|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005301|srh-80|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005315|srh-95|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005315|srh-95|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005317|srh-98|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005317|srh-98|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005318|srh-99|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005319|srh-100|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005319|srh-100|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005321|srh-102|197nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005328|srh-109|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005328|srh-109|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005328|srh-109|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00005330|srh-111|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005331|srh-112|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005331|srh-112|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00005332|srh-113|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005332|srh-113|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005332|srh-113|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005334|srh-115|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005334|srh-115|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005335|srh-116|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005335|srh-116|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005335|srh-116|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005337|srh-118|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005338|srh-119|425nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005339|srh-120|1431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005339|srh-120|1439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005341|srh-123|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005342|srh-125|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005344|srh-127|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00005344|srh-127|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005345|srh-128|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005346|srh-129|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005346|srh-129|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005347|srh-130|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005347|srh-130|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005348|srh-131|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005348|srh-131|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005348|srh-131|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005348|srh-131|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005348|srh-131|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005348|srh-131|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005349|srh-132|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005349|srh-132|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005349|srh-132|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005350|srh-133|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00005350|srh-133|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00005351|srh-134|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005351|srh-134|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005351|srh-134|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005352|srh-135|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005353|srh-136|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005356|srh-139|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005356|srh-139|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005359|srh-142|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005361|srh-145|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005363|srh-147|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005363|srh-147|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005363|srh-147|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005364|srh-148|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005364|srh-148|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00005364|srh-148|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005364|srh-148|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005365|srh-149|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005365|srh-149|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005370|srh-154|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005375|srh-159|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005375|srh-159|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005375|srh-159|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005375|srh-159|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005375|srh-159|328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005381|srh-165|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005381|srh-165|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005382|srh-166|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005383|srh-167|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005386|srh-170|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005386|srh-170|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005388|srh-172|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005389|srh-173|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005389|srh-173|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005389|srh-173|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005389|srh-173|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005390|srh-174|1009nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005390|srh-174|1560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005390|srh-174|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005390|srh-174|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005390|srh-174|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005392|srh-177|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005393|srh-178|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005394|srh-179|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005394|srh-179|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005395|srh-180|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005396|srh-181|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00005396|srh-181|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00005397|srh-182|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005397|srh-182|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005397|srh-182|884nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005399|srh-184|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005399|srh-184|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005399|srh-184|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005400|srh-185|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005400|srh-185|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005400|srh-185|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005401|srh-186|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005401|srh-186|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005401|srh-186|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005402|srh-187|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005402|srh-187|1343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=438|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005402|srh-187|1350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005402|srh-187|1358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005402|srh-187|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005402|srh-187|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005404|srh-190|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005405|srh-192|1286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005405|srh-192|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005406|srh-193|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005406|srh-193|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005406|srh-193|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005407|srh-194|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005407|srh-194|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005407|srh-194|961nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005407|srh-194|963nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005408|srh-195|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005410|srh-199|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00005410|srh-199|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005410|srh-199|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005411|srh-200|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005411|srh-200|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005411|srh-200|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005411|srh-200|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00005411|srh-200|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005411|srh-200|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005412|srh-201|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005415|srh-204|1329nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005415|srh-204|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005415|srh-204|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005415|srh-204|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005415|srh-204|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005415|srh-204|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005416|srh-206|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005417|srh-207|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005417|srh-207|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005418|srh-208|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005418|srh-208|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005420|srh-210|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=465|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005420|srh-210|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005420|srh-210|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005422|srh-212|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005422|srh-212|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005423|srh-213|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00005423|srh-213|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005423|srh-213|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005423|srh-213|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00005424|srh-214|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005426|srh-216|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005427|srh-217|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005427|srh-217|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005427|srh-217|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00005429|srh-219|889nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005430|srh-220|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005430|srh-220|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005430|srh-220|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005432|srh-222|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005433|srh-223|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005433|srh-223|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005437|srh-229|1340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005437|srh-229|1343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005437|srh-229|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1555|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005437|srh-229|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005437|srh-229|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005439|srh-231|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005440|srh-233|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005441|srh-234|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005441|srh-234|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005442|srh-235|1437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005442|srh-235|1440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005442|srh-235|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00005443|srh-236|810nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005444|srh-237|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=420|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005444|srh-237|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005444|srh-237|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005444|srh-237|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005446|srh-239|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005446|srh-239|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005446|srh-239|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005446|srh-239|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00005447|srh-240|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005447|srh-240|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005447|srh-240|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005448|srh-241|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005448|srh-241|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005448|srh-241|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005449|srh-243|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005450|srh-244|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005450|srh-244|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005452|srh-246|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005456|srh-250|1090nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005457|srh-251|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005461|srh-255|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=288|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005461|srh-255|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005461|srh-255|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005461|srh-255|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005461|srh-255|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005464|srh-258|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005472|srh-266|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00005472|srh-266|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005472|srh-266|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00005474|srh-268|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005474|srh-268|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005474|srh-268|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005474|srh-268|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005474|srh-268|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005474|srh-268|298nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005474|srh-268|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005475|srh-269|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00005475|srh-269|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00005476|srh-270|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005477|srh-271|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005477|srh-271|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005480|srh-275|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005480|srh-275|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005480|srh-275|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005480|srh-275|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005481|srh-276|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005481|srh-276|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00005481|srh-276|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005482|srh-277|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005482|srh-277|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005483|srh-278|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005484|srh-279|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00005484|srh-279|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005484|srh-279|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005484|srh-279|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00005487|srh-282|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=198|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005487|srh-282|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005507|srh-303|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005508|srh-304|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005509|srh-305|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00005509|srh-305|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00005512|srh-105|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005513|sri-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005514|sri-2|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00005514|sri-2|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=191|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00005516|sri-4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005517|sri-5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005517|sri-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005517|sri-5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005517|sri-5|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005518|sri-6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005519|sri-7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005521|sri-9|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005521|sri-9|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005524|sri-12|1173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005524|sri-12|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005525|sri-13|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005525|sri-13|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005525|sri-13|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005526|sri-14|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005526|sri-14|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005527|sri-15|1442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005527|sri-15|1455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005527|sri-15|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005528|sri-16|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005530|sri-18|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005530|sri-18|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005530|sri-18|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005530|sri-18|1587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005531|sri-19|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005531|sri-19|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005532|sri-20|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005532|sri-20|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=719|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005532|sri-20|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005533|sri-21|1347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005533|sri-21|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005533|sri-21|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005533|sri-21|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005533|sri-21|651nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005536|sri-24|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005536|sri-24|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005537|sri-25|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005537|sri-25|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005538|sri-26|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005540|sri-28|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005542|sri-30|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005542|sri-30|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005543|sri-31|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005544|sri-32|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00005544|sri-32|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00005544|sri-32|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005546|sri-34|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005548|sri-36|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005550|sri-38|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005551|sri-39|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005551|sri-39|1561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00005551|sri-39|1563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3046|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=359|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005552|sri-40|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005554|sri-42|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005554|sri-42|949nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005555|sri-43|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=608|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|1445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|261nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|264nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|266nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|268nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005557|sri-45|889nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005558|sri-46|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005559|sri-47|1122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005559|sri-47|1125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005559|sri-47|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=569|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005559|sri-47|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005560|sri-48|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005560|sri-48|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005560|sri-48|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005560|sri-48|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005560|sri-48|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005560|sri-48|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005562|sri-50|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005563|sri-51|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005563|sri-51|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005566|sri-54|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005569|sri-57|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005572|sri-60|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005573|sri-61|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005573|sri-61|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005574|sri-62|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005574|sri-62|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005574|sri-62|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005574|sri-62|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005575|sri-63|348nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005577|sri-65|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005578|sri-66|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005581|sri-69|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005584|sri-72|324nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005584|sri-72|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005585|sri-73|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005585|sri-73|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005585|sri-73|1241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005585|sri-73|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005585|sri-73|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005585|sri-73|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005586|sri-74|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005586|sri-74|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005589|sri-77|849nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005590|sri-78|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00005590|sri-78|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|1255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|1414nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005591|srj-1|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=128|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|370nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005592|srj-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005595|srj-7|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005595|srj-7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005597|srj-9|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005598|srj-10|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005598|srj-10|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005598|srj-10|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005599|srj-11|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005599|srj-11|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005599|srj-11|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=435|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00005599|srj-11|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005601|srj-13|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005601|srj-13|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005602|srj-14|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005602|srj-14|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005602|srj-14|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005606|srj-18|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005606|srj-18|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005606|srj-18|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005606|srj-18|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005607|srj-19|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005607|srj-19|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005607|srj-19|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005609|srj-21|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005609|srj-21|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005609|srj-21|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005610|srj-22|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005611|srj-23|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|777nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|780nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|897nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|908nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|945nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005614|srj-26|947nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005616|srj-29|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005617|srj-32|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005622|srj-38|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005631|srj-52|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005634|srj-55|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005638|srm-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005638|srm-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005638|srm-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005638|srm-1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00005639|srm-2|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005640|srn-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005640|srn-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005640|srn-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00005640|srn-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=583|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005640|srn-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005641|sro-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005641|sro-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005641|sro-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005641|sro-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005641|sro-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005641|sro-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005642|srp-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005642|srp-1|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005642|srp-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005642|srp-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=686|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005643|srp-2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005643|srp-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1388|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005643|srp-2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005644|srp-3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005644|srp-3|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005644|srp-3|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005644|srp-3|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005644|srp-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005644|srp-3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005647|srp-6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005647|srp-6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005647|srp-6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005647|srp-6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005647|srp-6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005647|srp-6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3673|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005647|srp-6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4174|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1383|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1052|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005648|srp-7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005649|srp-8|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005649|srp-8|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005649|srp-8|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005649|srp-8|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005649|srp-8|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005649|srp-8|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005649|srp-8|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005652|srr-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005652|srr-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005652|srr-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005653|srr-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005654|srr-3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=660|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005655|srr-4|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005655|srr-4|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005655|srr-4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005655|srr-4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005655|srr-4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005655|srr-4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1910|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005656|srr-5|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005656|srr-5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005656|srr-5|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005656|srr-5|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005657|srr-6|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=604|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005660|srr-9|1039nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00005660|srr-9|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00005660|srr-9|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00005661|srr-10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=706|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005662|sars-2|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=280|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=657|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2461|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33080|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2867|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=286|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=641|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|217nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00005663|sars-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005664|sru-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00005664|sru-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005664|sru-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005664|sru-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|698nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=232|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005665|sru-2|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005666|sru-3|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00005666|sru-3|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=309|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00005666|sru-3|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005666|sru-3|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005666|sru-3|979nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005666|sru-3|985nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005666|sru-3|988nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005667|sru-4|533nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005669|sru-6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005669|sru-6|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005669|sru-6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005669|sru-6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005669|sru-6|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005670|sru-7|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005670|sru-7|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005670|sru-7|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=447|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005670|sru-7|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005670|sru-7|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005671|sru-8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005671|sru-8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005671|sru-8|426nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005671|sru-8|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005671|sru-8|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005675|sru-12|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005676|sru-13|1529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005676|sru-13|1541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005676|sru-13|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005676|sru-13|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005678|sru-15|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00005678|sru-15|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00005679|sru-16|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005682|sru-19|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005682|sru-19|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005682|sru-19|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005683|sru-20|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005683|sru-20|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005684|sru-21|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005685|sru-22|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005686|sru-23|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005686|sru-23|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005686|sru-23|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005686|sru-23|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005687|sru-24|1353nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005688|sru-25|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005688|sru-25|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005689|sru-26|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005689|sru-26|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005689|sru-26|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005689|sru-26|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005689|sru-26|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005690|sru-27|18nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005690|sru-27|24nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005691|sru-28|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005691|sru-28|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005692|sru-29|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005692|sru-29|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005693|sru-30|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005694|sru-31|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005696|sru-33|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005698|sru-35|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005699|sru-36|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005700|sru-37|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005701|sru-38|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005701|sru-38|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00005701|sru-38|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005702|sru-39|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005702|sru-39|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=760|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005703|sru-40|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005703|sru-40|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005705|sru-42|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005705|sru-42|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005705|sru-42|267nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005710|sru-47|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005710|sru-47|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005710|sru-47|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005711|sru-48|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005711|sru-48|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=945|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|187nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|253nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005712|srv-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005713|srv-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005713|srv-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005713|srv-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005713|srv-2|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005713|srv-2|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005715|srv-4|899nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00005715|srv-4|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00005715|srv-4|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005716|srv-5|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=184|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00005716|srv-5|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00005717|srv-6|232nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005717|srv-6|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005717|srv-6|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005717|srv-6|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005717|srv-6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005717|srv-6|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005718|srv-7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005718|srv-7|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005718|srv-7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00005718|srv-7|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005719|srv-8|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005719|srv-8|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005719|srv-8|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005719|srv-8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005719|srv-8|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005720|srv-9|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005720|srv-9|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005721|srv-10|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005722|srv-11|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005724|srv-13|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005724|srv-13|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005724|srv-13|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005724|srv-13|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005724|srv-13|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005724|srv-13|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005724|srv-13|881nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005725|srv-14|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00005725|srv-14|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005725|srv-14|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005725|srv-14|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00005726|srv-15|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00005726|srv-15|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005726|srv-15|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005726|srv-15|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005727|srv-16|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005728|srv-17|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005732|srv-21|1600nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005735|srv-24|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005735|srv-24|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005735|srv-24|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005735|srv-24|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005736|srv-25|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005737|srv-26|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|1428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005738|srv-27|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005739|srv-28|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005739|srv-28|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005739|srv-28|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005739|srv-28|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005739|srv-28|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005739|srv-28|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005740|srv-29|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005740|srv-29|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005742|srv-31|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005742|srv-31|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00005742|srv-31|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005743|srv-32|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005743|srv-32|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005743|srv-32|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005743|srv-32|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005743|srv-32|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005743|srv-32|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005744|ops-1|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005744|ops-1|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005744|ops-1|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005744|ops-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005745|srv-34|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005745|srv-34|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1267|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005745|srv-34|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005745|srv-34|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005748|srw-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005753|srw-6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005753|srw-6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005753|srw-6|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005753|srw-6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005754|srw-7|166nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=213|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00005754|srw-7|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005754|srw-7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005754|srw-7|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005754|srw-7|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005755|srw-8|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005755|srw-8|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005755|srw-8|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005756|srw-9|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00005756|srw-9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005756|srw-9|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005757|srw-10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005757|srw-10|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005757|srw-10|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=976|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005757|srw-10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4827|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005757|srw-10|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005758|srw-11|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005759|srw-12|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005759|srw-12|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=524|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005759|srw-12|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005759|srw-12|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005760|srw-13|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005760|srw-13|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005760|srw-13|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005761|srw-14|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005761|srw-14|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005763|srw-16|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005764|srw-17|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005764|srw-17|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005766|srw-19|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005767|srw-20|1297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005780|srw-33|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005780|srw-33|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005782|srw-35|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005782|srw-35|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005791|srw-44|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005791|srw-44|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005791|srw-44|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005791|srw-44|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005803|srw-56|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005807|srw-60|1491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005808|srw-61|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005808|srw-61|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005808|srw-61|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005810|srw-63|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005810|srw-63|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005810|srw-63|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005813|srw-66|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005815|srw-68|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005815|srw-68|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005815|srw-68|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005815|srw-68|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005815|srw-68|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005816|srw-69|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005816|srw-69|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005818|srw-71|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005818|srw-71|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005818|srw-71|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005818|srw-71|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005818|srw-71|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005818|srw-71|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005818|srw-71|421nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005819|srw-72|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005820|srw-73|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005824|srw-77|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005824|srw-77|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005826|srw-79|826nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005830|srw-83|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005831|srw-84|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005832|srw-85|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=568|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005832|srw-85|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005833|srw-86|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005833|srw-86|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00005833|srw-86|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005833|srw-86|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005833|srw-86|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00005833|srw-86|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005833|srw-86|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005834|srw-87|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005835|srw-88|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005835|srw-88|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005835|srw-88|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00005835|srw-88|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005835|srw-88|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005836|srw-89|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005836|srw-89|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005836|srw-89|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005837|srw-90|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005838|srw-91|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005841|srw-94|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00005841|srw-94|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00005841|srw-94|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005841|srw-94|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005844|srw-97|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005845|srw-98|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005845|srw-98|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005845|srw-98|747nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005845|srw-98|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005847|srw-100|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00005847|srw-100|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00005849|srw-102|444nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005849|srw-102|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005849|srw-102|676nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005850|srw-103|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005850|srw-103|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005850|srw-103|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005854|srw-107|1006nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005855|srw-108|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005858|srw-111|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005859|srw-112|802nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005862|srw-115|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005867|srw-120|572nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005868|srw-121|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005868|srw-121|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005868|srw-121|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005868|srw-121|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005868|srw-121|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005868|srw-121|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005876|srw-129|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005883|srw-136|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005886|srw-139|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005886|srw-139|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005887|srw-140|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005887|srw-140|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005887|srw-140|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005887|srw-140|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005888|srw-141|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005892|srx-1|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005892|srx-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005892|srx-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005892|srx-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005893|srx-2|1341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005893|srx-2|1421nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005893|srx-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00005893|srx-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00005893|srx-2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005893|srx-2|996nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005894|srx-3|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005894|srx-3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005894|srx-3|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00005898|srx-7|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005900|srx-9|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005900|srx-9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005901|srx-10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005901|srx-10|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005901|srx-10|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005903|srx-12|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005903|srx-12|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005903|srx-12|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005903|srx-12|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005903|srx-12|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005903|srx-12|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005904|srx-13|1107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|655nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|661nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|665nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|729nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|744nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005905|srx-14|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005907|srx-16|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005909|srx-18|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005909|srx-18|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005909|srx-18|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005910|srx-19|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005910|srx-19|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005910|srx-19|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00005910|srx-19|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005910|srx-19|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005912|srx-21|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005929|srx-38|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005929|srx-38|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005929|srx-38|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005929|srx-38|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005929|srx-38|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005929|srx-38|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00005929|srx-38|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|540nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005931|fbxa-199|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005932|srx-41|1191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005932|srx-41|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005934|srx-43|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005934|srx-43|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005934|srx-43|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005934|srx-43|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005934|srx-43|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005934|srx-43|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005935|srx-44|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005935|srx-44|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005935|srx-44|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005935|srx-44|1219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005935|srx-44|1346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005935|srx-44|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005935|srx-44|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=477|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1233|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005936|srx-45|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005937|srx-46|1002nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005937|srx-46|1005nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005937|srx-46|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005937|srx-46|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005937|srx-46|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005937|srx-46|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005937|srx-46|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00005938|srx-47|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00005938|srx-47|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00005938|srx-47|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00005939|srx-48|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005941|srx-50|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005941|srx-50|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005941|srx-50|72nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005942|srx-51|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005942|srx-51|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005947|srx-56|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005947|srx-56|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005947|srx-56|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1485|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005949|srx-58|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005949|srx-58|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005950|srx-59|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005951|srx-60|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005953|srx-62|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005953|srx-62|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005955|srx-64|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005955|srx-64|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005955|srx-64|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005957|srx-66|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005957|srx-66|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|917nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005958|srx-67|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1437|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005959|srx-68|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00005964|srx-73|1488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005964|srx-73|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005964|srx-73|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005964|srx-73|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005964|srx-73|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005964|srx-73|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005964|srx-73|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005965|srx-74|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005965|srx-74|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005965|srx-74|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005965|srx-74|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005965|srx-74|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005967|srx-76|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005967|srx-76|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005967|srx-76|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005967|srx-76|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005968|srx-77|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00005968|srx-77|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00005969|srx-78|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005971|srx-80|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005971|srx-80|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005971|srx-80|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005971|srx-80|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005973|srx-82|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|823nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005975|srx-84|998nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005976|srx-85|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005976|srx-85|1179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005977|srx-86|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00005977|srx-86|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005977|srx-86|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005977|srx-86|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00005978|srx-87|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00005978|srx-87|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005978|srx-87|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005979|srx-88|1577nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005980|srx-89|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005980|srx-89|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00005980|srx-89|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00005986|srx-95|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005988|srx-97|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00005988|srx-97|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00005988|srx-97|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00005989|srx-98|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00005999|srx-108|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00005999|srx-108|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00005999|srx-108|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005999|srx-108|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00005999|srx-108|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006001|srx-110|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006001|srx-110|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006002|srx-111|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006002|srx-111|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006002|srx-111|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006003|srx-112|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006004|srx-113|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006005|srx-114|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006006|srx-115|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006007|srx-116|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006008|srx-117|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006008|srx-117|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006009|srx-118|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006009|srx-118|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006011|srx-120|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006016|srx-125|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006016|srx-125|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006016|srx-125|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006016|srx-125|335nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006019|srx-128|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006019|srx-128|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006019|srx-128|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006019|srx-128|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006020|srx-129|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006021|srx-130|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006021|srx-130|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006022|srx-131|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006022|srx-131|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006024|srx-133|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006025|srx-134|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006025|srx-134|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006026|srx-135|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006026|srx-135|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006026|srx-135|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006026|srx-135|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006026|srx-135|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006026|srx-135|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006026|srx-135|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00006027|srx-136|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006028|srx-137|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00006028|srx-137|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11584|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6336|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=971|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006038|ssp-9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006039|ssp-10|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006039|ssp-10|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006039|ssp-10|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006039|ssp-10|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006039|ssp-10|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=618|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006039|ssp-10|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8191|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006039|ssp-10|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1328|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006044|ssp-16|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006044|ssp-16|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006044|ssp-16|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006044|ssp-16|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5465|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006044|ssp-16|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3792|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006047|ssp-19|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1401|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006047|ssp-19|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006047|ssp-19|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006048|ssp-31|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006048|ssp-31|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006048|ssp-31|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=294|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006048|ssp-31|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006048|ssp-31|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006048|ssp-31|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=652|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006048|ssp-31|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006049|ssp-32|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006050|ssq-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006050|ssq-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006050|ssq-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006050|ssq-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1885|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006050|ssq-1|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5344|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006051|ssq-2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006051|ssq-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006051|ssq-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7022|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00006051|ssq-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006052|ssq-3|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1963|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006052|ssq-3|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006052|ssq-3|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006053|ssq-4|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006053|ssq-4|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6220|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006053|ssq-4|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006053|ssq-4|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006053|ssq-4|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2060|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1205|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006055|ssr-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006056|sss-1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=506|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006056|sss-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2486|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006058|sst-20|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006058|sst-20|77nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=533|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006058|sst-20|80nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=304|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006058|sst-20|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|1451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2321|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3432|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006059|stc-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006060|sth-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6039|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006060|sth-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006060|sth-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4291|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00006060|sth-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006060|sth-1|353nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006060|sth-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006061|stl-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006061|stl-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006061|stl-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3445|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006061|stl-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006061|stl-1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006061|stl-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006061|stl-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|318nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|328nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|331nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1286|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=787|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006062|stn-1|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=710|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=220|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006063|sto-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006064|sto-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006064|sto-2|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006064|sto-2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006064|sto-2|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006064|sto-2|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2661|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006064|sto-2|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006065|sto-3|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7902|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1209|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006066|sto-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006067|sto-5|1069nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006067|sto-5|1146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006067|sto-5|1148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006067|sto-5|1163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4275|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006067|sto-5|1171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006067|sto-5|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2284|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2131|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=141|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006068|sto-6|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=276|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006071|str-3|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006071|str-3|1217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006071|str-3|553nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00006071|str-3|556nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006071|str-3|560nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006072|str-4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006072|str-4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006075|str-7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006075|str-7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006075|str-7|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006076|str-8|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006076|str-8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006077|str-9|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00006077|str-9|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006077|str-9|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006080|str-12|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006080|str-12|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006080|str-12|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006082|str-14|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006082|str-14|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006083|str-15|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006083|str-15|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006083|str-15|1306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006084|str-16|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006085|str-18|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006085|str-18|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006086|str-19|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=740|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006086|str-19|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006086|str-19|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006086|str-19|834nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006086|str-19|94nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006086|str-19|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006092|str-25|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006092|str-25|88nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006093|str-27|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006093|str-27|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006097|str-31|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006097|str-31|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006098|str-32|1030nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00006098|str-32|1037nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006098|str-32|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006098|str-32|1087nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006102|str-37|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006102|str-37|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006102|str-37|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006102|str-37|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006102|str-37|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006103|str-38|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006103|str-38|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006103|str-38|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006103|str-38|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006103|str-38|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006104|str-39|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006106|str-41|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006108|str-43|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006109|str-44|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006109|str-44|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006109|str-44|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2230|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006110|str-45|1459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006110|str-45|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006110|str-45|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006112|str-47|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006113|str-48|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00006113|str-48|548nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006113|str-48|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006122|str-57|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006125|str-61|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006126|str-63|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006126|str-63|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006127|str-64|1264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006127|str-64|1275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006129|str-67|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006130|str-68|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006135|str-74|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006138|str-78|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006138|str-78|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006139|str-79|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006139|str-79|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006139|str-79|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006141|str-82|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006142|str-83|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006143|str-84|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006143|str-84|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006143|str-84|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006146|str-87|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006148|str-89|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006148|str-89|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006148|str-89|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006149|str-90|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|637nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006150|str-92|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006151|str-93|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006151|str-93|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006152|str-94|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006152|str-94|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006153|str-96|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006153|str-96|1310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006153|str-96|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006153|str-96|958nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006154|str-97|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006154|str-97|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006154|str-97|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006157|str-102|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006158|str-103|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006160|str-108|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006160|str-108|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006161|str-109|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006161|str-109|1565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006163|str-112|1222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006163|str-112|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=214|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006163|str-112|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006163|str-112|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006164|str-113|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006165|str-114|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006166|str-115|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00006166|str-115|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006166|str-115|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006166|str-115|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006167|str-116|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006170|str-119|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006170|str-119|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006172|str-121|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006175|str-124|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006176|str-125|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006178|str-129|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006178|str-129|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006178|str-129|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006179|str-130|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00006179|str-130|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006179|str-130|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006180|str-131|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00006180|str-131|513nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006180|str-131|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006180|str-131|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006182|str-134|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006182|str-134|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006183|str-135|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006183|str-135|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006186|str-139|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006187|str-138|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006188|str-140|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006188|str-140|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006189|str-141|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006189|str-141|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006189|str-141|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006189|str-141|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006189|str-141|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006191|str-144|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006191|str-144|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006191|str-144|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00006192|str-145|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006192|str-145|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006193|str-146|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006193|str-146|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006193|str-146|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006195|str-148|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006198|str-151|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006199|str-153|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006199|str-153|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006201|str-155|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006201|str-155|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006202|str-156|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006202|str-156|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006202|str-156|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006205|str-160|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006205|str-160|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006207|str-162|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006207|str-162|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006207|str-162|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006207|str-162|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006207|str-162|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=280|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006207|str-162|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006207|str-162|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006208|str-163|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006208|str-163|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006208|str-163|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006209|str-164|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006209|str-164|181nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006209|str-164|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006209|str-164|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006209|str-164|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006210|str-165|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006211|str-166|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006212|str-168|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006212|str-168|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006212|str-168|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006212|str-168|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006212|str-168|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006212|str-168|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006213|str-169|1267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006213|str-169|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006213|str-169|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006215|str-171|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006215|str-171|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006216|str-172|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006216|str-172|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006216|str-172|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006216|str-172|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006216|str-172|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006217|str-173|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006217|str-173|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006218|str-174|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006218|str-174|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006218|str-174|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006219|str-175|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006220|str-176|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006220|str-176|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006220|str-176|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006220|str-176|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006221|str-177|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006221|str-177|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006221|str-177|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006221|str-177|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006221|str-177|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006224|str-180|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006224|str-180|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006224|str-180|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006224|str-180|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006224|str-180|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006224|str-180|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006226|str-182|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006226|str-182|1596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006226|str-182|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006226|str-182|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006226|str-182|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006227|str-183|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006227|str-183|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006228|str-185|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006229|str-187|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00006229|str-187|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006229|str-187|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006229|str-187|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00006231|str-190|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00006231|str-190|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00006234|str-198|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006234|str-198|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006235|str-199|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006236|str-200|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006237|str-204|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006237|str-204|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006237|str-204|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006239|str-206|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006241|str-208|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006241|str-208|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006244|str-211|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006244|str-211|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006253|str-222|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006258|str-227|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006258|str-227|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006260|str-229|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006261|str-230|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006261|str-230|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006261|str-230|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006261|str-230|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006261|str-230|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006262|str-231|1598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006262|str-231|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006262|str-231|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006263|str-232|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006263|str-232|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006266|str-238|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006266|str-238|1538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006268|str-240|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006268|str-240|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006270|str-243|1391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006270|str-243|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006271|str-244|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1066nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1076nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=558|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2086|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1222nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=608|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=297|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1480nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1489nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1492nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1504nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1506nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1509nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|1539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006272|str-245|993nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006273|str-246|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006274|str-247|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006278|str-252|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006279|str-253|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006280|str-254|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006282|str-256|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006282|str-256|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006282|str-256|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006286|str-260|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006286|str-260|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006286|str-260|367nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006286|str-260|372nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006286|str-260|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006286|str-260|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006286|str-260|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006287|str-261|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006287|str-261|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006287|str-261|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006288|str-262|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006288|str-262|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4314|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=469|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006306|sue-1|992nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006307|suf-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006307|suf-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4403|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006307|suf-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006307|suf-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006307|suf-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006307|suf-1|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006308|sul-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006308|sul-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006308|sul-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006308|sul-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006308|sul-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006309|sul-2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006309|sul-2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006309|sul-2|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006309|sul-2|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00006309|sul-2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1368|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00006309|sul-2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006309|sul-2|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006310|sul-3|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2514|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006311|sun-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=780|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=458|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1645|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006318|sup-9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006319|sup-10|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006319|sup-10|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006319|sup-10|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006319|sup-10|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2872|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=468|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|870nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|896nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006321|sup-12|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|475nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2861|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|480nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=238|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|482nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2501|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|486nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=291|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|491nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|495nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006324|sup-17|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|1143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|1145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|1147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1336|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|1152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|1154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2491|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|1159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006331|sup-26|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|1045nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|1050nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|1166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=924|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|1169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|1172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|1174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=620|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006342|sup-37|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006349|sur-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=579|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006349|sur-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1078|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2971|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|333nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|344nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|348nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|424nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006351|sur-5|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|1075nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=958|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|677nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|688nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=673|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|698nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|700nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|707nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1446|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3604|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|894nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1288|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006352|sur-6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|1021nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|1211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|1215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|1220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=527|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|737nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|967nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|972nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006353|sur-7|975nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|254nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1016|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006359|swp-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=629|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|377nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1898|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|393nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006363|syd-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006364|syd-2|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1106|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006364|syd-2|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006365|syg-1|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006365|syg-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006365|syg-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006365|syg-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1311|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006365|syg-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006365|syg-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006365|syg-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2087|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006366|sym-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|354nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2358|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006367|sym-2|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006368|sym-3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006368|sym-3|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006368|sym-3|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1680|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006368|sym-3|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006368|sym-3|465nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006368|sym-3|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|1404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|1410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=997|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006369|sym-4|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1183|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|1110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|1119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|1262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=615|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|405nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006371|syx-3|409nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006372|syx-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006372|syx-2|392nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006372|syx-2|397nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1086|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006372|syx-2|400nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006372|syx-2|404nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006372|syx-2|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5691|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006373|syx-5|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006374|syx-4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006374|syx-4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00006375|syp-1|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006375|syp-1|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006375|syp-1|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1862|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006375|syp-1|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006375|syp-1|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2041|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006376|syp-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006377|syp-3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006377|syp-3|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006377|syp-3|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1977|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006377|syp-3|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006377|syp-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006377|syp-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|1402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|1410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=817|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006379|sys-1|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4547|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2593|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=673|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006380|tab-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|1394nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3835|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1783|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006381|tac-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=934|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|25nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|446nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006382|taf-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006383|taf-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006383|taf-2|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006383|taf-2|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1896|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006383|taf-2|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006383|taf-2|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006383|taf-2|433nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006383|taf-2|436nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|376nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|384nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|441nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=748|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006384|taf-3|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=767|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|152nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006385|taf-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1008|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2924|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006386|taf-5|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006387|taf-6.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006387|taf-6.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006387|taf-6.1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=911|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006387|taf-6.1|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006388|taf-7.1|92nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|1554nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|776nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|780nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|783nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|786nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|789nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=219|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|793nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|798nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006389|taf-7.2|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006390|taf-8|1040nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006390|taf-8|1057nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006390|taf-8|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006390|taf-8|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=713|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006390|taf-8|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006390|taf-8|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006390|taf-8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1786|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=565|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006391|taf-9|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=432|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006392|taf-10|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006392|taf-10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006392|taf-10|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006392|taf-10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1853|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006392|taf-10|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006393|taf-11.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006393|taf-11.1|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006393|taf-11.1|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=673|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006393|taf-11.1|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1319|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006394|taf-11.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006395|taf-11.3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006395|taf-11.3|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006395|taf-11.3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006395|taf-11.3|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=491|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006395|taf-11.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006396|taf-12|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006396|taf-12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1813|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00006396|taf-12|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006396|taf-12|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=572|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006397|taf-13|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006397|taf-13|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006397|taf-13|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006397|taf-13|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14902|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006397|taf-13|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006397|taf-13|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006397|taf-13|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4264|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|1530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006402|fut-3|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006404|tag-10|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006404|tag-10|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006404|tag-10|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1877|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006404|tag-10|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006404|tag-10|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006404|tag-10|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006404|tag-10|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2013|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2928|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006405|itsn-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1815|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|298nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3275|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|466nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|473nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006406|srgp-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|772nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|785nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|790nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1035|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|795nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=615|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|804nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5436|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|814nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1206|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|818nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006407|lim-9|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11098|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2010|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|38nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|40nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006408|tag-18|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006409|hdl-2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006409|hdl-2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|1492nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=239|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|1502nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|200nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=823|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|418nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4188|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|508nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006410|nck-1|540nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006411|octr-1|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006411|octr-1|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006411|octr-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006411|octr-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006411|octr-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006411|octr-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006411|octr-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=786|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006412|nlg-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4252|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1200|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|424nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006414|raga-1|429nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006415|tag-30|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4382|total_reads(99.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006415|tag-30|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006416|sams-5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006416|sams-5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006416|sams-5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1394|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006416|sams-5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006416|sams-5|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006418|tag-38|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006423|asd-2|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006423|asd-2|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006423|asd-2|662nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006423|asd-2|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2046|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006423|asd-2|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006423|asd-2|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1579|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006424|ctbp-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1933|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006428|tkr-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006429|arrd-3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006429|arrd-3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006430|tag-51|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=246|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006430|tag-51|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006430|tag-51|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006430|tag-51|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006430|tag-51|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006430|tag-51|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006430|tag-51|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006431|tag-52|1051nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006431|tag-52|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006431|tag-52|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006431|tag-52|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=525|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006432|tag-53|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006432|tag-53|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006432|tag-53|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006432|tag-53|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006432|tag-53|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1042|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6003|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9147|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2531|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3210|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|200nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|20nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=201|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006433|sdhb-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1903|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28081|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10748|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3764|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006434|prdx-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006435|stdh-4|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006436|ttn-1|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006436|ttn-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006436|ttn-1|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006436|ttn-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1369|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006436|ttn-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006436|ttn-1|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006436|ttn-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|1230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|639nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3593|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|644nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|647nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006437|mrck-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=478|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5388|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=522|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006438|nrfl-1|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2087|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3412|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218592|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25976|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15264|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5657|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=332|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=596|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196282|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2262|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4233|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1496|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|77nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|87nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|98nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006439|ant-1.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006440|tag-63|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006440|tag-63|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1100|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006440|tag-63|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00006441|cpna-4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006441|cpna-4|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006441|cpna-4|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006441|cpna-4|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=531|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006442|tag-65|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=690|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006443|pak-2|333nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|308nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|365nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006444|shn-1|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|1323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|454nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|459nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006445|tag-68|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2070|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006446|atx-3|496nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006447|tag-72|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006447|tag-72|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006447|tag-72|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=262|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006447|tag-72|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=932|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006447|tag-72|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006447|tag-72|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006448|glod-4|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006448|glod-4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006448|glod-4|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006448|glod-4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006448|glod-4|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006448|glod-4|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1095|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006448|glod-4|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1771|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006449|alg-4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1477|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006449|alg-4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006449|alg-4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|1165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1150|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=271|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006450|tag-77|864nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006452|heh-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006452|heh-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006452|heh-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2142|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006452|heh-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5672|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00006452|heh-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006454|aex-4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006454|aex-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006454|aex-4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006454|aex-4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=526|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00006454|aex-4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006454|aex-4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006459|tag-89|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1866|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006459|tag-89|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006459|tag-89|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006459|tag-89|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006459|tag-89|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006459|tag-89|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|1121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|486nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14535|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|494nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006460|ppm-1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006461|tag-96|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006461|tag-96|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006461|tag-96|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00006461|tag-96|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|358nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|643nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|649nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|657nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|666nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1189|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|668nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006462|tag-97|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006463|nduf-2.2|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006463|nduf-2.2|1491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006463|nduf-2.2|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5822|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006463|nduf-2.2|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=234|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006463|nduf-2.2|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006464|bath-47|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006464|bath-47|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3564|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1883|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006465|fntb-1|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|1095nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1784|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=406|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|876nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|913nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|936nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|939nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|946nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|948nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006466|tag-115|954nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=436|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006467|magu-2|558nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=662|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006468|rhgf-1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2631|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1782|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006470|tag-120|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|1444nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|427nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=932|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|430nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|433nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1065|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006472|tag-123|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|1045nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|1278nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2808|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00006473|tag-124|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=934|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2156|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006474|wdr-5.1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006475|tyra-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006475|tyra-3|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006475|tyra-3|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=990|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006475|tyra-3|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00006475|tyra-3|224nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006475|tyra-3|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006475|tyra-3|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006476|rhgf-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|494nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006477|chup-1|498nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006478|tag-131|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006478|tag-131|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006478|tag-131|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006478|tag-131|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1217|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006478|tag-131|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006478|tag-131|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006478|tag-131|302nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4028|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006479|tmbi-4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3638|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006481|plrg-1|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|697nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|699nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1459|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|701nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=752|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|703nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2529|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|707nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|709nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=321|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006483|dgk-4|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006484|tag-138|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006486|tag-140|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006486|tag-140|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006486|tag-140|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006486|tag-140|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006487|tag-141|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006487|tag-141|781nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006487|tag-141|783nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006487|tag-141|787nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006487|tag-141|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006487|tag-141|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=810|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|1359nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006489|zhit-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006490|kdin-1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3485|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006490|kdin-1|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006490|kdin-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006491|acl-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006491|acl-3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=969|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006491|acl-3|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006491|acl-3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006491|acl-3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006492|let-391|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006492|let-391|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006492|let-391|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006492|let-391|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5753|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006493|tag-147|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1459|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2080|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006494|hke-4.2|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006495|cpna-1|225nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=492|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006495|cpna-1|227nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006495|cpna-1|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=638|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006495|cpna-1|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006495|cpna-1|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006495|cpna-1|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006495|cpna-1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006496|cgef-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006496|cgef-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006496|cgef-1|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1685|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006496|cgef-1|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006496|cgef-1|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006496|cgef-1|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006497|tag-151|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006497|tag-151|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006497|tag-151|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006497|tag-151|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3438|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|494nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|498nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|503nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1438|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006498|ten-1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|483nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2699|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|494nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=605|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006499|tag-153|595nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|1508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2873|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006503|snx-3|737nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006504|kcc-1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006504|kcc-1|775nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006504|kcc-1|781nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2509|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00006504|kcc-1|783nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006504|kcc-1|785nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006504|kcc-1|826nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006505|lagr-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006505|lagr-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006505|lagr-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|21nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1020|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=838|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=609|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006508|tag-163|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006509|tag-164|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006509|tag-164|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006509|tag-164|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=676|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006510|mtrr-1|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006510|mtrr-1|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5059|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006510|mtrr-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006510|mtrr-1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1196|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3724|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006512|abcf-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006513|rimb-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006513|rimb-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006513|rimb-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006513|rimb-1|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006513|rimb-1|415nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2067|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006513|rimb-1|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=492|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006513|rimb-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2914|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006514|tdp-1|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8350|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006515|txdc-9|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006516|vps-16|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1803|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006516|vps-16|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1353|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|713nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006517|madd-3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1091|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6385|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006518|tag-173|34nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5674|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=460|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7298|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4150|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2353|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=291|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|366nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|373nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006519|tag-174|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006520|tag-175|1327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006520|tag-175|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006520|tag-175|1417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006520|tag-175|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006520|tag-175|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006520|tag-175|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006520|tag-175|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1731|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006522|abcx-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=618|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4060|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006523|tam-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006524|tap-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006524|tap-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006524|tap-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006524|tap-1|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006524|tap-1|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006524|tap-1|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1612|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006525|tax-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006525|tax-2|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006525|tax-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006525|tax-2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006525|tax-2|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006525|tax-2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006526|tax-4|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|433nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|780nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=267|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|784nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|786nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|790nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|792nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|794nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|798nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|806nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|967nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|977nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|981nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=415|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|986nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5397|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|989nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|993nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=914|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006527|tax-6|996nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1017|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20168|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=792|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|1325nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|149nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=341|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17680|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1759|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=368|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006528|tba-1|996nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3102|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1270|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|1586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4068|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1532|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=473|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24261|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11643|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006529|tba-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1137|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006530|tba-4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006530|tba-4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=797|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006530|tba-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=377|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006530|tba-4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006531|tba-5|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006531|tba-5|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006531|tba-5|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006531|tba-5|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006531|tba-5|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006532|tba-6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006532|tba-6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006532|tba-6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006532|tba-6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006533|tba-7|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1132|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006533|tba-7|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006533|tba-7|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006533|tba-7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006534|tba-8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006534|tba-8|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006534|tba-8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006534|tba-8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006534|tba-8|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006534|tba-8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006534|tba-8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|1474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|1491nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=751|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1615|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006535|tba-9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25305|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=818|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006536|tbb-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2096|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=404|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45581|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16252|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=865|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2089|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1902|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006537|tbb-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=603|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=259|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|297nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006538|tbb-4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=578|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|677nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006539|tbb-6|682nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3000|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|373nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|380nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|502nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|510nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|569nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|633nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|642nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|649nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|676nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006540|tbg-1|684nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|260nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=703|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=430|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2997|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006541|tbh-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2882|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|184nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|187nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1795|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006542|tbp-1|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2693|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006543|tbx-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006544|tbx-7|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006544|tbx-7|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006545|tbx-8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|809nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006546|tbx-9|967nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006547|tbx-11|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006547|tbx-11|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006550|tbx-31|1433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|617nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006551|tbx-32|855nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006552|tbx-33|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006552|tbx-33|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006552|tbx-33|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006552|tbx-33|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00006553|tbx-34|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006553|tbx-34|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006553|tbx-34|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=347|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006553|tbx-34|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006555|tbx-36|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006555|tbx-36|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006555|tbx-36|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006555|tbx-36|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006556|tbx-37|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006556|tbx-37|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006556|tbx-37|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006557|tbx-38|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006558|tbx-39|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006559|tbx-40|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006561|tcl-2|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006561|tcl-2|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006561|tcl-2|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=141|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2849|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1886|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=230|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=450|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1689|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4839|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=801|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=502|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1045|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006562|tdc-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006563|teg-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006563|teg-1|479nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1960|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006563|teg-1|497nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006563|teg-1|500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=366|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8414|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1082|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|543nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006565|tfg-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006566|tgt-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006566|tgt-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1403|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006566|tgt-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006566|tgt-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006566|tgt-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006566|tgt-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006566|tgt-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006567|tgt-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006567|tgt-2|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006567|tgt-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1172|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006567|tgt-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006568|thk-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006568|thk-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006568|thk-1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1133|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006568|thk-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1104|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00006568|thk-1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006568|thk-1|220nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006568|thk-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4294|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006570|tig-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1018|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006571|tim-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006571|tim-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006571|tim-1|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006571|tim-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1204|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006571|tim-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006571|tim-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006571|tim-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2775|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=343|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|562nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006572|tin-9.1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2567|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=469|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1575|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006573|tin-10|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4541|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006574|tin-13|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|1528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|321nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|329nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|352nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|359nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|362nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|369nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|587nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|590nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=620|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|593nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1431|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|596nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|600nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006575|tir-1|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|122nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|916nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006576|tkr-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|559nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|562nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=910|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=813|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006577|tlf-1|822nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2293|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=572|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006578|tli-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=937|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|375nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|384nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4567|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|386nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=963|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|389nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|392nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|424nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|427nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=661|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006579|tlk-1|494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006580|tlp-1|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1163|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006580|tlp-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|1080nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=580|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006582|tmd-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=571|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006583|tnc-2|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=286|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4898|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006584|tni-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2547|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1684|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006585|tni-3|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2281|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=949|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006586|tni-4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2057|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26621|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006587|tnt-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1861|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|563nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1051|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006588|tnt-3|722nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1619|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006589|tnt-4|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2645|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006590|toc-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=762|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006591|toh-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006592|dpy-31|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006592|dpy-31|1316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006592|dpy-31|1510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006592|dpy-31|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006592|dpy-31|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|1284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1601|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006593|tol-1|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1748|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=525|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006594|tom-1|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|406nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|409nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|411nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4585|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006595|top-1|689nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3219|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00006596|top-3|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006596|top-3|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006596|top-3|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006596|top-3|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006597|tor-1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006597|tor-1|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00006597|tor-1|594nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006598|tor-2|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006598|tor-2|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|1590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|1597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1578|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|605nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006599|tpa-1|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006600|tph-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006600|tph-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006600|tph-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00006600|tph-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|403nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12675|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=664|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|436nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|442nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006601|tpi-1|449nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|1033nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|1043nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|1047nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2086|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006602|tps-1|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006603|tps-2|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006603|tps-2|124nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006603|tps-2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2539|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006603|tps-2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006603|tps-2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|1197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|1204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2442|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|1207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=141|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|1210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006604|tra-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006605|tra-2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006605|tra-2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1352|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006605|tra-2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006605|tra-2|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006605|tra-2|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006605|tra-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006606|tra-3|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006606|tra-3|268nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006606|tra-3|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006606|tra-3|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2529|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3505|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=882|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006607|tre-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2700|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006608|tre-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006609|tre-3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006609|tre-3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006609|tre-3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=975|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006609|tre-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1230|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006609|tre-3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006610|tre-4|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006610|tre-4|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006611|tre-5|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006612|trf-1|1507nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006612|trf-1|1545nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006612|trf-1|1563nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006612|trf-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006612|trf-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006613|trm-1|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2148|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006613|trm-1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006613|trm-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006613|trm-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006613|trm-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=742|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006614|trp-1|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006615|trp-2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006615|trp-2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2144|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006615|trp-2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006615|trp-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006615|trp-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006616|trp-4|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006616|trp-4|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=483|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11898|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2534|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1170|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006617|tars-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006618|trt-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006618|trt-1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006618|trt-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006618|trt-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=615|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006619|try-1|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1634|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006619|try-1|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006619|try-1|1226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006619|try-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006620|svh-1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006620|svh-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006621|try-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006621|try-3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006622|try-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006622|try-4|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006623|try-5|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006623|try-5|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006624|try-6|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006624|try-6|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006624|try-6|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006624|try-6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006625|try-7|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006625|try-7|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=189|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006625|try-7|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006625|try-7|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|106nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|1360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|397nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10620|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|403nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=355|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006626|tsn-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006627|tsp-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=735|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006627|tsp-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006628|tsp-2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006628|tsp-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=516|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006628|tsp-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006628|tsp-2|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006628|tsp-2|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006628|tsp-2|941nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006629|tsp-3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006630|tsp-4|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006630|tsp-4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006630|tsp-4|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006630|tsp-4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2456|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006630|tsp-4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006630|tsp-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006631|tsp-5|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006631|tsp-5|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006631|tsp-5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006631|tsp-5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=419|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006631|tsp-5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|107nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|1389nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|1477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|1481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|1483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|1489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006632|tsp-6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3737|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1961|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|122nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=954|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|137nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=305|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|147nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=330|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|149nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1693|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|153nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|160nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|163nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=656|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1184|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|692nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|698nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|718nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|729nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=969|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2121|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2741|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006633|tsp-7|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=719|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006634|tsp-8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=360|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006634|tsp-8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006634|tsp-8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006634|tsp-8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3683|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00006634|tsp-8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006634|tsp-8|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=817|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006635|tsp-9|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006636|tsp-10|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|638nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|642nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|664nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|737nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|739nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006637|tsp-11|757nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|1030nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|1315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3400|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006638|tsp-12|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006639|tsp-13|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006639|tsp-13|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006639|tsp-13|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006639|tsp-13|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006639|tsp-13|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006640|tsp-14|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006640|tsp-14|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006640|tsp-14|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1105|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00006640|tsp-14|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006641|tsp-15|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006641|tsp-15|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006641|tsp-15|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006641|tsp-15|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006641|tsp-15|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006641|tsp-15|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006642|tsp-16|1128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006642|tsp-16|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006642|tsp-16|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006643|tsp-17|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006644|tsp-18|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006644|tsp-18|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006644|tsp-18|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006644|tsp-18|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006645|tsp-19|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006645|tsp-19|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=614|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|598nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|605nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006646|tsp-20|608nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006647|tsr-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006647|tsr-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006647|tsr-1|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=870|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006647|tsr-1|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1164|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006648|ttb-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|382nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|385nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1712|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6889|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|395nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|418nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006649|tth-1|421nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006652|ttx-1|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006652|ttx-1|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=557|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006654|ttx-3|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006655|tub-1|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006655|tub-1|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006655|tub-1|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006655|tub-1|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006655|tub-1|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006656|twk-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00006656|twk-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006656|twk-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006656|twk-1|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006656|twk-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006656|twk-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006656|twk-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006657|twk-2|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006658|twk-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006658|twk-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006658|twk-3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006658|twk-3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006658|twk-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00006658|twk-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006660|twk-5|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006660|twk-5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006661|twk-6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006661|twk-6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006662|twk-7|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006662|twk-7|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006662|twk-7|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006662|twk-7|475nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006662|twk-7|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006662|twk-7|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1393|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006663|twk-8|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=774|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006663|twk-8|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006664|twk-9|222nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006664|twk-9|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006664|twk-9|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006664|twk-9|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006664|twk-9|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006665|twk-10|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006665|twk-10|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006665|twk-10|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006665|twk-10|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006665|twk-10|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006666|twk-11|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006666|twk-11|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006667|twk-12|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006667|twk-12|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006667|twk-12|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1275|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006668|twk-13|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006669|twk-14|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1189|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006669|twk-14|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006669|twk-14|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006670|twk-16|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006670|twk-16|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006670|twk-16|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=240|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|553nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|555nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|559nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=380|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006671|twk-17|562nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006672|twk-18|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006672|twk-18|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006672|twk-18|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006672|twk-18|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006672|twk-18|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006673|twk-20|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006673|twk-20|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006673|twk-20|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006674|twk-21|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006675|twk-22|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006675|twk-22|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00006675|twk-22|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006675|twk-22|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006675|twk-22|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006675|twk-22|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006675|twk-22|804nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006676|twk-23|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006676|twk-23|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006676|twk-23|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=489|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006676|twk-23|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006676|twk-23|565nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006676|twk-23|569nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006677|twk-24|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006677|twk-24|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=276|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006677|twk-24|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006677|twk-24|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006677|twk-24|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=423|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006678|twk-25|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006679|twk-26|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006679|twk-26|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2232|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006679|twk-26|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006679|twk-26|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006680|twk-28|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006680|twk-28|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006680|twk-28|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006681|twk-29|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006681|twk-29|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006681|twk-29|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006681|twk-29|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3460|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006681|twk-29|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006682|twk-30|1355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006682|twk-30|1360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006682|twk-30|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=850|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006682|twk-30|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006682|twk-30|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006683|twk-31|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006683|twk-31|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00006683|twk-31|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006683|twk-31|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006684|twk-32|1259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006684|twk-32|334nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006684|twk-32|484nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006684|twk-32|488nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006684|twk-32|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006685|twk-33|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006685|twk-33|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00006686|twk-34|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006686|twk-34|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006687|twk-35|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006687|twk-35|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006687|twk-35|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006687|twk-35|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006687|twk-35|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006688|twk-36|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006689|twk-37|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006690|twk-39|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006690|twk-39|1149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006690|twk-39|1152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=839|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006690|twk-39|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006690|twk-39|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006690|twk-39|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006690|twk-39|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1016|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006691|twk-40|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006692|twk-42|15nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006692|twk-42|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006692|twk-42|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006692|twk-42|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00006692|twk-42|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|1410nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=184|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=609|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=315|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1686|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006693|twk-43|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006694|twk-44|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006694|twk-44|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006694|twk-44|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006694|twk-44|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006694|twk-44|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006695|twk-45|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006695|twk-45|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006695|twk-45|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006695|twk-45|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=871|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1223|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=747|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00006696|twk-46|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1569|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5439|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006697|uaf-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1684|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2869|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=380|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006698|uaf-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19681|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006699|uba-1|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|1042nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|1044nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|858nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|860nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|942nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|972nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006700|uba-2|982nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1846|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|1060nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|1063nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|1074nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6976|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|1088nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006701|ubc-1|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|342nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7316|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|346nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006702|ubc-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=562|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3431|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1247|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006703|ubc-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=691|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10628|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|431nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|612nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1018|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|721nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006704|ubc-7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006705|ubc-8|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006705|ubc-8|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006705|ubc-8|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1813|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006705|ubc-8|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7743|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1354|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=918|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006706|ubc-9|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|119nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1044|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3361|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006707|ubc-12|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10899|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1214|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006708|ubc-13|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=323|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|1021nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|23nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3128|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4949|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1884|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006709|ubc-14|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006710|ubc-15|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006710|ubc-15|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006710|ubc-15|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006710|ubc-15|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006711|ubc-16|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006712|ubc-17|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=747|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006712|ubc-17|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16393|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006713|ubc-18|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006714|ubc-19|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006714|ubc-19|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006714|ubc-19|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5707|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3457|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=284|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=592|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006715|ubc-20|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006716|ubc-21|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006716|ubc-21|826nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006716|ubc-21|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|1490nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|1569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|204nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=869|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|213nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=762|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|219nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=208|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006717|ubc-22|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006719|ubc-24|1539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006719|ubc-24|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006719|ubc-24|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|548nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4296|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|551nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5100|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|554nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2156|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006720|ubc-25|678nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|1120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=897|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|1122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2242|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|1158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|1160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7439|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006721|ubh-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2622|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006723|ubh-3|537nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3068|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1045|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006724|ubh-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90166|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43099|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1581|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006725|ubl-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006726|ubl-5|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3478|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006726|ubl-5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00006726|ubl-5|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006726|ubl-5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006726|ubl-5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006726|ubl-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1543|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67596|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2712|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006727|ubq-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9351|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|109nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|122nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=207|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=939|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91119|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9759|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006728|ubq-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2000|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=968|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=568|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00006729|ucp-4|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7770|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|1372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|1376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006730|uev-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006731|uev-2|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006731|uev-2|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=359|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006731|uev-2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006731|uev-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=778|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006732|uev-3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1296|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2332|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=595|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006733|ufd-1|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2853|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006734|ufd-2|991nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006735|ula-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006735|ula-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006735|ula-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1504|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00006735|ula-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006735|ula-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006735|ula-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006735|ula-1|389nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|1283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1022|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3109|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006736|ulp-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006737|ulp-2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006737|ulp-2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006737|ulp-2|356nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006737|ulp-2|361nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2909|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006737|ulp-2|365nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006737|ulp-2|369nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006737|ulp-2|372nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006738|ulp-3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1248|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006738|ulp-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=987|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006739|ulp-4|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006739|ulp-4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006739|ulp-4|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006739|ulp-4|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006739|ulp-4|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006739|ulp-4|790nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006739|ulp-4|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006740|ulp-5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006740|ulp-5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006740|ulp-5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006740|ulp-5|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006740|ulp-5|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=559|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006740|ulp-5|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3686|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=762|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=314|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006741|unc-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|1005nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|596nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|613nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|701nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2516|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006742|unc-2|998nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1670|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006743|unc-3|763nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2416|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006744|unc-4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006745|unc-5|1166nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006745|unc-5|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006745|unc-5|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1370|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006745|unc-5|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=554|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006745|unc-5|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006745|unc-5|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006745|unc-5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006746|unc-6|513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006746|unc-6|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006746|unc-6|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006746|unc-6|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=931|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006746|unc-6|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=912|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006746|unc-6|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|1442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|72nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|78nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|800nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|869nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|952nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|954nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|957nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=240|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|959nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1663|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|964nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006747|unc-7|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006748|unc-8|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006748|unc-8|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006748|unc-8|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006748|unc-8|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006748|unc-8|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006748|unc-8|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|894nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|902nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1212|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|907nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1148|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00006749|unc-9|909nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3668|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=606|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|290nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006750|unc-10|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=959|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|710nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|804nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2675|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006751|unc-11|956nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|367nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|369nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3416|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|373nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|377nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|382nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|385nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=225|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|390nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006752|unc-13|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|376nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4173|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3659|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2781|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1625|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006753|unc-14|526nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|1348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1293|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|392nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|395nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=585|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29538|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2272|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4669|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1537|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|693nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|698nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|703nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|710nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006754|unc-15|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=822|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2800|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|395nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1237|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=447|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|875nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|878nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=239|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|880nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=137|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|897nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|901nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006755|unc-16|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006756|unc-17|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006756|unc-17|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006756|unc-17|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3208|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006756|unc-17|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006756|unc-17|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006756|unc-17|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006756|unc-17|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|1026nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|1238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|1517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|1593nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|542nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|545nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|547nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|551nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|618nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|621nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|624nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|630nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|790nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|796nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|800nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4217|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|803nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3966|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|807nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|909nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006757|unc-18|957nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|825nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|947nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=285|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|950nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=141|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|955nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=2440|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|968nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|983nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006759|unc-22|988nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9594|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=439|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006760|unc-23|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006761|unc-24|1021nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006761|unc-24|1418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006761|unc-24|1518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006761|unc-24|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006761|unc-24|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006761|unc-24|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5956|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006761|unc-24|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=366|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=450|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|119nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1028|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2054|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|1480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|1487nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8444|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26234|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2370|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=677|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3836|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1376|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=399|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|558nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3996|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006762|unc-25|96nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1503|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006763|unc-26|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|1189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26891|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13204|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006764|unc-27|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006765|unc-29|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=506|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4921|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1298|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006766|unc-30|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006767|unc-31|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006767|unc-31|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006767|unc-31|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006767|unc-31|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006767|unc-31|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006767|unc-31|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1290|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006767|unc-31|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=839|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2858|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7977|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006768|unc-32|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|1021nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|1028nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3648|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|849nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006769|unc-33|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3260|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1552nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|1571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006770|unc-34|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|1224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=582|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=687|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006771|tln-1|467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006772|unc-36|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006772|unc-36|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=913|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006772|unc-36|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1382|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|1494nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3304|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006773|unc-37|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1035|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1220|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006774|unc-38|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006775|unc-39|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006775|unc-39|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006775|unc-39|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006775|unc-39|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006775|unc-39|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|523nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4040|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|526nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=357|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|532nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006776|unc-40|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=600|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2462|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006777|unc-41|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=737|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8642|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006778|unc-42|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|1210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|1231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|1234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|1243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|1601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|669nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|672nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|679nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13770|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|685nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=622|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|689nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|719nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=295|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|724nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|735nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|740nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1408|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|745nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006779|unc-43|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1307|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1982|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1053|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5519|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|237nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|822nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3759|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1353|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|830nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1044|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|837nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|846nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|849nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006780|unc-44|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|543nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|545nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=615|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|551nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=764|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|555nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|560nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|563nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|571nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|842nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|859nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|861nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1474|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|870nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006781|unc-45|878nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|1266nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|1269nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|275nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|282nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3280|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=262|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|294nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|347nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|351nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|355nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6622|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006782|unc-46|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31354|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=240|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|330nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|522nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006783|unc-47|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|1538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4094|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|498nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|501nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006784|unc-49|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1453|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=753|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|414nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|421nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=301|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006785|unc-50|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|187nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1313|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3529|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006786|unc-51|947nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=561|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=567|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|391nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|394nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1847|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1027|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006787|unc-52|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1378|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1662|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006788|unc-53|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3606|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=920|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=889|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133905|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1093|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6591|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=851|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10249|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130485|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20685|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=829|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=338|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3443|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3240|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3122|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6064|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|281nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3026388|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|285nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=190821|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|288nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=70489|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|290nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=130375|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|292nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25243|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=527|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=472|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|306nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3994|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=403|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1113|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=405|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1334|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=598|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=848|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6531|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006789|unc-54|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1977|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006790|unc-55|1147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006790|unc-55|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006790|unc-55|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006790|unc-55|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=410|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006790|unc-55|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|14nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|510nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=329|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5546|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|605nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|676nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|836nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006791|unc-57|839nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|1100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|393nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|477nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|482nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|487nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|489nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1536|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|491nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006792|unc-58|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=715|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=859|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|236nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006793|unc-59|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4128|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2404|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|704nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|712nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18400|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|719nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36221|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|722nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=200|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006794|unc-60|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|333nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|336nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|344nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3469|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=238|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|382nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006795|unc-61|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3254|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|561nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|565nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|573nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|576nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006796|unc-62|611nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006797|unc-63|1335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006797|unc-63|1347nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006797|unc-63|1355nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006797|unc-63|1363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006797|unc-63|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006797|unc-63|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006797|unc-63|44nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1399nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1426nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=220|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3159|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1438nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=258|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1440nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|1483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2551|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|246nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|37nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=267|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006798|unc-64|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|276nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|279nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1558|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006801|unc-68|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27647|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7912|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=864|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2136|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006802|unc-69|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1048nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1066nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1813|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1068nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=787|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1070nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1073nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1497nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1500nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9127|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1505nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=163|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1509nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=152|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|1588nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|957nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|960nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006803|unc-70|962nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1318|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=517|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|667nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006804|unc-71|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|591nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=352|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|598nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5212|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006805|unc-73|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006807|unc-75|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006807|unc-75|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006807|unc-75|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006807|unc-75|391nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006807|unc-75|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|428nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|434nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|441nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13764|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=591|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|446nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006808|unc-76|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1971|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006809|unc-77|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|1349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2200|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=602|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1380|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006810|unc-78|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1091|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=537|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|1358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|1481nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006811|unc-79|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=673|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006812|unc-80|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006812|unc-80|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006812|unc-80|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006812|unc-80|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6020|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006812|unc-80|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1972|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006814|unc-82|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|405nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2688|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|911nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|950nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|958nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006815|unc-83|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1694|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006816|unc-84|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3026|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1315|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006817|unc-85|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3708|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|344nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|427nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006818|unc-86|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23849|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1902|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|247nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|251nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|254nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=94|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|258nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|260nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=405|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1228|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|409nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|544nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|547nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006819|unc-87|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|1525nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|431nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1325|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3041|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006820|unc-89|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006822|unc-93|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006822|unc-93|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006822|unc-93|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|251nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|505nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|509nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|512nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6570|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006823|unc-94|778nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=230|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006824|unc-95|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006825|unc-96|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006825|unc-96|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006825|unc-96|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006825|unc-96|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00006825|unc-96|318nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|424nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1036|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|428nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=974|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006826|unc-97|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|262nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1110|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|267nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=237|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|368nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|671nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|676nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006827|unc-98|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006829|unc-101|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006829|unc-101|513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006829|unc-101|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006829|unc-101|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2155|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006829|unc-101|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|812nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|814nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|823nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|831nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2035|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006830|unc-103|835nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|1514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|414nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1147|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4574|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|421nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|481nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006831|unc-104|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|294nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|297nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006832|unc-105|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|1577nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4163|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31019|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|484nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|559nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|561nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|564nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=332|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006833|unc-108|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|268nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|271nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2842|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006836|unc-112|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1027nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15184|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1031nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1033nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1641|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=546|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1041nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=764|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1045nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1055nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1057nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1061nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1096nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=445|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|639nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|642nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|645nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|650nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|689nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|707nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|710nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006839|unc-115|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3681|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|646nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3935|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006840|unc-116|879nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4175|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=872|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006843|unc-119|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006844|unc-120|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006844|unc-120|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006844|unc-120|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006844|unc-120|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006844|unc-120|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006844|unc-120|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006844|unc-120|991nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2673|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4440|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=424|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=212|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|40nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=91|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|42nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=740|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|47nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|52nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|55nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=261|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=493|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|721nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|733nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|933nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|937nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006845|unc-122|997nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=654|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=339|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=888|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006852|unc-129|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006853|unc-130|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006853|unc-130|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006853|unc-130|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006853|unc-130|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006853|unc-130|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006853|unc-130|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13862|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006856|usp-14|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7672|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006861|cal-5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=508|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|250nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|252nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|257nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00006862|pnk-4|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3897|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006863|gyg-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006864|npr-16|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006864|npr-16|164nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=738|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006864|npr-16|166nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=395|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006864|npr-16|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006864|npr-16|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006865|slcf-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3067|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|526nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|529nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|651nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|673nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|756nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|765nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|864nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|871nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006868|vab-1|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006869|vab-2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006869|vab-2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|653nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|794nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|910nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|925nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1181|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|927nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1820|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006870|vab-3|947nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006873|vab-7|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=367|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1595|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006874|vab-8|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006875|vab-9|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1096|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4562|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=671|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|551nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|559nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006876|vab-10|617nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006881|vab-15|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006881|vab-15|689nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006881|vab-15|692nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006882|vab-19|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006882|vab-19|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006882|vab-19|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00006886|vap-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006886|vap-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006886|vap-1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006886|vap-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00006886|vap-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|593nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=890|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|595nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|597nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|599nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|602nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|623nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|744nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006887|vav-1|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9096|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|1277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=619|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|774nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|777nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|925nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006888|vbh-1|942nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=314|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14384|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006889|pfd-3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4423|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006890|vem-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=283|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006893|spon-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006895|ver-2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006895|ver-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006895|ver-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006895|ver-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006896|ver-3|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006896|ver-3|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006896|ver-3|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=831|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006897|ver-4|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006897|ver-4|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006897|ver-4|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006897|ver-4|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006902|vet-6|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006902|vet-6|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006902|vet-6|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1077nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1086nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=491|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1089nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=915|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19774|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1557|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=590|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1080|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3236|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1400nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1406nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31489|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1524nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1533nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|1554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1141|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20117|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=490|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006910|vha-1|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|213nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|891nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|896nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2133|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006912|vha-3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|104nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|108nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7623|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3101|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006913|vha-4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1110|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006914|vha-5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006915|vha-6|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006915|vha-6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006915|vha-6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8031|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006915|vha-6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=760|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2897|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006916|vha-7|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=537|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=764|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=742|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=394|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|301nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=109|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1609|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|349nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1080|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|351nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=517|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|441nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11053|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|443nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|481nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|566nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=905|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006917|vha-8|695nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=586|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1045|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12568|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=944|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006918|vha-9|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|210nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|215nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1602|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5236|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10974|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4166|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|266nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006919|vha-10|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|425nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|429nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9850|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|431nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2230|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006920|vha-11|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1349|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|321nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1412|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17263|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|443nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006921|vha-12|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006922|vhl-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006922|vhl-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=587|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006922|vhl-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006922|vhl-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006922|vhl-1|250nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006922|vhl-1|256nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|1029nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|1031nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|582nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5057|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|584nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1020|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|588nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006923|vhp-1|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|1573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|210nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|213nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|221nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30654|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|225nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=517|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3976|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006924|vig-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50339|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=302|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6919|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006925|vit-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87240|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1746|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=407|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=683625|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006926|vit-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16337|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12301|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140016|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3383|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2695|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4665|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=733|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=906|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1355|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006927|vit-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1596|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|1540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6041|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90582|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1972|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=266|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|692nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006928|vit-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1766|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36045|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264585|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5936|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=956|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006929|vit-5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108941|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2155|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006930|vit-6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326720|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|378nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|393nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1263|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|399nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2059|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|403nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|405nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006931|vps-26|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006932|vps-34|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006932|vps-34|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1657|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006932|vps-34|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|511nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=161|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|513nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3082|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|517nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|521nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006933|vps-35|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1702|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006934|vps-54|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006935|vars-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00006935|vars-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006935|vars-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006935|vars-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006935|vars-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|1472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|242nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=457|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|244nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=557|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2439|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=933|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|510nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|514nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|601nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|635nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|793nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|867nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|870nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006936|vars-2|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006937|wah-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1681|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006937|wah-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006938|wee-1.1|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|361nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|366nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4305|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|370nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|374nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006940|wee-1.3|625nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|604nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2431|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=916|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|786nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006941|wnk-1|789nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1100|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6505|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|652nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006942|wrk-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006943|wrm-1|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006943|wrm-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006943|wrm-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006943|wrm-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1492|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006943|wrm-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=628|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|581nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=51|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006944|wrn-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006945|wars-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006945|wars-1|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006945|wars-1|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006945|wars-1|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006945|wars-1|746nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5086|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00006945|wars-1|755nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006946|prx-10|1026nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006946|prx-10|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1042|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006946|prx-10|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006946|prx-10|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006946|prx-10|454nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1542|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=628|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006947|wrt-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=953|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=707|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006948|wrt-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006949|wrt-3|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006949|wrt-3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006949|wrt-3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006949|wrt-3|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00006949|wrt-3|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00006949|wrt-3|200nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006950|wrt-4|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006950|wrt-4|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006951|wrt-5|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1443|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006951|wrt-5|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006951|wrt-5|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006951|wrt-5|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|1420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006952|wrt-6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006953|wrt-7|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006953|wrt-7|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006954|wrt-8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006955|wrt-9|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006955|wrt-9|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006955|wrt-9|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00006955|wrt-9|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1837|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1113|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006956|wrt-10|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2514|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006957|wsp-1|867nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006958|wve-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006958|wve-1|728nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=416|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006958|wve-1|736nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1116|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006958|wve-1|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5075|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1873|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148008|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172419|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8122|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1004|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=857|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|608nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006959|xbp-1|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006960|xbx-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006960|xbx-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006960|xbx-1|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=965|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006960|xbx-1|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00006960|xbx-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006960|xbx-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1336|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=451|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=815|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|390nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|392nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006961|xnp-1|605nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006962|xol-1|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|1472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=263|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2381|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006963|xpa-1|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006964|xrn-2|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006964|xrn-2|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3020|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006964|xrn-2|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=419|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006965|xtr-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00006965|xtr-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00006965|xtr-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006965|xtr-1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006965|xtr-1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006965|xtr-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006965|xtr-1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006968|yars-2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006968|yars-2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006968|yars-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4016|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006968|yars-2|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006968|yars-2|876nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006968|yars-2|878nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006968|yars-2|978nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006970|zag-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006970|zag-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006970|zag-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006970|zag-1|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1612|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006970|zag-1|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006970|zag-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006971|zak-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006971|zak-1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006971|zak-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3031|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=744|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|348nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|352nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006974|zen-4|59nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|1413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|1415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=202|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|390nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|654nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=560|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|660nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1669|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|749nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|836nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|875nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006975|zfp-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006976|zhp-3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2130|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006977|zif-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006977|zif-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006977|zif-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006977|zif-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2333|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006977|zif-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006977|zif-1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2100|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|598nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|601nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|614nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|621nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|635nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006978|zig-1|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=311|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1585|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17958|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|26nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|31nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006979|zig-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006980|zig-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006980|zig-3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006980|zig-3|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006980|zig-3|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|1040nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29519|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=463|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006981|zig-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|1309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7474|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|203nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006982|zig-5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006983|zig-6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|1109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|1120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=982|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1285|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|45nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|50nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=350|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|78nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|80nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006984|zig-7|84nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4625|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=370|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00006985|zig-8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=189|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=642|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|481nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006986|zip-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006987|zmp-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006988|zyg-1|1195nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006988|zyg-1|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006988|zyg-1|1319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006988|zyg-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1011|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006988|zyg-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006993|zyg-8|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006993|zyg-8|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006993|zyg-8|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1488|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00006993|zyg-8|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006993|zyg-8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|1101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1598|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2799|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00006994|zyg-9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006996|zyg-11|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006996|zyg-11|402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6289|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00006996|zyg-11|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006997|zyg-12|498nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006997|zyg-12|500nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006997|zyg-12|502nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006997|zyg-12|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006997|zyg-12|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3924|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006997|zyg-12|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00006997|zyg-12|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24727|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10816|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00006999|zyx-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2950|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1504|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2969|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=642|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=775|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|383nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|393nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|438nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|445nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|581nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|594nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|661nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|749nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|869nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007000|tufm-1|888nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007001|tufm-2|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007001|tufm-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1187|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007001|tufm-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007001|tufm-2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007001|tufm-2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007001|tufm-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00007001|tufm-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007006|npr-3|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007006|npr-3|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007006|npr-3|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007006|npr-3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007006|npr-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1427|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1926|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007007|mak-2|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1169|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007008|rfp-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|1033nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|306nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|534nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|543nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|570nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4279|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|574nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|578nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007009|wwp-1|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1619|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4583|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007010|alx-1|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007011|mdt-1.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007011|mdt-1.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007011|mdt-1.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007011|mdt-1.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007011|mdt-1.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007011|mdt-1.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007011|mdt-1.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007012|mdt-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007012|mdt-4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007012|mdt-4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=528|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007012|mdt-4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1877|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007012|mdt-4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007012|mdt-4|895nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007013|mdt-8|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007013|mdt-8|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007013|mdt-8|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=266|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007013|mdt-8|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=462|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007013|mdt-8|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1233|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007013|mdt-8|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=457|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007013|mdt-8|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007014|mdt-10|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007014|mdt-10|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007014|mdt-10|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1923|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007014|mdt-10|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1101|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007014|mdt-10|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007015|mdt-11|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007015|mdt-11|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007015|mdt-11|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2672|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007015|mdt-11|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007015|mdt-11|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1073nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1095nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1113nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|624nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|867nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|912nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007016|mdt-15|917nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=573|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2193|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|1219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007017|mdt-17|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|1541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=224|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2182|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3724|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007018|mdt-18|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007020|mdt-20|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007020|mdt-20|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1823|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00007020|mdt-20|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007021|immp-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007021|immp-1|1437nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007021|immp-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1385|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007021|immp-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|1253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|1372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|1498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15651|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=811|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007022|mdt-22|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007023|mdt-27|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2032|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007023|mdt-27|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1006|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007023|mdt-27|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007023|mdt-27|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007023|mdt-27|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|1374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1848|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3049|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10375|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007024|plin-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|205nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1269|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=674|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007025|mdt-29|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007026|mdt-31|14nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007026|mdt-31|19nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007026|mdt-31|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007026|mdt-31|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007026|mdt-31|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2373|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007026|mdt-31|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007026|mdt-31|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|1021nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|1029nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=760|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|1054nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|787nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2473|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|794nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|799nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007027|ssl-1|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|210nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|216nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2688|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007028|trr-1|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007029|mys-1|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1198|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007029|mys-1|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=876|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007029|mys-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007029|mys-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1055nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1086nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1093nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=397|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|1201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|337nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|772nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3193|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|850nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|905nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|907nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007030|epc-1|909nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007036|sod-5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2166|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007036|sod-5|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3339|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007036|sod-5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007036|sod-5|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007041|tag-180|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007041|tag-180|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007041|tag-180|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007041|tag-180|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1584|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007041|tag-180|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=503|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007041|tag-180|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007041|tag-180|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4252|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=764|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|338nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|342nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=719|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|349nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|352nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|354nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|356nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007042|pbrm-1|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007043|tag-179|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007043|tag-179|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007043|tag-179|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007043|tag-179|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|1078nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|1517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|1522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|225nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=994|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4806|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|321nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|325nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|327nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007044|cpna-5|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|1126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|1339nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1430|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=419|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007045|tag-189|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007047|wts-1|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007047|wts-1|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=262|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007047|wts-1|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007047|wts-1|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=175|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1441nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1445nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1476nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|1488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6388|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007048|nfx-1|567nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007049|tag-191|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007049|tag-191|389nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007049|tag-191|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1902|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007050|tag-184|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|515nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=236|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3502|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|542nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007053|chd-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|813nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|816nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|821nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|823nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3828|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|828nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|831nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|920nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=123|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|951nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007054|scpl-1|982nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007055|tag-196|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007055|tag-196|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007055|tag-196|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3672|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007055|tag-196|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1588|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007055|tag-196|1324nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007055|tag-196|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007056|crn-7|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=570|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007056|crn-7|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007056|crn-7|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007056|crn-7|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007057|ant-1.2|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007057|ant-1.2|1531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00007057|ant-1.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4730|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|358nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|364nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|367nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007058|dmd-6|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007059|vps-52|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007059|vps-52|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007059|vps-52|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007059|vps-52|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007059|vps-52|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007059|vps-52|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007060|wht-6|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007060|wht-6|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=307|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007060|wht-6|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007060|wht-6|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|1408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2218|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007062|ebp-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007063|2L52.1a|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007063|2L52.1a|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007063|2L52.1a|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007063|2L52.1a|868nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007063|2L52.1a|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007064|2RSSE.1a|1026nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007064|2RSSE.1a|1028nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007064|2RSSE.1a|1034nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00007064|2RSSE.1a|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007064|2RSSE.1b|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007064|2RSSE.1b|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007065|pot-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007065|pot-3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=951|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007065|pot-3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007065|pot-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|922nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007067|4R79.2b|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00007068|cTel55X.1b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007068|cTel55X.1b|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1352|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00007068|cTel55X.1b|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=786|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007068|cTel55X.1b|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007069|6R55.2|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007070|ugt-49|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007070|ugt-49|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007070|ugt-49|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007070|ugt-49|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00007070|ugt-49|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007070|ugt-49|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|1164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|1167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1240|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007071|AC3.5a.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007072|ugt-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007073|ugt-2|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007073|ugt-2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007073|ugt-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007073|ugt-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007076|AC8.4|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=319|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007076|AC8.4|425nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007076|AC8.4|428nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007076|AC8.4|436nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007076|AC8.4|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007080|sfxn-1.1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007080|sfxn-1.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007080|sfxn-1.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007080|sfxn-1.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007081|AH6.3|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007081|AH6.3|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=339|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00007081|AH6.3|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007082|acs-10|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007082|acs-10|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007082|acs-10|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1213|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007082|acs-10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007082|acs-10|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007083|AH10.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007084|AH10.3|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007084|AH10.3|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007084|AH10.3|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007084|AH10.3|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007084|AH10.3|855nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007084|AH10.3|861nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007087|B0001.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007087|B0001.2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007087|B0001.2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=905|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00007087|B0001.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007087|B0001.2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007088|B0001.3c|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007088|B0001.3c|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007088|B0001.3c|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007088|B0001.3c|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007088|B0001.3c|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2231|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2194|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2782|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|450nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007089|B0001.4a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007090|B0001.5|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2625|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007090|B0001.5|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=880|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007090|B0001.5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007090|B0001.5|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007091|eri-12|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007091|eri-12|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4589|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007091|eri-12|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=359|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007091|eri-12|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007091|eri-12|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007091|eri-12|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007091|eri-12|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|1376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|1401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|1416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|1464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1396|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007092|B0001.7c|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=839|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1182|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007093|B0001.8c|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007094|B0019.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007094|B0019.2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007094|B0019.2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007094|B0019.2|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007094|B0019.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007094|B0019.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=749|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007096|B0024.3|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007096|B0024.3|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=369|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=957|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=217|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=549|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007097|B0024.4|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|106nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=472|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=663|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|93nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007099|trx-2|98nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=410|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2013|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007100|B0024.10|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007101|B0024.11|1121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007101|B0024.11|1354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007101|B0024.11|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007101|B0024.11|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007101|B0024.11|772nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007101|B0024.11|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007101|B0024.11|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2615|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1185|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007102|B0024.13|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007103|crm-1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007104|B0024.15.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=261|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|678nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007105|B0035.1b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9483|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=787|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007106|B0035.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=309|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=261|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12170|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|856nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007107|pfd-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007108|gspd-1|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007108|gspd-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007108|gspd-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007108|gspd-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007108|gspd-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3476|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007109|B0035.6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007109|B0035.6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007109|B0035.6|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007109|B0035.6|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3792|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007109|B0035.6|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007109|B0035.6|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=780|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1840|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007110|leo-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|1231nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|276nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|283nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3823|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|286nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=565|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|290nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|845nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007111|sart-3|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|271nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2179|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4612|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=173|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007112|B0035.13|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=672|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1158|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007113|B0035.15|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007114|mttu-1|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007114|mttu-1|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=242|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00007114|mttu-1|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00007114|mttu-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007115|B0198.2a|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007115|B0198.2a|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007115|B0198.2a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007115|B0198.2b|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007115|B0198.2b|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=731|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007115|B0198.2b|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007115|B0198.2b|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=325|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=239|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|376nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007116|B0198.3a|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007117|spe-42|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007117|spe-42|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007118|npp-22|174nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=427|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007118|npp-22|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007118|npp-22|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007118|npp-22|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007118|npp-22|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3116|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007118|npp-22|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=799|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1077|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5122|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6196|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3625|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1944|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007119|calf-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=963|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2496|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=345|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|801nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|807nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007122|B0250.5|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007124|B0250.7b|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=565|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007124|B0250.7b|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007124|B0250.7b|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1369|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82105|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1598nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|1600nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007125|B0250.8|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|101nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|1121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|1146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|569nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|93nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007126|dhcr-7|98nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=455|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007128|memb-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007129|B0272.3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007129|B0272.3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2805|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007129|B0272.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007129|B0272.3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007129|B0272.3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007129|B0272.3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007129|B0272.3|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007130|B0272.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007131|B0284.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007131|B0284.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007131|B0284.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007131|B0284.1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007131|B0284.1|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00007131|B0284.1|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007132|B0284.2|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007132|B0284.2|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007133|B0284.3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00007133|B0284.3|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007133|B0284.3|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007133|B0284.3|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007133|B0284.3|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007133|B0284.3|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|1309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|1517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|1585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=898|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007135|cdk-12|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007136|B0285.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2255|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|1435nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2855|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007137|B0285.4|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007138|B0285.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007139|mnp-1|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007139|mnp-1|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007139|mnp-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007139|mnp-1|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007139|mnp-1|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007140|cyp-29A4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007140|cyp-29A4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007140|cyp-29A4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007140|cyp-29A4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00007141|pitr-4|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00007141|pitr-4|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00007142|ttr-18|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10463|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007142|ttr-18|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007142|ttr-18|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007143|B0334.3b|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2466|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007143|B0334.3b|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3901|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00007143|B0334.3b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007143|B0334.3b|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|177nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|179nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|183nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4223|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|188nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=846|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|192nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007144|B0334.4|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007145|B0334.5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007145|B0334.5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1314|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007145|B0334.5|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1910|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007145|B0334.5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007145|B0334.5|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007145|B0334.5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007146|B0334.6|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=458|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007149|B0334.13|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2675|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007150|acly-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|1393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|617nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007152|clec-225|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007153|clec-41|1000nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=850|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007153|clec-41|1003nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6939|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007153|clec-41|1006nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007153|clec-41|1010nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007153|clec-41|1013nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007153|clec-41|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007153|clec-41|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007154|dhc-3|1375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007154|dhc-3|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007154|dhc-3|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007154|dhc-3|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007154|dhc-3|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007154|dhc-3|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007154|dhc-3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007155|B0379.1a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007155|B0379.1a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007155|B0379.1a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4580|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007155|B0379.1a|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007155|B0379.1a|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007155|B0379.1a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007155|B0379.1a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007156|B0379.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00007156|B0379.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007156|B0379.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007159|B0379.7.2|1249nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007159|B0379.7.2|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007159|B0379.7.2|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=833|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007159|B0379.7.2|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007162|fbxa-153|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=735|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007162|fbxa-153|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007163|fbxa-154|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007163|fbxa-154|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007164|fbxa-139|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|1006nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|1010nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007166|fbxa-152|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|1263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4226|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007167|rbg-3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=678|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2151|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007168|B0393.3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007169|B0393.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007169|B0393.4|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=281|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007169|B0393.4|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007169|B0393.4|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007169|B0393.4|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007170|B0393.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007170|B0393.5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007170|B0393.5|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007170|B0393.5|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007170|B0393.5|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007170|B0393.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007170|B0393.5|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007171|B0393.6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007171|B0393.6|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007171|B0393.6|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007171|B0393.6|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007171|B0393.6|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=939|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007171|B0393.6|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1416|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007171|B0393.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007172|B0393.7|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=219|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007172|B0393.7|349nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007172|B0393.7|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007172|B0393.7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=273|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007172|B0393.7|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007174|mboa-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007174|mboa-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007174|mboa-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007174|mboa-1|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2220|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007175|B0395.3.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007176|kcnl-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007176|kcnl-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007176|kcnl-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007176|kcnl-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4088|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007176|kcnl-1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007177|oac-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007177|oac-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007178|B0457.2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007178|B0457.2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007178|B0457.2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007178|B0457.2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007178|B0457.2|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007178|B0457.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007178|B0457.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007179|B0457.4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007180|B0457.6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007180|B0457.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10256|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007180|B0457.6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007180|B0457.6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007182|fbxb-119|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007182|fbxb-119|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007182|fbxb-119|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007183|B0462.4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007183|B0462.4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1076|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1477|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|333nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|643nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007184|ctr-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=421|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4640|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1245|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|156nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|160nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|163nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|189nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007185|nlp-36|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1426|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2805|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|670nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|735nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007186|B0464.6.1|743nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007187|tag-342|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007187|tag-342|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007187|tag-342|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00007187|tag-342|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007187|tag-342|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=717|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007188|B0464.9|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007189|B0491.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007189|B0491.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1415|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007189|B0491.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007189|B0491.1|1275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007189|B0491.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1887|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|1426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|1428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007190|rmd-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007191|lgc-20|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007191|lgc-20|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007191|lgc-20|229nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=880|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007191|lgc-20|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3290|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1464|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3086|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007192|B0491.5.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2659|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007193|B0491.6b|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007194|B0491.7|1335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007194|B0491.7|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007194|B0491.7|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007194|B0491.7|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007194|B0491.7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007194|B0491.7|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007195|B0513.2a.1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=502|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007195|B0513.2a.1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2004|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007195|B0513.2a.1|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1700|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007195|B0513.2a.1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007195|B0513.2a.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|1048nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|20nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|30nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3517|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24639|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007196|B0513.4a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=909|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007197|B0513.5b|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007197|B0513.5b|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007197|B0513.5b|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2672|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007197|B0513.5b|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007197|B0513.5b|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007197|B0513.5b|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007197|B0513.5b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007200|vamp-8|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007200|vamp-8|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007200|vamp-8|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007200|vamp-8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3049|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00007200|vamp-8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007200|vamp-8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007201|exos-4.1|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007201|exos-4.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007201|exos-4.1|1104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007201|exos-4.1|1256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007201|exos-4.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007201|exos-4.1|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2774|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007201|exos-4.1|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007202|B0564.2a|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=828|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007202|B0564.2a|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007202|B0564.2a|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007202|B0564.2a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007203|best-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007203|best-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007203|best-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007203|best-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007204|best-2|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007206|B0564.6|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007206|B0564.6|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007206|B0564.6|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007206|B0564.6|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007206|B0564.6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007206|B0564.6|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1096|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1031|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|1489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|27nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007207|B0564.7a.1|30nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007209|BE10.1|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=814|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007209|BE10.1|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007209|BE10.1|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007210|agmo-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=667|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007210|agmo-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007211|BE10.3|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007212|BE10.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007213|C01A2.1b|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007213|C01A2.1b|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007213|C01A2.1b|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=754|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007214|C01A2.2a|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007214|C01A2.2a|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|1375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|1586nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|197nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|201nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|205nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|208nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1086|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|505nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007215|oxa-1|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19325|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3332|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007216|C01A2.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1178|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5000|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3782|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=501|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007217|tads-1|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007218|C01A2.6|1289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007218|C01A2.6|1580nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007218|C01A2.6|1584nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007218|C01A2.6|1591nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007218|C01A2.6|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=507|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|337nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007219|nlp-38|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007220|C01B9.1b|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007220|C01B9.1b|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007220|C01B9.1b|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007220|C01B9.1b|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|1330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|1361nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|1370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3404|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00007221|cpna-3|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007222|C01F6.2|1530nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007222|C01F6.2|1550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007222|C01F6.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007222|C01F6.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007222|C01F6.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1974|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12281|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007223|C01F6.9c|945nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007224|C01G6.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007224|C01G6.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1428|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|291nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|410nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007225|C01G6.3|416nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1653|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1256|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|565nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|576nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007226|C01G6.4|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|1184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5142|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|766nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=535|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|770nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|775nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|875nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007227|C01G6.5|879nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1215|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007228|acs-7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007229|C01G6.9|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007229|C01G6.9|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007229|C01G6.9|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007229|C01G6.9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007229|C01G6.9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007230|C01G10.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007230|C01G10.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007231|C01G10.4|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007231|C01G10.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007231|C01G10.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007232|C01G10.5|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007232|C01G10.5|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00007232|C01G10.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007233|C01G10.6|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007233|C01G10.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007233|C01G10.6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007234|C01G10.7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007234|C01G10.7|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007234|C01G10.7|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007234|C01G10.7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007234|C01G10.7|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=839|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1874|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=390|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17245|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007235|C01G10.8.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007236|C01G10.9|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007236|C01G10.9|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007236|C01G10.9|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007236|C01G10.9|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=525|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007236|C01G10.9|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007236|C01G10.9|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007236|C01G10.9|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1010|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007237|C01G10.10a|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007239|C01G10.14|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007239|C01G10.14|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007239|C01G10.14|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=701|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007239|C01G10.14|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007239|C01G10.14|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007240|C01G10.15|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007240|C01G10.15|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007240|C01G10.15|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007240|C01G10.15|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007240|C01G10.15|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007240|C01G10.15|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007240|C01G10.15|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007241|C01G10.16|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00007241|C01G10.16|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00007242|madf-5|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=777|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15047|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007243|nspb-7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007244|C01G12.3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007244|C01G12.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007244|C01G12.3|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007244|C01G12.3|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=785|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007245|C01G12.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007246|nspb-10|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8278|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00007246|nspb-10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7312|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007246|nspb-10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007247|C01G12.7|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007247|C01G12.7|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=932|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007247|C01G12.7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007248|catp-4|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007248|catp-4|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=477|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00007248|catp-4|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007248|catp-4|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007249|C01G12.9|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007249|C01G12.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14325|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1456|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007250|nspb-8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007251|nspb-9|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6905|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007251|nspb-9|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007251|nspb-9|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007251|nspb-9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007252|mlt-2|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007252|mlt-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007252|mlt-2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007252|mlt-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1588|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|400nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|554nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007253|C01H6.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=405|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007254|C01H6.4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1310nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1332nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1335nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|1364nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007255|C01H6.6.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|203nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=981|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2068|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=709|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|937nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007256|swsn-9|942nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007257|C01H6.8a|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007258|hasp-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007258|hasp-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007258|hasp-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007258|hasp-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007258|hasp-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007258|hasp-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007258|hasp-1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|238nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1026|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007260|olrn-1|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2453|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2266|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=330|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007261|lron-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007262|jud-4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007262|jud-4|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007262|jud-4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007262|jud-4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007262|jud-4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007262|jud-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007264|C02F4.4|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007264|C02F4.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007264|C02F4.4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007264|C02F4.4|77nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007264|C02F4.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007264|C02F4.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=994|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007264|C02F4.4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1155|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=570|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|558nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007266|C03A3.1a|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1057|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=616|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007267|C03A3.2|503nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007268|C03A3.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007268|C03A3.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007268|C03A3.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007269|C03C10.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007269|C03C10.2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007269|C03C10.2|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007269|C03C10.2|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007269|C03C10.2|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=932|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1982|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|246nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=424|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007270|C03C10.4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007273|C03C10.7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00007273|C03C10.7|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00007274|C03C11.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1044|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007274|C03C11.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007274|C03C11.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007275|C03D6.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007275|C03D6.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007275|C03D6.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007277|asfl-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007277|asfl-1|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1836|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007277|asfl-1|380nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|115nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|123nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=802|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|63nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|74nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|78nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=340|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007278|lab-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007279|C03E10.1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|277nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|279nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=424|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007281|C03E10.3|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007282|clec-223|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007282|clec-223|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007282|clec-223|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007282|clec-223|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=550|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007282|clec-223|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00007283|clec-222|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007283|clec-222|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=747|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007283|clec-222|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007284|C03H12.1a|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=843|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007284|C03H12.1a|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007285|C04A11.1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007285|C04A11.1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007285|C04A11.1|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007285|C04A11.1|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=956|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007285|C04A11.1|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007285|C04A11.1|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007285|C04A11.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007286|C04A11.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007286|C04A11.2|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00007286|C04A11.2|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007286|C04A11.2|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007286|C04A11.2|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007286|C04A11.2|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007286|C04A11.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007287|gck-4|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007287|gck-4|750nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007287|gck-4|760nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007287|gck-4|768nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=915|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007288|C04A11.5|1387nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007288|C04A11.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007288|C04A11.5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007288|C04A11.5|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007288|C04A11.5|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007288|C04A11.5|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007288|C04A11.5|844nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007289|C04B4.1.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00007289|C04B4.1.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007290|C04B4.2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007295|C04C11.1a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007295|C04C11.1a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007295|C04C11.1a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007295|C04C11.1a|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007295|C04C11.1a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|467nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|469nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2659|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|472nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|480nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|486nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|489nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|491nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007296|arrd-25|758nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|1179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|1182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007297|C04F12.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1094|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2250|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1035|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007299|C04F12.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007301|C04F12.7|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007301|C04F12.7|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007301|C04F12.7|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8273|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007301|C04F12.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007301|C04F12.7|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007301|C04F12.7|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|335nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1380|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|337nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|373nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|376nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|380nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007302|C04F12.8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|440nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=506|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=765|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007303|rnh-1.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4307|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69647|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1552|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|843nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=615|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007304|ttr-39|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1670|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007305|C04G2.2|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007305|C04G2.2|1172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007305|C04G2.2|1176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=979|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00007305|C04G2.2|1179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007305|C04G2.2|1183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007305|C04G2.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007305|C04G2.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=783|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007306|C04G2.5|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007306|C04G2.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007306|C04G2.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007306|C04G2.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007307|spch-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007307|spch-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007307|spch-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007307|spch-1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7641|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007307|spch-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9909|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1620|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007308|C04G2.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007309|C04G2.10a|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=327|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007309|C04G2.10a|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007309|C04G2.10a|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007309|C04G2.10a|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007309|C04G2.10a|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007310|irld-21|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007310|irld-21|716nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007310|irld-21|730nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|810nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=492|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|818nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=961|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|820nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=696|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007312|C04H5.1|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007313|clec-147|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=470|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007313|clec-147|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007314|gcy-29|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007314|gcy-29|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007314|gcy-29|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=520|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1035|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1728|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4867|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=656|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7b|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007315|C04H5.7b|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007316|nlp-41|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007316|nlp-41|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007316|nlp-41|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7754|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007316|nlp-41|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007316|nlp-41|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|473nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|777nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=974|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|822nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007317|C05A9.2|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007319|C05B5.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007319|C05B5.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007320|C05B5.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2807|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007320|C05B5.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007321|C05B5.4|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007321|C05B5.4|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007321|C05B5.4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007322|C05B5.5a|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007322|C05B5.5a|806nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007322|C05B5.5a|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007322|C05B5.5a|822nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007322|C05B5.5a|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007322|C05B5.5a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007323|fbxa-155|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007324|C05B5.8|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007324|C05B5.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1266|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007324|C05B5.8|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007324|C05B5.8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007325|C05C9.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007325|C05C9.1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007326|C05C9.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007326|C05C9.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007326|C05C9.2|836nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|374nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=58|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|380nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|382nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007327|C05C9.3|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007328|pho-10|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007328|pho-10|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007329|C05C10.2b.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007329|C05C10.2b.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007329|C05C10.2b.2|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007329|C05C10.2b.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1845|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007329|C05C10.2b.2|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007329|C05C10.2b.2|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=893|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1175|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007330|C05C10.3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007331|pho-11|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2243|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007331|pho-11|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17966|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007331|pho-11|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007331|pho-11|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=717|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007331|pho-11|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007331|pho-11|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007331|pho-11|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8152|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|460nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|463nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007332|C05C10.5a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3530|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5919|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007333|ufd-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007334|C05C10.7|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1570|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007334|C05C10.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=913|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007334|C05C10.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007334|C05C10.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007334|C05C10.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007335|C05C12.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007335|C05C12.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=455|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1335|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007336|C05C12.4|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007337|C05C12.5|1202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007337|C05C12.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007337|C05C12.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2449|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007338|C05C12.6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007338|C05C12.6|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2794|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007338|C05C12.6|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007338|C05C12.6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007338|C05C12.6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007339|C05D12.1.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007339|C05D12.1.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007339|C05D12.1.1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007339|C05D12.1.1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007339|C05D12.1.1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007340|C05D12.2|1118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007340|C05D12.2|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007340|C05D12.2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007340|C05D12.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007340|C05D12.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007341|C05D12.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007341|C05D12.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007342|C05D12.5|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007342|C05D12.5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007343|C05E7.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007343|C05E7.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007343|C05E7.1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007343|C05E7.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007343|C05E7.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007343|C05E7.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007343|C05E7.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007344|C05E7.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007344|C05E7.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=643|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007345|C05E7.3|1451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007345|C05E7.3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007345|C05E7.3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007345|C05E7.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007345|C05E7.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007346|frpr-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007346|frpr-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007346|frpr-2|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007346|frpr-2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007346|frpr-2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=826|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007347|C05G5.1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007348|C05G5.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007348|C05G5.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007348|C05G5.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007348|C05G5.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=443|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=879|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007349|C05G5.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|1398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|221nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5612|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=234|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|230nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=420|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=554|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|300nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|304nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|308nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|312nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|314nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|71nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|78nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007350|sucl-1|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007351|C05G5.5c|132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007351|C05G5.5c|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007351|C05G5.5c|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007351|C05G5.5c|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007351|C05G5.5c|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12697|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1124|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|302nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1208|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007352|cdc-48.1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3802|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3846|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007353|C06A1.2a|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007354|C06A1.3|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007354|C06A1.3|500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007354|C06A1.3|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=687|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007354|C06A1.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007354|C06A1.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8940|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1467|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007355|rpb-6|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007356|C06A1.6|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007356|C06A1.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007356|C06A1.6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007356|C06A1.6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=949|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3052|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9132|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=490|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007357|C06A12.3b.2|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007358|lact-6|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007360|C06B3.1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007361|oac-3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007361|oac-3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1340|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|439nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007362|cyp-35C1|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|1530nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1677|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007363|stdh-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007364|stdh-3|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007364|stdh-3|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00007364|stdh-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=355|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7458|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1746|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007365|C06B3.6.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1222|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|804nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|807nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|811nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007366|C06B3.7|890nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007367|nhr-150|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007368|C06B8.2c.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007368|C06B8.2c.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007368|C06B8.2c.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007368|C06B8.2c.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007369|C06B8.3|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007370|str-264|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|1037nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|1379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007372|C06B8.7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007374|C06C3.3|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007375|C06C3.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007375|C06C3.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007375|C06C3.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007377|C06C3.7|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007378|C06C3.8b|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007378|C06C3.8b|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007378|C06C3.8b|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007380|C06C6.6|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007381|C06C6.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007382|C06C6.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007382|C06C6.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007382|C06C6.8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007382|C06C6.8|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007383|C06C6.9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007383|C06C6.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007384|swt-3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007384|swt-3|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007384|swt-3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007384|swt-3|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2669|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00007384|swt-3|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|1274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=802|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46058|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=628|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=399|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007385|atp-5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|1485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|1491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1932|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|427nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|429nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=395|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|431nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|440nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|446nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007386|C06H2.2|918nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007387|jmjd-5|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007387|jmjd-5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=321|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007388|folt-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007389|glb-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007389|glb-3|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007389|glb-3|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007389|glb-3|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007389|glb-3|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1417|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007389|glb-3|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007389|glb-3|494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|1507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3994|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=736|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|883nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007390|lmtr-3|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007391|C06H2.7a|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007392|fbxa-156|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007392|fbxa-156|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007392|fbxa-156|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007392|fbxa-156|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007392|fbxa-156|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007392|fbxa-156|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007393|fbxa-157|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007393|fbxa-157|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007394|C06H5.6b|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=597|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007394|C06H5.6b|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007394|C06H5.6b|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007395|dcar-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007395|dcar-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=922|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007395|dcar-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007395|dcar-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=777|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|382nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|392nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|579nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007396|tiar-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007397|C07A4.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007397|C07A4.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007397|C07A4.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=195|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1006|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007398|C07A4.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007400|C07A9.2.2|1096nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007400|C07A9.2.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007400|C07A9.2.2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3092|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007400|C07A9.2.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007400|C07A9.2.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007400|C07A9.2.2|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007401|C07A9.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007401|C07A9.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007401|C07A9.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|107nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|118nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|1343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|440nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007402|ugt-60|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=961|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1083|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007403|set-3|631nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007404|best-5|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007404|best-5|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007404|best-5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007405|C07A9.9|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007405|C07A9.9|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1373|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007405|C07A9.9|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007407|C07B5.2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007407|C07B5.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007407|C07B5.2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007407|C07B5.2|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007407|C07B5.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007407|C07B5.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=644|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1325|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007408|C07B5.3|316nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007409|C07B5.4a|139nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007409|C07B5.4a|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007409|C07B5.4a|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007409|C07B5.4a|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=231|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007409|C07B5.4a|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007409|C07B5.4b.2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007410|C07B5.6|464nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007410|C07B5.6|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|1121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|464nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|469nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007411|C07C7.1.2|472nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1262|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007412|stip-1|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=784|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=781|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=406|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007413|pro-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=857|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007414|C07E3.3a|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007414|C07E3.3a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007415|C07E3.4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007415|C07E3.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007415|C07E3.4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|640nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|643nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|645nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|650nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007416|ceh-57|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007417|ceh-58|1211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007417|ceh-58|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007417|ceh-58|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007417|ceh-58|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007417|ceh-58|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1401|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007417|ceh-58|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007417|ceh-58|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007418|C07E3.8|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1541|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007419|C07E3.9|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007420|C07E3.10|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007420|C07E3.10|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007421|C07H4.1a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007422|ugt-17|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=849|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007422|ugt-17|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007423|C08B6.2a|1501nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007423|C08B6.2a|807nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007423|C08B6.2a|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007423|C08B6.2a|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007423|C08B6.2a|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007423|C08B6.2a|821nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007424|C08B6.3b|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007425|C08B6.4b|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=395|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007425|C08B6.4b|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007425|C08B6.4b|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007425|C08B6.4b|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007425|C08B6.4b|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007426|C08B6.5|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007427|C08B6.6|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007427|C08B6.6|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007428|wdr-20|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007428|wdr-20|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=197|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007428|wdr-20|364nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4030|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007428|wdr-20|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007428|wdr-20|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|1371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1657|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=274|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007429|C08B6.8b.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1981|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=504|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007430|C08B6.10|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007432|srxa-18|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=487|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|614nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|618nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2073|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|622nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=933|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|625nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=188|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|629nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007433|swsn-7|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007434|arp-6|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007434|arp-6|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007434|arp-6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1448|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007434|arp-6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007434|arp-6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007434|arp-6|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007434|arp-6|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007435|C08B11.8|1306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007435|C08B11.8|1309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007435|C08B11.8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=760|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007435|C08B11.8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007435|C08B11.8|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007435|C08B11.8|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007435|C08B11.8|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007436|C08B11.9|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3032|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007436|C08B11.9|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=739|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007436|C08B11.9|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007436|C08B11.9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007437|C08E8.1.1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007439|C08E8.3|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007439|C08E8.3|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007440|C08E8.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=659|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007441|C08E8.5|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1816|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|1340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4199|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2049|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|941nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007443|pfd-1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=411|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007444|C08F8.2a|1238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007444|C08F8.2a|1242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007444|C08F8.2a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1257|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00007444|C08F8.2a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007444|C08F8.2a|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007444|C08F8.2a|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007444|C08F8.2a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1717|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007445|C08F8.3a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007446|mboa-4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007446|mboa-4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007447|fbxb-9|1033nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007448|C08F8.6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007448|C08F8.6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007448|C08F8.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007449|C08F8.9|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007449|C08F8.9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007449|C08F8.9|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007449|C08F8.9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007449|C08F8.9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4137|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007449|C08F8.9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007450|C08F11.1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007450|C08F11.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007450|C08F11.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007452|C08F11.3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007453|fbxa-98|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007453|fbxa-98|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007454|C08F11.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007454|C08F11.7|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=516|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007454|C08F11.7|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007454|C08F11.7|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1515|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=720|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1066|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|361nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|369nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|672nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007455|ugt-22|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007456|srz-29|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007456|srz-29|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|1069nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|1226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|1231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007457|C08F11.10|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|137nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43738|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8156|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|426nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|432nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=317|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|436nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=360|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1574|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007458|C08F11.11.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007459|C08F11.12.2|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3468|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007459|C08F11.12.2|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1267|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1053|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13a.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13b|1333nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13b|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007460|C08F11.13b|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007462|C08H9.1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007462|C08H9.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007462|C08H9.1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007462|C08H9.1|1587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16669|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7906|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007463|vgln-1|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007464|C08H9.3a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007464|C08H9.3a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007464|C08H9.3a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007464|C08H9.3a|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007464|C08H9.3a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007465|chil-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007466|chil-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007467|chil-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007467|chil-3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007469|chil-4|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007470|chil-5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007470|chil-5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007470|chil-5|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007471|chil-6|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00007471|chil-6|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00007472|chil-7|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007472|chil-7|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007473|chil-8|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00007473|chil-8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00007474|C08H9.15|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007474|C08H9.15|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007474|C08H9.15|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00007474|C08H9.15|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007474|C08H9.15|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007474|C08H9.15|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007474|C08H9.15|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007476|C09E9.1a|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007476|C09E9.1a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1965|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007476|C09E9.1a|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=764|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007476|C09E9.1a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007478|C09F9.1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007478|C09F9.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007478|C09F9.1|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007478|C09F9.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007479|C09F9.2|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007479|C09F9.2|848nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007479|C09F9.2|855nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007480|glna-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007480|glna-1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007480|glna-1|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007482|C09F12.2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00007482|C09F12.2|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|379nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|382nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|514nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|601nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|810nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007483|C09F12.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007484|C09G1.2|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007485|C09G1.3|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007485|C09G1.3|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007486|C09G1.4|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007486|C09G1.4|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007486|C09G1.4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007486|C09G1.4|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007486|C09G1.4|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2821|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007486|C09G1.4|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1645|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007486|C09G1.4|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007487|C09G1.5.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007487|C09G1.5.2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3022|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007487|C09G1.5.2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5218|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007487|C09G1.5.2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007487|C09G1.5.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007487|C09G1.5.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007487|C09G1.5.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1047|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007488|dph-2|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007489|C09G5.7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007489|C09G5.7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007490|mks-5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1652|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1a|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|1536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2383|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007492|C09G9.1b|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|1042nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|1045nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2070|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007493|npp-23|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007494|C09G9.3a|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007494|C09G9.3b|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007495|C09G9.5a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00007495|C09G9.5a|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00007495|C09G9.5a|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007496|npax-4|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00007496|npax-4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00007497|C09G9.8a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007497|C09G9.8a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007497|C09G9.8b|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2621|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|748nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|929nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=302|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|940nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007499|C09H10.5b|950nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1129|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1055|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007500|nasp-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007502|glb-4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=504|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00007502|glb-4|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007503|C09H10.9|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007503|C09H10.9|1107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007503|C09H10.9|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007503|C09H10.9|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007503|C09H10.9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007503|C09H10.9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007504|C09H10.10|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007504|C09H10.10|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1023|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007504|C09H10.10|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007505|pezo-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007505|pezo-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007505|pezo-1|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2601|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007505|pezo-1|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007505|pezo-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007505|pezo-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007506|C10C5.2|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007506|C10C5.2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007506|C10C5.2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007506|C10C5.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=537|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007506|C10C5.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007507|C10C5.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007507|C10C5.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1031|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007507|C10C5.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007508|C10C5.4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007508|C10C5.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007508|C10C5.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007508|C10C5.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007509|C10C5.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007509|C10C5.5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007509|C10C5.5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007509|C10C5.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007509|C10C5.5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007509|C10C5.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007509|C10C5.5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=609|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1939|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007511|C10C5.7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007512|C10C6.3a|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007512|C10C6.3a|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1660|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007513|wht-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3578|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3033|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007514|catp-8|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1153|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2127|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=894|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2769|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007515|C10C6.7c|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=851|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6500|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007516|gpx-5|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1279|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|188nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|194nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007517|gpx-3|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00007518|del-8|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|427nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|430nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|438nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007520|C11E4.6|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007521|C11E4.7a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007521|C11E4.7a|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007521|C11E4.7a|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007521|C11E4.7a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007522|C11E4.8|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007522|C11E4.8|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00007523|C11G6.2|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007525|C11G10.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007525|C11G10.1|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007525|C11G10.1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007525|C11G10.1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1620|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007525|C11G10.1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007525|C11G10.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007525|C11G10.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007526|C11G10.2|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007528|C11H1.2|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007528|C11H1.2|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007528|C11H1.2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007528|C11H1.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007529|C11H1.3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007529|C11H1.3|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007529|C11H1.3|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=999|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007529|C11H1.3|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007529|C11H1.3|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007530|C11H1.5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007530|C11H1.5|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007530|C11H1.5|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007530|C11H1.5|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007530|C11H1.5|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007531|C11H1.7a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007531|C11H1.7a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007531|C11H1.7a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007531|C11H1.7a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3255|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007531|C11H1.7a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007531|C11H1.7a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007531|C11H1.7a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=245|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1839|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=476|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=388|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007533|cbl-1|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12272|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=259|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=319|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007534|C12D8.1c.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=326|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007535|ttr-19|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007535|ttr-19|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007535|ttr-19|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007535|ttr-19|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007536|daf-36|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007536|daf-36|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007536|daf-36|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007536|daf-36|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007536|daf-36|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00007536|daf-36|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007536|daf-36|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|1212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|1214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|1438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|1442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|1446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7083|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=232|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007537|fipr-8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007538|C12D8.9b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007538|C12D8.9b|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007540|C12D8.13|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=652|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007540|C12D8.13|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007540|C12D8.13|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007540|C12D8.13|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1731|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2182|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007541|fipr-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=485|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=167|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=766|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=284|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007542|C12D8.15|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007543|fipr-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007543|fipr-7|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007543|fipr-7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007543|fipr-7|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4948|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007543|fipr-7|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=860|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007543|fipr-7|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007544|fipr-6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007544|fipr-6|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007544|fipr-6|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1875|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007544|fipr-6|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4321|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007544|fipr-6|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007545|C13B4.1c|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007545|C13B4.1c|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=847|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007545|C13B4.1c|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007545|C13B4.1c|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007545|C13B4.1c|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007546|nhr-153|1513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007546|nhr-153|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007546|nhr-153|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007546|nhr-153|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007546|nhr-153|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007546|nhr-153|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=616|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007547|nhr-154|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1194|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007548|C13C4.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007549|spin-1|1421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007549|spin-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007549|spin-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007549|spin-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007549|spin-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007549|spin-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007550|C13C4.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007550|C13C4.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007550|C13C4.6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007550|C13C4.6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007550|C13C4.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007550|C13C4.6|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007550|C13C4.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1615|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007551|C13C4.7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007552|C13C12.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007552|C13C12.2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=596|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007552|C13C12.2|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=405|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1311|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17261|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31608|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|363nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|372nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007553|C13G3.1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|326nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|331nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=248|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|333nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3665|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=751|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|343nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3312|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007554|pptr-2|763nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|1079nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1460|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1219|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007555|dohh-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|198nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|200nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1526|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|205nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|211nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|308nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|310nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007556|C14A4.3|401nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007557|C14A4.6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007557|C14A4.6|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=723|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007557|C14A4.6|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007557|C14A4.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007557|C14A4.6|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007558|C14A4.7a|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=923|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007559|C14A4.8|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007559|C14A4.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007559|C14A4.8|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007560|C14A4.9|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007561|ccm-3|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007561|ccm-3|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007561|ccm-3|399nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007561|ccm-3|401nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007561|ccm-3|409nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2559|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00007561|ccm-3|412nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007561|ccm-3|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007562|C14A4.12a|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007562|C14A4.12a|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007562|C14A4.12a|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007562|C14A4.12a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007562|C14A4.12a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007563|C14A4.13|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007563|C14A4.13|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007563|C14A4.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007564|mrps-22|1313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007564|mrps-22|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007564|mrps-22|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1970|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007564|mrps-22|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007564|mrps-22|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007565|clec-48|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007565|clec-48|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007565|clec-48|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2918|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00007565|clec-48|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007565|clec-48|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007565|clec-48|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007567|C14A6.3|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007567|C14A6.3|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007569|C14A6.5|920nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007570|C14A6.6|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=207|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007570|C14A6.6|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007570|C14A6.6|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007571|C14A6.7|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007571|C14A6.7|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007572|C14A6.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007572|C14A6.8|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007572|C14A6.8|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|1011nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|1014nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4389|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|878nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007573|C14B1.2|969nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2450|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1687|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9290|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007574|C14B1.3|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007576|dph-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007576|dph-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=316|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007576|dph-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007576|dph-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007576|dph-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007576|dph-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007576|dph-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=549|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|1099nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=839|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007577|nrde-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007578|C14B1.7a|1523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007578|C14B1.7a|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007578|C14B1.7a|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007578|C14B1.7a|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007578|C14B1.7a|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007578|C14B1.7a|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1237|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007578|C14B1.7a|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3426|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007579|C14B1.8|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007580|C14B1.9|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007580|C14B1.9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007580|C14B1.9|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007580|C14B1.9|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007580|C14B1.9|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3984|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00007580|C14B1.9|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007580|C14B1.9|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007581|alkb-8|1109nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007581|alkb-8|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007581|alkb-8|466nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007581|alkb-8|473nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=882|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007581|alkb-8|475nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007583|C14B4.2|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007583|C14B4.2|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007583|C14B4.2|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007583|C14B4.2|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007583|C14B4.2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|12nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1547|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007584|C14C10.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007585|C14C10.2a|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007585|C14C10.2a|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007585|C14C10.2a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007585|C14C10.2a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007585|C14C10.2a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3504|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007586|ril-2|365nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007587|mma-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007587|mma-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007587|mma-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007587|mma-1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1963|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007587|mma-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007587|mma-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007587|mma-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|370nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=305|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9204|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1523|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007588|C14C10.5a|941nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2271|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007589|erg-28|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007590|ttr-43|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007590|ttr-43|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1621|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007590|ttr-43|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007590|ttr-43|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007590|ttr-43|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1041|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1117|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007591|C14H10.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007592|C14H10.2b.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007592|C14H10.2b.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007592|C14H10.2b.1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007592|C14H10.2b.1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1001|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007592|C14H10.2b.1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007592|C14H10.2b.1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007592|C14H10.2b.1|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3157|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|556nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|558nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007593|C14H10.3b.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007594|lgc-23|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007594|lgc-23|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007594|lgc-23|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4182|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007595|C15A7.2|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=440|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007595|C15A7.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007595|C15A7.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007595|C15A7.2|321nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007595|C15A7.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007595|C15A7.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007597|C15A11.2.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=741|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007597|C15A11.2.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007598|C15A11.4|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007598|C15A11.4|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007598|C15A11.4|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007598|C15A11.4|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007598|C15A11.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=630|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1664|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007599|C15A11.7a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007600|C15C6.1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007600|C15C6.1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1050|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007601|C15C6.2b|1453nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007601|C15C6.2b|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007601|C15C6.2b|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007601|C15C6.2b|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2853|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007602|C15C6.3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007602|C15C6.3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007602|C15C6.3|474nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=766|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007602|C15C6.3|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=616|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007602|C15C6.3|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007603|C15C6.4|1226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007603|C15C6.4|1228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007603|C15C6.4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1004|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007604|xbx-9|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007604|xbx-9|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007604|xbx-9|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3594|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007604|xbx-9|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1115|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3936|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007605|asp-10|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=408|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|334nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=576|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1754|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007606|C15C8.4|350nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007607|C15C8.5|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007607|C15C8.5|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007607|C15C8.5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007607|C15C8.5|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007608|C15C8.6|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007608|C15C8.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007608|C15C8.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6234|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007609|C15C8.7|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007610|C15H7.3|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007610|C15H7.3|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007610|C15H7.3|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007611|C15H7.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007611|C15H7.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007613|C15H11.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007613|C15H11.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1152|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007613|C15H11.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=535|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|669nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007614|gnrr-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007615|set-31|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007615|set-31|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007615|set-31|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007615|set-31|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1162|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007615|set-31|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007615|set-31|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007615|set-31|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007616|rpoa-12|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2370|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007616|rpoa-12|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2383|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007616|rpoa-12|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007616|rpoa-12|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007616|rpoa-12|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007616|rpoa-12|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007616|rpoa-12|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007617|rrbs-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007617|rrbs-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1791|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007617|rrbs-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007617|rrbs-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007618|C15H11.10|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007618|C15H11.10|1102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007618|C15H11.10|793nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007619|C15H11.11a|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007619|C15H11.11a|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007619|C15H11.11a|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=358|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007619|C15H11.11a|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=833|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007619|C15H11.11a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|1171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|306nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007620|ocrl-1|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2483|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|1185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|1194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|1211nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=866|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4135|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|49nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|53nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|60nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007621|C16C2.4|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007622|C16C10.1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2015|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007622|C16C10.1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007622|C16C10.1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007622|C16C10.1|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007622|C16C10.1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007622|C16C10.1|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007622|C16C10.1|800nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=53|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=475|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007623|C16C10.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5365|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007624|hrde-1|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1811|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=563|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007625|C16C10.4.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=885|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1473nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1475nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|1527nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1406|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=593|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007626|rnf-121|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007627|ccdc-55|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007627|ccdc-55|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2363|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007627|ccdc-55|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|221nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=378|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007628|C16C10.8|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1114|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007629|C16C10.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00007629|C16C10.9|797nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007630|har-1|1400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007630|har-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007630|har-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=279|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007630|har-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007630|har-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17745|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007631|wht-3|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007631|wht-3|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007631|wht-3|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007631|wht-3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007631|wht-3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007631|wht-3|343nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007631|wht-3|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007632|C16C10.13.1|1404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007632|C16C10.13.1|1449nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007632|C16C10.13.1|1454nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007632|C16C10.13.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00007632|C16C10.13.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007632|C16C10.13.1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007633|C16D2.1a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=745|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007633|C16D2.1a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007633|C16D2.1a|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007633|C16D2.1a|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007635|npr-4|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007635|npr-4|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007635|npr-4|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1482|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007635|npr-4|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007635|npr-4|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007635|npr-4|511nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007635|npr-4|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|403nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|407nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=429|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=573|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|569nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|573nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007637|dhhc-7|576nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007639|C17D12.5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007640|C17D12.7|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007641|C17E4.1b|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007642|C17E4.2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007642|C17E4.2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1797|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007643|marc-3|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1074nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|1187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007644|C17E4.4|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|1195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|1206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|1540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|524nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|535nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4392|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007645|C17E4.6|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1061nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1073nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1441|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1081nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12832|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1085nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1096nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007646|nkb-1|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|242nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4164|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1305|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=726|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007647|C17E4.10a.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007648|C17G1.1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007649|C17G1.2|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007649|C17G1.2|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007649|C17G1.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007649|C17G1.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1779|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007650|ugt-23|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007650|ugt-23|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007650|ugt-23|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=872|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007650|ugt-23|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007650|ugt-23|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1144|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|554nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007651|nra-3|777nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=852|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007652|C17G1.5|602nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=267|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7472|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007653|cysl-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007655|C17H1.2|1069nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007655|C17H1.2|561nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007655|C17H1.2|581nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007656|C17H1.3|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007657|C17H1.4a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007658|C17H1.5|488nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00007658|C17H1.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00007660|C17H1.7|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007660|C17H1.7|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00007660|C17H1.7|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00007660|C17H1.7|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007662|C17H1.9|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007662|C17H1.9|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007662|C17H1.9|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|406nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=434|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|409nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1169|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007664|seb-3|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3797|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007666|C18B12.4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007667|fbxa-97|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007667|fbxa-97|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1209|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007668|C18B12.6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007669|C18D1.2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007670|stg-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3490|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007670|stg-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007670|stg-1|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007675|C18D4.6a|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00007675|C18D4.6a|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007675|C18D4.6a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007675|C18D4.6a|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007675|C18D4.6d|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007675|C18D4.6d|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007675|C18D4.6d|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007678|srz-90|884nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1269|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007679|C18D11.1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007680|maa-1|163nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007680|maa-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007680|maa-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007680|maa-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007680|maa-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007680|maa-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|525nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|529nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2846|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|532nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6325|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|534nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2280|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|539nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|542nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007681|C18D11.3.2|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007682|C18D11.6|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007682|C18D11.6|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007682|C18D11.6|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=591|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007682|C18D11.6|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=129|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|1433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|1435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11273|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2326|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007683|C18E9.2a|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007684|C18E9.4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8372|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007684|C18E9.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007684|C18E9.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007684|C18E9.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=423|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2378|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007685|C18E9.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3866|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2264|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007686|tomm-40|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007687|C18E9.7|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007687|C18E9.7|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=321|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007687|C18E9.7|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007687|C18E9.7|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007687|C18E9.7|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007687|C18E9.7|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007688|C18E9.8|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007688|C18E9.8|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=349|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007688|C18E9.8|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007689|C18E9.9|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2717|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007689|C18E9.9|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007689|C18E9.9|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2252|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=384|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007690|sftd-3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007691|C23H4.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007691|C23H4.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007692|C23H4.3|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007692|C23H4.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007692|C23H4.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007692|C23H4.3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007692|C23H4.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007693|C23H4.4a|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007693|C23H4.4a|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007693|C23H4.4a|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007693|C23H4.4a|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007693|C23H4.4a|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007694|C23H4.6a|1495nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007694|C23H4.6a|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007694|C23H4.6a|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00007694|C23H4.6a|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007695|C23H4.7|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007695|C23H4.7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007695|C23H4.7|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2667|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8914|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1683|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|486nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|488nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|490nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|505nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|508nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007696|tram-1|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=429|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=376|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=497|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=358|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007697|C24F3.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007698|qns-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007698|qns-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2604|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007698|qns-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007698|qns-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007699|C24H11.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007700|C24H11.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007701|srd-74|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007701|srd-74|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007702|C24H11.5b|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2463|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00007702|C24H11.5b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007702|C24H11.5b|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007702|C24H11.5b|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007703|gbf-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007703|gbf-1|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007703|gbf-1|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1606|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007703|gbf-1|500nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=539|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|590nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007704|mdt-21|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|349nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1642|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|353nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1286|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=200|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007705|C25A1.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|1520nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6018|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007706|C25A1.4.1|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|346nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=984|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1131|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007707|C25A1.5|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1415|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=921|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42509|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007709|clec-87|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4396|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007710|rsa-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007711|lid-1|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007711|lid-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007711|lid-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1445|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007711|lid-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2313|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007711|lid-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007711|lid-1|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007711|lid-1|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007712|mrpl-34|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007712|mrpl-34|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007712|mrpl-34|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007712|mrpl-34|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=420|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007712|mrpl-34|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1365|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007712|mrpl-34|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007714|C25D7.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007714|C25D7.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007714|C25D7.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007714|C25D7.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007714|C25D7.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007716|fbxa-82|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007716|fbxa-82|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007716|fbxa-82|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007716|fbxa-82|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007716|fbxa-82|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007717|C25D7.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007717|C25D7.5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007717|C25D7.5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=491|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8472|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007718|otub-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007720|C25D7.10|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00007720|C25D7.10|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007720|C25D7.10|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4797|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007722|C25D7.15a|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007723|C25F9.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007724|C25F9.4|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007724|C25F9.4|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007724|C25F9.4|1552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007724|C25F9.4|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007724|C25F9.4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007724|C25F9.4|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007725|C25F9.5.2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007726|C25F9.6|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007726|C25F9.6|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007726|C25F9.6|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007728|C25F9.9|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00007728|C25F9.9|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00007728|C25F9.9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007729|clec-185|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007729|clec-185|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007730|C25G4.2.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4398|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007730|C25G4.2.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007730|C25G4.2.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007730|C25G4.2.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007730|C25G4.2.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007730|C25G4.2.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007731|C25G4.3b|1120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007731|C25G4.3b|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1638|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007731|C25G4.3b|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007732|spe-44|1230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007732|spe-44|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007732|spe-44|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1723|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007732|spe-44|228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007733|smz-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007733|smz-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2384|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007733|smz-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007733|smz-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007733|smz-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007733|smz-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007734|C25G4.7b|1459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007735|C25G4.8|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007735|C25G4.8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007735|C25G4.8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007736|igdb-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007736|igdb-2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007736|igdb-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007736|igdb-2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007736|igdb-2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1079|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|1201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|1450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|1457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|324nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|854nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|920nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007739|C26C6.4a|973nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007740|C26C6.6|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=365|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007741|glb-8|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007742|C26C6.8|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007742|C26C6.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007743|C26C6.9|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007743|C26C6.9|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=756|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007743|C26C6.9|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007743|C26C6.9|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007743|C26C6.9|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007743|C26C6.9|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007744|C26D10.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007744|C26D10.3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007744|C26D10.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007744|C26D10.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=422|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007744|C26D10.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007745|C26D10.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007745|C26D10.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007745|C26D10.4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007745|C26D10.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007745|C26D10.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1851|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007746|C26D10.6a|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007748|C26E1.2a|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=285|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007749|ceh-79|188nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007749|ceh-79|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00007749|ceh-79|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007749|ceh-79|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007749|ceh-79|293nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007750|syg-2|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1035|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007750|syg-2|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007751|C26G2.2|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007751|C26G2.2|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007751|C26G2.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|1538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|361nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|365nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=316|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|372nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=578|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|374nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|377nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=754|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007752|wdfy-3|504nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007753|C27A7.1a|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007753|C27A7.1a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007753|C27A7.1a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007753|C27A7.1a|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007753|C27A7.1a|528nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007753|C27A7.1a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007755|C27A7.3a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5b|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5b|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5d|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5d|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5d|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5d|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3321|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5d|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=930|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5d|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007756|C27A7.5d|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007757|C27A7.6d.2|283nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007757|C27A7.6d.2|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007757|C27A7.6d.2|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007757|C27A7.6d.2|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2185|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007757|C27A7.6d.2|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=518|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007757|C27A7.6d.2|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5015|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1659|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|439nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007758|C27A7.8a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007759|C27A7.9|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007759|C27A7.9|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007759|C27A7.9|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007759|C27A7.9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1181|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|220nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|237nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|247nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|518nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007760|C27B7.2|558nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|105nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1870|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=338|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|95nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007761|rad-26|97nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=65|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007762|C27B7.5|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2694|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007762|C27B7.5|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007762|C27B7.5|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007763|C27B7.6|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007763|C27B7.6|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=267|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00007763|C27B7.6|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007763|C27B7.6|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|1187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|1464nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|1469nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|291nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007764|C27B7.7a|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8673|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|194nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|200nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|205nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007765|C27B7.9|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007766|C27C7.1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007766|C27C7.1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2918|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007766|C27C7.1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007766|C27C7.1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007769|C27C7.7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007770|nhr-259|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007770|nhr-259|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007770|nhr-259|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007770|nhr-259|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007770|nhr-259|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007771|C27C12.1|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007771|C27C12.1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=419|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00007771|C27C12.1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=563|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007771|C27C12.1|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007771|C27C12.1|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|547nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|557nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|704nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|706nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|714nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|724nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=804|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007772|egrh-1|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007773|C27C12.3|625nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007773|C27C12.3|713nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007773|C27C12.3|792nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007773|C27C12.3|794nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007773|C27C12.3|799nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007773|C27C12.3|802nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|864nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2389|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007774|C27C12.4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007775|acd-3|1333nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007775|acd-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007775|acd-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007775|acd-3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007775|acd-3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007775|acd-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00007776|dmd-4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007776|dmd-4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007776|dmd-4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007776|dmd-4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=388|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007776|dmd-4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007776|dmd-4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007776|dmd-4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007777|C27D8.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007777|C27D8.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1510|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007777|C27D8.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007778|C27D8.2|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=638|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007779|C27D8.3a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007779|C27D8.3a|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007779|C27D8.3a|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007779|C27D8.3a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007780|C27D8.4|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007780|C27D8.4|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007780|C27D8.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007780|C27D8.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007780|C27D8.4|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007784|ruvb-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007784|ruvb-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007784|ruvb-1|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3084|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007784|ruvb-1|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3510|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007784|ruvb-1|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=497|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007784|ruvb-1|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007785|tofu-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007785|tofu-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007785|tofu-1|213nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007785|tofu-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007785|tofu-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4671|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007785|tofu-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2342|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007785|tofu-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=285|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1499|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11057|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|1376nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4885|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1180|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=300|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|1525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|322nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|808nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|810nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007786|rmd-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007787|C27H6.8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1929|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007787|C27H6.8|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4477|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007787|C27H6.8|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007787|C27H6.8|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=282|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007787|C27H6.8|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007787|C27H6.8|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007787|C27H6.8|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007788|C28A5.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1114|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007788|C28A5.1|484nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007788|C28A5.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007789|C28A5.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007789|C28A5.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007791|C28A5.6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007791|C28A5.6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007791|C28A5.6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007792|C28D4.4|24nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007792|C28D4.4|27nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007792|C28D4.4|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007792|C28D4.4|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007793|C28D4.5|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007793|C28D4.5|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=603|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007793|C28D4.5|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007793|C28D4.5|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007793|C28D4.5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007793|C28D4.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007793|C28D4.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007794|C28D4.7|1196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007794|C28D4.7|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007794|C28D4.7|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=393|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007794|C28D4.7|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007794|C28D4.7|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007795|C28D4.8|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007795|C28D4.8|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007796|C28D4.10a|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007796|C28D4.10a|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007796|C28D4.10a|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00007796|C28D4.10a|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007796|C28D4.10a|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007796|C28D4.10a|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1589|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007797|C29A12.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1387|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2772|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007799|nrx-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007800|C29A12.6a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007800|C29A12.6a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007800|C29A12.6a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007800|C29A12.6a|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007800|C29A12.6a|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007801|trpa-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007801|trpa-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007801|trpa-1|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=399|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007801|trpa-1|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007802|cutl-27|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007802|cutl-27|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007804|C29F3.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007804|C29F3.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007804|C29F3.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007806|clec-230|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=314|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007806|clec-230|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007806|clec-230|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007806|clec-230|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007807|C29F3.7a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2174|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007807|C29F3.7a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007807|C29F3.7a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|1410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|220nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007808|best-7|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007809|C29F4.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007809|C29F4.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007810|C29F7.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007810|C29F7.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=552|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1453|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|823nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|865nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|871nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|903nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007811|C29F7.2a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|1390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=467|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=926|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3645|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=323|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007812|C29F7.3|881nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007813|jmjd-3.3|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007813|jmjd-3.3|479nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007813|jmjd-3.3|482nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007816|C30F2.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007816|C30F2.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2575|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007816|C30F2.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007816|C30F2.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007817|C30F2.3|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=301|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007817|C30F2.3|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007817|C30F2.3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007817|C30F2.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007817|C30F2.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007818|C30F2.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=605|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007818|C30F2.4|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007818|C30F2.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007818|C30F2.4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007819|C30F2.5|390nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007819|C30F2.5|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007819|C30F2.5|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007819|C30F2.5|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007820|clec-199|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007820|clec-199|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007820|clec-199|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007823|C30H6.5a|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007823|C30H6.5a|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007823|C30H6.5a|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=253|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007823|C30H6.5a|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007823|C30H6.5a|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007823|C30H6.5a|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007823|C30H6.5a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007824|C30H6.7a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007824|C30H6.7a|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007824|C30H6.7a|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7029|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00007824|C30H6.7a|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2584|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007824|C30H6.7a|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007824|C30H6.7a|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007825|C30H6.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007825|C30H6.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007825|C30H6.8|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2190|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=464|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=920|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=297|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007826|C30H6.9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|105nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|114nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|118nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3014|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33165|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1489|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|360nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007827|C30H6.10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007829|oac-5|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007829|oac-5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007831|srbc-83|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007832|srbc-82|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007832|srbc-82|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00007832|srbc-82|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007833|oac-6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=711|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007833|oac-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007833|oac-6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007833|oac-6|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007834|srxa-7|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007835|oac-7|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007835|oac-7|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007835|oac-7|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00007835|oac-7|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=326|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3246|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007836|C31C9.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1037|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|963nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007837|fbxa-167|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007838|fbxa-168|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00007838|fbxa-168|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00007838|fbxa-168|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00007838|fbxa-168|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00007840|C31C9.6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007840|C31C9.6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007840|C31C9.6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007840|C31C9.6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007840|C31C9.6|767nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|1265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3472|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007841|C31C9.7|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007842|C31E10.1|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007842|C31E10.1|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007845|C31E10.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007845|C31E10.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007845|C31E10.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007845|C31E10.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007845|C31E10.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007845|C31E10.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007845|C31E10.4|734nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|1438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|1442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|1493nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=559|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|1565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|411nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|583nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007846|C31E10.5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007847|C31E10.6|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007847|C31E10.6|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=518|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007847|C31E10.6|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007847|C31E10.6|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1345|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=527|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|1239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2391|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1015|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007848|cytb-5.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007849|tbc-19|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007849|tbc-19|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007849|tbc-19|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007849|tbc-19|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00007849|tbc-19|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007850|C31G12.1|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007850|C31G12.1|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007850|C31G12.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007850|C31G12.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007850|C31G12.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007850|C31G12.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007851|clec-245|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007851|clec-245|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007853|C31G12.4b|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007854|C31H5.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007855|C31H5.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5590|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007855|C31H5.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007855|C31H5.4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4743|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1117|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007856|C31H5.5|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=659|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|969nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007857|C31H5.6b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007858|C31H5.7|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007858|C31H5.7|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007858|C31H5.7|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007858|C31H5.7|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007858|C31H5.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007858|C31H5.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007858|C31H5.7|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007859|mrps-31|1057nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007859|mrps-31|1060nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007859|mrps-31|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007859|mrps-31|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007859|mrps-31|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007859|mrps-31|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007859|mrps-31|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8065|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007860|rilp-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007861|C32A9.1|342nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00007861|C32A9.1|375nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2747|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=902|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007862|C32C4.1f|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007863|C32C4.3c|41nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007863|C32C4.3c|45nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=84|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007864|C32H11.1a|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007864|C32H11.1b|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007866|C32H11.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007866|C32H11.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=386|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=943|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007867|C32H11.4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1969|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007868|C32H11.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007869|C32H11.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=695|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007869|C32H11.6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007869|C32H11.6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|1120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|1122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|1346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|1353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|1357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|1362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|784nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|952nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007870|C32H11.7a|954nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|1195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=983|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|1200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|1202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|1204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|1294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2929|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007872|C32H11.9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007873|dod-21|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007873|dod-21|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007873|dod-21|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2869|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007873|dod-21|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007873|dod-21|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007873|dod-21|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007873|dod-21|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007874|C32H11.11|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007874|C32H11.11|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007874|C32H11.11|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1017|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007874|C32H11.11|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007874|C32H11.11|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007874|C32H11.11|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2299|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007875|dod-24|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007876|dct-19|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007876|dct-19|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|609nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|612nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|615nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|618nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|621nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3718|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=610|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007877|nbid-1|643nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007878|C33A11.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007878|C33A11.2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007878|C33A11.2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1361|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007878|C33A11.2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2454|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007878|C33A11.2|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007878|C33A11.2|564nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1321|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|129nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3839|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007880|C33A12.1|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3286|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7599|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007881|nlp-35|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10012|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|744nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007882|C33A12.3b|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=316|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|1289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7987|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1804|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2778|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2542|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=377|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=220908|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7874|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1585|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=275|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1011|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|230nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007883|C33A12.4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007885|ugt-21|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007885|ugt-21|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007885|ugt-21|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007885|ugt-21|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007885|ugt-21|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2017|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007886|ethe-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007887|gadr-2|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00007887|gadr-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00007888|ttr-9|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007888|ttr-9|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007888|ttr-9|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007888|ttr-9|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=425|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=858|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|253nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007890|C33A12.19a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007891|C33B4.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007892|C33B4.4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007892|C33B4.4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007892|C33B4.4|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007892|C33B4.4|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2628|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007892|C33B4.4|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2240|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007892|C33B4.4|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007892|C33B4.4|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007894|C33D3.3|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007894|C33D3.3|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007894|C33D3.3|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007894|C33D3.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007897|clec-182|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1620|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|635nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007898|C33D9.3b.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|215nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|219nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|223nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=841|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007900|C33D9.6b|800nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1091nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1094nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007901|C33D9.8|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007903|lgc-21|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1117|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007903|lgc-21|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007903|lgc-21|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007904|C33G3.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007904|C33G3.4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007904|C33G3.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|1272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007906|C33G3.6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|1481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|1551nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|180nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3733|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|709nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007907|C34B4.2a.2|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1378|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007908|C34B4.3|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007909|C34B4.4|1511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007909|C34B4.4|1532nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007909|C34B4.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|1166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|131nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007910|C34B4.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|1300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|1580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|1587nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00007911|C34B7.1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=502|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007912|C34B7.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1940|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007913|cyp-36A1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|671nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|673nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|711nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=724|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|749nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007914|mys-4|752nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=163|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00007916|C34C6.3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007916|C34C6.3|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007916|C34C6.3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007916|C34C6.3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007917|C34C6.4|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007917|C34C6.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007917|C34C6.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2159|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007917|C34C6.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|1228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=438|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1020|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=404|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007918|sphk-1|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007919|C34C6.7a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=599|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007919|C34C6.7a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007920|C34C12.1|1568nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007920|C34C12.1|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007921|C34C12.2|1206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007921|C34C12.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1866|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007921|C34C12.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1303|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=447|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|741nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|748nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|751nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|796nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|862nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|904nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007922|pph-6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5007|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|294nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1604|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=340|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=633|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|574nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|585nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|614nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007923|C34C12.4.1|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|135nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2990|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007924|rsu-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007925|C34C12.6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=535|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007926|C34C12.7|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007927|C34C12.8|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007927|C34C12.8|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007927|C34C12.8|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3372|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007927|C34C12.8|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007927|C34C12.8|544nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007928|C34C12.9|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007928|C34C12.9|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007928|C34C12.9|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007928|C34C12.9|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007928|C34C12.9|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|680nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|686nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|701nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|703nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00007929|dmd-10|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1974|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1069|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007931|C34D1.4c.2|323nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007932|zip-5|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007932|zip-5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007932|zip-5|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007932|zip-5|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1065|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007932|zip-5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007933|C34E7.3|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1673|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1721|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007934|C34E7.4.1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007935|C34E11.2b|1544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007935|C34E11.2b|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007935|C34E11.2b|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007937|C34E11.4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007937|C34E11.4|16nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007937|C34E11.4|19nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=456|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007937|C34E11.4|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007938|C34F6.1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00007938|C34F6.1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007939|C34F6.5b|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007939|C34F6.5b|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1401|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007939|C34F6.5b|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007939|C34F6.5b|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007941|C34F6.7|788nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00007941|C34F6.7|790nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007941|C34F6.7|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007942|idh-2|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007942|idh-2|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007942|idh-2|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007942|idh-2|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=279|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007942|idh-2|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1025|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007942|idh-2|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=457|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007942|idh-2|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007943|C34F6.9|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007943|C34F6.9|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=639|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007943|C34F6.9|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007943|C34F6.9|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007943|C34F6.9|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007943|C34F6.9|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|502nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|581nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|587nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4533|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|593nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=706|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|638nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007944|C34F6.10|649nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007945|C34F6.11|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=662|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007945|C34F6.11|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007945|C34F6.11|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007945|C34F6.11|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007945|C34F6.11|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007945|C34F6.11|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007945|C34F6.11|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007946|ugt-33|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007946|ugt-33|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007946|ugt-33|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007947|C35A5.3|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007948|C35A5.4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007948|C35A5.4|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007948|C35A5.4|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007948|C35A5.4|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007948|C35A5.4|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007949|C35A5.5|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007949|C35A5.5|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00007949|C35A5.5|45nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007949|C35A5.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007950|C35A5.6a|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007950|C35A5.6a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007950|C35A5.6a|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007950|C35A5.6a|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|1594nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=782|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007951|dmsr-8|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|1550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2838|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=513|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1066|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007952|C35A5.8|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007953|hda-11|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007953|hda-11|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007953|hda-11|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007953|hda-11|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007953|hda-11|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=644|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007953|hda-11|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3277|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=433|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007955|C35C5.3a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|1048nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|1053nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=511|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007956|trpp-9|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007957|C35C5.8a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4510|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007958|C35C5.9.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007959|C35C5.10a.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007959|C35C5.10a.2|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1875|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007959|C35C5.10a.2|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007959|C35C5.10a.2|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007960|C35D6.3|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007960|C35D6.3|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007961|C35D6.4|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007963|cyp-25A1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007963|cyp-25A1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007963|cyp-25A1|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1183|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007964|cyp-25A2|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007964|cyp-25A2|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007964|cyp-25A2|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1778|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=643|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2587|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|278nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|286nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007965|C36A4.4|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|1590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|1592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=395|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1170|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1597|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4733|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007966|maph-1.3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007967|cyp-25A4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007967|cyp-25A4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00007967|cyp-25A4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007967|cyp-25A4|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007967|cyp-25A4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|1162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|1180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13800|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=524|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|455nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|521nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007969|acs-19|877nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|228nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2542|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|370nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|585nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007970|C36A4.10|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=579|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1547|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3288|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007971|rpb-3|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2778|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007972|prp-4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1393|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007972|prp-4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007972|prp-4|1245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007972|prp-4|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007972|prp-4|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007973|C36B1.6a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007973|C36B1.6a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007973|C36B1.6a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1828|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1860|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|1547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|323nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007974|dhfr-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|1013nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|591nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|603nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|607nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|609nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|614nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|617nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|619nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|752nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007975|gls-1|755nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=630|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1419nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1485nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1502nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|1575nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007976|C36B1.9|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007977|gska-3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007977|gska-3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007977|gska-3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|120nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|128nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5177|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007978|C36B1.11|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6089|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=462|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007979|imp-1|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=399|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19053|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1477|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007980|C36E8.1.1|460nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=425|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1313|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007981|glb-11|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007982|pxd-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007982|pxd-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007982|pxd-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007982|pxd-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007982|pxd-1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1329|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|1353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|637nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007983|C36E8.4|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|645nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|651nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|655nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=598|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007984|irx-1|657nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007985|swah-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007986|C36F7.5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007986|C36F7.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007986|C36F7.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007986|C36F7.5|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007987|C36H8.1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007987|C36H8.1|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=766|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007987|C36H8.1|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=293|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007988|best-8|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007988|best-8|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007988|best-8|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007989|fipr-22|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007989|fipr-22|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007989|fipr-22|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1661|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007989|fipr-22|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007990|fipr-23|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00007991|C37A5.7.2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007991|C37A5.7.2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=329|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007991|C37A5.7.2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007991|C37A5.7.2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007992|fipr-24|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6187|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007992|fipr-24|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007992|fipr-24|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007992|fipr-24|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007992|fipr-24|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007992|fipr-24|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007992|fipr-24|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|512nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=157|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|595nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|598nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|600nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1081|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|602nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1033|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|604nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=257|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|606nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|609nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|612nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|721nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007993|idhb-1|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007994|C37E2.2a|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007994|C37E2.2a|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00007994|C37E2.2a|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00007994|C37E2.2a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007994|C37E2.2a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007994|C37E2.2a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007996|C38C6.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007996|C38C6.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00007996|C38C6.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00007996|C38C6.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00007996|C38C6.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007997|sre-13|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=896|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00007997|sre-13|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007998|C38C6.5|279nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00007998|C38C6.5|281nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007999|tag-297|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00007999|tag-297|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00007999|tag-297|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=337|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6787|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=421|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|624nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|627nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008000|slc-17.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008001|C38C10.3|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008001|C38C10.3|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=357|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008001|C38C10.3|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008001|C38C10.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008001|C38C10.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6798|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008002|C38C10.6|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008003|enu-3.2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5193|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008003|enu-3.2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008003|enu-3.2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008003|enu-3.2|575nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008005|C38D4.4|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1167|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008005|C38D4.4|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008005|C38D4.4|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008006|tag-325|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008006|tag-325|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008006|tag-325|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2331|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008006|tag-325|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008006|tag-325|364nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008007|C38D4.7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00008007|C38D4.7|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008007|C38D4.7|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1090|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008008|C38D4.9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008009|fbxa-171|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008010|C38D9.2.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008010|C38D9.2.1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008010|C38D9.2.1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008010|C38D9.2.1|571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008010|C38D9.2.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008014|fbxa-172|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008014|fbxa-172|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008014|fbxa-172|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008016|C38D9.8|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008017|fbxa-176|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00008017|fbxa-176|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00008017|fbxa-176|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00008018|tbc-8|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008018|tbc-8|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1022|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008018|tbc-8|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1545|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008018|tbc-8|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|558nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1637|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008019|C38H2.2|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008020|C38H2.3|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008020|C38H2.3|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008020|C38H2.3|328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008020|C38H2.3|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008020|C38H2.3|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008020|C38H2.3|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008021|C39B10.1|119nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008021|C39B10.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008021|C39B10.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008021|C39B10.1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008021|C39B10.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008021|C39B10.1|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008021|C39B10.1|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008022|lgc-41|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008023|C39B10.3|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008023|C39B10.3|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008024|C39B10.4|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008024|C39B10.4|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008024|C39B10.4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=724|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008025|C39B10.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008027|scl-5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008027|scl-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1476|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00008027|scl-5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008027|scl-5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008027|scl-5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008028|scl-6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008028|scl-6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008028|scl-6|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008028|scl-6|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008028|scl-6|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008028|scl-6|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008029|scl-7|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=218|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008029|scl-7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008030|scl-8|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008031|C39E9.7|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008031|C39E9.7|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008031|C39E9.7|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008031|C39E9.7|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=934|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=406|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1623|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=498|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008032|C39E9.8a|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008033|spin-2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008033|spin-2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008033|spin-2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1181|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3115|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=163|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1494|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00008034|C39E9.11|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=415|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008035|C39E9.12|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008035|C39E9.12|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1252|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008035|C39E9.12|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008035|C39E9.12|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=238|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008035|C39E9.12|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008035|C39E9.12|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008035|C39E9.12|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008036|C40C9.3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008036|C40C9.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=888|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008036|C40C9.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008036|C40C9.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008037|C40C9.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008038|C40H1.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008038|C40H1.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008039|C40H1.3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008039|C40H1.3|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008039|C40H1.3|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008039|C40H1.3|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008039|C40H1.3|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008039|C40H1.3|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008040|ttr-5|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008040|ttr-5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008040|ttr-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2391|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008040|ttr-5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=582|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|108nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|657nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2881|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008041|ufc-1|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008043|C40H1.8.1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008043|C40H1.8.1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00008043|C40H1.8.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008043|C40H1.8.1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=305|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008044|C40H1.9|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|343nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=978|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008045|C40H5.2a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008047|lact-7|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008047|lact-7|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008047|lact-7|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008050|C41C4.1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008050|C41C4.1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008050|C41C4.1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008051|lron-4|1514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008051|lron-4|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008051|lron-4|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008051|lron-4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008051|lron-4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2995|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008051|lron-4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008051|lron-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=464|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=189|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|120nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4181|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=385|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|406nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|412nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|425nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|639nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|645nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008052|ctns-1|647nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2847|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2128|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4215|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008053|cdc-48.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008057|irld-25|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008059|C41G6.13|1437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008059|C41G6.13|1597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008059|C41G6.13|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008060|C41G6.16|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008060|C41G6.16|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008061|C41G7.3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2474|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008061|C41G7.3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008061|C41G7.3|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008061|C41G7.3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008062|set-32|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008062|set-32|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=804|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008062|set-32|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008063|C41G7.6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008063|C41G7.6|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=584|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008063|C41G7.6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008063|C41G7.6|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008063|C41G7.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008064|C41G7.7|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008064|C41G7.7|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1813|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008064|C41G7.7|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008065|npr-18|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=890|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008065|npr-18|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008065|npr-18|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008066|fbxb-65|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008066|fbxb-65|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008067|C43D7.4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008068|sdz-6|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008068|sdz-6|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008068|sdz-6|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008068|sdz-6|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008069|C43D7.7|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008070|C43D7.8|590nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008070|C43D7.8|592nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008072|C43F9.4a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00008072|C43F9.4a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00008073|C43F9.5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008073|C43F9.5|246nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008073|C43F9.5|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008074|nkb-2|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008074|nkb-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=804|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008074|nkb-2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008075|C43F9.7|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008075|C43F9.7|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008075|C43F9.7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1380|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008075|C43F9.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008075|C43F9.7|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008076|lgc-43|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008076|lgc-43|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008076|lgc-43|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008076|lgc-43|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008077|oac-8|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00008077|oac-8|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00008077|oac-8|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00008077|oac-8|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008077|oac-8|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008078|vesa-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008078|vesa-1|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008078|vesa-1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=736|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008079|C44B9.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008079|C44B9.2|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008079|C44B9.2|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008079|C44B9.2|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008079|C44B9.2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008080|C44B9.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008081|athp-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008081|athp-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008081|athp-1|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008081|athp-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008081|athp-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008081|athp-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1067|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008082|com-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=529|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008082|com-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=425|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008082|com-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008082|com-1|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008084|C44C10.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00008084|C44C10.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008084|C44C10.3|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008084|C44C10.3|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00008085|C44C10.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008085|C44C10.4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008085|C44C10.4|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008085|C44C10.4|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008086|C44C10.5|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008086|C44C10.5|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008086|C44C10.5|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008088|C44C10.7|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|1187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|1190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|1241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=888|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9d|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9e|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9e|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008089|C44C10.9e|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008091|C44F1.1|1304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008091|C44F1.1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008091|C44F1.1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008091|C44F1.1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008092|gmeb-3|1205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008092|gmeb-3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008092|gmeb-3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00008092|gmeb-3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008093|lron-1|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00008093|lron-1|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2032|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|422nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|513nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008094|C44H4.4|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008095|C44H4.6|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=588|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00008096|C44H4.8|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008097|ugt-15|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008097|ugt-15|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008099|C44H9.4|234nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008099|C44H9.4|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008099|C44H9.4|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008099|C44H9.4|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008100|C44H9.5|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008100|C44H9.5|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008100|C44H9.5|831nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00008101|C44H9.6.1|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008101|C44H9.6.1|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008102|C44H9.7b|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00008102|C44H9.7b|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00008105|C45B11.2|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=305|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008105|C45B11.2|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008105|C45B11.2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008105|C45B11.2|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008105|C45B11.2|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008105|C45B11.2|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008105|C45B11.2|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008106|C45B11.5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008106|C45B11.5|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008106|C45B11.5|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008107|aspm-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008107|aspm-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=999|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008107|aspm-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008107|aspm-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008107|aspm-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008107|aspm-1|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008107|aspm-1|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008110|C46C2.2.2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008110|C46C2.2.2|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008110|C46C2.2.2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1172|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008110|C46C2.2.2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4057|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008110|C46C2.2.2|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008110|C46C2.2.2|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008110|C46C2.2.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008111|C46C2.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008111|C46C2.3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008111|C46C2.3|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008111|C46C2.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=664|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=280|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008113|C46C2.5|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008114|C46C2.6a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008114|C46C2.6a|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008114|C46C2.6a|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008114|C46C2.6a|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008116|C46E1.3|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008116|C46E1.3|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=462|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5669|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008117|gsr-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008118|madf-8|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=658|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008118|madf-8|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1003|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008118|madf-8|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=601|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008118|madf-8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008118|madf-8|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008118|madf-8|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008119|C46F11.4|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008119|C46F11.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008119|C46F11.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008119|C46F11.4|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008119|C46F11.4|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1697|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|160nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|171nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|175nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=505|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=978|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008120|C46F11.5a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2024|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008121|C46F11.6|741nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008123|ent-4|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=390|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008123|ent-4|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008123|ent-4|41nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008123|ent-4|46nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008123|ent-4|48nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008123|ent-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008123|ent-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008124|C47A4.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00008124|C47A4.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00008125|C47A4.5|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008125|C47A4.5|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00008125|C47A4.5|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008125|C47A4.5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008125|C47A4.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008125|C47A4.5|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008125|C47A4.5|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=779|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008126|sre-21|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008127|ddo-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008127|ddo-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008127|ddo-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008127|ddo-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008127|ddo-1|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008127|ddo-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008128|srab-12|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008128|srab-12|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008129|C47A10.12|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008130|fbxa-140|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008130|fbxa-140|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008130|fbxa-140|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008130|fbxa-140|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008130|fbxa-140|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2457|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1839|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008131|C47B2.2.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1121|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=428|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=901|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008132|gale-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008133|efsc-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008133|efsc-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00008133|efsc-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008133|efsc-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008134|C47B2.9|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2258|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008134|C47B2.9|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008136|C47D12.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008136|C47D12.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=526|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008136|C47D12.2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1602|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008136|C47D12.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008136|C47D12.2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008137|sfxn-1.4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008137|sfxn-1.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008137|sfxn-1.4|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008137|sfxn-1.4|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008137|sfxn-1.4|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008137|sfxn-1.4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008137|sfxn-1.4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008138|C47D12.4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008138|C47D12.4|745nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008138|C47D12.4|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008138|C47D12.4|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008139|C47D12.5|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008139|C47D12.5|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1732|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008139|C47D12.5|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=152|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008139|C47D12.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1427|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008140|xpf-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008141|C47E8.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008142|C47E8.3|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=441|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00008142|C47E8.3|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008142|C47E8.3|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008142|C47E8.3|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=503|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|140nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2320|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=339|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008143|C47E8.4c|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=351|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008144|gasr-8|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008145|set-5|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008146|C47E8.9a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008146|C47E8.9a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|192nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5092|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=400|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|197nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=592|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|200nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008147|C47E12.2.1|489nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=856|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=878|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008148|C47E12.3a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|1258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3824|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4121|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4792|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=467|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2072|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|332nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|337nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|345nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008149|pyp-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008150|mam-2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008150|mam-2|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008150|mam-2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008150|mam-2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008150|mam-2|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008150|mam-2|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008151|C47E12.7|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008151|C47E12.7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008151|C47E12.7|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00008151|C47E12.7|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008151|C47E12.7|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008152|C47E12.9|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008152|C47E12.9|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008152|C47E12.9|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008152|C47E12.9|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008153|C47E12.10a|1476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008153|C47E12.10a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008154|C47E12.11a|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008154|C47E12.11a|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008154|C47E12.11a|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008154|C47E12.11a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008155|C47E12.12|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008155|C47E12.12|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008155|C47E12.12|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008156|C47E12.13a|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008156|C47E12.13a|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008156|C47E12.13a|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008157|C47F8.1|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008162|C47F8.6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008163|C47F8.7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008164|C47G2.3|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=506|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008164|C47G2.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008164|C47G2.3|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008164|C47G2.3|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2305|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008164|C47G2.3|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008164|C47G2.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5535|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1011|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008165|C47G2.4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008166|saps-1|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008166|saps-1|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008166|saps-1|644nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2887|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008166|saps-1|652nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008166|saps-1|654nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008166|saps-1|748nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008167|acox-5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008167|acox-5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008167|acox-5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008167|acox-5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1576|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008168|C48B4.3.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008168|C48B4.3.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008168|C48B4.3.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008168|C48B4.3.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008168|C48B4.3.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|1104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2928|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=849|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008169|C48B4.6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1125|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008170|C48B4.7|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008171|C48B4.8b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008171|C48B4.8b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008171|C48B4.8b|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008171|C48B4.8b|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1389|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008171|C48B4.8b|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008171|C48B4.8b|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008172|C48B4.9|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008172|C48B4.9|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=640|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008172|C48B4.9|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008172|C48B4.9|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008172|C48B4.9|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008172|C48B4.9|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008173|C48B4.10|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2421|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008173|C48B4.10|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008173|C48B4.10|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008173|C48B4.10|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008173|C48B4.10|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008173|C48B4.10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008174|C48B4.11|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008174|C48B4.11|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1640|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008175|C48B4.12a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00008175|C48B4.12a|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00008176|C48B4.13|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008176|C48B4.13|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008176|C48B4.13|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008176|C48B4.13|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008176|C48B4.13|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008177|C48D1.1b|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008177|C48D1.1b|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008177|C48D1.1b|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008177|C48D1.1b|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008177|C48D1.1b|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=553|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008177|C48D1.1b|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008178|C48D1.5c|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008178|C48D1.5c|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008178|C48D1.5c|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008180|C48D5.3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008180|C48D5.3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008180|C48D5.3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008180|C48D5.3|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1373|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|481nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|486nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008183|rin-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008184|C49A1.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008184|C49A1.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008184|C49A1.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008185|best-10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008185|best-10|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008186|best-11|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008186|best-11|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008186|best-11|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008188|clec-115|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008191|C49A1.10|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=874|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00008191|C49A1.10|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008191|C49A1.10|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008194|C49C3.4a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008194|C49C3.4a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008194|C49C3.4a|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2593|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008194|C49C3.4a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00008194|C49C3.4a|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008195|ceh-88|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008195|ceh-88|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008195|ceh-88|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1545|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008195|ceh-88|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008195|ceh-88|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=854|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008196|C49C3.6|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1691|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008197|C49C3.7|841nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008198|C49C3.8a|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008198|C49C3.8a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008198|C49C3.8a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008198|C49C3.8a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3287|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008198|C49C3.8a|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008198|C49C3.8a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008198|C49C3.8a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=910|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=253|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008199|C49C3.9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008200|C49C3.10b|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=379|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00008200|C49C3.10b|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008201|C49C3.11|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008202|clec-197|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008202|clec-197|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008202|clec-197|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008202|clec-197|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008203|clec-198|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008203|clec-198|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008203|clec-198|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008204|C49C3.15|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|445nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|468nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|475nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|721nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|726nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6236|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|748nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=225|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008205|sams-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|1432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008206|set-6|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=288|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008207|C49F5.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008207|C49F5.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008207|C49F5.3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008208|nhr-167|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008208|nhr-167|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008208|nhr-167|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008209|C49F5.5|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008209|C49F5.5|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00008210|C49F5.6|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5200|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=137|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7822|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008211|C49F5.7|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1297|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008212|C49F5.8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008213|C49F8.1|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008213|C49F8.1|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|327nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1222|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008214|gem-1|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00008215|C49F8.3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1882|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008215|C49F8.3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008215|C49F8.3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008215|C49F8.3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008215|C49F8.3|342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008215|C49F8.3|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008215|C49F8.3|348nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008216|mec-19|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008216|mec-19|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008216|mec-19|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008216|mec-19|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00008216|mec-19|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008218|nasp-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008218|nasp-2|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17859|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008218|nasp-2|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008218|nasp-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008218|nasp-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008218|nasp-2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008218|nasp-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=877|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1043|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008219|C50B6.3a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=433|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=169|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008220|C50B6.7|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008221|nhr-168|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00008221|nhr-168|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008222|C50B6.9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008222|C50B6.9|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008222|C50B6.9|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00008222|C50B6.9|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008223|lgc-48|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008223|lgc-48|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008223|lgc-48|418nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=791|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=952|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1456|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2234|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008224|C50B8.1|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|76nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|78nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=202|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|87nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1029|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008225|nuaf-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008226|C50B8.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008226|C50B8.4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008226|C50B8.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008226|C50B8.4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008226|C50B8.4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008226|C50B8.4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2122|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008227|C50B8.5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008227|C50B8.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008227|C50B8.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=503|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008227|C50B8.5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008228|C50B8.6|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008228|C50B8.6|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008228|C50B8.6|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008228|C50B8.6|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=713|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008228|C50B8.6|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008228|C50B8.6|273nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008228|C50B8.6|278nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=973|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008229|C50F4.1.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=646|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00008230|pfk-1.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008230|pfk-1.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008230|pfk-1.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008230|pfk-1.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008230|pfk-1.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008231|tag-329|1174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008231|tag-329|1177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00008231|tag-329|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|17nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|22nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=503|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|499nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|506nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|528nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|536nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008232|C50F4.4|592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=614|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1856|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=529|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008233|C50F4.8|999nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008234|C50F4.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008234|C50F4.9|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008234|C50F4.9|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008234|C50F4.9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008234|C50F4.9|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008234|C50F4.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008235|C50F4.10|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=432|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008236|C50F4.12|992nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|1392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1423|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=523|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=233|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1531|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1428|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008237|nstp-10|674nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008238|C50F4.16|1053nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008238|C50F4.16|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008238|C50F4.16|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008238|C50F4.16|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2946|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008238|C50F4.16|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008238|C50F4.16|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008239|fshr-1|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008239|fshr-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1563|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008239|fshr-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008240|C50H2.4a|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008240|C50H2.4a|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008243|C50H2.7|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008244|fipr-11|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008244|fipr-11|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008244|fipr-11|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2687|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008245|fipr-10|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008245|fipr-10|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008245|fipr-10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6138|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008245|fipr-10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008246|C50H2.13|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008247|srsx-26|658nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008247|srsx-26|674nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008247|srsx-26|679nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00008248|srsx-27|1446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008248|srsx-27|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1778|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|1235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|304nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|428nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008249|srsx-28|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=775|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008250|srsx-29|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008250|srsx-29|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008251|srsx-30|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008251|srsx-30|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00008251|srsx-30|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008251|srsx-30|429nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008251|srsx-30|435nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008254|C51E3.9a|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008254|C51E3.9a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2621|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008254|C51E3.9a|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2010|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008255|C51E3.10b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008256|glb-12|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=764|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00008256|glb-12|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008256|glb-12|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008256|glb-12|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008256|glb-12|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|205nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|212nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008257|C52A11.3|877nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|241nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1654|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|251nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=961|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|804nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008258|mans-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|682nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008259|C52E4.7|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008260|C52G5.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008260|C52G5.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3572|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008260|C52G5.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008260|C52G5.2|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008260|C52G5.2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008261|C52G5.3|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008261|C52G5.3|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34884|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008262|ril-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008263|C53A5.2|1590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008263|C53A5.2|1596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008263|C53A5.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008263|C53A5.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=545|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=769|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=422|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008265|kcnl-4|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=252|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|808nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|811nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=678|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00008266|C53A5.6a|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008267|C53A5.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008267|C53A5.9|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008268|srt-32|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008268|srt-32|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|147nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|158nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008270|C53A5.13a|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008271|C53B4.1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008272|C53B4.2|1121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008272|C53B4.2|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008272|C53B4.2|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008273|C53B4.3.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008273|C53B4.3.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008273|C53B4.3.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008273|C53B4.3.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1119|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3936|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008274|C53B4.4a|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008275|nstp-1|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008275|nstp-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008275|nstp-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008275|nstp-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1566|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008275|nstp-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008277|mltn-12|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008277|mltn-12|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00008278|npr-10|972nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00008279|C53C7.3|779nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00008279|C53C7.3|799nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|608nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008280|acc-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008281|C53D6.4b|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1144|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008281|C53D6.4b|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=705|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008283|C53D6.6.2|848nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008284|C53D6.7|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008284|C53D6.7|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008284|C53D6.7|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008284|C53D6.7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008284|C53D6.7|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008285|C53D6.8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008286|C54C6.4a|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008286|C54C6.4a|366nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008287|C54C6.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1090|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008287|C54C6.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008288|C54C6.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008288|C54C6.6|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008288|C54C6.6|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008288|C54C6.6|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008288|C54C6.6|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5793|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008288|C54C6.6|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008288|C54C6.6|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008290|C54C8.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008290|C54C8.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008290|C54C8.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008290|C54C8.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008292|C54C8.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008292|C54C8.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008292|C54C8.4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008292|C54C8.4|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008292|C54C8.4|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008292|C54C8.4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008295|nlp-39|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008295|nlp-39|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00008295|nlp-39|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008296|cdr-2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1192|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008296|cdr-2|58nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008296|cdr-2|60nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=70|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008296|cdr-2|62nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=46|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008297|cdr-3|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2257|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1464|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=436|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008298|C54D10.3|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2257|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008299|C54D10.4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008299|C54D10.4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008299|C54D10.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008299|C54D10.4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008299|C54D10.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00008300|C54D10.5|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=648|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008300|C54D10.5|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008300|C54D10.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008300|C54D10.5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008300|C54D10.5|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008300|C54D10.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008301|dct-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008301|dct-3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008301|dct-3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008302|C54D10.8b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008302|C54D10.8b|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008303|C54D10.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008303|C54D10.9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00008303|C54D10.9|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008303|C54D10.9|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008303|C54D10.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008303|C54D10.9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008304|C54D10.10|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00008304|C54D10.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008304|C54D10.10|26nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008306|C54E10.1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00008306|C54E10.1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00008307|ncs-5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008307|ncs-5|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008307|ncs-5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1337|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008309|nhr-170|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008309|nhr-170|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008310|C54E10.6|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=348|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00008310|C54E10.6|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1948|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008310|C54E10.6|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008310|C54E10.6|467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008310|C54E10.6|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008311|rskn-2|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008311|rskn-2|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008311|rskn-2|513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3454|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008311|rskn-2|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008311|rskn-2|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008311|rskn-2|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008311|rskn-2|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008312|C54G4.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008312|C54G4.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008313|C54G4.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008313|C54G4.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=876|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008314|C54G4.4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1877|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008315|C54G4.5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008316|dod-18|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008316|dod-18|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=951|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008316|dod-18|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=592|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008316|dod-18|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008316|dod-18|612nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008316|dod-18|616nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008316|dod-18|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1778|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|281nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|288nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|752nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008317|C54G4.7.1|759nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008318|C54G4.9|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1235|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00008318|C54G4.9|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008318|C54G4.9|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008318|C54G4.9|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008318|C54G4.9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008319|C54G10.1|1300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008319|C54G10.1|1304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008319|C54G10.1|1307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008320|C54G10.4b.2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008320|C54G10.4b.2|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008320|C54G10.4b.2|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00008320|C54G10.4b.2|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008322|C55A1.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008323|C55A1.6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008323|C55A1.6|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008323|C55A1.6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1476|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008323|C55A1.6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008323|C55A1.6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008323|C55A1.6|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008325|C55A1.9|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008325|C55A1.9|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008327|srz-44|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008328|srz-43|359nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008328|srz-43|361nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008328|srz-43|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008330|C55A6.1.1|205nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008330|C55A6.1.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008330|C55A6.1.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3585|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008330|C55A6.1.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4355|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008331|ttll-5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008332|C55A6.3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008332|C55A6.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008332|C55A6.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00008332|C55A6.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008332|C55A6.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008333|C55A6.4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008333|C55A6.4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008333|C55A6.4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1134|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008333|C55A6.4|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008333|C55A6.4|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008333|C55A6.4|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=323|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008333|C55A6.4|264nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008334|sdz-8|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008334|sdz-8|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008334|sdz-8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008335|C55A6.6|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008335|C55A6.6|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008335|C55A6.6|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008335|C55A6.6|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008335|C55A6.6|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2552|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|155nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008336|C55A6.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=300|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7014|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008338|pafo-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008339|C55A6.10a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008339|C55A6.10a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008339|C55A6.10a|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008339|C55A6.10a|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1810|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1406nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1415nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1431nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|1563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008340|C55A6.11|597nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=809|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1583|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008341|ttr-44|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|372nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1459|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|423nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008342|frpr-5|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10472|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1259|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008343|C56A3.4b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008344|C56A3.5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3527|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008344|C56A3.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008345|C56A3.6a.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4197|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008345|C56A3.6a.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008345|C56A3.6a.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008345|C56A3.6a.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008345|C56A3.6a.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008345|C56A3.6a.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008346|C56A3.8a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00008346|C56A3.8a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008346|C56A3.8a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008346|C56A3.8c|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|32nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1205|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008348|C56G7.3a|964nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008349|CE7X_3.1|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008349|CE7X_3.1|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008349|CE7X_3.1|467nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008349|CE7X_3.1|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008352|fbxa-6|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008352|fbxa-6|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008352|fbxa-6|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008352|fbxa-6|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008352|fbxa-6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00008352|fbxa-6|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|1496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|1586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|1592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1577|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008353|D1025.1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008354|gcsh-1|1282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008354|gcsh-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008354|gcsh-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008354|gcsh-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=987|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008355|fbxa-141|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008355|fbxa-141|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008355|fbxa-141|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008355|fbxa-141|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008355|fbxa-141|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=377|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38639|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008356|nspc-20|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2654|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4699|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1224|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008358|nspc-18|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008360|nspc-19|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008360|nspc-19|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3314|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008360|nspc-19|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3150|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008360|nspc-19|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008360|nspc-19|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008360|nspc-19|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2258|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008361|D1043.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|1175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|1178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|1180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|1185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|1279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008362|cfim-2|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008363|D1046.2.1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008363|D1046.2.1|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=880|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008363|D1046.2.1|411nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008363|D1046.2.1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008363|D1046.2.1|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008363|D1046.2.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|263nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|265nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|498nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008364|D1046.3|505nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=559|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008365|D1046.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008366|tpra-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008366|tpra-1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=734|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008366|tpra-1|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=727|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008366|tpra-1|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=695|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008366|tpra-1|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008367|D1053.2|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008368|D1053.3|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008368|D1053.3|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008368|D1053.3|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=628|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008368|D1053.3|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008368|D1053.3|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008369|D1053.4|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00008369|D1053.4|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008369|D1053.4|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008369|D1053.4|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008370|D1054.1|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008370|D1054.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008370|D1054.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008370|D1054.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008370|D1054.1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008370|D1054.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008370|D1054.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10341|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1735|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008371|D1054.3a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008372|D1054.5|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008372|D1054.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008372|D1054.5|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008372|D1054.5|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008372|D1054.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008372|D1054.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008375|D1054.8|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008375|D1054.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1996|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008375|D1054.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008375|D1054.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008376|D1054.9a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008376|D1054.9a|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1304|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008376|D1054.9a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008376|D1054.9a|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008376|D1054.9a|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008376|D1054.9a|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008376|D1054.9a|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=389|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6306|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2750|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51562|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17556|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36144|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3602|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1797|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=454|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008377|D1054.10|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14236|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30666|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1308|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008378|D1054.11|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008379|secs-1|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008379|secs-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008379|secs-1|64nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008379|secs-1|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008379|secs-1|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008379|secs-1|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=432|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008379|secs-1|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=233|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2917|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|156nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|158nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008380|prp-38|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008381|D1081.3|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00008381|D1081.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008381|D1081.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008382|D1081.4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=850|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008382|D1081.4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008382|D1081.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008383|D1081.5|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008383|D1081.5|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008383|D1081.5|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008383|D1081.5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008383|D1081.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00008383|D1081.5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008383|D1081.5|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008384|D1081.6a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008384|D1081.6a|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1548|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008384|D1081.6b|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008384|D1081.6b|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008384|D1081.6b|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008385|D1081.7|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008385|D1081.7|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008385|D1081.7|1117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008385|D1081.7|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008385|D1081.7|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008385|D1081.7|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=321|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008385|D1081.7|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5213|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=452|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5772|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2637|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008386|cdc-5L|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008387|D1081.9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008387|D1081.9|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008387|D1081.9|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008387|D1081.9|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1063|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008387|D1081.9|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008387|D1081.9|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008387|D1081.9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|400nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=923|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008388|D1086.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008389|D1086.2b|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008389|D1086.2b|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008389|D1086.2b|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008389|D1086.2b|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00008389|D1086.2b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008389|D1086.2b|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10871|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008390|D1086.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008392|D1086.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008392|D1086.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=553|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|1322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|1440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|1442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|1586nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=324|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|1594nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3598|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008393|D1086.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=798|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1119|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=396|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008394|D1086.7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008395|D1086.8a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008395|D1086.8a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008395|D1086.8a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008395|D1086.8a|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008395|D1086.8a|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00008395|D1086.8a|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008396|D1086.9|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1728|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=833|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008397|D2005.1|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008398|D2005.3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008398|D2005.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008398|D2005.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008398|D2005.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8613|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00008398|D2005.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3262|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008398|D2005.3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008398|D2005.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008399|D2005.4.2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1392|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00008399|D2005.4.2|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008399|D2005.4.2|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008399|D2005.4.2|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=768|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008400|drh-3|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008400|drh-3|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008400|drh-3|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2523|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008400|drh-3|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008400|drh-3|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008400|drh-3|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008400|drh-3|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008401|D2005.6|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008401|D2005.6|727nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008401|D2005.6|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008401|D2005.6|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008401|D2005.6|796nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008401|D2005.6|798nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008401|D2005.6|803nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=958|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2319|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008402|wdfy-2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008403|D2013.3|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008403|D2013.3|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=375|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008403|D2013.3|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|273nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|332nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|334nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|340nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1777|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008404|D2013.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8545|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2157|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=897|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|234nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|238nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|241nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008405|ttll-12|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|1594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8169|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1998|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|302nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|309nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=407|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|321nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008407|D2023.3b|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008408|D2023.4|513nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008408|D2023.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008408|D2023.4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2315|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008408|D2023.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1142|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008408|D2023.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008409|mpst-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008409|mpst-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1388|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008409|mpst-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=630|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|1184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2266|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008410|D2023.6|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2738|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|697nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008411|mans-1|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2965|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|256nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008412|D2030.2a.3|87nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1448|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008413|D2030.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008414|D2030.4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008414|D2030.4|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008414|D2030.4|120nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3953|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008414|D2030.4|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6648|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008414|D2030.4|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=457|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008414|D2030.4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008414|D2030.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4128|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=550|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008415|mce-1|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=594|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2542|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=805|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=278|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008417|D2030.7|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=419|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|629nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|677nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008418|D2030.8|740nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008419|wdr-23|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008419|wdr-23|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008419|wdr-23|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008419|wdr-23|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008419|wdr-23|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008419|wdr-23|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=193|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3048|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1225|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008420|D2030.11|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008421|D2030.12|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008421|D2030.12|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008421|D2030.12|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008421|D2030.12|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008421|D2030.12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008421|D2030.12|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008421|D2030.12|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1178|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|229nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|234nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|73nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=438|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|78nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1201|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|88nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008422|D2045.2|93nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=232|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|315nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008423|D2045.5|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008424|D2045.7|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008424|D2045.7|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=575|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008424|D2045.7|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008424|D2045.7|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008425|D2045.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008425|D2045.8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008426|D2045.9|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008426|D2045.9|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=705|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008426|D2045.9|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008426|D2045.9|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008427|atg-10|1014nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008427|atg-10|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=478|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008427|atg-10|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008427|atg-10|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008428|D2085.3|276nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1662|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00008428|D2085.3|279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008428|D2085.3|314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008428|D2085.3|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008428|D2085.3|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=444|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2489|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008429|D2085.4|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008430|hgap-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008430|hgap-2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008430|hgap-2|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1911|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008430|hgap-2|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008430|hgap-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008430|hgap-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008431|piga-1|1165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008431|piga-1|1211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008431|piga-1|1289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008431|piga-1|1294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008431|piga-1|1299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008431|piga-1|1303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008431|piga-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1917|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008432|D2085.7a|697nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008432|D2085.7a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2174|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008432|D2085.7a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008433|marc-2|1467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008433|marc-2|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008433|marc-2|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008433|marc-2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008433|marc-2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008434|D2089.3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008434|D2089.3|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008434|D2089.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008434|D2089.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008434|D2089.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008434|D2089.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008434|D2089.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=509|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00008435|glna-2|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008436|DH11.2.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5a|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5a|1239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5a|1295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5a|1297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5a|560nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1277|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1581|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|352nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5b|464nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=840|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4697|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008438|DH11.5d|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008439|mfb-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008439|mfb-1|524nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008439|mfb-1|535nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1476|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|1328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2567|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|195nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008440|DY3.8|634nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008441|E01B7.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008441|E01B7.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008441|E01B7.1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=886|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008441|E01B7.1|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=672|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008442|E01B7.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008443|pde-3|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008443|pde-3|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008443|pde-3|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008443|pde-3|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008443|pde-3|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1286|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008444|tbc-14|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|185nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|188nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2599|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28663|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1137|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008446|E01G4.3b.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|1133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=855|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008447|E01G4.5|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008448|E01G4.6|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008448|E01G4.6|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1324|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008448|E01G4.6|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008448|E01G4.6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008448|E01G4.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008449|E01G6.1|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=249|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008449|E01G6.1|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008449|E01G6.1|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008449|E01G6.1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|405nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008450|E01G6.2|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008451|E01G6.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008451|E01G6.3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008451|E01G6.3|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008451|E01G6.3|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008451|E01G6.3|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008452|mrps-5|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008452|mrps-5|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2639|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008452|mrps-5|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2334|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008452|mrps-5|149nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008452|mrps-5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008453|E02A10.3b|1111nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008453|E02A10.3b|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008453|E02A10.3b|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008453|E02A10.3b|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008453|E02A10.3b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22928|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008453|E02A10.3b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1085|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008454|E02A10.4|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008454|E02A10.4|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008454|E02A10.4|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3310|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008454|E02A10.4|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008454|E02A10.4|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008454|E02A10.4|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008454|E02A10.4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1086|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|1600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=304|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008455|E02H1.1.1|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=824|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|1574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=410|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008456|E02H1.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008457|E02H1.5|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008457|E02H1.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008457|E02H1.5|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008457|E02H1.5|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008457|E02H1.5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=390|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008457|E02H1.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1373|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008457|E02H1.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=423|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00008458|E02H1.6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1023|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008458|E02H1.6|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3132|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008458|E02H1.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008459|mrpl-53|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5572|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008459|mrpl-53|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008459|mrpl-53|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008459|mrpl-53|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008460|E02H4.2|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=583|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=494|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008462|E02H4.4|99nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008463|E02H4.5|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008464|E02H4.6|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008464|E02H4.6|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1119|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008464|E02H4.6|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008468|E03G2.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008468|E03G2.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008468|E03G2.1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008471|E03H4.3|26nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008475|oac-13|1167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00008475|oac-13|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008475|oac-13|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2325|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008476|E03H4.8|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008477|clec-17|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008477|clec-17|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008477|clec-17|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008477|clec-17|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008477|clec-17|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008477|clec-17|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008477|clec-17|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=624|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2253|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1805|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=686|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=865|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|290nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|295nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=950|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7411|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1a.2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1b|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1b|1094nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1b|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1b|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008480|E04D5.1b|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|166nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=712|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008481|E04D5.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008482|cut-4|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008482|cut-4|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008482|cut-4|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008482|cut-4|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008483|E04D5.4a|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008483|E04D5.4a|695nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008483|E04D5.4a|702nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008483|E04D5.4a|706nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008483|E04D5.4a|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008483|E04D5.4a|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=380|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1176|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|344nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|347nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32236|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3309|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008484|E04D5.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008485|ugt-43|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008485|ugt-43|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008485|ugt-43|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008485|ugt-43|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008485|ugt-43|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008485|ugt-43|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008485|ugt-43|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008486|ugt-44|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008486|ugt-44|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2162|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008486|ugt-44|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008486|ugt-44|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008486|ugt-44|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008488|F01D4.5b|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=444|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008488|F01D4.5b|1338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008488|F01D4.5b|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008488|F01D4.5b|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008488|F01D4.5b|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008489|srb-17|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008490|F01D4.8|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008490|F01D4.8|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008491|F01D4.9|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008491|F01D4.9|397nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008491|F01D4.9|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008491|F01D4.9|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008491|F01D4.9|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008491|F01D4.9|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008492|F01D5.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1296|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008492|F01D5.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008493|F01D5.2|21nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008493|F01D5.2|27nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=370|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00008493|F01D5.2|30nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008493|F01D5.2|33nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008493|F01D5.2|35nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008493|F01D5.2|39nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008494|F01D5.3|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008494|F01D5.3|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008494|F01D5.3|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008494|F01D5.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008494|F01D5.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00008494|F01D5.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008494|F01D5.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008495|F01D5.5|1219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008495|F01D5.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008495|F01D5.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008495|F01D5.5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008495|F01D5.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1491|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008495|F01D5.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008495|F01D5.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008496|F01D5.6|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008496|F01D5.6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008497|F01D5.7b|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008497|F01D5.7b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008497|F01D5.7b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008497|F01D5.7b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008498|F01D5.8a.2|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008498|F01D5.8a.2|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=836|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008498|F01D5.8a.2|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008498|F01D5.8a.2|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008498|F01D5.8a.2|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008498|F01D5.8a.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008499|cyp-37A1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008499|cyp-37A1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=643|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008499|cyp-37A1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008499|cyp-37A1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008499|cyp-37A1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008500|F01D5.10|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008500|F01D5.10|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1009|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|1417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=492|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008502|skih-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=529|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|341nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=716|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=739|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|413nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|418nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|420nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|423nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008503|F01G4.4a|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=441|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1554|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008504|F01G4.5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=848|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=603|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|262nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39331|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|273nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=461|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=744|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2061|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=870|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2708|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|327nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|335nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=849|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|340nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1386|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7447|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3422|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1296|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|413nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|415nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|435nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|446nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|449nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008505|F01G4.6b.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2367|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008506|tkt-1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17243|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008507|F01G10.4|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008508|F01G10.5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008508|F01G10.5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008508|F01G10.5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008508|F01G10.5|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008509|F01G10.6|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008509|F01G10.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008509|F01G10.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008509|F01G10.6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008509|F01G10.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008510|lipl-7|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008510|lipl-7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008510|lipl-7|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008510|lipl-7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008511|F01G10.9|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008511|F01G10.9|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008511|F01G10.9|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008511|F01G10.9|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008512|F01G10.10|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008512|F01G10.10|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2674|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008513|F02A9.1|969nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1732|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=638|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|249nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|253nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=437|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|258nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=847|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=795|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=448|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=369|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|413nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|418nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008514|F02A9.4b|592nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=398|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=693|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008515|F02C12.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=438|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|479nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|489nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|497nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008516|F02C12.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008517|F02C12.3|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008517|F02C12.3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008518|irld-2|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008519|cyp-13B1|1244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008519|cyp-13B1|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008519|cyp-13B1|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008519|cyp-13B1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008519|cyp-13B1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008520|F02D8.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008521|F02D8.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=478|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008521|F02D8.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=835|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008521|F02D8.4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008521|F02D8.4|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008521|F02D8.4|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008521|F02D8.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008521|F02D8.4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008522|F02D8.5|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008522|F02D8.5|396nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4763|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008522|F02D8.5|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008522|F02D8.5|444nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008522|F02D8.5|494nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008522|F02D8.5|536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008524|F02D10.3|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008526|F02D10.6|1370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008526|F02D10.6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008526|F02D10.6|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|324nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1015|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=742|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008528|F02E9.1|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=351|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008529|F02E9.3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008529|F02E9.3|152nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008529|F02E9.3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008529|F02E9.3|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008529|F02E9.3|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=416|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5064|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1199|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|731nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008530|F02E9.5b|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008531|F02E9.7|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008531|F02E9.7|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1550|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008531|F02E9.7|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008532|dpt-1|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3281|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008532|dpt-1|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008532|dpt-1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008532|dpt-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008532|dpt-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008532|dpt-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008533|F02E9.10c.1|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3311|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008533|F02E9.10c.1|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008535|F02H6.2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008536|F02H6.3a.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008536|F02H6.3a.2|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008536|F02H6.3a.2|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008536|F02H6.3b|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008538|sqrd-1|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008538|sqrd-1|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008538|sqrd-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008538|sqrd-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1571|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008539|F02H6.6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008540|F02H6.7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008541|F07A5.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3827|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008541|F07A5.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008541|F07A5.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008541|F07A5.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008542|scav-6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008542|scav-6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008542|scav-6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008542|scav-6|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|1162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1386|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|1512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|1515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|1526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|1531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=366|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008543|F07A5.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008545|F07A11.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00008545|F07A11.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15676|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008546|gfat-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008547|F07A11.4a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008547|F07A11.4a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008547|F07A11.4a|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008547|F07A11.4a|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=600|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00008547|F07A11.4a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008548|F07A11.5|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008548|F07A11.5|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008548|F07A11.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1342|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|600nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|604nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|608nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|613nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|618nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4583|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|622nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=414|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008549|din-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008550|F07B10.4a|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00008550|F07B10.4a|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=491|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008550|F07B10.4a|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008551|lgc-36|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008551|lgc-36|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008551|lgc-36|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008551|lgc-36|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008552|srsx-31|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008552|srsx-31|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008553|F07C6.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008553|F07C6.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008553|F07C6.2|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008553|F07C6.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008553|F07C6.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008553|F07C6.2|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008553|F07C6.2|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=432|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008554|F07C6.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4d|503nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=715|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4d|509nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=999|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4e|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4e|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4e|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4e|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4e|514nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008555|F07C6.4e|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=744|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008556|F07D3.3|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008556|F07D3.3|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008556|F07D3.3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008556|F07D3.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008556|F07D3.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008556|F07D3.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008557|F07H5.6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8613|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|793nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008558|F07H5.7|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008559|F07H5.8|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008559|F07H5.8|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008559|F07H5.8|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008559|F07H5.8|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008560|pho-13|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008560|pho-13|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008560|pho-13|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008560|pho-13|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008560|pho-13|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008560|pho-13|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008561|F07H5.10|1058nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008561|F07H5.10|1073nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008561|F07H5.10|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1883|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008561|F07H5.10|255nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008561|F07H5.10|257nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008561|F07H5.10|264nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|1013nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|534nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|539nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008563|F07H5.13|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=596|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|1096nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=455|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008564|acox-1|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008565|acox-2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008565|acox-2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008565|acox-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008565|acox-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=868|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008565|acox-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008566|acox-3|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008566|acox-3|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=498|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008566|acox-3|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008566|acox-3|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008566|acox-3|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008566|acox-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|1257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|1376nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|1381nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|1410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008567|F08A8.4.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008568|F08A8.5a|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008568|F08A8.5a|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008568|F08A8.5a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008569|fbxa-101|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008569|fbxa-101|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008569|fbxa-101|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=939|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008569|fbxa-101|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=558|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008570|kcnl-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008570|kcnl-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1006|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008570|kcnl-2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1154|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008570|kcnl-2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008570|kcnl-2|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008570|kcnl-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008571|prmn-1|1066nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008571|prmn-1|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008571|prmn-1|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1330|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008571|prmn-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008571|prmn-1|547nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008571|prmn-1|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15058|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2076|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|1364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008572|F08B12.4c.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008574|srbc-61|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008574|srbc-61|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008574|srbc-61|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00008574|srbc-61|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008575|scl-24|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008576|F08G2.4|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=286|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00008576|F08G2.4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008576|F08G2.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008576|F08G2.4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008576|F08G2.4|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=929|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|177nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2369|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008577|F08G2.5|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008578|F08G2.7|1275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008578|F08G2.7|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008578|F08G2.7|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008578|F08G2.7|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008578|F08G2.7|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008578|F08G2.7|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008579|F08G2.8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008579|F08G2.8|676nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008580|dsb-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008580|dsb-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008580|dsb-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1179|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008580|dsb-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008580|dsb-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008581|acl-13|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008581|acl-13|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=682|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008581|acl-13|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008582|F08G5.3b|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008582|F08G5.3b|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7296|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008582|F08G5.3b|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008582|F08G5.3b|22nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008582|F08G5.3b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008582|F08G5.3b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008583|ugt-65|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008583|ugt-65|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008583|ugt-65|1560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008583|ugt-65|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008583|ugt-65|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=522|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008583|ugt-65|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008583|ugt-65|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3604|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008584|F08G5.6|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008585|F08G12.1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008585|F08G12.1|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=251|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008585|F08G12.1|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=171|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008585|F08G12.1|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008585|F08G12.1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008585|F08G12.1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008585|F08G12.1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7543|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=193|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008586|F08G12.2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008587|F08G12.3|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00008587|F08G12.3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008587|F08G12.3|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008587|F08G12.3|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008587|F08G12.3|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008588|F08G12.5|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=481|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|358nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1090|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1810|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6255|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20605|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008589|F08G12.8|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=410|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|28nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|33nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|37nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8580|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008590|F08H9.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008591|F08H9.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008591|F08H9.3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19346|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008592|F08H9.4b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6171|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008593|clec-227|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008594|clec-57|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=613|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008595|clec-56|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1745|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008595|clec-56|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008596|clec-54|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008596|clec-54|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008596|clec-54|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008596|clec-54|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008597|clec-55|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008597|clec-55|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008598|spin-3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008598|spin-3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008598|spin-3|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008599|F09A5.2|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008599|F09A5.2|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008599|F09A5.2|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008599|F09A5.2|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008600|F09A5.3b|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008600|F09A5.3b|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008600|F09A5.3b|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008600|F09A5.3b|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008601|F09A5.4g.1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008601|F09A5.4g.1|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4861|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00008601|F09A5.4g.1|627nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008602|oac-14|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008602|oac-14|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008602|oac-14|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008602|oac-14|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008602|oac-14|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008602|oac-14|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008603|F09B9.4|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008603|F09B9.4|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008603|F09B9.4|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=926|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008603|F09B9.4|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008603|F09B9.4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2055|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008604|F09B9.5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008605|mlt-9|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=189|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008605|mlt-9|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008605|mlt-9|314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1325|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00008605|mlt-9|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=150|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008605|mlt-9|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008606|dhhc-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008606|dhhc-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2532|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008606|dhhc-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008606|dhhc-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008606|dhhc-1|804nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4130|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008607|F09B12.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008609|F09B12.5|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008609|F09B12.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008609|F09B12.5|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008609|F09B12.5|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008609|F09B12.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008609|F09B12.5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|1223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14508|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008610|F09C3.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008611|fbxb-68|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008612|fbxa-103|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00008612|fbxa-103|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00008613|fbxb-69|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008613|fbxb-69|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008613|fbxb-69|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008613|fbxb-69|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=334|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008613|fbxb-69|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008613|fbxb-69|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008615|F09C6.1|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008615|F09C6.1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008615|F09C6.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008616|fbxa-44|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00008616|fbxa-44|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00008617|F09C6.3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008620|F09C6.10|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008620|F09C6.10|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008620|F09C6.10|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008620|F09C6.10|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00008621|F09C8.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2022|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008621|F09C8.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|850nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|859nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|865nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=831|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|869nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|872nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|879nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008622|F09C8.2|883nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008623|F09E8.1a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008623|F09E8.1a|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008623|F09E8.1a|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1057|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=491|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=603|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008624|F09E8.2b|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008625|scl-14|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008625|scl-14|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008626|F09E8.8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008626|F09E8.8|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=744|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008626|F09E8.8|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=607|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00008626|F09E8.8|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008627|F09F3.5|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008628|ttr-21|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008628|ttr-21|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008628|ttr-21|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6023|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008628|ttr-21|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008629|cpt-5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008629|cpt-5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008629|cpt-5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008630|nhr-175|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008631|F10A3.1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00008631|F10A3.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008631|F10A3.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008632|fbxa-88|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008632|fbxa-88|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008633|fbxa-18|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008633|fbxa-18|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008633|fbxa-18|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008634|F10A3.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008634|F10A3.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008636|F10A3.11|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=551|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008639|F10B5.2|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008640|F10B5.3|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008640|F10B5.3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008640|F10B5.3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008640|F10B5.3|746nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=449|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=469|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008641|pch-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2695|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008642|F10B5.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008643|F10B5.9|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008643|F10B5.9|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008643|F10B5.9|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008643|F10B5.9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008643|F10B5.9|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008643|F10B5.9|923nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|19nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008644|F10C2.3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008645|F10C2.4|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=360|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008645|F10C2.4|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2082|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008645|F10C2.4|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008645|F10C2.4|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008645|F10C2.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008645|F10C2.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008646|F10C2.5|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008646|F10C2.5|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008646|F10C2.5|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008646|F10C2.5|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=585|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008646|F10C2.5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008646|F10C2.5|745nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008647|F10C2.7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008647|F10C2.7|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|1030nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2588|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|319nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=753|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008648|F10D11.2|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=971|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008649|F10D11.3|1529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008650|F10D11.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008650|F10D11.4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008650|F10D11.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008651|F10D11.5|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00008651|F10D11.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008651|F10D11.5|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008652|F10D11.6b|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008652|F10D11.6b|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008652|F10D11.6b|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008652|F10D11.6b|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008652|F10D11.6b|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008652|F10D11.6b|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008652|F10D11.6b|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008654|F10F2.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008654|F10F2.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008654|F10F2.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008654|F10F2.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00008654|F10F2.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=725|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008654|F10F2.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008655|lips-3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008655|lips-3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008655|lips-3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=849|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008655|lips-3|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1692|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3088|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3794|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008656|lron-5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008659|clec-151|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008659|clec-151|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008659|clec-151|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008659|clec-151|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008660|clec-153|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008660|clec-153|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008660|clec-153|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008660|clec-153|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008660|clec-153|666nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008660|clec-153|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008661|F10G8.1a|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=449|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008661|F10G8.1a|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008661|F10G8.1a|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008661|F10G8.1a|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008661|F10G8.1a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008662|F10G8.2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008662|F10G8.2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008663|eak-6|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008663|eak-6|1095nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008663|eak-6|1103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008663|eak-6|1105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1143|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008663|eak-6|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008663|eak-6|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008664|nubp-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3449|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008664|nubp-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008664|nubp-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008664|nubp-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008664|nubp-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008664|nubp-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008664|nubp-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=927|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2019|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008665|ercc-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008666|F10G8.8a|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008666|F10G8.8a|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008666|F10G8.8a|386nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008666|F10G8.8a|388nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1019|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008666|F10G8.8a|390nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008666|F10G8.8a|395nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008666|F10G8.8a|397nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008667|F10G8.9b|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008667|F10G8.9b|22nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008667|F10G8.9b|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008667|F10G8.9b|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=468|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=676|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=644|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008669|acs-14|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008670|F11A3.2a|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008670|F11A3.2a|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008670|F11A3.2a|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008670|F11A3.2a|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008670|F11A3.2a|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=977|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008670|F11A3.2a|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008670|F11A3.2a|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008671|F11A5.3|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008671|F11A5.3|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008671|F11A5.3|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008672|F11A5.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008672|F11A5.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008672|F11A5.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008673|F11A5.5b|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008673|F11A5.5b|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008673|F11A5.5b|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008676|oac-15|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008677|F11A5.9|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008677|F11A5.9|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008677|F11A5.9|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008677|F11A5.9|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008677|F11A5.9|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008677|F11A5.9|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008678|stdh-2|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008678|stdh-2|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008680|F11A5.15|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008680|F11A5.15|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008680|F11A5.15|8nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|220nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008681|scrm-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|133nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|327nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|335nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|339nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=108|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|344nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5306|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4352|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008682|lex-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|1322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|417nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|529nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|562nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7661|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008683|repo-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=314|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=693|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=326|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008684|mig-32|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2045|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008685|mon-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008686|F11A10.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008686|F11A10.5|1287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008686|F11A10.5|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008686|F11A10.5|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1657|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00008686|F11A10.5|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008686|F11A10.5|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008686|F11A10.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008687|F11A10.6b.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008687|F11A10.6b.1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008687|F11A10.6b.1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2876|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008688|F11A10.7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008688|F11A10.7|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008688|F11A10.7|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2182|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00008688|F11A10.7|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=248|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008688|F11A10.7|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008690|F11C1.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1928|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008691|mff-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008691|mff-1|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008691|mff-1|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1587|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008691|mff-1|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008691|mff-1|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008691|mff-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008692|scav-4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008692|scav-4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008692|scav-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008692|scav-4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=302|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008693|F11C1.4|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008693|F11C1.4|1418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008693|F11C1.4|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008693|F11C1.4|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008693|F11C1.4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008693|F11C1.4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008693|F11C1.4|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5a.3|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5a.3|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5a.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=925|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5a.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5a.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5e.3|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1286|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5e.3|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008694|F11C1.5e.3|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008695|F11C3.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008695|F11C3.1|1474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008695|F11C3.1|30nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00008695|F11C3.1|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008698|F11D11.3|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008698|F11D11.3|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008698|F11D11.3|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008698|F11D11.3|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008698|F11D11.3|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008698|F11D11.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008702|clec-252|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008702|clec-252|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008706|gba-3|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008706|gba-3|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=565|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008706|gba-3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19681|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1479|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008707|F11E6.3.1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008708|F11E6.4c|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00008709|F11E6.6|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008709|F11E6.6|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008709|F11E6.6|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008709|F11E6.6|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008709|F11E6.6|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008710|F11E6.7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008710|F11E6.7|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008710|F11E6.7|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=785|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008710|F11E6.7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1687|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008710|F11E6.7|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008710|F11E6.7|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008710|F11E6.7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008711|F11E6.8c|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008711|F11E6.8c|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008711|F11E6.8c|410nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008711|F11E6.8c|413nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=430|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008711|F11E6.8c|433nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|1023nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008712|F11E6.9|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008713|F11E6.10b|1201nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008713|F11E6.10b|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008713|F11E6.10b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008713|F11E6.10b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00008713|F11E6.10b|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008714|F11F1.1a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008714|F11F1.1a|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008714|F11F1.1b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008714|F11F1.1b|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008714|F11F1.1b|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008717|F11F1.5|1258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008719|ttr-52|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=777|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008719|ttr-52|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008719|ttr-52|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008720|F12F6.1|1280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008720|F12F6.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008720|F12F6.1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008720|F12F6.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008720|F12F6.1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1854|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008720|F12F6.1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2019|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008720|F12F6.1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1243|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008722|F12F6.7.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008724|F13A7.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008724|F13A7.1|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008724|F13A7.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008724|F13A7.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008724|F13A7.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008725|F13A7.7|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008725|F13A7.7|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008725|F13A7.7|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008725|F13A7.7|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008725|F13A7.7|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008726|F13A7.11|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008726|F13A7.11|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008726|F13A7.11|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008726|F13A7.11|667nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008727|F13A7.12|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008727|F13A7.12|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008727|F13A7.12|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008727|F13A7.12|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008727|F13A7.12|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008727|F13A7.12|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008727|F13A7.12|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008728|sre-36|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00008728|sre-36|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4068|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008729|F13B12.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008730|F13B12.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008731|F13B12.3a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008731|F13B12.3a|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008731|F13B12.3a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008732|F13B12.4a.1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008733|F13B12.6|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008733|F13B12.6|672nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008733|F13B12.6|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1046|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008733|F13B12.6|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1705|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008733|F13B12.6|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008734|F13B12.7|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008734|F13B12.7|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=959|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008735|F13D2.1a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008736|gnrr-6|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008736|gnrr-6|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008737|gnrr-7|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008737|gnrr-7|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008737|gnrr-7|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008737|gnrr-7|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008737|gnrr-7|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008737|gnrr-7|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008739|F13D12.3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1897|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008739|F13D12.3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008739|F13D12.3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008739|F13D12.3|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008739|F13D12.3|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008739|F13D12.3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008739|F13D12.3|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008740|F13D12.5|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=801|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008740|F13D12.5|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1106|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008740|F13D12.5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008740|F13D12.5|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008740|F13D12.5|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|1157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|1166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|347nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|349nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|438nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=798|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12767|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|524nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=862|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008741|F13D12.6.1|883nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1837|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=539|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=278|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008742|F13D12.8|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=726|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008743|F13D12.9.3|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008744|F13D12.10|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1471|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008744|F13D12.10|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8088|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5213|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008745|F13E6.1|886nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008746|F13E6.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008746|F13E6.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=326|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008747|phf-31|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008747|phf-31|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008747|phf-31|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|331nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=712|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008748|yap-1|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|181nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=341|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|190nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=718|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008749|F13E6.5|192nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2404|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008750|F13E9.1|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008754|F13E9.5|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008754|F13E9.5|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008754|F13E9.5|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008755|sdz-13|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008755|sdz-13|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008757|F13E9.8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008757|F13E9.8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008759|F13E9.10|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008760|F13E9.11b|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008760|F13E9.11b|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6847|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008760|F13E9.11b|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008760|F13E9.11b|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008760|F13E9.11b|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008761|F13E9.12|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008761|F13E9.12|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3105|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|681nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|686nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|881nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00008762|ztf-2|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008763|F13G3.3b|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008763|F13G3.3b|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008764|dylt-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008764|dylt-1|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008764|dylt-1|290nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5613|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008764|dylt-1|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4419|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9461|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008765|ttx-7|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008766|F13G3.6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2190|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008767|F13G3.7b.2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008767|F13G3.7b.2|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2787|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008767|F13G3.7b.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008768|F13G3.10c|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008768|F13G3.10c|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008768|F13G3.10c|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7054|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008768|F13G3.10c|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1823|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=444|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=320|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|121nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008769|mrpl-13|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|1218nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008770|F13G3.12|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008772|irld-4|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008772|irld-4|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=323|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008772|irld-4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008773|F13H10.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008773|F13H10.1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=709|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008773|F13H10.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008773|F13H10.1|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008773|F13H10.1|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|1226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|395nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1247|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|404nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008774|F13H10.3c.1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008775|mogs-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008775|mogs-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2631|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008775|mogs-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008776|F13H10.5|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008776|F13H10.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008776|F13H10.5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008776|F13H10.5|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=914|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|1398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=607|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2331|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1358|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4581|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=754|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|643nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008777|F13H10.6a|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008778|nhr-264|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008779|F14B4.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1368|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008779|F14B4.1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008779|F14B4.1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008779|F14B4.1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008779|F14B4.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|1128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|1130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|1134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|404nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|407nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9090|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=605|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|459nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|462nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|466nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|483nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|756nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008780|hxk-1|758nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|1250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1395|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=385|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008781|rpoa-2|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008782|sdz-14|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008782|sdz-14|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008782|sdz-14|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008782|sdz-14|253nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008782|sdz-14|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008783|F14B6.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008783|F14B6.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1338|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008783|F14B6.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008783|F14B6.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008784|F14B6.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008784|F14B6.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008787|F14B6.6a|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008787|F14B6.6a|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008787|F14B6.6a|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008787|F14B6.6a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008787|F14B6.6a|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008788|F14D7.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=381|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008789|F14D7.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|1205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|510nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008790|F14D7.3|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008792|F14D7.5b|1573nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008792|F14D7.5b|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008792|F14D7.5b|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008792|F14D7.5b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008793|F14D7.6d|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=983|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008793|F14D7.6d|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008794|F14D7.7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008794|F14D7.7|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008794|F14D7.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008794|F14D7.7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008795|F14D7.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008795|F14D7.8|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=862|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008795|F14D7.8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008796|F14D7.9|1548nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008797|F14D7.10|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=721|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00008797|F14D7.10|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008797|F14D7.10|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008798|F14D7.11|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008798|F14D7.11|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008798|F14D7.11|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1176|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008798|F14D7.11|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1116|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008798|F14D7.11|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008799|F14E5.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4752|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008800|F14E5.2a.1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008801|acp-3|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008801|acp-3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008801|acp-3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008802|acp-2|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008802|acp-2|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008802|acp-2|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=459|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008802|acp-2|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008802|acp-2|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008802|acp-2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008802|acp-2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|1333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|1470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|1506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4922|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=395|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008803|lips-10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008804|acp-4|282nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008804|acp-4|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008805|git-1|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008806|mboa-7|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=605|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008806|mboa-7|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=344|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008806|mboa-7|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008806|mboa-7|742nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008807|F14F3.4|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=726|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008807|F14F3.4|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008807|F14F3.4|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008807|F14F3.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008807|F14F3.4|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008807|F14F3.4|945nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008808|ntr-2|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008808|ntr-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00008808|ntr-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008809|cyp-13A11|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008810|cyp-13A12|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008810|cyp-13A12|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008811|F14F7.4|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008811|F14F7.4|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008811|F14F7.4|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008811|F14F7.4|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=499|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008811|F14F7.4|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008811|F14F7.4|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008812|F14F7.5b|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008815|srz-103|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1805|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008816|F14F8.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008818|srz-101|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00008818|srz-101|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1127|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1983|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|176nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|179nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|527nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008819|shw-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15614|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|646nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008820|F14F11.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008821|best-12|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008821|best-12|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008821|best-12|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008821|best-12|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008822|F14H3.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008822|F14H3.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008822|F14H3.3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00008822|F14H3.3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008823|F14H3.4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008823|F14H3.4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008823|F14H3.4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008823|F14H3.4|226nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008823|F14H3.4|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008823|F14H3.4|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008823|F14H3.4|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008824|F14H3.5|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008824|F14H3.5|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008824|F14H3.5|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008824|F14H3.5|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|1304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3833|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008825|F14H3.6|842nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008826|fbxa-100|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008829|cyp-35D1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008829|cyp-35D1|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008830|nhr-176|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008830|nhr-176|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008830|nhr-176|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008831|F14H3.12|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008831|F14H3.12|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008832|obr-2|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1110|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008832|obr-2|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=439|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008832|obr-2|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008832|obr-2|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008833|F14H8.2|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008833|F14H8.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008833|F14H8.2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008833|F14H8.2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008833|F14H8.2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008834|F14H8.4|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008834|F14H8.4|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008838|F15A4.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008838|F15A4.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008838|F15A4.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008838|F15A4.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008838|F15A4.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008838|F15A4.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008839|sre-37|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008839|sre-37|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008840|F15A4.5|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008840|F15A4.5|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008840|F15A4.5|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008840|F15A4.5|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6090|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008841|F15A4.6|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008843|arrd-9|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008843|arrd-9|318nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008844|F15A4.10|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=602|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008844|F15A4.10|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008844|F15A4.10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008844|F15A4.10|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008847|fbxb-102|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008848|inft-2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008848|inft-2|365nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1921|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008848|inft-2|368nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008849|try-10|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008849|try-10|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008849|try-10|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008849|try-10|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00008849|try-10|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008849|try-10|723nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008850|F15B9.6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008850|F15B9.6|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008850|F15B9.6|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008851|F15B9.8.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008851|F15B9.8.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008851|F15B9.8.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=633|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008851|F15B9.8.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=687|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=951|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8750|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27656|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|511nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|528nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|564nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|755nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|760nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|783nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008852|ubql-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008853|clec-101|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008853|clec-101|20nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008853|clec-101|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00008854|F15D3.4|1595nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008854|F15D3.4|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|329nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2309|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=192|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008856|F15D3.6|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008857|timm-23|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008857|timm-23|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008857|timm-23|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4771|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008857|timm-23|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008857|timm-23|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008857|timm-23|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|427nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|438nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008858|F15D3.8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008859|F15D4.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008859|F15D4.2|605nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008859|F15D4.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008859|F15D4.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2039|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008859|F15D4.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008859|F15D4.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008860|rmo-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008860|rmo-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2562|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008860|rmo-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008860|rmo-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=778|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008860|rmo-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008861|F15D4.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008861|F15D4.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008862|F15D4.5|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=700|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008862|F15D4.5|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008862|F15D4.5|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008862|F15D4.5|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008863|F15D4.6.2|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=588|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18143|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=717|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008865|F15G9.1a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|1080nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=934|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|1082nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|1435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|1498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|1502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008868|F15G9.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008869|F15G9.6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008869|F15G9.6|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008869|F15G9.6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008869|F15G9.6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008870|F15H9.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008870|F15H9.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008871|tag-314|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008871|tag-314|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008871|tag-314|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008871|tag-314|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008871|tag-314|993nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008872|F15H10.5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|695nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008874|F15H10.7|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008875|F15H10.8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008875|F15H10.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|515nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|517nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2034|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|520nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|522nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008876|F16A11.1b|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=768|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008877|rtcb-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|1519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|1548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|1550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|1552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4838|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1315|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008878|ppfr-1|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008879|F16B12.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008879|F16B12.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1178|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008880|F16B12.4|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008880|F16B12.4|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008880|F16B12.4|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008880|F16B12.4|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008880|F16B12.4|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008880|F16B12.4|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008881|F16B12.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=648|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008882|F16B12.6|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008883|F16B12.7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008883|F16B12.7|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008883|F16B12.7|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008884|nhr-281|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00008884|nhr-281|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00008885|F16C3.1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008885|F16C3.1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1436|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00008885|F16C3.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008886|F16C3.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008887|tbcd-1|1268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008887|tbcd-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008887|tbcd-1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2580|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008887|tbcd-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008889|F16D3.6|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008889|F16D3.6|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008889|F16D3.6|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008889|F16D3.6|521nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008890|ser-5|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=708|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00008890|ser-5|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008890|ser-5|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008891|clec-42|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008891|clec-42|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008891|clec-42|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008892|clec-246|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008892|clec-246|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008892|clec-246|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008892|clec-246|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008892|clec-246|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008894|F16H6.4a|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008894|F16H6.4b|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008894|F16H6.4b|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008897|F16H6.7|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008899|F16H6.9|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00008899|F16H6.9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008899|F16H6.9|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1121|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008900|F16H6.10|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008901|nhr-27|56nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008901|nhr-27|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008901|nhr-27|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008901|nhr-27|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008902|phf-32|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008902|phf-32|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008902|phf-32|544nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008903|F17A2.4|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008904|F17A2.13|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008904|F17A2.13|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008904|F17A2.13|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008904|F17A2.13|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008905|F17B5.1a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00008905|F17B5.1a|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00008908|F17B5.4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008908|F17B5.4|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008908|F17B5.4|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=184|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00008908|F17B5.4|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008908|F17B5.4|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008910|F17C8.3|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008910|F17C8.3|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008910|F17C8.3|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008910|F17C8.3|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008910|F17C8.3|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008910|F17C8.3|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008911|F17C8.6|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008911|F17C8.6|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=589|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008911|F17C8.6|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008911|F17C8.6|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|1134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|1136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1283|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008912|F17C8.7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008913|F17C11.1|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00008913|F17C11.1|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28103|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3504|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13960|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|329nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|334nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008914|F17C11.2|903nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=342|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4883|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=629|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|469nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008915|F17C11.4b|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008916|clec-221|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008916|clec-221|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|17nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1483|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008917|F17C11.6.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2418|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00008918|F17C11.7a|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=388|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=493|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|1518nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3929|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=316|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008919|vps-36|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=256|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1159|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102534|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1405|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=859|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92685|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3792|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008920|eef-1G|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1232|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1551|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=337|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|906nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008921|F17C11.10|908nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=365|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|404nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|507nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|517nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=788|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35701|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19943|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=788|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=337|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008922|F17C11.11b|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008923|F17C11.12b.1|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008923|F17C11.12b.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=890|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008923|F17C11.12b.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008924|F17E5.2|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008924|F17E5.2|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00008924|F17E5.2|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00008924|F17E5.2|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008924|F17E5.2|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008924|F17E5.2|684nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008925|F17H10.1.2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2582|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008925|F17H10.1.2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=756|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008926|F17H10.2a|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008927|snx-17|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008927|snx-17|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1498|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008927|snx-17|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008927|snx-17|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008927|snx-17|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008929|F18A11.2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008929|F18A11.2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008929|F18A11.2|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008929|F18A11.2|439nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008929|F18A11.2|912nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008929|F18A11.2|916nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15597|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6479|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008930|F18A11.3|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=444|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=673|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5b|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5b|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5b|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5b|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5b|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=404|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008932|F18A11.5b|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008934|F18C12.3|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1510|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008934|F18C12.3|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008935|F18C12.4|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008935|F18C12.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008935|F18C12.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=256|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=333|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=895|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008936|papl-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008937|srt-43|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008937|srt-43|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|1030nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=494|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008939|F18H3.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=713|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=703|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1371|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|755nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008940|F18H3.4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3490|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1189|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=188|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008944|F19B2.5.1|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008945|F19B2.6|1601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00008945|F19B2.6|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008945|F19B2.6|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008946|F19B2.7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3948|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=605|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|931nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008948|F19B6.1c|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008949|F19B6.3|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008949|F19B6.3|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008950|wht-5|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008950|wht-5|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|467nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=687|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|469nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1490|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|475nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|477nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008951|F19C6.2b|568nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|295nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|297nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|366nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00008952|F19C6.3|659nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008953|F19C6.4a|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008953|F19C6.4a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008953|F19C6.4a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00008953|F19C6.4a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008953|F19C6.4a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008953|F19C6.4a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008954|F19C6.5|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008954|F19C6.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008954|F19C6.5|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008954|F19C6.5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008955|F19D8.2|625nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008955|F19D8.2|631nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=156|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008955|F19D8.2|633nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008955|F19D8.2|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008956|nekl-3|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=474|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008956|nekl-3|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008956|nekl-3|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008956|nekl-3|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008957|glb-13|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008957|glb-13|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=843|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008957|glb-13|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008958|F19H6.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008958|F19H6.3|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008958|F19H6.3|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008959|F19H6.4|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008959|F19H6.4|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=834|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008959|F19H6.4|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=520|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008959|F19H6.4|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008959|F19H6.4|151nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=68|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008959|F19H6.4|156nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008960|F19H6.5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00008960|F19H6.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00008961|F19H6.6|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008963|F19H8.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008963|F19H8.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008963|F19H8.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008963|F19H8.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008963|F19H8.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008963|F19H8.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008963|F19H8.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008964|mltn-9|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008964|mltn-9|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008964|mltn-9|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008964|mltn-9|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=388|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008964|mltn-9|470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008965|mltn-10|133nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00008965|mltn-10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008965|mltn-10|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008965|mltn-10|947nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008967|F20B10.3.2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008967|F20B10.3.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008968|F20C5.3d|402nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008968|F20C5.3d|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008968|F20C5.3d|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008968|F20C5.3d|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3570|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008968|F20C5.3d|693nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008968|F20C5.3d|695nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008969|F20C5.4|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008969|F20C5.4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008969|F20C5.4|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008969|F20C5.4|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008969|F20C5.4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008969|F20C5.4|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008969|F20C5.4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008970|F20C5.5.2|219nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008970|F20C5.5.2|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008970|F20C5.5.2|228nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=844|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008971|F20C5.6|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008972|F20C5.7|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008972|F20C5.7|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008972|F20C5.7|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008972|F20C5.7|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008972|F20C5.7|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00008972|F20C5.7|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6636|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008973|F20D1.1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2041|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008974|tbc-1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11853|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2809|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008975|F20D1.3|482nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1229nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8238|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1069|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|1258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008976|plp-2|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008977|iglr-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00008977|iglr-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008977|iglr-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008977|iglr-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1072|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008978|cutl-3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008978|cutl-3|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008978|cutl-3|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008978|cutl-3|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008978|cutl-3|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008978|cutl-3|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008979|F20D1.9|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008979|F20D1.9|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1452|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008979|F20D1.9|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1631|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=319|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2585|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|935nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|938nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|945nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|948nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008980|emre-1|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008982|srsx-2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008982|srsx-2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008982|srsx-2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008982|srsx-2|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008985|F20G2.1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=204|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008986|F20G2.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008986|F20G2.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1522|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008986|F20G2.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=873|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008986|F20G2.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008986|F20G2.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1661|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|1151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008987|F20G2.3b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00008988|F20G2.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008989|F20G2.6b|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008989|F20G2.6b|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2477|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008989|F20G2.6b|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008989|F20G2.6b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1660|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008990|smgl-1|963nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008991|F20G4.2|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008992|F21A3.2|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008993|F21A3.3|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=460|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008993|F21A3.3|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008994|F21A3.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008995|prde-1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008995|prde-1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=615|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008995|prde-1|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008996|glb-14|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008997|lgc-31|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3426|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00008998|ncs-4|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00008998|ncs-4|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008998|ncs-4|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008998|ncs-4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|599nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|609nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|668nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|679nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=467|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|857nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1554|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|859nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4363|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|862nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|864nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|869nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00008999|myrf-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009000|arrd-28|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009000|arrd-28|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009000|arrd-28|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009000|arrd-28|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009001|tyr-3|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009001|tyr-3|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4997|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009002|hint-1|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26155|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009004|pfd-6|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009005|F21C3.6|381nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009005|F21C3.6|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009005|F21C3.6|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009005|F21C3.6|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009005|F21C3.6|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009005|F21C3.6|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009005|F21C3.6|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|1260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|1336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|1338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|1342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|1348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5163|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|361nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|372nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009006|F21D5.1|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=449|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3729|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009007|otub-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009008|F21D5.3a.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1971|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00009008|F21D5.3a.2|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009009|F21D5.4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|1047nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2819|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|1360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|1575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009010|F21D5.5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009011|F21D5.6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009011|F21D5.6|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009011|F21D5.6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2325|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009011|F21D5.6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00009011|F21D5.6|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009011|F21D5.6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009011|F21D5.6|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|1414nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1707|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1535|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=748|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009012|F21D5.7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009013|mrps-33|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009013|mrps-33|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009013|mrps-33|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009013|mrps-33|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009013|mrps-33|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009013|mrps-33|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3222|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009014|F21D5.9|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009014|F21D5.9|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009014|F21D5.9|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009014|F21D5.9|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009015|F21D9.1|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009015|F21D9.1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009016|F21D9.2|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009016|F21D9.2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009016|F21D9.2|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=358|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009016|F21D9.2|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=169|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009018|F21D9.4a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009018|F21D9.4a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009018|F21D9.4a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009023|F21G4.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009024|F21G4.3|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00009024|F21G4.3|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|425nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=400|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|429nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|511nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|516nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009025|phf-34|518nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009026|F21G4.5|1093nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009026|F21G4.5|1108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009026|F21G4.5|1111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009026|F21G4.5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009026|F21G4.5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009026|F21G4.5|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009026|F21G4.5|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009027|F21G4.6|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009028|F21H7.2.1|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=251|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009029|F21H7.3|1560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009029|F21H7.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009029|F21H7.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009029|F21H7.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009029|F21H7.3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009029|F21H7.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009030|clec-233|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=987|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2898|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|49nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009031|F21H7.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009032|F21H7.10.1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009032|F21H7.10.1|416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009033|F21H7.12|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009033|F21H7.12|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009033|F21H7.12|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009033|F21H7.12|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009035|gfat-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009035|gfat-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009035|gfat-2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13064|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009035|gfat-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=706|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009035|gfat-2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009035|gfat-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009039|F22B3.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009039|F22B3.8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009041|cut-3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00009041|cut-3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009041|cut-3|1142nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009041|cut-3|1573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009041|cut-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8974|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3213|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009042|F22B5.4.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009043|F22B5.5|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009043|F22B5.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009043|F22B5.5|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009043|F22B5.5|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009043|F22B5.5|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009044|F22B5.6|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009044|F22B5.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00009044|F22B5.6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=990|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009044|F22B5.6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|1316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|1454nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1064|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2161|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=845|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=321|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4464|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009045|F22B5.10|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009048|cth-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009048|cth-1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009048|cth-1|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2277|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009048|cth-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009048|cth-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009048|cth-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009049|F22B8.7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009049|F22B8.7|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009049|F22B8.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009049|F22B8.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009049|F22B8.7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1339|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009049|F22B8.7|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009049|F22B8.7|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1065|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2024|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6374|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1027|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|772nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6024|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11625|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009050|F22D6.2.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=124|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9262|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=345|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=298|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009051|nduf-6|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=737|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1169|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|921nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|929nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1593|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|932nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|934nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009052|ekl-1|937nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009054|F22D6.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3904|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009054|F22D6.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009054|F22D6.9|805nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009056|F22D6.15|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009056|F22D6.15|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009056|F22D6.15|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009056|F22D6.15|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009056|F22D6.15|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009056|F22D6.15|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009056|F22D6.15|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009057|cept-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009057|cept-1|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009057|cept-1|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=730|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009057|cept-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=725|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|369nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009058|F22E12.1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009059|chw-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009059|chw-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009059|chw-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009059|chw-1|641nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009060|F22E12.3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009060|F22E12.3|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=490|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009061|F22G12.1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009061|F22G12.1|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009061|F22G12.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009063|F22G12.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009063|F22G12.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009064|F22G12.4c|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009064|F22G12.4c|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009064|F22G12.4c|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009064|F22G12.4c|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1911|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009065|F22G12.5a|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009065|F22G12.5a|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009065|F22G12.5a|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009065|F22G12.5a|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2162|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009065|F22G12.5a|295nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009067|F23A7.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009067|F23A7.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009067|F23A7.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009068|F23A7.3|1375nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009068|F23A7.3|1383nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009068|F23A7.3|1385nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|728nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=701|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|730nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1605|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|737nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009069|F23A7.4.1|745nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009070|F23A7.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009070|F23A7.5|202nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009070|F23A7.5|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009073|delm-1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009075|F23B2.7a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009075|F23B2.7a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009075|F23B2.7a|968nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009077|F23B2.10|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009077|F23B2.10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009078|rpb-12|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009078|rpb-12|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4081|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009078|rpb-12|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009078|rpb-12|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009078|rpb-12|439nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009078|rpb-12|837nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=554|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|1434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=884|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|232nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|265nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|269nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4a.2|272nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|453nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009081|F23B12.4c.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=604|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1773|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|256nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4528|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009082|dlat-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009084|F23B12.7.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2105|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009085|F23D12.1|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009085|F23D12.1|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009085|F23D12.1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009085|F23D12.1|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009086|F23D12.2|1350nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009086|F23D12.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009086|F23D12.2|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009086|F23D12.2|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009086|F23D12.2|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33650|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=868|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009087|F23D12.3|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009088|F23D12.4|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009088|F23D12.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009089|jmjd-3.2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009089|jmjd-3.2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009089|jmjd-3.2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009089|jmjd-3.2|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6183|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009090|fipr-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1407|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009091|F23D12.7|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009092|tomm-20|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00009092|tomm-20|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5095|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00009092|tomm-20|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1818|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009092|tomm-20|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009092|tomm-20|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1395|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=549|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|1588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|169nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|20nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=373|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009093|F23H12.3a|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009094|F23H12.5|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009094|F23H12.5|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009094|F23H12.5|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009094|F23H12.5|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009094|F23H12.5|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009094|F23H12.5|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5478|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|194nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=603|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009095|F23H12.7a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4727|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2495|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009096|fipr-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|102nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=450|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=684|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10238|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|92nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009097|fipr-2|99nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009098|ehbp-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009098|ehbp-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009098|ehbp-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009098|ehbp-1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009098|ehbp-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1825|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009098|ehbp-1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009098|ehbp-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009099|F25B3.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009099|F25B3.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009099|F25B3.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009099|F25B3.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009099|F25B3.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|215nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|224nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|229nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|677nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=129|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|680nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=427|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|683nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=790|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|687nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=850|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009100|rgef-1|762nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009101|F25B3.4|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009101|F25B3.4|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009101|F25B3.4|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009101|F25B3.4|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|318nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|324nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|328nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|334nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009102|F25B3.5a|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1822|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009103|rtfo-1|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009106|acs-12|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009107|F25D1.2|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009107|F25D1.2|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009107|F25D1.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=570|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00009107|F25D1.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009107|F25D1.2|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009107|F25D1.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009108|F25D1.3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009108|F25D1.3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009108|F25D1.3|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009108|F25D1.3|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009109|degt-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1275|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009109|degt-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009109|degt-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009109|degt-1|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009109|degt-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009110|F25D1.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6803|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009112|tag-353|840nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=312|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2037|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009113|maph-1.2|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009114|F25D7.5|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009115|F25F2.1a|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=300|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|232nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1071|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=741|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009116|snx-27|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4621|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=528|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=498|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|863nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|912nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=497|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009118|F25H2.4|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|1100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1928|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|472nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6728|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=420868|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=606|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009119|ndk-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=929|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2363|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=528|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=400|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009120|F25H2.6.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009121|F25H2.7|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=956|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57178|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=240|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=228|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=591|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32796|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00009122|tct-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1908|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009123|F25H2.12a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1358|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009123|F25H2.12a|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009123|F25H2.12a|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1529|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009124|rtel-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009125|F25H5.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009125|F25H5.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009125|F25H5.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=555|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009125|F25H5.2|775nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=439|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=650|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2737|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16065|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|378nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|454nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|626nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=437|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|632nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009126|pyk-1|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1409|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009127|F25H5.5b|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009128|mrpl-54|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=196|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009128|mrpl-54|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009128|mrpl-54|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1450|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00009129|F25H5.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009129|F25H5.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00009129|F25H5.7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1138|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|323nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|335nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|521nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=337|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|580nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11912|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009130|F25H5.8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2185|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009131|F25H8.1a|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009132|F25H8.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009132|F25H8.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1290|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009132|F25H8.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=981|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009132|F25H8.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009133|bed-3|1285nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009133|bed-3|406nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009133|bed-3|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009133|bed-3|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009134|lurp-2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009134|lurp-2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00009134|lurp-2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009134|lurp-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009135|F25H9.2|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009136|lurp-3|14nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009136|lurp-3|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=650|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009136|lurp-3|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009136|lurp-3|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009136|lurp-3|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009136|lurp-3|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009136|lurp-3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=532|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=202|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2138|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|214nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009137|bath-39|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=862|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|281nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=749|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009138|F25H9.6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009139|F25H9.7a|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009139|F25H9.7a|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2503|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009139|F25H9.7a|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009139|F25H9.7a|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1450|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009140|F26A3.1|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009141|ncbp-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1290|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009141|ncbp-2|594nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3813|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009141|ncbp-2|598nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1086|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009141|ncbp-2|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009141|ncbp-2|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009141|ncbp-2|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009141|ncbp-2|960nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1670|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3551|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009142|F26A3.4|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009143|F26A3.5|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009143|F26A3.5|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=512|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00009143|F26A3.5|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009144|del-3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009144|del-3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009144|del-3|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009145|F26A3.7|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009145|F26A3.7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1157|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009145|F26A3.7|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00009145|F26A3.7|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009146|F26C11.1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009146|F26C11.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009146|F26C11.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009146|F26C11.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009146|F26C11.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009147|F26C11.3f|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009148|F26D2.3a|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00009148|F26D2.3a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00009149|F26D2.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009150|clec-234|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009152|F26D2.14|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009153|F26D2.15|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00009153|F26D2.15|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00009154|F26D2.16|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009155|F26D10.11|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009155|F26D10.11|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009155|F26D10.11|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009156|clec-196|1279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009156|clec-196|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009156|clec-196|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009156|clec-196|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009156|clec-196|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009156|clec-196|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009156|clec-196|766nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|558nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009157|F26E4.2|861nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4136|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18275|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22519|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=832|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|329nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009158|F26E4.3.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1585|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009159|F26E4.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009160|F26E4.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00009160|F26E4.5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009160|F26E4.5|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009161|F26E4.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009161|F26E4.6|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29603|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009161|F26E4.6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=408|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009161|F26E4.6|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=967|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009161|F26E4.6|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009161|F26E4.6|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009161|F26E4.6|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009162|F26E4.7a|215nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009162|F26E4.7a|217nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009162|F26E4.7a|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009162|F26E4.7a|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009162|F26E4.7a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009162|F26E4.7a|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009162|F26E4.7a|994nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009163|drsh-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1674|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009163|drsh-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009163|drsh-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009164|hrdl-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009164|hrdl-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6821|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00009164|hrdl-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009164|hrdl-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009164|hrdl-1|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009164|hrdl-1|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009164|hrdl-1|908nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009165|gpx-1|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009165|gpx-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009165|gpx-1|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009165|gpx-1|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009165|gpx-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=985|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009165|gpx-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2189|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009165|gpx-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009166|F26F2.1|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009166|F26F2.1|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009167|F26F2.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009169|F26F2.4b|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009170|F26F2.5|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009172|F26F2.7|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=475|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00009172|F26F2.7|267nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=872|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009172|F26F2.7|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009172|F26F2.7|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|365nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=377|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=650|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|733nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009173|prom-1|743nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1401|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=702|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|464nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1517|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|466nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|469nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|471nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009174|F26H9.2|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009176|nmat-2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009176|nmat-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=525|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009176|nmat-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009176|nmat-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009176|nmat-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009176|nmat-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4704|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1287|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009177|F26H9.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009178|uggt-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009178|uggt-2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009178|uggt-2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009178|uggt-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009178|uggt-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009179|kbp-3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009179|kbp-3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2304|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009179|kbp-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=939|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009179|kbp-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009179|kbp-3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009179|kbp-3|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009179|kbp-3|991nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33366|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=259|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=195|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=233|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1034|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6796|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5431|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009180|nurf-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16575|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009182|F26H11.4|1270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009182|F26H11.4|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009182|F26H11.4|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009182|F26H11.4|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|631nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009183|F27C8.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|1007nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=534|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|1011nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|1013nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1727|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00009184|F27C8.3|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009185|F27C8.5|1109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009185|F27C8.5|1403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009185|F27C8.5|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009185|F27C8.5|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009185|F27C8.5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009185|F27C8.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009185|F27C8.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009186|trcs-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009186|trcs-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009186|trcs-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5360|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00009186|trcs-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009186|trcs-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10611|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|560nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009187|F27D4.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|1228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|1245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=434|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=429|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3141|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|680nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|683nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=113|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|689nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|691nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009188|lsy-22|704nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5106|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009189|F27D4.4a|371nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009190|F27D4.6b|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009190|F27D4.6b|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=838|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009190|F27D4.6b|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009190|F27D4.6b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009190|F27D4.6b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=724|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2599|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009191|F27D4.7|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=612|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009192|F27E5.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009193|F27E5.3|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009193|F27E5.3|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009193|F27E5.3|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009194|F27E5.5|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009194|F27E5.5|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009194|F27E5.5|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009194|F27E5.5|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009194|F27E5.5|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009194|F27E5.5|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009200|F28C1.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009200|F28C1.1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3448|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009200|F28C1.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=948|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009200|F28C1.1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009200|F28C1.1|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|821nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=933|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009201|F28C1.3a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009202|aptf-4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009202|aptf-4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009202|aptf-4|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=412|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009202|aptf-4|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009202|aptf-4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009202|aptf-4|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009202|aptf-4|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009203|aptf-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009204|F28C6.4a.1|14nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009204|F28C6.4a.1|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=617|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00009204|F28C6.4a.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009204|F28C6.4a.1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009204|F28C6.4a.1|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009204|F28C6.4b.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009205|F28C6.5|1063nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009205|F28C6.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009205|F28C6.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=937|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009205|F28C6.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009205|F28C6.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009205|F28C6.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3540|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009207|F28C6.8a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009208|F28C6.9b|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009208|F28C6.9b|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009208|F28C6.9b|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=387|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009208|F28C6.9b|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009209|F28C6.10|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1129|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009211|wdr-46|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009212|F28D1.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009212|F28D1.2|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009212|F28D1.2|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009212|F28D1.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009212|F28D1.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009213|thn-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009214|thn-3|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009214|thn-3|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|101nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|107nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|128nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1727|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009215|thn-2|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=352|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2278|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009216|F28D1.6|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=160|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009217|oig-7|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009217|oig-7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009217|oig-7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|1499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|1503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|1571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|1579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|1590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1261|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009218|acs-20|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009219|dpm-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009219|dpm-3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009219|dpm-3|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009219|dpm-3|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009219|dpm-3|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2900|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009219|dpm-3|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=332|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009219|dpm-3|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009220|F28D9.4.1|425nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009220|F28D9.4.1|429nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=156|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009220|F28D9.4.1|436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009220|F28D9.4.1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009220|F28D9.4.1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009221|acs-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009221|acs-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009221|acs-2|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1170|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009221|acs-2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30002|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009221|acs-2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009221|acs-2|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009222|fbxa-95|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009222|fbxa-95|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009222|fbxa-95|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=799|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009223|F28F8.5b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009224|F28F8.7|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009224|F28F8.7|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=841|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009224|F28F8.7|276nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009224|F28F8.7|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009224|F28F8.7|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009224|F28F8.7|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009224|F28F8.7|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009225|fbxa-94|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009225|fbxa-94|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009225|fbxa-94|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009226|cyp-37B1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009226|cyp-37B1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009227|F28G4.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009227|F28G4.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009227|F28G4.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009228|F28G4.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009229|F28G4.4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009229|F28G4.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009231|ceh-89|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009232|nkat-1|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009232|nkat-1|666nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009233|F28H6.4|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=289|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|511nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|516nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|519nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=136|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009234|F28H6.6|521nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009235|F28H6.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009235|F28H6.7|812nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009236|F28H7.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009236|F28H7.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|303nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|310nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10448|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2699|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009237|F28H7.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|67nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009238|F28H7.4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009239|irld-6|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009239|irld-6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009239|irld-6|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00009239|irld-6|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009240|F28H7.7|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009240|F28H7.7|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00009240|F28H7.7|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009240|F28H7.7|946nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009241|F28H7.8|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=128|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009241|F28H7.8|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009241|F28H7.8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009241|F28H7.8|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009241|F28H7.8|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009241|F28H7.8|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009241|F28H7.8|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009242|sre-6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009242|sre-6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009243|F29C6.1a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=886|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009243|F29C6.1a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009243|F29C6.1a|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009243|F29C6.1a|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009243|F29C6.1a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1520|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009245|rict-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2003|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=574|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009246|gfm-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009247|bath-45|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009248|F29C12.6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009248|F29C12.6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009250|F29D10.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009250|F29D10.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009251|F29D10.2|115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009251|F29D10.2|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009252|F29D10.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009252|F29D10.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3111|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|640nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|642nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|952nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009254|capg-1|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009255|ugt-34|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00009255|ugt-34|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00009255|ugt-34|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1903|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=642|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009256|tut-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009257|F29G6.1|1342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009257|F29G6.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009258|F29G6.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009258|F29G6.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3595|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009258|F29G6.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009258|F29G6.2|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009258|F29G6.2|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009258|F29G6.2|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009258|F29G6.2|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009259|hpo-34|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009259|hpo-34|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009259|hpo-34|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10457|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009259|hpo-34|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009259|hpo-34|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009259|hpo-34|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009259|hpo-34|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009260|calm-1|1307nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009260|calm-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009260|calm-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009260|calm-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1608|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009260|calm-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009260|calm-1|724nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009261|F30A10.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009261|F30A10.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009261|F30A10.2|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=211|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009261|F30A10.2|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=372|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009261|F30A10.2|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009261|F30A10.2|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|277nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5808|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009262|F30A10.3.1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5288|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1100|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009264|sac-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1344|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1019|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|412nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009266|F30A10.9|430nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|1240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|1290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3149|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009267|usp-48|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009268|F30A10.11|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00009268|F30A10.11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00009269|F30A10.12|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009269|F30A10.12|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=339|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1207|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=384|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009270|F30F8.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009271|glna-3|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009271|glna-3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009271|glna-3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009271|glna-3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3393|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009272|gras-1|1310nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009272|gras-1|1312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009272|gras-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009272|gras-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009272|gras-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009272|gras-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3615|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009272|gras-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2393|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=471|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009274|F30F8.5b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009276|F30F8.9b.2|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009276|F30F8.9b.2|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3253|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00009276|F30F8.9b.2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009276|F30F8.9b.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009276|F30F8.9b.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009276|F30F8.9b.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|21nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=226|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009277|F30F8.10a|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009278|npr-33|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009278|npr-33|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009278|npr-33|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009278|npr-33|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009278|npr-33|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009280|F31B9.3|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009280|F31B9.3|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009280|F31B9.3|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009280|F31B9.3|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009280|F31B9.3|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00009280|F31B9.3|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009280|F31B9.3|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009281|F31B9.4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009283|F31B12.4|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009283|F31B12.4|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3472|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009283|F31B12.4|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1340|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1275|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009284|F31C3.2a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3012|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009285|F31C3.3|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009286|F31C3.4|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009286|F31C3.4|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009286|F31C3.4|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00009286|F31C3.4|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3199|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009286|F31C3.4|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009286|F31C3.4|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009286|F31C3.4|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009287|psf-2|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009287|psf-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009287|psf-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009287|psf-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009287|psf-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1803|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00009287|psf-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009287|psf-2|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009288|F31C3.6a|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=435|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009288|F31C3.6a|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009288|F31C3.6a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1585|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|573nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009289|exos-7|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|341nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5156|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|571nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009290|F31D4.2|584nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009291|clec-264|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009292|F31D4.5a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009292|F31D4.5a|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009292|F31D4.5a|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009292|F31D4.5a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009292|F31D4.5a|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=458|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009293|F31D4.8|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3789|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7214|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009294|F31D4.9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009296|F31E9.3|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009296|F31E9.3|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009297|sdz-16|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009299|F31E9.6|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009299|F31E9.6|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009299|F31E9.6|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009299|F31E9.6|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009301|F31F6.2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009303|lips-8|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1329|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=421|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009304|eva-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009305|F32A7.4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009305|F32A7.4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1803|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009305|F32A7.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009305|F32A7.4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009305|F32A7.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009305|F32A7.4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009305|F32A7.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=614|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4480|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009306|maph-1.1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4829|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|404nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009307|F32A11.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009308|F32A11.3|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009308|F32A11.3|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4090|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009308|F32A11.3|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009308|F32A11.3|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009311|mltn-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009312|F32B4.1|1081nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009312|F32B4.1|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009312|F32B4.1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009312|F32B4.1|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009313|F32B4.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009313|F32B4.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=860|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009313|F32B4.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009313|F32B4.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009313|F32B4.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1418|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|393nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|474nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|491nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009314|F32B4.4a|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21014|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|124nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2952|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=982|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009315|F32B4.5b.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2034|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009316|abhd-11.1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009318|F32B4.8|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00009318|F32B4.8|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00009319|mccc-1|1011nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009319|mccc-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009319|mccc-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009319|mccc-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3340|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00009319|mccc-1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2206|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00009319|mccc-1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=743|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009320|F32B6.3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009321|F32B6.4.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009321|F32B6.4.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1384|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009321|F32B6.4.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009321|F32B6.4.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5174|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2310|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009322|tbc-3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009323|best-13|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009323|best-13|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009323|best-13|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009323|best-13|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=275|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009323|best-13|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009323|best-13|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009323|best-13|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009324|F32B6.10a|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00009324|F32B6.10a|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009324|F32B6.10a|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009324|F32B6.10a|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009324|F32B6.10a|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=369|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|137nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=523|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|140nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|142nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|144nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009325|F32D8.15|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009326|F32D8.1|1490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009326|F32D8.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009326|F32D8.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=609|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009326|F32D8.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009326|F32D8.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009327|F32D8.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009327|F32D8.2|964nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009328|F32D8.3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009328|F32D8.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009328|F32D8.3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009328|F32D8.3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009328|F32D8.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009328|F32D8.3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|1056nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=517|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009329|F32D8.4|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|1043nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|1046nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|155nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4589|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|164nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=674|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|920nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|922nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|947nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009330|F32D8.5b|969nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009331|F32D8.7a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=869|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009331|F32D8.7a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009331|F32D8.7a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009331|F32D8.7a|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009332|F32D8.8|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009332|F32D8.8|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009333|F32D8.10|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009333|F32D8.10|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009333|F32D8.10|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009333|F32D8.10|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=984|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=258|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|538nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=867|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|541nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009334|F32D8.12c.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009335|F32D8.13a|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009335|F32D8.13a|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009335|F32D8.13a|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=297|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009335|F32D8.13a|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009335|F32D8.13a|867nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009335|F32D8.13a|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4817|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3046|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|860nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|865nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|871nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009336|F32D8.14b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009337|uig-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009337|uig-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009337|uig-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009337|uig-1|431nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009337|uig-1|437nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=792|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009337|uig-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00009338|F32G8.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009338|F32G8.2|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009339|F32G8.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009339|F32G8.3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00009339|F32G8.3|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009340|best-14|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009340|best-14|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009340|best-14|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=850|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|766nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2010|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=334|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009341|thoc-3|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009342|fasn-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009342|fasn-1|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1820|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009342|fasn-1|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5036|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009342|fasn-1|590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009342|fasn-1|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009342|fasn-1|997nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009343|F32H2.6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009343|F32H2.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1864|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009344|F32H2.7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009345|F32H2.8|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009346|F32H2.10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009346|F32H2.10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=860|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009346|F32H2.10|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1467|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009347|F32H5.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009349|F32H5.3a|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009349|F32H5.3a|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1071|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009349|F32H5.3a|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009350|F32H5.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009350|F32H5.4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009350|F32H5.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1074|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009352|F33A8.4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1212|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13439|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=587|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=402|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009353|sdhd-1|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009354|F33A8.6|113nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009354|F33A8.6|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009354|F33A8.6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009354|F33A8.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009354|F33A8.6|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009354|F33A8.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009355|F33A8.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009355|F33A8.7|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1557|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009355|F33A8.7|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009355|F33A8.7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|538nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|542nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|545nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|550nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009356|F33A8.10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009357|F33C8.2|1306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009358|F33C8.4|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009358|F33C8.4|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009358|F33C8.4|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=505|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009358|F33C8.4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009358|F33C8.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009358|F33C8.4|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009360|F33E2.4.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009360|F33E2.4.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009360|F33E2.4.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00009361|F33E2.5.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009361|F33E2.5.2|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009361|F33E2.5.2|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=352|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009361|F33E2.5.2|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009363|F33E2.7|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1966|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009364|F33H1.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2192|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|521nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|523nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|525nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|527nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009365|F33H1.4|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1510|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=644|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009366|F33H2.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4817|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009367|F33H2.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009368|pole-1|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009368|pole-1|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009368|pole-1|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009368|pole-1|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009368|pole-1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1806|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009368|pole-1|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=323|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009369|F33H2.6|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009369|F33H2.6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009369|F33H2.6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009369|F33H2.6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2289|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00009369|F33H2.6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009370|set-10|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=302|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009370|set-10|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009371|F33H2.8b|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009371|F33H2.8b|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009371|F33H2.8b|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=571|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009372|evl-18|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009372|evl-18|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009372|evl-18|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009372|evl-18|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=874|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009372|evl-18|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009372|evl-18|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009372|evl-18|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|10nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2008|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1392|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009373|F34D10.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009374|F34D10.4|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009374|F34D10.4|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009374|F34D10.4|389nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009374|F34D10.4|394nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1697|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009374|F34D10.4|397nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009375|F34D10.6b.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009375|F34D10.6b.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009375|F34D10.6b.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009375|F34D10.6b.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3096|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009377|F34D10.8|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009377|F34D10.8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4108|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009377|F34D10.8|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009377|F34D10.8|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009378|F34H10.1|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009378|F34H10.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009378|F34H10.1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1182|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|339nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=606|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|382nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009379|F34H10.2|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009380|F34H10.3.1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009380|F34H10.3.1|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009380|F34H10.3.1|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009380|F34H10.3.1|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1619|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009380|F34H10.3.1|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009380|F34H10.3.1|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009380|F34H10.3.1|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009381|F34H10.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00009381|F34H10.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00009382|F34H10.5|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00009382|F34H10.5|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=175|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009382|F34H10.5|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009383|F35B12.3|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009383|F35B12.3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009383|F35B12.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009383|F35B12.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009383|F35B12.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=913|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009383|F35B12.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009383|F35B12.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009384|piit-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1688|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009384|piit-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009384|piit-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009384|piit-1|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009384|piit-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009384|piit-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009384|piit-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1693|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1841|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009385|sas-5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009386|tag-290|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009386|tag-290|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=432|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009386|tag-290|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=298|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009386|tag-290|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009386|tag-290|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009386|tag-290|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=992|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|651nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009387|glb-15|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009388|F35B12.9|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009388|F35B12.9|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009388|F35B12.9|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009388|F35B12.9|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=828|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009388|F35B12.9|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009388|F35B12.9|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2003|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|515nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009389|F35B12.10b|548nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009390|F35C5.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009390|F35C5.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009390|F35C5.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009390|F35C5.1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009392|F35C5.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009393|clec-62|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009393|clec-62|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009393|clec-62|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=773|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009393|clec-62|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=402|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009393|clec-62|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=136|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|144nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=409|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23052|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1649|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009394|clec-63|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009395|clec-64|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009396|clec-65|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009396|clec-65|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009396|clec-65|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009396|clec-65|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5789|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009396|clec-65|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=461|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009397|clec-66|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009398|nspb-11|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18160|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009398|nspb-11|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009399|F35C5.11|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009399|F35C5.11|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009399|F35C5.11|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009399|F35C5.11|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009399|F35C5.11|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1406|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009399|F35C5.11|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=527|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009400|F35C5.12|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009401|F35C11.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009401|F35C11.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009401|F35C11.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009401|F35C11.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009401|F35C11.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009401|F35C11.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009402|F35C11.3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009402|F35C11.3|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009402|F35C11.3|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=388|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009402|F35C11.3|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009402|F35C11.3|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009402|F35C11.3|922nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009403|F35C11.4|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009403|F35C11.4|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009403|F35C11.4|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=638|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009403|F35C11.4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1013|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1944|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009404|F35C11.5|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009405|F35C11.6|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=416|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009405|F35C11.6|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009405|F35C11.6|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009405|F35C11.6|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009405|F35C11.6|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009406|F35C11.7|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009406|F35C11.7|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009406|F35C11.7|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009406|F35C11.7|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=793|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=939|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=805|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009408|F35C12.3b|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1109|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009409|F35E2.1|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009409|F35E2.1|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009409|F35E2.1|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00009410|F35E2.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009412|F35E2.5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009413|oac-19|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009413|oac-19|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009413|oac-19|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009415|F35E2.8|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009415|F35E2.8|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009415|F35E2.8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009416|F35E2.9|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=420|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009417|F35E8.1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009418|F35E8.2.2|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009419|F35E8.4|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009420|F35E8.6|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009420|F35E8.6|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009420|F35E8.6|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009420|F35E8.6|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009421|F35E8.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009421|F35E8.7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009424|F35E8.13|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009426|F35E12.2b|14nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009426|F35E12.2b|18nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009427|fbxa-181|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009427|fbxa-181|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009427|fbxa-181|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009427|fbxa-181|881nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009429|F35E12.5|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009429|F35E12.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6457|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009429|F35E12.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1528|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00009429|F35E12.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009429|F35E12.5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2931|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009430|F35E12.6.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009431|dct-17|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=764|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009431|dct-17|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009432|cld-9|22nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009432|cld-9|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009432|cld-9|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009432|cld-9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009432|cld-9|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009432|cld-9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009432|cld-9|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9a|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9a|597nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9a|608nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9c|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009433|F35E12.9c|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=662|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009434|F35E12.10|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3334|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009434|F35E12.10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009434|F35E12.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009434|F35E12.10|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1105|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|145nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|735nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|749nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3075|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|752nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|755nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009435|F35G2.1a.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3128|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=325|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|534nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|799nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|801nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|810nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|838nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|843nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009436|marb-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009437|F35G2.3|463nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009437|F35G2.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009438|F35G2.5a|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009438|F35G2.5a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00009438|F35G2.5a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00009438|F35G2.5a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009438|F35G2.5a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009438|F35G2.5a|985nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009439|mlcd-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009439|mlcd-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1794|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009439|mlcd-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009439|mlcd-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009439|mlcd-1|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009439|mlcd-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|291nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8106|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|302nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1347|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|304nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|698nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|712nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|719nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|723nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009440|idhg-1|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009441|wdr-48|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009441|wdr-48|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2537|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009441|wdr-48|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009441|wdr-48|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009441|wdr-48|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009441|wdr-48|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009442|F35G12.5a|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009442|F35G12.5a|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009442|F35G12.5a|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009442|F35G12.5a|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009442|F35G12.5a|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009442|F35G12.5a|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009442|F35G12.5a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1265|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=978|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1340|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009443|F35G12.7|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4663|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009444|F35G12.11.2|960nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|1139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3077|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009445|F35G12.12|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=614|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009446|F35H8.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009446|F35H8.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009446|F35H8.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009447|F35H8.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009447|F35H8.2|1552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3539|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|236nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009448|zfp-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009449|F35H8.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009449|F35H8.4|15nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009449|F35H8.4|24nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009449|F35H8.4|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009449|F35H8.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009449|F35H8.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=524|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009450|ugt-58|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009451|cids-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009451|cids-2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009451|cids-2|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009451|cids-2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009451|cids-2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5312|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009451|cids-2|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009451|cids-2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=892|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009452|F36A2.2|273nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009453|F36A2.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1758|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16685|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|1024nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|1119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|1300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1143|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34069|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009454|F36A2.7.2|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009455|phip-1|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009455|phip-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009455|phip-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1212|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009455|phip-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2463|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009455|phip-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009455|phip-1|82nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=128|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009456|F36A2.9a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009456|F36A2.9a|381nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2619|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009457|F36A2.10.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009457|F36A2.10.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009457|F36A2.10.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009457|F36A2.10.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2062|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009458|F36A2.11|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009458|F36A2.11|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=309|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009458|F36A2.11|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=172|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|1050nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2323|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|891nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009459|F36A2.12|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1791|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2669|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009460|ubr-5|466nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009461|madf-2|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=641|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009461|madf-2|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009461|madf-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009462|sre-22|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009462|sre-22|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009462|sre-22|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009463|F36D1.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1547|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009464|F36D1.5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009465|F36D1.6|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009466|F36D1.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009466|F36D1.7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009467|F36D1.8|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009467|F36D1.8|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009467|F36D1.8|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009468|F36D1.9|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=962|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=345|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|660nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009469|F36D3.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1138|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=187|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009470|F36D3.4|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009471|F36D3.5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009471|F36D3.5|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009471|F36D3.5|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009471|F36D3.5|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009473|F36D3.8|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009473|F36D3.8|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009473|F36D3.8|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=729|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009475|F36F2.1a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009476|F36F2.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1470|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009476|F36F2.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009476|F36F2.2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009477|rbpl-1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009477|rbpl-1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1445|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009477|rbpl-1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009477|rbpl-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009478|syx-7|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6164|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009478|syx-7|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009478|syx-7|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009478|syx-7|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009478|syx-7|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|486nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|489nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1421|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009479|fcp-1|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009480|F36F2.7|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009480|F36F2.7|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009480|F36F2.7|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009480|F36F2.7|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009480|F36F2.7|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009481|F36F2.8|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009481|F36F2.8|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1228|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009481|F36F2.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009481|F36F2.8|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|328nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009482|F36G3.1|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=815|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009483|F36G3.2|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5546|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009484|F36G3.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009485|F36G9.3a|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009485|F36G9.3a|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009485|F36G9.3a|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009486|F36G9.7|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009487|clec-232|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009488|oac-20|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009488|oac-20|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009488|oac-20|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=400|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009488|oac-20|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009489|F36G9.13|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009489|F36G9.13|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009489|F36G9.13|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009490|fbxa-99|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009490|fbxa-99|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00009490|fbxa-99|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009491|F36G9.15.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009491|F36G9.15.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009492|F36H1.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009492|F36H1.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00009492|F36H1.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009493|hrg-4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009493|hrg-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009493|hrg-4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009494|hrg-5|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009494|hrg-5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009494|hrg-5|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00009494|hrg-5|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009495|hrg-6|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009495|hrg-6|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009495|hrg-6|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=167|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009495|hrg-6|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009495|hrg-6|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009495|hrg-6|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009496|F36H1.11|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009496|F36H1.11|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009496|F36H1.11|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009496|F36H1.11|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009497|F36H1.12|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|37nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1699|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3630|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009498|tat-5|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009499|ent-6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009499|ent-6|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009499|ent-6|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009499|ent-6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5519|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009499|ent-6|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009499|ent-6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009500|F36H2.3a|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009501|F37A8.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009502|F37A8.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009502|F37A8.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009503|F37A8.5|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009503|F37A8.5|651nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=481|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009503|F37A8.5|659nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=710|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009503|F37A8.5|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009503|F37A8.5|691nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1399|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00009504|F37B12.1|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009504|F37B12.1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009504|F37B12.1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009504|F37B12.1|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3085|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|678nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009505|F37B12.3.2|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=980|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009507|mus-101|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2472|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=999|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009508|row-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009509|F37D6.3|15nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009509|F37D6.3|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009509|F37D6.3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009509|F37D6.3|949nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009509|F37D6.3|957nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009510|F37D6.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009510|F37D6.4|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009511|F37H8.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009511|F37H8.2|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009511|F37H8.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009511|F37H8.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009511|F37H8.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=438|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00009512|F37H8.3a|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00009513|sfxn-1.2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009513|sfxn-1.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009513|sfxn-1.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009513|sfxn-1.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|19nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3822|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=746|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009514|F37H8.5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009515|clec-170|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009515|clec-170|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009515|clec-170|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009515|clec-170|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009515|clec-170|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009517|clec-167|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009517|clec-167|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00009517|clec-167|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=319|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009518|clec-166|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009520|clec-168|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|661nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1424|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009521|F38A1.8|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009522|F38A1.9|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009523|clec-165|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009525|F38A1.13|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009525|F38A1.13|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009525|F38A1.13|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009525|F38A1.13|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009526|clec-169|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009526|clec-169|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009528|F38A6.4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009528|F38A6.4|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009528|F38A6.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=513|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009529|F38B2.2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009529|F38B2.2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7910|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009529|F38B2.2|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009530|F38B2.3|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009530|F38B2.3|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=289|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00009530|F38B2.3|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009530|F38B2.3|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009530|F38B2.3|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1324|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3681|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|476nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009531|F38B2.4a|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009532|ccch-1|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2010|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009532|ccch-1|1041nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009532|ccch-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009532|ccch-1|584nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009532|ccch-1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009533|F38B7.2b|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009533|F38B7.2b|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=879|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00009533|F38B7.2b|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009533|F38B7.2b|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009533|F38B7.2b|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12195|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2424|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009534|F38B7.3|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009535|F38C2.1b|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009535|F38C2.1b|1358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009535|F38C2.1b|1363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009535|F38C2.1b|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009535|F38C2.1d|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009535|F38C2.1d|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009535|F38C2.1d|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009536|F38C2.4a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009536|F38C2.4a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009537|ccch-2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009537|ccch-2|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009537|ccch-2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009539|F38C2.7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009539|F38C2.7|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009539|F38C2.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009539|F38C2.7|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009540|hlh-31|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009540|hlh-31|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009540|hlh-31|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009540|hlh-31|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009540|hlh-31|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|403nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009541|cutl-17|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=755|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|647nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|649nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|655nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|659nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|663nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=494|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|668nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=304|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3594|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009542|copb-2|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|1181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|475nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|651nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009543|F38E11.6a|954nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009544|F38E11.9.2|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009544|F38E11.9.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009544|F38E11.9.2|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009546|fbxb-3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00009546|fbxb-3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009546|fbxb-3|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00009547|F38H4.3|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=531|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009548|F38H4.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00009548|F38H4.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009548|F38H4.4|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009548|F38H4.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00009548|F38H4.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009548|F38H4.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009548|F38H4.4|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009549|F38H4.5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009550|F38H4.6|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009551|F38H4.10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009551|F38H4.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2817|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009551|F38H4.10|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009552|piki-1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=895|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009552|piki-1|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=596|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009553|hinf-1|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|41nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009554|F39B2.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009556|F39B2.5|1571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009556|F39B2.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009556|F39B2.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1441|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00009556|F39B2.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009557|mtcu-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009557|mtcu-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009557|mtcu-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|676nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|691nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|749nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|772nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=915|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2770|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=555|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009558|F39B2.8|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009559|mtx-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009559|mtx-1|1195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009559|mtx-1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=132|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009559|mtx-1|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7436|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00009559|mtx-1|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009559|mtx-1|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009559|mtx-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009560|psa-3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009560|psa-3|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009561|F39D8.3b|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009561|F39D8.3b|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009561|F39D8.3b|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2994|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=544|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1833|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22456|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5691|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|313nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|665nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009562|flp-22|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|1565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4526|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1516|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|276nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|623nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009563|F39H2.3.2|861nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|627nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=720|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00009565|F39H11.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1108|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009566|srsx-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009566|srsx-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009569|srz-66|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009569|srz-66|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009569|srz-66|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009572|F40D4.13a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009572|F40D4.13a|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009572|F40D4.13a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009572|F40D4.13a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009573|F40E10.5|1098nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009573|F40E10.5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009573|F40E10.5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009573|F40E10.5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009573|F40E10.5|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1866|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009573|F40E10.5|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4859|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2272|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009574|F40E10.6.3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3100|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4777|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=868|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|170nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009575|F40F8.1a.1|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009576|F40F8.3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009576|F40F8.3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009576|F40F8.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=778|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009576|F40F8.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009576|F40F8.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009577|F40F8.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009577|F40F8.4|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009577|F40F8.4|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1794|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4863|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009578|F40F8.5b|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009579|arrd-6|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009579|arrd-6|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009579|arrd-6|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009579|arrd-6|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=356|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009579|arrd-6|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009579|arrd-6|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1273|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009579|arrd-6|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|171nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|253nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2908|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2716|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=336|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1049|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4347|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009580|xbx-6|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009581|F40F9.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009581|F40F9.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009581|F40F9.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=514|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009581|F40F9.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009582|F40F9.5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009582|F40F9.5|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009582|F40F9.5|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=925|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009582|F40F9.5|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1019|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6346|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|328nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|355nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|357nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|359nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009583|aagr-3|911nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|1488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|423nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|427nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3326|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|429nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10472|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|436nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|438nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009584|drap-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009585|cal-7|1049nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009585|cal-7|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009585|cal-7|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00009585|cal-7|957nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009586|F40F9.10|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009586|F40F9.10|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009586|F40F9.10|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=676|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009587|mig-38|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|1075nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2479|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|799nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009588|F40F11.3a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009589|F40F11.4|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009589|F40F11.4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009589|F40F11.4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009589|F40F11.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009589|F40F11.4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009589|F40F11.4|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009589|F40F11.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009593|mam-7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009593|mam-7|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009593|mam-7|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009593|mam-7|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009593|mam-7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15292|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009594|cyld-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|1369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|1436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|1439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=509|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009595|F40F12.7.3|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009596|sre-8|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009597|F40G12.2|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009597|F40G12.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009597|F40G12.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009597|F40G12.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009600|F40G12.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009600|F40G12.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009601|F40G12.6|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009602|F40G12.7|1395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009602|F40G12.7|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009604|F40G12.9|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009605|F40G12.10|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009605|F40G12.10|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009605|F40G12.10|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009605|F40G12.10|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=248|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009606|F40G12.11|278nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009608|nhr-265|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009609|oac-27|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009611|F41D3.6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009614|F41D3.9|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00009614|F41D3.9|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00009617|F41E7.1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=335|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00009617|F41E7.1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009617|F41E7.1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009617|F41E7.1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009617|F41E7.1|391nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009617|F41E7.1|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009618|F41E7.2.3|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009618|F41E7.2.3|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009618|F41E7.2.3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00009618|F41E7.2.3|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009619|npr-6|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009619|npr-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009619|npr-6|311nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009619|npr-6|316nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=461|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009619|npr-6|332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009619|npr-6|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009619|npr-6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|1032nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4135|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|1035nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|1045nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3327|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=633|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1529|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009620|fip-5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11313|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=723|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=818|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009621|fipr-21|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009622|F41E7.6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009622|F41E7.6|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009622|F41E7.6|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009622|F41E7.6|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009622|F41E7.6|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5558|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1848|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=616|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009623|F41E7.7b|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009624|cnc-8|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009624|cnc-8|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009624|cnc-8|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009624|cnc-8|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009624|cnc-8|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4816|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009624|cnc-8|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2317|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009624|cnc-8|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009625|F41E7.9|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009625|F41E7.9|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009625|F41E7.9|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009625|F41E7.9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=747|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009626|F42A8.1|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009627|F42A8.3|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009627|F42A8.3|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1072|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009627|F42A8.3|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2417|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00009627|F42A8.3|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009627|F42A8.3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009627|F42A8.3|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4508|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009628|tatn-1|358nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009629|sprr-2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009629|sprr-2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009629|sprr-2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=953|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009629|sprr-2|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009630|F42E8.1|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009630|F42E8.1|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=828|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1287|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009632|ttyh-1|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2023|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|578nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|904nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009633|F42E11.3|969nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009634|nspc-9|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=473|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009635|F42F12.3|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009636|F42F12.4.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009636|F42F12.4.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009636|F42F12.4.1|1307nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009636|F42F12.4.1|459nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009636|F42F12.4.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=912|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009636|F42F12.4.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009636|F42F12.4.1|96nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=63|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009638|nspc-14|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009638|nspc-14|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009638|nspc-14|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009638|nspc-14|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20514|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009638|nspc-14|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8675|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009638|nspc-14|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009638|nspc-14|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1440|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14169|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=490|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009639|nspc-15|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20443|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=389|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009640|nspc-10|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009641|F42G4.2|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=737|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009641|F42G4.2|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=379|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009641|F42G4.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009642|F42G4.5b|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009642|F42G4.5b|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=825|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009642|F42G4.5b|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009642|F42G4.5b|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009643|F42G4.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009643|F42G4.6|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=792|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009643|F42G4.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009643|F42G4.6|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=326|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009643|F42G4.6|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009644|F42G4.7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009644|F42G4.7|438nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009644|F42G4.7|442nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=293|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|1236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|1260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=384|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009645|F42G10.1.1|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009646|F42H11.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009646|F42H11.1|657nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009646|F42H11.1|698nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00009647|F43C1.1|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009647|F43C1.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00009647|F43C1.1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009647|F43C1.1|654nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009647|F43C1.1|661nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009648|zhit-2|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1313|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009648|zhit-2|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009648|zhit-2|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009648|zhit-2|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009648|zhit-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009649|F43C1.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009649|F43C1.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009649|F43C1.5|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=147|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009650|ccnk-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009650|ccnk-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009650|ccnk-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3306|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009650|ccnk-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1289|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00009652|F43D2.3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00009652|F43D2.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009652|F43D2.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009653|F43D9.1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009653|F43D9.1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3a|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|703nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1575|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009654|F43D9.3b|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009657|F43G6.4|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009657|F43G6.4|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009657|F43G6.4|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009657|F43G6.4|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009657|F43G6.4|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1092nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009658|F43G6.5|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009659|F43G6.7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009659|F43G6.7|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009659|F43G6.7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009659|F43G6.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1267|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8924|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2870|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009660|F43G6.8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|355nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|358nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|365nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1871|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2125|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009661|patr-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009662|F43G6.10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009662|F43G6.10|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009662|F43G6.10|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009662|F43G6.10|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009662|F43G6.10|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009662|F43G6.10|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009663|hda-5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=678|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|354nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=355|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2189|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3873|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1256|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|382nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|384nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009664|idha-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=613|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009665|lmd-1|299nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2064|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009666|F43G9.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009667|F43G9.4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009667|F43G9.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009668|cfim-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009668|cfim-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009668|cfim-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009668|cfim-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3175|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009668|cfim-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009668|cfim-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009670|F43G9.8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00009670|F43G9.8|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009670|F43G9.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009671|mfap-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009671|mfap-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009671|mfap-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009671|mfap-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1815|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009671|mfap-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1750|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009671|mfap-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1915|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=205|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009672|F43G9.12a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|369nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|374nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|376nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6034|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009673|F43G9.13|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=331|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2660|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009674|nucb-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009675|F44A6.3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00009675|F44A6.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009675|F44A6.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2161|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=779|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009676|F44A6.4|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009677|F44A6.5|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00009677|F44A6.5|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009677|F44A6.5|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009677|F44A6.5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009678|magu-4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009678|magu-4|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009678|magu-4|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009678|magu-4|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009678|magu-4|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009678|magu-4|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=485|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009678|magu-4|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009679|F44D12.2|874nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009681|gipc-2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5945|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009681|gipc-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009681|gipc-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009681|gipc-2|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009682|msd-2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009682|msd-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009682|msd-2|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2312|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009682|msd-2|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009682|msd-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009683|F44D12.6|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009683|F44D12.6|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009683|F44D12.6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009683|F44D12.6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009683|F44D12.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009685|F44D12.8a|1589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009685|F44D12.8a|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009685|F44D12.8a|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009685|F44D12.8a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009686|ent-7|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009686|ent-7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009686|ent-7|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009686|ent-7|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009686|ent-7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009686|ent-7|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009687|F44D12.10|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41562|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=985|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9497|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1146|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=300|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009688|F44E5.1.2|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009690|F44E5.3|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009690|F44E5.3|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009690|F44E5.3|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009690|F44E5.3|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009690|F44E5.3|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1034nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1079nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1083nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=315|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1279nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1285nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1294nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=266|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1300nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1308nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2082|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|1598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=627|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=493|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2112|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3577|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7651|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5279|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1201|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=528|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=627|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=464|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=733|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=671|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2463|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=549|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2313|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009691|F44E5.4|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1712759|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|1173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6042|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=547|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=643|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=918|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|1552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=387|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|708nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|735nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1329|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1730|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6132|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009692|F44E5.5.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40748|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009695|F44F1.3|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009695|F44F1.3|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009696|F44F1.4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009696|F44F1.4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009698|F44F1.6a|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009698|F44F1.6a|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009700|lurp-1|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009700|lurp-1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009700|lurp-1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00009700|lurp-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009700|lurp-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009700|lurp-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009701|egg-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009701|egg-3|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009701|egg-3|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2805|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009701|egg-3|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009702|F44F4.3|1573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009702|F44F4.3|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009702|F44F4.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009702|F44F4.3|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009702|F44F4.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009702|F44F4.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009704|F44F4.9|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009704|F44F4.9|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=249|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009705|F44F4.10|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009705|F44F4.10|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009705|F44F4.10|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009705|F44F4.10|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009706|F44G3.2|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009706|F44G3.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009706|F44G3.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009706|F44G3.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009707|srxa-16|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009708|F44G3.7|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00009708|F44G3.7|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009708|F44G3.7|1455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009708|F44G3.7|1459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009708|F44G3.7|1464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009709|fbxa-144|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00009709|fbxa-144|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009709|fbxa-144|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009710|F44G3.10|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009710|F44G3.10|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009711|F44G4.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009711|F44G4.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009711|F44G4.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4524|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009711|F44G4.1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009711|F44G4.1|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=895|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7519|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1546|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2529|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=746|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009712|F44G4.2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3199|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009713|F44G4.3|688nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009714|F44G4.5|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009714|F44G4.5|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=540|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009714|F44G4.5|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009715|F44G4.6a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009715|F44G4.6a|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00009715|F44G4.6a|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009715|F44G4.6a|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009715|F44G4.6a|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009715|F44G4.6a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|1306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=718|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=321|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009716|F44G4.7|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3111|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009717|dep-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009717|dep-1|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009717|dep-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009717|dep-1|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2311|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00009717|dep-1|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009717|dep-1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009720|F45B8.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009720|F45B8.3|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00009720|F45B8.3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009720|F45B8.3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009721|F45D3.1|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=574|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=454|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009722|F45D3.2b|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3458|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009723|F45D3.3|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5907|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14720|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009724|F45D3.4a.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009725|F45E6.1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009725|F45E6.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009725|F45E6.1|677nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009725|F45E6.1|686nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|954nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|971nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009726|tbc-13|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009727|lips-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009727|lips-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009727|lips-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009727|lips-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009727|lips-1|420nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009727|lips-1|423nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009728|sdz-19|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1909|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|458nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009729|F45E10.2a|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=163|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009730|myo-6|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009730|myo-6|445nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1322|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|1472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|1479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|709nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|865nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009731|exo-1|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13496|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10358|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=390|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=371|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009732|cope-1|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=618|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009733|F45G2.7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009734|F45G2.8|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009734|F45G2.8|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3538|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009734|F45G2.8|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009734|F45G2.8|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009734|F45G2.8|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009735|F45G2.9|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2062|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009735|F45G2.9|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|15nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2229|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1488|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009736|F45G2.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009738|hecw-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009738|hecw-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009738|hecw-1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009738|hecw-1|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=605|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00009738|hecw-1|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009738|hecw-1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=321|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1358|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=149|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009739|F45H10.2.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17710|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009740|F45H10.3|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009740|F45H10.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009740|F45H10.3|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9925|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009741|drr-1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009741|drr-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=950|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009741|drr-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009741|drr-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009741|drr-1|950nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009742|F45H10.5.1|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009742|F45H10.5.1|1217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009742|F45H10.5.1|1222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=163|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009742|F45H10.5.1|1226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=182|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009742|F45H10.5.1|1232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8923|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009743|sptf-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|543nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1647|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|545nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=500|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|549nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009744|hpo-35|552nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1096|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009745|F45H11.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=490|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009746|F46A8.3|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009748|F46A8.5|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009748|F46A8.5|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009748|F46A8.5|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009749|F46A8.6|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009749|F46A8.6|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009749|F46A8.6|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009749|F46A8.6|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009750|F46A8.7|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009751|F46A8.8|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009751|F46A8.8|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009751|F46A8.8|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009753|scrm-6|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009753|scrm-6|42nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009753|scrm-6|44nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009753|scrm-6|48nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009754|F46A9.1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009754|F46A9.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009754|F46A9.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2001|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009755|F46A9.2|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009755|F46A9.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009755|F46A9.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00009755|F46A9.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00009758|ttr-11|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009758|ttr-11|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009758|ttr-11|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009759|ttr-12|14nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009759|ttr-12|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009759|ttr-12|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009759|ttr-12|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009759|ttr-12|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009760|F46B3.7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009766|F46B3.15|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009768|F46B6.2|1106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009768|F46B6.2|1258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009768|F46B6.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009768|F46B6.2|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009768|F46B6.2|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=601|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009768|F46B6.2|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=306|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|1094nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|1204nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=830|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|942nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|957nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009769|F46B6.4|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009770|F46B6.5a|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7505|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009770|F46B6.5a|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009770|F46B6.5a|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009770|F46B6.5a|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009771|F46B6.6a|1121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009771|F46B6.6a|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2180|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009771|F46B6.6a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009771|F46B6.6a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009771|F46B6.6a|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|1038nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|1057nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|1067nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|1224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|388nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25737|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009772|ztf-7|591nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009773|lipl-2|15nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009773|lipl-2|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009773|lipl-2|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009773|lipl-2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1206|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009774|F46B6.9|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009774|F46B6.9|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009774|F46B6.9|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1280|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009774|F46B6.9|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009774|F46B6.9|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=641|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=259|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009776|F46B6.12|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3392|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009777|F46C3.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009777|F46C3.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009777|F46C3.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009777|F46C3.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009778|F46C5.1|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009779|F46C5.2.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009779|F46C5.2.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009779|F46C5.2.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=693|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009779|F46C5.2.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009779|F46C5.2.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009779|F46C5.2.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|138nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4499|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009780|F46C5.4|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009781|F46C5.6|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|1408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1511|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=867|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=429|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009782|F46C5.7|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|1076nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|1165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2161|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=530|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=228|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=156|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=853|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4379|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|376nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|378nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|380nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|558nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|561nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=324|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009783|rer-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=809|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2196|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=398|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=592|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009784|F46C5.9|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=802|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009785|F46C5.10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=275|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4995|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9829|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009787|F46F2.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009788|F46F2.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009788|F46F2.4|596nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00009788|F46F2.4|674nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|1133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|1303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|1307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|1518nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|1533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|758nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=317|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|780nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009789|F46F2.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009790|lgc-44|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009790|lgc-44|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009790|lgc-44|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009790|lgc-44|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009790|lgc-44|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009791|F46F3.3a|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009791|F46F3.3a|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009791|F46F3.3a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009791|F46F3.3a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009791|F46F3.3a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1055|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|585nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|601nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|606nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|609nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|612nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1203|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=711|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009793|pkn-1|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|102nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7122|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=856|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009796|F46G10.1a.1|94nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009797|F46G10.2|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009798|F46G10.4|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=927|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11579|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2414|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009799|lgc-47|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009800|rrc-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009800|rrc-1|1547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009800|rrc-1|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009800|rrc-1|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=685|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009800|rrc-1|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009800|rrc-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009800|rrc-1|288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|418nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=260|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1108|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009801|ipla-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009802|F47B8.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1550|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5887|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1303|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009803|F47B8.2|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=445|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6162|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=978|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009804|F47B8.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009805|F47B8.4a|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009805|F47B8.4a|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009805|F47B8.4a|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009805|F47B8.4a|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009805|F47B8.4a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009806|F47B8.5a|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009806|F47B8.5a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009807|pepm-1|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009807|pepm-1|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009807|pepm-1|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009807|pepm-1|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009807|pepm-1|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009808|srm-4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009808|srm-4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009808|srm-4|1379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=592|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1884|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009809|F47B8.8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009810|srm-6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009810|srm-6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009810|srm-6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009810|srm-6|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1235|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009811|F47B8.10|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009811|F47B8.10|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00009811|F47B8.10|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009811|F47B8.10|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6758|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2780|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009812|suca-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1922|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009813|haly-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=371|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=503|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009814|F47B10.3|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=286|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009815|F47B10.4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009816|F47B10.5|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009816|F47B10.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009816|F47B10.5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009816|F47B10.5|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009816|F47B10.5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009817|F47B10.6|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009817|F47B10.6|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009817|F47B10.6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009817|F47B10.6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009817|F47B10.6|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009818|acbp-3|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009818|acbp-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009818|acbp-3|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009818|acbp-3|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009818|acbp-3|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009818|acbp-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2042|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1091|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009819|F47B10.8a|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009820|F47B10.9|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009820|F47B10.9|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009820|F47B10.9|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009822|clec-113|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009822|clec-113|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009822|clec-113|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009823|gadr-6|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009823|gadr-6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009823|gadr-6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009823|gadr-6|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009823|gadr-6|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=468|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009823|gadr-6|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009824|gpdh-1|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009824|gpdh-1|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=468|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00009824|gpdh-1|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=496|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009824|gpdh-1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009824|gpdh-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009824|gpdh-1|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009824|gpdh-1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1987|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009825|F47G4.4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009826|F47G4.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=828|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009827|hmg-6|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009827|hmg-6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|165nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|170nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|176nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|180nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8233|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=370|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009829|F47G9.1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009830|cutl-18|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009830|cutl-18|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009830|cutl-18|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009831|F47G9.4.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009831|F47G9.4.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009834|lsy-27|1348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009834|lsy-27|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009834|lsy-27|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009834|lsy-27|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=995|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009834|lsy-27|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009834|lsy-27|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009835|F47H4.2a.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009835|F47H4.2a.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009839|fbxa-188|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009839|fbxa-188|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009839|fbxa-188|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009839|fbxa-188|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009840|fbxa-189|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009840|fbxa-189|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009840|fbxa-189|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009841|fbxa-134|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009841|fbxa-134|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009842|igeg-2|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009842|igeg-2|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009842|igeg-2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009843|F48C5.2|917nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009844|cwp-5|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009844|cwp-5|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009844|cwp-5|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009844|cwp-5|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009844|cwp-5|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009848|F48F5.6a.1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009848|F48F5.6a.1|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009848|F48F5.6a.1|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009848|F48F5.6a.1|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009849|F48F7.3|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009850|F48F7.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009850|F48F7.5|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009850|F48F7.5|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009850|F48F7.5|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009850|F48F7.5|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=891|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=281|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=648|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009851|F48F7.6|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009852|arrd-24|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009854|clec-31|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009854|clec-31|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009854|clec-31|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009854|clec-31|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009855|clec-22|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00009855|clec-22|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00009856|clec-24|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009856|clec-24|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009857|clec-28|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009857|clec-28|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009857|clec-28|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009859|clec-33|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009859|clec-33|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009860|clec-32|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009861|fbxb-8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009862|fbxb-67|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=128|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009865|F49B2.6|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009865|F49B2.6|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009865|F49B2.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009866|F49C5.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009867|F49C5.4|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009867|F49C5.4|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009869|F49C5.7|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009871|F49C12.1|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009872|F49C12.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=550|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009873|F49C12.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=291|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009873|F49C12.3|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009874|F49C12.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009874|F49C12.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009874|F49C12.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009874|F49C12.4|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009874|F49C12.4|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009875|F49C12.5|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009875|F49C12.5|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009876|F49C12.6|1107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009876|F49C12.6|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009876|F49C12.6|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009876|F49C12.6|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009877|F49C12.7c.1|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1774|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00009877|F49C12.7c.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8471|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009878|F49C12.9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|104nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|854nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4289|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1570|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009879|F49C12.10|99nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=520|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2787|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34371|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2446|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3074|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=523|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009880|F49C12.11|764nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16382|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=911|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009881|F49C12.12b|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1330|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=297|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|282nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|284nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13344|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1819|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009882|vha-17|919nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009883|F49C12.14|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009883|F49C12.14|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009883|F49C12.14|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009883|F49C12.14|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009883|F49C12.14|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009883|F49C12.14|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=728|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009883|F49C12.14|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009884|F49C12.15|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009884|F49C12.15|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=590|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00009884|F49C12.15|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=623|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009885|F49E2.1b|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009885|F49E2.1b|1376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009885|F49E2.1b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1051|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=540|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=398|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009886|F49E2.2c|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009887|glb-17|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009887|glb-17|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009887|glb-17|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009887|glb-17|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009887|glb-17|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009887|glb-17|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009887|glb-17|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|239nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=332|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|462nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|465nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|915nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5a.2|929nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7089|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5e.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5f.2|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009888|F49E2.5f.2|669nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|1009nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|1011nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|1040nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|1046nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|847nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|854nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|877nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009889|F49E11.2|884nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009890|scl-9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009891|scl-10|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009891|scl-10|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009892|scl-11|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009892|scl-11|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009893|F49E11.7|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009893|F49E11.7|57nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2692|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=515|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009895|scl-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009896|scl-3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009896|scl-3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009897|skpo-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12132|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009897|skpo-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009897|skpo-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009897|skpo-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=970|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=971|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1234|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3187|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3014|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009898|dod-23|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009899|efl-3|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009899|efl-3|349nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009899|efl-3|354nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=597|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009900|F49E12.7|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009900|F49E12.7|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=545|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009900|F49E12.7|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009900|F49E12.7|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009900|F49E12.7|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=587|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009900|F49E12.7|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009900|F49E12.7|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|26nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|29nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3899|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=239|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009901|F49E12.8|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1754|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|1486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009902|drd-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009903|F49E12.10|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009903|F49E12.10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009904|F49E12.12|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009904|F49E12.12|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009906|clec-241|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009907|F49H6.3|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009908|F49H6.5a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009908|F49H6.5a|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009912|srz-94|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009912|srz-94|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009912|srz-94|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009914|F49H6.13|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009914|F49H6.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009914|F49H6.13|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009914|F49H6.13|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00009914|F49H6.13|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1448|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|282nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9373|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3373|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=199|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009915|F52A8.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009916|F52A8.3b|1137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009916|F52A8.3b|1147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009916|F52A8.3b|1530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009916|F52A8.3b|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009916|F52A8.3b|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3020|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009916|F52A8.3b|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5886|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1187|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1079|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1789|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1032|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|317nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|321nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009917|glb-18|882nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3131|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=513|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|196nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|295nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009918|F52A8.5.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=410|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1941|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=930|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|385nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6b|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009919|F52A8.6b|1277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|1191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9066|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|372nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=289|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009920|abts-1|721nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|334nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|343nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|347nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2508|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|351nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=761|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009921|F52B5.2|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009922|F52B5.3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009922|F52B5.3|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2191|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009922|F52B5.3|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009922|F52B5.3|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009922|F52B5.3|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009922|F52B5.3|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009922|F52B5.3|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|1021nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=713|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00009923|F52B5.7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|440nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|443nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|449nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|452nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=863|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|526nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|529nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|542nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|544nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009924|cfp-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2428|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=612|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|1585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009925|F52B11.2a|990nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009926|noah-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009927|F52B11.5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=566|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009927|F52B11.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009927|F52B11.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009929|abts-2|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009929|abts-2|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009929|abts-2|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|601nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|605nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009930|F52D10.2|607nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009931|F52D10.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=525|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009932|F52D10.6|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009935|F52E10.4d|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009935|F52E10.4d|308nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00009935|F52E10.4d|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009935|F52E10.4d|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009935|F52E10.4d|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3634|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009937|lsl-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009938|F52F12.5|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009938|F52F12.5|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009938|F52F12.5|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=359|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|1188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|1482nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|1484nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=404|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|1491nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|1499nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009939|ztf-11|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00009940|strl-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3560|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009941|F52F12.8|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009941|F52F12.8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=490|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009942|F52F12.9|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00009942|F52F12.9|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009942|F52F12.9|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009943|F52G2.3|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00009943|F52G2.3|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009943|F52G2.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=790|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009944|mtcu-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|424nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|426nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|544nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2307|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1930|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=535|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009945|bath-38|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009946|F52H3.4|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=541|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009947|F52H3.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009948|F52H3.6|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009948|F52H3.6|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009948|F52H3.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009948|F52H3.6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009948|F52H3.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009948|F52H3.6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009949|F53A2.1|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009949|F53A2.1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=827|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009949|F53A2.1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=167|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009949|F53A2.1|225nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009949|F53A2.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009949|F53A2.1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009949|F53A2.1|644nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009950|sdz-20|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009951|F53A2.3|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009951|F53A2.3|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=572|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009951|F53A2.3|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009951|F53A2.3|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13124|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009952|acaa-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009953|F53A2.9|1178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009953|F53A2.9|1180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009953|F53A2.9|1182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009953|F53A2.9|1188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009953|F53A2.9|1293nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009953|F53A2.9|1351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009953|F53A2.9|1357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009954|F53B2.1|1445nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009955|eak-4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009955|eak-4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009956|F53B2.5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009956|F53B2.5|1491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009956|F53B2.5|1494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009956|F53B2.5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009956|F53B2.5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009956|F53B2.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4858|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009957|F53B2.8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=471|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3198|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1443|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|324nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009958|madd-4|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=586|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009959|F53B6.4b|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009959|F53B6.4b|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009959|F53B6.4b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3969|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009959|F53B6.4b|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009960|F53B6.5|944nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009961|cutl-7|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009962|F53B6.7|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=612|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009962|F53B6.7|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009962|F53B6.7|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00009963|fipr-26|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009963|fipr-26|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009963|fipr-26|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00009963|fipr-26|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009963|fipr-26|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|1243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3060|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=496|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=916|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009964|fip-6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009965|frpr-9|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009965|frpr-9|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=486|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009965|frpr-9|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009966|F53B7.3.1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009966|F53B7.3.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009966|F53B7.3.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1833|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009966|F53B7.3.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=379|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009966|F53B7.3.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009966|F53B7.3.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=915|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=593|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|991nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009967|F53B7.4|998nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009968|fig-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=704|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009969|F53B7.7.1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009971|F53C11.1a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1177|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009971|F53C11.1a|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009971|F53C11.1a|792nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|127nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|283nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|441nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6867|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1213|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009973|F53C11.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|634nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4776|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|672nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009974|F53C11.4a.1|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|308nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|310nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|313nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4797|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|322nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=865|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009975|F53C11.5a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=461|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=484|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|608nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009976|swan-2|798nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|356nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=887|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009977|swan-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2896|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=584|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009978|F53E4.1c.1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009979|cutl-1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=508|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=295|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009980|F53F1.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1597|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00009981|F53F1.3|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009981|F53F1.3|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1241|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16145|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009982|F53F1.4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9363|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|165nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|170nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|365nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009983|cut-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009984|F53F1.6a|1148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009984|F53F1.6a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009984|F53F1.6a|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009985|F53F4.1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=202|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009986|F53F4.2|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009986|F53F4.2|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009986|F53F4.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00009986|F53F4.2|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4652|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009987|tbcb-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009988|F53F4.4a|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009988|F53F4.4a|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009988|F53F4.4a|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009990|F53F4.7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5741|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2831|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009992|F53F4.10|871nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009993|F53F4.11.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009993|F53F4.11.1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7296|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009993|F53F4.11.1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009993|F53F4.11.1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1076nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1084nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1338nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1417nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|1541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009994|F53F4.12|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009995|F53F4.13|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009995|F53F4.13|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009995|F53F4.13|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009995|F53F4.13|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8784|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00009995|F53F4.13|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=818|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2085|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00009996|F53F4.14.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|782nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|838nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|845nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00009997|F53F4.15|848nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00009998|klf-2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00009999|srsx-35|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010000|F53F8.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010000|F53F8.3|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010000|F53F8.3|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010000|F53F8.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1712|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010000|F53F8.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010001|F53F8.4|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010001|F53F8.4|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010001|F53F8.4|1364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010001|F53F8.4|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=526|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010001|F53F8.4|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=266|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1965|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=600|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|788nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010002|F53F8.5|795nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010003|F53F8.6|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010003|F53F8.6|1226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010003|F53F8.6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010003|F53F8.6|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6731|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00010003|F53F8.6|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010003|F53F8.6|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010003|F53F8.6|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010004|F53H2.1a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010004|F53H2.1a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00010004|F53H2.1a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00010005|cnc-7|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1190|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00010005|cnc-7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010005|cnc-7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010005|cnc-7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|1120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|1163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|1165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=329|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|1168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4388|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|1175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=216|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010006|F53H2.3c|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5157|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3785|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1018|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=619|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|961nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010007|F53H4.2.1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010008|F53H4.3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010008|F53H4.3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00010009|F53H4.4|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010009|F53H4.4|445nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010009|F53H4.4|451nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010009|F53H4.4|455nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=563|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010010|gmeb-2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010010|gmeb-2|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010010|gmeb-2|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010010|gmeb-2|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010011|F53H4.6|1000nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010011|F53H4.6|1356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010011|F53H4.6|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010011|F53H4.6|991nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=411|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010011|F53H4.6|997nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=457|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3478|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1970|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|443nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010012|saeg-1|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010013|F54B3.1a|1567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010013|F54B3.1a|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010013|F54B3.1a|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2827|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010013|F54B3.1a|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010013|F54B3.1a|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010013|F54B3.1a|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010013|F54B3.1a|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010014|F54B3.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010014|F54B3.2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010014|F54B3.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010014|F54B3.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010015|atad-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010015|atad-3|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010015|atad-3|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00010015|atad-3|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2101|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010015|atad-3|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010015|atad-3|314nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010015|atad-3|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010016|F54B8.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010016|F54B8.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010017|nhr-282|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010018|fbxa-69|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=224|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010019|F54B8.4b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1630|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010019|F54B8.4b|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=963|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010019|F54B8.4b|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010019|F54B8.4b|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010019|F54B8.4b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010021|srbc-49|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010023|srbc-51|1501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010023|srbc-51|1503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010023|srbc-51|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010023|srbc-51|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010025|srbc-54|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010027|F54B11.4|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010027|F54B11.4|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010027|F54B11.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010027|F54B11.4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010027|F54B11.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010027|F54B11.4|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010027|F54B11.4|98nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=27|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010028|F54B11.5|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010028|F54B11.5|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010028|F54B11.5|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10399|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010028|F54B11.5|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010028|F54B11.5|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010028|F54B11.5|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010028|F54B11.5|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010030|F54B11.7|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010030|F54B11.7|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010032|F54B11.9|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010032|F54B11.9|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010032|F54B11.9|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00010032|F54B11.9|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010032|F54B11.9|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010033|F54B11.10|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010033|F54B11.10|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=457|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010033|F54B11.10|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010033|F54B11.10|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010033|F54B11.10|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010033|F54B11.10|618nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010035|F54C8.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=870|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010036|cpar-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010036|cpar-1|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010036|cpar-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010036|cpar-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010036|cpar-1|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010036|cpar-1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=829|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=427|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11786|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=441|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010037|F54C8.4b|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5974|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1039|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010038|rheb-1|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|1298nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|1304nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|1550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|1553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|1582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|583nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00010039|F54C8.6d|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|1402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1548|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6238|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010040|F54C8.7f|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|1053nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14010|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=794|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010041|F54C9.3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010042|bcs-1|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010042|bcs-1|771nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010042|bcs-1|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1413|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010043|F54C9.7|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010043|F54C9.7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1742|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010044|F54C9.9|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1204|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010044|F54C9.9|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010044|F54C9.9|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|1277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|1587nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|1594nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|259nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|268nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3903|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010045|F54C9.11|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010046|F54D1.1|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010046|F54D1.1|1383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010046|F54D1.1|1388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010046|F54D1.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010046|F54D1.1|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=736|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010046|F54D1.1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|1439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|1443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|1511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|378nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=680|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010047|F54D1.6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010048|F54D5.2|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010048|F54D5.2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010048|F54D5.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010048|F54D5.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010048|F54D5.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1372|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010048|F54D5.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010048|F54D5.2|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6270|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1554|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010049|F54D5.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010050|F54D5.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4721|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010050|F54D5.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010050|F54D5.4|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010051|F54D5.5a|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7166|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010052|F54D5.7.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|1065nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|166nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=652|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|176nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3376|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|181nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|183nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|910nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010053|F54D5.9|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|1574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=860|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11881|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010054|F54D5.11.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|540nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=546|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4999|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=568|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010055|F54D5.12|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6598|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=573|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010056|smc-6|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010057|F54D5.15b.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010057|F54D5.15b.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010058|F54E4.2|1096nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010058|F54E4.2|1198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010058|F54E4.2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010058|F54E4.2|719nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00010058|F54E4.2|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010058|F54E4.2|767nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010058|F54E4.2|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|1533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|654nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|661nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3214|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1136|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|672nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|680nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=273|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010059|F54E4.3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010060|F54E4.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010060|F54E4.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010060|F54E4.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=649|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010060|F54E4.4|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010060|F54E4.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|1291nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2206|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2179|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|438nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010061|F54E12.2.1|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010062|lipl-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010062|lipl-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010062|lipl-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010062|lipl-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010062|lipl-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010063|dhrs-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010063|dhrs-4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010063|dhrs-4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1111|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|228nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=650|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010064|F54F7.2|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17201|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10416|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5598|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010065|F54F7.3|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010066|F54F7.6.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010066|F54F7.6.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010066|F54F7.6.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010066|F54F7.6.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010066|F54F7.6.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010067|dot-1.2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010068|F54F7.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00010068|F54F7.8|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00010068|F54F7.8|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010069|F54F11.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010069|F54F11.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010069|F54F11.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010069|F54F11.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4581|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=505|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010070|nep-17|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010071|sre-45|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010071|sre-45|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010071|sre-45|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00010071|sre-45|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010072|F54F12.1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010072|F54F12.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=946|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1243|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010073|F54F12.2a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=415|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00010074|irld-34|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010074|irld-34|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=680|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00010074|irld-34|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010074|irld-34|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1754|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6069|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3496|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1251|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010075|F55A11.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=766|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010077|F55A11.4a|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010079|F55A11.6c|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010079|F55A11.6c|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010079|F55A11.6c|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010079|F55A11.6c|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1499|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010079|F55A11.6c|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=907|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010079|F55A11.6c|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010079|F55A11.6c|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1693|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010080|F55A11.7|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010081|F55A11.8a|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010081|F55A11.8a|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010082|F55A11.11|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010082|F55A11.11|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=799|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010082|F55A11.11|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010082|F55A11.11|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010082|F55A11.11|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010083|F55B11.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=707|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010083|F55B11.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010083|F55B11.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=349|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|427nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2021|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6946|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37251|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=961|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5008|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=542|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010084|F55B11.2.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|27nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7850|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=300|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010085|F55B11.3|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010086|F55B11.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010086|F55B11.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2362|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010086|F55B11.4|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010086|F55B11.4|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010086|F55B11.4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010086|F55B11.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010086|F55B11.4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|1181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|1207nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|1253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|1258nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|1260nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|1397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|1400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|27nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6927|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=211|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010087|F55B11.5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010088|F55B12.2|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010089|hpo-31|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2312|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010091|ssp-35|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010091|ssp-35|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010091|ssp-35|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010091|ssp-35|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010091|ssp-35|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010091|ssp-35|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1421|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=741|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=248|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|186nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010093|capg-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=768|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|1357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|1359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1299|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|25nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010094|tsfm-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|1330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1519|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|1560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|622nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010096|rskd-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5142|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|435nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|453nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010097|srpa-68|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010098|F55C5.10|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010098|F55C5.10|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010099|fbxb-117|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010101|fbxb-57|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010101|fbxb-57|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010101|fbxb-57|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010102|F55C9.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010102|F55C9.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010104|fbxb-60|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010105|fbxb-62|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010106|fbxb-61|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010106|fbxb-61|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010108|F55C10.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010108|F55C10.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1969|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1203|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010109|F55C10.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=536|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010110|F55D12.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010110|F55D12.1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00010110|F55D12.1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010111|F55D12.2a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010111|F55D12.2a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=681|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2283|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1018|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010113|F55D12.5b|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010114|F55D12.6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010114|F55D12.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=726|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010114|F55D12.6|26nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010114|F55D12.6|35nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010114|F55D12.6|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010115|aakb-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010115|aakb-1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010115|aakb-1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010115|aakb-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010115|aakb-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010115|aakb-1|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010115|aakb-1|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010116|F55F3.2a|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010116|F55F3.2a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=836|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010116|F55F3.2a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=563|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=333|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=377|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|691nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2778|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1564|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|716nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=616|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|806nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|813nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|817nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|819nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010117|nkb-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010118|F55F3.4|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010118|F55F3.4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010119|F55G7.1|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010119|F55G7.1|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010119|F55G7.1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010120|dot-1.4|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010120|dot-1.4|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010120|dot-1.4|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010120|dot-1.4|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010121|F55G7.3|1272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010122|F55G11.1|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010122|F55G11.1|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010123|F55G11.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010123|F55G11.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1129|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010124|F55G11.4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010124|F55G11.4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010124|F55G11.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2284|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010124|F55G11.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010124|F55G11.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00010125|dod-22|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010126|F55G11.6|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010126|F55G11.6|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010127|F55G11.7.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010127|F55G11.7.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=355|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=279|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=305|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010128|F55G11.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7771|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|350nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1710|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1652|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=363|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010130|vha-14|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|572nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|576nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2338|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010131|F55H2.5|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|1195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1768|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=307|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010132|F55H2.7.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1624|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010133|F55H12.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010134|F55H12.3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=400|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010134|F55H12.3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010134|F55H12.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010134|F55H12.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010134|F55H12.3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010134|F55H12.3|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010134|F55H12.3|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010135|F55H12.4|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8171|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010135|F55H12.4|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010135|F55H12.4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010135|F55H12.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010136|F55H12.5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010136|F55H12.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=600|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010136|F55H12.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010137|ztf-26|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010137|ztf-26|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010137|ztf-26|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010137|ztf-26|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010138|anoh-1|1023nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010138|anoh-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010138|anoh-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|1588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=836|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2029|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2886|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|710nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010139|F56A8.3b.4|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010140|F56A8.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010140|F56A8.4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010140|F56A8.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010141|F56A8.5|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010141|F56A8.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010141|F56A8.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1611|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010141|F56A8.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010141|F56A8.5|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010141|F56A8.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010141|F56A8.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010142|F56A8.8|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010143|F56A12.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=610|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|320nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|323nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|328nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|527nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010144|F56C4.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010145|F56C4.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1257|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1919|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1677|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010146|glb-19|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010147|F56D5.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010148|F56D5.3|1378nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010148|F56D5.3|1396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010148|F56D5.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010148|F56D5.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010149|F56D5.5|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010150|F56D5.6a|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010150|F56D5.6a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010150|F56D5.6a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=774|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010150|F56D5.6a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010150|F56D5.6a|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010150|F56D5.6c|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010153|srxa-2|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010153|srxa-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|1369nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|1579nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=229|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=604|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|854nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010155|F56F3.4|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=302|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010157|oac-34|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010158|pes-2.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=941|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010158|pes-2.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010158|pes-2.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010159|F56G4.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010159|F56G4.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1540|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010159|F56G4.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=692|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010159|F56G4.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010160|png-1|419nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010160|png-1|477nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010160|png-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010160|png-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010161|F56G4.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=509|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010161|F56G4.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010161|F56G4.6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010163|F56H6.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010166|gmd-2|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010166|gmd-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00010166|gmd-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010166|gmd-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010167|F56H6.6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010169|clec-18|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010169|clec-18|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010169|clec-18|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010173|F56H6.13|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010173|F56H6.13|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00010173|F56H6.13|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17177|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2307|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010174|F56H9.2a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|103nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|114nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010175|F56H11.2c|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010176|F56H11.6|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010176|F56H11.6|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010176|F56H11.6|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010176|F56H11.6|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|404nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1283|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=591|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010177|F57A8.1.2|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=514|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|1428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|205nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=702|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1137|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|417nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010178|yif-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010179|F57A8.4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010180|nhr-192|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010180|nhr-192|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010181|F57A8.6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010181|F57A8.6|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010181|F57A8.6|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010181|F57A8.6|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010181|F57A8.6|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010182|F57A8.7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010183|fipr-13|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010183|fipr-13|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010184|F57A10.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010184|F57A10.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00010185|F57A10.4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010185|F57A10.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010185|F57A10.4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010186|nhr-283|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00010186|nhr-283|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00010187|F57B1.1|1218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010187|F57B1.1|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010187|F57B1.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010187|F57B1.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010187|F57B1.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010188|F57B1.5|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010188|F57B1.5|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010188|F57B1.5|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1857|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010188|F57B1.5|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010189|F57B1.6a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010189|F57B1.6a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010189|F57B1.6a|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010189|F57B1.6a|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=334|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=998|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=199|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|599nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010191|dmsr-1|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010192|F57B7.2a|1279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010192|F57B7.2a|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010192|F57B7.2a|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3932|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010192|F57B7.2a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010192|F57B7.2a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010192|F57B7.2a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010193|btb-20|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=982|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2094|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010194|btb-19|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010195|pot-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010195|pot-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1016|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010195|pot-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010195|pot-2|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|260nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22183|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010196|F57C2.4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2083|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=428|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010197|F57C2.5c|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010198|spat-1|517nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010198|spat-1|725nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010198|spat-1|729nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010198|spat-1|733nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1252|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010198|spat-1|737nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010198|spat-1|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|1558nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=417|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2332|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|513nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|531nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010199|bet-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010200|F57C7.4|264nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010200|F57C7.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010200|F57C7.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010200|F57C7.4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010200|F57C7.4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010202|F57E7.1a|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010202|F57E7.1a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010202|F57E7.1a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|280nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2457|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37883|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19599|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010204|F57F5.1|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010205|F57F5.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010205|F57F5.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010205|F57F5.3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010205|F57F5.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010205|F57F5.3|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010212|fbxa-192|1296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010212|fbxa-192|1299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010212|fbxa-192|1303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010212|fbxa-192|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=353|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010214|F57G8.5|481nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010214|F57G8.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010214|F57G8.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010215|nhr-193|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010215|nhr-193|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010215|nhr-193|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010215|nhr-193|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010215|nhr-193|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010215|nhr-193|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010216|F57G8.7|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010216|F57G8.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010216|F57G8.7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010217|sre-31|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010218|sre-30|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010219|F57G9.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010219|F57G9.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010220|sre-29|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010220|sre-29|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|1009nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|1398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2225|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|1402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=315|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|551nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010221|F57G12.1|555nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010222|F57G12.2b|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010222|F57G12.2b|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010222|F57G12.2b|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010222|F57G12.2b|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010222|F57G12.2b|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010223|F58A3.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010223|F58A3.3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010224|F58A3.4|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010224|F58A3.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00010224|F58A3.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1899|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010224|F58A3.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010225|ttr-31|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2346|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010225|ttr-31|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010225|ttr-31|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010225|ttr-31|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010226|F58A4.1|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010227|F58A4.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010227|F58A4.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010227|F58A4.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010227|F58A4.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010227|F58A4.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010227|F58A4.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1835|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010228|clec-161|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=402|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=875|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010229|F58A4.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4107|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=426|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010230|rpac-19|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010231|F58B3.4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010231|F58B3.4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010231|F58B3.4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010231|F58B3.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1148|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010231|F58B3.4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010231|F58B3.4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=674|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6779|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1684|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010232|F58B3.6|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010233|F58B3.7|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010233|F58B3.7|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010233|F58B3.7|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010233|F58B3.7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010233|F58B3.7|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010233|F58B3.7|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1563|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|1377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=569|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|219nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|229nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=169|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00010234|ttr-50|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010235|F58B4.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010235|F58B4.2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010235|F58B4.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010235|F58B4.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1521|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010235|F58B4.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=490|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=918|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=878|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10510|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|233nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=248|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=371|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|241nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010236|F58B4.3a|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010237|scvp-1|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010237|scvp-1|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010237|scvp-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010237|scvp-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010237|scvp-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00010237|scvp-1|965nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010237|scvp-1|969nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1536|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010238|F58B4.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=442|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=841|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2436|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010239|F58B4.6|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=569|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010241|F58D2.2|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=476|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010241|F58D2.2|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010241|F58D2.2|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010242|F58D5.2b.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010242|F58D5.2b.2|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010242|F58D5.2b.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010242|F58D5.2b.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010242|F58D5.2b.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010242|F58D5.2b.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010242|F58D5.2b.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010243|F58D5.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010243|F58D5.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010244|F58D5.5|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010244|F58D5.5|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00010244|F58D5.5|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010244|F58D5.5|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010244|F58D5.5|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010244|F58D5.5|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010244|F58D5.5|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010246|F58D5.7|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010246|F58D5.7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2131|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010247|F58D5.8|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010247|F58D5.8|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010247|F58D5.8|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010247|F58D5.8|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010247|F58D5.8|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010247|F58D5.8|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|1511nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|449nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010248|F58D5.9|802nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=531|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010249|F58D12.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00010249|F58D12.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00010251|sta-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010251|sta-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010251|sta-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010253|F58E6.4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010253|F58E6.4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010254|F58E6.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010254|F58E6.5|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010254|F58E6.5|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010254|F58E6.5|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010254|F58E6.5|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=874|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010254|F58E6.5|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010256|hrg-3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010256|hrg-3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010256|hrg-3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=750|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010256|hrg-3|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010256|hrg-3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010257|F58E6.8|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010257|F58E6.8|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010258|F58E6.11|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010258|F58E6.11|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010258|F58E6.11|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010258|F58E6.11|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010258|F58E6.11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2550|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010259|ric-7|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=723|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|309nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1226|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25384|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=405|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|356nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|858nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|862nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010260|ddx-17|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|150nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|153nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66357|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53669|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1336|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|245nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|468nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010262|droe-4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010263|wago-4|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010263|wago-4|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3061|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010263|wago-4|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010263|wago-4|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010264|F58G1.2a.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010264|F58G1.2a.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=443|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010264|F58G1.2a.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1750|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010264|F58G1.2a.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010264|F58G1.2a.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010264|F58G1.2a.2|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010264|F58G1.2a.2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010265|F58G1.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1459|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010265|F58G1.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010266|dct-18|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010266|dct-18|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010266|dct-18|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010266|dct-18|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1355|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00010266|dct-18|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3743|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010267|lips-9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010267|lips-9|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00010267|lips-9|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010268|arrd-10|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010268|arrd-10|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00010268|arrd-10|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010268|arrd-10|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010268|arrd-10|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010268|arrd-10|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010269|F58G1.7|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010269|F58G1.7|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010269|F58G1.7|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=332|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010269|F58G1.7|386nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010270|F58G1.8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3440|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|467nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010272|amph-1|471nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010273|srm-3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010273|srm-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010273|srm-3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1065|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1025|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010274|F58G6.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010275|acc-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010275|acc-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010275|acc-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1373|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010275|acc-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010275|acc-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010275|acc-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010275|acc-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|237nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|241nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|248nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1431|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010277|F58G6.7|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1031|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|44nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010278|F58G6.8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1650|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1811|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|854nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010279|letm-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=853|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=442|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2720|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2589|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010280|rde-12|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2436|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2567|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010281|F58G11.3a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010282|F58G11.4a|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010282|F58G11.4a|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010283|ccz-1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010283|ccz-1|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1620|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010283|ccz-1|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010283|ccz-1|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1996|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010284|aman-2|811nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010285|F58H1.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010285|F58H1.2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=871|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010285|F58H1.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010285|F58H1.2|1342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010285|F58H1.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010285|F58H1.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1321|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010285|F58H1.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010286|F58H1.3a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2374|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010286|F58H1.3a|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010288|F58H1.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010288|F58H1.5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010288|F58H1.5|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010289|F58H1.6|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010289|F58H1.6|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010289|F58H1.6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010289|F58H1.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010289|F58H1.6|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6114|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2276|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=539|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010290|F58H1.7a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4399|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010291|F58H10.1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010292|F59A1.6|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|1417nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|1420nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|1446nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|1450nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|1452nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|1462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=557|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010293|fbxa-108|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010296|dgat-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010296|dgat-2|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=825|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010297|F59A1.11a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010298|F59A1.12|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010299|F59A1.13|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010299|F59A1.13|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010300|F59A1.15|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010300|F59A1.15|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010302|F59A2.2a|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010302|F59A2.2b|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010302|F59A2.2b|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8243|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010303|cri-3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6026|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010304|clpf-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010305|F59A2.5|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010305|F59A2.5|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2130|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010305|F59A2.5|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010306|golg-4|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010306|golg-4|710nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=913|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010306|golg-4|716nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|257nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1674|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1070|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010307|skat-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010308|F59B2.3.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2027|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010308|F59B2.3.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010308|F59B2.3.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010308|F59B2.3.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010308|F59B2.3.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010308|F59B2.3.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=624|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|285nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010309|rpn-6.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=571|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010310|F59B2.8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|1533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|1588nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010311|F59B2.9|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010314|F59B2.12|1462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010314|F59B2.12|1465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010314|F59B2.12|1470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010314|F59B2.12|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010315|F59B2.13|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010315|F59B2.13|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010315|F59B2.13|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010315|F59B2.13|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010315|F59B2.13|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010315|F59B2.13|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010315|F59B2.13|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=515|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=613|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8855|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010316|F59B8.1a.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|1094nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|1117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|137nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|141nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|144nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|149nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|151nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=112|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10182|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010317|idh-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010318|F59B10.2|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=202|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2519|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2117|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010319|F59B10.3|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010320|F59B10.4b|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010320|F59B10.4b|273nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010320|F59B10.4b|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=552|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010320|F59B10.4b|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010321|F59B10.5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010321|F59B10.5|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=888|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010321|F59B10.5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4721|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010321|F59B10.5|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010321|F59B10.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010323|dhhc-12|1452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010323|dhhc-12|1581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010323|dhhc-12|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010323|dhhc-12|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010324|F59C6.3|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010324|F59C6.3|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1535|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|1225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|1293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010325|exos-3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9960|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2353|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1798|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=538|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=801|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2340|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010326|F59C6.5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010327|F59C6.8|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010327|F59C6.8|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010327|F59C6.8|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010328|F59C6.11|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010328|F59C6.11|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010328|F59C6.11|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010328|F59C6.11|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|320nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|326nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|393nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|501nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=684|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|504nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|506nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010329|F59D12.1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010330|F59D12.2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010330|F59D12.2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010330|F59D12.2|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010330|F59D12.2|477nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010330|F59D12.2|479nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010330|F59D12.2|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010331|F59D12.3|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010331|F59D12.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010331|F59D12.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010332|F59D12.5|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010332|F59D12.5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010332|F59D12.5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010332|F59D12.5|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010332|F59D12.5|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=476|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00010332|F59D12.5|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010332|F59D12.5|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4034|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4593|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010333|copz-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1550|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010334|del-5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010334|del-5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010334|del-5|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010334|del-5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010334|del-5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00010335|F59F3.6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010335|F59F3.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010335|F59F3.6|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010335|F59F3.6|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10166|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010336|F59F4.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010336|F59F4.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010336|F59F4.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010336|F59F4.1|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010336|F59F4.1|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19625|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|293nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010337|F59F4.2|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010338|F59F4.3|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010338|F59F4.3|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=891|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010338|F59F4.3|413nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=53|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010339|acl-1|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2594|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010339|acl-1|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010339|acl-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010339|acl-1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010339|acl-1|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|787nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|790nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00010340|slcf-1|792nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010341|glo-3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00010341|glo-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010341|glo-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010342|F59F5.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010342|F59F5.3|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010343|F59F5.4|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010343|F59F5.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=136|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010344|F59F5.5|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010345|F59F5.7|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010345|F59F5.7|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010345|F59F5.7|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010345|F59F5.7|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010345|F59F5.7|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|221nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=609|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010348|H01G02.1a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010349|dyf-18|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010349|dyf-18|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010349|dyf-18|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010349|dyf-18|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00010349|dyf-18|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010349|dyf-18|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010349|dyf-18|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=249|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=380|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1551|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010350|H01G02.3c|417nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|1339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|1343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48933|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1585|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|865nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010351|cbd-1|870nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1013nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=508|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1039nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1042nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1087nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1089nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1960|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=369|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|1506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|401nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=895|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1015|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|876nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9098|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|945nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|969nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010352|fbxb-76|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3175|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010353|H02I12.5|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|1585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=986|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010354|cyp-31A2|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1438|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010355|clec-229|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010355|clec-229|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010355|clec-229|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010355|clec-229|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010355|clec-229|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=631|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=810|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010356|H03A11.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|1156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|1160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010357|H03A11.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010358|H03G16.1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010359|mam-6|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010360|fbxa-96|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010361|H03G16.5|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5565|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=428|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|579nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|584nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=679|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|586nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=487|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010362|enu-3.1|588nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=500|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010363|H04D03.2b|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=577|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010364|H04D03.3|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010364|H04D03.3|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010364|H04D03.3|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010364|H04D03.3|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010364|H04D03.3|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010364|H04D03.3|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010364|H04D03.3|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010365|H04D03.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010365|H04D03.4|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010366|H05L14.1|237nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010366|H05L14.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010366|H05L14.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00010367|H05L14.2|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010367|H05L14.2|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1217|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010367|H05L14.2|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010367|H05L14.2|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010367|H05L14.2|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010367|H05L14.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010368|H06A10.1|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=165|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010368|H06A10.1|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=252|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010368|H06A10.1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010368|H06A10.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010368|H06A10.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010368|H06A10.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|366nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|370nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=241|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|373nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=381|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|380nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010369|chd-1|702nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5243|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=508|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010370|ctg-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010372|H08J19.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00010372|H08J19.1|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010372|H08J19.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010372|H08J19.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010372|H08J19.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010372|H08J19.1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010373|H08M01.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00010373|H08M01.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00010374|rga-5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010374|rga-5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010374|rga-5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010375|H09F14.1a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010375|H09F14.1a|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010375|H09F14.1a|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010375|H09F14.1a|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010375|H09F14.1a|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=274|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010375|H09F14.1a|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=152|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00010378|H12D21.2b|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010380|mpst-2|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010381|H12D21.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010381|H12D21.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010381|H12D21.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010382|H12D21.6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00010382|H12D21.6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=671|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=701|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010383|mpst-3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010385|H12D21.9|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010385|H12D21.9|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010385|H12D21.9|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010386|H12D21.10a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010386|H12D21.10a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010386|H12D21.10a|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010386|H12D21.10a|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010386|H12D21.10a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010387|H12D21.11|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010394|srz-59|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010396|H13N06.2|1516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010396|H13N06.2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010396|H13N06.2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010397|suox-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010397|suox-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=994|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010397|suox-1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010397|suox-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010397|suox-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010399|clec-13|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00010399|clec-13|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00010403|otpl-8|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=503|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|26nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5912|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|389nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|394nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|400nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010405|erfa-3|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|1015nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=445|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|503nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|506nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|515nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1806|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|518nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|596nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|666nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4452|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010406|math-33|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1974|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=507|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|553nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|564nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010407|H19N07.3b|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010408|mboa-2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010408|mboa-2|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5393|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010408|mboa-2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010408|mboa-2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|107nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|334nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|541nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=493|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=508|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010409|H21P03.2.1|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1037|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00010410|nhr-267|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|374nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|663nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010411|H25K10.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010413|H25K10.4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010414|hpa-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010414|hpa-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010415|irld-39|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00010415|irld-39|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010415|irld-39|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010416|hxk-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010416|hxk-2|300nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4004|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010416|hxk-2|303nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010417|H25P06.4|1338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1266|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010418|H27A22.1b|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4956|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75464|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17982|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=315|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1134|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2827|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=562|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1a.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15005|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010419|H28O16.1b|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010420|mcrs-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1217|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010420|mcrs-1|68nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010420|mcrs-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010421|slc-36.4|1231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010421|slc-36.4|1237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010421|slc-36.4|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010421|slc-36.4|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=508|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010421|slc-36.4|181nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010421|slc-36.4|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010421|slc-36.4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010422|H32K16.2|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010422|H32K16.2|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=665|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010422|H32K16.2|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010422|H32K16.2|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010422|H32K16.2|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|1302nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|1362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|1546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|1602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010423|H36L18.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3344|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32316|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|330nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|341nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=262|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010424|H36L18.2b|352nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3489|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=348|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|544nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=590|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|547nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|552nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=591|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|555nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=422|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010425|lpin-1|629nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010426|H37A05.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010427|hpo-11|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010427|hpo-11|1340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010427|hpo-11|1385nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010427|hpo-11|1393nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010427|hpo-11|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010427|hpo-11|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010427|hpo-11|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1477|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3150|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|1159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|921nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|938nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010428|dcn-1|941nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010429|H38K22.4|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010432|H39E23.2|516nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2914|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3674|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010433|H40L08.1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010434|H40L08.3|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010434|H40L08.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1530|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1443|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=870|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010435|JC8.2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010436|JC8.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=488|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010436|JC8.4|1372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010436|JC8.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010436|JC8.4|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010436|JC8.4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010437|cox-11|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=588|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010437|cox-11|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010437|cox-11|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010437|cox-11|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010437|cox-11|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=777|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=589|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010439|JC8.7a|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010440|ttr-51|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010440|ttr-51|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010440|ttr-51|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=292|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010440|ttr-51|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4609|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010440|ttr-51|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7116|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010440|ttr-51|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010440|ttr-51|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010442|bus-12|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1402|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010442|bus-12|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3115|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|283nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=802|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|287nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=893|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|293nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|74nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010444|magi-1|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010446|K01A6.4|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010446|K01A6.4|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010447|K01A6.5a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010447|K01A6.5a|1324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010447|K01A6.5a|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00010447|K01A6.5a|1331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010447|K01A6.5a|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010447|K01A6.5a|1374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010447|K01A6.5a|1381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010448|K01A6.6b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010448|K01A6.6b|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010448|K01A6.6b|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1959|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010448|K01A6.6b|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=282|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010448|K01A6.6b|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=191|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010448|K01A6.6b|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010449|K01A11.1|347nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1704|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010449|K01A11.1|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010450|K01A11.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010450|K01A11.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2141|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010450|K01A11.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010453|fozi-1|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010453|fozi-1|646nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010453|fozi-1|652nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=690|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010453|fozi-1|657nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010453|fozi-1|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010454|K01B6.3|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010454|K01B6.3|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010454|K01B6.3|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010455|K01B6.4|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010456|K01C8.1.2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010456|K01C8.1.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010456|K01C8.1.2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010456|K01C8.1.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010456|K01C8.1.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=739|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010456|K01C8.1.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1289|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010456|K01C8.1.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010457|K01C8.2|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010457|K01C8.2|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=285|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010457|K01C8.2|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1002|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010457|K01C8.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010457|K01C8.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|1314nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1039|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010458|mrpl-10|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010459|K01C8.7a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010459|K01C8.7a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010459|K01C8.7a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010459|K01C8.7a|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1102|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010459|K01C8.7a|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010459|K01C8.7a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010459|K01C8.7a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010460|clec-142|1134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010460|clec-142|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00010460|clec-142|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010460|clec-142|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010460|clec-142|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00010461|K01D12.1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010461|K01D12.1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010461|K01D12.1|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010461|K01D12.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010461|K01D12.1|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010464|K01D12.5|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010464|K01D12.5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010464|K01D12.5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010464|K01D12.5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010465|K01D12.6|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010465|K01D12.6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010465|K01D12.6|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010465|K01D12.6|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3776|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010465|K01D12.6|237nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=564|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2539|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010466|K01D12.7.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010467|K01D12.8|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010467|K01D12.8|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010467|K01D12.8|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=262|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1687|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|203nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010468|K01D12.9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010469|K01D12.10|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010470|cdr-4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010470|cdr-4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010470|cdr-4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010470|cdr-4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010470|cdr-4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38490|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00010470|cdr-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1028|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|1295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1824|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4643|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010471|cdr-6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010472|cdr-7|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010472|cdr-7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010472|cdr-7|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010472|cdr-7|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010472|cdr-7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010472|cdr-7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010472|cdr-7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1068nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1073nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1077nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=845|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010473|hrg-2|621nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010475|K01F9.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010475|K01F9.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010475|K01F9.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010475|K01F9.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1389|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010475|K01F9.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5186|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010475|K01F9.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010475|K01F9.2|96nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010476|rnf-113|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010476|rnf-113|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010476|rnf-113|1027nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010476|rnf-113|1041nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010476|rnf-113|1045nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010476|rnf-113|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010476|rnf-113|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1703|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010477|enu-3.6|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2523|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010477|enu-3.6|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010477|enu-3.6|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010477|enu-3.6|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010477|enu-3.6|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010477|enu-3.6|563nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010477|enu-3.6|569nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=705|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=700|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12136|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4068|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010478|K01G5.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7525|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010479|K01G5.8a|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=646|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3608|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2144|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010480|K01G5.9.3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010481|K01G5.10|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010481|K01G5.10|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010481|K01G5.10|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010483|K01G12.3|1219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010483|K01G12.3|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010483|K01G12.3|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010483|K01G12.3|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010483|K01G12.3|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010483|K01G12.3|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010484|dph-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010484|dph-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1981|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010484|dph-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=792|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010484|dph-3|482nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010484|dph-3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010485|ant-1.3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010485|ant-1.3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010485|ant-1.3|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2205|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010485|ant-1.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010486|K01H12.4|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010486|K01H12.4|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=572|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010487|K02A11.2|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010487|K02A11.2|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=699|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=325|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1026|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1536|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=248|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4189|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2420|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010488|K02A11.3|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=437|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010491|K02B7.3b|1127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010491|K02B7.3b|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1795|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00010491|K02B7.3b|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010491|K02B7.3b|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010492|meg-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010492|meg-1|434nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2392|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010492|meg-1|438nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010492|meg-1|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010493|meg-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010493|meg-2|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010493|meg-2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010493|meg-2|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=302|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010493|meg-2|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010493|meg-2|522nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010494|K02B9.3a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010494|K02B9.3a|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010494|K02B9.3a|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010494|K02B9.3a|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010494|K02B9.3a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010494|K02B9.3a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010494|K02B9.3a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010495|K02B12.2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010495|K02B12.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010495|K02B12.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010495|K02B12.2|1452nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010495|K02B12.2|844nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|135nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|138nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|142nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1613|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2081|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010496|sec-12|630nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010497|axl-1|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010497|axl-1|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010497|axl-1|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010497|axl-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010498|K02B12.5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010498|K02B12.5|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010498|K02B12.5|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=947|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010498|K02B12.5|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=504|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010498|K02B12.5|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010498|K02B12.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010499|K02B12.6|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010499|K02B12.6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010499|K02B12.6|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010499|K02B12.6|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4168|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010500|K02B12.7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010501|K02C4.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010501|K02C4.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010501|K02C4.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|424nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|430nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|434nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2200|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|437nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=960|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010502|K02C4.3|443nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010503|K02C4.5|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010503|K02C4.5|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010503|K02C4.5|291nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010503|K02C4.5|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010503|K02C4.5|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=407|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010503|K02C4.5|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=591|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010503|K02C4.5|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010504|K02D3.1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010504|K02D3.1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00010504|K02D3.1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=917|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010505|K02D3.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010505|K02D3.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010505|K02D3.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010505|K02D3.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010505|K02D3.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010506|K02E2.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010506|K02E2.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010506|K02E2.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=558|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010506|K02E2.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010506|K02E2.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010506|K02E2.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|1090nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3913|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10102|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010507|K02E2.6.2|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010508|K02E2.7b|1406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010508|K02E2.7b|431nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010508|K02E2.7b|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010508|K02E2.7b|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010508|K02E2.7b|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010509|K02E2.8a|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010509|K02E2.8a|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010509|K02E2.8a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010510|ent-3|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010510|ent-3|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=311|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010510|ent-3|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010511|sre-7|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010512|K02E11.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010512|K02E11.3|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010512|K02E11.3|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010512|K02E11.3|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010512|K02E11.3|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010512|K02E11.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010512|K02E11.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010513|K02E11.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010513|K02E11.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010513|K02E11.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010514|K02E11.5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010514|K02E11.5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010514|K02E11.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010514|K02E11.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010514|K02E11.5|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010515|K02E11.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010515|K02E11.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010515|K02E11.6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010515|K02E11.6|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010515|K02E11.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010516|K02E11.7|1159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010516|K02E11.7|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010516|K02E11.7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010516|K02E11.7|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010516|K02E11.7|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010518|K02E11.9|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010518|K02E11.9|879nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010519|K03A11.1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010519|K03A11.1|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010519|K03A11.1|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010519|K03A11.1|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010519|K03A11.1|309nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010520|cpx-2|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010520|cpx-2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=594|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010520|cpx-2|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010520|cpx-2|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010520|cpx-2|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010520|cpx-2|579nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010520|cpx-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010521|K03A11.4|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010521|K03A11.4|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010522|K03A11.5|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010522|K03A11.5|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010524|K03B8.6.2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010524|K03B8.6.2|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010524|K03B8.6.2|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010524|K03B8.6.2|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00010524|K03B8.6.2|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=730|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010524|K03B8.6.2|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010525|K03B8.8|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010525|K03B8.8|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010525|K03B8.8|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010525|K03B8.8|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=402|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010525|K03B8.8|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010525|K03B8.8|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010525|K03B8.8|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010526|K03B8.11|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010527|srz-74|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010527|srz-74|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|1562nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|304nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1171|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010528|K03D3.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010530|srz-61|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010530|srz-61|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010531|K03D3.5|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010531|K03D3.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010537|mys-2|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010537|mys-2|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010537|mys-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=769|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010537|mys-2|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1018|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010538|ttr-3|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010538|ttr-3|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=285|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010538|ttr-3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010538|ttr-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00010538|ttr-3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|1323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|1401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3132|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7116|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010539|ttr-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010540|K03H1.5|1410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010540|K03H1.5|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=286|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010540|K03H1.5|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=266|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010540|K03H1.5|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5149|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=899|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15536|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68555|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2449|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|737nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=790|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1911|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010541|ttr-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010542|K03H1.7|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010542|K03H1.7|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010542|K03H1.7|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010542|K03H1.7|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010542|K03H1.7|372nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1864|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010542|K03H1.7|381nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=355|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010544|K03H1.9|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010544|K03H1.9|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=127|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010544|K03H1.9|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|1353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|1356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010545|cbp-2|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|1202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|46nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|496nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|498nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=816|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|502nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|504nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|51nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010546|K03H1.11|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010547|K03H1.12|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010547|K03H1.12|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=600|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010547|K03H1.12|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010547|K03H1.12|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|477nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|493nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|497nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1342|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010550|K04B12.2b.2|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010551|smg-8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010551|smg-8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010551|smg-8|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1404|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010551|smg-8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010551|smg-8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010551|smg-8|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010552|K04C1.2a|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010552|K04C1.2a|392nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010552|K04C1.2a|397nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=336|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010552|K04C1.2a|401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010552|K04C1.2a|403nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010553|K04C1.3|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010553|K04C1.3|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010553|K04C1.3|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010553|K04C1.3|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010553|K04C1.3|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010553|K04C1.3|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010554|mlc-6|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010554|mlc-6|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010554|mlc-6|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010554|mlc-6|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010555|K04C1.5|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1622|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|1042nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=346|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1590|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141790|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13381|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=391|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4423|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010556|rack-1|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|1127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|1138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|147nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2983|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1452|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010557|mspn-1|487nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=552|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|1123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|55nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010558|ptp-4|58nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1025|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1967|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=401|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|904nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010559|K04D7.6|907nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|1304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|1317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7824|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3479|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010560|iftb-1|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010562|cdc-48.3|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010562|cdc-48.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010562|cdc-48.3|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010562|cdc-48.3|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010562|cdc-48.3|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1456|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010562|cdc-48.3|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010563|K04G2.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|1295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=344|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1069|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6111|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010564|ath-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010565|vacl-14|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010565|vacl-14|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=611|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010565|vacl-14|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010565|vacl-14|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1238|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010565|vacl-14|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010565|vacl-14|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010565|vacl-14|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010566|K04G2.7b|1104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010566|K04G2.7b|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010566|K04G2.7b|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=174|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010566|K04G2.7b|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010566|K04G2.7b|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010566|K04G2.7b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010567|K04G2.9|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010568|K04G2.10|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010568|K04G2.10|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010568|K04G2.10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010568|K04G2.10|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010568|K04G2.10|997nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010569|scbp-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010569|scbp-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010569|scbp-2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010569|scbp-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5672|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010569|scbp-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=415|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010570|K04G11.1|1530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010571|K04G11.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010571|K04G11.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00010571|K04G11.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010572|wdr-5.2|841nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010573|K04H4.2a.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010573|K04H4.2a.2|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010573|K04H4.2a.2|367nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=521|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010573|K04H4.2a.2|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010573|K04H4.2a.2|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010573|K04H4.2a.2|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010574|K04H4.5|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010574|K04H4.5|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010574|K04H4.5|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1402|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010574|K04H4.5|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=431|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00010574|K04H4.5|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2779|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=692|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010575|flp-25|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010578|K04H8.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010579|K05C4.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010579|K05C4.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010579|K05C4.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010579|K05C4.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7030|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010579|K05C4.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010579|K05C4.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010580|K05C4.3|855nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010581|K05C4.4|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010581|K05C4.4|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010581|K05C4.4|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010581|K05C4.4|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010581|K05C4.4|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010582|K05C4.5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010582|K05C4.5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3019|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010582|K05C4.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010582|K05C4.5|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010583|K05C4.7.2|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2432|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010583|K05C4.7.2|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010583|K05C4.7.2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010583|K05C4.7.2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010583|K05C4.7.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010583|K05C4.7.2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010584|K05C4.8|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010585|K05C4.9|668nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010585|K05C4.9|672nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010585|K05C4.9|698nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010585|K05C4.9|762nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010585|K05C4.9|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010585|K05C4.9|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010586|K05C4.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010586|K05C4.10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=840|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010587|sol-2|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010588|srz-14|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010589|cyp-33D1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010589|cyp-33D1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010589|cyp-33D1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010589|cyp-33D1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010591|K05D4.9|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|1094nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1078|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1166|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010592|K06A4.2a|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010593|gsnl-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1423|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010593|gsnl-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=770|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010593|gsnl-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010594|swt-5|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010594|swt-5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010594|swt-5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010594|swt-5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010595|haao-1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010595|haao-1|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010595|haao-1|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010595|haao-1|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010595|haao-1|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=641|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010595|haao-1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010595|haao-1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010596|K06A4.6|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010596|K06A4.6|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3195|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7992|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010597|K06A4.7|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010598|K06B4.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010599|K06B4.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010599|K06B4.4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010600|nhr-196|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010600|nhr-196|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010600|nhr-196|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010601|nhr-268|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010602|nhr-197|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010602|nhr-197|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010602|nhr-197|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010602|nhr-197|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010602|nhr-197|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010602|nhr-197|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00010602|nhr-197|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|736nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010603|nhr-198|88nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010604|nhr-199|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010604|nhr-199|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010604|nhr-199|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|46nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|57nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=715|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|63nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8416|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2074|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010605|K06G5.1a.3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010606|cyp-13B2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010607|K06G5.3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010607|K06G5.3|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00010608|K07A1.1|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010608|K07A1.1|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010608|K07A1.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010608|K07A1.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5917|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010609|dut-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010609|dut-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010609|dut-1|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5307|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010609|dut-1|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=519|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1960|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010610|K07A1.3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=583|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010611|K07A1.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010611|K07A1.4|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010611|K07A1.4|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010611|K07A1.4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010611|K07A1.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010611|K07A1.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00010611|K07A1.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010612|K07A1.5|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010612|K07A1.5|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=522|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=768|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3910|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00010613|K07A1.6|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2067|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010614|cri-1|1519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010614|cri-1|1521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010614|cri-1|1524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010614|cri-1|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2482|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9c|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9c|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9c|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9c|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9c|726nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010615|K07A1.9c|729nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2529|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1449|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=477|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|628nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010616|K07A1.10|792nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010617|K07A1.13|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010617|K07A1.13|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2046|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010617|K07A1.13|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010617|K07A1.13|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010617|K07A1.13|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010617|K07A1.13|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010619|K07A1.15|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1196|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010619|K07A1.15|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010620|K07A12.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010620|K07A12.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010620|K07A12.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010620|K07A12.1|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010620|K07A12.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010620|K07A12.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010620|K07A12.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5073|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|386nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=190|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6345|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=350|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010621|egg-6|459nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010622|K07A12.4a|1488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010622|K07A12.4a|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010622|K07A12.4a|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1429|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010622|K07A12.4a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010622|K07A12.4a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010623|K07A12.5e|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=513|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010623|K07A12.5e|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010623|K07A12.5e|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010624|mrps-15|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010624|mrps-15|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010624|mrps-15|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2277|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010624|mrps-15|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010624|mrps-15|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010625|K07C5.2|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010625|K07C5.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010625|K07C5.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010625|K07C5.2|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010625|K07C5.2|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=861|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010625|K07C5.2|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=209|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010626|K07C5.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010626|K07C5.3|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1301|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010626|K07C5.3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010627|K07C5.4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010627|K07C5.4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010627|K07C5.4|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25998|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010627|K07C5.4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010627|K07C5.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010628|ceeh-2|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010628|ceeh-2|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010628|ceeh-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1090|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010628|ceeh-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|695nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|697nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2358|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010629|K07C5.6|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010630|ttll-15|1242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010630|ttll-15|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010630|ttll-15|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010630|ttll-15|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010630|ttll-15|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|1338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1045|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4153|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=897|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010631|cash-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010632|K07C5.9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010632|K07C5.9|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5592|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2857|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7787|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=950|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010633|nspd-2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010634|K07F5.6|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010634|K07F5.6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00010634|K07F5.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010634|K07F5.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010634|K07F5.6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010636|K07F5.8|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010636|K07F5.8|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010636|K07F5.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010636|K07F5.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=771|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010636|K07F5.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010636|K07F5.8|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010636|K07F5.8|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010637|K07F5.12|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010637|K07F5.12|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=766|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00010637|K07F5.12|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010638|K07F5.14|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1765|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010638|K07F5.14|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=427|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15a|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|1563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14409|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010639|K07F5.15b.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1818|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16a|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16b|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010640|K07F5.16b|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|443nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=166|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|446nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1226|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|449nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1683|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|451nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=548|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|455nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|458nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010641|crml-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010642|mks-6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010643|K07G5.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010643|K07G5.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010644|K07G5.5|811nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010644|K07G5.5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010644|K07G5.5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010644|K07G5.5|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010645|fecl-1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2848|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010645|fecl-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010645|fecl-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010645|fecl-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010645|fecl-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010645|fecl-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010645|fecl-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010646|K08C7.1|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=207|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010646|K08C7.1|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010646|K08C7.1|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=485|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010646|K08C7.1|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010646|K08C7.1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|452nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1150|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010647|K08C7.4|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010648|K08C7.6|16nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010648|K08C7.6|18nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010648|K08C7.6|21nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010648|K08C7.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010648|K08C7.6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=584|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010648|K08C7.6|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=725|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010649|K08C7.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=762|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010649|K08C7.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010649|K08C7.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010649|K08C7.7|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010650|K08C9.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010650|K08C9.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010650|K08C9.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010651|K08C9.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010651|K08C9.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1807|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00010651|K08C9.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010651|K08C9.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010652|K08C9.5|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010652|K08C9.5|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010653|K08C9.6|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010654|K08C9.7|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010655|K08D8.1|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010655|K08D8.1|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010657|K08D8.3|214nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=604|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010657|K08D8.3|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010657|K08D8.3|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010657|K08D8.3|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010658|K08D8.4a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010658|K08D8.4a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010658|K08D8.4a|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010658|K08D8.4a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=891|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010658|K08D8.4a|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010658|K08D8.4a|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010659|K08D8.5|118nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010659|K08D8.5|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010659|K08D8.5|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010659|K08D8.5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2802|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010659|K08D8.5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2689|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010660|K08D8.6b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010661|tyr-2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010661|tyr-2|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010661|tyr-2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=868|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010661|tyr-2|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010661|tyr-2|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010661|tyr-2|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010661|tyr-2|323nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010662|K08E3.2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010662|K08E3.2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010662|K08E3.2|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2599|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010663|toca-2|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1318|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2965|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010664|dbn-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|1436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=552|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|183nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|186nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=91|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|190nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1256|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|194nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|196nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|199nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|202nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6202|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1299|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010665|K08E3.5a.2|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|121nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|146nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|150nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=550|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010666|K08E4.2b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=258|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=407|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010667|K08E4.3b|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010669|bath-37|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010669|bath-37|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=236|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1454|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2558|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010670|K08E4.6|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3534|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2537|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010671|eak-7|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010672|K08E7.4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010672|K08E7.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010672|K08E7.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010672|K08E7.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010672|K08E7.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010673|K08E7.5c|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010673|K08E7.5c|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010674|K08E7.6|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010674|K08E7.6|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=642|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010674|K08E7.6|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010674|K08E7.6|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010675|K08E7.8b|1126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010675|K08E7.8b|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010675|K08E7.8b|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=681|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010675|K08E7.8b|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010675|K08E7.8b|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2729|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010676|K08F4.1.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|1537nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|1543nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8682|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7790|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010677|gtbp-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010678|K08F4.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010678|K08F4.3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5996|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010678|K08F4.3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=900|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00010678|K08F4.3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010678|K08F4.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010678|K08F4.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010679|K08F4.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010680|K08F4.12|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010680|K08F4.12|1498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010680|K08F4.12|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010680|K08F4.12|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=377|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4351|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1074|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010681|mak-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010682|K08F8.5b|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010682|K08F8.5b|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010682|K08F8.5b|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00010682|K08F8.5b|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010682|K08F8.5b|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010683|K08F8.7|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010683|K08F8.7|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010683|K08F8.7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010683|K08F8.7|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010683|K08F8.7|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010684|K08F9.1a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010684|K08F9.1a|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010684|K08F9.1a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010684|K08F9.1a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010684|K08F9.1a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010684|K08F9.1a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=166|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010685|aipl-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|1356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|1372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010686|K08F9.3d|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1551|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=307|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|237nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=288|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010687|K08F9.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010688|srz-12|1587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010689|K08H2.2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010690|K08H2.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00010691|K08H2.4|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010692|K08H2.5|80nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010692|K08H2.5|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010694|K08H2.9|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010697|uda-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010697|uda-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010697|uda-1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5443|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010698|K08H10.6|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010698|K08H10.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010698|K08H10.6|749nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010698|K08H10.6|992nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010699|trpp-6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010699|trpp-6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3456|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010699|trpp-6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1578|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010699|trpp-6|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|1512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6970|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=734|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=787|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010700|nipi-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|1589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1614|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2927|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|449nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|452nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|455nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|484nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|487nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|617nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010701|ent-2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010702|usp-33|1358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010702|usp-33|1525nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010702|usp-33|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010702|usp-33|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010702|usp-33|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010702|usp-33|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010702|usp-33|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010703|K09A9.6a|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010703|K09A9.6a|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010703|K09A9.6a|177nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010703|K09A9.6a|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00010703|K09A9.6a|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010703|K09A9.6a|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=814|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010703|K09A9.6a|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010704|K09A11.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010705|cyp-14A1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010705|cyp-14A1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00010705|cyp-14A1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00010705|cyp-14A1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00010706|cyp-14A2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00010706|cyp-14A2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010707|cyp-14A3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010708|phf-33|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010709|nol-9|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010709|nol-9|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010709|nol-9|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=794|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010711|K09B11.4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010711|K09B11.4|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010711|K09B11.4|242nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010711|K09B11.4|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010711|K09B11.4|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010712|K09B11.5b|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010712|K09B11.5b|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010713|uso-1|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010713|uso-1|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010713|uso-1|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010713|uso-1|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1337|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00010713|uso-1|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010713|uso-1|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010713|uso-1|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=292|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010714|mam-3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010714|mam-3|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010716|lge-1|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=526|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010716|lge-1|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010716|lge-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010717|K09C8.7|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010717|K09C8.7|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010717|K09C8.7|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010718|K09C8.8|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010719|K09E4.1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010719|K09E4.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=931|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010720|K09E4.2b|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1012|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010720|K09E4.2b|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010720|K09E4.2b|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010721|K09E4.3b|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=832|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=279|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1329|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1079|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00010722|K09E4.4.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1472|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=446|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=971|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010723|cpg-7|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010724|K09E9.1c.1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010724|K09E9.1c.1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010724|K09E9.1c.1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010724|K09E9.1c.1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010724|K09E9.1c.1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1661|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010724|K09E9.1c.1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010724|K09E9.1c.1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1513|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|626nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010725|erv-46|629nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010726|K09E9.3|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010726|K09E9.3|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00010726|K09E9.3|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010726|K09E9.3|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=621|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010726|K09E9.3|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010726|K09E9.3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010726|K09E9.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010727|K09G1.1d|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010727|K09G1.1d|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010727|K09G1.1d|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010727|K09G1.1d|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010727|K09G1.1d|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010727|K09G1.1d|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4395|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010727|K09G1.1d|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010728|K09G1.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010728|K09G1.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1666|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|1143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|1150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|1504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|1506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1341|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|591nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|595nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|598nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1037|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|607nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|611nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|613nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|617nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8722|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|621nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|627nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|629nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010730|ensa-1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2756|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|1368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010731|K10C3.4b|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|122nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1055|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1885|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=399|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010732|K10C3.5a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010734|parn-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1870|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010734|parn-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010734|parn-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010734|parn-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010735|frpr-15|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1348|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32794|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2413|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=796|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|567nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|676nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010736|istr-1|97nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=1291|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|1154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|1198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|156nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=289|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|559nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|863nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010737|K10C8.4|865nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010738|K10D3.4|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010738|K10D3.4|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010738|K10D3.4|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010738|K10D3.4|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|218nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=74|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010740|K10D3.6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010741|lgc-49|298nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010741|lgc-49|307nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=740|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010741|lgc-49|310nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010741|lgc-49|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010742|K10D6.2a|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010742|K10D6.2a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010742|K10D6.2a|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010742|K10D6.2a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010742|K10D6.2c|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010743|K10D6.3a|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00010743|K10D6.3a|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010743|K10D6.3a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010743|K10D6.3a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1604|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|429nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010744|K10D6.4b|765nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010745|dod-17|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010745|dod-17|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010745|dod-17|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010745|dod-17|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=663|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010745|dod-17|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010745|dod-17|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010746|K10D11.2|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010746|K10D11.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010746|K10D11.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010747|K10D11.3c|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010749|K10D11.5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010749|K10D11.5|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=789|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010749|K10D11.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010749|K10D11.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010750|K10D11.6|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=308|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010750|K10D11.6|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010752|K10G4.3|1323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010752|K10G4.3|1330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010754|K10G4.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010755|vglu-2|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010755|vglu-2|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010755|vglu-2|342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=826|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010756|K10G9.2|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2038|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00010756|K10G9.2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1631|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010756|K10G9.2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010756|K10G9.2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010756|K10G9.2|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010757|pad-2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00010757|pad-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010757|pad-2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010758|vnut-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010758|vnut-1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2212|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010758|vnut-1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010758|vnut-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010759|cysl-2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010759|cysl-2|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010759|cysl-2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1286|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010759|cysl-2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010759|cysl-2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010759|cysl-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010759|cysl-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010760|K10H10.4a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010760|K10H10.4a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010761|K10H10.5|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010761|K10H10.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010761|K10H10.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010761|K10H10.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010762|K10H10.6|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010763|K10H10.7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010763|K10H10.7|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010763|K10H10.7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=558|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010763|K10H10.7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010764|K10H10.9|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010765|K10H10.10a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010765|K10H10.10a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010765|K10H10.10a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2773|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010766|K11B4.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2084|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=611|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=571|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010767|K11B4.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010768|K11D2.1b|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010768|K11D2.1b|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010768|K11D2.1b|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=300|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010768|K11D2.1b|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010769|asah-1|109nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010769|asah-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010769|asah-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010769|asah-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2746|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010769|asah-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010769|asah-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1575|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010770|K11D2.4a|763nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010770|K11D2.4a|769nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3270|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010770|K11D2.4a|772nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010770|K11D2.4a|777nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010770|K11D2.4a|827nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010770|K11D2.4a|833nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010771|K11D2.5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=805|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010771|K11D2.5|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=889|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|517nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|524nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|529nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010772|K11D9.3.1|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010773|K11E4.1|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010774|K11E4.2|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010774|K11E4.2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010774|K11E4.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00010774|K11E4.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010775|poml-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010775|poml-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010775|poml-1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010775|poml-1|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|980nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|984nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|986nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010776|pix-1|988nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1841|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6554|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|830nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010778|gpdh-2|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010779|K11H3.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010779|K11H3.2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010779|K11H3.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010779|K11H3.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1078|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2836|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|846nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|923nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|931nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010780|K11H3.3|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010781|K11H3.4|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00010781|K11H3.4|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=896|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00010782|K11H3.5a|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010782|K11H3.5a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010782|K11H3.5a|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=395|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010782|K11H3.5a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010783|mrpl-36|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010783|mrpl-36|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010783|mrpl-36|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2645|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010783|mrpl-36|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010783|mrpl-36|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2129|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|328nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|385nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010784|twk-48|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6113|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010785|top-2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010786|K12D12.4|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010786|K12D12.4|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010787|K12D12.5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010787|K12D12.5|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010787|K12D12.5|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1313|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010787|K12D12.5|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010787|K12D12.5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010788|sulp-4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010788|sulp-4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010788|sulp-4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010788|sulp-4|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010788|sulp-4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010789|sulp-5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010789|sulp-5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1576|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7899|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1237|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1262|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=874|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|164nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=767|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|215nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010790|sodh-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010791|sodh-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010791|sodh-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010791|sodh-2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010791|sodh-2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010792|K12G11.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010792|K12G11.6|1329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010792|K12G11.6|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010792|K12G11.6|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010793|LLC1.2a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1348|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010793|LLC1.2a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5525|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010793|LLC1.2a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=536|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8759|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=472|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010794|dld-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010795|M01A8.1a|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00010795|M01A8.1a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=669|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010795|M01A8.1a|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|374nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|377nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010796|clip-1|382nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010797|srbc-75|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010799|chil-12|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010799|chil-12|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010800|srsx-37|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010801|M01B2.8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010801|M01B2.8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010801|M01B2.8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010801|M01B2.8|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010803|M01B2.10|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010803|M01B2.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=753|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010804|M01E5.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010804|M01E5.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010805|M01E5.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=977|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|770nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|775nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4902|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|780nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|783nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|786nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010806|M01E5.3c|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|1111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5243|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010807|M01E5.4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1365nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1369nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1411nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|1421nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|849nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|904nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|915nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010808|sepa-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1155|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2045|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=465|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010809|M01F1.3.1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010810|M01F1.4b|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2795|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010810|M01F1.4b|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010811|hmit-1.3|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010811|hmit-1.3|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010811|hmit-1.3|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010811|hmit-1.3|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1020|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010812|mrpl-35|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010813|pitp-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010813|pitp-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010813|pitp-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1899|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00010813|pitp-1|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010814|M01F1.8a|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=902|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010814|M01F1.8a|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=425|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010814|M01F1.8a|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|452nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|456nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|462nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=592|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|469nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=331|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|471nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=381|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|475nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|700nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|703nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|713nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010815|M01F1.9|850nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010819|M01G12.5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010819|M01G12.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010819|M01G12.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010819|M01G12.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010820|M01G12.6|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010821|M01G12.7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|885nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010822|M01G12.9|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|408nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|419nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1856|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|421nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010827|M02B1.2|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|383nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6354|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|397nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=469|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2370|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|689nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|692nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010828|M02B1.3a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010829|M02B1.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010829|M02B1.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010829|M02B1.4|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010829|M02B1.4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010829|M02B1.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010830|M02G9.1a|217nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010830|M02G9.1a|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=424|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010831|M02G9.2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010831|M02G9.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010832|M02G9.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010832|M02G9.3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010832|M02G9.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00010832|M02G9.3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=814|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|358nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|361nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010833|M03B6.1|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=781|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=797|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010834|mct-3|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010835|M03B6.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010835|M03B6.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010835|M03B6.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4a|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4a|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4a|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4a|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4a|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4a|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4b|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010836|M03B6.4b|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010837|M03B6.5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010837|M03B6.5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010838|M03C11.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010838|M03C11.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010838|M03C11.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010838|M03C11.1|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010838|M03C11.1|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010838|M03C11.1|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010838|M03C11.1|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1237|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010839|chl-1|1073nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010839|chl-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=561|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010839|chl-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010839|chl-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010839|chl-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010839|chl-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1181nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1156|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1185nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=392|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00010840|M03C11.3a|1189nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010842|ymel-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010842|ymel-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010842|ymel-1|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3814|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010843|M03C11.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=467|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010843|M03C11.6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010843|M03C11.6|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010843|M03C11.6|306nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010844|prp-3|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3100|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010844|prp-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010844|prp-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010845|M03C11.8|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010845|M03C11.8|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010845|M03C11.8|501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2514|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010845|M03C11.8|503nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010845|M03C11.8|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|282nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|284nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010846|M04B2.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010847|M04B2.4|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010847|M04B2.4|1500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010847|M04B2.4|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1069|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010847|M04B2.4|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00010847|M04B2.4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5186|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010848|M04B2.6|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010849|M04B2.7c|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010849|M04B2.7c|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1223|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010849|M04B2.7c|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1585|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010849|M04B2.7c|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=722|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010849|M04B2.7c|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010849|M04B2.7c|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010850|M04C3.1a|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010850|M04C3.1a|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010850|M04C3.1a|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010850|M04C3.1a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010850|M04C3.1d|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010851|M04C3.2a|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00010851|M04C3.2a|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010854|M04C7.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010854|M04C7.3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010855|M04C7.4|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010855|M04C7.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010855|M04C7.4|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010855|M04C7.4|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010856|M04C9.1b|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010856|M04C9.1b|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010856|M04C9.1b|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010857|M04C9.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010857|M04C9.2|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010857|M04C9.2|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010857|M04C9.2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010858|M04C9.3b|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010858|M04C9.3b|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=585|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00010859|M04C9.4|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010859|M04C9.4|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010859|M04C9.4|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=334|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|421nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|425nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|439nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010862|M04D8.4|695nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010863|M04D8.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010863|M04D8.5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010863|M04D8.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8982|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010864|xbx-3|575nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010865|M04D8.7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010865|M04D8.7|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010865|M04D8.7|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010865|M04D8.7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010865|M04D8.7|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3609|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00010865|M04D8.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010865|M04D8.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010866|M04D8.8|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=855|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010867|tag-260|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|1119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2183|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010868|somi-1|604nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010869|M05B5.1|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=430|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010869|M05B5.1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010870|let-522|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010870|let-522|1552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010870|let-522|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010870|let-522|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010870|let-522|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010870|let-522|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1283|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010870|let-522|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010871|M05B5.3b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010871|M05B5.3b|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=642|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010871|M05B5.3b|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010871|M05B5.3b|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010871|M05B5.3b|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010871|M05B5.3b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010872|M05B5.4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010872|M05B5.4|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1149|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010872|M05B5.4|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010872|M05B5.4|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=373|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010872|M05B5.4|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=497|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010873|trpa-2|358nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010874|M05D6.1.1|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=182|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010874|M05D6.1.1|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00010874|M05D6.1.1|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00010874|M05D6.1.1|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=310|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010874|M05D6.1.1|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010874|M05D6.1.1|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|1068nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3507|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|21nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|737nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|740nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010875|M05D6.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010876|M05D6.3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010876|M05D6.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010876|M05D6.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010876|M05D6.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010876|M05D6.3|669nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|1251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|1253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|1256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|583nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1496|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010877|lact-4|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|1415nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3288|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2028|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010878|M05D6.5b|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10546|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1818|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010879|M05D6.6.2|605nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010880|M05D6.8a|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010880|M05D6.8a|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010880|M05D6.8b|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010880|M05D6.8b|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010880|M05D6.8b|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010880|M05D6.8b|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010881|M05D6.9|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010881|M05D6.9|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1519|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3213|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010882|atg-7|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010883|M7.7|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010883|M7.7|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010883|M7.7|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010884|M7.8|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010884|M7.8|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010884|M7.8|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2992|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00010884|M7.8|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010885|M7.9|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010885|M7.9|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010886|M7.10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010887|M7.12|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010887|M7.12|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010887|M7.12|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3351|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010887|M7.12|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3881|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|1406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|1581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|1590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010888|dlc-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1178|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010889|M18.3|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2171|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1257|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010890|ddb-1|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2246|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|1278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|1285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010891|M18.6a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010892|dhhc-6|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010892|dhhc-6|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1831|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010892|dhhc-6|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1736|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010892|dhhc-6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010892|dhhc-6|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010895|M28.4|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010895|M28.4|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7820|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1600|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48471|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1225|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3386|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2466|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=651|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010896|M28.5.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010897|lact-3|1492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010897|lact-3|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010897|lact-3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2919|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00010897|lact-3|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=784|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010897|lact-3|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010898|nphp-1|24nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010898|nphp-1|27nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010898|nphp-1|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010898|nphp-1|294nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010898|nphp-1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010898|nphp-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010898|nphp-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00010899|M28.8|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010899|M28.8|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=604|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010899|M28.8|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010899|M28.8|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010901|M28.10|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1908|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010902|M79.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010902|M79.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010902|M79.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010902|M79.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010902|M79.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010904|ugt-62|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010904|ugt-62|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=441|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010904|ugt-62|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010904|ugt-62|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010904|ugt-62|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3156|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1112|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=675|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|221nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010905|mrps-34|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010906|M88.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010906|M88.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010906|M88.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010906|M88.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|1182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|1475nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010907|M88.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|1283nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|1426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|683nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4846|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|693nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1962|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010908|zbp-1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010909|cisd-3.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010909|cisd-3.1|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010909|cisd-3.1|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010909|cisd-3.1|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=983|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010909|cisd-3.1|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010909|cisd-3.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010909|cisd-3.1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|728nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|741nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1752|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|875nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|881nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010910|M106.2|884nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5004|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|454nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|457nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010911|M106.3b.1|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|204nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|208nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|211nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4003|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010912|gmps-1|516nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=410|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3599|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010913|M110.3|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010915|M110.7|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010916|M110.8a|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010916|M110.8a|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010916|M110.8a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010916|M110.8a|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010916|M110.8a|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010916|M110.8a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010916|M110.8a|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00010917|M110.9|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|1131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|1597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1658|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=902|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010918|M117.1a|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010919|M117.3|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010919|M117.3|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010920|M117.4|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010920|M117.4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010920|M117.4|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010920|M117.4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|1151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2419|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|863nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010922|M142.5|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|829nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4436|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|834nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010923|rle-1|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=521|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010924|M153.1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010925|M153.2|1116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00010925|M153.2|1120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010925|M153.2|1124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010925|M153.2|1127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010926|M153.3|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010927|clec-259|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010928|clec-258|505nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00010928|clec-258|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00010931|M162.5|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010931|M162.5|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010933|M162.7|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010933|M162.7|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010933|M162.7|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010934|fbxa-118|263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010934|fbxa-118|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010934|fbxa-118|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|1028nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|885nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|889nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2148|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|893nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|898nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010935|M163.1|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010936|ztf-14|899nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|1210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|1473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|1527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010937|M163.5|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010938|M163.6|1396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010938|M163.6|282nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010939|M163.7|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010940|M163.8.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1331|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010941|gss-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010941|gss-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=531|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010941|gss-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1133|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010941|gss-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1110|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00010941|gss-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010941|gss-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010941|gss-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010942|chch-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010942|chch-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010942|chch-3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010942|chch-3|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010942|chch-3|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7379|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010942|chch-3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1860|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=535|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|351nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010943|M176.4|355nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010944|M176.5|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010944|M176.5|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010944|M176.5|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3999|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010944|M176.5|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1990|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010944|M176.5|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010944|M176.5|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010945|chil-13|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010945|chil-13|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010945|chil-13|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010945|chil-13|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010945|chil-13|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010946|M176.10|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010946|M176.10|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010946|M176.10|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010946|M176.10|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010946|M176.10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=685|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010947|M176.11|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010948|M195.2b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010948|M195.2b|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010948|M195.2b|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010948|M195.2b|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010948|M195.2b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010949|M195.4a|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010951|M199.2.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010951|M199.2.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010951|M199.2.1|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010951|M199.2.1|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00010951|M199.2.1|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010953|clec-190|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010953|clec-190|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=970|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010953|clec-190|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010953|clec-190|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010955|M199.7|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010968|R01E6.2|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010968|R01E6.2|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=685|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010968|R01E6.2|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010968|R01E6.2|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010968|R01E6.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010968|R01E6.2|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010968|R01E6.2|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00010969|R01E6.5|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010969|R01E6.5|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|1399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|1401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|1483nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|1486nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|1594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10308|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010970|glb-20|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010971|R01E6.7|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=585|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010971|R01E6.7|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010971|R01E6.7|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010971|R01E6.7|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010971|R01E6.7|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=127|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010971|R01E6.7|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010972|R01H10.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010972|R01H10.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010972|R01H10.4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010972|R01H10.4|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010972|R01H10.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010973|rip-1|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010973|rip-1|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=209|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010973|rip-1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010974|bbs-5|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010974|bbs-5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=984|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010974|bbs-5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010974|bbs-5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1140|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010975|R01H10.7|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010976|R02D5.1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010976|R02D5.1|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010976|R02D5.1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=845|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010976|R02D5.1|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010976|R02D5.1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010976|R02D5.1|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010977|R02D5.3|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010977|R02D5.3|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=360|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010978|R02D5.4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010978|R02D5.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010978|R02D5.4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010979|R02D5.6c|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010979|R02D5.6c|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00010979|R02D5.6c|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1394|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010979|R02D5.6c|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010980|R02D5.7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010980|R02D5.7|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1253|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010980|R02D5.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010980|R02D5.7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3292|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=648|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010981|R03A10.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41166|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1380|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=661|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010982|flp-32|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010983|mocs-1|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010983|mocs-1|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1207|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010984|nkat-3|256nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010985|R03A10.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010985|R03A10.5|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010985|R03A10.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010985|R03A10.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010985|R03A10.5|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=392|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=108|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010986|sprr-1|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010987|R03C1.1a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010987|R03C1.1a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010987|R03C1.1a|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010987|R03C1.1a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010988|metr-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010988|metr-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5269|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010988|metr-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=722|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00010988|metr-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010989|R03D7.2|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010989|R03D7.2|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=780|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010989|R03D7.2|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010989|R03D7.2|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1804|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010990|R03D7.4|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010991|R03D7.5a|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00010991|R03D7.5a|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010992|R03D7.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010992|R03D7.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12179|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010993|vha-20|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1639|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17649|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5838|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010994|lgc-25|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00010995|ceh-90|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|1094nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010998|R03G8.3|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00010999|R03G8.4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011000|R03G8.6|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011000|R03G8.6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011000|R03G8.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=553|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011001|R04B5.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011001|R04B5.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011001|R04B5.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00011002|nhr-205|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011003|R04B5.5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011003|R04B5.5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011003|R04B5.5|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011003|R04B5.5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011004|R04B5.6|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011004|R04B5.6|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011004|R04B5.6|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011005|R04B5.7|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011005|R04B5.7|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011005|R04B5.7|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00011005|R04B5.7|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011006|ugt-47|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011006|ugt-47|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011006|ugt-47|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1780|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011006|ugt-47|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011006|ugt-47|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011008|R04B5.11|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=584|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011008|R04B5.11|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011009|cyp-14A4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011009|cyp-14A4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011010|R04D3.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1499|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011010|R04D3.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011010|R04D3.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=847|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011011|R04D3.3.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011012|R04D3.4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011013|srxa-8|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011014|hpo-30|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1774|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=546|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=494|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1116|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=604|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=291|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12461|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1931|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=214|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1436|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=849|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1977|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=612|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1993|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011015|R04F11.2.4|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=193|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|1014nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3383|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011016|R04F11.3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2204|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|1048nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|637nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|658nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|665nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|767nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|866nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|946nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|950nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011017|R04F11.5|960nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011018|R05A10.1b|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011018|R05A10.1b|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011018|R05A10.1b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011018|R05A10.1b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011019|R05A10.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00011019|R05A10.2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011019|R05A10.2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011019|R05A10.2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011019|R05A10.2|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011019|R05A10.2|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011019|R05A10.2|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011020|R05A10.3|1159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011020|R05A10.3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011020|R05A10.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011021|R05A10.4|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011021|R05A10.4|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011023|R05A10.6|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011023|R05A10.6|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011023|R05A10.6|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011023|R05A10.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011024|R05A10.7|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011024|R05A10.7|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011024|R05A10.7|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011024|R05A10.7|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011025|R05A10.8|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011025|R05A10.8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011025|R05A10.8|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011026|R05D7.1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011026|R05D7.1|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011026|R05D7.1|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011026|R05D7.1|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011026|R05D7.1|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2136|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011026|R05D7.1|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011026|R05D7.1|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011027|R05D7.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00011027|R05D7.2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00011027|R05D7.2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011028|R05D7.3a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011028|R05D7.3a|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011028|R05D7.3a|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011028|R05D7.3a|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011028|R05D7.3a|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011028|R05D7.3a|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011028|R05D7.3a|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011029|abhd-11.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011029|abhd-11.2|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011029|abhd-11.2|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1992|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011029|abhd-11.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011029|abhd-11.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=566|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011029|abhd-11.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011030|R05D7.5|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011030|R05D7.5|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011030|R05D7.5|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011030|R05D7.5|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=762|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011030|R05D7.5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=441|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=344|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=769|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|485nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|487nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|490nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011032|R05D11.4|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4031|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011033|R05D11.5|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011034|paxt-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011034|paxt-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011034|paxt-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2864|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011034|paxt-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011034|paxt-1|397nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011034|paxt-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011035|snrp-27|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=715|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011035|snrp-27|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011035|snrp-27|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2745|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011035|snrp-27|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011035|snrp-27|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011035|snrp-27|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011035|snrp-27|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1246|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5997|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011036|edc-3|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011037|R05D11.9|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011037|R05D11.9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011037|R05D11.9|1146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011037|R05D11.9|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011037|R05D11.9|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1636|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19246|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=797|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011038|R05H5.3.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|1166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=982|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=565|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=533|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011039|R05H5.4|734nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011040|R05H5.5|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011040|R05H5.5|1497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011040|R05H5.5|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011040|R05H5.5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011040|R05H5.5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1008|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011041|R05H5.7|561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011041|R05H5.7|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011041|R05H5.7|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011041|R05H5.7|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011042|R05H10.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=329|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00011042|R05H10.1|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00011043|rbm-28|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011043|rbm-28|265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1102|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011043|rbm-28|326nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011043|rbm-28|335nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011043|rbm-28|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011043|rbm-28|712nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011043|rbm-28|993nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011044|R05H10.3a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011044|R05H10.3a|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011044|R05H10.3a|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011044|R05H10.3a|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011044|R05H10.3a|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1257|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011044|R05H10.3a|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7409|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|656nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|851nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|861nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|864nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011045|gpx-2|890nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011046|R05H10.7|1112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011046|R05H10.7|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011046|R05H10.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011046|R05H10.7|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011046|R05H10.7|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=933|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011047|R06A4.2|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011049|sdz-26|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011049|sdz-26|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011049|sdz-26|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011050|agl-1|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011050|agl-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011050|agl-1|135nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011050|agl-1|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011050|agl-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011050|agl-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2164|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011050|agl-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011051|pfs-2|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2936|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011051|pfs-2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011052|arrd-11|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011053|arrd-12|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011053|arrd-12|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011054|arrd-13|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011054|arrd-13|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2234|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011054|arrd-13|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011055|arrd-14|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011055|arrd-14|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011055|arrd-14|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011055|arrd-14|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011058|fdps-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011058|fdps-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2381|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011058|fdps-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011058|fdps-1|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011058|fdps-1|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011058|fdps-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8184|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95726|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011059|R06C1.4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1264|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|21nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1303|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011060|R06C1.6|887nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1705|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|192nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8007|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|200nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011061|wago-1|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|389nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011062|R06C7.2|915nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011063|cpg-3|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011063|cpg-3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011063|cpg-3|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011063|cpg-3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011063|cpg-3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=589|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011063|cpg-3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29890|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011063|cpg-3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1370|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011064|adsl-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1356|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011065|R06C7.6|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011065|R06C7.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011065|R06C7.6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=440|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011065|R06C7.6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=431|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011066|ztf-15|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011066|ztf-15|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011066|ztf-15|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1548|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|1339nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|1451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|1459nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|291nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1956|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011067|vps-11|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1655|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=370|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011068|set-14|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011069|ceh-62|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011069|ceh-62|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011069|ceh-62|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011069|ceh-62|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011069|ceh-62|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011070|R06F6.7|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011070|R06F6.7|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011070|R06F6.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=873|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011070|R06F6.7|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1141|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011070|R06F6.7|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011070|R06F6.7|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011071|R06F6.8a|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=460|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011072|tag-209|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011072|tag-209|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3457|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011072|tag-209|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011072|tag-209|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011072|tag-209|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011072|tag-209|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011072|tag-209|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=542|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011073|R07A4.2|959nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011074|R07A4.3|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011074|R07A4.3|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011075|R07A4.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011075|R07A4.4|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011075|R07A4.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011075|R07A4.4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011076|scav-5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011077|R07B1.5|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011077|R07B1.5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011077|R07B1.5|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011077|R07B1.5|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011077|R07B1.5|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011078|R07B1.6|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011079|R07B1.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011079|R07B1.7|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011079|R07B1.7|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=709|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011081|R07B1.9|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011082|R07B1.11|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011082|R07B1.11|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011082|R07B1.11|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00011083|glo-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011083|glo-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011083|glo-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00011083|glo-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011084|srsx-21|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011084|srsx-21|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011087|R07B7.2a|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011087|R07B7.2a|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1087|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011088|R07B7.4a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011088|R07B7.4a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011088|R07B7.4a|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=788|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011088|R07B7.4a|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011088|R07B7.4a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00011088|R07B7.4a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011088|R07B7.4a|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011089|kmo-1|1196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011089|kmo-1|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011089|kmo-1|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011089|kmo-1|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011089|kmo-1|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=545|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011090|R07B7.6b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011090|R07B7.6b|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=465|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011092|R07B7.8|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011092|R07B7.8|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011092|R07B7.8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011092|R07B7.8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011092|R07B7.8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011093|R07B7.9a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011093|R07B7.9a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=480|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011093|R07B7.9a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011093|R07B7.9a|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=976|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=350|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011094|R07B7.10|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011095|gana-1|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=700|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011096|R07B7.12a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00011096|R07B7.12a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00011097|nhr-206|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011097|nhr-206|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011097|nhr-206|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011097|nhr-206|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011097|nhr-206|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011097|nhr-206|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011098|nhr-207|24nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011098|nhr-207|26nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011098|nhr-207|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00011098|nhr-207|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011099|nhr-208|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011099|nhr-208|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011099|nhr-208|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011100|nhr-209|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00011100|nhr-209|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011100|nhr-209|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00011100|nhr-209|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011101|R07D5.2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011101|R07D5.2|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011101|R07D5.2|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=469|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011101|R07D5.2|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011101|R07D5.2|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2782|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1840|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011102|R07E3.1b.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3003|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011103|R07E3.2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011104|cut-5|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=986|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=530|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011105|R07E3.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011106|acl-5|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=840|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011106|acl-5|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011106|acl-5|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011106|acl-5|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011106|acl-5|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011106|acl-5|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011106|acl-5|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011107|R07E3.6|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011107|R07E3.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011107|R07E3.6|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011107|R07E3.6|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011107|R07E3.6|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011108|R07E3.7|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011108|R07E3.7|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011108|R07E3.7|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00011108|R07E3.7|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011108|R07E3.7|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00011108|R07E3.7|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011109|R07E5.1|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=214|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011109|R07E5.1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011109|R07E5.1|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=606|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|1505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|1600nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11984|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2928|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011110|prdx-3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3530|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011111|snfc-5|679nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00011112|R07E5.4|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011113|R07E5.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011113|R07E5.5|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011113|R07E5.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00011114|R07E5.6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011114|R07E5.6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011115|R07E5.7|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011115|R07E5.7|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1585|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00011115|R07E5.7|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4002|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011115|R07E5.7|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011115|R07E5.7|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011115|R07E5.7|676nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011115|R07E5.7|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|1447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|1550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|1556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|1595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1537|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|180nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011116|pdcd-2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3058|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011117|R07E5.11|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2533|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011117|R07E5.11|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011117|R07E5.11|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011117|R07E5.11|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011117|R07E5.11|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1033|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011119|R07E5.13|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011120|R07E5.15|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011120|R07E5.15|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=311|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011120|R07E5.15|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011120|R07E5.15|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=695|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011120|R07E5.15|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=958|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011120|R07E5.15|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011120|R07E5.15|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011121|R07E5.17|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011121|R07E5.17|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011121|R07E5.17|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011121|R07E5.17|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|176nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|179nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|186nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5903|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011122|cpt-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011123|nuaf-3|1328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011123|nuaf-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011123|nuaf-3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011123|nuaf-3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011123|nuaf-3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011123|nuaf-3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011123|nuaf-3|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|22nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2667|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3145|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011124|sdz-27|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011127|fbxb-79|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011127|fbxb-79|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11356|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1086|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011128|R07H5.8|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011129|R07H5.9|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011130|zip-6|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011131|R07H5.11a|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011131|R07H5.11a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011131|R07H5.11b|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011131|R07H5.11b|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011131|R07H5.11b|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1792|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011132|R08A2.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011133|R08A2.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011133|R08A2.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011133|R08A2.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011134|ssp-33|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011134|ssp-33|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00011134|ssp-33|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011135|fbxa-147|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011135|fbxa-147|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011136|R08A2.5a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011137|R08A2.7|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011137|R08A2.7|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011137|R08A2.7|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=736|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011137|R08A2.7|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011139|R08B4.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011139|R08B4.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011139|R08B4.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011139|R08B4.3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011139|R08B4.3|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2132|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011139|R08B4.3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1358|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011139|R08B4.3|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011140|R08B4.4|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3265|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011141|R08B4.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011142|R08D7.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011142|R08D7.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011142|R08D7.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011142|R08D7.1|25nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011142|R08D7.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1218|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011142|R08D7.1|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011142|R08D7.1|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011143|R08D7.2.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011143|R08D7.2.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011143|R08D7.2.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1534|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011143|R08D7.2.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4a.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4a.2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4a.2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4a.2|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3478|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4a.2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4b.2|1297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4b.2|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4b.2|1321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011144|R08D7.4b.2|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2705|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|154nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|157nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|493nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011145|R08D7.5|683nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4735|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011146|pde-2|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|131nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|139nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|194nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|199nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011147|R08D7.7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011150|nhr-269|1455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011152|R09A8.1c|440nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011152|R09A8.1c|442nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011152|R09A8.1c|444nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00011152|R09A8.1c|447nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011152|R09A8.1c|452nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011153|R09A8.2|1426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011153|R09A8.2|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011153|R09A8.2|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011153|R09A8.2|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011154|R09A8.5|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011154|R09A8.5|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011154|R09A8.5|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011154|R09A8.5|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011154|R09A8.5|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1304|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011154|R09A8.5|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011154|R09A8.5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|1151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|1165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=283|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=744|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40144|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16897|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7082|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011155|R09B3.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7454|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1776|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98839|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5798|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36360|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16227|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26150|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47408|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011156|R09B3.3|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011161|chil-18|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011162|chil-19|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011163|chil-20|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011164|chil-21|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011164|chil-21|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011166|chil-22|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011166|chil-22|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011167|chil-23|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011167|chil-23|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011168|R09D1.12|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011171|R09E10.1.2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011171|R09E10.1.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011171|R09E10.1.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011171|R09E10.1.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011172|R09E10.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011172|R09E10.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011172|R09E10.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011172|R09E10.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011173|acs-18|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011173|acs-18|15nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00011173|acs-18|17nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011173|acs-18|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011173|acs-18|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011173|acs-18|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011174|R09E10.4a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011174|R09E10.4a|337nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011174|R09E10.4a|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011174|R09E10.4a|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011175|R09E10.5|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5745|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1265|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011176|R09E10.6|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011177|R09E10.8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011179|R09H10.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011180|R09H10.2a|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011180|R09H10.2a|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011180|R09H10.2a|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011180|R09H10.2a|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011180|R09H10.2a|181nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011180|R09H10.2a|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1079|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2268|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4315|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011181|R09H10.3a|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=445|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|329nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=470|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00011182|R09H10.5.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1085|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011183|R09H10.6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011183|R09H10.6|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011184|R09H10.7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011185|R10D12.1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011186|clec-226|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011186|clec-226|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011186|clec-226|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011186|clec-226|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00011187|R10D12.6|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011187|R10D12.6|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011188|R10D12.7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011188|R10D12.7|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011188|R10D12.7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011189|R10D12.8|1335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011189|R10D12.8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011189|R10D12.8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011189|R10D12.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00011189|R10D12.8|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011189|R10D12.8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011189|R10D12.8|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011190|swt-6|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011190|swt-6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=810|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011190|swt-6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011190|swt-6|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011191|R10D12.10|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011191|R10D12.10|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011191|R10D12.10|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011191|R10D12.10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011192|srh-24|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011192|srh-24|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=417|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=644|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011193|algn-13|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011194|R10D12.13a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011194|R10D12.13a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011194|R10D12.13a|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011194|R10D12.13a|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=958|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00011194|R10D12.13a|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011195|sao-1|614nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9436|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011195|sao-1|616nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=839|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00011195|sao-1|619nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011195|sao-1|622nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011196|R10D12.15b|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011197|srw-145|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011197|srw-145|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011197|srw-145|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3013|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1233|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|264nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011198|R10E4.1.2|273nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011200|R10E4.3|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011200|R10E4.3|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00011200|R10E4.3|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011200|R10E4.3|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|1425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011201|nth-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|1358nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|1364nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=171|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011202|R10E4.6|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011203|R10E4.7|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2403|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011205|R10E4.9|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011206|R10E4.11b|969nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011206|R10E4.11b|971nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=860|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011206|R10E4.11b|978nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011206|R10E4.11b|981nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011206|R10E4.11b|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011206|R10E4.11b|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011207|R10E8.1a.2|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011207|R10E8.1a.2|276nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011207|R10E8.1a.2|278nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=225|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011207|R10E8.1a.2|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011207|R10E8.1a.2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011208|R10E8.2|282nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011209|R10E8.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011212|R10E8.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011212|R10E8.6|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011212|R10E8.6|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011212|R10E8.6|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011212|R10E8.6|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011212|R10E8.6|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011213|R10E8.8.2|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00011213|R10E8.8.2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011213|R10E8.8.2|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011213|R10E8.8.2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011213|R10E8.8.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00011214|R10E9.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011214|R10E9.2|1256nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011214|R10E9.2|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011214|R10E9.2|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2446|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011214|R10E9.2|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=467|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011214|R10E9.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011215|R10E9.3a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011215|R10E9.3a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=648|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011215|R10E9.3a|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|227nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|229nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1529|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|239nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|241nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|374nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011216|usp-46|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|1186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|810nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011217|R10E11.5b.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011218|R10E11.6a|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011218|R10E11.6a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011218|R10E11.6a|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1500|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011218|R10E11.6a|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011218|R10E11.6a|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011218|R10E11.6a|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011219|srxa-10|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011219|srxa-10|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011220|R10E11.9|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011220|R10E11.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011220|R10E11.9|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00011220|R10E11.9|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011220|R10E11.9|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011220|R10E11.9|811nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011221|R10E12.2|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1399|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011221|R10E12.2|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011221|R10E12.2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011221|R10E12.2|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011221|R10E12.2|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011221|R10E12.2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011222|R10H10.3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011222|R10H10.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011222|R10H10.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5552|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011222|R10H10.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011222|R10H10.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011222|R10H10.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011223|R10H10.4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011223|R10H10.4|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2624|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011223|R10H10.4|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=196|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011224|R10H10.6|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011224|R10H10.6|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011224|R10H10.6|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011224|R10H10.6|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=657|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011224|R10H10.6|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011224|R10H10.6|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011224|R10H10.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011225|R10H10.7|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011225|R10H10.7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1363|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011225|R10H10.7|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011226|R11.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1001|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011226|R11.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011226|R11.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=287|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=335|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|740nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|750nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|767nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|802nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=185|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|807nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=256|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011227|R11.2|811nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011229|R11.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00011229|R11.4|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1133|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|345nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=701|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1401|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011230|nud-2|770nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|158nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=78|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011231|R11A5.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2894|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46911|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=441|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2301|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=344|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3567|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011232|pck-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011234|R11A5.6|582nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011235|suro-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011236|R11A8.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011236|R11A8.1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011236|R11A8.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=824|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011236|R11A8.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=537|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011236|R11A8.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=783|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2292|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011237|R11A8.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011238|ugt-59|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=303|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011238|ugt-59|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011238|ugt-59|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011238|ugt-59|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3458|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011239|pges-2|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1248|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3273|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011240|R11A8.7a|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011241|mpz-5|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011241|mpz-5|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2382|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011242|R11D1.1d|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011243|R11D1.2|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011243|R11D1.2|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=480|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011243|R11D1.2|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011243|R11D1.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011243|R11D1.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011243|R11D1.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011244|R11D1.3|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011244|R11D1.3|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=228|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00011244|R11D1.3|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011244|R11D1.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011244|R11D1.3|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011245|R11D1.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011246|R11D1.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2199|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=354|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00011247|mrpl-49|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011248|R11D1.10a.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011248|R11D1.10a.2|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011248|R11D1.10a.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=537|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011248|R11D1.10a.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011248|R11D1.10a.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011248|R11D1.10a.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011249|R11G10.2|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011249|R11G10.2|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011249|R11G10.2|586nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011249|R11G10.2|592nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|1538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9012|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011250|R11H6.2.2|223nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2873|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011251|glb-22|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3428|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011252|R11H6.4a|892nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011253|R11H6.5|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2418|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30980|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|426nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011254|R12G8.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|834nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=315|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011255|R12H7.4|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011257|npax-3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011257|npax-3|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011257|npax-3|974nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011258|best-15|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|1012nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|1014nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|1175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|1449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|1453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|1455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|478nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|925nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|942nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|952nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|954nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|959nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4451|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|963nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|965nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|969nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011259|miz-1|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011260|R13G10.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011260|R13G10.4|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011260|R13G10.4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011260|R13G10.4|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011260|R13G10.4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011261|nphp-4|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011261|nphp-4|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011261|nphp-4|237nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011261|nphp-4|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=322|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00011261|nphp-4|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011262|pho-8|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011262|pho-8|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011262|pho-8|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011262|pho-8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011262|pho-8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=475|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011262|pho-8|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=504|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5493|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=527|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011263|R13H4.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011264|R13H4.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011264|R13H4.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00011264|R13H4.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00011265|R13H4.7a|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=769|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011265|R13H4.7a|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011266|R13H4.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011266|R13H4.8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011266|R13H4.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011266|R13H4.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011267|fbxb-85|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1372|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5841|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011268|pde-12|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|836nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|839nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|842nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|846nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|851nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=425|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|858nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|864nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|866nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011269|R17.3|875nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4536|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|605nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011270|R31.2a|882nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011271|flad-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011271|flad-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011271|flad-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011271|flad-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011271|flad-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011271|flad-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011271|flad-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1670|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4121|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011272|dtmk-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20344|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36279|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011273|R53.4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2055|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1263|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011274|R53.5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011275|psf-1|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011275|psf-1|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1831|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011275|psf-1|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011275|psf-1|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011275|psf-1|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=391|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1470|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|452nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|457nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=470|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|467nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=351|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|469nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=832|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|582nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011276|aakg-5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011277|R53.8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011277|R53.8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011277|R53.8|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011277|R53.8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011278|R74.2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|1544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=755|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3119|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=796|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|469nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|471nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|474nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|477nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011279|asd-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011280|R74.6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011280|R74.6|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011280|R74.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3933|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011280|R74.6|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011280|R74.6|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011280|R74.6|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011280|R74.6|199nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1005nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1010nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1031nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1035nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=59|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1038nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=111|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1043nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2356|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|1598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|924nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|926nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|929nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|931nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|973nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011281|R74.7|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1070|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12827|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3259|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|165nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|667nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011282|R74.8a|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1242|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2122|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011283|R90.1|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4686|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011284|ttr-27|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011285|ttr-28|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011285|ttr-28|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011285|ttr-28|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00011286|ttr-29|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011286|ttr-29|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011286|ttr-29|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1300|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011286|ttr-29|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011286|ttr-29|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011286|ttr-29|654nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1172|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011287|glb-24|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21732|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=690|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011288|R102.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2942|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265691|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|801nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|804nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011289|R102.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011290|R102.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011290|R102.3|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=725|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=331|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=884|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011291|R102.4c.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4027|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7673|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011292|R102.5a|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011293|R102.6|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011293|R102.6|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011293|R102.6|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011293|R102.6|468nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011293|R102.6|470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011293|R102.6|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011295|R102.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011295|R102.8|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011295|R102.8|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011295|R102.8|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011295|R102.8|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011295|R102.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011296|glb-21|445nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011296|glb-21|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011297|R102.10|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=496|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011297|R102.10|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011298|R107.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=743|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011298|R107.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1781|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011298|R107.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011298|R107.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|488nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|491nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=374|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|496nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=930|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2453|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011299|ikke-1|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14369|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2112|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1933|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|475nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|578nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011300|R107.5b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|200nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2095|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2873|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011302|R166.2|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8599|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011303|R166.3|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|1310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|1332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|1354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|724nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011304|mnk-1|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011305|R186.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011305|R186.1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4263|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011306|R186.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011307|mpst-7|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011307|mpst-7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011307|mpst-7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011307|mpst-7|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011307|mpst-7|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011308|R186.7|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011308|R186.7|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011308|R186.7|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011308|R186.7|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011308|R186.7|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011308|R186.7|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1560|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011308|R186.7|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1049|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011309|R186.8.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011309|R186.8.2|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011309|R186.8.2|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011309|R186.8.2|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2916|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00011309|R186.8.2|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011309|R186.8.2|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011309|R186.8.2|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011310|T01B4.3|418nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011310|T01B4.3|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011310|T01B4.3|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=926|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011310|T01B4.3|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011310|T01B4.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011310|T01B4.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011311|T01B7.5a.2|1588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011312|trcs-2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011312|trcs-2|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3489|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011312|trcs-2|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011312|trcs-2|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011312|trcs-2|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011313|T01B7.8|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011313|T01B7.8|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=563|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011313|T01B7.8|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011313|T01B7.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011313|T01B7.8|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011313|T01B7.8|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011314|T01B7.9|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011314|T01B7.9|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011314|T01B7.9|537nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011314|T01B7.9|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2331|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011314|T01B7.9|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011314|T01B7.9|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=966|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|369nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011315|mbr-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|150nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3995|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3282|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011317|T01C1.4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011318|cdt-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011318|cdt-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011318|cdt-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011318|cdt-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011318|cdt-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=935|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1709|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=554|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011319|T01C3.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1585|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2237|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011320|T01C3.3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011321|fil-1|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011321|fil-1|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011321|fil-1|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011321|fil-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011321|fil-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011322|irld-14|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011322|irld-14|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1661|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011323|mut-15|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2131|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011324|T01C3.9|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=429|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1040nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1057nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|760nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=324|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|945nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011325|T01C3.11a|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1a|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1a|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1a|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1256|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1a|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2143|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1a|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1b|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011326|T01D3.1b|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011327|hlh-34|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011327|hlh-34|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011327|hlh-34|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011327|hlh-34|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011328|T01D3.3b.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011328|T01D3.3b.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2009|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011329|T01D3.5|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2253|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=216|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=303|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011330|T01D3.6a|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3016|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3700|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011333|nrde-2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011334|mrps-14|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5332|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011334|mrps-14|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=799|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00011334|mrps-14|463nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4923|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|628nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011335|T01E8.8|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011336|ubxn-5|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=898|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00011336|ubxn-5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011336|ubxn-5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6433|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1392|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|472nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011337|T01G1.2|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=976|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1458|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=786|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011338|sec-31|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011339|T01G5.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011339|T01G5.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011339|T01G5.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011339|T01G5.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011339|T01G5.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011339|T01G5.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011340|ugt-30|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011340|ugt-30|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011340|ugt-30|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011340|ugt-30|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011341|T01G5.6|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011341|T01G5.6|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011342|T01G5.7|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011342|T01G5.7|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011342|T01G5.7|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011342|T01G5.7|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011344|T01G9.2a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2313|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1797|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4706|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=395|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011345|dma-1|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011348|T01H3.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011348|T01H3.2|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011348|T01H3.2|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2394|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011348|T01H3.2|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011348|T01H3.2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011348|T01H3.2|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|1447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1474|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011349|T01H3.3|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2509|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011350|perm-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011351|T01H3.5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=418|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011351|T01H3.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011351|T01H3.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3479|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8339|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2153|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011352|rskn-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011353|T01H8.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011353|T01H8.2|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011353|T01H8.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00011353|T01H8.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=849|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011353|T01H8.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011353|T01H8.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011354|lgc-13|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011354|lgc-13|1060nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011354|lgc-13|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011354|lgc-13|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011354|lgc-13|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011354|lgc-13|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011354|lgc-13|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=160|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=255|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=176|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011355|lgc-14|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011356|lgc-15|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011356|lgc-15|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011360|lgc-18|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011360|lgc-18|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011360|lgc-18|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011361|T01H10.8|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011361|T01H10.8|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011361|T01H10.8|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011362|T02B5.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011362|T02B5.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011362|T02B5.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011362|T02B5.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011363|ocam-1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011363|ocam-1|222nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011364|T02B5.3|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011364|T02B5.3|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=358|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011364|T02B5.3|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011365|T02C1.1|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=182|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011365|T02C1.1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011366|T02C1.2|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011366|T02C1.2|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011366|T02C1.2|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=528|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1435|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011367|snpc-3.4|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011368|tftc-5|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011368|tftc-5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011368|tftc-5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2757|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=437|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=891|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011371|T02D1.4|580nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011372|npr-26|1102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011372|npr-26|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1737|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011372|npr-26|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011372|npr-26|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011373|T02D1.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1075|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1011|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011374|T02D1.8|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1139|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011375|T02E1.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3290|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011376|gla-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011378|T02E1.6|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011378|T02E1.6|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011379|T02E1.7|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011379|T02E1.7|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=824|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011379|T02E1.7|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011379|T02E1.7|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011380|T02E1.8a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011380|T02E1.8a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011380|T02E1.8a|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011380|T02E1.8a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1330|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011380|T02E1.8a|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011380|T02E1.8a|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011380|T02E1.8a|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|1384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|1386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=845|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=440|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=410|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011381|npr-25|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011382|dop-5|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2021|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011382|dop-5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011382|dop-5|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011382|dop-5|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|583nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|610nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|770nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1173|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1236|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|789nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2851|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|797nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|827nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011383|T02E9.5.2|944nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011386|T02G6.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011388|T02G6.5b|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00011388|T02G6.5b|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011388|T02G6.5b|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011388|T02G6.5b|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011391|mrps-12|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011391|mrps-12|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2542|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011391|mrps-12|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011391|mrps-12|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011391|mrps-12|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1587|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267173|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2772|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=517|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|338nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011392|sbt-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1010|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011393|T03D8.6a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011394|T03D8.7|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011394|T03D8.7|35nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011394|T03D8.7|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011394|T03D8.7|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=129|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011394|T03D8.7|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011394|T03D8.7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011396|nhr-271|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|487nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00011397|T03E6.8|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3126|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1507|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011398|qdpr-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4765|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011399|T03F6.3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011400|T03F6.4|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=172|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011400|T03F6.4|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011400|T03F6.4|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011400|T03F6.4|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=509|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011400|T03F6.4|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011401|T03F6.6.1|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1591|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011401|T03F6.6.1|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011402|T03F7.5|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011403|T03F7.6|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011403|T03F7.6|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011403|T03F7.6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00011403|T03F7.6|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011403|T03F7.6|917nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011403|T03F7.6|969nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011404|T03F7.7b|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011404|T03F7.7b|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011404|T03F7.7b|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011404|T03F7.7b|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011404|T03F7.7b|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011404|T03F7.7b|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011404|T03F7.7b|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=342|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011407|ppat-1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1000|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3127|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011408|T04A8.6|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|1250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2880|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2252|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011409|T04A8.7a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011410|T04A8.8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011410|T04A8.8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011410|T04A8.8|1529nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011410|T04A8.8|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011410|T04A8.8|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3821|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011410|T04A8.8|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011410|T04A8.8|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|102nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|1527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011411|sel-13|97nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011412|mrpl-16|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011412|mrpl-16|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011412|mrpl-16|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2469|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011414|T04A8.13|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011414|T04A8.13|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=713|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011415|him-18|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011416|T04A11.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011417|T04A11.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011417|T04A11.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011418|igdb-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=918|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011422|T04B2.3a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1917|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011422|T04B2.3a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011422|T04B2.3a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011422|T04B2.3a|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1638|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|516nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|520nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|530nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|534nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|537nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|545nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=289|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011423|ipla-7|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011424|dhs-31|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011424|dhs-31|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011424|dhs-31|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011424|dhs-31|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011424|dhs-31|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011424|dhs-31|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011424|dhs-31|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011425|T04B2.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011425|T04B2.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011425|T04B2.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=418|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011425|T04B2.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011426|T04C10.3|1451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011426|T04C10.3|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011427|T04C12.1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011427|T04C12.1|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011427|T04C12.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|162nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|171nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=519|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|182nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|184nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3686|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25833|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3150|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011428|T04C12.3.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011429|T04C12.7|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011429|T04C12.7|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011429|T04C12.7|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00011429|T04C12.7|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|645nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011430|T04C12.8.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011431|T04D3.1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011431|T04D3.1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011432|sdz-30|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011432|sdz-30|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011432|sdz-30|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1643|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011433|pde-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=463|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4592|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011434|T04D3.5.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011435|T04D3.8|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011436|T04F3.1a|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011436|T04F3.1a|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011436|T04F3.1a|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011436|T04F3.1a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011436|T04F3.1a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011436|T04F3.1a|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011437|T04F3.2|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011437|T04F3.2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011438|T04F3.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011438|T04F3.3|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011438|T04F3.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011439|T04F3.4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011439|T04F3.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011439|T04F3.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011439|T04F3.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1562|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011439|T04F3.4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=797|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00011439|T04F3.4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011439|T04F3.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011440|sfxn-1.5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011440|sfxn-1.5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011440|sfxn-1.5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011440|sfxn-1.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1061|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011440|sfxn-1.5|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011440|sfxn-1.5|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011440|sfxn-1.5|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1457|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011441|T04F8.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011442|T04F8.3|1512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011442|T04F8.3|602nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011442|T04F8.3|971nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011443|cutl-11|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011443|cutl-11|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011443|cutl-11|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011443|cutl-11|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011443|cutl-11|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011443|cutl-11|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011444|T04F8.6|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011444|T04F8.6|195nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011444|T04F8.6|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011444|T04F8.6|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011444|T04F8.6|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=797|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011444|T04F8.6|424nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011444|T04F8.6|431nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011445|T04F8.7b|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011445|T04F8.7b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011445|T04F8.7b|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011445|T04F8.7b|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1542|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8421|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1382|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|158nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2930|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011446|T04F8.8a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011447|T04F8.9|506nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=271|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|358nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12488|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2261|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|372nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011449|T04H1.2.1|873nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|158nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|328nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011450|ttr-22|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011451|T04H1.5|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011451|T04H1.5|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1098|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011451|T04H1.5|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=544|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011452|ugt-55|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011452|ugt-55|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00011452|ugt-55|495nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=496|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1420|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|11nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|13nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=560|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|24nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011453|ugt-56|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011454|lron-14|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1124|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|762nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1146|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|783nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|788nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|795nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011456|T05A1.5b|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011458|irld-47|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00011458|irld-47|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1416|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11195|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1443|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4774|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1064|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3562|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=660|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011460|ttr-14|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=681|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011462|vap-2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011462|vap-2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00011462|vap-2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011463|T05A10.6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011463|T05A10.6|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011464|T05B9.1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011464|T05B9.1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011464|T05B9.1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9654|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011464|T05B9.1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011464|T05B9.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011465|T05B9.2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011465|T05B9.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011465|T05B9.2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011465|T05B9.2|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011465|T05B9.2|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=623|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011465|T05B9.2|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011465|T05B9.2|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011466|T05C12.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011466|T05C12.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011466|T05C12.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011467|decr-1.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011467|decr-1.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011467|decr-1.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011467|decr-1.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011467|decr-1.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011467|decr-1.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011468|T05C12.4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011468|T05C12.4|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011468|T05C12.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011468|T05C12.4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00011469|dylt-3|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011469|dylt-3|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011469|dylt-3|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011469|dylt-3|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=569|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|71nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011471|T05C12.8|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011472|T05C12.9|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011472|T05C12.9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011472|T05C12.9|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011473|T05C12.11|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011473|T05C12.11|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00011473|T05C12.11|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=519|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3166|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38983|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4431|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2126|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=374|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011474|aldo-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011475|T05D4.2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00011475|T05D4.2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011475|T05D4.2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011475|T05D4.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011476|T05D4.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011476|T05D4.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00011476|T05D4.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011478|T05D4.5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011478|T05D4.5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011478|T05D4.5|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011478|T05D4.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011479|T05E11.2b|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1691|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30525|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17696|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7064|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|674nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011480|enpl-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|310nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|314nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10105|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3796|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=412|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011481|imp-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|1294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|1432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1137|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011482|hpo-4|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011484|T05E11.8|1592nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011484|T05E11.8|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011484|T05E11.8|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011484|T05E11.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=605|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011486|T05E12.3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6a|21nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6a|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1262|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6a|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=809|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6a|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3612|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6a|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=124|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6a|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|1007nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011487|T05E12.6b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1562|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1547|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=866|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|806nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|812nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011488|nra-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|1048nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4871|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011489|T05F1.2|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011490|T05F1.4.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011490|T05F1.4.1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2013|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011491|T05F1.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011491|T05F1.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=524|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011491|T05F1.5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011491|T05F1.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011492|T05F1.7|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011493|T05F1.8|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011493|T05F1.8|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011493|T05F1.8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011493|T05F1.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011494|T05F1.9|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011494|T05F1.9|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011495|T05F1.11|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011495|T05F1.11|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|1078nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1557|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011497|T05F1.13|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011498|T05G5.1b|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011498|T05G5.1b|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011498|T05G5.1b|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011499|T05G5.4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011499|T05G5.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|1019nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|1026nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5048|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=345|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011500|T05G5.5c|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011501|rmd-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011501|rmd-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14684|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011501|rmd-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011501|rmd-1|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=850|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011501|rmd-1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2865|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011501|rmd-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011502|vps-53|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=678|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011502|vps-53|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=425|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011502|vps-53|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011502|vps-53|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011502|vps-53|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011503|gcc-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011503|gcc-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011503|gcc-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011503|gcc-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011503|gcc-2|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2920|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011503|gcc-2|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011505|pzf-1|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011505|pzf-1|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=336|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|1041nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|1449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6412|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011507|T05H10.1|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=987|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|1281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011508|T05H10.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011509|T05H10.4a|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1134|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011509|T05H10.4a|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=457|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011509|T05H10.4a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1458|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16091|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|298nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|304nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011510|pdha-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|1167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4211|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=445|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|303nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|359nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011511|gpcp-2|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=901|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011512|T05H10.8|749nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011513|fbxa-197|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011513|fbxa-197|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011513|fbxa-197|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011513|fbxa-197|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011513|fbxa-197|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011513|fbxa-197|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011515|oac-42|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011515|oac-42|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011515|oac-42|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011515|oac-42|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011517|cgt-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011517|cgt-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011519|T06C12.12|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011519|T06C12.12|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011520|nhr-213|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011520|nhr-213|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011520|nhr-213|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011520|nhr-213|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011520|nhr-213|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011521|T06C12.14|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011522|srap-1|403nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1178|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|35nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|43nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|46nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011523|T06D8.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011524|T06D8.3|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011524|T06D8.3|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011524|T06D8.3|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011524|T06D8.3|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011524|T06D8.3|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011526|cox-15|1160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011526|cox-15|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4134|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011526|cox-15|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011526|cox-15|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011526|cox-15|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011527|cchl-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011527|cchl-1|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9463|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011527|cchl-1|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=176|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011527|cchl-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011527|cchl-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011528|T06D8.7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011528|T06D8.7|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011528|T06D8.7|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6913|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011528|T06D8.7|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1311|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011528|T06D8.7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|1313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5458|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=214|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011529|T06D8.9.2|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011530|T06D8.10|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011530|T06D8.10|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=606|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011530|T06D8.10|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1088nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3223|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|1483nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|846nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|926nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011531|rsbp-1|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|1382nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=335|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=171|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=372|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=596|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00011532|chaf-1|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1257|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011533|T06E4.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011534|T06E4.7|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011534|T06E4.7|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011534|T06E4.7|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011534|T06E4.7|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011535|T06E4.8|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011535|T06E4.8|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3354|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011535|T06E4.8|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011535|T06E4.8|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011535|T06E4.8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011536|T06E4.9|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011536|T06E4.9|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011536|T06E4.9|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3014|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011536|T06E4.9|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011536|T06E4.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011537|T06E4.10|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011537|T06E4.10|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=378|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011537|T06E4.10|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2012|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011537|T06E4.10|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011537|T06E4.10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011538|T06E6.1|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011538|T06E6.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011538|T06E6.1|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011538|T06E6.1|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1331|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011539|fbxa-135|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011540|T06E6.10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=954|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011540|T06E6.10|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011542|fbxa-104|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011543|acl-2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011543|acl-2|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2826|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011543|acl-2|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011543|acl-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|104nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=843|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011545|T06G6.3a|99nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011546|T06G6.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011546|T06G6.4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011546|T06G6.4|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011546|T06G6.4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011546|T06G6.4|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011546|T06G6.4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1276|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011548|T06G6.6b|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3323|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1999|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00011551|T06G6.12|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011554|T07A5.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011554|T07A5.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011554|T07A5.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011554|T07A5.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011556|vglu-3|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011556|vglu-3|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011556|vglu-3|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011556|vglu-3|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011556|vglu-3|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011557|ostf-4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011558|T07A5.5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011558|T07A5.5|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3921|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011558|T07A5.5|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011558|T07A5.5|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3427|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|171nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011559|umps-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|1488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|361nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1361|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|364nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2362|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|370nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=344|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011560|T07C4.3a.2|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50231|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011561|ttr-15|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=869|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|574nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|581nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011562|T07C4.10|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|1239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36552|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8576|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|1461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=447|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2730|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2610|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=809|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|901nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011564|ugt-50|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6921|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011565|nhr-272|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00011565|nhr-272|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00011566|nhr-214|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=454|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00011566|nhr-214|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011566|nhr-214|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011567|nhr-215|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011568|nhr-26|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011568|nhr-26|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011570|sre-28|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011570|sre-28|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2497|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2926|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011571|ttr-46|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011572|mam-5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1618|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=265|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011573|anmt-3|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011574|T07C12.10|1599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011574|T07C12.10|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011574|T07C12.10|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011574|T07C12.10|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011575|madf-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011575|madf-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=551|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011575|madf-4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011575|madf-4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011575|madf-4|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=358|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011576|T07C12.12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011578|npr-20|916nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011578|npr-20|918nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=280|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011579|T07D4.2a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011579|T07D4.2a|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011579|T07D4.2a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011579|T07D4.2a|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011579|T07D4.2a|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=947|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3304|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011580|ddx-19|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011581|T07D10.1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00011581|T07D10.1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011582|ntr-1|1156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011582|ntr-1|1160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011582|ntr-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011582|ntr-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011582|ntr-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011582|ntr-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011583|T07D10.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011583|T07D10.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011583|T07D10.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011583|T07D10.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011583|T07D10.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011583|T07D10.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7276|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011586|flp-33|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011587|T07F10.1a|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=858|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=618|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|1432nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|328nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011589|T07F10.3|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|608nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|624nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011590|bus-19|634nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011591|T07F10.5.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011591|T07F10.5.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|15nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011592|T07F10.6|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011593|T07G12.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00011593|T07G12.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011593|T07G12.2|515nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011594|T07G12.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011594|T07G12.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011596|T07G12.5b|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011597|zim-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011597|zim-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011597|zim-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1143|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011597|zim-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011597|zim-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011597|zim-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011600|zim-2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1126|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011600|zim-2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|1299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=601|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011601|zim-3|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1274|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011604|T08A11.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2243|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=716|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|330nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011605|T08A11.2|433nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011609|T08D2.4|1518nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011610|T08D2.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|653nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|658nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|660nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|666nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|669nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011611|T08D2.6|765nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=280|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011614|nfya-1|577nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00011615|lsd-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011615|lsd-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011615|lsd-1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011615|lsd-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011615|lsd-1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011615|lsd-1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011616|T08D10.3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011619|T08G3.7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011619|T08G3.7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011621|T08G3.13|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011621|T08G3.13|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011621|T08G3.13|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011621|T08G3.13|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011622|T08G5.1|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011622|T08G5.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011622|T08G5.1|845nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011623|T08G5.2|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011623|T08G5.2|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011624|T08G5.3b|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=995|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011624|T08G5.3b|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011624|T08G5.3b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1808|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1069|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011625|vps-39|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|1120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9282|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|385nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|639nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011629|T08G11.1a|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|727nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011630|T08G11.3|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011631|T08G11.4b.1|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4710|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011631|T08G11.4b.1|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011631|T08G11.4b.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011631|T08G11.4b.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011631|T08G11.4b.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011633|T09A5.4|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011633|T09A5.4|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2262|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=314|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011634|T09A5.5|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011635|T09A5.7|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011635|T09A5.7|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011635|T09A5.7|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011635|T09A5.7|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4902|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011635|T09A5.7|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011635|T09A5.7|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011635|T09A5.7|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7010|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011636|cec-3|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011637|sds-22|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011637|sds-22|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011637|sds-22|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011637|sds-22|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011637|sds-22|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011637|sds-22|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011637|sds-22|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4644|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6539|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=875|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|449nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011638|ostb-1|764nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|242nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|558nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|560nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|565nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|605nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2417|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|761nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|765nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011639|ztf-17|818nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=994|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011640|T09A5.14|384nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011641|T09A5.15|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011641|T09A5.15|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2833|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011641|T09A5.15|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011641|T09A5.15|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011641|T09A5.15|735nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011641|T09A5.15|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011641|T09A5.15|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011642|T09B9.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011642|T09B9.1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011642|T09B9.1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011642|T09B9.1|264nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011642|T09B9.1|267nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011642|T09B9.1|271nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011642|T09B9.1|274nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011643|slc-17.9|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011643|slc-17.9|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011643|slc-17.9|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011644|T09B9.3|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=369|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011644|T09B9.3|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=610|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011644|T09B9.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011645|T09B9.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011645|T09B9.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011645|T09B9.4|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1612|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011646|T09B9.5|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=248|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011646|T09B9.5|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011646|T09B9.5|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2393|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3204|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|522nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|529nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=888|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011647|noca-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011648|cni-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011648|cni-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=971|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011648|cni-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8516|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011648|cni-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011649|T09E8.4|1475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011649|T09E8.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011655|T09E11.6|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011661|ztf-27|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011661|ztf-27|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1409|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011661|ztf-27|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011661|ztf-27|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4511|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=526|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|530nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|536nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011662|T09F3.2|543nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011663|T09F3.4|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011663|T09F3.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011663|T09F3.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011664|T09F3.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=567|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011664|T09F3.5|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011664|T09F3.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011664|T09F3.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011664|T09F3.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011665|T09F5.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011665|T09F5.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011665|T09F5.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=618|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3122|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011668|clec-47|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011669|T09F5.10|29nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011669|T09F5.10|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011669|T09F5.10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011669|T09F5.10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011669|T09F5.10|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011669|T09F5.10|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011670|fbxa-84|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011670|fbxa-84|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011670|fbxa-84|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011670|fbxa-84|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011671|cyp-13A4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=418|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00011672|cyp-13A5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011673|cyp-13A6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011673|cyp-13A6|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011673|cyp-13A6|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011674|cyp-13A8|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011674|cyp-13A8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011675|cyp-13A3|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011675|cyp-13A3|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=383|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|370nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|378nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|383nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|425nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|427nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011676|cyp-13A2|575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011677|cyp-13A1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011677|cyp-13A1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011677|cyp-13A1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011677|cyp-13A1|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1341|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011678|T10B9.9|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011679|ucr-2.2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3830|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011679|ucr-2.2|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011679|ucr-2.2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011679|ucr-2.2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011679|ucr-2.2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011679|ucr-2.2|611nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=569|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011680|T10B10.3|642nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=422|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|435nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3765|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011681|T10B10.4a|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011682|snt-7|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=540|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011682|snt-7|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011682|snt-7|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=244|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011682|snt-7|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011682|snt-7|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011682|snt-7|63nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011682|snt-7|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011683|phat-6|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011683|phat-6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1344|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=482|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011684|T10B10.8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011685|T10B10.9|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011685|T10B10.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011687|T10C6.5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3730|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011687|T10C6.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011687|T10C6.5|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011687|T10C6.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011687|T10C6.5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011687|T10C6.5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=472|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=906|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1435|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011688|T10C6.6a|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011689|T10C6.7|1539nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011691|T10C6.10a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011691|T10C6.10b|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011691|T10C6.10b|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=484|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011691|T10C6.10b|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011691|T10C6.10b|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011691|T10C6.10b|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011691|T10C6.10b|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=494|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|262nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|886nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|891nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011692|T10G3.1|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011693|T10G3.2|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=371|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011693|T10G3.2|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011693|T10G3.2|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011694|T10G3.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011694|T10G3.3|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011694|T10G3.3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011695|T10G3.4a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011695|T10G3.4a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011695|T10G3.4a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011696|eea-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011696|eea-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011696|eea-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3012|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011696|eea-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011696|eea-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011696|eea-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011697|T10H4.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011697|T10H4.4|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011698|cyp-34A1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011699|cyp-34A2|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011699|cyp-34A2|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011699|cyp-34A2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011699|cyp-34A2|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011699|cyp-34A2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011701|srab-17|284nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011701|srab-17|287nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011701|srab-17|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011701|srab-17|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011701|srab-17|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011702|srab-18|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011704|sdz-31|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011705|T11A5.6b|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011705|T11A5.6c|1017nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011705|T11A5.6c|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011705|T11A5.6c|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1195|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011705|T11A5.6c|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011706|T11B7.1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011706|T11B7.1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011706|T11B7.1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011706|T11B7.1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011706|T11B7.1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011706|T11B7.1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=543|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1081|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|20nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=234|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|22nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011707|T11B7.2c|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011708|T11B7.5|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011708|T11B7.5|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=406|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011709|T11F9.1a|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011709|T11F9.1a|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011710|T11F9.7|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011712|T11F9.10|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011712|T11F9.10|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011713|T11F9.12|173nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011713|T11F9.12|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011713|T11F9.12|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011713|T11F9.12|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011713|T11F9.12|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011713|T11F9.12|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011713|T11F9.12|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011715|T11F9.14|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011715|T11F9.14|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=886|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=642|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011717|T11G6.2b.1|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|1248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|243nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|247nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=384|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011718|T11G6.3|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011719|T11G6.4|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011719|T11G6.4|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011719|T11G6.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011719|T11G6.4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011719|T11G6.4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011719|T11G6.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011720|T11G6.5b.1|233nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011720|T11G6.5b.1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011720|T11G6.5b.1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2460|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|1250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|1286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|1310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13092|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011722|T11G6.8a|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011723|T12A7.2a.1|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011723|T12A7.2a.1|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011723|T12A7.2a.1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011723|T12A7.2a.1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011723|T12A7.2a.1|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3558|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011725|lips-5|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011726|lpr-2|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011726|lpr-2|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011726|lpr-2|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=299|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011727|T12A7.6|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011727|T12A7.6|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00011727|T12A7.6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011727|T12A7.6|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011727|T12A7.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011727|T12A7.6|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011728|T12A7.7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011728|T12A7.7|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011728|T12A7.7|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011728|T12A7.7|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011728|T12A7.7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011728|T12A7.7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2138|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|306nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=346|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011729|set-16|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=935|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2174|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011730|drr-2|358nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|1371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|1375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|1402nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|1404nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=351|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1101|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011731|acbp-5|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011732|arrd-17|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011732|arrd-17|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4775|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=648|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1953|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1617|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011733|T12D8.5a|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9584|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011734|mlc-5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5837|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7016|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011735|hip-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011736|T12D8.9b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011736|T12D8.9b|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011736|T12D8.9b|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011736|T12D8.9b|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1922|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011736|T12D8.9b|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011736|T12D8.9b|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011736|T12D8.9b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10214|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1016|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2612|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011737|sqst-1|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=526|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=99|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=870|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|251nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011738|T12G3.2g|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=566|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011739|T12G3.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2145|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=569|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011740|mrpl-51|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=641|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1144|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011741|T12G3.6a|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011742|tgn-38|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011742|tgn-38|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1143|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011742|tgn-38|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011742|tgn-38|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011742|tgn-38|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011742|tgn-38|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011742|tgn-38|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=901|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011743|T13F2.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011743|T13F2.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011743|T13F2.2|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4069|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011743|T13F2.2|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3707|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011743|T13F2.2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011744|T13F2.4|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1357|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011745|sre-4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1256|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=622|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2962|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|785nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|868nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011746|T13F2.6|922nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|1407nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=269|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1989|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=411|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|456nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011747|sna-2|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|1391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|1498nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011749|ssp-36|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011752|fbxa-2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011752|fbxa-2|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011752|fbxa-2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011752|fbxa-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011752|fbxa-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011752|fbxa-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1100|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5280|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011753|T13F3.6|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011754|T13F3.7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011754|T13F3.7|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011754|T13F3.7|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=328|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011754|T13F3.7|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011754|T13F3.7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|384nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=893|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|388nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011755|T13H5.1i|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|1128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|1436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=305|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011756|ctg-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011757|cht-2|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011757|cht-2|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011757|cht-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00011758|T13H5.4|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011758|T13H5.4|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3044|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011758|T13H5.4|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011758|T13H5.4|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011758|T13H5.4|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011759|mrps-18B|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=516|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011759|mrps-18B|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1570|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011759|mrps-18B|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011759|mrps-18B|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011760|T13H5.6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011760|T13H5.6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011760|T13H5.6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011760|T13H5.6|1589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011761|T13H5.8|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011761|T13H5.8|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011761|T13H5.8|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3193|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011761|T13H5.8|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011761|T13H5.8|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011762|T13H10.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011762|T13H10.2|15nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00011762|T13H10.2|18nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011762|T13H10.2|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|1309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1061|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|1336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|1346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|415nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011763|T14B1.1.1|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011765|frpr-17|1286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011765|frpr-17|1288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011765|frpr-17|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1706|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011767|T14D7.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=525|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011768|oac-46|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011770|T14G8.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011770|T14G8.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|337nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|550nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2974|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|561nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1136|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|564nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011771|T14G8.3a|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011772|T14G8.4|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=583|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|1436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3077|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|352nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|448nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|460nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|510nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|513nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011773|ttr-53|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011774|ttr-54|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011774|ttr-54|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=528|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011774|ttr-54|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3156|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1405|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011775|T14G10.5b|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1447|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=997|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|22nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011776|hpo-5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011777|T14G10.8a.2|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011777|T14G10.8a.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011777|T14G10.8a.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1333|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011777|T14G10.8a.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011777|T14G10.8a.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011777|T14G10.8a.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011777|T14G10.8a.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011788|T15H9.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011788|T15H9.2|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011788|T15H9.2|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=755|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011788|T15H9.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011788|T15H9.2|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011789|T15H9.4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011789|T15H9.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011790|T15H9.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011790|T15H9.5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00011791|T15H9.6|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011793|T16A9.3|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011793|T16A9.3|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00011793|T16A9.3|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011794|nep-21|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011794|nep-21|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011794|nep-21|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1991|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011794|nep-21|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=617|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011794|nep-21|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011794|nep-21|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011794|nep-21|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011795|T16A9.5.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011795|T16A9.5.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1283|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00011795|T16A9.5.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=678|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011795|T16A9.5.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011795|T16A9.5.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011795|T16A9.5.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011795|T16A9.5.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011796|T16G1.2a|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011796|T16G1.2a|1303nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011796|T16G1.2a|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011796|T16G1.2a|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011796|T16G1.2a|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011796|T16G1.2a|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011796|T16G1.2a|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011797|T16G1.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00011797|T16G1.3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00011798|T16G1.4|1069nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011799|T16G1.5|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011799|T16G1.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011799|T16G1.5|834nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011799|T16G1.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|1206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|1212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|1282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|1534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|1538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=696|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011800|T16G1.6|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011801|T16G1.7|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011801|T16G1.7|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00011801|T16G1.7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1204|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011802|T16G1.9|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011803|T16G12.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011803|T16G12.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011803|T16G12.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011803|T16G12.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=604|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011803|T16G12.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011803|T16G12.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011803|T16G12.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011804|T16G12.3|1060nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011804|T16G12.3|1291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1652|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011804|T16G12.3|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011805|T16G12.4|1405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011805|T16G12.4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=505|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011805|T16G12.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=845|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011805|T16G12.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4229|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011806|ekl-6|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2092|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011807|T16G12.6|239nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011808|T16G12.7|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011808|T16G12.7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011809|T16G12.8|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011809|T16G12.8|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011809|T16G12.8|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011809|T16G12.8|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011809|T16G12.8|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011810|T16G12.9c|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011810|T16G12.9c|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011810|T16G12.9c|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011810|T16G12.9c|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011810|T16G12.9c|467nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=19|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011811|T16H12.1a|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011812|T16H12.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011812|T16H12.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00011812|T16H12.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011813|T16H12.3a|676nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011813|T16H12.3a|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2391|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011813|T16H12.3a|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011814|T16H12.4.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011814|T16H12.4.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011814|T16H12.4.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011814|T16H12.4.1|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011814|T16H12.4.1|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011814|T16H12.4.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011814|T16H12.4.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1641|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|276nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=457|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3092|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011815|bath-43|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011817|T16H12.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011819|hal-2|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1558|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011819|hal-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011819|hal-2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=465|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011820|T18D3.1|527nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|50nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00011821|cdf-2|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011822|T18D3.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=441|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|576nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011823|T18D3.6|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|560nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|644nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1467|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|651nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|654nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|663nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|666nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|668nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|673nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=351|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|680nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011824|T18D3.7a.2|682nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|301nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011826|T18D3.9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|674nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|683nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|687nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|698nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|702nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2981|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|705nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=387|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|711nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|772nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|894nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011827|T19A6.1a.1|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3594|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|353nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1883|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|356nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011828|nepr-1|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011829|T19A6.4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011829|T19A6.4|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011830|cyp-29A2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2344|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00011830|cyp-29A2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3241|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011831|T19B10.2.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|166nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=563|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011832|bgal-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011833|T19B10.5|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011833|T19B10.5|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011833|T19B10.5|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011834|dvc-1|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011834|dvc-1|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3457|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011834|dvc-1|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=714|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011834|dvc-1|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011834|dvc-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2434|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|361nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1220|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011835|T19B10.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011836|mam-4|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011836|mam-4|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011837|srsx-33|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011838|T19C4.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011838|T19C4.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1304|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00011839|T19C4.5a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011841|scl-25|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011844|T19C9.8|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011844|T19C9.8|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011844|T19C9.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011844|T19C9.8|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011844|T19C9.8|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011844|T19C9.8|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=99|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011844|T19C9.8|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011846|chil-25|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011847|chil-26|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8359|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011849|T19H5.4b.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011850|T20B3.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011852|clec-26|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011852|clec-26|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011853|clec-40|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011853|clec-40|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33155|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|72nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011854|T20B3.14|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011855|clec-183|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22250|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011856|T20D3.2.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3859|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|470nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3a.1|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3c.1|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3c.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3c.1|1461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3c.1|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3c.1|1495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011857|T20D3.3c.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|1315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|1319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|1434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|16nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|18nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|26nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=734|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=906|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011858|T20D3.5|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=439|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1117|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2806|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011859|T20D3.6b|432nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=735|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2969|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011860|T20D3.8|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4441|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=738|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011864|T20F10.2a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1632|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=847|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=810|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011866|T20F10.5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|1426nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=528|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18154|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011867|chc-1|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011868|best-18|958nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|342nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|344nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|347nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=184|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|352nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2109|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|354nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41344|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|366nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=241|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011869|dod-6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15375|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011870|T20G5.8|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011871|T20G5.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011871|T20G5.9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=617|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011871|T20G5.9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2044|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011871|T20G5.9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011871|T20G5.9|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011871|T20G5.9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011871|T20G5.9|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1448|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011872|blos-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011873|T20G5.12|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011874|T20G5.13|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011874|T20G5.13|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011874|T20G5.13|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2020|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=990|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5632|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|509nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|511nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011875|T20G5.14|513nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011876|srz-6|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011876|srz-6|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011876|srz-6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011877|T21B4.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00011877|T21B4.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011877|T21B4.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011878|ador-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011878|ador-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011878|ador-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011878|ador-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011878|ador-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1209|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011878|ador-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00011878|ador-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011879|pho-7|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011879|pho-7|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011880|T21B6.3|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011880|T21B6.3|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011880|T21B6.3|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011880|T21B6.3|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=731|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011880|T21B6.3|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011882|nstp-9|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011882|nstp-9|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011882|nstp-9|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00011883|mrpl-50|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3292|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011883|mrpl-50|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=793|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011883|mrpl-50|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=209|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011883|mrpl-50|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=333|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011883|mrpl-50|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011883|mrpl-50|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27421|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3148|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16452|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|184nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8667|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|188nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=160|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|194nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|196nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|200nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=384|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011884|enol-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4784|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011885|T21B10.3|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011886|T21B10.4|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011886|T21B10.4|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011886|T21B10.4|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3162|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011886|T21B10.4|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011886|T21B10.4|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1688|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|383nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=592|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|385nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|458nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|471nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011887|set-17|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=204|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6031|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011888|cutl-15|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|1494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|452nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4258|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011890|mics-1|458nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|1345nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|1411nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|212nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2890|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011891|del-6|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15664|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011892|T21C9.4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011893|T21C9.6|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011893|T21C9.6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011893|T21C9.6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011893|T21C9.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011893|T21C9.6|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011894|ttr-23|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011894|ttr-23|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011894|ttr-23|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011894|ttr-23|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011894|ttr-23|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=952|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011894|ttr-23|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011895|T21C9.9|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011895|T21C9.9|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00011895|T21C9.9|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011896|T21C9.11|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011896|T21C9.11|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011896|T21C9.11|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|360nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|364nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=352|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|366nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3564|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00011897|scpl-4|376nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=442|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|1094nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4091|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011898|T21C9.13|986nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1239|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|699nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|709nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|813nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=60|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|822nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011899|T21C12.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011900|T21C12.4a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00011900|T21C12.4a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011900|T21C12.4a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011902|T21E8.4|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011903|T21E8.5|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011903|T21E8.5|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00011903|T21E8.5|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011903|T21E8.5|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2394|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011904|hlb-1|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|1194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|1196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=202|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011906|hsp-12.1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011908|pash-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2623|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011909|T22A3.6|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011909|T22A3.6|1100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011909|T22A3.6|1259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011909|T22A3.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011909|T22A3.6|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011910|alg-3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011910|alg-3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011910|alg-3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011910|alg-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011911|T22B3.3|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1027|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3763|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=753|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=769|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011912|T22C1.1.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011913|glb-26|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|1336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|1343nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|1512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|608nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=860|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011914|T22C1.3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=958|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1106|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=963|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011915|T22C1.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|1232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|863nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=733|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011916|T22C1.5|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|1051nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|1057nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4321|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|256nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=655|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|299nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|392nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|852nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011917|T22C1.6|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011918|T22C1.8|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=287|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011918|T22C1.8|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011918|T22C1.8|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=520|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=593|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011919|T22C1.9|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011920|T22C1.11|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=439|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011920|T22C1.11|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011920|T22C1.11|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011920|T22C1.11|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=181|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011920|T22C1.11|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011920|T22C1.11|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011921|T22C1.12|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011922|T22C8.1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011923|chhy-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011923|chhy-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011923|chhy-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011924|T22C8.3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011924|T22C8.3|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011924|T22C8.3|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011924|T22C8.3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011925|T22C8.4|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011925|T22C8.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011925|T22C8.4|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011925|T22C8.4|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011926|sptf-2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011926|sptf-2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011926|sptf-2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011926|sptf-2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011926|sptf-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011926|sptf-2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011926|sptf-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011927|T22C8.6|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011927|T22C8.6|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011927|T22C8.6|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011927|T22C8.6|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011927|T22C8.6|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011927|T22C8.6|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011927|T22C8.6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011928|cutl-12|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011928|cutl-12|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011928|cutl-12|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011930|T22G5.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011930|T22G5.3|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011930|T22G5.3|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011930|T22G5.3|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011930|T22G5.3|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011931|srsx-19|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011931|srsx-19|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011931|srsx-19|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011931|srsx-19|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2484|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011932|sptl-3|391nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011934|T22H2.4|1323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011934|T22H2.4|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011934|T22H2.4|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011934|T22H2.4|1591nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|1573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2671|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=866|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011935|scrm-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=379|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=576|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011936|pgrn-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011937|T22H6.1|660nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011938|alh-13|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011938|alh-13|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011938|alh-13|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=587|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011938|alh-13|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011938|alh-13|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011938|alh-13|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011939|prmt-3|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011939|prmt-3|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011939|prmt-3|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2717|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011939|prmt-3|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011939|prmt-3|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011939|prmt-3|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3b|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4208|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011940|T23B5.3d|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2091|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011941|T23B5.4a|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|1569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5513|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|627nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011944|T23D8.3.2|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|374nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|378nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|385nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1671|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|387nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|435nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|450nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011945|hpo-24|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011948|T23F1.5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011949|T23F6.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011949|T23F6.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1090|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011949|T23F6.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011949|T23F6.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011949|T23F6.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011949|T23F6.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011950|T23F6.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00011950|T23F6.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00011951|T23F6.3c|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011951|T23F6.3c|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011951|T23F6.3c|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011951|T23F6.3c|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011952|T23F6.5|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00011952|T23F6.5|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|697nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|701nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3159|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|707nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=848|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|740nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|748nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011953|ppm-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|1077nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|1085nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|545nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|548nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|553nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1845|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|684nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|716nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|932nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011954|T23F11.2|952nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1747|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3558|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|264nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=698|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|270nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|276nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20354|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|281nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|285nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|328nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|760nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|771nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|938nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011955|cdka-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=628|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011956|T23F11.4|914nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011957|T23F11.6|1179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011957|T23F11.6|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011957|T23F11.6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011957|T23F11.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011957|T23F11.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011957|T23F11.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011958|T23G4.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011959|nyn-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011960|oac-48|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011961|T23G4.5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|316nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2402|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=454|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2a.1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2b|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011962|T23G5.2b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011963|T23G5.3|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011963|T23G5.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011963|T23G5.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1721|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011964|saeg-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1037nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1040nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1055nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1071nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1092nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3004|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|1232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011965|T23G7.2a.1|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011966|T23G7.3|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011966|T23G7.3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5483|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011966|T23G7.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=440|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011967|pir-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2660|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011968|T23G11.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011968|T23G11.1|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011968|T23G11.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011968|T23G11.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2996|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011968|T23G11.1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00011968|T23G11.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011969|T23G11.4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011969|T23G11.4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011969|T23G11.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1704|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00011969|T23G11.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=654|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011969|T23G11.4|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011969|T23G11.4|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|1244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|1341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|1423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|504nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|508nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1461|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011970|rlbp-1|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=498|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|1378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=920|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18049|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1390|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=690|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|406nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=812|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|418nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1477|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011971|lron-9|776nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|1077nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|1464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|1486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|1510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|1512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|1522nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2738|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1513|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011972|T23G11.7b|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011973|T23G11.10|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|1463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|340nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|555nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011974|xbx-5|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1708|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1118|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|314nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011975|T24B1.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|1531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2070|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011976|T24B8.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|394nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|626nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|629nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1336|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7395|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|663nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011977|T24B8.3c.3|710nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011978|T24B8.4d|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011978|T24B8.4d|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011978|T24B8.4d|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011978|T24B8.4d|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011978|T24B8.4d|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011978|T24B8.4d|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=843|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|114nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|121nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24042|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2356|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011979|T24B8.5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|1261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|1263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2698|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|1268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|69nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7c.1|809nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7e.1|1064nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7e.1|1078nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7e.1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7e.1|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7e.1|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011980|T24B8.7e.1|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011981|T24C2.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011981|T24C2.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011981|T24C2.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011983|fbxa-81|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011983|fbxa-81|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011984|T24C2.5|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011984|T24C2.5|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011984|T24C2.5|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00011984|T24C2.5|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011984|T24C2.5|1286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011984|T24C2.5|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=161|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011984|T24C2.5|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2700|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|712nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011985|T24D1.2|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|1061nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1200|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1054|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011986|T24D1.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011988|har-2|1162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011988|har-2|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011988|har-2|1436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011988|har-2|1439nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011988|har-2|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011988|har-2|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1665|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011989|T24D5.1|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|524nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|530nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=678|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00011990|T24D5.2|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|1093nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1067|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2043|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=381|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011994|samp-1|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=549|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2654|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011995|rsf-1|1459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00011996|T24F1.4|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011997|T24F1.5|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2344|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00011997|T24F1.5|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=443|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1983|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=786|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00011999|T24F1.7|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012000|T24H10.1|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012000|T24H10.1|229nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012000|T24H10.1|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012000|T24H10.1|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=667|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012000|T24H10.1|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012000|T24H10.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12945|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012002|T24H10.4|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012003|T24H10.5|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012003|T24H10.5|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012003|T24H10.5|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20136|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1639|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012004|dyrb-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|1116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|233nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|240nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|244nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|250nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5794|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9642|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=554|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|361nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1645|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012005|jun-1|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012007|T25B9.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012007|T25B9.1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012007|T25B9.1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012007|T25B9.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1004|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012007|T25B9.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012008|T25B9.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012008|T25B9.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|1154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012009|T25B9.3a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012010|T25B9.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012011|T25B9.5a|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012012|T25B9.6a|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=592|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012012|T25B9.6a|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012013|ugt-54|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012013|ugt-54|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012013|ugt-54|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012013|ugt-54|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012013|ugt-54|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012013|ugt-54|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012014|T25B9.8|103nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012014|T25B9.8|436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012014|T25B9.8|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012014|T25B9.8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012014|T25B9.8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00012014|T25B9.8|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1691|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00012014|T25B9.8|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012015|T25B9.9|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012015|T25B9.9|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012015|T25B9.9|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21771|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00012015|T25B9.9|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012016|inpp-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012016|inpp-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2523|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012017|T25C8.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012017|T25C8.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00012017|T25C8.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00012017|T25C8.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|380nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|391nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|394nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|396nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|624nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11772|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00012018|T25C12.3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|458nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|463nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3270|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|468nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=243|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|472nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012019|dkf-2|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4811|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2010|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012020|gyg-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012021|T25E12.6|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012021|T25E12.6|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012021|T25E12.6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012021|T25E12.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012021|T25E12.6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=312|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012021|T25E12.6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012023|clec-34|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012023|clec-34|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012025|clec-38|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012026|srz-100|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012026|srz-100|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012026|srz-100|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012027|fbxa-127|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012027|fbxa-127|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012028|srz-99|1601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012028|srz-99|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012028|srz-99|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012028|srz-99|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012028|srz-99|980nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012029|T25G3.1.2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012029|T25G3.1.2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012029|T25G3.1.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012029|T25G3.1.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=731|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012029|T25G3.1.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|183nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2264|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|186nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6382|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|193nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|201nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|204nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012030|T25G3.3|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5733|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|344nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|441nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|448nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012031|T25G3.4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012032|T26C5.2|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00012032|T26C5.2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3025|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012033|T26C5.3c|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|62nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|65nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|68nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7624|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=805|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012034|T26C5.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2583|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17028|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1813|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=406|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35831|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29306|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|76nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=39|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012035|T26C5.5.1|996nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012036|clec-103|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012037|T26E3.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=819|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012037|T26E3.4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4190|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012038|T26E3.5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012038|T26E3.5|1252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012039|T26E3.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1059nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1061nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1066nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1069nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|1585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|331nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|334nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|961nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|967nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|969nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1686|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|974nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=296|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|976nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|979nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=405|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012040|T26E3.7|988nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012041|T26E3.8|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012042|T26E3.10|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012042|T26E3.10|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012042|T26E3.10|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012042|T26E3.10|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1058|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012042|T26E3.10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012042|T26E3.10|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012043|irld-52|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012044|T26E4.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012046|T26E4.4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012046|T26E4.4|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012046|T26E4.4|98nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012049|T26E4.7|1553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012051|T26E4.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012052|T26E4.10|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012055|srsx-36|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012056|nhr-285|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012056|nhr-285|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012057|T26F2.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012059|T26G10.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012059|T26G10.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012059|T26G10.1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012059|T26G10.1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012059|T26G10.1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012062|T26G10.5|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012062|T26G10.5|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012062|T26G10.5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012062|T26G10.5|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1205|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012063|fbxb-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012064|fbxb-115|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012064|fbxb-115|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012065|fbxb-2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012065|fbxb-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012066|fbxb-116|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012066|fbxb-116|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012068|oac-49|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00012068|oac-49|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012068|oac-49|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012069|T26H5.4b|106nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00012069|T26H5.4b|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012069|T26H5.4b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012069|T26H5.4b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012069|T26H5.4b|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012070|T26H5.8.4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012070|T26H5.8.4|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012070|T26H5.8.4|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012070|T26H5.8.4|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012072|T26H8.4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012073|cpd-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012073|cpd-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1112|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012073|cpd-2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012074|T27A8.2|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012074|T27A8.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012074|T27A8.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012081|T27C5.8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012083|T27C5.10|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012083|T27C5.10|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1381|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|652nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|667nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012084|npr-15|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012085|T27D12.1b|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012085|T27D12.1b|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012085|T27D12.1b|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012085|T27D12.1b|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=766|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012085|T27D12.1b|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012085|T27D12.1b|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012085|T27D12.1b|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012086|clec-144|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00012086|clec-144|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00012087|T27E7.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012087|T27E7.1|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012087|T27E7.1|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012087|T27E7.1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012087|T27E7.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2115|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012088|T27E7.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012088|T27E7.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012089|T27E7.4|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012089|T27E7.4|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00012089|T27E7.4|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012089|T27E7.4|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012089|T27E7.4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012090|T27E7.5|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012093|T27E7.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012093|T27E7.9|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=969|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|1218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|1227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22942|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|1323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|1328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012094|T27E9.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=571|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=781|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012095|pssy-2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012096|T27E9.6|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012096|T27E9.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012096|T27E9.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012096|T27E9.6|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10539|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2323|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|694nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012097|abcf-2|698nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012098|fbxb-86|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1577|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|513nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|516nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012099|acc-4|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4740|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1693|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|563nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|567nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012100|sipa-1|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012101|zip-10|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012101|zip-10|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2657|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012101|zip-10|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012101|zip-10|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012101|zip-10|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012102|T27F6.1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012102|T27F6.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012102|T27F6.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00012103|clec-12|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7527|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012104|sygl-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012105|T27F6.6|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012105|T27F6.6|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=625|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012105|T27F6.6|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=376|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012105|T27F6.6|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=128|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012106|T27F6.7|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012106|T27F6.7|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012106|T27F6.7|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3142|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012106|T27F6.7|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012106|T27F6.7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012106|T27F6.7|406nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012107|T27F6.8|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012107|T27F6.8|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012107|T27F6.8|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012107|T27F6.8|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012107|T27F6.8|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012107|T27F6.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=396|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012109|T28A8.3.2|947nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012110|T28A8.4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=754|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012111|T28A8.5|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012111|T28A8.5|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1142|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012112|T28A8.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012112|T28A8.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=765|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012112|T28A8.6|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012112|T28A8.6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6970|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=513|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012113|T28B8.1.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012114|T28B8.3a|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012114|T28B8.3a|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012114|T28B8.3a|733nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012115|T28B8.4|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012116|del-4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012116|del-4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012116|del-4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012116|del-4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|1431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|836nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|839nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=94|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|841nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|938nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|940nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2054|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|969nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1898|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012117|T28B11.1b.2|984nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012118|grsp-2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1344|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012118|grsp-2|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012119|T28C6.3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012119|T28C6.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012119|T28C6.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012119|T28C6.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012120|T28C6.5|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012120|T28C6.5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00012121|T28C6.7a|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012121|T28C6.7a|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012121|T28C6.7a|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012121|T28C6.7a|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2222|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012121|T28C6.7a|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012121|T28C6.7a|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|1481nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1411|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=279|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012122|T28C6.8|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012123|T28D6.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012123|T28D6.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5682|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012123|T28D6.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012123|T28D6.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012124|T28D6.4|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1152|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012124|T28D6.4|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012124|T28D6.4|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=740|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2261|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|352nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|361nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=314|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012125|T28D6.5d.2|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012126|T28D6.6b|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2274|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012126|T28D6.6b|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=583|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012126|T28D6.6b|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012126|T28D6.6b|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012126|T28D6.6b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012126|T28D6.6b|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|1111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|1115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012127|T28D6.7|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6547|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6551|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|486nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=166|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|753nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012128|nra-1|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1626|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012130|slc-17.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012131|T28F3.5a|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00012131|T28F3.5a|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=494|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|1163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|1166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4853|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012132|ifta-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012134|T28F3.8|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1066|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012134|T28F3.8|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012135|T28F3.9|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012135|T28F3.9|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012135|T28F3.9|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=108|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012135|T28F3.9|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012135|T28F3.9|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012135|T28F3.9|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=182|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|204nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1049|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|451nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012136|T28F4.1.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012137|asic-2|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012138|T28F4.3|1012nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012138|T28F4.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012138|T28F4.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012138|T28F4.3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012138|T28F4.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012139|T28F4.4|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1387|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=505|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25399|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19812|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|244nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|807nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|827nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|844nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012140|T28F4.5.2|846nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012141|T28F4.6|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012141|T28F4.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012142|T28H10.1|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012142|T28H10.1|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012143|T28H10.2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012143|T28H10.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012143|T28H10.2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012143|T28H10.2|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012143|T28H10.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012143|T28H10.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012144|T28H10.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012144|T28H10.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5049|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012144|T28H10.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1537|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012144|T28H10.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012144|T28H10.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012145|nlp-46|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012145|nlp-46|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012145|nlp-46|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=505|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012145|nlp-46|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012145|nlp-46|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012145|nlp-46|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012145|nlp-46|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|1575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|622nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|628nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=230|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|630nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012146|VB0393L.2|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012147|VC27A7L.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012147|VC27A7L.1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012147|VC27A7L.1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012147|VC27A7L.1|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012148|inos-1|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19270|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012148|inos-1|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=844|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012148|inos-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012148|inos-1|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012149|VF13D12L.3|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012149|VF13D12L.3|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5662|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012149|VF13D12L.3|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012149|VF13D12L.3|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012149|VF13D12L.3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012149|VF13D12L.3|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=187|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2520|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|588nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012150|syx-17|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012151|VH15N14R.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012151|VH15N14R.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012151|VH15N14R.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012151|VH15N14R.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012152|cnc-10|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012152|cnc-10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012152|cnc-10|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012152|cnc-10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1441|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012152|cnc-10|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012152|cnc-10|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012155|VW02B12L.2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012155|VW02B12L.2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3147|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1255|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012156|ebp-2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012157|adbp-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012157|adbp-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012157|adbp-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012157|adbp-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012157|adbp-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012157|adbp-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2111|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012157|adbp-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=615|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4314|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1704|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012158|ucr-2.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012159|VY10G11R.1|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012162|sek-6|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012162|sek-6|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012162|sek-6|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|568nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1255|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|647nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012163|VZK822L.2|654nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012164|W01A8.2a|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012164|W01A8.2a|55nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012165|cutl-6|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012165|cutl-6|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00012165|cutl-6|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012165|cutl-6|277nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012165|cutl-6|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012165|cutl-6|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012165|cutl-6|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3803|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1982|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=279|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012166|nuo-6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|798nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2249|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012167|tofu-5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=672|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012168|W01A8.6|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012169|W01B6.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012169|W01B6.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012169|W01B6.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012170|W01B6.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012171|W01B6.4|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012171|W01B6.4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012171|W01B6.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012171|W01B6.4|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012171|W01B6.4|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012171|W01B6.4|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012171|W01B6.4|922nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012172|W01B6.5|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012173|W01B6.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012173|W01B6.6|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012173|W01B6.6|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012173|W01B6.6|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012174|W01B6.8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012175|W01C9.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012175|W01C9.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012176|W01C9.2|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012176|W01C9.2|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012176|W01C9.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012177|decr-1.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012177|decr-1.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012177|decr-1.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012177|decr-1.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012177|decr-1.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012177|decr-1.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012178|glb-27|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012178|glb-27|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012178|glb-27|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012178|glb-27|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012178|glb-27|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012178|glb-27|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012178|glb-27|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1566|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|101nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|106nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|108nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=893|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77868|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13468|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2431|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|57nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3309|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012179|W01D2.1.2|97nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1054|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012180|W01D2.3b.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012181|srt-11|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|1017nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|1148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2581|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012182|osta-3|984nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012183|W01D2.6|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012183|W01D2.6|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012184|mnr-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012184|mnr-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012184|mnr-1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012184|mnr-1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012184|mnr-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1955|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012184|mnr-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012185|W01F3.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012185|W01F3.2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012185|W01F3.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1952|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=535|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012186|mlt-11|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012187|rpb-11|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5328|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012188|W01G7.4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2323|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012188|W01G7.4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012188|W01G7.4|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012188|W01G7.4|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012190|W02A2.5|1453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012190|W02A2.5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|186nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|562nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|582nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=312|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012191|W02A2.8c|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1486|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012192|W02A11.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=600|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25159|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1770|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1876|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012193|vps-25|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2328|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012194|toe-4|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012195|bath-34|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012196|bath-35|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=188|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012196|bath-35|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012196|bath-35|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|553nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012197|W02B8.1.2|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012198|W02B8.2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012198|W02B8.2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012198|W02B8.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012199|mltn-3|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012199|mltn-3|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=471|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=718|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012201|W02B12.1|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012202|W02B12.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012202|W02B12.4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012202|W02B12.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012202|W02B12.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012202|W02B12.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012202|W02B12.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012202|W02B12.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2888|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012203|rga-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012204|mfn-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012204|mfn-1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012204|mfn-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012204|mfn-1|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1842|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012204|mfn-1|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1508|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012204|mfn-1|365nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012204|mfn-1|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012205|W02B12.10|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3336|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012205|W02B12.10|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=283|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|270nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|272nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3706|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|282nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=689|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012206|W02B12.11.2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012207|W02B12.12b|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1840|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012207|W02B12.12b|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012207|W02B12.12b|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012207|W02B12.12b|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012207|W02B12.12b|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012207|W02B12.12b|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012207|W02B12.12b|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=386|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|1492nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|213nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|221nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|225nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1028|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|229nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=2262|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|251nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012208|W02D9.2a|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012209|hmg-20|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1315|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012209|hmg-20|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012209|hmg-20|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012210|W02D9.4|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=388|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012210|W02D9.4|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3680|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012211|ssp-37|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=695|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|1013nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4704|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012212|W02D9.6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1021|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24595|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=805|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=758|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012213|W02D9.7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=438|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012214|W02D9.8|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012214|W02D9.8|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012214|W02D9.8|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012214|W02D9.8|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012214|W02D9.8|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012215|W02D9.9|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012215|W02D9.9|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=413|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012215|W02D9.9|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012215|W02D9.9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=414|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00012215|W02D9.9|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012215|W02D9.9|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9208|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012216|W02D9.10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012217|W02H3.1b|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012217|W02H3.1b|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012217|W02H3.1b|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=728|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00012219|W03C9.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012219|W03C9.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=314|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1110|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=229|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012220|W03C9.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012221|W03C9.5|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012221|W03C9.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2118|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012221|W03C9.5|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2130|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012221|W03C9.5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012221|W03C9.5|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012221|W03C9.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012221|W03C9.5|833nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012222|W03C9.6.2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012222|W03C9.6.2|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012223|W03C9.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012223|W03C9.8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=805|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012223|W03C9.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012223|W03C9.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1040nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1099nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|1315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|454nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|464nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|468nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|470nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|473nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|478nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=762|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|808nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|876nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=465|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012224|W03G11.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012225|W03G11.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012225|W03G11.3|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012225|W03G11.3|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=255|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00012225|W03G11.3|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=283|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012225|W03G11.3|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012226|W03G11.4.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012226|W03G11.4.3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012226|W03G11.4.3|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2792|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012226|W03G11.4.3|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012226|W03G11.4.3|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1087nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1098nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|367nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|370nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=331|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|375nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012228|W03H9.2b|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012230|cacn-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012230|cacn-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3607|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00012230|cacn-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012230|cacn-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012230|cacn-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012230|cacn-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1778|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1049|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012231|W04A4.2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012233|W04A4.4|1331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012233|W04A4.4|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012234|W04A4.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012234|W04A4.5|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2445|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012234|W04A4.5|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012234|W04A4.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=869|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012235|W04A4.6|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|322nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|382nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|384nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=530|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012236|W04A8.1b|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012237|W04A8.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012237|W04A8.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012238|W04A8.3|1584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00012238|W04A8.3|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012238|W04A8.3|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00012239|W04A8.4a|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012239|W04A8.4a|1458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012239|W04A8.4a|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012239|W04A8.4a|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1272|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012239|W04A8.4a|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012240|W04A8.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012240|W04A8.5|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012240|W04A8.5|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012240|W04A8.5|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012241|W04A8.6a|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012241|W04A8.6a|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012241|W04A8.6a|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012241|W04A8.6a|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012241|W04A8.6a|370nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=963|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012241|W04A8.6a|376nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012242|srt-39|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012243|W04D2.4|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1445|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012243|W04D2.4|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012243|W04D2.4|670nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012243|W04D2.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012243|W04D2.4|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1114|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3089|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012244|mrps-11|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|1556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|1560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1884|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2131|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1348|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012245|W04D2.6a|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012247|W04E12.2|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012247|W04E12.2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012247|W04E12.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012247|W04E12.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012247|W04E12.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012247|W04E12.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012248|W04E12.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012248|W04E12.3|913nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012249|W04E12.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012249|W04E12.4|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012249|W04E12.4|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012249|W04E12.4|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=369|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012249|W04E12.4|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012250|W04E12.5a|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=410|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012250|W04E12.5a|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012250|W04E12.5a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012251|clec-49|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012251|clec-49|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012251|clec-49|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1006|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00012251|clec-49|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012251|clec-49|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012251|clec-49|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012251|clec-49|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012252|W04E12.7|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012252|W04E12.7|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012252|W04E12.7|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012252|W04E12.7|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012252|W04E12.7|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012252|W04E12.7|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=641|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012252|W04E12.7|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012253|clec-50|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012253|clec-50|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11893|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00012253|clec-50|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012253|clec-50|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=143|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012254|W04E12.9b|1496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012254|W04E12.9b|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012254|W04E12.9b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|1574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3494|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012255|lpr-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012256|lpr-5|1331nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012256|lpr-5|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012256|lpr-5|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012256|lpr-5|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012256|lpr-5|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1519|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012256|lpr-5|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1160|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012256|lpr-5|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=150|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2637|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012257|lpr-4|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4937|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012258|W04G3.5a|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|251nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=309|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012259|sulp-7|268nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012260|W04G3.7|749nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=406|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2006|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=892|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=412|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012261|lpr-3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012265|W04G5.4|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012265|W04G5.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012265|W04G5.4|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012265|W04G5.4|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012265|W04G5.4|695nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012265|W04G5.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012265|W04G5.4|863nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012266|W04G5.5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012267|W04G5.7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012267|W04G5.7|930nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012267|W04G5.7|932nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012268|W04G5.8|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012268|W04G5.8|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012268|W04G5.8|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012271|W05B2.2|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012271|W05B2.2|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00012271|W05B2.2|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012272|dhc-4|341nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012272|dhc-4|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012272|dhc-4|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012272|dhc-4|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012272|dhc-4|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012273|W05B2.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012273|W05B2.7|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1e.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1e.2|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1e.2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8133|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1e.2|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1e.2|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1e.2|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1f|1518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012274|W05B5.1f|1522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012275|npr-14|1438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=731|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012275|npr-14|1443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|1130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10270|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|478nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|490nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012276|his-74|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012277|ccch-3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012277|ccch-3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012277|ccch-3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012278|W05B10.3|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012278|W05B10.3|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012278|W05B10.3|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012278|W05B10.3|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012279|W05B10.4|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012279|W05B10.4|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=294|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00012279|W05B10.4|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012279|W05B10.4|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012280|W05E10.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012280|W05E10.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=541|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2736|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1724|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7008|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=417|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2846|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|138nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|145nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|147nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|151nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=488|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|468nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=446|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|471nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|492nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5759|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=679|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=535|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012281|W05E10.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=852|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=683|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=822|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1116|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012282|W05E10.5c|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012283|W05H5.1|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012285|pitr-6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012285|pitr-6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=838|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012285|pitr-6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012285|pitr-6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012285|pitr-6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012286|sre-35|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012287|sre-33|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012287|sre-33|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012288|sre-32|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00012288|sre-32|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00012288|sre-32|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8861|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012289|W05H12.1|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3197|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012290|W05H12.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012291|W06A7.2a|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012293|W06A7.4a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012294|nspa-8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=525|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012294|nspa-8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3213|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012294|nspa-8|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012295|nmat-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012295|nmat-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012295|nmat-1|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=663|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012295|nmat-1|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012295|nmat-1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012295|nmat-1|723nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012296|spe-46|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=604|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012296|spe-46|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012297|W06D4.3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012297|W06D4.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012298|prmt-7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012298|prmt-7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=489|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012298|prmt-7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1986|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012298|prmt-7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012298|prmt-7|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012298|prmt-7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012299|W06D11.1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=860|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012299|W06D11.1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012299|W06D11.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012300|W06D11.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012300|W06D11.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012300|W06D11.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012301|W06D11.3|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012301|W06D11.3|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012301|W06D11.3|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012301|W06D11.3|719nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012301|W06D11.3|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012302|dot-1.3|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012304|cutl-4|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012304|cutl-4|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012304|cutl-4|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=602|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012306|W06F12.2a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012307|W06F12.3|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012307|W06F12.3|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012307|W06F12.3|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=287|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012307|W06F12.3|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012308|oac-53|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012308|oac-53|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012311|W06G6.9|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012312|W06G6.10|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012312|W06G6.10|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012315|immt-2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012315|immt-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3028|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012315|immt-2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012315|immt-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6638|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=691|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012316|ctps-1|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012317|ztf-6|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012317|ztf-6|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012317|ztf-6|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2671|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012318|srxa-1|1299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012318|srxa-1|1324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012318|srxa-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00012318|srxa-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|1337nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2362|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012319|ipla-3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012321|srxa-6|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012321|srxa-6|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012322|W07A12.4|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00012322|W07A12.4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012322|W07A12.4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012322|W07A12.4|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012322|W07A12.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012323|oac-54|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00012323|oac-54|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00012324|rhy-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012324|rhy-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012324|rhy-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012324|rhy-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=772|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012324|rhy-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2767|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=740|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012325|W07A12.8|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2976|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2467|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012326|W07E11.1a|758nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012328|W07G1.1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00012328|W07G1.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012328|W07G1.1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012329|sre-44|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012329|sre-44|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012330|zip-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2308|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00012330|zip-3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012330|zip-3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012330|zip-3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012330|zip-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012330|zip-3|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012332|W07G1.5a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00012332|W07G1.5a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012332|W07G1.5a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012332|W07G1.5a|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012333|sre-43|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012333|sre-43|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012333|sre-43|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012334|W07G1.7|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012334|W07G1.7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012335|W07G4.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012335|W07G4.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012336|W07G4.2|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012337|W07G4.3.1|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012337|W07G4.3.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=304|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012339|W07G4.5|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012339|W07G4.5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012339|W07G4.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2458|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012339|W07G4.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012339|W07G4.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012339|W07G4.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012340|dct-15|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012340|dct-15|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012340|dct-15|451nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=207|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012340|dct-15|459nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012340|dct-15|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1034|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012340|dct-15|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2993|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012341|catp-6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1359|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=940|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012342|mtr-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012343|W08E3.2|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11999|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012344|ola-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012345|W08E3.4|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012345|W08E3.4|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012345|W08E3.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012346|W08G11.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012346|W08G11.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012346|W08G11.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012346|W08G11.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012347|W08G11.3a|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012347|W08G11.3a|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012347|W08G11.3a|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1392|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012347|W08G11.3a|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|1014nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|1046nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|847nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|859nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|864nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|871nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|873nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1511|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=617|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|925nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1045|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012348|pptr-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=846|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11018|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012351|W09C5.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012352|dkf-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012352|dkf-1|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012352|dkf-1|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=682|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012352|dkf-1|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012352|dkf-1|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012352|dkf-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4643|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|298nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012353|W09C5.7a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17555|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7392|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012354|W09C5.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7309|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012356|W09D6.1c|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012356|W09D6.1c|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012356|W09D6.1c|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012357|W09D6.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012357|W09D6.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2360|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012357|W09D6.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3004|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012358|W09D6.5|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=143|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|342nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1561|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1751|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012359|W09D10.1.2|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012360|tat-3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012360|tat-3|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012360|tat-3|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012360|tat-3|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2473|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012360|tat-3|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1314|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1356|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012361|mrpl-12|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|452nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|460nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|463nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|465nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|856nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3826|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|861nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012362|W09D10.4|864nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1130|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|153nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012363|W09D10.5|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1201|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012364|W09D12.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012365|W09G3.1a|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012365|W09G3.1a|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1215|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012365|W09G3.1a|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012365|W09G3.1a|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|1517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1064|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012366|maea-1|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=526|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1630|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=346|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012369|W09G3.6b|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012370|W09G3.7a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012370|W09G3.7a|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=705|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012370|W09G3.7a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012370|W09G3.7a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012370|W09G3.7a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012371|W09G3.8.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012371|W09G3.8.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012371|W09G3.8.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012371|W09G3.8.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=793|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00012372|W09H1.1b|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012372|W09H1.1b|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012372|W09H1.1b|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=761|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|1596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012374|W09H1.4|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012375|mecr-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012375|mecr-1|1064nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012375|mecr-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4437|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012375|mecr-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012375|mecr-1|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4130|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3406|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012376|nduf-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012378|W10G6.1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00012378|W10G6.1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00012379|Y1A5A.1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1172|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012379|Y1A5A.1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012379|Y1A5A.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012379|Y1A5A.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012380|Y1A5A.2|647nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012381|Y2H9A.4b|1153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012381|Y2H9A.4b|1156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012381|Y2H9A.4b|1159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7060|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19134|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|427nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|440nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=934|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2395|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012382|ttr-16|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20731|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012383|ttr-17|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012383|ttr-17|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012383|ttr-17|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012383|ttr-17|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6099|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012383|ttr-17|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012383|ttr-17|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=616|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012383|ttr-17|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012385|Y5F2A.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012385|Y5F2A.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2137|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012385|Y5F2A.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|1045nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|1214nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1863|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1424|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012386|agef-1|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012387|Y6B3B.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012387|Y6B3B.1|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012387|Y6B3B.1|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012387|Y6B3B.1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012387|Y6B3B.1|445nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012388|Y6B3B.3|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012389|Y6B3B.4|1191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012389|Y6B3B.4|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2373|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00012389|Y6B3B.4|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012390|Y6B3B.5a|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=570|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00012390|Y6B3B.5a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012391|Y6B3B.7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012391|Y6B3B.7|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012391|Y6B3B.7|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1039|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012391|Y6B3B.7|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012391|Y6B3B.7|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012391|Y6B3B.7|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012391|Y6B3B.7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012393|Y6B3B.9b|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1005|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012393|Y6B3B.9b|436nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012395|Y6D1A.1|1002nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012395|Y6D1A.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012395|Y6D1A.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012395|Y6D1A.1|994nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012395|Y6D1A.1|997nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012395|Y6D1A.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=184|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012396|Y6D1A.2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012397|Y6E2A.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012398|Y6E2A.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=568|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012399|Y6E2A.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012399|Y6E2A.5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00012399|Y6E2A.5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012400|Y6E2A.7|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012400|Y6E2A.7|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012401|irld-57|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012401|irld-57|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012402|sfxn-1.3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012402|sfxn-1.3|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012402|sfxn-1.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012402|sfxn-1.3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012404|Y6G8.2a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012404|Y6G8.2a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00012405|ztf-25|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012405|ztf-25|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012405|ztf-25|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012406|srz-91|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012407|Y7A5A.1.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=575|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012407|Y7A5A.1.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012407|Y7A5A.1.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012407|Y7A5A.1.1|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012407|Y7A5A.1.1|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=976|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012407|Y7A5A.1.1|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012408|Y7A5A.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012411|Y7A5A.5|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012412|Y7A5A.6|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012412|Y7A5A.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012413|Y7A5A.7|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012413|Y7A5A.7|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012413|Y7A5A.7|362nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=214|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012413|Y7A5A.7|369nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012414|Y7A5A.8|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012414|Y7A5A.8|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012414|Y7A5A.8|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012414|Y7A5A.8|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012414|Y7A5A.8|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012415|Y7A5A.9|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012416|Y7A9A.1|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012416|Y7A9A.1|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012416|Y7A9A.1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012420|Y7A9D.1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012420|Y7A9D.1|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012420|Y7A9D.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012420|Y7A9D.1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012420|Y7A9D.1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1657|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012420|Y7A9D.1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012420|Y7A9D.1|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012421|Y9C2UA.1b|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5318|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012421|Y9C2UA.1b|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1350|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012421|Y9C2UA.1b|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012421|Y9C2UA.1b|414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012421|Y9C2UA.1b|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2302|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012423|Y10G11A.1a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012424|dlc-3|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00012424|dlc-3|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=425|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00012425|dlc-4|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|150nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1363|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012428|Y11D7A.3b|704nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012429|Y11D7A.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=627|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|262nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|280nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|283nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=456|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012431|Y11D7A.7|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012432|Y11D7A.8|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012433|Y11D7A.9|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012433|Y11D7A.9|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00012433|Y11D7A.9|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012433|Y11D7A.9|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1940|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4439|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=535|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012434|Y11D7A.10c|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1472|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1399|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|322nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012435|flh-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012436|flh-3|285nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012436|flh-3|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012436|flh-3|293nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=466|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012436|flh-3|297nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012436|flh-3|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012436|flh-3|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=328|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012436|flh-3|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012437|hum-9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012437|hum-9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012439|Y12A6A.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|1050nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=811|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4321|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=400|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2533|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|621nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012440|Y12A6A.2|662nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012441|glb-28|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012441|glb-28|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012441|glb-28|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012442|Y15E3A.3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012442|Y15E3A.3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012443|Y15E3A.4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012443|Y15E3A.4|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012443|Y15E3A.4|313nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1710|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1385|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012444|Y15E3A.5.2|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1552|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012445|Y16B4A.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|715nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|722nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|748nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012446|nhr-230|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012448|cyp-33D3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012448|cyp-33D3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012449|nhr-231|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012449|nhr-231|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=293|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|1450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2813|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=554|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012450|Y17D7B.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012451|Y17D7B.3|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012451|Y17D7B.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=514|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012451|Y17D7B.3|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012451|Y17D7B.3|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012452|Y17D7B.4.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=451|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012452|Y17D7B.4.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4663|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012452|Y17D7B.4.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012455|Y17D7C.1a|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012455|Y17D7C.1a|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012456|Y17D7C.2|100nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012456|Y17D7C.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012457|acbp-6|1314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012457|acbp-6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012457|acbp-6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012457|acbp-6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41217|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012457|acbp-6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15419|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012457|acbp-6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|397nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|406nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1528|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=663|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|444nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|449nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012458|ash-2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|1002nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|1108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|989nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|995nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=317|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|997nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012459|Y17G7B.3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012460|dhps-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012460|dhps-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=557|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012460|dhps-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012460|dhps-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012460|dhps-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012461|glb-29|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012461|glb-29|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1390|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012461|glb-29|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012461|glb-29|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012461|glb-29|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012461|glb-29|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012461|glb-29|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012462|Y17G7B.8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012462|Y17G7B.8|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=596|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012462|Y17G7B.8|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012462|Y17G7B.8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012462|Y17G7B.8|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012463|Y17G7B.10a.5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3222|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012463|Y17G7B.10a.5|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012463|Y17G7B.10a.5|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012463|Y17G7B.10a.5|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012464|arrd-7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012464|arrd-7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012464|arrd-7|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012465|Y17G7B.12.2|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012465|Y17G7B.12.2|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012465|Y17G7B.12.2|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=475|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00012465|Y17G7B.12.2|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|667nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|673nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|747nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|870nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|877nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|882nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1450|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|885nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012466|Y17G7B.13|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012467|arrd-8|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012467|arrd-8|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012467|arrd-8|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012467|arrd-8|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|173nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8431|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012468|Y17G7B.17.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|686nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|689nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|700nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=512|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|731nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012469|Y17G7B.18a|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012470|Y17G7B.19|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=710|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|471nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|479nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|488nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|615nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1866|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6148|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|663nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012471|Y17G7B.20d|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|1280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|516nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|518nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|770nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|783nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|808nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|811nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|817nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|828nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|843nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|851nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|857nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|859nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=967|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|861nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|864nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|867nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|875nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21a|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=335|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21b|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012472|Y17G7B.21b|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012473|Y17G7B.22|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012473|Y17G7B.22|1081nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012473|Y17G7B.22|1085nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012473|Y17G7B.22|1088nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012473|Y17G7B.22|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2143|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012474|attf-6|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012476|Y18D10A.3|899nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012476|Y18D10A.3|903nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012476|Y18D10A.3|906nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012476|Y18D10A.3|909nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012476|Y18D10A.3|912nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=889|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012478|Y18D10A.8|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012479|Y18D10A.9|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=695|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012479|Y18D10A.9|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012479|Y18D10A.9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012479|Y18D10A.9|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012480|clec-104|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012480|clec-104|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012480|clec-104|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012480|clec-104|928nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012480|clec-104|935nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012480|clec-104|96nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1109|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1283|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6108|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012481|Y18D10A.11|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012482|clec-106|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|444nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|542nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|620nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=374|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012483|Y18D10A.16|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3739|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|165nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18787|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7776|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=503|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1979|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|574nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|579nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14394|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|582nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1761|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|587nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|653nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|657nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|661nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012484|car-1|749nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012486|Y18D10A.21|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012487|Y18D10A.23|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012487|Y18D10A.23|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012487|Y18D10A.23|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012487|Y18D10A.23|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012489|Y19D2B.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012489|Y19D2B.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=798|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012489|Y19D2B.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=355|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00012489|Y19D2B.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012490|Y19D2B.2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00012490|Y19D2B.2|512nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012490|Y19D2B.2|585nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012491|Y20C6A.1a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012491|Y20C6A.1a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012492|fbxb-7|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=349|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012492|fbxb-7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012492|fbxb-7|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012494|nhr-232|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00012494|nhr-232|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012494|nhr-232|176nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012494|nhr-232|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=533|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1539|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|223nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012496|Y24F12A.1a|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1266|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3864|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|965nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012497|ragc-1|993nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012501|Y26D4A.3.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012502|clec-107|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012503|Y26D4A.5a|759nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012504|clec-108|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012509|Y26D4A.12|26nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012509|Y26D4A.12|30nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012509|Y26D4A.12|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012509|Y26D4A.12|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2192|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012512|ekl-5|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012513|Y26E6A.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012513|Y26E6A.2|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=984|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1052|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012514|Y26E6A.3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012515|Y26G10.1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012518|comt-2|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012518|comt-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012519|Y32B12A.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012519|Y32B12A.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012519|Y32B12A.4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012519|Y32B12A.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012521|Y32B12B.1a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012522|Y32B12B.2a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1757|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012524|Y32B12B.4a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012524|Y32B12B.4a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=773|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012524|Y32B12B.4a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012525|Y32B12C.1|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012526|Y32B12C.3|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012526|Y32B12C.3|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=610|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012527|set-22|256nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1027nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1033nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1045nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1048nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1930|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|1473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|866nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|868nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|871nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012528|pap-1|875nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=947|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012529|Y32F6A.4|304nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|350nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4968|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1046|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012530|Y32F6A.5b.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1047|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012531|Y32F6B.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012532|crp-1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1036|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012532|crp-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012532|crp-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012532|crp-1|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012532|crp-1|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012533|fbxa-209|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012533|fbxa-209|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012535|Y37A1A.2|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=241|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00012535|Y37A1A.2|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|57nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|721nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012536|Y37A1A.3|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=241|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1685|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=268|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012538|Y37A1B.5a|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012540|Y37A1B.7|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012540|Y37A1B.7|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012540|Y37A1B.7|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1685|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012540|Y37A1B.7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012541|irld-55|200nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012541|irld-55|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012541|irld-55|496nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012542|irld-56|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2695|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|724nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|831nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|833nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012543|nkcc-1|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012544|Y37D8A.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012544|Y37D8A.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012544|Y37D8A.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012544|Y37D8A.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8558|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00012544|Y37D8A.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012544|Y37D8A.2|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012545|Y37D8A.3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012546|Y37D8A.4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012546|Y37D8A.4|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012546|Y37D8A.4|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012546|Y37D8A.4|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1150|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012546|Y37D8A.4|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012547|Y37D8A.5|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012547|Y37D8A.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012547|Y37D8A.5|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012547|Y37D8A.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012547|Y37D8A.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012548|Y37D8A.6|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3781|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012548|Y37D8A.6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012548|Y37D8A.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012548|Y37D8A.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012548|Y37D8A.6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012549|Y37D8A.8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012549|Y37D8A.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012549|Y37D8A.8|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012549|Y37D8A.8|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=677|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10626|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1627|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012550|hpo-21|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|1534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|1539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|205nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|237nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1636|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=227|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012551|cec-7|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012552|enu-3.5|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5274|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012552|enu-3.5|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012552|enu-3.5|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012552|enu-3.5|663nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17672|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15009|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=559|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=861|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=643|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=793|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|663nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012553|cco-2|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012554|Y37D8A.16|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012554|Y37D8A.16|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012554|Y37D8A.16|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012554|Y37D8A.16|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=960|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012554|Y37D8A.16|464nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|1043nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|1188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|1219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|1263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3802|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|1480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012555|Y37D8A.17|832nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=216|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1009|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|637nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012556|mrps-10|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167784|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012557|Y37D8A.19|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012558|Y37D8A.21|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1847|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012558|Y37D8A.21|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012558|Y37D8A.21|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012558|Y37D8A.21|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012559|epg-3|1528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3329|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012559|epg-3|1565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012559|epg-3|1580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012559|epg-3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012560|Y37D8A.25|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012560|Y37D8A.25|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=688|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012560|Y37D8A.25|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012560|Y37D8A.25|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012561|Y37D8A.26|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012562|Y37H2A.1a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2596|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012562|Y37H2A.1a|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012562|Y37H2A.1a|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1185|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012562|Y37H2A.1a|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012562|Y37H2A.1a|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012564|fbxa-107|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012564|fbxa-107|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012564|fbxa-107|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012565|fbxa-210|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012565|fbxa-210|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012565|fbxa-210|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012565|fbxa-210|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=932|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012565|fbxa-210|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=300|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012566|fbxa-211|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012570|Y37H2A.10a|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012570|Y37H2A.10a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012571|Y37H2A.11|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012573|Y37H2C.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012576|Y37H9A.1a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012576|Y37H9A.1a|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012576|Y37H9A.1a|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=395|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012578|Y37H9A.3|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012578|Y37H9A.3|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00012578|Y37H9A.3|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1404|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00012578|Y37H9A.3|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=294|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012578|Y37H9A.3|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012580|Y38E10A.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012580|Y38E10A.2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012581|Y38E10A.3|1154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00012581|Y38E10A.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012581|Y38E10A.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012582|clec-8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012582|clec-8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012582|clec-8|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00012582|clec-8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012583|clec-4|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012583|clec-4|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012583|clec-4|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012583|clec-4|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012583|clec-4|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012583|clec-4|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=270|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012584|ceh-100|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012584|ceh-100|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2623|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012584|ceh-100|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012585|lips-15|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012585|lips-15|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012585|lips-15|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012585|lips-15|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012585|lips-15|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012585|lips-15|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012586|Y38E10A.8|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012587|Y38E10A.9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012588|lips-16|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012589|nspe-4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00012589|nspe-4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012589|nspe-4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012590|nspe-3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012591|nspe-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1832|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00012591|nspe-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=590|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012591|nspe-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012591|nspe-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=881|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2306|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012592|Y38E10A.14|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012593|nspe-7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012593|nspe-7|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1459|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012593|nspe-7|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012593|nspe-7|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=300|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|1215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|1335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|1337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|1342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|1387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012594|nspe-5|1393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012595|Y38E10A.17|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012595|Y38E10A.17|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012595|Y38E10A.17|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=299|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012595|Y38E10A.17|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=263|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012596|nhr-234|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012596|nhr-234|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012597|nhr-235|346nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00012597|nhr-235|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|1053nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|1060nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|1062nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|1367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|465nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=852|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|57nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|937nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22b|946nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1236|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22c|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22c|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012600|Y38E10A.22c|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|77nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5786|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1986|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3238|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012602|Y38E10A.24.1|92nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012603|nspe-6|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012604|nspe-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012604|nspe-2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012604|nspe-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012605|Y38F1A.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012605|Y38F1A.1|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012605|Y38F1A.1|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=804|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012605|Y38F1A.1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1235|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012606|Y38F1A.2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012606|Y38F1A.2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1445|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012606|Y38F1A.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012606|Y38F1A.2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012607|Y38F1A.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012607|Y38F1A.4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012608|Y38F1A.6.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11738|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00012608|Y38F1A.6.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1403|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012608|Y38F1A.6.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12908|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012608|Y38F1A.6.1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1734|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012608|Y38F1A.6.1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012608|Y38F1A.6.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012608|Y38F1A.6.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=664|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|1527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012609|Y38F1A.7|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012610|Y38F1A.8|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012610|Y38F1A.8|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=650|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012610|Y38F1A.8|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012612|Y38H6A.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012614|Y38H6A.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012614|Y38H6A.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012614|Y38H6A.3|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012614|Y38H6A.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|534nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149414|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47635|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|711nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012615|dct-16|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012616|dct-14|1488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012616|dct-14|1491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012616|dct-14|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012616|dct-14|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00012616|dct-14|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012616|dct-14|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=435|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10882|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|850nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012621|Y38H6C.8|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=448|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=413|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|328nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|489nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012622|Y38H6C.9a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012623|fbxa-149|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00012623|fbxa-149|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012624|fbxa-150|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012624|fbxa-150|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012624|fbxa-150|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=827|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012624|fbxa-150|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012624|fbxa-150|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012625|Y38H6C.13|1040nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012625|Y38H6C.13|1046nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012625|Y38H6C.13|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012625|Y38H6C.13|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012625|Y38H6C.13|1066nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012625|Y38H6C.13|1142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012625|Y38H6C.13|1245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012626|Y38H6C.14|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012626|Y38H6C.14|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012626|Y38H6C.14|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012627|Y38H6C.15|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012627|Y38H6C.15|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012627|Y38H6C.15|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00012627|Y38H6C.15|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00012628|Y38H6C.16|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00012628|Y38H6C.16|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012628|Y38H6C.16|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012628|Y38H6C.16|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012628|Y38H6C.16|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012629|slc-36.3|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012631|Y38H6C.19|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012632|Y38H6C.20|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012632|Y38H6C.20|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012632|Y38H6C.20|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012632|Y38H6C.20|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012633|Y38H6C.21|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012633|Y38H6C.21|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012633|Y38H6C.21|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|310nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=502|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012634|Y38H6C.23.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012635|Y38H8A.1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=416|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012635|Y38H8A.1|566nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012635|Y38H8A.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012635|Y38H8A.1|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012636|Y38H8A.2a|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012636|Y38H8A.2a|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00012636|Y38H8A.2a|716nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012637|Y38H8A.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012637|Y38H8A.3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1043|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012637|Y38H8A.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012637|Y38H8A.3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=523|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00012638|Y38H8A.4|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012638|Y38H8A.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012638|Y38H8A.4|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00012638|Y38H8A.4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012639|fezf-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012639|fezf-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|663nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012640|Y38H8A.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012641|epg-6|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2044|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012642|Y39A1A.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012642|Y39A1A.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012643|Y39A1A.3|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3796|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012643|Y39A1A.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012643|Y39A1A.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012643|Y39A1A.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1338|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00012644|rabx-5|1042nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012644|rabx-5|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012644|rabx-5|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012644|rabx-5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2423|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|81nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|87nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|91nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|93nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=68|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012645|mrpl-22|95nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=86|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=394|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3661|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012646|lron-10|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012647|swt-4|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1176|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012647|swt-4|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=681|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012647|swt-4|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012648|Y39A1A.9|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012648|Y39A1A.9|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012648|Y39A1A.9|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012648|Y39A1A.9|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1797|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1637|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012650|orc-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012651|orc-4|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012651|orc-4|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1116|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012651|orc-4|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=956|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00012651|orc-4|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=372|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012651|orc-4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2078|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00012652|Y39A1A.14|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012654|Y39A1A.16|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012654|Y39A1A.16|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00012654|Y39A1A.16|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012655|Y39A1A.17|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012656|Y39A1A.18|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012656|Y39A1A.18|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012656|Y39A1A.18|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012656|Y39A1A.18|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012656|Y39A1A.18|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012656|Y39A1A.18|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00012656|Y39A1A.18|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012657|Y39A1A.20|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012657|Y39A1A.20|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1182|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012657|Y39A1A.20|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012657|Y39A1A.20|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012658|Y39A1A.21c|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012658|Y39A1A.21c|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1791|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00012658|Y39A1A.21c|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012658|Y39A1A.21c|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4262|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1285|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012660|Y39A1A.24|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012662|Y39A1C.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012662|Y39A1C.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012662|Y39A1C.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012662|Y39A1C.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012662|Y39A1C.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=538|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012662|Y39A1C.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012662|Y39A1C.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=492|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00012663|hex-3|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012663|hex-3|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012664|Y39B6A.1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012664|Y39B6A.1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7546|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012664|Y39B6A.1|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=471|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2964|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012665|pph-5|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6054|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012666|Y39B6A.3a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=652|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2497|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4664|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8992|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14472|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2120|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012668|Y39B6A.5b|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4726|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012669|Y39B6A.7|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012669|Y39B6A.7|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012669|Y39B6A.7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012670|Y39B6A.8|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012671|Y39B6A.9|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012672|Y39B6A.10|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012672|Y39B6A.10|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012672|Y39B6A.10|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1354|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012672|Y39B6A.10|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012672|Y39B6A.10|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012673|dyf-17|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012673|dyf-17|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00012673|dyf-17|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012673|dyf-17|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012673|dyf-17|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012673|dyf-17|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|1069nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|927nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012674|bed-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=952|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3490|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012675|Y39B6A.13|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1095nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1394|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012676|pro-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012678|Y39B6A.16|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012678|Y39B6A.16|1357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012678|Y39B6A.16|1359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012678|Y39B6A.16|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=535|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012678|Y39B6A.16|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012679|Y39B6A.18|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012681|asp-15|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012682|asp-16|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012683|asp-17|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012683|asp-17|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012684|Y39B6A.25|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012684|Y39B6A.25|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012684|Y39B6A.25|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012686|Y39B6A.27|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012686|Y39B6A.27|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012688|Y39B6A.29b|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012689|Y39B6A.30|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012689|Y39B6A.30|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012691|Y39B6A.32|1335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012691|Y39B6A.32|846nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012691|Y39B6A.32|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012692|Y39B6A.33|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3047|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012692|Y39B6A.33|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012693|Y39B6A.34a|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012693|Y39B6A.34a|655nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012693|Y39B6A.34a|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012693|Y39B6A.34a|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2490|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012693|Y39B6A.34a|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=321|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1259|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=960|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012694|Y39B6A.36|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1640|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012695|Y39B6A.37|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1839|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|739nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|743nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|751nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|753nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|863nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|967nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012696|reps-1|981nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=575|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012697|mrps-35|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012698|sws-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=850|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012699|Y39B6A.41|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012700|Y39B6A.42|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012700|Y39B6A.42|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2288|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012701|Y39B6A.43c|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012701|Y39B6A.43c|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012701|Y39B6A.43c|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012702|ztf-20|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012702|ztf-20|837nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012702|ztf-20|844nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012702|ztf-20|903nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012703|nhr-145|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012703|nhr-145|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012703|nhr-145|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012704|mlt-3|1248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012704|mlt-3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012704|mlt-3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012704|mlt-3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012705|sre-18|1247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012705|sre-18|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012705|sre-18|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012705|sre-18|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012707|sre-16|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012708|sre-19|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012709|sre-15|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012710|Y39C12A.9|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012711|Y39E4A.1|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012712|ttm-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1198|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7154|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=752|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|513nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|520nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|650nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|653nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012713|Y39E4A.3a|694nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012714|abce-1|376nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3181|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012714|abce-1|384nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2914|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012714|abce-1|387nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012714|abce-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012714|abce-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012714|abce-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|267nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1107|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|273nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|277nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012715|snpc-1.2|501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012716|Y39E4B.5|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012716|Y39E4B.5|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012716|Y39E4B.5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012716|Y39E4B.5|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012716|Y39E4B.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012716|Y39E4B.5|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1188|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|444nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|654nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|656nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|658nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|664nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|667nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=982|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|678nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12556|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|684nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|718nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|724nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|726nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6a.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=424|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012717|Y39E4B.6b|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|1024nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|773nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|925nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|971nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1542|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012718|dhhc-8|988nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012719|Y39E4B.10|1200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1533|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012719|Y39E4B.10|1215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012719|Y39E4B.10|393nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012720|Y39E4B.11|30nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012720|Y39E4B.11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=731|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012721|Y39E4B.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4150|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1a|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=485|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012722|Y39G8B.1b|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012723|Y39G8B.2|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012723|Y39G8B.2|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012723|Y39G8B.2|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012723|Y39G8B.2|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012723|Y39G8B.2|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=375|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012723|Y39G8B.2|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012723|Y39G8B.2|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012724|sre-48|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012726|Y39G8B.5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012727|Y39G8B.7|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=252|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012727|Y39G8B.7|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012728|Y39G8B.9|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012728|Y39G8B.9|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2477|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012728|Y39G8B.9|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012728|Y39G8B.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012728|Y39G8B.9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012729|Y39G8B.10|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012730|xrn-1|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012730|xrn-1|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012730|xrn-1|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1929|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012730|xrn-1|993nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=574|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012731|Y39G8C.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012731|Y39G8C.2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1642|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012731|Y39G8C.2|172nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3791|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=554|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012732|Y40B1A.1b|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|1057nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|739nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|748nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|925nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|933nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|939nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|967nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012734|Y40B1A.3c|977nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1309|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012735|sptf-3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012735|sptf-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012735|sptf-3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012735|sptf-3|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012735|sptf-3|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1185|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012735|sptf-3|647nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012735|sptf-3|944nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012738|eif-3.J|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012738|eif-3.J|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9196|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012738|eif-3.J|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012738|eif-3.J|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=207|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012738|eif-3.J|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012738|eif-3.J|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012738|eif-3.J|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012739|Y40B1B.7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012739|Y40B1B.7|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012739|Y40B1B.7|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012739|Y40B1B.7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3864|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|1335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1760|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|460nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012740|Y40B1B.8|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012741|Y40H4A.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012741|Y40H4A.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012741|Y40H4A.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012742|Y40H7A.2a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012742|Y40H7A.2a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012743|Y40H7A.3b|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012743|Y40H7A.3b|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012744|Y40H7A.4c|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012744|Y40H7A.4c|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012744|Y40H7A.4c|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012744|Y40H7A.4c|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012744|Y40H7A.4c|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012744|Y40H7A.4c|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012747|Y40H7A.10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1806|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012747|Y40H7A.10|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012747|Y40H7A.10|820nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012747|Y40H7A.10|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012747|Y40H7A.10|881nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012747|Y40H7A.10|887nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012747|Y40H7A.10|891nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012748|Y40H7A.11|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012748|Y40H7A.11|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012750|faah-6|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012750|faah-6|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012750|faah-6|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012750|faah-6|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15601|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5185|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=452|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012753|Y41C4A.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012754|Y41C4A.7|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012754|Y41C4A.7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012754|Y41C4A.7|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012754|Y41C4A.7|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=804|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00012754|Y41C4A.7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012755|Y41C4A.8|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=930|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012755|Y41C4A.8|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=555|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012756|Y41C4A.9|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5088|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012757|Y41C4A.11|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012758|Y41C4A.12a|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=323|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012758|Y41C4A.12a|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012758|Y41C4A.12a|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012758|Y41C4A.12a|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012758|Y41C4A.12a|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012758|Y41C4A.12a|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|221nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=549|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14197|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1455|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012759|sup-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1096nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1124|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|1569nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29951|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4509|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=596|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1184|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|591nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|770nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012760|Y41C4A.17|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012761|Y41C4A.18|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012761|Y41C4A.18|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3640|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012762|Y41E3.1d|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012763|atln-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012763|atln-2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012763|atln-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012763|atln-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012763|atln-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1034nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1054nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1094nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8689|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|1486nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9449|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012764|Y41E3.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9852|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7a|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012765|Y41E3.7f|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5923|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20933|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012766|Y41E3.8b|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012767|fcd-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=970|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012767|fcd-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012767|fcd-2|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|1206nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=517|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28865|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=463|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|1602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3039|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012768|eef-1B.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=536|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3051|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=749|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=313|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012769|Y41E3.11a|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012770|srt-47|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00012770|srt-47|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00012770|srt-47|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00012770|srt-47|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00012772|srt-49|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012773|srt-48|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00012773|srt-48|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00012776|Y42A5A.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012776|Y42A5A.1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012776|Y42A5A.1|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00012777|lact-8|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012777|lact-8|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012777|lact-8|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012777|lact-8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012777|lact-8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012778|Y42A5A.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012778|Y42A5A.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012778|Y42A5A.3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=914|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012778|Y42A5A.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1200|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012779|cdkl-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012780|Y42A5A.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012780|Y42A5A.5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012780|Y42A5A.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012780|Y42A5A.5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00012780|Y42A5A.5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012781|nspd-7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012781|nspd-7|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6542|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2588|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1199|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=612|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=357|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012782|Y43C5A.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|164nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2838|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012783|Y43C5A.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012784|Y43C5A.4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012784|Y43C5A.4|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012785|Y43C5B.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012785|Y43C5B.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012785|Y43C5B.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012785|Y43C5B.2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012785|Y43C5B.2|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012786|Y43C5B.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012791|Y43D4A.5a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012791|Y43D4A.5a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012792|Y43D4A.6|392nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=999|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=847|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012794|Y43E12A.2|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012795|Y43E12A.3a|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=660|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012795|Y43E12A.3a|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012796|Y43F4A.1a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012796|Y43F4A.1a|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=830|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012796|Y43F4A.1a|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=269|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012796|Y43F4A.1a|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012796|Y43F4A.1a|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012796|Y43F4A.1a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012798|Y43F4A.3|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012798|Y43F4A.3|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012798|Y43F4A.3|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012798|Y43F4A.3|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012799|Y43F4A.4|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012799|Y43F4A.4|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012799|Y43F4A.4|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|253nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|600nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|603nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|618nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=387|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|837nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012802|set-25|848nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4964|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5a|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012803|Y43F4B.5b|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012804|Y43F4B.7|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012804|Y43F4B.7|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012804|Y43F4B.7|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2801|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012804|Y43F4B.7|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012804|Y43F4B.7|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012806|Y43F4B.9a.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012806|Y43F4B.9a.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012806|Y43F4B.9a.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012806|Y43F4B.9a.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012806|Y43F4B.9a.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=577|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012806|Y43F4B.9a.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012806|Y43F4B.9a.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1619|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2647|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1003|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012807|Y43F4B.10.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1124|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012808|Y43F8A.1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012808|Y43F8A.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=965|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00012808|Y43F8A.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012808|Y43F8A.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012809|Y43F8A.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012809|Y43F8A.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00012809|Y43F8A.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012809|Y43F8A.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012810|nceh-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012810|nceh-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012810|nceh-1|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012811|Y43F8A.5|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012811|Y43F8A.5|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1b|1550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|849nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|867nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|894nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|944nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|948nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2578|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|952nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=637|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|955nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=435|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|959nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012812|Y43F8B.1c|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=574|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28374|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39103|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2770|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1422|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=943|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1286|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012813|Y43F8B.2f.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=765|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012814|Y43F8B.3a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012814|Y43F8B.3a|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012814|Y43F8B.3a|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012814|Y43F8B.3a|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012814|Y43F8B.3a|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012814|Y43F8B.3a|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012815|phy-4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012815|phy-4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012815|phy-4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012815|phy-4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012816|scl-21|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012819|Y43F8B.9|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012819|Y43F8B.9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012819|Y43F8B.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012820|Y43F8B.10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012821|Y43F8B.11|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012821|Y43F8B.11|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012821|Y43F8B.11|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012821|Y43F8B.11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012822|Y43F8B.12|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012822|Y43F8B.12|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012822|Y43F8B.12|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012823|Y43F8B.13|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012823|Y43F8B.13|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00012823|Y43F8B.13|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012824|Y43F8B.14|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|486nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1315|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012825|Y43F8C.3|594nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012826|dyf-19|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012826|dyf-19|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012826|dyf-19|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012826|dyf-19|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012827|Y43F8C.5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012827|Y43F8C.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012827|Y43F8C.5|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2333|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012828|Y43F8C.6a|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012828|Y43F8C.6a|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012828|Y43F8C.6a|1352nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012828|Y43F8C.6a|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012828|Y43F8C.6b|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012828|Y43F8C.6b|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=957|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2117|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012829|Y43F8C.7.1|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012830|mrps-28|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012830|mrps-28|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012830|mrps-28|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=745|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012830|mrps-28|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=687|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012830|mrps-28|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012831|Y43F8C.9|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012831|Y43F8C.9|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012831|Y43F8C.9|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012831|Y43F8C.9|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3419|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012831|Y43F8C.9|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1067|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012832|dmd-3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012833|Y43F8C.11|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012833|Y43F8C.11|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1712|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012833|Y43F8C.11|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012833|Y43F8C.11|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012834|Y43F8C.13|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012834|Y43F8C.13|1054nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012834|Y43F8C.13|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012834|Y43F8C.13|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012834|Y43F8C.13|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1492|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012834|Y43F8C.13|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012835|ani-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012835|ani-3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1205|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012838|Y43F8C.17|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012838|Y43F8C.17|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012839|Y43F8C.18|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012839|Y43F8C.18|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012839|Y43F8C.18|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4665|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=912|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012840|grsp-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=826|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012844|Y43F11A.4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012845|set-24|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012845|set-24|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1285|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012846|srxa-14|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012846|srxa-14|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012846|srxa-14|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012846|srxa-14|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012847|srxa-15|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012847|srxa-15|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012847|srxa-15|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00012848|Y44A6B.3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012849|ttr-13|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012849|ttr-13|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012849|ttr-13|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|1309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|236nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|242nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=355|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|248nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|255nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2444|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012850|Y44A6C.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012851|Y44A6C.2|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012852|Y44A6D.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012852|Y44A6D.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00012852|Y44A6D.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012852|Y44A6D.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120598|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10220|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|365nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012853|Y44A6D.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|1529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|1549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=740|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|267nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|346nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|358nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|383nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012854|Y44A6D.3a|454nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|34nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=54|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012855|Y44A6D.5|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012856|Y44A6D.6|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=440|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012856|Y44A6D.6|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012857|pbo-5|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012857|pbo-5|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=420|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012857|pbo-5|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012857|pbo-5|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012858|Y44F5A.1|1039nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012858|Y44F5A.1|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=625|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00012858|Y44F5A.1|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=372|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012859|Y45F3A.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012860|acdh-11|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012860|acdh-11|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012860|acdh-11|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012860|acdh-11|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012860|acdh-11|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2007|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012860|acdh-11|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=779|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012860|acdh-11|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3349|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012861|Y45F3A.4|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012862|Y45F3A.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012863|Y45F3A.8|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012863|Y45F3A.8|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=491|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012863|Y45F3A.8|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012864|Y45F3A.9|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012864|Y45F3A.9|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=596|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012864|Y45F3A.9|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012864|Y45F3A.9|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012864|Y45F3A.9|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012864|Y45F3A.9|216nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012864|Y45F3A.9|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012866|Y45F10A.3a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|1383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|1449nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012867|seld-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012868|tbc-9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012868|tbc-9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012868|tbc-9|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012868|tbc-9|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1362|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012868|tbc-9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012868|tbc-9|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012869|Y45F10A.7a|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012869|Y45F10A.7a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012869|Y45F10A.7a|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012869|Y45F10A.7a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012869|Y45F10A.7a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=727|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012869|Y45F10A.7a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012871|Y45F10B.3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=416|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012871|Y45F10B.3|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012871|Y45F10B.3|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1406|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012871|Y45F10B.3|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012872|Y45F10B.8|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012872|Y45F10B.8|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012872|Y45F10B.8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012873|Y45F10B.9|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012873|Y45F10B.9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012875|Y45F10B.13c|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012875|Y45F10B.13c|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012875|Y45F10B.13c|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012875|Y45F10B.13c|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012875|Y45F10B.13c|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012875|Y45F10B.13c|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012875|Y45F10B.13c|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012877|Y45F10C.1|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012877|Y45F10C.1|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=876|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1711|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012878|Y45F10C.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012879|fbxa-215|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012879|fbxa-215|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3680|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00012879|fbxa-215|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012879|fbxa-215|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012879|fbxa-215|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012880|Y45F10C.4|1050nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012880|Y45F10C.4|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012880|Y45F10C.4|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2037|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012880|Y45F10C.4|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3645|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012880|Y45F10C.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=934|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00012880|Y45F10C.4|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012880|Y45F10C.4|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012883|Y45F10D.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012885|Y45F10D.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012885|Y45F10D.4|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6329|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012885|Y45F10D.4|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012885|Y45F10D.4|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012886|Y45F10D.6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012886|Y45F10D.6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012886|Y45F10D.6|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012886|Y45F10D.6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012886|Y45F10D.6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012886|Y45F10D.6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012887|Y45F10D.7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012887|Y45F10D.7|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=805|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012887|Y45F10D.7|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012887|Y45F10D.7|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012887|Y45F10D.7|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012887|Y45F10D.7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012887|Y45F10D.7|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|567nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|569nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|572nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5356|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1785|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00012888|sas-6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012889|Y45F10D.10b|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012889|Y45F10D.10b|1102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012889|Y45F10D.10b|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012889|Y45F10D.10b|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012889|Y45F10D.10b|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2603|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012889|Y45F10D.10b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012890|lact-9|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012890|lact-9|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=933|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012891|sorb-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012891|sorb-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012891|sorb-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012891|sorb-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012892|Y45F10D.14|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012893|Y45F10D.15|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|339nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2257|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|346nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|348nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|380nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012894|tbc-17|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012895|cox-10|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=627|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4064|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012896|snrp-200|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4535|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012897|pisy-1|845nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012899|Y46G5A.7|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012899|Y46G5A.7|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012899|Y46G5A.7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012900|Y46G5A.8|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012900|Y46G5A.8|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=467|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012900|Y46G5A.8|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=893|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=412|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1405|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11504|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9291|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1139|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012901|cnp-2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2786|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=211|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=571|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012903|vps-2|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=341|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|1120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|1124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|1184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=821|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|1190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012904|tiar-2|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012905|Y46G5A.14|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012905|Y46G5A.14|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012905|Y46G5A.14|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012905|Y46G5A.14|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012906|Y46G5A.15|266nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012906|Y46G5A.15|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=647|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012906|Y46G5A.15|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012906|Y46G5A.15|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4394|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|349nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|365nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012907|cpt-1|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012908|Y46G5A.18a|102nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012908|Y46G5A.18a|108nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012908|Y46G5A.18a|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1503|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012908|Y46G5A.18a|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012908|Y46G5A.18b|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012908|Y46G5A.18b|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012909|spds-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012909|spds-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012909|spds-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012909|spds-1|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012909|spds-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1590|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012909|spds-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012909|spds-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012910|Y46G5A.20|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012911|acl-7|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012911|acl-7|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012911|acl-7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=616|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012911|acl-7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012911|acl-7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012911|acl-7|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012911|acl-7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012912|Y46G5A.22b|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012912|Y46G5A.22b|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012913|Y46G5A.23|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012914|bcmo-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012915|lgc-35|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012915|lgc-35|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=585|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012915|lgc-35|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=399|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012915|lgc-35|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012915|lgc-35|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012916|Y46G5A.28|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012917|Y46G5A.29|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012917|Y46G5A.29|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012917|Y46G5A.29|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012919|Y46G5A.34|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=200|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012919|Y46G5A.34|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=319|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012919|Y46G5A.34|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012919|Y46G5A.34|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012920|Y46G5A.35|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012921|Y46G5A.36|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=522|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012921|Y46G5A.36|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012921|Y46G5A.36|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00012921|Y46G5A.36|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012922|Y47D3A.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012923|fbxa-128|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012923|fbxa-128|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012923|fbxa-128|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=298|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012923|fbxa-128|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012923|fbxa-128|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012925|wht-8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012925|wht-8|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=255|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012925|wht-8|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012925|wht-8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012925|wht-8|810nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=991|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1227|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012926|Y47D3A.13|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=123|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012927|Y47D3A.14|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012927|Y47D3A.14|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=522|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012927|Y47D3A.14|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1077nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=252|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1082nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2432|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|1406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012928|aakb-2|635nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012929|rsks-1|1016nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012929|rsks-1|1197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00012929|rsks-1|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012929|rsks-1|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012930|obr-1|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3433|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1639|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|441nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|510nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012931|Y47D3A.20|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2623|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012932|Y47D3A.21|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012933|mib-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012933|mib-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=810|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012933|mib-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012933|mib-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=766|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012934|gly-9|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012934|gly-9|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012934|gly-9|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2053|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012934|gly-9|751nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=442|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012935|mcm-10|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|223nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2745|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012936|Y47D3A.29b|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012937|Y47D3A.31|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012938|Y47D3A.32b|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012938|Y47D3A.32b|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012938|Y47D3A.32b|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012938|Y47D3A.32b|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=583|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012938|Y47D3A.32b|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012938|Y47D3A.32b|737nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012938|Y47D3A.32b|902nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012939|Y47D3B.1|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00012939|Y47D3B.1|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012939|Y47D3B.1|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012939|Y47D3B.1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00012939|Y47D3B.1|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012939|Y47D3B.1|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012940|Y47D3B.3|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00012940|Y47D3B.3|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012940|Y47D3B.3|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012940|Y47D3B.3|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012940|Y47D3B.3|350nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012941|Y47D3B.4|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00012941|Y47D3B.4|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012941|Y47D3B.4|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012941|Y47D3B.4|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012941|Y47D3B.4|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00012941|Y47D3B.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012942|Y47D3B.6|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012942|Y47D3B.6|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6699|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012942|Y47D3B.6|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012942|Y47D3B.6|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012942|Y47D3B.6|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012942|Y47D3B.6|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012942|Y47D3B.6|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=184|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|215nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1022|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=488|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012943|bed-2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012945|Y47H9A.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012945|Y47H9A.1|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012946|Y47H9B.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012946|Y47H9B.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012946|Y47H9B.2|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012946|Y47H9B.2|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012946|Y47H9B.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00012946|Y47H9B.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012946|Y47H9B.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012947|Y47H9C.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00012947|Y47H9C.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=412|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012947|Y47H9C.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012948|dhhc-2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012948|dhhc-2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012948|dhhc-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012948|dhhc-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012948|dhhc-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=922|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00012950|Y47H9C.7|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012950|Y47H9C.7|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2875|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012950|Y47H9C.7|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012951|Y47H9C.8|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012951|Y47H9C.8|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2713|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012951|Y47H9C.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012952|Y47H9C.9|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012953|fbxa-216|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012953|fbxa-216|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012955|Y47H9C.12|1401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012958|Y47H10A.2|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012958|Y47H10A.2|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012958|Y47H10A.2|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012959|Y47H10A.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012959|Y47H10A.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012959|Y47H10A.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00012960|Y47H10A.4|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00012960|Y47H10A.4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012960|Y47H10A.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1354|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012961|Y47H10A.5|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012962|dmsr-5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=738|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7218|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5314|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=704|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012964|Y48A6B.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012965|fipr-17|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=249|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012965|fipr-17|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00012965|fipr-17|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012965|fipr-17|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012966|exos-1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012966|exos-1|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00012966|exos-1|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012966|exos-1|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=935|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012966|exos-1|413nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012966|exos-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|104nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=103|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=386|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012967|kvs-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012968|Y48A6B.7|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012968|Y48A6B.7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012968|Y48A6B.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=943|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012968|Y48A6B.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012969|Y48A6B.8|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012970|Y48A6B.9a|154nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012970|Y48A6B.9a|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012970|Y48A6B.9a|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012970|Y48A6B.9a|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=275|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012970|Y48A6B.9a|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012972|rsa-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1803|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012972|rsa-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1578|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012972|rsa-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|1130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|1194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6071|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|1199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012973|spat-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|861nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|864nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|927nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|935nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=511|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|943nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=382|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012976|sup-35|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|197nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012977|Y48A6C.4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2680|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|358nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012978|Y48B6A.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012979|Y48B6A.5|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012980|efhd-1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2597|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00012980|efhd-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=860|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012980|efhd-1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012980|efhd-1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012980|efhd-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012980|efhd-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012981|Y48B6A.10|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|1344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|1354nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|1390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1329|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012982|jmjd-2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=386|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3134|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=898|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=285|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012983|men-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012984|Y48B6A.13a|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012984|Y48B6A.13a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012984|Y48B6A.13a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012984|Y48B6A.13a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012984|Y48B6A.13a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=910|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012984|Y48B6A.13a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012985|Y48C3A.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012985|Y48C3A.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012985|Y48C3A.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012987|Y48C3A.3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012987|Y48C3A.3|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=997|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012987|Y48C3A.3|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|353nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1685|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00012988|ztf-22|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012989|Y48C3A.5a|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2874|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1043nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1047nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1495nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|1516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1517|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012990|sam-10|549nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012992|mrpl-20|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1236|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012992|mrpl-20|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012992|mrpl-20|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012993|dmsr-3|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012993|dmsr-3|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=371|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012993|dmsr-3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012993|dmsr-3|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012993|dmsr-3|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012993|dmsr-3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00012993|dmsr-3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|906nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|908nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|911nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|938nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|941nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=365|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|945nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=239|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|948nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=617|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012994|Y48C3A.12|956nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=678|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00012995|Y48C3A.14a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=608|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012995|Y48C3A.14a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012995|Y48C3A.14a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012995|Y48C3A.14a|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012996|pinn-4|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012996|pinn-4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012996|pinn-4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00012996|pinn-4|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=401|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012997|Y48C3A.18a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1249|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00012998|Y48C3A.20|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1287|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00012998|Y48C3A.20|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00012998|Y48C3A.20|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012999|rpoa-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012999|rpoa-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00012999|rpoa-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00012999|rpoa-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=577|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00012999|rpoa-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1879|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00012999|rpoa-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00012999|rpoa-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013000|ddl-2|1326nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=494|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013000|ddl-2|1334nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013000|ddl-2|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013000|ddl-2|1338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|1320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1015|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00013001|Y48E1B.2b.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013002|Y48E1B.3b|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013002|Y48E1B.3b|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3011|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013002|Y48E1B.3b|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1136|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00013004|mrpl-37|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=911|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013004|mrpl-37|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013004|mrpl-37|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013006|lin-38|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013006|lin-38|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013006|lin-38|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013006|lin-38|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013006|lin-38|1048nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013007|Y48E1B.8|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013007|Y48E1B.8|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1750|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013007|Y48E1B.8|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013008|clec-146|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013008|clec-146|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013008|clec-146|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013008|clec-146|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013008|clec-146|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013008|clec-146|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013008|clec-146|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013009|fbxc-23|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013009|fbxc-23|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1842|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=324|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013011|snx-14|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=271|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=529|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1410|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4801|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013013|clec-145|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013014|Y48E1C.1c|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013014|Y48E1C.1c|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1620|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013014|Y48E1C.1c|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013015|Y48E1C.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013015|Y48E1C.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=642|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013015|Y48E1C.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013015|Y48E1C.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|831nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|835nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|838nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=933|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013016|tbc-15|843nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013017|Y48E1C.4a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2882|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013017|Y48E1C.4a|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013017|Y48E1C.4a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013017|Y48E1C.4a|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013017|Y48E1C.4a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=879|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1084|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013018|Y48G10A.1.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1144|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|256nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013019|Y48G10A.2b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|1221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2597|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|1226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1033|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|1230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|1232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|1551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|468nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013020|Y48G10A.3|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=727|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013021|Y48G10A.4b|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013023|Y48G10A.6|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013023|Y48G10A.6|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2011|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013023|Y48G10A.6|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1823|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013023|Y48G10A.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|1026nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|1030nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|1032nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|1037nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6061|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|1267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013024|cept-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|268nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4623|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=514|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1205|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=992|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13011|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=392|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013025|vha-13|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=920|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013026|Y49A3A.3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013027|Y49A3A.4|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013027|Y49A3A.4|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013027|Y49A3A.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013027|Y49A3A.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013028|Y49A10A.1|184nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013028|Y49A10A.1|187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013028|Y49A10A.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013028|Y49A10A.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013029|glrx-5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013029|glrx-5|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013029|glrx-5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3277|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013029|glrx-5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=772|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013029|glrx-5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|1389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|1395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1807|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=331|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013030|Y49E10.4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013033|Y49E10.10.1|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013033|Y49E10.10.1|338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013033|Y49E10.10.1|366nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|366nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1442|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1058|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013034|tat-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=605|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013035|Y49E10.16a|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013036|fbxa-218|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=176|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013037|Y49E10.18|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=229|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013037|Y49E10.18|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013037|Y49E10.18|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013037|Y49E10.18|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013037|Y49E10.18|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1079|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013038|ani-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013038|ani-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013038|ani-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1421|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013038|ani-1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=572|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013038|ani-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013038|ani-1|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013038|ani-1|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013039|scav-3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3447|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013039|scav-3|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|1195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=814|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21a|704nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21b|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013040|Y49E10.21b|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013041|pstk-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013041|pstk-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013042|cccp-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013042|cccp-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1352|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013042|cccp-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013042|cccp-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013042|cccp-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013042|cccp-1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013043|arrd-16|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013043|arrd-16|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013043|arrd-16|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013044|Y49E10.25|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013044|Y49E10.25|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013046|Y50E8A.1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013046|Y50E8A.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013046|Y50E8A.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013046|Y50E8A.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013046|Y50E8A.1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00013048|Y50E8A.5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013048|Y50E8A.5|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013048|Y50E8A.5|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013048|Y50E8A.5|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013049|Y50E8A.6|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013052|scrm-7|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013052|scrm-7|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013052|scrm-7|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013052|scrm-7|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013053|Y50E8A.10|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=879|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013053|Y50E8A.10|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013054|Y50E8A.11|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013054|Y50E8A.11|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013055|Y50E8A.12b|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=480|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013055|Y50E8A.12b|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013055|Y50E8A.12c|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013055|Y50E8A.12c|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013055|Y50E8A.12c|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013058|clec-247|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013060|Y51A2A.4a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013063|clec-249|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013063|clec-249|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013066|Y51A2B.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00013066|Y51A2B.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00013066|Y51A2B.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013066|Y51A2B.2|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013066|Y51A2B.2|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013068|Y51A2B.4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00013068|Y51A2B.4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00013069|Y51A2B.5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013069|Y51A2B.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013069|Y51A2B.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013070|Y51A2B.6|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013071|Y51A2B.8|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00013071|Y51A2B.8|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013071|Y51A2B.8|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013071|Y51A2B.8|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013072|Y51A2D.1a|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013073|hmit-1.1|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=567|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013073|hmit-1.1|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013073|hmit-1.1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013074|hmit-1.2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013074|hmit-1.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013075|Y51A2D.7b|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013075|Y51A2D.7b|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=992|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013075|Y51A2D.7b|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013076|Y51A2D.8|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013076|Y51A2D.8|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013077|ttr-24|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013077|ttr-24|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013077|ttr-24|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013077|ttr-24|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5339|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013077|ttr-24|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2620|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013078|ttr-25|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013078|ttr-25|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013078|ttr-25|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=990|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013078|ttr-25|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2809|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013078|ttr-25|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=391|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=966|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1335|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1702|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=445|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013079|ttr-26|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013080|Y51A2D.13a|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013080|Y51A2D.13a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2855|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013080|Y51A2D.13a|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013081|Y51A2D.14.1|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013081|Y51A2D.14.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013081|Y51A2D.14.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013081|Y51A2D.14.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3353|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013081|Y51A2D.14.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6599|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013081|Y51A2D.14.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013081|Y51A2D.14.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013082|grdn-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013082|grdn-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013082|grdn-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013082|grdn-1|689nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013082|grdn-1|694nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013083|Y51A2D.18|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013085|mpz-6|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013085|mpz-6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013086|arrd-2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013087|Y51B9A.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013087|Y51B9A.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013087|Y51B9A.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013087|Y51B9A.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013088|Y51B9A.6b|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013089|Y51B9A.7|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013091|Y51B9A.9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013091|Y51B9A.9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013091|Y51B9A.9|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013093|Y51H1A.2e.1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013093|Y51H1A.2e.1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2074|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013093|Y51H1A.2e.1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013093|Y51H1A.2e.1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013094|Y51H1A.3a.1|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013094|Y51H1A.3a.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013094|Y51H1A.3a.1|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013094|Y51H1A.3a.1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8099|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013094|Y51H1A.3a.1|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1603|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013094|Y51H1A.3a.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=467|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1875|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013095|ing-3|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|244nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1151|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|246nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=571|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|249nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013096|mcd-1|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|1558nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5985|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013098|Y51H4A.1|746nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|159nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013100|zip-7|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00013101|Y51H4A.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013101|Y51H4A.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013101|Y51H4A.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013103|Y51H4A.7.2|29nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013103|Y51H4A.7.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1179|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013104|Y51H4A.8|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013104|Y51H4A.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013104|Y51H4A.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013104|Y51H4A.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013104|Y51H4A.8|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013105|fip-7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013106|set-26|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013106|set-26|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=965|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013106|set-26|654nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013107|Y51H4A.13|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=882|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013107|Y51H4A.13|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013107|Y51H4A.13|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013107|Y51H4A.13|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013107|Y51H4A.13|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013107|Y51H4A.13|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2539|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|551nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013109|Y51H4A.15|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013111|sta-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013111|sta-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013111|sta-1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2651|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00013116|Y51H4A.22|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013116|Y51H4A.22|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013118|Y51H4A.24|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=642|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013118|Y51H4A.24|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25b|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25d|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013119|Y51H4A.25d|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013120|fipr-28|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013121|spe-38|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00013121|spe-38|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013121|spe-38|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013121|spe-38|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013121|spe-38|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013122|impt-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013122|impt-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1515|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013123|Y52B11A.3a.2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013123|Y52B11A.3a.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1501|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013123|Y52B11A.3a.2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013123|Y52B11A.3a.2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013123|Y52B11A.3a.2|160nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=53|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013123|Y52B11A.3a.2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|352nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|365nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|377nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|379nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|381nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|387nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1315|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013124|Y52B11A.4.2|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013125|clec-92|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013125|clec-92|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013126|mltn-2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013127|Y52B11A.8|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1670|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013127|Y52B11A.8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013127|Y52B11A.8|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013127|Y52B11A.8|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013127|Y52B11A.8|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=306|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013127|Y52B11A.8|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4209|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013128|dxbp-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013128|dxbp-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013128|dxbp-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1327|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013128|dxbp-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013128|dxbp-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013129|Y52B11A.10|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013129|Y52B11A.10|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013129|Y52B11A.10|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=495|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013130|Y52B11B.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013130|Y52B11B.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|1074nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|1077nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|1079nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1700|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|416nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|424nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=304|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013131|Y52B11C.1|507nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2172|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013132|strd-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013135|rga-2|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013135|rga-2|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=329|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013135|rga-2|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1276|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=634|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013136|Y53C10A.5|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1979|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|293nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013137|Y53C10A.6a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013138|Y53C10A.10|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013139|Y53C12A.3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013139|Y53C12A.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013139|Y53C12A.3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2150|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013139|Y53C12A.3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013139|Y53C12A.3|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013139|Y53C12A.3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013139|Y53C12A.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2567|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|785nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013140|mop-25.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013141|Y53C12A.6b|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013141|Y53C12A.6b|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00013141|Y53C12A.6b|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013142|Y53C12A.7.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013142|Y53C12A.7.2|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013142|Y53C12A.7.2|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013142|Y53C12A.7.2|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013142|Y53C12A.7.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013142|Y53C12A.7.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013143|Y53C12B.1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013143|Y53C12B.1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1730|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013143|Y53C12B.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2015|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5505|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|442nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|445nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|450nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013144|Y53C12B.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013145|cutl-2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013145|cutl-2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013145|cutl-2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=658|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|232nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|416nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|422nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|425nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013146|Y53C12B.7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013147|eyg-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013147|eyg-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013148|Y53F4A.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013148|Y53F4A.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013149|Y53F4B.1|1052nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013149|Y53F4B.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013149|Y53F4B.1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013149|Y53F4B.1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013149|Y53F4B.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013149|Y53F4B.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013150|Y53F4B.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013150|Y53F4B.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=484|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013150|Y53F4B.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013151|nsun-5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013151|nsun-5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=657|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|518nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013156|Y53F4B.9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013157|Y53F4B.10|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013157|Y53F4B.10|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013158|Y53F4B.11a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013158|Y53F4B.11a|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013158|Y53F4B.11a|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|1358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1139|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013159|Y53F4B.12a|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|1061nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|817nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1565|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|833nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|840nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013160|Y53F4B.13a|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|137nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|1463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013161|Y53F4B.14a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96962|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00013162|Y53F4B.16|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=873|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|965nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|981nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013164|Y53F4B.18|992nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013165|Y53F4B.19|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013165|Y53F4B.19|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013166|Y53F4B.20|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013166|Y53F4B.20|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013166|Y53F4B.20|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013166|Y53F4B.20|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013167|Y53F4B.21|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013167|Y53F4B.21|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=757|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013167|Y53F4B.21|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013167|Y53F4B.21|998nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013168|arp-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013168|arp-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013168|arp-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013168|arp-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013168|arp-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7677|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013168|arp-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013169|Y53F4B.23|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013169|Y53F4B.23|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013169|Y53F4B.23|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013169|Y53F4B.23|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013169|Y53F4B.23|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013169|Y53F4B.23|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00013170|Y53F4B.24|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00013170|Y53F4B.24|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013171|Y53F4B.25a|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013171|Y53F4B.25a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013171|Y53F4B.25a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013171|Y53F4B.25a|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013171|Y53F4B.25a|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013173|Y53F4B.27a|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013173|Y53F4B.27a|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013173|Y53F4B.27a|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=337|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013175|Y53F4B.36|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013175|Y53F4B.36|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013175|Y53F4B.36|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|1441nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=941|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013176|Y53F4B.39b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1687|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013177|rsy-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=718|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013178|Y53H1A.2b|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013179|clec-100|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013180|cutl-10|1546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013180|cutl-10|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013180|cutl-10|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013180|cutl-10|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7229|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013181|Y53H1B.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2308|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013184|Y53H1B.6|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013184|Y53H1B.6|684nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013184|Y53H1B.6|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013186|Y53H1C.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013186|Y53H1C.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013187|npr-34|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013187|npr-34|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013188|smg-9|1011nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013188|smg-9|1021nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=922|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013188|smg-9|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013188|smg-9|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013188|smg-9|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013188|smg-9|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013189|Y54E2A.4a|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013189|Y54E2A.4a|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5524|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013189|Y54E2A.4a|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013189|Y54E2A.4a|915nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013190|Y54E2A.5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013190|Y54E2A.5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013190|Y54E2A.5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013192|Y54E2A.7|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013193|Y54E2A.8a|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013193|Y54E2A.8a|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1047|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013193|Y54E2A.8a|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013193|Y54E2A.8a|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013193|Y54E2A.8a|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013194|Y54E2A.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00013194|Y54E2A.9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00013195|Y54E2A.10|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013195|Y54E2A.10|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013195|Y54E2A.10|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013195|Y54E2A.10|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2328|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013195|Y54E2A.10|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013195|Y54E2A.10|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013196|tbc-20|1174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013196|tbc-20|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013196|tbc-20|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2014|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013196|tbc-20|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013196|tbc-20|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013196|tbc-20|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013197|ttm-5|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=785|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00013197|ttm-5|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013197|ttm-5|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013197|ttm-5|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1126|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=299|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|946nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|953nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013198|Y54E5A.2|976nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013200|Y54E5A.5|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4223|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013200|Y54E5A.5|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013200|Y54E5A.5|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013201|Y54E5A.6|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=945|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00013201|Y54E5A.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=458|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013201|Y54E5A.6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013201|Y54E5A.6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013201|Y54E5A.6|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013201|Y54E5A.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013201|Y54E5A.6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|1298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|1301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|1306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|235nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2516|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013202|Y54E5A.7a|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|265nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1658|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013203|Y54E5A.8a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=560|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013204|Y54E5B.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013207|Y54G9A.4|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1633|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013208|Y54G9A.5|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013209|bub-3|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013210|Y54G9A.7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013210|Y54G9A.7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013210|Y54G9A.7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013210|Y54G9A.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1531|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013211|Y54G9A.9|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013211|Y54G9A.9|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013211|Y54G9A.9|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013211|Y54G9A.9|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013211|Y54G9A.9|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013211|Y54G9A.9|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1053nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1075nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1082nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=800|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013212|Y54G11A.1|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=470|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=431|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|1392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|1425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|157nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=998|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013213|Y54G11A.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013214|Y54G11A.3|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013214|Y54G11A.3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3975|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013215|Y54G11A.4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013215|Y54G11A.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013215|Y54G11A.4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013215|Y54G11A.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013215|Y54G11A.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013216|Y54G11A.7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013216|Y54G11A.7|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=836|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013216|Y54G11A.7|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=491|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013216|Y54G11A.7|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1340|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=908|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|695nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013217|ddl-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|1259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=810|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1950|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013218|Y54G11A.9|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|316nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5484|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013219|Y54G11A.11.2|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013220|ctl-3|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013220|ctl-3|104nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013220|ctl-3|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013220|ctl-3|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013220|ctl-3|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2021|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013220|ctl-3|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013221|Y54G11A.14a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013221|Y54G11A.14a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013222|dmsr-6|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=524|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013222|dmsr-6|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013222|dmsr-6|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013222|dmsr-6|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013222|dmsr-6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=876|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2690|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013223|efa-6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013224|Y55D9A.2a|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013224|Y55D9A.2a|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=377|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013224|Y55D9A.2a|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1293|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013224|Y55D9A.2a|173nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013224|Y55D9A.2a|175nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=372|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013224|Y55D9A.2a|179nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1042nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1050nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=934|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1055nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1059nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1073nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1095nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|1160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013225|Y56A3A.2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013226|faah-5|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013227|Y56A3A.6.1|1507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013227|Y56A3A.6.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=724|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013227|Y56A3A.6.1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013227|Y56A3A.6.1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013228|Y56A3A.7a|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2392|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00013228|Y56A3A.7a|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013230|fbxb-22|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013230|fbxb-22|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013231|tsen-2|746nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013231|tsen-2|750nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013231|tsen-2|755nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013231|tsen-2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1367|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013231|tsen-2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013232|faah-4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013232|faah-4|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3829|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013232|faah-4|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013232|faah-4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013232|faah-4|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013232|faah-4|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013233|sdz-33|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013233|sdz-33|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013233|sdz-33|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013234|fbxb-24|490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013234|fbxb-24|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013234|fbxb-24|633nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013234|fbxb-24|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013234|fbxb-24|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013235|Y56A3A.16a|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013235|Y56A3A.16a|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013235|Y56A3A.16a|1205nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013235|Y56A3A.16a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013235|Y56A3A.16a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013235|Y56A3A.16a|975nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2144|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00013235|Y56A3A.16a|981nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3099|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=557|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013236|Y56A3A.18|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6930|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013237|Y56A3A.19|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2088|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=346|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3779|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14723|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=314|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=640|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013238|trap-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=772|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1416|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013239|Y56A3A.22|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2077|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013240|Y56A3A.28|1071nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013240|Y56A3A.28|1074nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1057|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00013240|Y56A3A.28|1080nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013240|Y56A3A.28|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013240|Y56A3A.28|1087nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013240|Y56A3A.28|137nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013240|Y56A3A.28|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013241|ung-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013241|ung-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2837|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013242|Y56A3A.30|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013242|Y56A3A.30|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=804|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013242|Y56A3A.30|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013242|Y56A3A.30|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013243|Y56A3A.31|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013243|Y56A3A.31|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013243|Y56A3A.31|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=454|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013243|Y56A3A.31|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013243|Y56A3A.31|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013244|Y56A3A.33|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013246|Y57A10A.1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=395|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=453|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=456|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013247|Y57A10A.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013248|Y57A10A.3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013248|Y57A10A.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013248|Y57A10A.3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=431|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013249|Y57A10A.4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=324|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013250|Y57A10A.5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013250|Y57A10A.5|241nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=569|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00013250|Y57A10A.5|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013252|Y57A10A.7|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013252|Y57A10A.7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013252|Y57A10A.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013252|Y57A10A.7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013253|Y57A10A.8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=638|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013253|Y57A10A.8|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013253|Y57A10A.8|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013254|tag-276|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013254|tag-276|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013254|tag-276|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013254|tag-276|177nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013254|tag-276|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013254|tag-276|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|70nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|756nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|841nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2262|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013255|Y57A10A.10|952nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013256|Y57A10A.13|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013256|Y57A10A.13|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013256|Y57A10A.13|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013256|Y57A10A.13|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013256|Y57A10A.13|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=870|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013256|Y57A10A.13|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1346|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013256|Y57A10A.13|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013257|Y57A10A.14|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013257|Y57A10A.14|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1065|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013257|Y57A10A.14|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00013257|Y57A10A.14|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013257|Y57A10A.14|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013258|polg-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013258|polg-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=540|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2119|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013259|trpp-5|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|139nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|1455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|322nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|326nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|397nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|983nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7140|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013260|rsr-2|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013261|sinh-1|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00013261|sinh-1|1040nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013261|sinh-1|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013261|sinh-1|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013261|sinh-1|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013261|sinh-1|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013261|sinh-1|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013263|Y57A10A.23|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013263|Y57A10A.23|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3638|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013263|Y57A10A.23|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013263|Y57A10A.23|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013264|Y57A10A.24|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013264|Y57A10A.24|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013264|Y57A10A.24|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=790|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=598|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|656nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013265|parn-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013266|Y57A10A.26.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013266|Y57A10A.26.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=895|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013266|Y57A10A.26.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013266|Y57A10A.26.2|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013266|Y57A10A.26.2|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013266|Y57A10A.26.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013266|Y57A10A.26.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013267|Y57A10A.27|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013267|Y57A10A.27|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1238|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013267|Y57A10A.27|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013267|Y57A10A.27|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013267|Y57A10A.27|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|1351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|1353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=620|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|633nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|815nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013268|Y57A10A.28|854nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=970|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013269|Y57A10A.29.2|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|494nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|505nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1721|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013270|Y57A10A.31|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|453nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|460nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|521nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013272|aqp-12|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013273|marc-5|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1642|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013273|marc-5|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013274|Y57A10B.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013275|btb-14|14nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013275|btb-14|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=634|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013275|btb-14|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013275|btb-14|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013276|sre-42|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013276|sre-42|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013277|sre-41|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013278|Y57A10B.6|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=132|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013279|Y57A10B.7|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=329|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013279|Y57A10B.7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013279|Y57A10B.7|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00013279|Y57A10B.7|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013280|Y57A10C.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013281|sre-27|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013284|daf-22|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013284|daf-22|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013284|daf-22|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013284|daf-22|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013284|daf-22|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013285|dct-12|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013285|dct-12|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013286|Y57A10C.8|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013286|Y57A10C.8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013286|Y57A10C.8|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013286|Y57A10C.8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013287|Y57A10C.9|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013288|Y57A10C.10|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=974|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=905|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|1494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013289|tag-273|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013290|Y57G11A.2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013290|Y57G11A.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1741|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013290|Y57G11A.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013292|Y57G11A.4.1|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013292|Y57G11A.4.1|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013292|Y57G11A.4.1|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=632|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013295|Y57G11B.2a|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013295|Y57G11B.2a|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=790|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013295|Y57G11B.2a|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=719|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013295|Y57G11B.2a|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013295|Y57G11B.2a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013295|Y57G11B.2a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013295|Y57G11B.2a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013296|Y57G11B.3|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013297|Y57G11B.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013297|Y57G11B.5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013297|Y57G11B.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4166|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013297|Y57G11B.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2560|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013297|Y57G11B.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013297|Y57G11B.5|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013298|Y57G11B.6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013298|Y57G11B.6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013298|Y57G11B.6|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013299|irld-18|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013299|irld-18|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013299|irld-18|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013299|irld-18|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013299|irld-18|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013300|lgc-7|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4702|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013301|Y57G11C.3a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|194nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|201nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1904|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|355nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013302|vti-1|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013303|Y57G11C.5c|1266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013303|Y57G11C.5c|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013303|Y57G11C.5c|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013304|Y57G11C.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013304|Y57G11C.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013304|Y57G11C.6|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013306|Y57G11C.8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013306|Y57G11C.8|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013306|Y57G11C.8|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013306|Y57G11C.8|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013306|Y57G11C.8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013306|Y57G11C.8|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013306|Y57G11C.8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=556|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=850|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3874|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=978|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|174nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|176nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=169|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2138|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3187|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=280|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9c|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9c|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9c|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9c|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9c|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013307|Y57G11C.9c|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50916|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2104|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=976|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|865nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013308|nuo-3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=543|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013310|Y57G11C.14|1531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013310|Y57G11C.14|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1143|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=397|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21353|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4386|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27056|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013311|sec-61|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013312|hhat-2|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013315|Y57G11C.20|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013317|Y57G11C.22a|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=137|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013317|Y57G11C.22a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013317|Y57G11C.22a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1214|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013317|Y57G11C.22a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4411|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013317|Y57G11C.22a|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013318|Y57G11C.23|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013318|Y57G11C.23|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013318|Y57G11C.23|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013318|Y57G11C.23|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013318|Y57G11C.23|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013319|ccch-5|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013319|ccch-5|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013321|Y57G11C.31.2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013321|Y57G11C.31.2|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013321|Y57G11C.31.2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013321|Y57G11C.31.2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013321|Y57G11C.31.2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013322|Y57G11C.32|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=406|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00013322|Y57G11C.32|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2309|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013323|Y57G11C.33a|992nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013324|mrps-7|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013324|mrps-7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=836|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013324|mrps-7|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013324|mrps-7|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013324|mrps-7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013324|mrps-7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=996|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2121|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013325|Y57G11C.36.1|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013326|anoh-2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=629|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013326|anoh-2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013326|anoh-2|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013326|anoh-2|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013326|anoh-2|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013327|Y57G11C.38a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013327|Y57G11C.38a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013327|Y57G11C.38a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013327|Y57G11C.38a|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013327|Y57G11C.38a|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013327|Y57G11C.38a|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013327|Y57G11C.38a|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013328|Y57G11C.39|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013329|Y57G11C.40|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013329|Y57G11C.40|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013329|Y57G11C.40|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013329|Y57G11C.40|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013329|Y57G11C.40|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013330|Y57G11C.41|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00013330|Y57G11C.41|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00013331|Y57G11C.42a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013331|Y57G11C.42a|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013331|Y57G11C.42a|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013331|Y57G11C.42a|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013332|Y57G11C.43|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013332|Y57G11C.43|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013332|Y57G11C.43|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1901|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00013332|Y57G11C.43|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013332|Y57G11C.43|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013333|Y57G11C.44c|1599nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013333|Y57G11C.44c|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013333|Y57G11C.44c|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013333|Y57G11C.44c|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1301|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013333|Y57G11C.44c|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013333|Y57G11C.44c|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013333|Y57G11C.44c|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1039|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013334|Y57G11C.45b|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013335|Y57G11C.46|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013335|Y57G11C.46|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013335|Y57G11C.46|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=535|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00013336|pnc-2|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1092|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00013336|pnc-2|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013337|Y57G11C.48|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013337|Y57G11C.48|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013337|Y57G11C.48|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013338|lgc-8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013338|lgc-8|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=304|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013339|phf-14|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013340|tcc-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013340|tcc-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013340|tcc-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013340|tcc-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013340|tcc-1|449nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6593|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013340|tcc-1|456nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013343|prp-6|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2347|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013343|prp-6|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1357|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013343|prp-6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013343|prp-6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|1400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1923|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013344|ebp-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013345|Y59A8B.8|1156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013345|Y59A8B.8|1228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013345|Y59A8B.8|1236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013345|Y59A8B.8|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=951|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013345|Y59A8B.8|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1160|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|1116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4700|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013347|Y59A8B.10c|360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013348|fbxa-106|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=813|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1008|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|797nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013349|Y59A8B.12|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013350|slr-2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013350|slr-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013350|slr-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=676|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013350|slr-2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013350|slr-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013350|slr-2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013350|slr-2|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013351|Y59A8B.19a|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013351|Y59A8B.19a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013351|Y59A8B.19a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=856|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|1272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013352|lon-8|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=379|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|1192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013353|Y59A8B.21|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|1013nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2484|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=427|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|808nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|933nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013354|snx-6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|383nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|386nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=918|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|393nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=469|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013355|gck-3|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013356|Y59A8B.24|1046nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013356|Y59A8B.24|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00013356|Y59A8B.24|1285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013356|Y59A8B.24|1290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013357|clec-260|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013357|clec-260|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2283|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3956|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013358|abhd-3.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013359|Y60A3A.8|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1951|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00013359|Y60A3A.8|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013359|Y60A3A.8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013359|Y60A3A.8|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013359|Y60A3A.8|621nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013359|Y60A3A.8|626nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013359|Y60A3A.8|628nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1606|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1539|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2031|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013360|Y60A3A.9|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2217|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|190nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013361|fars-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|1243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1497|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|1285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013362|algn-7|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013364|Y60A3A.16|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013364|Y60A3A.16|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013364|Y60A3A.16|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013364|Y60A3A.16|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013364|Y60A3A.16|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013365|Y60A3A.19b|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013365|Y60A3A.19b|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2639|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00013365|Y60A3A.19c|1315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21a|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21a|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21a|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21a|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21a|489nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21a|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1231|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21b|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21b|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21b|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21b|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21b|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21b|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013366|Y60A3A.21b|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013367|Y60A3A.23|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00013367|Y60A3A.23|403nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00013368|Y60A9.1|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013370|Y60A9.3|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013370|Y60A9.3|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00013370|Y60A9.3|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013373|Y62E10A.2.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013373|Y62E10A.2.4|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013373|Y62E10A.2.4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013373|Y62E10A.2.4|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013373|Y62E10A.2.4|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013373|Y62E10A.2.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6356|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013373|Y62E10A.2.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013374|Y62E10A.3|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013374|Y62E10A.3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013374|Y62E10A.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013374|Y62E10A.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|1143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|1148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013375|srsx-25|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013376|Y62E10A.6|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013376|Y62E10A.6|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013376|Y62E10A.6|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013376|Y62E10A.6|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1935|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013376|Y62E10A.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013376|Y62E10A.6|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=390|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2243|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=271|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3135|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013378|emc-3|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1543|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5401|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013379|Y62E10A.13d|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1131|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1069|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013380|Y62E10A.14|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013381|cyp-31A5|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013381|cyp-31A5|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013381|cyp-31A5|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013381|cyp-31A5|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=944|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013381|cyp-31A5|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=571|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013381|cyp-31A5|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013382|gcl-1|597nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013382|gcl-1|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013382|gcl-1|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013382|gcl-1|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013382|gcl-1|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013383|aptf-2|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=442|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013383|aptf-2|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=376|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013383|aptf-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013383|aptf-2|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013385|Y62E10A.19|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013385|Y62E10A.19|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013385|Y62E10A.19|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013385|Y62E10A.19|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013385|Y62E10A.19|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013387|Y62F5A.9|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013387|Y62F5A.9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013387|Y62F5A.9|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013387|Y62F5A.9|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013387|Y62F5A.9|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013387|Y62F5A.9|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013387|Y62F5A.9|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013388|Y62F5A.10|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013388|Y62F5A.10|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013389|Y62H9A.1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013389|Y62H9A.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013389|Y62H9A.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|38nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7232|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013391|Y62H9A.3|68nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|1006nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|1011nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|1017nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|1027nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11066|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1450|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013392|Y62H9A.4.1|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16222|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22676|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24991|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013393|Y62H9A.5|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1107|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25630|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4240|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=891|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1402|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=721|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013394|Y62H9A.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013395|Y62H9A.7|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013395|Y62H9A.7|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013397|Y62H9A.9|937nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013398|Y62H9A.10|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013398|Y62H9A.10|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013399|Y62H9A.11|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013399|Y62H9A.11|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013399|Y62H9A.11|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013399|Y62H9A.11|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013400|Y62H9A.12|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013400|Y62H9A.12|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013400|Y62H9A.12|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013400|Y62H9A.12|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013401|Y62H9A.13|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00013401|Y62H9A.13|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013401|Y62H9A.13|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013401|Y62H9A.13|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013402|Y62H9A.14|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013402|Y62H9A.14|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013402|Y62H9A.14|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013403|fbxb-100|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00013403|fbxb-100|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013403|fbxb-100|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013405|tdpt-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1254|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013406|Y63D3A.7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013406|Y63D3A.7|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013406|Y63D3A.7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013406|Y63D3A.7|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1136|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013406|Y63D3A.7|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5767|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2292|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013407|Y63D3A.8|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013408|fbxb-93|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00013408|fbxb-93|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013408|fbxb-93|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013408|fbxb-93|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013409|fbxb-56|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013409|fbxb-56|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00013409|fbxb-56|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013412|Y64G10A.2|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013412|Y64G10A.2|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013415|Y64G10A.6|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013415|Y64G10A.6|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2192|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013415|Y64G10A.6|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013415|Y64G10A.6|802nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1579|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013416|Y64G10A.7a|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013417|srab-24|769nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=840|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013418|Y65A5A.1b|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013419|Y65A5A.2a|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013421|fbxa-220|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013421|fbxa-220|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013421|fbxa-220|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013422|Y66A7A.2b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1749|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013424|Y66A7A.4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013424|Y66A7A.4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013424|Y66A7A.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013425|ceh-91|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00013425|ceh-91|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013425|ceh-91|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013425|ceh-91|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013425|ceh-91|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013426|Y66A7A.7|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013426|Y66A7A.7|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013426|Y66A7A.7|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013426|Y66A7A.7|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1405|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013427|Y66D12A.1|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013429|Y66D12A.3|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013429|Y66D12A.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013429|Y66D12A.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=441|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=211|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=214|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013431|ceh-92|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|1134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|1169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|15nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=440|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013432|Y66D12A.6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|523nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|527nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013433|Y66D12A.7|640nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013434|Y66D12A.8a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4504|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013435|Y66D12A.9|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2891|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1188|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013436|Y66D12A.10|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013437|Y66D12A.11|1191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013437|Y66D12A.11|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00013437|Y66D12A.11|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013437|Y66D12A.11|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=389|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013437|Y66D12A.11|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013438|ztf-29|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013439|Y66D12A.13|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013439|Y66D12A.13|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013439|Y66D12A.13|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013439|Y66D12A.13|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013439|Y66D12A.13|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013439|Y66D12A.13|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013440|Y66D12A.14|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=408|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1693|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013441|xpb-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1492|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|1197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|1199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013442|Y66D12A.16b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013443|such-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|1419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|1422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|1427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|912nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013445|Y66D12A.19|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013446|Y66D12A.21|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013446|Y66D12A.21|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1208|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013446|Y66D12A.21|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2003|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013447|nars-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1302|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013448|Y66D12A.24|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013448|Y66D12A.24|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013448|Y66D12A.24|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1319|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00013448|Y66D12A.24|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013448|Y66D12A.24|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013448|Y66D12A.24|409nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013448|Y66D12A.24|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013449|Y67A6A.1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013449|Y67A6A.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013449|Y67A6A.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013449|Y67A6A.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=700|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013449|Y67A6A.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013449|Y67A6A.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013450|oac-56|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013452|Y67A10A.3a|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013452|Y67A10A.3a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013452|Y67A10A.3a|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013453|fbxa-83|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013453|fbxa-83|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013453|fbxa-83|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013455|ssu-2|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013455|ssu-2|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013455|ssu-2|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013455|ssu-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1239|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013456|Y67A10A.7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013457|paqr-3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013457|paqr-3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013458|Y67A10A.9|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013458|Y67A10A.9|203nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013458|Y67A10A.9|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013459|Y67A10A.10|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|1165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1452|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013460|cpsf-3|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013461|Y67H2A.2b|1273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013461|Y67H2A.2b|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013461|Y67H2A.2b|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3191|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013461|Y67H2A.2b|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|1062nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|1066nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|1071nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=992|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9776|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=301|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013462|micu-1|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6949|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|841nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013463|Y67H2A.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25938|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013464|Y67H2A.7a|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1075|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1485|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013465|Y67H2A.10c|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013466|srz-47|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013469|Y68A4A.10a|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013470|clec-243|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013470|clec-243|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013471|clec-242|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013471|clec-242|169nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=12|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013471|clec-242|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00013471|clec-242|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013473|Y69E1A.1.2|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013473|Y69E1A.1.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013473|Y69E1A.1.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1383|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013473|Y69E1A.1.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=614|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013473|Y69E1A.1.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013474|Y69E1A.2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013474|Y69E1A.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013474|Y69E1A.2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013474|Y69E1A.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013474|Y69E1A.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013474|Y69E1A.2|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1697|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013475|Y69E1A.3|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=143|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013476|Y69E1A.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00013476|Y69E1A.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00013477|Y69E1A.5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2938|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013477|Y69E1A.5|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013477|Y69E1A.5|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013477|Y69E1A.5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013477|Y69E1A.5|56nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013478|Y69E1A.8|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013478|Y69E1A.8|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=267|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013479|Y69H2.1b|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013480|egas-3|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013480|egas-3|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=214|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013480|egas-3|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013480|egas-3|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2317|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6097|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3b|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013481|Y69H2.3b|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013482|Y69H2.7a|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1800|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013482|Y69H2.7a|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013482|Y69H2.7a|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013482|Y69H2.7a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013482|Y69H2.7a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013482|Y69H2.7a|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013484|Y69H2.9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013484|Y69H2.9|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013484|Y69H2.9|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013484|Y69H2.9|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013485|Y69H2.10a|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013485|Y69H2.10a|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013485|Y69H2.10c|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013486|egas-1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013486|egas-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013486|egas-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16363|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26433|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013489|col-42|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013490|Y70C5A.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013492|Y70C5C.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013493|clec-9|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013494|irld-58|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013496|Y70D2A.1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013496|Y70D2A.1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013496|Y70D2A.1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013497|hex-5|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=555|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013497|hex-5|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|343nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|635nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|637nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|641nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|643nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=245|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013499|Y70G10A.3.2|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013501|Y71A12B.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013501|Y71A12B.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013503|clec-112|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013505|Y71A12B.8|1209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00013505|Y71A12B.8|1231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00013505|Y71A12B.8|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00013505|Y71A12B.8|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00013506|usp-3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013506|usp-3|802nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=980|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013507|Y71A12B.10a|1365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013507|Y71A12B.10a|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013508|Y71A12B.11|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013508|Y71A12B.11|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013508|Y71A12B.11|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013509|Y71A12B.12a.1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013509|Y71A12B.12a.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013509|Y71A12B.12a.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013509|Y71A12B.12a.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013511|Y71A12B.15|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013512|nhr-276|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013513|Y71A12C.2|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013513|Y71A12C.2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66645|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1575|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1784|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1380|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1412|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|198nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|203nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|206nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=510|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|210nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=528|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3862|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=605|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=418557|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013514|Y73F4A.1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1065|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|1007nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=305|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6931|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|180nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=654|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=443|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013515|Y73F4A.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013516|Y73F4A.3|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013516|Y73F4A.3|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=679|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013516|Y73F4A.3|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013516|Y73F4A.3|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=725|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013517|lgc-52|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013518|Y73F8A.5|1401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013518|Y73F8A.5|1408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013518|Y73F8A.5|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013518|Y73F8A.5|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013518|Y73F8A.5|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013518|Y73F8A.5|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013518|Y73F8A.5|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013520|best-21|1454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013520|best-21|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013520|best-21|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013520|best-21|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013520|best-21|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013520|best-21|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00013521|Y73F8A.12|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013522|Y73F8A.13|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013522|Y73F8A.13|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=718|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013522|Y73F8A.13|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013522|Y73F8A.13|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013522|Y73F8A.13|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013523|Y73F8A.14|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013523|Y73F8A.14|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013523|Y73F8A.14|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013523|Y73F8A.14|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013523|Y73F8A.14|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013523|Y73F8A.14|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1166|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013524|Y73F8A.15|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013525|irld-59|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013526|Y73F8A.20|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013527|Y73F8A.22|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013529|Y73F8A.24b|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1746|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013529|Y73F8A.24b|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1077|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=674|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|16nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|20nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013530|ntl-11|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|1174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|1533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|531nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013531|Y73F8A.26a|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1356|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013532|Y73F8A.27|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|1212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013534|acr-24|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013536|Y73F8A.32a|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013536|Y73F8A.32a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013536|Y73F8A.32a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013536|Y73F8A.32a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013536|Y73F8A.32a|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5025|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2003|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1664|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013538|tag-349|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013539|Y73F8A.35b|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013539|Y73F8A.35b|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013539|Y73F8A.35b|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013540|Y75B8A.3|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=333|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013540|Y75B8A.3|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013541|Y75B8A.4|1142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013541|Y75B8A.4|1147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013541|Y75B8A.4|25nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013541|Y75B8A.4|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013541|Y75B8A.4|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013541|Y75B8A.4|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013542|lron-12|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013542|lron-12|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013542|lron-12|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00013542|lron-12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013542|lron-12|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013542|lron-12|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013543|Y75B8A.6|1185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013543|Y75B8A.6|1289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013543|Y75B8A.6|1292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013543|Y75B8A.6|1318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013543|Y75B8A.6|1337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013543|Y75B8A.6|1340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013543|Y75B8A.6|1342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013544|Y75B8A.7|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013544|Y75B8A.7|756nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013544|Y75B8A.7|759nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=434|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013544|Y75B8A.7|765nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=532|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00013544|Y75B8A.7|768nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013544|Y75B8A.7|932nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|376nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|540nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1584|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|567nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013545|Y75B8A.8|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013547|Y75B8A.10|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013547|Y75B8A.10|1415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00013547|Y75B8A.10|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11416|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1455|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|93nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013548|Y75B8A.11a|98nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013549|Y75B8A.13|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013549|Y75B8A.13|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1374|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013550|Y75B8A.14|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013550|Y75B8A.14|1202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013550|Y75B8A.14|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013550|Y75B8A.14|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2000|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013550|Y75B8A.14|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013550|Y75B8A.14|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013550|Y75B8A.14|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=464|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=444|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|1245nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013551|Y75B8A.16|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=681|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013552|gmn-1|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013552|gmn-1|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013552|gmn-1|733nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013552|gmn-1|740nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1596|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013552|gmn-1|745nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1007|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013552|gmn-1|750nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013553|Y75B8A.18b|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013553|Y75B8A.18b|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2907|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013553|Y75B8A.18b|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013554|Y75B8A.19|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00013554|Y75B8A.19|542nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013554|Y75B8A.19|546nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013554|Y75B8A.19|552nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013554|Y75B8A.19|554nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00013554|Y75B8A.19|557nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00013555|fbxa-89|1443nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013555|fbxa-89|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2761|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|608nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013556|Y75B8A.23|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1092|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=467|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013557|Y75B8A.24|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013558|Y75B8A.25|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013558|Y75B8A.25|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013558|Y75B8A.25|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3413|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013558|Y75B8A.25|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013559|Y75B8A.28|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013559|Y75B8A.28|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013560|zip-12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1029|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00013560|zip-12|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013560|zip-12|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013560|zip-12|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013561|Y75B8A.31|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013561|Y75B8A.31|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013561|Y75B8A.31|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013561|Y75B8A.31|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013561|Y75B8A.31|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013561|Y75B8A.31|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1288|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013561|Y75B8A.31|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=712|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013562|Y75B8A.32|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013562|Y75B8A.32|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013562|Y75B8A.32|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013562|Y75B8A.32|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013562|Y75B8A.32|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013562|Y75B8A.32|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013563|Y75B8A.33|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013563|Y75B8A.33|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013564|Y75B8A.34|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013564|Y75B8A.34|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1198nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|1603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4086|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|450nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|453nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|460nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|462nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|465nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013567|Y75B12B.1c|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013568|Y75B12B.3|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013568|Y75B12B.3|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1016|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013568|Y75B12B.3|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013568|Y75B12B.3|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013569|bath-36|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013569|bath-36|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=489|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013569|bath-36|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013569|bath-36|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013569|bath-36|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013569|bath-36|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013572|Y75B12B.10|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013572|Y75B12B.10|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013573|Y75B12B.11|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013573|Y75B12B.11|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013574|lron-13|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013575|acs-5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013575|acs-5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013575|acs-5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1435|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013575|acs-5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013575|acs-5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=939|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013576|Y76A2B.4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=224|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1981|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2539|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013577|Y76A2B.5.1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2750|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|599nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|602nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=638|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|604nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=240|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013578|scav-2|610nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013579|Y79H2A.2b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013579|Y79H2A.2b|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013579|Y79H2A.2b|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2565|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013579|Y79H2A.2b|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013579|Y79H2A.2b|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013579|Y79H2A.2b|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013579|Y79H2A.2b|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3b|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3g|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3g|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=964|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3g|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3g|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3g|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3g|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2489|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013580|Y79H2A.3g|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013583|ceh-51|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013584|nhr-243|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013584|nhr-243|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00013584|nhr-243|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013585|cyp-42A1|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013585|cyp-42A1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013585|cyp-42A1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013585|cyp-42A1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00013585|cyp-42A1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013586|Y80D3A.8|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013587|Y80D3A.9|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013587|Y80D3A.9|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013587|Y80D3A.9|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1032|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013587|Y80D3A.9|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013587|Y80D3A.9|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6002|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1928|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=836|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013588|nlp-42|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013590|Y81G3A.1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013590|Y81G3A.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013590|Y81G3A.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013590|Y81G3A.1|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=334|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2247|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013591|gcn-2|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013592|Y81G3A.4a|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=159|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013593|Y87G2A.1|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013593|Y87G2A.1|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1245|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013593|Y87G2A.1|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013593|Y87G2A.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013593|Y87G2A.1|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013594|Y87G2A.2|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00013594|Y87G2A.2|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1020|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013594|Y87G2A.2|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013594|Y87G2A.2|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013594|Y87G2A.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013594|Y87G2A.2|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1611|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013595|atg-4.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=686|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013596|nyn-2|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10221|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2468|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=297|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013597|gpi-1|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=610|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|801nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3158|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1168|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013598|vps-28|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=273|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|308nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=513|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013599|Y87G2A.11|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|1030nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1282|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013601|Y87G2A.13|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013602|Y87G2A.16|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013602|Y87G2A.16|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=399|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013602|Y87G2A.16|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013603|Y87G2A.17|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013603|Y87G2A.17|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013603|Y87G2A.17|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013603|Y87G2A.17|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1341|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00013603|Y87G2A.17|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1195|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013603|Y87G2A.17|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013603|Y87G2A.17|696nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013604|Y87G2A.18|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3786|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013604|Y87G2A.18|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013604|Y87G2A.18|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1960|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013605|Y95D11A.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|1184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1581|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1357|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=754|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3978|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|751nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|756nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|759nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|866nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|869nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|876nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013606|cand-1|880nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013607|clec-27|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013608|clec-35|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00013608|clec-35|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00013609|clec-37|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013609|clec-37|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013609|clec-37|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013610|fbxa-206|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1144|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013610|fbxa-206|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=549|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013610|fbxa-206|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013610|fbxa-206|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013611|Y102A5C.2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013613|Y102A5C.4|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013616|fbxa-148|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013619|fbxa-112|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013621|clec-239|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013621|clec-239|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013621|clec-239|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013622|clec-238|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013622|clec-238|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013623|fbxa-90|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013623|fbxa-90|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1463|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013623|fbxa-90|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013629|srz-95|266nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=246|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00013632|Y105C5A.1|342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=363|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013633|Y105C5A.8a|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013634|Y105C5A.9a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013637|Y105C5A.13a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1433|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013637|Y105C5A.13a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013637|Y105C5A.13a|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013637|Y105C5A.13a|867nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|1363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|1365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|474nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=861|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|478nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|481nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|484nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|582nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|584nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|717nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|721nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|750nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013639|Y105C5A.15c|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013642|daf-38|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=891|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013642|daf-38|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013643|Y105C5A.24|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013643|Y105C5A.24|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013643|Y105C5A.24|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013643|Y105C5A.24|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013643|Y105C5A.24|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013643|Y105C5A.24|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013645|Y105C5B.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013645|Y105C5B.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013646|Y105C5B.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=420|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7571|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5000|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=944|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013647|Y105C5B.5a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013649|Y105C5B.8a|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013649|Y105C5B.8a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013649|Y105C5B.8a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013650|Y105C5B.9|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013650|Y105C5B.9|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013650|Y105C5B.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013650|Y105C5B.9|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013650|Y105C5B.9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013650|Y105C5B.9|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013651|Y105C5B.11a|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013653|Y105C5B.14|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013654|Y105C5B.15a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013654|Y105C5B.15a|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013654|Y105C5B.15a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1848|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013654|Y105C5B.15a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013654|Y105C5B.15a|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013655|lgc-19|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013655|lgc-19|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013655|lgc-19|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013655|lgc-19|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013656|Y105C5B.17|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=628|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013657|Y105C5B.18|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00013657|Y105C5B.18|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1554|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013657|Y105C5B.18|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=392|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013658|Y105C5B.19|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013659|Y105C5B.20|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013659|Y105C5B.20|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013662|Y105C5B.25a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2838|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013662|Y105C5B.25a|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1247|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2033|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013665|hlh-32|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013666|Y105E8A.1a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013666|Y105E8A.1a|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013666|Y105E8A.1a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013666|Y105E8A.1a|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013666|Y105E8A.1b|991nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=804|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013666|Y105E8A.1b|993nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1877|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|251nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013667|Y105E8A.2|707nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013668|Y105E8A.3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013668|Y105E8A.3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013668|Y105E8A.3|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1806|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013668|Y105E8A.3|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=518|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013668|Y105E8A.3|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=485|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013669|Y105E8A.8|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013670|hpo-13|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013670|hpo-13|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2100|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013670|hpo-13|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013670|hpo-13|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=457|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1575|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013671|Y105E8A.11|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013672|catp-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013673|Y105E8A.13b|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3332|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013674|Y105E8A.14|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=439|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1179|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|1446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|328nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|384nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|858nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013676|ekl-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=861|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1439|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=800|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013677|yars-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013678|Y105E8A.20a.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013678|Y105E8A.20a.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013678|Y105E8A.20a.1|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013678|Y105E8A.20a.1|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4212|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013678|Y105E8A.20a.1|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013678|Y105E8A.20a.1|890nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013679|Y105E8A.21b|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013679|Y105E8A.21b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013679|Y105E8A.21b|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013679|Y105E8A.21b|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013679|Y105E8A.21b|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=899|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013679|Y105E8A.21b|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013679|Y105E8A.21b|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013680|rpom-1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013680|rpom-1|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013680|rpom-1|448nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013680|rpom-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=684|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00013680|rpom-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013680|rpom-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013680|rpom-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013682|Y105E8A.25b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013682|Y105E8A.25e|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=524|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013682|Y105E8A.25e|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2374|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013682|Y105E8A.25e|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013682|Y105E8A.25e|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013682|Y105E8A.25e|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013682|Y105E8A.25e|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013683|zoo-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013683|zoo-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013683|zoo-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=528|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00013684|Y105E8A.27|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013684|Y105E8A.27|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013684|Y105E8A.27|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013684|Y105E8A.27|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013685|Y105E8A.28|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013685|Y105E8A.28|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013685|Y105E8A.28|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=355|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013685|Y105E8A.28|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=299|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2214|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013687|exoc-8|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2546|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013688|riok-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013689|bath-40|1042nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013689|bath-40|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013689|bath-40|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4923|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013689|bath-40|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1137|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=497|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2288|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013690|hprt-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013691|Y105E8B.6|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1692|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013692|Y105E8B.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=920|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013692|Y105E8B.7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1481|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013692|Y105E8B.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013692|Y105E8B.7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|1004nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|1013nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|1031nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|1067nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|1083nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013693|Y105E8B.9|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013694|Y106G6A.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2392|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013694|Y106G6A.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013694|Y106G6A.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|1052nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|1065nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=891|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=538|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=757|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013695|epg-8|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013696|Y106G6A.4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013696|Y106G6A.4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013696|Y106G6A.4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1129|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|1253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|1269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|1317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|1535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6059|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013697|dsbn-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013698|Y106G6D.1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013698|Y106G6D.1|459nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=188|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00013698|Y106G6D.1|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013699|Y106G6D.2|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013699|Y106G6D.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013700|Y106G6D.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013700|Y106G6D.3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013700|Y106G6D.3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013700|Y106G6D.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013701|Y106G6D.4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013701|Y106G6D.4|1227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013701|Y106G6D.4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013701|Y106G6D.4|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013701|Y106G6D.4|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013701|Y106G6D.4|575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013701|Y106G6D.4|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013702|Y106G6D.6|133nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013702|Y106G6D.6|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013702|Y106G6D.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2596|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013702|Y106G6D.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013702|Y106G6D.6|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|343nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=822|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=482|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|349nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013703|Y106G6D.7|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|1208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|1213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|1237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|1245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013704|Y106G6D.8.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4738|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013705|Y106G6E.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013708|Y106G6E.4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013708|Y106G6E.4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013708|Y106G6E.4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1388|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013708|Y106G6E.4|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013708|Y106G6E.4|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1047nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1051nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=167|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1056nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7943|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1060nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=355|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1064nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=132|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1079nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1242nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|678nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|688nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|780nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|787nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013709|csnk-1|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=359|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013710|Y106G6G.1|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013711|Y106G6G.2|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013711|Y106G6G.2|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013711|Y106G6G.2|1213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013711|Y106G6G.2|1328nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013711|Y106G6G.2|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013712|dlc-6|16nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013712|dlc-6|19nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013712|dlc-6|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013712|dlc-6|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2010|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=321|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013713|Y106G6G.4|925nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013715|Y106G6G.6|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00013715|Y106G6G.6|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|1179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|234nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1060|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00013716|Y106G6H.1|704nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=679|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=611|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=852|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=607|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1425|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=907|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|1598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013717|madf-10|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013718|Y106G6H.5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1391|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013718|Y106G6H.5|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3202|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013718|Y106G6H.5|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013718|Y106G6H.5|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|1089nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1576|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013719|Y106G6H.6e.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013720|Y106G6H.8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013720|Y106G6H.8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4769|total_reads(99.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013721|Y106G6H.9|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013721|Y106G6H.9|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013723|Y106G6H.13|26nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013723|Y106G6H.13|36nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=3397|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013723|Y106G6H.13|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013724|Y106G6H.14|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2823|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013724|Y106G6H.14|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013725|ska-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013725|ska-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013725|ska-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013725|ska-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1276|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013726|Y106G6H.16|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013726|Y106G6H.16|1313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013726|Y106G6H.16|1326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013726|Y106G6H.16|17nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013726|Y106G6H.16|22nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013726|Y106G6H.16|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2345|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013726|Y106G6H.16|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013727|Y111B2A.1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=650|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|145nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5127|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013728|Y111B2A.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|1048nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|339nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|345nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013729|Y111B2A.3|791nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013730|sql-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013730|sql-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013730|sql-1|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5940|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|748nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013732|aakg-1|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013734|Y111B2A.10b|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013734|Y111B2A.10b|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013734|Y111B2A.10b|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2684|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013734|Y111B2A.10b|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013734|Y111B2A.10b|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1929|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013735|Y111B2A.12a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|1450nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|1467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|289nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|293nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=463|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1632|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00013736|Y111B2A.13|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2789|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|251nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013737|tpst-1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|653nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|656nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|695nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|701nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|762nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|767nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013738|elpc-2|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013739|spin-4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=279|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3267|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013740|hut-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013741|Y111B2A.21|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=229|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013742|Y111B2A.24|1362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013742|Y111B2A.24|1367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013742|Y111B2A.24|576nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013742|Y111B2A.24|586nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=608|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013742|Y111B2A.24|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013744|Y111B2A.27|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013746|lgc-55|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1085|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013746|lgc-55|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013747|spe-19|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013747|spe-19|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013747|spe-19|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013747|spe-19|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013748|ssu-1|106nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013748|ssu-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2555|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013749|Y113G7A.12|772nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013750|Y113G7A.13|243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013750|Y113G7A.13|247nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013750|Y113G7A.13|250nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00013750|Y113G7A.13|253nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013751|Y113G7A.14|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013751|Y113G7A.14|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15a|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15b|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15b|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15b|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013752|Y113G7A.15b|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013753|Y113G7A.16|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013753|Y113G7A.16|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013753|Y113G7A.16|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013754|fbxa-116|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=311|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013754|fbxa-116|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013755|fbxa-115|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=335|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013756|ftr-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013756|ftr-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013757|fbxa-113|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013758|fbxa-114|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013758|fbxa-114|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013758|fbxa-114|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013758|fbxa-114|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013758|fbxa-114|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013758|fbxa-114|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=255|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013759|fbxb-59|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013760|srbc-34|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013761|Y113G7B.11|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013761|Y113G7B.11|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013761|Y113G7B.11|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013762|Y113G7B.12|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013762|Y113G7B.12|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=673|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013762|Y113G7B.12|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013764|Y113G7B.15|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013764|Y113G7B.15|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013764|Y113G7B.15|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=533|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013765|cdkr-3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=546|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17835|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5029|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|337nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|350nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013766|prmt-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|409nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=401|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|414nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=457|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|417nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|420nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|454nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|456nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|472nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|476nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013768|sld-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013771|Y113G7C.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013771|Y113G7C.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013771|Y113G7C.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013771|Y113G7C.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013771|Y113G7C.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013773|Y116A8A.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013774|clec-193|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013775|Y116A8A.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013775|Y116A8A.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013776|Y116A8A.6|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013776|Y116A8A.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013776|Y116A8A.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013777|Y116A8A.7|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1226|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013778|clec-194|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013779|Y116A8B.1.2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013779|Y116A8B.1.2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013781|Y116A8B.4|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013781|Y116A8B.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013781|Y116A8B.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013781|Y116A8B.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013781|Y116A8B.4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013782|npr-32|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013782|npr-32|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013782|npr-32|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2134|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1986|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50458|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14765|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|613nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2012|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013784|Y116A8C.3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013785|nep-23|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013786|nep-24|1011nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013786|nep-24|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=786|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|1421nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013789|Y116A8C.9b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013790|Y116A8C.10b.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1451|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013790|Y116A8C.10b.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013791|Y116A8C.11|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013792|Y116A8C.13b|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013792|Y116A8C.13b|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=326|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013792|Y116A8C.13b|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013794|dct-13|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013794|dct-13|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013794|dct-13|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013794|dct-13|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013795|nhr-229|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013796|Y116A8C.19|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013796|Y116A8C.19|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013796|Y116A8C.19|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013797|Y116A8C.20|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013799|athp-3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013799|athp-3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013799|athp-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00013799|athp-3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013799|athp-3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013800|Y116A8C.23|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013800|Y116A8C.23|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013800|Y116A8C.23|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013800|Y116A8C.23|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013801|Y116A8C.24a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013801|Y116A8C.24a|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013802|Y116A8C.25c.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013802|Y116A8C.25c.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013802|Y116A8C.25f.1|256nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013802|Y116A8C.25f.1|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1012nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=700|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=271|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013803|snx-13|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1444|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=718|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013804|Y116A8C.27b.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013805|bca-2|1006nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013805|bca-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3217|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00013805|bca-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013805|bca-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013805|bca-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013805|bca-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013805|bca-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013806|Y116A8C.29|1242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013806|Y116A8C.29|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013806|Y116A8C.29|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=613|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013806|Y116A8C.29|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013806|Y116A8C.29|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013806|Y116A8C.29|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1379|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013807|Y116A8C.30a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|688nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=899|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|691nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|694nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|711nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|717nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|725nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2703|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|728nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|731nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013808|sfa-1|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013809|Y116A8C.33a|1374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013809|Y116A8C.33a|1400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013809|Y116A8C.33a|1459nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013809|Y116A8C.33a|1462nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013809|Y116A8C.33a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013810|Y116A8C.37|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013810|Y116A8C.37|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013811|Y116A8C.38|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00013811|Y116A8C.38|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00013812|Y116A8C.40a|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00013812|Y116A8C.40a|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013812|Y116A8C.40a|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=576|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013812|Y116A8C.40a|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013812|Y116A8C.40a|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013812|Y116A8C.40a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013814|Y116A8C.43a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013815|Y116A8C.44|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013815|Y116A8C.44|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013816|Y116F11A.1|242nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013816|Y116F11A.1|249nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013817|Y116F11A.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1606|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|123nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013819|Y116F11A.6|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013820|Y116F11B.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00013820|Y116F11B.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00013822|Y116F11B.6|624nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013823|Y116F11B.7|109nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013823|Y116F11B.7|116nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00013823|Y116F11B.7|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013824|Y116F11B.8|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00013824|Y116F11B.8|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00013825|Y116F11B.9a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013827|Y116F11B.11|1526nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013827|Y116F11B.11|1562nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013827|Y116F11B.11|1584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013828|Y116F11B.13|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013829|Y116F11B.14|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013829|Y116F11B.14|1129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013830|ZC15.1|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013830|ZC15.1|1113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013832|ZC15.3|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013833|ZC15.5|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013833|ZC15.5|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013835|mlt-4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013835|mlt-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013835|mlt-4|942nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013836|fbxa-29|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013836|fbxa-29|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013836|fbxa-29|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013836|fbxa-29|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013836|fbxa-29|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013837|fbxa-30|1246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013837|fbxa-30|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013837|fbxa-30|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013837|fbxa-30|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013838|fbxa-31|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013838|fbxa-31|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=360|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013839|fbxa-32|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013839|fbxa-32|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013839|fbxa-32|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013839|fbxa-32|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|1202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|1361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|1365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013844|fbxa-50|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|1289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6044|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3950|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013845|fbxa-37|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013846|ZC84.1|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00013846|ZC84.1|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013846|ZC84.1|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2898|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013847|cls-3|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013848|npr-29|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013848|npr-29|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013848|npr-29|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013848|npr-29|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013848|npr-29|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3571|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013849|ZC84.6|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013850|ZC84.7|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=198|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00013850|ZC84.7|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013850|ZC84.7|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00013850|ZC84.7|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00013852|hhat-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|1059nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1064|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013853|ZC116.1a|947nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013854|cyc-2.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013854|cyc-2.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013854|cyc-2.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5734|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013854|cyc-2.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013854|cyc-2.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1160|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013855|ZC116.3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013856|ZC168.2|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013857|orc-5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013857|orc-5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013857|orc-5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013857|orc-5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1343|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013857|orc-5|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013857|orc-5|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013858|ssp-34|1452nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013858|ssp-34|1458nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013858|ssp-34|1469nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013858|ssp-34|1473nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013858|ssp-34|1475nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013858|ssp-34|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1928|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013858|ssp-34|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013859|ZC247.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013859|ZC247.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013859|ZC247.1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2955|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013859|ZC247.1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013860|ZC247.2|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1408|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013862|wdr-5.3|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013863|ZC302.3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013863|ZC302.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013863|ZC302.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013865|ZC334.7|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00013865|ZC334.7|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013866|cbs-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013866|cbs-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013866|cbs-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013866|cbs-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105991|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013867|ZC373.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013868|ZC373.3b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|329nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|331nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|336nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|339nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013869|ZC373.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013870|ZC373.5|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013870|ZC373.5|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013870|ZC373.5|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013870|ZC373.5|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013870|ZC373.5|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013871|gnrr-3|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013871|gnrr-3|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013871|gnrr-3|908nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013871|gnrr-3|910nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|208nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|213nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|218nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|221nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013872|ZC374.2|225nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013873|ZC376.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013873|ZC376.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013874|ZC376.2b|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013874|ZC376.2b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1520|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013874|ZC376.2b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013874|ZC376.2b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013874|ZC376.2b|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013874|ZC376.2c|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013874|ZC376.2c|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=189|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013875|ZC376.3|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|1238nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|310nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013876|ceh-74|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013877|ZC376.6a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013877|ZC376.6a|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013877|ZC376.6a|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2123|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00013877|ZC376.6a|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013878|atfs-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013878|atfs-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013878|atfs-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013878|atfs-1|275nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4943|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013878|atfs-1|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013878|atfs-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013878|atfs-1|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013879|ZC376.8|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013879|ZC376.8|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013880|mppb-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013880|mppb-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2460|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00013880|mppb-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013881|mans-4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013881|mans-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013881|mans-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013881|mans-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013881|mans-4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1228|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013881|mans-4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1802|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19877|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18574|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290928|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46011|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013882|ZC410.5a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=939|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013883|npr-13|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013884|ZC412.3.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2771|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013884|ZC412.3.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18209|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013885|ZC412.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013886|ZC412.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013886|ZC412.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013887|nspa-5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013887|nspa-5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013889|ZC412.8|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00013889|ZC412.8|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=494|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|1351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013890|ZC412.9|950nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14247|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013891|ZC434.3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013891|ZC434.3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1954|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013891|ZC434.3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013891|ZC434.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013891|ZC434.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|1082nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1560|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=599|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013892|ZC434.4.1|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1755|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7b.3|1034nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7b.3|1079nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7b.3|1207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7b.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7b.3|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1601|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7b.3|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013893|ZC434.7b.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5309|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3400|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013894|ZC434.8.1|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2145|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013895|ZC434.9a|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013896|ZC443.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1164|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013897|ZC443.2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013897|ZC443.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=940|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013897|ZC443.2|147nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013897|ZC443.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013897|ZC443.2|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|1049nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|293nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2268|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=480|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2177|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|309nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013898|ZC443.3|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14541|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=978|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8898|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|675nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|678nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013899|ZC443.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013900|ugt-18|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013900|ugt-18|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013901|ugt-16|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013902|ZC455.1c|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013902|ZC455.1c|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013902|ZC455.1c|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013902|ZC455.1c|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013903|ugt-3|1297nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013904|ugt-6|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=379|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013905|ugt-4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013906|ugt-5|1094nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013906|ugt-5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013906|ugt-5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=601|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013906|ugt-5|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013906|ugt-5|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013906|ugt-5|965nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=679|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013907|sre-20|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013909|srbc-44|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013911|irld-60|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013911|irld-60|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013911|irld-60|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013911|irld-60|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013911|irld-60|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013912|irld-19|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013913|irld-61|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013914|lgc-37|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013914|lgc-37|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013914|lgc-37|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013914|lgc-37|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013914|lgc-37|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013915|irld-20|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013916|ZC504.1a|1468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013916|ZC504.1a|1554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013916|ZC504.1a|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013916|ZC504.1a|348nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013916|ZC504.1a|358nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013916|ZC504.1a|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013917|ZC504.3|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013917|ZC504.3|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013917|ZC504.3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013917|ZC504.3|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013917|ZC504.3|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013917|ZC504.3|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013917|ZC504.3|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|221nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1457|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013919|ZC506.1|764nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|362nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|366nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|376nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1257|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|379nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|383nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013920|pssy-1|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013921|best-22|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013921|best-22|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013921|best-22|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013921|best-22|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013921|best-22|679nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013921|best-22|687nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013923|ghi-1|1030nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013923|ghi-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013923|ghi-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013923|ghi-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013923|ghi-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013923|ghi-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013923|ghi-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|347nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9310|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3786|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|408nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00013924|rad-23|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=975|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=793|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013925|ZK20.4a.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1215|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013926|nep-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013927|clec-95|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00013927|clec-95|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00013928|clec-94|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00013928|clec-94|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00013930|clec-96|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00013930|clec-96|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00013931|clec-97|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013931|clec-97|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013931|clec-97|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013931|clec-97|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013931|clec-97|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013931|clec-97|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013933|clec-99|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013933|clec-99|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013933|clec-99|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013934|ZK131.11b|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013934|ZK131.11b|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013934|ZK131.11b|315nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013934|ZK131.11b|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013934|ZK131.11b|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013934|ZK131.11b|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4294|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013935|ZK218.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013937|ZK218.3|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013938|ZK218.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013939|ZK218.5|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013941|ZK218.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013942|ZK218.8|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013942|ZK218.8|1240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013942|ZK218.8|1482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013942|ZK218.8|1584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013943|ZK218.11|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013946|ZK228.3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=589|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013946|ZK228.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013947|ZK228.4a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1449|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013947|ZK228.4a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013947|ZK228.4a|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013947|ZK228.4a|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013947|ZK228.4a|607nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013947|ZK228.4a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=776|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013947|ZK228.4a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013949|ZK262.2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00013949|ZK262.2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013949|ZK262.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013949|ZK262.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00013949|ZK262.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013949|ZK262.2|473nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013950|ZK262.3|850nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013950|ZK262.3|857nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013950|ZK262.3|860nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00013950|ZK262.3|867nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013950|ZK262.3|870nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013950|ZK262.3|875nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013951|ZK262.4|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013951|ZK262.4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013951|ZK262.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013951|ZK262.4|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013954|ZK262.9|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013954|ZK262.9|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013955|kri-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00013956|ZK265.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013956|ZK265.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013956|ZK265.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=885|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013956|ZK265.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|1258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1402|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013957|sre-23|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013958|ZK265.6|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013958|ZK265.6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=859|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013958|ZK265.6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1113|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013958|ZK265.6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013958|ZK265.6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013958|ZK265.6|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013958|ZK265.6|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8310|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013959|ZK265.7|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013960|cutl-8|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013960|cutl-8|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013960|cutl-8|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013960|cutl-8|209nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=26|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013960|cutl-8|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013961|ZK285.2|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013961|ZK285.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013961|ZK285.2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013961|ZK285.2|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1141|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1722|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=621|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013962|ZK287.1b|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013963|sulp-8|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013963|sulp-8|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013963|sulp-8|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013963|sulp-8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013963|sulp-8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013963|sulp-8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|295nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2169|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013964|ZK287.3|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013965|ZK287.4a|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013965|ZK287.4a|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013965|ZK287.4a|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013965|ZK287.4a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013966|ztf-9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1017|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00013966|ztf-9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013966|ztf-9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013967|ZK287.7.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1137|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013967|ZK287.7.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013967|ZK287.7.2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013967|ZK287.7.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00013967|ZK287.7.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013968|ZK287.9|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013968|ZK287.9|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013968|ZK287.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013968|ZK287.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013968|ZK287.9|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=846|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013968|ZK287.9|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013969|tep-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013969|tep-1|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013969|tep-1|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=676|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013969|tep-1|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013970|klu-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013970|klu-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013970|klu-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013970|klu-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00013970|klu-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013971|scl-19|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013971|scl-19|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013971|scl-19|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013971|scl-19|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013972|scl-20|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013972|scl-20|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013972|scl-20|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013972|scl-20|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013973|asp-18|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=392|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013973|asp-18|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=863|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013973|asp-18|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013973|asp-18|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013974|npr-9|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00013974|npr-9|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013974|npr-9|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013974|npr-9|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013974|npr-9|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013974|npr-9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00013975|ZK455.5|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013975|ZK455.5|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013975|ZK455.5|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013976|nhr-33|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013976|nhr-33|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013976|nhr-33|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013976|nhr-33|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013976|nhr-33|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013976|nhr-33|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013976|nhr-33|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013978|ZK507.1|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013978|ZK507.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013978|ZK507.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013978|ZK507.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013978|ZK507.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013978|ZK507.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013979|ZK507.3|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013979|ZK507.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013979|ZK507.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013979|ZK507.3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013979|ZK507.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013979|ZK507.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013980|dos-1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013980|dos-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013980|dos-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013980|dos-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013980|dos-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013980|dos-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013980|dos-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013982|ZK512.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013982|ZK512.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=339|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013983|ZK512.2b|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2083|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=942|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=997|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=438|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013984|ZK512.4|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1822|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013985|sec-16|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|1522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|1555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3493|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=731|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1271|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013986|ZK512.7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013987|ZK512.8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013987|ZK512.8|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013987|ZK512.8|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1854|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013987|ZK512.8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|1541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|1544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|1599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|1601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|289nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1257|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|616nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|620nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|624nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013988|ZK512.10|878nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013989|ZK512.11|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013989|ZK512.11|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1035|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013989|ZK512.11|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013989|ZK512.11|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013989|ZK512.11|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013994|ZK524.4|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013994|ZK524.4|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013994|ZK524.4|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013994|ZK524.4|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1626|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013994|ZK524.4|513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013994|ZK524.4|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013994|ZK524.4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013996|ZK550.2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00013996|ZK550.2|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00013997|ZK550.3|1045nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00013997|ZK550.3|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4368|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013997|ZK550.3|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013998|ZK550.4|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013998|ZK550.4|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013998|ZK550.4|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013998|ZK550.4|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=941|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00013998|ZK550.4|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=337|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013998|ZK550.4|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00013998|ZK550.4|328nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=123|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00013999|ZK550.5|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00013999|ZK550.5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00013999|ZK550.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00013999|ZK550.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00013999|ZK550.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00013999|ZK550.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014000|ZK550.6|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014000|ZK550.6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3345|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014000|ZK550.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014000|ZK550.6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014001|pyk-2|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014001|pyk-2|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00014001|pyk-2|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014001|pyk-2|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014001|pyk-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3218|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014001|pyk-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014002|ZK593.2a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2090|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014003|ZK593.3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014004|fic-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014004|fic-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014004|fic-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00014004|fic-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1373|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014004|fic-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2123|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014006|ZK596.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014007|ZK596.2|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014007|ZK596.2|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00014007|ZK596.2|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014007|ZK596.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014008|ZK596.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014008|ZK596.3|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014008|ZK596.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014009|lips-6|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014009|lips-6|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014011|ZK632.2|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014011|ZK632.2|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014011|ZK632.2|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014011|ZK632.2|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1895|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014011|ZK632.2|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014011|ZK632.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4332|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|906nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|909nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|912nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014012|riok-3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|1171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|1220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|1364nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|1369nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1975|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1506|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014013|ZK632.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1321|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|1338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|1541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|1551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|1577nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014014|ZK632.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|664nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2629|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014015|panl-3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19329|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12731|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|289nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|295nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014016|ZK632.9.1|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|1450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|186nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|190nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=73|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14882|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1840|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|503nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|524nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|527nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014017|ZK632.10|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014018|ZK632.11|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1776|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00014018|ZK632.11|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=562|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014018|ZK632.11|115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014018|ZK632.11|1188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014018|ZK632.11|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014018|ZK632.11|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014018|ZK632.11|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2985|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014019|ZK632.12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=244|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=378|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=808|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014020|ZK632.14|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014021|svop-1|1131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014021|svop-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014021|svop-1|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3290|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014021|svop-1|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014021|svop-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014021|svop-1|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014021|svop-1|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=302|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4762|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014022|ZK637.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3766|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=269|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014023|lnkn-1|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1338|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014024|ZK637.4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=279|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6267|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014025|asna-1|729nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014027|tpk-1|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014028|trxr-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014028|trxr-2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014028|trxr-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=687|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014028|trxr-2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014028|trxr-2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014029|ZK637.12.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1470|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014029|ZK637.12.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6246|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2594|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|56nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|63nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014030|glb-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=694|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14523|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=713|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014031|ZK637.14|896nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014032|ZK637.15|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014032|ZK637.15|572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|1185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3793|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|1355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|1375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1365|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014033|arrd-15|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014034|ZK643.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014034|ZK643.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014034|ZK643.2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=713|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014034|ZK643.2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1373|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00014034|ZK643.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2792|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014035|seb-2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014036|ZK643.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014036|ZK643.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014036|ZK643.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=736|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014036|ZK643.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1616|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014036|ZK643.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014037|ZK643.6|1219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014037|ZK643.6|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014037|ZK643.6|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014039|ZK662.2|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014039|ZK662.2|113nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014039|ZK662.2|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3638|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014039|ZK662.2|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4607|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014039|ZK662.2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014039|ZK662.2|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=169|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014039|ZK662.2|99nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014040|ZK662.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014041|ZK666.1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014042|ZK666.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014043|clec-58|1337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014044|ZK666.4|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00014044|ZK666.4|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00014045|clec-59|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014046|clec-60|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014046|clec-60|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014046|clec-60|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014046|clec-60|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014046|clec-60|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014047|clec-61|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014047|clec-61|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014047|clec-61|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014048|ZK666.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014048|ZK666.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014049|ZK666.11b|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014050|ZK666.12|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2628|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|1295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|297nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014051|spv-1|817nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014052|ZK669.2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014052|ZK669.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2469|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014053|ZK669.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1474|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|275nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3198|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=244|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014054|ZK669.4|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014055|ZK669.5b|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014055|ZK669.5b|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014055|ZK669.5b|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=705|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014055|ZK669.5b|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014055|ZK669.5b|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014055|ZK669.5b|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014055|ZK669.5b|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1a|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1b|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=687|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1b|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1b|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1b|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1b|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014057|ZK673.1b|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|350nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1174|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5809|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014058|ZK673.2|715nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014060|ZK673.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014061|ZK673.5|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014062|ZK673.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014062|ZK673.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014062|ZK673.6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=381|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014062|ZK673.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014063|clec-143|1459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014063|clec-143|1467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014063|clec-143|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014063|clec-143|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014063|clec-143|240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014063|clec-143|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014063|clec-143|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014064|sdz-37|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014064|sdz-37|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014065|ZK673.11c|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=587|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014066|rev-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014067|ZK675.4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014067|ZK675.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014067|ZK675.4|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014068|nhr-255|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014070|srxa-9|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014073|ZK757.1b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014073|ZK757.1b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1994|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014074|ZK757.2|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|1515nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|1531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=734|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|535nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|540nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|544nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|547nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=616|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|551nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=784|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|555nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|588nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014075|dhhc-4|820nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=707|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|58nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|69nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014076|ZK792.1b|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014077|ZK792.4a|165nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014077|ZK792.4a|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014077|ZK792.4a|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014077|ZK792.4a|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014078|ZK792.5|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2583|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014078|ZK792.5|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014078|ZK792.5|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014078|ZK792.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014078|ZK792.5|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|1142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|1145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|1458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|1578nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|1583nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|1585nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=266|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2093|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2812|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014079|ZK792.7a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014080|atg-4.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014080|atg-4.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00014080|atg-4.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014080|atg-4.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014080|atg-4.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014080|atg-4.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|1313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|1492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|313nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=292|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|471nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014081|ZK795.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014082|ZK795.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014083|ZK795.3|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014083|ZK795.3|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014083|ZK795.3|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014083|ZK795.3|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=282|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00014083|ZK795.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014083|ZK795.3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014083|ZK795.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1614|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014084|snb-7|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00014084|snb-7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00014085|ZK809.1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014085|ZK809.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1753|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6123|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=846|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=951|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014086|ZK809.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2706|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014087|ZK809.5b|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014089|ZK822.1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014089|ZK822.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014090|ZK822.2.1|1551nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014090|ZK822.2.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014090|ZK822.2.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014090|ZK822.2.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3978|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014090|ZK822.2.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014090|ZK822.2.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014090|ZK822.2.1|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014091|ZK822.4|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014092|ZK822.5a.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014092|ZK822.5a.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014092|ZK822.5a.2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014092|ZK822.5a.2|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014092|ZK822.5a.2|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014092|ZK822.5a.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1203|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014093|ZK829.1|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014093|ZK829.1|184nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014093|ZK829.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014093|ZK829.1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014094|ZK829.3|384nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014094|ZK829.3|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=439|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=273|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29258|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014095|gdh-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=440|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|286nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|324nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|336nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=594|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|344nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5824|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|349nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|355nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|357nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014096|ZK829.7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|1046nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=631|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|292nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|739nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|826nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014097|ZK829.9|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014098|ZK836.2b.1|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2626|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014098|ZK836.2b.1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014098|ZK836.2b.1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=765|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014098|ZK836.2b.1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014099|ZK836.3|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00014099|ZK836.3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014099|ZK836.3|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014099|ZK836.3|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014099|ZK836.3|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014100|ZK849.1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1957|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014100|ZK849.1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014100|ZK849.1|227nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014100|ZK849.1|572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6072|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7273|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014101|gopc-1|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014102|best-25|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014102|best-25|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014102|best-25|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014102|best-25|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014102|best-25|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014103|best-26|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014103|best-26|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014103|best-26|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014103|best-26|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014103|best-26|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014103|best-26|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014104|ZK849.6|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=722|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014104|ZK849.6|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=192|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014104|ZK849.6|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014105|ZK856.4b|1558nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014105|ZK856.4b|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014105|ZK856.4b|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1017|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3909|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014106|ZK856.5|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|413nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=983|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|419nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014107|ZK856.6|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=529|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=421|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5950|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014108|ZK856.7.2|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4710|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014109|chpf-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1368|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014111|rpc-25|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|1039nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|1056nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2523|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014112|ZK856.11|590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=857|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|290nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=839|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014113|hpo-40|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=426|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=603|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014114|tftc-3|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8562|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1840|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|1438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014115|gld-4|853nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|1046nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|1054nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|1188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|1193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|1196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=712|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014116|ZK858.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014117|clec-91|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7745|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014117|clec-91|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014117|clec-91|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014117|clec-91|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014117|clec-91|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014117|clec-91|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014117|clec-91|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1716|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014118|ZK858.5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2695|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1912|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=857|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014119|ZK858.6b.2|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014120|ZK858.7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2341|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014120|ZK858.7|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014120|ZK858.7|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014120|ZK858.7|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014120|ZK858.7|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014120|ZK858.7|978nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=939|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014121|ZK858.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014122|ZK863.1|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014122|ZK863.1|1462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1037|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00014122|ZK863.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014122|ZK863.1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014122|ZK863.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014123|elpc-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2329|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4343|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014124|usip-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=806|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=761|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014125|ZK863.8|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014127|ZK892.3|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014127|ZK892.3|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014128|ZK892.4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014128|ZK892.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014128|ZK892.4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00014129|ZK892.5|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014129|ZK892.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014129|ZK892.5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014129|ZK892.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014130|ZK892.6|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014130|ZK892.6|400nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014130|ZK892.6|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014130|ZK892.6|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014131|sdz-38|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014132|ZK896.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014135|ZK896.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=402|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014136|ZK896.5.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014137|clec-187|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014137|clec-187|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014137|clec-187|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014137|clec-187|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1032|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014137|clec-187|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=474|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4380|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014138|clec-186|94nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|1081nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|453nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|526nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|528nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=385|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|532nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=438|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|536nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|538nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=113|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|542nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|545nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=99|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=696|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014139|nstp-5|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|421nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=570|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=531|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014140|ZK899.1|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014141|ZK899.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014141|ZK899.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014141|ZK899.2|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=620|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00014141|ZK899.2|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=754|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014141|ZK899.2|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014141|ZK899.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014142|ZK899.3|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014144|ZK899.6|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014144|ZK899.6|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014144|ZK899.6|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00014145|ZK899.7|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014145|ZK899.7|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014145|ZK899.7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014145|ZK899.7|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014148|ZK909.3.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014148|ZK909.3.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014148|ZK909.3.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4025|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014149|fbxb-70|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014150|ZK909.6|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014150|ZK909.6|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014150|ZK909.6|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014150|ZK909.6|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014150|ZK909.6|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014150|ZK909.6|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=282|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014150|ZK909.6|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2117|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|1024nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1513|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=451|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|360nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|362nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014151|vps-15|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014152|ZK930.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014152|ZK930.2|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014152|ZK930.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014152|ZK930.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014152|ZK930.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014152|ZK930.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014152|ZK930.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014153|vab-23|726nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014153|vab-23|728nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014153|vab-23|731nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=718|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014153|vab-23|734nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=182|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014153|vab-23|737nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014154|ZK930.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014154|ZK930.4|205nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014154|ZK930.4|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014154|ZK930.4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1171|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014154|ZK930.4|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014154|ZK930.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014154|ZK930.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014155|ZK930.5|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014155|ZK930.5|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014156|ZK930.6|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014156|ZK930.6|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014156|ZK930.6|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014157|ZK930.7|1579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014157|ZK930.7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014157|ZK930.7|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014157|ZK930.7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=551|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014157|ZK930.7|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014158|ZK938.1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014158|ZK938.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1342|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014158|ZK938.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=663|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014158|ZK938.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014158|ZK938.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014158|ZK938.1|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00014158|ZK938.1|885nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=582|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=567|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014159|arrd-4|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014160|ZK938.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014160|ZK938.3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014160|ZK938.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00014160|ZK938.3|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014161|arrd-5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014161|arrd-5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014161|arrd-5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014163|rnh-1.2|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2131|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014164|lact-2|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014165|puf-12|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014165|puf-12|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014165|puf-12|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014165|puf-12|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014166|ZK945.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014168|ZK945.6a|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014168|ZK945.6a|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014168|ZK945.6a|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014169|ZK945.7|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014169|ZK945.7|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=574|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014169|ZK945.7|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1022|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014170|ZK945.8|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1373|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00014171|nep-26|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014172|clpp-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014172|clpp-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014172|clpp-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3788|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014172|clpp-1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014172|clpp-1|1596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014172|clpp-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014172|clpp-1|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014173|ZK970.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014173|ZK970.7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014173|ZK970.7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014173|ZK970.7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=729|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014173|ZK970.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=702|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014174|ZK970.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014174|ZK970.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014174|ZK970.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014174|ZK970.8|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014174|ZK970.8|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=330|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|58nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10860|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1382|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014175|ZK971.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014176|ZK1010.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014176|ZK1010.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014176|ZK1010.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014176|ZK1010.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=476|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014176|ZK1010.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1737|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014176|ZK1010.2|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014177|frg-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014177|frg-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014177|frg-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2351|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014177|frg-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014178|ZK1010.4a|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=524|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014178|ZK1010.4a|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014178|ZK1010.4a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014179|ZK1010.5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014179|ZK1010.5|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=718|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014180|ZK1010.6|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014180|ZK1010.6|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014180|ZK1010.6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014180|ZK1010.6|93nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014181|ZK1010.8.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014181|ZK1010.8.1|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014181|ZK1010.8.1|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014181|ZK1010.8.1|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014181|ZK1010.8.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00014181|ZK1010.8.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014182|ZK1025.2|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1023|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2354|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014183|ZK1025.3.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=828|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014184|ZK1025.4a|1271nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014184|ZK1025.4a|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014184|ZK1025.4a|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014186|nhr-244|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014188|ZK1025.8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2065|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014188|ZK1025.8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014189|nhr-245|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014189|nhr-245|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014189|nhr-245|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014189|nhr-245|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014189|nhr-245|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014189|nhr-245|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014194|ZK1037.6|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014194|ZK1037.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014195|srz-10|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014195|srz-10|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014195|srz-10|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014196|ZK1053.1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014196|ZK1053.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014197|ZK1053.2|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014197|ZK1053.2|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014197|ZK1053.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014197|ZK1053.2|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014197|ZK1053.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014198|ZK1053.3|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014199|ZK1053.4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014199|ZK1053.4|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014199|ZK1053.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014200|scrm-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014200|scrm-2|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014200|scrm-2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014200|scrm-2|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014200|scrm-2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014201|ZK1053.6|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014201|ZK1053.6|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014201|ZK1053.6|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3967|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1234|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=405|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014202|mmcm-1|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014203|ZK1058.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1432|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2617|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1598|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014204|ccdc-47|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014205|ZK1058.5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014205|ZK1058.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014205|ZK1058.5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=889|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014205|ZK1058.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014206|nit-1|1207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014206|nit-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014206|nit-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014206|nit-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014206|nit-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6335|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014207|ZK1058.9b|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|1372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|1511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|414nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3440|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|419nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|422nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|426nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014208|ZK1067.2b|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014209|ZK1067.3|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1137|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014209|ZK1067.3|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=911|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00014209|ZK1067.3|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014210|ZK1067.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=777|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014210|ZK1067.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=620|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9993|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014213|ZK1073.1.1|624nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1570|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|492nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|610nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014214|ZK1073.2|618nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=737|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|356nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=537|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014215|obr-3|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014218|ZK1098.1a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014218|ZK1098.1a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014218|ZK1098.1a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1111|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014218|ZK1098.1a|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014218|ZK1098.1a|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014218|ZK1098.1a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014218|ZK1098.1a|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014219|ZK1098.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=919|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014219|ZK1098.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014219|ZK1098.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014219|ZK1098.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014219|ZK1098.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014220|ZK1098.3|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=175|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014220|ZK1098.3|559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014220|ZK1098.3|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014221|ZK1098.4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014221|ZK1098.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1600|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014221|ZK1098.4|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=942|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014221|ZK1098.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014221|ZK1098.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014221|ZK1098.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014222|trpp-3|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014222|trpp-3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014222|trpp-3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014222|trpp-3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014222|trpp-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3475|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014222|trpp-3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014222|trpp-3|866nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014223|ZK1098.6|1141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014223|ZK1098.6|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014223|ZK1098.6|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014223|ZK1098.6|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014223|ZK1098.6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1159|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00014223|ZK1098.6|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|489nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3377|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014224|mrps-23|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014225|ZK1098.9|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014226|ZK1098.11|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014226|ZK1098.11|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2336|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014226|ZK1098.11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014227|ZK1128.1.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014227|ZK1128.1.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014227|ZK1128.1.1|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3150|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014227|ZK1128.1.1|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=395|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014228|mett-10|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014228|mett-10|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014228|mett-10|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014228|mett-10|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014228|mett-10|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014228|mett-10|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=576|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014229|ZK1128.3|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2215|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014230|ZK1128.4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|181nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=924|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|183nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=988|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|196nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|511nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|515nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|738nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014232|ttll-4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4582|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=197|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=269|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014233|ZK1128.7|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=786|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1774|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|271nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|276nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014234|vps-29|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014235|ZK1225.1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014235|ZK1225.1|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014238|ZK1225.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014239|ZK1225.5|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014240|htas-1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014240|htas-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1728|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014241|ZK1251.3|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014241|ZK1251.3|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014241|ZK1251.3|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014241|ZK1251.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014241|ZK1251.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014242|sdz-36|1423nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014242|sdz-36|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014242|sdz-36|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1942|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=284|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014243|dcaf-1|410nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4447|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=839|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014244|ZK1307.1b|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014245|ZK1307.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014245|ZK1307.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014245|ZK1307.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014245|ZK1307.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014246|ZK1307.3|1048nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014246|ZK1307.3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014246|ZK1307.3|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014246|ZK1307.3|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=609|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014246|ZK1307.3|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014247|ZK1307.4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014247|ZK1307.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014247|ZK1307.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014247|ZK1307.4|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014247|ZK1307.4|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2637|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=476|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|214nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014248|ZK1307.7a|920nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=455|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=181|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3521|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|222nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014249|ZK1307.8.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2539|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014250|ZK1307.9|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014251|gstk-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014251|gstk-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014251|gstk-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014251|gstk-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1573|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014251|gstk-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014251|gstk-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5771|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014252|ZK1320.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1791|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3431|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014253|ZK1320.3.1|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014254|cyp-13A10|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014254|cyp-13A10|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014254|cyp-13A10|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00014254|cyp-13A10|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=784|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014254|cyp-13A10|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014255|ZK1320.5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014255|ZK1320.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014256|ZK1320.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014256|ZK1320.7|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014256|ZK1320.7|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=683|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014258|ZK1320.9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014258|ZK1320.9|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014258|ZK1320.9|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7336|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00014258|ZK1320.9|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014258|ZK1320.9|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014258|ZK1320.9|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014258|ZK1320.9|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=660|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|1602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4859|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014259|ZK1320.11b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014260|ZK1321.1|1546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014260|ZK1321.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014260|ZK1321.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|1143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4835|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014261|shk-1|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014262|ZK1321.4a|185nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014262|ZK1321.4a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014262|ZK1321.4a|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1128|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014262|ZK1321.4a|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2316|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014262|ZK1321.4a|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014300|D2023.1b.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014300|D2023.1b.1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=571|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014300|D2023.1b.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014300|D2023.1b.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014300|D2023.1e|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|119nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=396|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|122nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|124nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1587|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014569|bkip-1|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7556|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=908|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014666|C05D12.3a.2|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014668|C06C3.9|1349nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014668|C06C3.9|1369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014668|C06C3.9|1379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00014668|C06C3.9|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014668|C06C3.9|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014668|C06C3.9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014669|C06G8.3c|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00014669|C06G8.3c|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014669|C06G8.3c|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014669|C06G8.3c|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=911|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014669|C06G8.3c|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014669|C06G8.3c|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014697|cyp-25A3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014697|cyp-25A3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014697|cyp-25A3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014697|cyp-25A3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014697|cyp-25A3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=795|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014698|C37A5.3.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014699|C37A5.5|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014700|C37A5.6|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014700|C37A5.6|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1161|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014761|F46A8.11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3372|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3189|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1180|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|191nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1341|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|199nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|206nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014793|H40L08.2a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014801|K08E5.1b|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014801|K08E5.1b|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00014801|K08E5.1b|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014807|M04D5.1|572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4821|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6560|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014826|R13H4.2a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014836|T09F5.12a|827nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014836|T09F5.12a|830nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014836|T09F5.12a|832nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014836|T09F5.12a|837nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014836|T09F5.12a|870nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|1496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|177nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=415|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6836|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|189nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014848|VM106R.1|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=309|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014864|Y18D10A.22|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=901|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014871|Y37H9A.5.1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014914|Y52B11A.11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014914|Y52B11A.11|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00014914|Y52B11A.11|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014924|Y57G11C.28|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014924|Y57G11C.28|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014926|Y57G11C.30a|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11755|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=501|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014938|mdt-9|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=918|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014965|Y106G6D.5b|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014989|best-23|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014989|best-23|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1101|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014989|best-23|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014989|best-23|561nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014989|best-23|877nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014997|AC7.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=857|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014997|AC7.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00014998|AH9.1|1255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00014998|AH9.1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00014998|AH9.1|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00014998|AH9.1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00014998|AH9.1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00014998|AH9.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00014999|AH9.3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=884|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015000|AH9.4|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015001|B0025.4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015001|B0025.4|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015001|B0025.4|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2609|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015001|B0025.4|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=493|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015001|B0025.4|1505nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015001|B0025.4|1530nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015002|B0034.1|1472nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015002|B0034.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015002|B0034.1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015002|B0034.1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015003|B0034.2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=604|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015003|B0034.2|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015004|B0034.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015005|B0034.5|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015005|B0034.5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015005|B0034.5|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015005|B0034.5|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015005|B0034.5|753nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015006|B0041.1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015006|B0041.1|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=283|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015006|B0041.1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015006|B0041.1|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|823nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|835nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10899|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015007|ain-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|1052nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|1217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=956|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|909nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015008|lmd-2|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3571|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=492|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015009|B0041.5|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|925nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015010|ptps-1|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|130nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1018|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=240|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=991|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5624|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015011|B0041.8.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015012|bath-20|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015012|bath-20|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015012|bath-20|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015012|bath-20|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015014|bath-24|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015014|bath-24|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015014|bath-24|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015014|bath-24|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015014|bath-24|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015014|bath-24|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=263|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015017|B0205.1b|1247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015017|B0205.1b|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1516|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015017|B0205.1b|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015017|B0205.1b|327nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015017|B0205.1b|493nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015017|B0205.1b|495nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|612nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|630nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015018|srz-85|814nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015019|B0205.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015019|B0205.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015019|B0205.4|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015019|B0205.4|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015019|B0205.4|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2090|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015021|B0205.6|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|1184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|1199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4724|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015022|B0205.8|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1977|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015023|B0205.9|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015024|B0205.10.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2523|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015024|B0205.10.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015024|B0205.10.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|1007nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4834|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|995nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015025|mrpl-9|998nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015026|B0207.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015027|B0207.2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015027|B0207.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015027|B0207.2|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015027|B0207.2|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015027|B0207.2|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015027|B0207.2|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015028|B0207.5a|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015029|B0207.6|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015029|B0207.6|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1342|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015029|B0207.6|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=235|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015030|B0207.7|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015032|B0207.9|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015032|B0207.9|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015032|B0207.9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015032|B0207.9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015033|B0207.10|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015033|B0207.10|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015033|B0207.10|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015033|B0207.10|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015033|B0207.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1347|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015034|B0207.11|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015034|B0207.11|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015034|B0207.11|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015034|B0207.11|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015035|otpl-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015035|otpl-1|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015035|otpl-1|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=167|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015035|otpl-1|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015036|sre-5|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015036|sre-5|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015037|B0212.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015037|B0212.3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015038|nstp-6|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=327|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015038|nstp-6|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015038|nstp-6|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015038|nstp-6|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015038|nstp-6|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015040|cyp-34A5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015040|cyp-34A5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015040|cyp-34A5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015040|cyp-34A5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015041|cyp-34A6|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015041|cyp-34A6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015041|cyp-34A6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015041|cyp-34A6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015042|cyp-34A7|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015042|cyp-34A7|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1556|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015043|cyp-34A8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=442|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015044|cyp-34A9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=544|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015044|cyp-34A9|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015044|cyp-34A9|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015044|cyp-34A9|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015044|cyp-34A9|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015044|cyp-34A9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015044|cyp-34A9|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015045|cyp-34A10|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015045|cyp-34A10|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015045|cyp-34A10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015045|cyp-34A10|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015046|nlp-34|126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015046|nlp-34|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015046|nlp-34|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=770|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015046|nlp-34|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2362|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00015046|nlp-34|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|1063nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1569|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=339|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015047|faah-1|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015048|faah-2|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015048|faah-2|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=367|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015048|faah-2|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1115|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015048|faah-2|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015048|faah-2|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015049|B0218.5|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015049|B0218.5|568nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015049|B0218.5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015049|B0218.5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015049|B0218.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015050|clec-51|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015050|clec-51|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=847|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015050|clec-51|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015050|clec-51|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015050|clec-51|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015051|B0218.7|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1064|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015052|clec-52|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1554|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015052|clec-52|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=229|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015052|clec-52|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1025|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3876|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015053|B0222.1|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015054|pitr-2|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015054|pitr-2|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015054|pitr-2|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015054|pitr-2|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015054|pitr-2|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015054|pitr-2|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015055|pitr-3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015055|pitr-3|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015055|pitr-3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015055|pitr-3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|298nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|300nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|312nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00015056|B0222.5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015057|gad-3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015057|gad-3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|261nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|263nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015058|B0222.10|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015059|B0228.1|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015059|B0228.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015059|B0228.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1046|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015059|B0228.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015059|B0228.1|962nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015059|B0228.1|965nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015059|B0228.1|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1180|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015061|cpna-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=285|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=930|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015062|trx-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|568nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|906nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015063|B0228.6|908nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015064|B0228.7.1|1278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015064|B0228.7.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015064|B0228.7.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4369|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015064|B0228.7.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=420|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015064|B0228.7.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015064|B0228.7.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015065|B0228.8|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015066|B0228.9|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015066|B0228.9|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015066|B0228.9|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015066|B0228.9|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|40nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015067|B0238.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015069|srt-67|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00015069|srt-67|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00015070|srt-70|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015070|srt-70|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015070|srt-70|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00015072|srt-69|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015072|srt-69|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015072|srt-69|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|1466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=227|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|364nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1179|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=745|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|571nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015073|B0238.9|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8157|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|218nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|223nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015074|natc-2|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=374|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1047|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=196|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1367|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015075|B0238.11|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015076|B0238.12|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015076|B0238.12|1361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015076|B0238.12|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015076|B0238.12|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015076|B0238.12|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1553|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00015079|B0244.4b|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015079|B0244.4b|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015079|B0244.4b|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015080|B0244.5|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015080|B0244.5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015080|B0244.5|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015081|B0244.6|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=190|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015081|B0244.6|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015081|B0244.6|999nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11888|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1257|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015083|egg-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015084|B0244.9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015084|B0244.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00015084|B0244.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015085|B0244.10|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015085|B0244.10|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015085|B0244.10|229nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015085|B0244.10|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015087|B0252.1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015087|B0252.1|94nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=132|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015087|B0252.1|97nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015088|B0252.3a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015088|B0252.3a|1349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015088|B0252.3a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015088|B0252.3a|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015088|B0252.3a|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015088|B0252.3a|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015088|B0252.3a|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015089|B0252.5|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015089|B0252.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015089|B0252.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=946|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015089|B0252.5|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2756|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015091|B0261.1|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1940|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|1253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015092|mrpl-47|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015093|B0261.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2036|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=973|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015094|B0261.6b|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2147|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1157|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|1346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=518|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=998|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015095|B0261.7|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015096|B0261.8|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1030|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015097|B0273.1a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015097|B0273.1a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015097|B0273.1a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015097|B0273.1a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1771|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015097|B0273.1a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015098|snpc-3.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=762|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015098|snpc-3.1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5550|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015099|ggtb-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015100|B0280.2|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00015100|B0280.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015100|B0280.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015100|B0280.2|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015100|B0280.2|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015100|B0280.2|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015101|rpia-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015101|rpia-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015101|rpia-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7350|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015101|rpia-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015101|rpia-1|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=123|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5585|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39491|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1728|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015102|cpg-2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015103|B0280.7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015103|B0280.7|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015103|B0280.7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015103|B0280.7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015103|B0280.7|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1533|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015103|B0280.7|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015104|B0280.9|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1374|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015104|B0280.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015104|B0280.9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015104|B0280.9|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015104|B0280.9|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015105|pot-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015105|pot-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015105|pot-1|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015105|pot-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1267|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015106|B0280.11|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00015106|B0280.11|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00015107|B0280.13|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015107|B0280.13|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015110|B0281.3|1389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015110|B0281.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015110|B0281.3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015110|B0281.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015110|B0281.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015110|B0281.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015110|B0281.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015111|B0281.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015111|B0281.4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015112|B0281.5a|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015112|B0281.5a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015113|B0281.6|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015115|B0286.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015115|B0286.1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015115|B0286.1|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015115|B0286.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015115|B0286.1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=976|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015115|B0286.1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015116|B0286.3|108nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015116|B0286.3|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015116|B0286.3|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015116|B0286.3|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2676|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015116|B0286.3|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|1053nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10653|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68190|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015117|B0294.1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|1479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1380|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|406nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015122|B0302.5|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015124|anmt-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=541|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|281nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|297nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=268|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|351nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|360nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|384nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=455|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015125|B0303.3.1|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015126|B0303.4.2|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6107|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015126|B0303.4.2|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=529|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015126|B0303.4.2|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015126|B0303.4.2|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015126|B0303.4.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1702|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4258|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=904|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|318nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|328nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015128|B0303.7a|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015129|sdz-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015129|sdz-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015129|sdz-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=478|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=748|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00015130|vps-33.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015131|B0303.11a|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015131|B0303.11a|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=569|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015131|B0303.11a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015132|B0303.14|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015132|B0303.14|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=522|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015132|B0303.14|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015132|B0303.14|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015132|B0303.14|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015132|B0303.14|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015133|mrpl-11|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=679|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015133|mrpl-11|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015133|mrpl-11|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015133|mrpl-11|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015133|mrpl-11|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1837|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015134|B0304.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015134|B0304.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015134|B0304.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1248|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015134|B0304.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015135|cyp-23A1|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=192|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015136|B0304.4|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=398|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|526nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015137|B0310.1a|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015138|B0310.2|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015139|B0310.3|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015139|B0310.3|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=166|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|209nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1977|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015141|ugt-46|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015142|B0310.6|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015142|B0310.6|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1035|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|440nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|443nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|453nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|456nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=684|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|703nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2783|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015143|B0336.3|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015145|B0336.5b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015145|B0336.5b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015145|B0336.5b|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015145|B0336.5b|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015145|B0336.5b|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3866|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015145|B0336.5b|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015145|B0336.5b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|1184nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4568|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015146|abi-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015147|B0336.7b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015147|B0336.7b|1204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015147|B0336.7b|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015147|B0336.7b|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1348|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015147|B0336.7b|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|1352nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2112|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015148|hpo-28|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015149|B0336.12|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=973|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|163nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1927|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|166nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=804|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|171nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=191|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|175nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|927nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015150|B0336.13|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015151|B0348.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015151|B0348.1|192nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015151|B0348.1|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015151|B0348.1|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015151|B0348.1|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015152|B0348.2a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1424|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015152|B0348.2a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015153|B0348.5a|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015153|B0348.5a|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|435nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|440nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1732|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015156|B0361.2a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015157|B0361.3.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015157|B0361.3.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015157|B0361.3.2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1807|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015157|B0361.3.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015157|B0361.3.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015158|B0361.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1148|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015159|psd-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015160|B0361.6|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3701|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00015160|B0361.6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015161|pho-5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015161|pho-5|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015161|pho-5|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1061|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015161|pho-5|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2401|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015161|pho-5|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015161|pho-5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2893|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|1269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|1272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|848nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015162|algn-11|971nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015163|B0361.9|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015163|B0361.9|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4299|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015163|B0361.9|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015163|B0361.9|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015163|B0361.9|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|535nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=252|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|537nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3508|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|540nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1548|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|544nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015164|ykt-6|549nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=244|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015165|B0361.11|1101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015165|B0361.11|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015165|B0361.11|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015167|B0403.3|664nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00015167|B0403.3|667nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015167|B0403.3|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015167|B0403.3|674nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5991|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61906|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6758|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1299|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|668nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015168|pdi-6|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|449nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015169|B0403.5|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015171|vang-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015171|vang-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00015171|vang-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015171|vang-1|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015171|vang-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015171|vang-1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1738|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1903|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|273nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015172|B0410.3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015173|trpp-11|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2110|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015173|trpp-11|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015175|srz-4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015175|srz-4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015175|srz-4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6245|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1134|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=359|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015176|vps-51|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015177|tmc-2|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015177|tmc-2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015178|B0416.2|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00015178|B0416.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|1135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|1139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|1207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015179|B0416.3|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015180|B0416.4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015180|B0416.4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015180|B0416.4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1723|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=968|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=689|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=569|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=428|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=689|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015181|B0416.5b|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015182|B0416.7b|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015182|B0416.7b|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015182|B0416.7b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015182|B0416.7b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015182|B0416.7b|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015183|B0432.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015183|B0432.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2087|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1428|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=717|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015184|djr-1.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015185|mrpl-41|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1901|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015185|mrpl-41|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015185|mrpl-41|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015185|mrpl-41|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015185|mrpl-41|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015185|mrpl-41|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015186|misc-1|1561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015186|misc-1|221nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015186|misc-1|225nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=914|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015186|misc-1|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1412|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015186|misc-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015186|misc-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|384nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|391nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|448nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015188|B0432.7b|457nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015189|B0432.8.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015189|B0432.8.1|435nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=587|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015189|B0432.8.1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015189|B0432.8.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015189|B0432.8.1|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015190|B0432.9|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015190|B0432.9|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015190|B0432.9|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015191|B0432.10.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=743|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015191|B0432.10.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015191|B0432.10.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015192|B0432.11|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00015192|B0432.11|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015192|B0432.11|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015193|clec-117|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015193|clec-117|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015193|clec-117|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015194|B0432.13.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015194|B0432.13.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00015194|B0432.13.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015194|B0432.13.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015196|B0454.5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015196|B0454.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015197|B0454.6|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015198|clec-2|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015199|B0454.8|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00015199|B0454.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015200|B0454.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015202|B0478.3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015202|B0478.3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015202|B0478.3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=161|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3090|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015203|B0495.2|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015204|B0495.5.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015204|B0495.5.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1508|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015204|B0495.5.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015204|B0495.5.1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015205|moa-2|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015205|moa-2|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3342|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1305|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015206|B0495.7.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8a|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8a|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8a|164nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1969|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8a|169nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=907|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8a|173nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015207|B0495.8b.1|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015208|B0495.9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015208|B0495.9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9386|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015208|B0495.9|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015208|B0495.9|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015208|B0495.9|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015210|B0496.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015210|B0496.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015214|srtx-1|1417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015214|srtx-1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015214|srtx-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00015215|B0496.6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015215|B0496.6|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015216|valv-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015216|valv-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2452|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015216|valv-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015216|valv-1|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015216|valv-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015216|valv-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015217|tes-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015217|tes-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015217|tes-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1216|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015217|tes-1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015217|tes-1|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015217|tes-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015218|B0507.1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015218|B0507.1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1094|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015218|B0507.1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015218|B0507.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015218|B0507.1|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015218|B0507.1|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2498|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015219|B0507.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015220|B0507.3a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015220|B0507.3a|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015220|B0507.3a|1332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015220|B0507.3a|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015221|B0507.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015221|B0507.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015223|B0507.6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015224|B0507.7|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015225|B0507.8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015225|B0507.8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015226|B0507.9|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015227|B0507.10|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015227|B0507.10|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015228|B0511.2|1226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015228|B0511.2|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=476|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015228|B0511.2|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015229|fbxa-125|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=313|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015229|fbxa-125|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015230|tag-344|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015230|tag-344|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015230|tag-344|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00015230|tag-344|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015231|cutl-14|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015231|cutl-14|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015231|cutl-14|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015231|cutl-14|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015231|cutl-14|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015231|cutl-14|767nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015232|B0511.6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015232|B0511.6|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015232|B0511.6|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015232|B0511.6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6472|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00015232|B0511.6|546nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015232|B0511.6|568nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=758|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=414|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015233|B0511.7|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015235|cdc-26|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015235|cdc-26|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015235|cdc-26|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015235|cdc-26|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3344|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015235|cdc-26|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015235|cdc-26|736nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015236|B0511.11|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015236|B0511.11|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015237|B0511.12a|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2982|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015237|B0511.12a|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=576|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015237|B0511.12a|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015237|B0511.12a|918nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015238|B0511.13a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015238|B0511.13a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1287|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|1005nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|1017nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015241|B0524.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015242|B0524.3|1202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015244|B0524.5|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015244|B0524.5|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015245|B0524.6|1412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015245|B0524.6|1416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3227|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015245|B0524.6|1423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015246|scl-23|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015246|scl-23|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015246|scl-23|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00015246|scl-23|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015246|scl-23|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015247|B0545.4.1|118nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015247|B0545.4.1|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=693|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|1179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|1189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|1198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=544|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|1202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|1217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16798|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5125|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015248|mai-2|960nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1502|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|399nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|405nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|415nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|548nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|557nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|586nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015249|otub-4|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015250|B0546.3c|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1183|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015250|B0546.3c|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015251|B0546.4b|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015251|B0546.4c.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015251|B0546.4c.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015251|B0546.4c.2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015251|B0546.4c.2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3236|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00015251|B0546.4c.2|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015251|B0546.4c.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|1192nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=37|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|1201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|1206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|1232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|1240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|1243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=211|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|1248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015252|B0546.5|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015253|B0547.2|1151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015254|B0554.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00015254|B0554.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00015257|B0554.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015258|B0554.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015259|dod-20|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015259|dod-20|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015259|dod-20|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015259|dod-20|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015260|B0554.7c|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015261|B0563.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015261|B0563.1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|180nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=357|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015262|B0563.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3037|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|359nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|368nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6a|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6c|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6c|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6c|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6c|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6c|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015263|B0563.6c|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015264|B0563.7|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015264|B0563.7|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015264|B0563.7|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1249|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015264|B0563.7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015264|B0563.7|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015264|B0563.7|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015265|B0563.8|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00015265|B0563.8|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00015266|BE0003N10.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015266|BE0003N10.1|223nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=305|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015266|BE0003N10.1|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015266|BE0003N10.1|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015266|BE0003N10.1|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015266|BE0003N10.1|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015267|chin-1|393nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1318|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015267|chin-1|396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015267|chin-1|398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015268|BE0003N10.3b|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015268|BE0003N10.3b|436nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015277|C01B7.7|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015277|C01B7.7|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015277|C01B7.7|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015277|C01B7.7|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015278|C01B10.3|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015278|C01B10.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015278|C01B10.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015278|C01B10.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015278|C01B10.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1840|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015279|C01B10.4b|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015279|C01B10.4b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015279|C01B10.4b|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2915|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|1210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=588|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=309|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015280|C01B10.6d.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015281|C01B10.7a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015281|C01B10.7a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015282|C01B10.8.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015282|C01B10.8.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1198|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015282|C01B10.8.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2255|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015282|C01B10.8.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015282|C01B10.8.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015283|C01B10.9|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015283|C01B10.9|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015283|C01B10.9|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015283|C01B10.9|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015283|C01B10.9|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015283|C01B10.9|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=168|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015283|C01B10.9|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1610|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015284|C01B10.10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2417|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|330nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|334nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015285|gmeb-1|879nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015286|best-3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015286|best-3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015286|best-3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015287|osta-1|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=214|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00015287|osta-1|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015287|osta-1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015287|osta-1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015287|osta-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015287|osta-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015288|best-4|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015288|best-4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015291|C01B12.8|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015291|C01B12.8|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2086|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015291|C01B12.8|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015291|C01B12.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015291|C01B12.8|57nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015291|C01B12.8|60nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015291|C01B12.8|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015292|C01C4.2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015292|C01C4.2|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|1228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2265|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|344nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|351nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|382nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|390nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|661nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3a|681nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3b|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3b|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3b|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015293|C01C4.3b|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015294|C01C10.2b|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015294|C01C10.2b|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015294|C01C10.2b|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015294|C01C10.2b|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015294|C01C10.2b|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=917|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=981|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015295|acl-12|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=928|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1011|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=688|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=538|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015296|C01F1.1|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|1172nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|121nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1509|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|132nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015297|sco-1|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=375|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015298|C01F1.3a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015299|C01F1.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015299|C01F1.4|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015299|C01F1.4|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00015299|C01F1.4|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015299|C01F1.4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=547|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015299|C01F1.4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015300|C01F1.5|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015300|C01F1.5|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|371nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=920|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|377nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=705|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|380nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|382nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015301|C01F1.6|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015303|rga-6|372nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015305|C01G5.3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015305|C01G5.3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015305|C01G5.3|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015305|C01G5.3|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015306|C01G5.4a|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00015306|C01G5.4a|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015306|C01G5.4a|844nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2436|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015307|C01G5.5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1541|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=369|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015308|C01G5.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015309|C01G5.7b|506nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015310|fan-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015310|fan-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015310|fan-1|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015310|fan-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1372|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015310|fan-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015310|fan-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015311|C01G5.9|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015311|C01G5.9|1405nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015311|C01G5.9|1416nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015311|C01G5.9|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015311|C01G5.9|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|1306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6060|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015312|C01G8.1a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|218nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2034|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|225nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|537nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015313|hpo-32|540nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015318|srbc-36|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015320|C02B8.1.1|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12465|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2592|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015322|C02B8.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015323|frpr-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015324|C02B8.6|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015324|C02B8.6|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015324|C02B8.6|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015324|C02B8.6|763nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015324|C02B8.6|766nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015324|C02B8.6|771nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015324|C02B8.6|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015325|C02B8.7|1213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2155|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1620|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1691|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015326|ivd-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3084|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|357nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|365nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015327|snpn-1|970nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|498nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|510nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|692nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5818|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|709nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|772nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|852nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|856nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015328|C02B10.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5262|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3242|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015329|C02B10.4|291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|453nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|457nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1016|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|463nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=302|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|466nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|469nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015330|C02B10.5a.1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015331|C02B10.6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015331|C02B10.6|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015331|C02B10.6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015331|C02B10.6|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|1009nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1378|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015332|tyr-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015333|slc-17.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015333|slc-17.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015334|sup-18|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015334|sup-18|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015334|sup-18|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015334|sup-18|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015334|sup-18|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015335|acdh-6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015335|acdh-6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015335|acdh-6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015335|acdh-6|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00015336|C02D5.2a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015336|C02D5.2a|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015336|C02D5.2a|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=725|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015336|C02D5.2a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015336|C02D5.2a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015336|C02D5.2a|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015337|gsto-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015337|gsto-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015337|gsto-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00015338|catp-2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015339|C02E7.6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015339|C02E7.6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25571|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015339|C02E7.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015339|C02E7.6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015339|C02E7.6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015340|C02E7.7|1401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015340|C02E7.7|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015340|C02E7.7|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015340|C02E7.7|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015340|C02E7.7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29345|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015340|C02E7.7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|225nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|229nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|234nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|260nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3598|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|266nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=224|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015344|nra-4|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015345|C02F5.2|1414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5195|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015346|C02F5.3|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015347|cids-1|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2713|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015347|cids-1|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015348|C02F5.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2483|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015348|C02F5.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015348|C02F5.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015349|henn-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015349|henn-1|1242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015349|henn-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015349|henn-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1680|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015349|henn-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4076|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=506|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|691nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015350|fbxl-1|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015351|C02F5.10|1528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015351|C02F5.10|1536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015351|C02F5.10|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=563|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015351|C02F5.10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015351|C02F5.10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015352|C02F5.12|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1770|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015352|C02F5.12|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1479|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015352|C02F5.12|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015352|C02F5.12|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015352|C02F5.12|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=969|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015352|C02F5.12|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015352|C02F5.12|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015353|C02F5.13|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015353|C02F5.13|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015353|C02F5.13|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015353|C02F5.13|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1518|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015353|C02F5.13|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015353|C02F5.13|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015353|C02F5.13|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=441|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74296|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43931|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294135|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|333nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42597|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|336nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6197|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=830|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|373nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|384nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|418nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|423nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|430nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|434nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015354|snet-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015355|C02F12.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015355|C02F12.5|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1939|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015355|C02F12.5|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1636|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015355|C02F12.5|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015355|C02F12.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015356|tag-278|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015356|tag-278|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=932|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015356|tag-278|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015356|tag-278|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015357|C02F12.8|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015357|C02F12.8|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015357|C02F12.8|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015357|C02F12.8|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=460|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015358|C02F12.9|1102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015359|C02G6.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015359|C02G6.1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015359|C02G6.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015359|C02G6.1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015360|C02G6.2|1477nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00015360|C02G6.2|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00015360|C02G6.2|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00015361|C02H6.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00015361|C02H6.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015361|C02H6.1|1360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015361|C02H6.1|1363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015361|C02H6.1|1449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015362|fbxa-105|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015362|fbxa-105|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015364|npr-19|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015364|npr-19|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=199|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015364|npr-19|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015364|npr-19|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015367|srt-64|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015367|srt-64|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015367|srt-64|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015367|srt-64|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015367|srt-64|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00015368|srt-65|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015368|srt-65|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015368|srt-65|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015368|srt-65|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015369|ugt-51|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015369|ugt-51|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015369|ugt-51|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015370|C03A7.12|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00015370|C03A7.12|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015370|C03A7.12|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015370|C03A7.12|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015372|C03B1.1|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00015372|C03B1.1|1191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00015372|C03B1.1|1230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00015372|C03B1.1|1410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00015372|C03B1.1|1536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00015372|C03B1.1|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00015373|C03B1.2|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015373|C03B1.2|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=213|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015373|C03B1.2|229nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015374|C03B1.3|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015375|C03B1.4|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015376|C03B1.5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015376|C03B1.5|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015376|C03B1.5|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015376|C03B1.5|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015376|C03B1.5|516nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015376|C03B1.5|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|53nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00015378|C03B1.7a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015379|C03B1.9|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015379|C03B1.9|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015380|C03B1.10|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015381|C03B1.13|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015381|C03B1.13|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=190|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015381|C03B1.13|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015381|C03B1.13|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015381|C03B1.13|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015382|C03B1.14|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015382|C03B1.14|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015382|C03B1.14|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015382|C03B1.14|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015382|C03B1.14|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015382|C03B1.14|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015382|C03B1.14|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015385|C03B8.2|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015386|C03B8.3|1462nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015386|C03B8.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015386|C03B8.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015386|C03B8.3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015387|kcnl-3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015387|kcnl-3|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015387|kcnl-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015387|kcnl-3|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015387|kcnl-3|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00015387|kcnl-3|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015388|C03F11.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015388|C03F11.2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015388|C03F11.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015389|scav-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015389|scav-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015389|scav-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=778|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015389|scav-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015389|scav-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=175|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=920|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015390|C03F11.4.1|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1349|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1063|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2881|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015391|sdha-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9556|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|765nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|772nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|893nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|897nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015392|nspc-7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015393|C03G6.5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015394|C03G6.6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015394|C03G6.6|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015394|C03G6.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015395|nhr-147|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015395|nhr-147|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015396|nhr-148|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015396|nhr-148|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015396|nhr-148|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015397|nhr-149|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=863|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015398|tag-293|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015399|cyp-35A1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015400|cyp-35A2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015400|cyp-35A2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015400|cyp-35A2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2421|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015401|srsx-24|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015402|C03G6.17|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015402|C03G6.17|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015402|C03G6.17|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=636|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015402|C03G6.17|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015402|C03G6.17|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015403|clec-10|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015403|clec-10|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015403|clec-10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015403|clec-10|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=593|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015403|clec-10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015403|clec-10|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2831|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=529|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015404|nstp-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|491nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2327|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015405|C03H5.3a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015406|C03H5.4a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015406|C03H5.4a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015407|C03H5.5|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015407|C03H5.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015407|C03H5.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015407|C03H5.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015407|C03H5.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015408|C03H5.6|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015408|C03H5.6|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=587|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015408|C03H5.6|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015409|C03H5.7a|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015409|C03H5.7a|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015409|C03H5.7a|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015409|C03H5.7a|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015409|C03H5.7a|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015409|C03H5.7a|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=706|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=377|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015410|tbc-6|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015411|srz-60|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015411|srz-60|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015412|lgc-9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015412|lgc-9|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=814|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015413|pdhb-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015413|pdhb-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=600|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015413|pdhb-1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015413|pdhb-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4892|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015413|pdhb-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1331|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015413|pdhb-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015414|C04C3.4|1097nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015414|C04C3.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015414|C04C3.4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015416|C04C3.6|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015416|C04C3.6|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015417|C04C3.7|1334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015417|C04C3.7|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=611|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|475nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2320|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|478nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015418|pac-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015419|srsx-18|488nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015419|srsx-18|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00015419|srsx-18|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015419|srsx-18|513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015419|srsx-18|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015421|C04E6.4|1007nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015421|C04E6.4|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015421|C04E6.4|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015422|C04E6.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00015422|C04E6.5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015423|C04E6.7|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015423|C04E6.7|274nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015423|C04E6.7|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2210|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00015423|C04E6.7|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015423|C04E6.7|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015424|C04E6.8|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2310|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015424|C04E6.8|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015424|C04E6.8|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015424|C04E6.8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015424|C04E6.8|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015424|C04E6.8|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015424|C04E6.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015425|C04E6.11|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1573|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015425|C04E6.11|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015425|C04E6.11|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2179|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|415nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20378|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158434|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=585|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|806nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015427|C04E6.13|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015428|C04E7.1|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015428|C04E7.1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015429|sor-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015429|sor-3|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015429|sor-3|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015429|sor-3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015429|sor-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015429|sor-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015431|C04E7.4|609nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015431|C04E7.4|618nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015431|C04E7.4|620nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=136|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015433|C04E12.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015433|C04E12.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015433|C04E12.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015433|C04E12.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015434|C04E12.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015434|C04E12.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015435|C04E12.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015436|C04E12.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015436|C04E12.6|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015436|C04E12.6|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015436|C04E12.6|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=598|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=419|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015437|scrm-3|258nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015439|C04E12.10|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015439|C04E12.10|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015440|arrd-20|1030nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|705nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|709nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|723nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015441|arrd-21|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=739|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015442|C04F1.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015444|C04F5.2|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015444|C04F5.2|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015444|C04F5.2|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015444|C04F5.2|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015447|srab-2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015448|srab-3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015448|srab-3|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015448|srab-3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015448|srab-3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015449|ugt-63|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=780|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015449|ugt-63|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015450|C04F5.8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015450|C04F5.8|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015450|C04F5.8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2429|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015450|C04F5.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015450|C04F5.8|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015450|C04F5.8|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015451|C04F5.9|1212nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=41|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015451|C04F5.9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1168|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015451|C04F5.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015451|C04F5.9|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015453|C04G6.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1188|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015453|C04G6.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015453|C04G6.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015453|C04G6.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1410|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|304nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015454|C04G6.4|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015455|C04G6.5|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015455|C04G6.5|669nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015455|C04G6.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1479|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015455|C04G6.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015455|C04G6.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015455|C04G6.5|755nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|1536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015456|C04G6.6|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015457|C04G6.7|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015457|C04G6.7|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015457|C04G6.7|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015457|C04G6.7|788nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015458|C04G6.10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015458|C04G6.10|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015458|C04G6.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015458|C04G6.10|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015460|C05C8.1b|1038nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015460|C05C8.1b|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015460|C05C8.1b|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015460|C05C8.1b|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015460|C05C8.1b|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3568|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1223|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015461|C05C8.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015462|C05C8.5|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015462|C05C8.5|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015462|C05C8.5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015462|C05C8.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1004|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015462|C05C8.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1168|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1114|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015463|hpo-9|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3369|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|526nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|529nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015464|C05C8.7.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015465|C05C8.8|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=177|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015465|C05C8.8|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015465|C05C8.8|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015465|C05C8.8|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015466|hyls-1|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2624|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015466|hyls-1|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015466|hyls-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015466|hyls-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015466|hyls-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015467|basl-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015467|basl-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015467|basl-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015467|basl-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015467|basl-1|960nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=319|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1001|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015468|madf-11|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=273|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1536|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1760|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015469|C05D2.8|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3086|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2027|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=566|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015470|C05D2.10a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015471|lmp-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015471|lmp-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015471|lmp-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015472|C05D9.3|18nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=76|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015472|C05D9.3|21nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=32|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015472|C05D9.3|25nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015472|C05D9.3|401nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=873|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015472|C05D9.3|403nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015473|C05D9.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015473|C05D9.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=591|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=622|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=959|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015474|C05D9.7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015476|C05D9.9b|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015476|C05D9.9b|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3423|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015476|C05D9.9b|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015476|C05D9.9b|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015476|C05D9.9b|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015477|attf-4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015477|attf-4|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015477|attf-4|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015477|attf-4|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015477|attf-4|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=945|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015477|attf-4|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=884|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015477|attf-4|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2a|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2a|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2a|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2a|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2a|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2a|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2a|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015478|C05D10.2c|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015479|wht-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015480|C05D10.4c|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=803|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015480|C05D10.4c|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015480|C05D10.4c|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015481|C05D11.1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3554|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015481|C05D11.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2223|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015481|C05D11.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015481|C05D11.1|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015483|C05D11.5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3850|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|386nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015484|atgl-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015485|C05D11.8|1501nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015485|C05D11.8|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015486|C05D11.9|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1467|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015486|C05D11.9|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015486|C05D11.9|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015486|C05D11.9|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015486|C05D11.9|618nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015487|mrps-17|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2253|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00015487|mrps-17|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015487|mrps-17|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015488|C05D11.13|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015488|C05D11.13|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015488|C05D11.13|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00015488|C05D11.13|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015489|C05E4.7|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1074|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015492|lnp-1|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=423|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015493|C05E11.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015494|C05E11.3b|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015495|C05E11.6|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015495|C05E11.6|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015495|C05E11.6|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015495|C05E11.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015495|C05E11.6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015496|C05E11.7|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015496|C05E11.7|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015496|C05E11.7|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015497|nhr-76|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015497|nhr-76|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1044|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=449|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015499|inst-1|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=305|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015500|C06A5.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015500|C06A5.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015500|C06A5.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00015501|C06A5.3a|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=732|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015501|C06A5.3a|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1388|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015501|C06A5.3a|282nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015501|C06A5.3a|397nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|1572nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|1576nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=281|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|1580nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=509|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|526nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015504|C06A5.6|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=506|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015505|C06A5.8b.1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015505|C06A5.8b.1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015505|C06A5.8b.1|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015505|C06A5.8b.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015505|C06A5.8b.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=858|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=810|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|771nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015507|C06A6.2a|808nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1621|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=294|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|236nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015508|mvb-12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015509|C06A6.4a.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2873|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00015509|C06A6.4a.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015509|C06A6.4a.1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015509|C06A6.4a.1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1153|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015509|C06A6.4a.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015509|C06A6.4a.1|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015510|C06A6.5|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=961|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015510|C06A6.5|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015510|C06A6.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015510|C06A6.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015510|C06A6.5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015510|C06A6.5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015510|C06A6.5|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015511|C06A6.7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=555|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015511|C06A6.7|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5811|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2889|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015512|mthf-1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|215nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|217nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=605|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1424|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=289|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015513|snpc-1.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|108nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|111nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=95|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94432|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015514|C06A8.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015515|spdl-1|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015515|spdl-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015515|spdl-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015515|spdl-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1252|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015515|spdl-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015515|spdl-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015516|C06A8.6|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015516|C06A8.6|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015516|C06A8.6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015516|C06A8.6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015516|C06A8.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015516|C06A8.6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015516|C06A8.6|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8a|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8a|1050nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8a|488nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8a|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|1396nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|1405nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|1517nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=671|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1078|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1449|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015517|C06A8.8b.2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015518|C06E1.1|162nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015518|C06E1.1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015518|C06E1.1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015519|doxa-1|628nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=324|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015519|doxa-1|630nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015520|fip-3|1120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015520|fip-3|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015520|fip-3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015520|fip-3|846nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015520|fip-3|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=525|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015520|fip-3|857nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015521|fipr-16|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015521|fipr-16|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015521|fipr-16|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015522|C06E1.7|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015522|C06E1.7|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015523|ztf-30|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015523|ztf-30|316nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015523|ztf-30|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015523|ztf-30|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015524|C06E1.9|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015524|C06E1.9|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2213|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=880|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=735|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015525|rha-2|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015526|C06E1.11|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015527|C06E2.1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015527|C06E2.1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=642|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015527|C06E2.1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015529|C06E2.5.2|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015529|C06E2.5.2|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=315|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015529|C06E2.5.2|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015529|C06E2.5.2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015529|C06E2.5.2|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015530|C06E4.1|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015531|C06E4.2b|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3307|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015531|C06E4.2b|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015531|C06E4.2b|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015531|C06E4.2b|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015531|C06E4.2b|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015532|C06E4.3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015532|C06E4.3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015532|C06E4.3|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015532|C06E4.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015532|C06E4.3|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015532|C06E4.3|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015532|C06E4.3|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015535|C06E4.6|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015535|C06E4.6|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015535|C06E4.6|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015535|C06E4.6|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|180nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=766|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|186nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015536|glb-2|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015537|C06E4.8|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015537|C06E4.8|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015537|C06E4.8|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1762|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6060|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|277nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|280nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|283nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|288nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015538|sams-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2511|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=990|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00015539|C06E7.2a.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=989|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6867|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|320nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|341nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|344nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015540|sams-4|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015541|C06E7.4b|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015541|C06E7.4b|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015541|C06E7.4b|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015541|C06E7.4b|302nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015544|C06E8.5|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015544|C06E8.5|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015545|C06G1.1a|464nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015546|C06G1.2|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1042nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1045nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1778|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|1478nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1795|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|627nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|973nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015547|ain-1|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|1092nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|1097nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|326nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|332nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=436|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015548|C06G1.5a|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015549|C06G3.3|304nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015549|C06G3.3|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015549|C06G3.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015549|C06G3.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015551|C06G3.5a|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6225|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015551|C06G3.5a|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015551|C06G3.5a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=723|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015551|C06G3.5a|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015551|C06G3.5a|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015551|C06G3.5a|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=390|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015551|C06G3.5a|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015552|C06G3.6|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015552|C06G3.6|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00015552|C06G3.6|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015552|C06G3.6|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00015552|C06G3.6|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015552|C06G3.6|917nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015553|trxr-1|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015553|trxr-1|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4101|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015553|trxr-1|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1449|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00015554|C06G3.8b|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=501|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=442|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2679|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015555|ufl-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015557|C06G4.1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015557|C06G4.1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1520|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1028|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015558|C06G4.4.1|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=955|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|340nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|373nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|383nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015559|npr-17|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1149|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015560|C07A12.2|705nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|1159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4501|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=527|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015561|C07A12.7c|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015565|C07D8.6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015565|C07D8.6|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015565|C07D8.6|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14747|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015565|C07D8.6|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015566|C07D10.1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015566|C07D10.1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00015566|C07D10.1|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015566|C07D10.1|657nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015566|C07D10.1|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015566|C07D10.1|864nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|1483nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5391|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015567|bath-44|582nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015568|sre-3|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015568|sre-3|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015568|sre-3|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015568|sre-3|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015569|C07D10.5.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015569|C07D10.5.2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015569|C07D10.5.2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015569|C07D10.5.2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015569|C07D10.5.2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015569|C07D10.5.2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015569|C07D10.5.2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015570|C07F11.2|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=159|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015572|C07G1.6|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015572|C07G1.6|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015572|C07G1.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=659|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015572|C07G1.6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015572|C07G1.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015573|C07G1.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015574|irg-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015574|irg-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015574|irg-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015574|irg-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015574|irg-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015574|irg-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015576|C07G3.8a.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1081|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=431|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015577|ugt-64|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015578|C07G3.10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015578|C07G3.10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015579|C07H6.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015579|C07H6.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015579|C07H6.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015579|C07H6.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=936|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015579|C07H6.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2425|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00015579|C07H6.2|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015579|C07H6.2|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=196|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=781|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=190|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015580|cls-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015581|C07H6.4|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015581|C07H6.4|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015581|C07H6.4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015581|C07H6.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015581|C07H6.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3587|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015581|C07H6.4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1811|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015582|C07H6.9a|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015582|C07H6.9a|1361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015582|C07H6.9a|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015582|C07H6.9a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015583|C08A9.3b|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015586|C08A9.6|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015586|C08A9.6|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015586|C08A9.6|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015586|C08A9.6|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015586|C08A9.6|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015586|C08A9.6|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015586|C08A9.6|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015587|sdz-2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015587|sdz-2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015587|sdz-2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015587|sdz-2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015587|sdz-2|371nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015588|C08A9.8|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00015588|C08A9.8|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015588|C08A9.8|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015589|C08A9.9.1|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00015589|C08A9.9.1|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015589|C08A9.9.1|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=989|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015590|bath-15|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015591|cyk-7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015591|cyk-7|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015591|cyk-7|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015591|cyk-7|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4046|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015591|cyk-7|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=712|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015591|cyk-7|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015592|C08D8.1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015592|C08D8.1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015592|C08D8.1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00015592|C08D8.1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015592|C08D8.1|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015592|C08D8.1|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015592|C08D8.1|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015593|C08E3.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1661|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015593|C08E3.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015593|C08E3.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015595|bath-33|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015598|fbxa-163|1445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015598|fbxa-163|1449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015598|fbxa-163|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015598|fbxa-163|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015601|fbxa-166|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015602|fbxa-158|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015602|fbxa-158|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015607|fbxb-13|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015607|fbxb-13|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015608|math-3|287nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=542|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015608|math-3|293nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015608|math-3|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015608|math-3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015609|math-4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015610|C08F1.6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015613|C08F1.10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015613|C08F1.10|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015613|C08F1.10|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015615|fbxc-48|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015615|fbxc-48|868nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015615|fbxc-48|905nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015615|fbxc-48|907nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015616|C08G5.3a|1505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015616|C08G5.3a|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015618|C08G5.6|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=473|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015618|C08G5.6|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|1118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22741|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015619|C08G9.1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015620|C08G9.2|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015620|C08G9.2|1504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015620|C08G9.2|1510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015620|C08G9.2|1512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015620|C08G9.2|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015621|C09B7.2.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015621|C09B7.2.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015621|C09B7.2.2|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015621|C09B7.2.2|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1685|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015622|C09B8.3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015622|C09B8.3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015622|C09B8.3|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015622|C09B8.3|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015623|C09B8.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015624|C09B8.5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015624|C09B8.5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015624|C09B8.5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015624|C09B8.5|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015624|C09B8.5|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015624|C09B8.5|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015625|C09B8.8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015625|C09B8.8|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015625|C09B8.8|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015626|C09B9.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015626|C09B9.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015626|C09B9.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015626|C09B9.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015627|C09B9.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015627|C09B9.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00015627|C09B9.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015627|C09B9.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015627|C09B9.2|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015628|best-6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015628|best-6|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015628|best-6|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015628|best-6|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015628|best-6|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015629|C09B9.4|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=261|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015630|C09B9.7|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015630|C09B9.7|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015630|C09B9.7|1378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7973|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015630|C09B9.7|1382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015630|C09B9.7|1392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015630|C09B9.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015631|clec-89|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015631|clec-89|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015631|clec-89|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015631|clec-89|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1326|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|462nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015632|C09D4.1a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=365|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|765nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=399|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|769nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2175|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015633|C09D4.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015634|C09D4.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015634|C09D4.3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015634|C09D4.3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015634|C09D4.3|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=787|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015634|C09D4.3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015634|C09D4.3|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=151|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2277|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015635|C09D4.4a|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|1600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015636|C09D4.6|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015637|srxa-5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015637|srxa-5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015637|srxa-5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015638|C09E7.4|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=375|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015638|C09E7.4|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=430|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015638|C09E7.4|787nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015638|C09E7.4|789nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015638|C09E7.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015639|C09E7.5|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015641|C09E7.7.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015641|C09E7.7.1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015641|C09E7.7.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1548|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015641|C09E7.7.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015641|C09E7.7.1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015641|C09E7.7.1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1287|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015642|C09E7.8b|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|196nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015644|C09E8.1a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015645|lips-7|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015646|mlt-10|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015646|mlt-10|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015646|mlt-10|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015646|mlt-10|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=586|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015646|mlt-10|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015646|mlt-10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015646|mlt-10|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015647|C09F5.1|220nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=522|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015647|C09F5.1|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1059|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2983|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|159nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015648|orai-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015649|C09F5.3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015649|C09F5.3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015649|C09F5.3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015649|C09F5.3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|1352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5064|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015650|pkg-2|513nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015651|ceh-53|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=324|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015652|srz-79|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015652|srz-79|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015652|srz-79|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015653|srz-78|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015653|srz-78|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015655|C09G12.5|1559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015655|C09G12.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015655|C09G12.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|845nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5732|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015658|tsg-101|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=636|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015660|catp-3|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1441|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015661|C09H5.7|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=299|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015662|C10A4.1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00015662|C10A4.1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015662|C10A4.1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015664|C10A4.3|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015664|C10A4.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015664|C10A4.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015664|C10A4.3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015664|C10A4.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015665|C10A4.4|1399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015665|C10A4.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015665|C10A4.4|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015665|C10A4.4|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015665|C10A4.4|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015666|gad-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015666|gad-2|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015666|gad-2|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015666|gad-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015666|gad-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015667|C10A4.6|1472nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015667|C10A4.6|1593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015668|C10A4.7|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015668|C10A4.7|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015670|C10B5.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015670|C10B5.1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015670|C10B5.1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015670|C10B5.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015670|C10B5.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00015670|C10B5.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015671|C10B5.3|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015671|C10B5.3|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1078|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015671|C10B5.3|298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1366|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015671|C10B5.3|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015671|C10B5.3|304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015671|C10B5.3|356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015672|C10E2.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015672|C10E2.1|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015672|C10E2.1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015672|C10E2.1|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015673|C10E2.2.2|1481nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015673|C10E2.2.2|1587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015673|C10E2.2.2|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=302|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015673|C10E2.2.2|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015673|C10E2.2.2|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015674|C10E2.4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015674|C10E2.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015674|C10E2.4|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015674|C10E2.4|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015674|C10E2.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3074|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|758nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015676|mct-6|839nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015677|cpg-4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015677|cpg-4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1492|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015678|mcp-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015678|mcp-1|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015678|mcp-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015678|mcp-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10035|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015678|mcp-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015679|C10F3.7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015679|C10F3.7|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015680|egal-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015680|egal-1|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015680|egal-1|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1119|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015680|egal-1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015680|egal-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015682|C10G8.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015682|C10G8.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=234|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9245|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2933|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015683|C10G8.4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015684|C10G8.8b.1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2142|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015684|C10G8.8b.1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=834|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015684|C10G8.8b.1|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015685|C10G11.1b|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015685|C10G11.1b|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015685|C10G11.1b|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015685|C10G11.1b|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|1121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|1133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=340|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|1139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1070|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|1141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=667|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|1144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015686|C10G11.6b|168nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1406nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1515nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|1518nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00015687|chdp-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|1301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1435|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=394|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015688|C10G11.8|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|1232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4605|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015689|spch-2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015690|C10G11.10|1046nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015690|C10G11.10|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015690|C10G11.10|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015690|C10G11.10|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015690|C10G11.10|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015690|C10G11.10|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015690|C10G11.10|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015691|viln-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015691|viln-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1652|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015691|viln-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015691|viln-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015692|ugt-25|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1016|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015692|ugt-25|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015692|ugt-25|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015692|ugt-25|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015692|ugt-25|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015693|ugt-28|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015693|ugt-28|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4520|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015693|ugt-28|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015693|ugt-28|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015693|ugt-28|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015694|ugt-27|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1296|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1474|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015695|ugt-26|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015696|C10H11.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015696|C10H11.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015696|C10H11.7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015696|C10H11.7|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|171nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=808|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015697|C10H11.8a|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2305|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015698|kca-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015700|asp-9|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015700|asp-9|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1181|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015701|C11D2.3|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015701|C11D2.3|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015701|C11D2.3|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015701|C11D2.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015701|C11D2.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015702|C11D2.4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015702|C11D2.4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6192|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015702|C11D2.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015703|C11D2.7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015703|C11D2.7|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015703|C11D2.7|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4181|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015703|C11D2.7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015703|C11D2.7|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015704|tiam-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015704|tiam-1|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=860|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015704|tiam-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015705|nhr-152|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015705|nhr-152|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=182|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015705|nhr-152|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015706|C12D5.3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=774|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015706|C12D5.3|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7752|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015706|C12D5.3|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015706|C12D5.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015706|C12D5.3|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015706|C12D5.3|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=536|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4998|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3082|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015707|C12D5.4|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015708|C12D5.5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015708|C12D5.5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015708|C12D5.5|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015708|C12D5.5|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=290|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=681|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=187|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00015709|cyp-33A1|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015710|C12D5.9|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00015710|C12D5.9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015710|C12D5.9|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015710|C12D5.9|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015711|C12D5.10|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015711|C12D5.10|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015712|sre-11|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015712|sre-11|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2135|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=558|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=986|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015713|C12D12.1b|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015714|C12D12.3|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015714|C12D12.3|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=682|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|321nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|93nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015716|sox-4|98nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015718|C13A2.1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015718|C13A2.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015719|C13A2.2|459nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015720|C13A2.3|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015720|C13A2.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015720|C13A2.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015721|C13A2.4.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015721|C13A2.4.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015722|C13A2.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015724|C13A2.7b|1485nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015724|C13A2.7b|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015724|C13A2.7b|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015725|C13A2.9|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015725|C13A2.9|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015725|C13A2.9|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015725|C13A2.9|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015726|C13A2.10|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015728|C13A10.1a|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015728|C13A10.1a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015729|C13A10.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015729|C13A10.2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12070|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015729|C13A10.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015729|C13A10.2|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=213|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015729|C13A10.2|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=288|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015731|C13B7.6|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1761|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015731|C13B7.6|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=394|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00015731|C13B7.6|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015731|C13B7.6|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015731|C13B7.6|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|1097nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|1100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|1104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|525nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015733|C13B9.2|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5162|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4161|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=871|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|290nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|293nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=98|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|297nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=67|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|300nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=134|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015734|copd-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|1596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=604|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=420|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1693|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3171|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015735|pdfr-1|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015736|srsx-11|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015736|srsx-11|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015736|srsx-11|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015737|srsx-12|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015738|srsx-13|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015739|ugt-7|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=195|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015739|ugt-7|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015740|C13E3.1|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=308|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015740|C13E3.1|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4803|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=792|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015741|C13F10.1a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=679|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015742|C13F10.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015743|soap-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015743|soap-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015743|soap-1|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015743|soap-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3340|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015743|soap-1|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015743|soap-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1036|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|63nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015745|C13F10.6|72nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2467|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015746|C13F10.7.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015747|C13G5.2|1429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015747|C13G5.2|1431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015747|C13G5.2|1436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015747|C13G5.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015747|C13G5.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1490|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015747|C13G5.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|1328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|1333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015748|C14A11.2|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015750|C14A11.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1210|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00015750|C14A11.5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=462|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015750|C14A11.5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015750|C14A11.5|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015750|C14A11.5|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015750|C14A11.5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015750|C14A11.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015751|C14A11.6|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015751|C14A11.6|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015751|C14A11.6|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2207|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015752|C14B9.2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015753|C14B9.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015753|C14B9.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015753|C14B9.3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015753|C14B9.3|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015753|C14B9.3|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015753|C14B9.3|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=292|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=998|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|358nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015754|C14B9.8|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015755|C14B9.10|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2343|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015755|C14B9.10|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015755|C14B9.10|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=313|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015755|C14B9.10|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13258|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015755|C14B9.10|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1438|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=541|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015756|C14C6.2a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015757|C14C6.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015758|nhr-155|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015758|nhr-155|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015758|nhr-155|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015758|nhr-155|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015758|nhr-155|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015759|C14C6.5a|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015759|C14C6.5a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015759|C14C6.5a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015759|C14C6.5a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015759|C14C6.5a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9526|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015759|C14C6.5a|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015760|C14C6.6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015760|C14C6.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015762|C14C6.8|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015764|C14C6.13|1580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015764|C14C6.13|1582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015764|C14C6.13|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015764|C14C6.13|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015765|C14C11.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00015765|C14C11.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015765|C14C11.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|1120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=906|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015766|C14C11.2.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015767|hex-2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015767|hex-2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1695|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00015767|hex-2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015767|hex-2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015767|hex-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015767|hex-2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015767|hex-2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|151nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=29|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015768|C14C11.4|337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1110|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015769|C14C11.7|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015773|C14E2.4|1331nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015775|C14E2.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=947|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1487|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015776|dct-1|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1340|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015777|sfxn-2|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015778|got-2.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015778|got-2.2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015778|got-2.2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015778|got-2.2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5691|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015778|got-2.2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3165|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015778|got-2.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=577|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015778|got-2.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015779|lrch-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1289|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015779|lrch-1|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2200|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3240|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=404|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=762|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9763|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13638|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|219nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=612|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015780|C14F11.4b|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7577|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|15nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|19nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|22nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015781|C14F11.6.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015782|C14F11.7|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015782|C14F11.7|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015782|C14F11.7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015782|C14F11.7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015782|C14F11.7|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015783|C15B12.1|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015784|C15B12.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015784|C15B12.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=402|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015784|C15B12.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015786|C15B12.4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015786|C15B12.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015786|C15B12.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=593|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015787|C15B12.6b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015788|C15B12.8|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015788|C15B12.8|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015788|C15B12.8|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015788|C15B12.8|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015788|C15B12.8|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015788|C15B12.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015788|C15B12.8|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015789|syx-6|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=207|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015789|syx-6|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015789|syx-6|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=787|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015789|syx-6|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=462|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015789|syx-6|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015789|syx-6|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|528nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=550|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=324|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=337|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|644nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|652nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|843nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|849nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15768|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|851nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3081|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|855nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|903nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015790|C15C7.4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1316|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=364|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8551|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015791|C15C7.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015792|C15C7.6|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015792|C15C7.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015793|C15C7.7|115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015793|C15C7.7|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015793|C15C7.7|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015793|C15C7.7|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015793|C15C7.7|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015793|C15C7.7|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015794|C15F1.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015794|C15F1.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015794|C15F1.1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015794|C15F1.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015795|C15F1.2|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015795|C15F1.2|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=143|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015795|C15F1.2|19nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015795|C15F1.2|22nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015795|C15F1.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015796|C15F1.5b|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015796|C15F1.5b|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=444|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015796|C15F1.5b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015796|C15F1.5b|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=628|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015797|C15F1.8|1098nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015797|C15F1.8|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015797|C15F1.8|830nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015797|C15F1.8|832nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015797|C15F1.8|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015798|C15H9.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015798|C15H9.2|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015799|C15H9.3|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=193|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015799|C15H9.3|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015799|C15H9.3|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|1107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|1601nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|725nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|733nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1764|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|735nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|739nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015800|C15H9.4|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|278nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|285nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|526nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|639nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1094|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|643nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=584|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015801|C15H9.5.2|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|1003nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=843|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=873|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015802|flu-2|996nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6238|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4303|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3324|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1313|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015803|C15H9.9.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015805|C15H9.11.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015805|C15H9.11.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015805|C15H9.11.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1072|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015805|C15H9.11.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1076|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|612nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015806|C16A3.1a|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015807|C16A3.2|1537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015807|C16A3.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1647|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015807|C16A3.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015807|C16A3.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015809|C16A3.4|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2015|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015809|C16A3.4|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015809|C16A3.4|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015809|C16A3.4|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015809|C16A3.4|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015809|C16A3.4|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015809|C16A3.4|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7837|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10977|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12226|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|647nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015810|C16A3.5.2|671nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13664|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015811|C16A3.6|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1070|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1298|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015813|thoc-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5795|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|562nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|564nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=696|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|570nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|576nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|578nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2336|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|580nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1385|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|584nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=525|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|587nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=428|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|590nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4056|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|642nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=551|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|647nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|650nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|660nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10a.1|712nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=260|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015814|C16A3.10c.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015815|C16A11.2a.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015815|C16A11.2a.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015815|C16A11.2a.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015815|C16A11.2a.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015815|C16A11.2a.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1767|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015815|C16A11.2a.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015815|C16A11.2a.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015816|C16A11.3a|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1034|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015816|C16A11.3a|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015816|C16A11.3a|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015816|C16A11.3a|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015816|C16A11.3a|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015816|C16A11.3a|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2330|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=902|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015817|C16A11.4a|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015818|C16A11.5|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=502|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015818|C16A11.5|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015819|fbxc-44|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1027|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015819|fbxc-44|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015819|fbxc-44|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015820|C16A11.7.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015820|C16A11.7.1|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015820|C16A11.7.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015820|C16A11.7.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015821|clec-135|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015822|C16B8.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015822|C16B8.2|113nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015822|C16B8.2|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015822|C16B8.2|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=498|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6426|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015823|C16B8.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015824|C16B8.4|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015825|C16C4.1|1500nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015825|C16C4.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015828|math-14|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015828|math-14|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015828|math-14|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015828|math-14|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015829|math-15|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015829|math-15|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015829|math-15|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015839|math-10|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015839|math-10|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015841|skpo-2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015842|C16C8.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1502|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015842|C16C8.4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015842|C16C8.4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015842|C16C8.4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015843|C16C8.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015843|C16C8.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015843|C16C8.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00015843|C16C8.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015843|C16C8.5|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015843|C16C8.5|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00015843|C16C8.5|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015845|C16C8.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015846|C16C8.8|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015847|C16C8.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015848|C16C8.10|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015849|C16C8.11|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=565|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015849|C16C8.11|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015850|C16C8.12|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015850|C16C8.12|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015851|C16C8.13|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00015851|C16C8.13|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00015852|C16C8.14|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015852|C16C8.14|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015852|C16C8.14|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015852|C16C8.14|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015853|C16C8.16|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015853|C16C8.16|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015853|C16C8.16|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1450|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015853|C16C8.16|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015855|C16C8.18|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015855|C16C8.18|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015855|C16C8.18|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=577|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015855|C16C8.18|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015855|C16C8.18|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015855|C16C8.18|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015855|C16C8.18|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015856|C16C8.19|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015856|C16C8.19|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015857|C16D9.1|529nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015858|C16D9.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015858|C16D9.3|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015859|C16D9.4|560nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015859|C16D9.4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015859|C16D9.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015859|C16D9.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015859|C16D9.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015860|C16D9.5|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015860|C16D9.5|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015860|C16D9.5|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015860|C16D9.5|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015861|C16D9.6|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1093|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015861|C16D9.6|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015861|C16D9.6|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015861|C16D9.6|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015862|srt-25|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=314|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015862|srt-25|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015863|C16D9.8|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015864|C16D9.9|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015865|C16E9.1|377nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00015865|C16E9.1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2066|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015866|C16E9.2a|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=794|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=370|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015867|ncs-7|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1471nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1481nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|1506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|359nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|363nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|365nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=830|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|371nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015868|C16H3.3b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015876|C17B7.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00015876|C17B7.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00015878|C17B7.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015878|C17B7.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015879|C17B7.5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015879|C17B7.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00015879|C17B7.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015879|C17B7.5|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015884|C17B7.10|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015884|C17B7.10|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015885|fbxa-65|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015885|fbxa-65|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00015885|fbxa-65|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015886|C17B7.12|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015886|C17B7.12|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2065|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00015887|C17C3.1c.2|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015889|C17C3.3|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015889|C17C3.3|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015889|C17C3.3|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015890|C17C3.5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015890|C17C3.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00015892|C17C3.9|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015892|C17C3.9|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00015892|C17C3.9|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015892|C17C3.9|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015893|C17C3.11.1|691nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=608|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015894|acdh-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|1421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|1423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|456nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=625|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015896|C17C3.15|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015898|sre-9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015898|sre-9|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015898|sre-9|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015898|sre-9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015898|sre-9|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015899|C17E7.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=526|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015900|nhr-157|435nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00015900|nhr-157|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015900|nhr-157|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015900|nhr-157|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015901|nhr-158|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015901|nhr-158|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015901|nhr-158|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1609|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015901|nhr-158|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015901|nhr-158|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015901|nhr-158|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015901|nhr-158|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015902|nhr-159|126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015902|nhr-159|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015902|nhr-159|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=859|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00015903|C17E7.9a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015903|C17E7.9a|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=588|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015903|C17E7.9a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015903|C17E7.9a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015903|C17E7.9a|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015905|C17E7.12|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=585|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015905|C17E7.12|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015905|C17E7.12|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015905|C17E7.12|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015906|C17E7.13|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015906|C17E7.13|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015906|C17E7.13|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015906|C17E7.13|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015906|C17E7.13|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015906|C17E7.13|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015907|C17F3.1|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015907|C17F3.1|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4836|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015907|C17F3.1|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015908|C17F3.3|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00015908|C17F3.3|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00015909|clec-124|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015910|C17F4.2|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015910|C17F4.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015910|C17F4.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=535|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015911|C17F4.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015911|C17F4.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015911|C17F4.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015911|C17F4.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=997|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015912|fbxc-50|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50262|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35309|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16535|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1748|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=551|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015913|C17F4.7|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015914|C17F4.8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00015914|C17F4.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015914|C17F4.8|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=513|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00015914|C17F4.8|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2374|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015915|C17G10.1.2|1579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015916|C17G10.2|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015916|C17G10.2|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015916|C17G10.2|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=622|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015916|C17G10.2|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015916|C17G10.2|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015916|C17G10.2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015916|C17G10.2|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015917|C17G10.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015917|C17G10.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015917|C17G10.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015917|C17G10.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015917|C17G10.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015918|C17G10.6b|1076nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015919|C17G10.7|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015919|C17G10.7|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1129|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015919|C17G10.7|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015919|C17G10.7|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5222|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1416|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|559nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|563nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015920|C17G10.9a|652nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=472|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=483|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015921|C17H11.1|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=720|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=571|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015922|C17H11.2|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015925|C17H11.5|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015925|C17H11.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00015925|C17H11.5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015926|C17H11.6f.1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015926|C17H11.6f.1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015926|C17H11.6f.1|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1533|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00015926|C17H11.6f.1|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015926|C17H11.6f.1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015926|C17H11.6f.1|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|555nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|558nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7197|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|566nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|579nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|832nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015927|dyci-1|842nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|593nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|602nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=684|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=963|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015928|C17H12.2.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015929|C17H12.3.1|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015929|C17H12.3.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015929|C17H12.3.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1173|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015929|C17H12.3.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015929|C17H12.3.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015930|C17H12.4|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=671|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015930|C17H12.4|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=277|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015931|C17H12.5|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015931|C17H12.5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=812|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015931|C17H12.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015932|C17H12.6a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5665|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015933|C17H12.8|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|381nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|383nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|388nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1316|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|641nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|643nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|648nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015934|ceh-48|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|1133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|1602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=234|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19225|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=191|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015935|C17H12.10|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=468|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015936|C17H12.11.3|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015937|C17H12.12|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015937|C17H12.12|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015937|C17H12.12|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015937|C17H12.12|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015937|C17H12.12|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|318nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7129|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=191|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|434nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|439nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|443nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|508nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|662nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015938|anat-1|691nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015939|C18A3.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015939|C18A3.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1337|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015939|C18A3.1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015939|C18A3.1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015939|C18A3.1|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015940|C18A3.2.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015940|C18A3.2.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015940|C18A3.2.2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015940|C18A3.2.2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3286|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015940|C18A3.2.2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015940|C18A3.2.2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015941|C18A3.3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015941|C18A3.3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4361|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015941|C18A3.3|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015941|C18A3.3|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015941|C18A3.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015941|C18A3.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015941|C18A3.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4190|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|306nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|351nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|584nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015942|osta-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1603|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3672|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015943|tiar-1|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|1015nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|1017nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|1028nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|1316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|1438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|1567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|1575nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|607nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|610nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=634|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|658nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|662nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|671nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=385|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|673nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|717nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|719nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|721nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3047|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|727nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|909nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|958nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|987nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015944|C18A3.7|997nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|1231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|1440nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|1443nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00015945|C18A3.9|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015946|C18A3.10|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015946|C18A3.10|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=173|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015946|C18A3.10|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015946|C18A3.10|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015946|C18A3.10|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=254|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015946|C18A3.10|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=126|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1756|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3964|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2819|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=454|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015947|C18A11.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015948|C18A11.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015948|C18A11.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015948|C18A11.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015948|C18A11.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015948|C18A11.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10124|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015949|C18A11.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015950|C18A11.4|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015952|C18B2.1|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00015952|C18B2.1|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00015953|C18B2.2|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015953|C18B2.2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015954|C18B2.3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015954|C18B2.3|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015954|C18B2.3|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015954|C18B2.3|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2444|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015954|C18B2.3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015954|C18B2.3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8491|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1280|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015955|C18B2.4|215nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015956|C18B2.5a|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015956|C18B2.5a|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5762|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015956|C18B2.5a|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=651|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015956|C18B2.5a|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015956|C18B2.5a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015956|C18B2.5a|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015956|C18B2.5a|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015957|del-9|1340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00015957|del-9|1342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00015958|srbc-11|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015958|srbc-11|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00015958|srbc-11|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015960|srbc-9|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015961|srbc-7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015961|srbc-7|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015962|srbc-8|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00015962|srbc-8|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015962|srbc-8|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015963|C18B10.6|1476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015963|C18B10.6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015963|C18B10.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015963|C18B10.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015964|glb-5|666nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015964|glb-5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015965|ugt-48|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=400|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015965|ugt-48|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015965|ugt-48|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015965|ugt-48|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015965|ugt-48|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015966|C18C4.5b|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015966|C18C4.5b|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015966|C18C4.5b|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015966|C18C4.5b|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015966|C18C4.5b|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1522|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015966|C18C4.5b|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015969|glb-6|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=256|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015969|glb-6|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015969|glb-6|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015969|glb-6|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00015969|glb-6|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015970|C18E3.1|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=265|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015970|C18E3.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1904|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015971|swsn-2.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015972|C18E3.3|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00015972|C18E3.3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=704|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015972|C18E3.3|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015972|C18E3.3|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015974|C18E3.5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1524|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015974|C18E3.5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015974|C18E3.5|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015974|C18E3.5|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015974|C18E3.5|784nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015975|cas-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3183|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015975|cas-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1003|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015975|cas-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1880|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|152nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|154nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015976|C18E3.9a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=940|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015977|C18F10.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015977|C18F10.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015977|C18F10.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015978|C18F10.7a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015978|C18F10.7a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4559|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015978|C18F10.7a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015978|C18F10.7a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015978|C18F10.7a|575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015978|C18F10.7b|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015978|C18F10.7b|982nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015980|C18G1.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015980|C18G1.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=552|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015981|elt-7|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015981|elt-7|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015981|elt-7|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015981|elt-7|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015981|elt-7|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00015981|elt-7|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015982|C18G1.3a|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015984|C18G1.6.2|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015984|C18G1.6.2|1528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015984|C18G1.6.2|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015984|C18G1.6.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015984|C18G1.6.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00015986|C18G1.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00015986|C18G1.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015986|C18G1.8|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00015987|C18G1.9|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015987|C18G1.9|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00015988|C18H2.1|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00015988|C18H2.1|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015988|C18H2.1|337nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015988|C18H2.1|340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015988|C18H2.1|977nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015988|C18H2.1|989nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015992|C18H2.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015993|C18H7.1b|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00015993|C18H7.1b|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00015993|C18H7.1b|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015993|C18H7.1b|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015994|C18H7.4.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00015996|C18H7.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00015996|C18H7.6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=815|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00015997|C18H7.7.1|1511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00015997|C18H7.7.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=981|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00015999|prmt-4|624nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016000|C18H9.1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016000|C18H9.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|1299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|876nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1417|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|905nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|914nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|916nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|920nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|925nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016002|C18H9.3|993nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1853|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|525nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|531nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|536nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|738nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|879nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016003|C18H9.5|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016004|C18H9.6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016004|C18H9.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5892|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016004|C18H9.6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016004|C18H9.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016004|C18H9.6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016004|C18H9.6|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016004|C18H9.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|566nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016005|ift-74|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|559nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|564nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=566|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|568nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=702|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016006|fln-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016008|C23F12.3|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016008|C23F12.3|607nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2374|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|243nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=154|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|246nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016009|C23F12.4|576nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016010|C23G10.1b|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016010|C23G10.1b|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016010|C23G10.1b|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016010|C23G10.1b|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=382|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00016010|C23G10.1b|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1085nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1088nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1494nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|1499nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6084|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016011|C23G10.2b|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016012|C23G10.5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016012|C23G10.5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016012|C23G10.5|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016013|C23G10.6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016013|C23G10.6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016013|C23G10.6|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016014|C23G10.7b|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=576|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016014|C23G10.7b|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3949|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016014|C23G10.7b|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016014|C23G10.7b|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016014|C23G10.7b|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1728|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016015|C23G10.8|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016016|C23G10.10|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1708|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|47nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|50nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016017|C23G10.11|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|1366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2569|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016018|C23H3.2b|352nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016019|C23H3.3b|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2407|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016019|C23H3.3b|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=554|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016019|C23H3.3b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016019|C23H3.3b|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=773|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2436|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=318|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016020|sptl-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016021|C23H3.5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016022|C23H3.9e|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016022|C23H3.9e|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016022|C23H3.9e|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6238|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016022|C23H3.9e|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016022|C23H3.9e|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016022|C23H3.9e|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016022|C23H3.9e|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016023|prmt-6|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016024|glb-7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016024|glb-7|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016024|glb-7|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016024|glb-7|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016024|glb-7|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016024|glb-7|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016025|xbx-4|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016027|C23H5.8a|1434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016027|C23H5.8a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016027|C23H5.8a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4506|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016027|C23H5.8a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5833|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016027|C23H5.8a|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016027|C23H5.8a|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016027|C23H5.8b.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|1466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|1478nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1066|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13370|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016028|flp-24|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|313nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016029|elf-1|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016030|C24A1.3a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016030|C24A1.3a|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016030|C24A1.3a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016030|C24A1.3a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016030|C24A1.3a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016030|C24A1.3a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016030|C24A1.3a|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016032|C24A3.1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016032|C24A3.1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2a.4|168nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2a.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3758|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8065|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016033|C24A3.2b.2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016034|C24A3.4|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=505|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016034|C24A3.4|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016034|C24A3.4|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016034|C24A3.4|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016034|C24A3.4|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016034|C24A3.4|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016034|C24A3.4|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016037|dop-6|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=241|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016037|dop-6|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016037|dop-6|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016037|dop-6|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2317|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00016037|dop-6|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016038|cst-2|960nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016039|C24A8.5|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016039|C24A8.5|876nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016039|C24A8.5|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016039|C24A8.5|902nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|399nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=554|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016040|C24A11.1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016041|C24A11.2|1399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016041|C24A11.2|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016044|C24B5.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016044|C24B5.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016044|C24B5.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016044|C24B5.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016044|C24B5.1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016044|C24B5.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=722|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016044|C24B5.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2468|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016045|spas-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016045|spas-1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016045|spas-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016045|spas-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1187|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016045|spas-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016045|spas-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016045|spas-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016046|C24B5.4|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016046|C24B5.4|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016046|C24B5.4|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016046|C24B5.4|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016046|C24B5.4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016046|C24B5.4|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016048|C24B9.3a|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3740|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016049|srt-28|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=479|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00016049|srt-28|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016049|srt-28|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016049|srt-28|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016052|dod-3|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016052|dod-3|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016052|dod-3|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016052|dod-3|26nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016052|dod-3|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1346|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016052|dod-3|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1954|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016052|dod-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016053|C24D10.1|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016053|C24D10.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016053|C24D10.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016053|C24D10.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016054|C24D10.2.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016054|C24D10.2.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016054|C24D10.2.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1811|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2676|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016055|C24D10.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016056|C24D10.5|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016056|C24D10.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016056|C24D10.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1378|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016057|C24D10.6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016058|nspd-3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016058|nspd-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016058|nspd-3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016058|nspd-3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2706|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016058|nspd-3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1116|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016058|nspd-3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016059|C24G6.2a|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016059|C24G6.2a|68nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016059|C24G6.2a|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016060|mms-19|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1004|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016060|mms-19|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=633|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016060|mms-19|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016061|hpo-15|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3927|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016061|hpo-15|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016061|hpo-15|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4088|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016062|C24G6.8.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016063|delm-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016063|delm-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016064|acd-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016064|acd-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016064|acd-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016066|acd-2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016067|C24H10.1|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=868|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016068|C24H10.2|867nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016069|C24H10.3|307nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016070|C24H10.4|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016070|C24H10.4|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016071|C24H12.1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=639|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016071|C24H12.1|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016072|C24H12.2|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=618|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016073|C24H12.4a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016073|C24H12.4a|727nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016073|C24H12.4a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1986|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016073|C24H12.4a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016074|C24H12.5e|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016074|C24H12.5e|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016074|C24H12.5e|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016074|C24H12.5e|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016074|C24H12.5e|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016075|C24H12.6|811nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|1523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2066|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016081|C25A6.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016083|C25A8.2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016083|C25A8.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016083|C25A8.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016083|C25A8.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016084|cht-3|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016084|cht-3|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016084|cht-3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016084|cht-3|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8401|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016084|cht-3|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1391|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016085|C25A8.5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016085|C25A8.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016085|C25A8.5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|216nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=428|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016087|C25A11.2|369nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1091|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016088|clec-266|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|1372nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|1374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1189|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016089|aexr-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016090|aexr-2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016090|aexr-2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016090|aexr-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016091|nhr-30|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016091|nhr-30|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016092|cyp-33B1|1248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016092|cyp-33B1|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016092|cyp-33B1|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016092|cyp-33B1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=431|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016093|srsx-34|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|1479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016094|C25E10.4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016095|C25E10.5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016095|C25E10.5|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=411|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016095|C25E10.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016096|C25E10.7|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016096|C25E10.7|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2205|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016096|C25E10.7|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016096|C25E10.7|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016096|C25E10.7|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016096|C25E10.7|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016097|C25E10.8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016097|C25E10.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2696|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016097|C25E10.8|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6778|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016097|C25E10.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016097|C25E10.8|512nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016097|C25E10.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=538|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|1202nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=289|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016099|C25E10.10|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016100|C25E10.11|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016100|C25E10.11|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016100|C25E10.11|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016100|C25E10.11|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016100|C25E10.11|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016100|C25E10.11|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016100|C25E10.11|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016101|C25E10.12|1521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016101|C25E10.12|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016101|C25E10.12|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016101|C25E10.12|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016101|C25E10.12|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1606|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016101|C25E10.12|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=657|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016101|C25E10.12|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016102|C25F6.1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016102|C25F6.1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016102|C25F6.1|401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016102|C25F6.1|403nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016102|C25F6.1|411nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=443|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016102|C25F6.1|413nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016102|C25F6.1|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016103|dpyd-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016103|dpyd-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016103|dpyd-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016103|dpyd-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016103|dpyd-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016103|dpyd-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2693|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00016104|ddr-1|720nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016105|C25F6.6|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016105|C25F6.6|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016105|C25F6.6|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016106|C25F6.7b|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=360|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3753|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1712|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016107|C25G6.1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016108|C25G6.3|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016108|C25G6.3|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016108|C25G6.3|700nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016108|C25G6.3|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1349|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5615|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016109|C25G6.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016110|npr-11|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016110|npr-11|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016110|npr-11|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016110|npr-11|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016110|npr-11|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4726|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|842nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|849nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016111|C25H3.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016112|C25H3.3|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016112|C25H3.3|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016112|C25H3.3|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016112|C25H3.3|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016112|C25H3.3|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1491|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00016112|C25H3.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016113|C25H3.4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016113|C25H3.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016113|C25H3.4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1441|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016113|C25H3.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=967|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016113|C25H3.4|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9762|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3378|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=376|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108589|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016114|flp-27|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=319|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1391nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1511nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|1563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1352|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|373nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|406nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|854nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|866nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|868nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1369|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|874nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8683|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|883nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016115|mdt-26|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|1207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1259|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1225|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1195|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2948|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=700|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|62nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|66nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016116|C25H3.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016117|C25H3.8|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016117|C25H3.8|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016117|C25H3.8|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016117|C25H3.8|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016117|C25H3.8|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1852|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|1210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|1226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|1230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|1232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1773|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|1237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|1241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9085|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2194|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00016118|C25H3.9a|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|362nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|383nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2168|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=445|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=234|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10b|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10b|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10b|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016119|C25H3.10b|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016120|C25H3.11|755nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|481nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8093|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016121|C25H3.12|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016123|C25H3.14|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016123|C25H3.14|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016123|C25H3.14|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016123|C25H3.14|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016123|C25H3.14|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016123|C25H3.14|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=901|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00016123|C25H3.14|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1884|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|1482nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016124|dnc-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016125|C26B2.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00016125|C26B2.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016125|C26B2.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016125|C26B2.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016125|C26B2.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=953|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016126|nhr-258|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=644|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=612|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=815|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00016128|elpc-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5485|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016129|C26B2.7a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=531|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016130|C26B2.8|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016130|C26B2.8|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016130|C26B2.8|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016131|C26B9.1a|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016132|C26B9.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016132|C26B9.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016132|C26B9.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016133|C26B9.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016133|C26B9.3|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016133|C26B9.3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2678|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016133|C26B9.3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016133|C26B9.3|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016133|C26B9.3|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016133|C26B9.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1848|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1058|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00016134|C26B9.5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|356nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|684nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|719nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016135|C26B9.6|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016136|C26B9.7|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=680|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016136|C26B9.7|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016137|C26E6.1|1182nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016137|C26E6.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|446nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|450nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|527nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016138|flh-2|530nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|1015nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1103|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|1018nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2416|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|1022nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1835|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|1026nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|815nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016139|ntl-9|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3116|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1281|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016140|rpb-2|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016142|mrps-18C|1316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016142|mrps-18C|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016142|mrps-18C|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016142|mrps-18C|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016142|mrps-18C|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1422|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016142|mrps-18C|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1448|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016143|eri-9|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1503|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016143|eri-9|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=963|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1401|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=830|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=486|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016144|mmab-1|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016145|C26E6.12|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016145|C26E6.12|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016145|C26E6.12|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016145|C26E6.12|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016145|C26E6.12|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=284|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016145|C26E6.12|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=974|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016145|C26E6.12|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016146|C26F1.1b|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016146|C26F1.1b|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=517|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016146|C26F1.1b|1198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016146|C26F1.1b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016146|C26F1.1b|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=318|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016146|C26F1.1b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016147|cyp-32A1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016147|cyp-32A1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016147|cyp-32A1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016147|cyp-32A1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|1178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|1203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|228nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1303|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1530|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016148|C26F1.3.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016149|frpr-3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016149|frpr-3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=576|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016149|frpr-3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016149|frpr-3|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=642|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2486|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=348|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016150|hint-3|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2554|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016151|smc-5|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016152|pho-12|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016152|pho-12|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016152|pho-12|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016153|C27A2.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1622|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1214|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|358nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016154|C27A12.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016155|C27A12.4|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016155|C27A12.4|1163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016155|C27A12.4|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016155|C27A12.4|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016155|C27A12.4|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=268|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1024|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1735|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|353nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|466nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016156|C27A12.6|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=475|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=606|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1967|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016157|C27A12.7b.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|314nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6445|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|402nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|409nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016158|ari-1|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1634|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016159|C27A12.9|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016160|C27D6.1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016161|C27D6.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016161|C27D6.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016161|C27D6.3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016161|C27D6.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1324|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016161|C27D6.3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|640nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|645nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5076|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|656nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=304|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016162|crh-2|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1949|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4549|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016163|C27D9.1|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016164|C27D9.2|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016164|C27D9.2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016164|C27D9.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016164|C27D9.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016165|C27F2.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|1077nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|1080nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1344|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=575|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|176nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=357|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|272nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|450nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|452nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|465nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|467nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|555nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016166|C27F2.4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|1439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5427|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016167|vps-22|506nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016168|C27F2.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016168|C27F2.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016169|C27F2.7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016169|C27F2.7|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=780|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016169|C27F2.7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016169|C27F2.7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|102nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=391|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3150|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016170|C27F2.8|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|1277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2310|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016171|C27F2.10|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=640|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2a|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2b|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2b|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2b|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2c|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016172|C27H5.2c|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016173|fust-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016173|fust-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016173|fust-1|175nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016173|fust-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016173|fust-1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=742|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016173|fust-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7458|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016173|fust-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016174|C27H5.4c|1317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016174|C27H5.4c|1324nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016174|C27H5.4c|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016174|C27H5.4c|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016174|C27H5.4c|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00016175|C27H5.6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016175|C27H5.6|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016175|C27H5.6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016175|C27H5.6|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=794|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016175|C27H5.6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016175|C27H5.6|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016177|C28C12.1a|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016177|C28C12.1a|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016177|C28C12.1a|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=310|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3782|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1936|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|310nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016178|mesp-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016179|C28C12.3|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016179|C28C12.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016180|C28C12.4|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016180|C28C12.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016180|C28C12.4|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016180|C28C12.4|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016180|C28C12.4|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1337|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016180|C28C12.4|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016181|C28C12.11b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016181|C28C12.11b|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016181|C28C12.11b|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=930|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016182|C28C12.12|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016182|C28C12.12|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3341|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016182|C28C12.12|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016184|glb-9|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016184|glb-9|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1298|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016184|glb-9|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016185|C28F5.4|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016187|C28G1.2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016187|C28G1.2|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016187|C28G1.2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016187|C28G1.2|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016188|sec-15|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016188|sec-15|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016188|sec-15|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=965|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016188|sec-15|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016188|sec-15|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016188|sec-15|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016188|sec-15|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016189|C28G1.4|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016189|C28G1.4|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016189|C28G1.4|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|1447nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|1455nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|1457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|1513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|1516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|1520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016190|C28G1.5a|646nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016191|C28G1.6|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016191|C28G1.6|556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016191|C28G1.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=451|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016191|C28G1.6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3677|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016192|bcl-7|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016193|C28H8.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016193|C28H8.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016193|C28H8.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016193|C28H8.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016193|C28H8.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=533|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1716|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8179|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1857|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|256nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|258nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|264nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=729|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016194|C28H8.3|267nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1879|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7193|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016195|C28H8.4.1|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016196|C28H8.5a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016196|C28H8.5a|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016196|C28H8.5a|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016196|C28H8.5a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016196|C28H8.5a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016197|pxl-1|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016197|pxl-1|358nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016197|pxl-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016197|pxl-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2178|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016197|pxl-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016198|C28H8.7|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016198|C28H8.7|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016199|C28H8.8|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00016199|C28H8.8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|1065nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|1320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=536|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2291|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016200|dpff-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016201|tdo-2|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016201|tdo-2|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016201|tdo-2|378nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016201|tdo-2|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016201|tdo-2|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016201|tdo-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1813|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016201|tdo-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2819|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=982|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016202|kle-2|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016203|tag-250|1350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016203|tag-250|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016203|tag-250|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016203|tag-250|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=586|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016203|tag-250|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00016203|tag-250|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016204|gsto-1|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016204|gsto-1|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016204|gsto-1|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016204|gsto-1|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1364|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3231|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016207|C29E4.10|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5334|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016209|C29E4.12|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016210|C29F5.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016210|C29F5.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016210|C29F5.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5669|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016210|C29F5.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016210|C29F5.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016212|C29F5.3|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1484|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00016212|C29F5.3|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016212|C29F5.3|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|1042nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|242nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|285nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2560|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=400|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|798nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|836nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|838nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016215|glb-10|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016216|C29F9.1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016216|C29F9.1|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016216|C29F9.1|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016216|C29F9.1|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=462|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016217|C29F9.2|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=205|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016217|C29F9.2|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016217|C29F9.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016217|C29F9.2|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3b|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3b|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3b|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|1304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|1558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|1566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|1570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=297|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016218|C29F9.3c|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016219|C29F9.4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016219|C29F9.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016219|C29F9.4|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=370|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016219|C29F9.4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016219|C29F9.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=345|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016219|C29F9.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016220|C29F9.5|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016221|C29F9.6.2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016221|C29F9.6.2|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016221|C29F9.6.2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016221|C29F9.6.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016225|fbxa-58|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016226|C29F9.12|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016227|nhr-280|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016227|nhr-280|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00016229|C29G2.1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016229|C29G2.1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016229|C29G2.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016231|C29G2.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00016231|C29G2.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00016231|C29G2.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00016232|srt-4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016232|srt-4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016234|C29G2.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016234|C29G2.6|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016234|C29G2.6|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=350|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016234|C29G2.6|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=315|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00016234|C29G2.6|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016234|C29G2.6|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|1055nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8117|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=569|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016235|C29H12.2.2|950nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016236|cec-9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016236|cec-9|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1257|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016236|cec-9|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016236|cec-9|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016237|C29H12.6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016237|C29H12.6|1137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016237|C29H12.6|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016237|C29H12.6|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2623|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016237|C29H12.6|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=582|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016237|C29H12.6|862nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3056|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1597|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016238|C30A5.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016239|C30A5.4|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016239|C30A5.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016242|C30A5.10a|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016242|C30A5.10a|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016242|C30A5.10a|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=996|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4556|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=583|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016244|C30B5.2a|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016245|C30B5.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1694|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016246|daf-37|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016246|daf-37|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016246|daf-37|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016246|daf-37|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016246|daf-37|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016247|C30B5.6a|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016247|C30B5.6b|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016248|C30B5.7|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016248|C30B5.7|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016248|C30B5.7|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016248|C30B5.7|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2568|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016248|C30B5.7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016249|mrpl-32|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1883|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016249|mrpl-32|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016249|mrpl-32|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016249|mrpl-32|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5235|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26135|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1297|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|427nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|593nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1522|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016250|hsp-110|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016251|C30E1.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016254|fbxb-114|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016254|fbxb-114|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7940|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016258|vha-16|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20344|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016259|C30F8.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016260|C30F12.1|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016260|C30F12.1|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016260|C30F12.1|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1420|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016260|C30F12.1|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016260|C30F12.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016260|C30F12.1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016261|C30F12.2.1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=600|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016261|C30F12.2.1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1722|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016261|C30F12.2.1|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016261|C30F12.2.1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016262|C30F12.3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016262|C30F12.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016262|C30F12.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016262|C30F12.3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016262|C30F12.3|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016262|C30F12.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2812|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|372nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|375nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016263|C30F12.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016264|C30F12.5b|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016265|nmur-4|250nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016265|nmur-4|255nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016265|nmur-4|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=320|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016265|nmur-4|277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016266|idhg-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016266|idhg-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=994|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016266|idhg-2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016266|idhg-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016266|idhg-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016268|C30G4.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00016268|C30G4.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016268|C30G4.2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016269|C30G4.4s.2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016269|C30G4.4s.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2301|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016269|C30G4.4s.2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016269|C30G4.4s.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016273|C30G12.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016273|C30G12.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016273|C30G12.1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=863|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2057|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016274|C30G12.2|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016275|C30G12.3|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016275|C30G12.3|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016275|C30G12.3|796nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=932|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016276|C30G12.4|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1214|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016276|C30G12.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016276|C30G12.4|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|1293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|1351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=674|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016277|C30G12.6a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|456nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3442|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|459nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|615nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|617nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|853nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|855nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016278|C30H7.2a.1|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016279|C31B8.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016280|C31B8.2|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016280|C31B8.2|456nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016280|C31B8.2|460nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016281|C31B8.4|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016281|C31B8.4|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016281|C31B8.4|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016281|C31B8.4|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016281|C31B8.4|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016282|C31B8.7|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016282|C31B8.7|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016283|C31B8.8|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016283|C31B8.8|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=507|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016285|C31B8.12|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016286|C31H1.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=493|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016286|C31H1.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016286|C31H1.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016287|C31H1.2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016287|C31H1.2|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016287|C31H1.2|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00016287|C31H1.2|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016287|C31H1.2|968nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016288|C31H1.5|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016288|C31H1.5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016288|C31H1.5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016288|C31H1.5|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016288|C31H1.5|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016288|C31H1.5|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=712|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016288|C31H1.5|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13104|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4796|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=527|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2081|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2261|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3521|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016289|lntl-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8756|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016291|C31H1.8d|830nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016292|tbc-7|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016292|tbc-7|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4287|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016292|tbc-7|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|1273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2471|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=688|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=543|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|765nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016293|C31H2.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016294|C31H2.4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016294|C31H2.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016295|fbxc-40|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016295|fbxc-40|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016297|fbxc-15|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016297|fbxc-15|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016298|fbxc-14|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016299|C32B5.6|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016299|C32B5.6|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016302|fbxc-7|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016302|fbxc-7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016303|fbxc-32|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016303|fbxc-32|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016303|fbxc-32|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016307|fbxc-18|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016308|C32B5.15|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016309|sdz-4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00016309|sdz-4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=392|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016310|C32D5.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016311|C32D5.3.2|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=203|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016311|C32D5.3.2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016311|C32D5.3.2|800nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016311|C32D5.3.2|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3889|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016312|C32D5.4|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016312|C32D5.4|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016312|C32D5.4|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016312|C32D5.4|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016312|C32D5.4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3353|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016313|set-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016314|C32D5.6|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016314|C32D5.6|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016314|C32D5.6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016314|C32D5.6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016314|C32D5.6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|1096nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1536|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=436|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016315|C32D5.7|805nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3602|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11610|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|723nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|726nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|729nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016316|C32D5.8a|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|1311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|1462nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|1572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|230nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016317|C32D5.10|368nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1955|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|19nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=220|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1342|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|23nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016318|C32D5.11|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|278nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|284nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|287nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016319|C32D5.12|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016320|C32E8.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016320|C32E8.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8516|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|1473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|218nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016321|tppp-1|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4053|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|643nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|649nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016322|C32E8.4.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=608|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2423|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016323|C32E8.5.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|181nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|183nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|220nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|228nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4623|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1221|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|1066nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|1082nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|1159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|1315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|906nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016324|C32E8.6b|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016325|C32E8.9|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016325|C32E8.9|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2240|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016325|C32E8.9|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=260|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016325|C32E8.9|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|1536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2530|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2386|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016326|ubr-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016327|C32E12.1.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00016327|C32E12.1.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00016328|pde-5|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016328|pde-5|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016328|pde-5|153nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016328|pde-5|156nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=43|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016328|pde-5|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016328|pde-5|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016328|pde-5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016329|osr-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016329|osr-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016329|osr-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016329|osr-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016330|C32E12.4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016330|C32E12.4|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016330|C32E12.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=710|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|322nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=716|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|330nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2727|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|333nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|335nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016331|obr-4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|1562nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|1568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|1570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|1573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|1591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1468|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016332|C32F10.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7499|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8a.4|754nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8b.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016333|C32F10.8b.4|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|558nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016335|gba-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016336|C33C12.4|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016336|C33C12.4|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016336|C33C12.4|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=326|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016337|fbxb-38|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016339|C33C12.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016339|C33C12.7|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1210|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016339|C33C12.7|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016339|C33C12.7|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016340|gba-2|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016341|mtq-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1884|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016341|mtq-2|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016341|mtq-2|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016341|mtq-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016341|mtq-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016341|mtq-2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016341|mtq-2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1268|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1590|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016342|C33C12.10|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016344|rsef-1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016344|rsef-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016344|rsef-1|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016344|rsef-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016344|rsef-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016345|C33E10.1|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016345|C33E10.1|664nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016345|C33E10.1|667nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016345|C33E10.1|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016346|fbxa-120|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016346|fbxa-120|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016349|C33E10.8|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016350|C33E10.10|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016351|C33F10.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016351|C33F10.1|24nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016351|C33F10.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2306|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016351|C33F10.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3132|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016351|C33F10.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016351|C33F10.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016351|C33F10.1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|1154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|1156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016352|tbck-1|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016353|C33F10.4|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016353|C33F10.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016353|C33F10.4|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016353|C33F10.4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=494|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016353|C33F10.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016353|C33F10.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016354|rig-6|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016354|rig-6|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016354|rig-6|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4510|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016354|rig-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016355|lact-5|705nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016355|lact-5|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016355|lact-5|772nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016355|lact-5|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016355|lact-5|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=744|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00016356|C33F10.8|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016356|C33F10.8|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016356|C33F10.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=644|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016356|C33F10.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|1445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|1449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|1458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2261|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2754|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=672|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016357|C33F10.11b.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016358|C33F10.12|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016358|C33F10.12|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1058|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00016358|C33F10.12|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016358|C33F10.12|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016358|C33F10.12|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016358|C33F10.12|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016359|fbxb-88|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016359|fbxb-88|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016359|fbxb-88|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016359|fbxb-88|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016359|fbxb-88|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016360|C33G8.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016360|C33G8.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016360|C33G8.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016360|C33G8.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016360|C33G8.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016360|C33G8.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016361|drd-10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016361|drd-10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016361|drd-10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016361|drd-10|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016361|drd-10|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=773|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=779|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|1497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016362|C33G8.4|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=357|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016363|srab-4|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016364|nhr-161|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016364|nhr-161|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016365|nhr-139|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016365|nhr-139|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016366|nhr-140|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016366|nhr-140|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016366|nhr-140|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00016367|nhr-162|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016368|nhr-163|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|215nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=384|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|218nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016369|C33G8.13|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016370|C33H5.1|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016370|C33H5.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016370|C33H5.1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016371|C33H5.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00016371|C33H5.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=201|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=500|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=279|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016373|swd-2.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|1404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2246|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=216|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=995|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016374|swd-2.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016375|C33H5.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016375|C33H5.8|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=719|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016375|C33H5.8|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=797|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00016375|C33H5.8|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=359|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1112|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016376|sec-10|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016378|imp-3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016378|imp-3|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1895|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016378|imp-3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2537|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00016378|imp-3|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016378|imp-3|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016378|imp-3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016378|imp-3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1891|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1486|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016379|C33H5.13c|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016380|ntp-1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016380|ntp-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1944|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016380|ntp-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=994|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=862|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016381|sgo-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016382|C33H5.16|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016382|C33H5.16|1592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016382|C33H5.16|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016382|C33H5.16|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016383|zgpa-1|1392nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016383|zgpa-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016383|zgpa-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00016383|zgpa-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|1142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|1426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|1529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|1531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|215nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5893|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016384|cdgs-1|863nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016386|tag-272|173nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016386|tag-272|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016386|tag-272|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016386|tag-272|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016387|kbp-5|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016387|kbp-5|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1667|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016387|kbp-5|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016387|kbp-5|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016388|C34B2.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016388|C34B2.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=400|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00016388|C34B2.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016388|C34B2.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016388|C34B2.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016389|C34B2.4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016389|C34B2.4|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016389|C34B2.4|940nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00016389|C34B2.4|948nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016390|C34B2.5|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016390|C34B2.5|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2817|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016390|C34B2.5|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016390|C34B2.5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3559|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016391|C34B2.6|969nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3666|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016392|sdha-2|751nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=678|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|1573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=353|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3193|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5739|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|225nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=253|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|230nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=284|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=192|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016393|C34B2.8|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=740|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016394|C34B2.9|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016394|C34B2.9|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1188|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016394|C34B2.9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016394|C34B2.9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|1443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1226|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38831|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=814|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|43nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|52nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016395|C34B2.10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|1221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=612|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016396|C34B2.11|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016397|C34D4.1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016397|C34D4.1|154nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016397|C34D4.1|173nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016397|C34D4.1|178nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016397|C34D4.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016397|C34D4.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016397|C34D4.1|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016398|C34D4.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016398|C34D4.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016398|C34D4.2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016398|C34D4.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1312|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016398|C34D4.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1852|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2315|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016399|C34D4.3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1039|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|1246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|1251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|191nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|194nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|196nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|201nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|203nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=217|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|218nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2180|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=472|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|227nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2769|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016400|C34D4.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016402|C34D4.10|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016402|C34D4.10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016402|C34D4.10|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016402|C34D4.10|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016402|C34D4.10|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2399|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016403|grsp-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016404|mutd-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016404|mutd-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4769|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016404|mutd-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=922|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016404|mutd-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016404|mutd-1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016404|mutd-1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9825|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016405|hecd-1|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|1011nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|1015nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016406|C34D10.1|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016407|C34D10.2b.2|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016407|C34D10.2b.2|1251nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016407|C34D10.2b.2|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016407|C34D10.2b.2|1448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1686|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016407|C34D10.2b.2|1455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016407|C34D10.2b.2|440nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016407|C34D10.2b.2|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016408|prmt-5|1056nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016408|prmt-5|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016408|prmt-5|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2207|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016408|prmt-5|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1126|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016408|prmt-5|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016409|sumv-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016409|sumv-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1995|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016409|sumv-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016409|sumv-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016410|C34E10.9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016410|C34E10.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016411|C34E10.10|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016411|C34E10.10|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016411|C34E10.10|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1331|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016411|C34E10.10|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016411|C34E10.10|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016412|mrps-26|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016412|mrps-26|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1510|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016412|mrps-26|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1613|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016412|mrps-26|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016412|mrps-26|773nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016413|C34F11.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016414|C34F11.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016414|C34F11.2|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016414|C34F11.2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=817|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016414|C34F11.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016414|C34F11.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016414|C34F11.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016414|C34F11.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016415|ampd-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1517|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016415|ampd-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7666|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016415|ampd-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|1001nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1595|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|1003nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|1043nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|945nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|975nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|986nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|990nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016416|C34F11.5|992nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10924|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=438|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=867|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016417|C34F11.8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016418|hpo-27|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1111|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016418|hpo-27|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016418|hpo-27|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1082|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=727|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3104|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016419|tyr-4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016420|C34G6.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=715|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016420|C34G6.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016420|C34G6.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016421|cdc-7|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016421|cdc-7|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1673|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016421|cdc-7|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016421|cdc-7|369nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016421|cdc-7|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|341nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|343nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1624|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016422|noah-1|566nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|544nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|552nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|555nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|558nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016423|tag-275|980nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|458nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|541nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=67|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|545nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=63|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|548nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=153|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|554nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016424|C34H4.1a|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=335|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1275|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016425|C34H4.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016427|C34H4.5b|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016427|C34H4.5b|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016427|C34H4.5b|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016427|C34H4.5b|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016428|dmsr-7|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016428|dmsr-7|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1404|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00016428|dmsr-7|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=440|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016428|dmsr-7|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016428|dmsr-7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016428|dmsr-7|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|186nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016429|C35A11.2|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016431|C35A11.4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|13nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4126|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=362|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|19nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|703nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2a|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|16nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016432|C35B1.2c|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016433|C35B1.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016434|C35B1.4.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016434|C35B1.4.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4445|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016434|C35B1.4.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|35nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|37nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=602|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5793|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016435|C35B1.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016436|C35B1.7|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016436|C35B1.7|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016436|C35B1.7|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016436|C35B1.7|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016436|C35B1.7|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016437|C35B1.8|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016437|C35B1.8|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=550|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|556nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016438|C35B8.3a.2|755nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016439|C35D10.1.2|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016439|C35D10.1.2|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=556|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016439|C35D10.1.2|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2676|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016439|C35D10.1.2|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3214|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016439|C35D10.1.2|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016439|C35D10.1.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016439|C35D10.1.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016440|gipc-1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016440|gipc-1|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016440|gipc-1|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016440|gipc-1|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016440|gipc-1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016440|gipc-1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7866|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016440|gipc-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016441|C35D10.3|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016441|C35D10.3|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016441|C35D10.3|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016441|C35D10.3|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016441|C35D10.3|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016442|C35D10.5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016442|C35D10.5|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016442|C35D10.5|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016442|C35D10.5|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1608|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00016442|C35D10.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016442|C35D10.5|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016443|C35D10.6|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016443|C35D10.6|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016443|C35D10.6|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016443|C35D10.6|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1985|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016443|C35D10.6|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1216|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016443|C35D10.6|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016444|C35D10.7a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3655|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016445|C35D10.8|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016445|C35D10.8|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016445|C35D10.8|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1557|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016445|C35D10.8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016445|C35D10.8|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|1040nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|1050nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|154nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=489|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1368|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|164nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|78nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016446|C35D10.10|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016447|msd-4|782nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016448|C35D10.12|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016448|C35D10.12|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00016448|C35D10.12|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1026|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4885|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016449|C35D10.13|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016450|clec-5|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016450|clec-5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1077|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016450|clec-5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016450|clec-5|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016450|clec-5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016451|clec-6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016451|clec-6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016452|C35D10.17|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016452|C35D10.17|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=969|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00016452|C35D10.17|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3175|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016452|C35D10.17|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016452|C35D10.17|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016453|vet-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016453|vet-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=517|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|1194nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|281nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=927|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|285nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=202|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016454|C35E7.2a|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016455|C35E7.3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016455|C35E7.3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016455|C35E7.3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016456|C35E7.4|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1019|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5b|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016457|C35E7.5b|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016459|C35E7.7|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016459|C35E7.7|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016459|C35E7.7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00016460|C35E7.8|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016460|C35E7.8|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016460|C35E7.8|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00016460|C35E7.8|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016460|C35E7.8|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016460|C35E7.8|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016460|C35E7.8|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016461|C35E7.9|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=456|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016461|C35E7.9|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016462|C35E7.10a|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016462|C35E7.10a|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016462|C35E7.10a|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016462|C35E7.10a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016462|C35E7.10a|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1258|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016462|C35E7.10a|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016462|C35E7.10a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1486|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4629|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016463|C35E7.11|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016464|C36B7.1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016464|C36B7.1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016464|C36B7.1|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00016464|C36B7.1|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016465|C36B7.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016466|C36B7.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016466|C36B7.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016467|C36B7.4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016467|C36B7.4|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016468|C36B7.5a|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016468|C36B7.5a|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|1013nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1590|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|302nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|307nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016469|C36B7.6|876nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016471|srab-8|15nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016472|srbc-6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016472|srbc-6|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016473|C36C5.4b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016474|C36C5.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016474|C36C5.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=976|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016474|C36C5.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016475|srab-9|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016476|srab-10|122nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=23|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016476|srab-10|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016477|srab-11|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016478|srt-72|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016481|C36C5.12|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=355|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016481|C36C5.12|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016483|C36C5.14|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00016483|C36C5.14|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00016484|C36C5.15|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00016484|C36C5.15|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00016485|meg-4|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=616|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00016485|meg-4|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016485|meg-4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016485|meg-4|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|1229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|1232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=438|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|1245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|1274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|293nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=368|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016486|fbxa-170|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016488|C36C9.5|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00016488|C36C9.5|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00016489|C36E6.1a|1196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016489|C36E6.1b|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016489|C36E6.1b|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016489|C36E6.1b|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3265|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|1098nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=465|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016490|C36E6.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016491|acdh-5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016491|acdh-5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016492|C37A2.6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016492|C37A2.6|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016492|C37A2.6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3440|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1095|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105532|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4057|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016493|C37A2.7|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|20nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|22nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|25nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4496|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8a|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|427nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|466nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016494|C37A2.8b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016495|C37C3.1a|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016495|C37C3.1a|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016495|C37C3.1a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016495|C37C3.1a|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1881|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016495|C37C3.1a|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016495|C37C3.1a|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016495|C37C3.1a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2a.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2896|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|1069nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=660|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9559|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4481|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|314nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016496|C37C3.2c.1|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016497|vps-32.2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016497|vps-32.2|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016497|vps-32.2|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016499|C37C3.7|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016499|C37C3.7|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=240|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016499|C37C3.7|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016500|memo-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016500|memo-1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016500|memo-1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016500|memo-1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3250|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016500|memo-1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=297|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6079|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|241nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|244nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|246nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016501|C37C3.9|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016502|C37C3.10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016502|C37C3.10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016502|C37C3.10|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016503|C37C3.11|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016503|C37C3.11|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=985|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016503|C37C3.11|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016503|C37C3.11|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016504|C37C3.12|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|1418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1622|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2727|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=505|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016505|ttr-33|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016506|abhd-5.1|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016506|abhd-5.1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016506|abhd-5.1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=919|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7777|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016507|abhd-5.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016508|C37H5.5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016508|C37H5.5|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016508|C37H5.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016508|C37H5.5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1983|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016508|C37H5.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14940|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1404|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=507|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016509|adss-1|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=339|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1553|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=298|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|316nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=489|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|322nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=382|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=765|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016511|C37H5.13a|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=635|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016512|C38C3.3b|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016512|C38C3.3b|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016512|C38C3.3b|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=433|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016512|C38C3.3b|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016512|C38C3.3b|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016512|C38C3.3b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016513|C38C3.4b|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016513|C38C3.4b|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016513|C38C3.4b|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=433|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016513|C38C3.4b|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016513|C38C3.4b|929nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016514|C38C3.6a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016514|C38C3.6a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016514|C38C3.6a|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016514|C38C3.6a|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=433|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016514|C38C3.6a|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016517|nhr-260|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016518|C38C5.1a|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016519|srz-56|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016519|srz-56|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016519|srz-56|287nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016519|srz-56|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016520|C39B5.2b|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016522|fbxa-38|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016523|C39B5.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1116|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016523|C39B5.5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=781|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016523|C39B5.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016523|C39B5.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016523|C39B5.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016523|C39B5.5|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016523|C39B5.5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016524|C39B5.6|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016524|C39B5.6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016524|C39B5.6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016524|C39B5.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016527|fbxa-47|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016527|fbxa-47|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016529|C39D10.1|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016529|C39D10.1|877nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2961|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|516nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1527|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|709nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016530|C39D10.2|924nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016531|C39D10.3a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1059|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016531|C39D10.3a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016531|C39D10.3a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016532|C39D10.5|909nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016532|C39D10.5|914nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016532|C39D10.5|918nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016532|C39D10.5|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016533|C39D10.6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016533|C39D10.6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016533|C39D10.6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016533|C39D10.6|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=652|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5152|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12530|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016534|C39D10.7.1|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016535|C39D10.8a|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016535|C39D10.8a|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016535|C39D10.8a|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016535|C39D10.8a|330nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5434|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016535|C39D10.8a|333nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016535|C39D10.8a|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016535|C39D10.8a|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016537|C39E6.2|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|242nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2296|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|414nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|422nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016538|C39F7.1a|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016539|madd-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016539|madd-2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016539|madd-2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016539|madd-2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016539|madd-2|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016539|madd-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016540|C39F7.5|1001nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016540|C39F7.5|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016540|C39F7.5|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016540|C39F7.5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016540|C39F7.5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016540|C39F7.5|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016540|C39F7.5|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016541|C39H7.1.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016541|C39H7.1.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016541|C39H7.1.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016541|C39H7.1.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2666|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016541|C39H7.1.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016541|C39H7.1.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|1476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=380|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016542|C39H7.4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016543|srsx-14|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016545|C40A11.2.1|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016545|C40A11.2.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016546|C40A11.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016546|C40A11.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016547|C40A11.4|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016547|C40A11.4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016547|C40A11.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016549|C40A11.6|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016549|C40A11.6|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016549|C40A11.6|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016550|C40A11.7|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016551|C40A11.8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016553|C40A11.10.2|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016553|C40A11.10.2|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016555|math-20|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=346|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016555|math-20|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016555|math-20|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016555|math-20|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016556|math-21|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016556|math-21|629nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016557|ceh-84|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016558|C41A3.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1344|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016558|C41A3.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|1064nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|1184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|1236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|1244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|1248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|1254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|1271nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=425|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016559|C41A3.2b|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|1086nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|24nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9751|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3390|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016561|eri-6|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016562|C41D11.3b.1|155nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016562|C41D11.3b.1|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016562|C41D11.3b.1|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016562|C41D11.3b.1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016562|C41D11.3b.1|530nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016562|C41D11.3b.1|539nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2041|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2328|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016564|cmt-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016565|C41D11.6|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016566|eri-7|1177nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016566|eri-7|1241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016566|eri-7|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016566|eri-7|271nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016566|eri-7|274nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016566|eri-7|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1701|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00016567|C41D11.9|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016567|C41D11.9|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1749|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016567|C41D11.9|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016567|C41D11.9|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016567|C41D11.9|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016568|C41G11.1b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016568|C41G11.1b|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016568|C41G11.1b|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2164|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00016568|C41G11.1b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016568|C41G11.1b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016570|gnrr-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016570|gnrr-4|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016570|gnrr-4|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1405|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016570|gnrr-4|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016570|gnrr-4|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016570|gnrr-4|344nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016571|C41H7.1|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=129|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016573|C41H7.3|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=898|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016573|C41H7.3|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016573|C41H7.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016573|C41H7.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016574|C41H7.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016574|C41H7.4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016574|C41H7.4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=737|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016574|C41H7.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=640|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016574|C41H7.4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016575|C41H7.5a|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1285|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016575|C41H7.5a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016575|C41H7.5b|810nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016576|C41H7.6|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016576|C41H7.6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4659|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016576|C41H7.6|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016576|C41H7.6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016576|C41H7.6|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016576|C41H7.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016576|C41H7.6|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016577|clec-3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016577|clec-3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016577|clec-3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016577|clec-3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016577|clec-3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016578|sdz-5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016578|sdz-5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016578|sdz-5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00016578|sdz-5|666nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016579|sre-14|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016579|sre-14|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|1209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|510nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016580|C42C1.2|956nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016581|C42C1.3a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=333|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016582|C42C1.4d|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2838|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|420nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016583|tag-335|939nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016585|oac-59|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016586|C42C1.8|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=360|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016586|C42C1.8|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1383|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016586|C42C1.8|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016586|C42C1.8|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016586|C42C1.8|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1258|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016586|C42C1.8|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016587|C42C1.9a|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016587|C42C1.9a|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=591|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016587|C42C1.9a|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|1053nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|1518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1995|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1530|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016588|hpo-12|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3273|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|280nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|294nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016589|C42C1.11c.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2097|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016590|C42C1.12.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016591|C42C1.13b|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016591|C42C1.13b|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4424|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016591|C42C1.13b|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016592|erl-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016592|erl-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016592|erl-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1540|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016592|erl-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016592|erl-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016594|C42D4.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016594|C42D4.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11979|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016594|C42D4.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016594|C42D4.1|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2469|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016594|C42D4.1|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=257|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016594|C42D4.1|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016595|C42D4.2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00016595|C42D4.2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|1314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1955|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016596|C42D4.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016597|clec-179|1092nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016597|clec-179|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016597|clec-179|690nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016598|C42D4.13b|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=154|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016598|C42D4.13b|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=293|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016598|C42D4.13b|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016598|C42D4.13b|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|383nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|386nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|396nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|404nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016599|C42D8.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016600|ets-5|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=606|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016600|ets-5|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016600|ets-5|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016600|ets-5|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|307nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1083|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1420|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016601|acin-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=929|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016602|mus-81|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|1249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|358nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=197|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|364nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2335|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=201|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=291|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|407nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|409nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016603|met-1|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016605|C43E11.5|1134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016605|C43E11.5|35nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016605|C43E11.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016605|C43E11.5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=726|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016605|C43E11.5|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016605|C43E11.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016606|exoc-7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016606|exoc-7|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2168|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016606|exoc-7|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016606|exoc-7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016606|exoc-7|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016606|exoc-7|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3825|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|1552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016607|C43E11.9|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016608|cogc-5|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016608|cogc-5|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016608|cogc-5|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016608|cogc-5|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016608|cogc-5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2323|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016609|C43E11.12a.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=939|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016609|C43E11.12a.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016609|C43E11.12a.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1293|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016609|C43E11.12a.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|325nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|340nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5705|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1196|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|417nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|420nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016610|paqr-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016611|bicd-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016611|bicd-1|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016611|bicd-1|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016611|bicd-1|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016611|bicd-1|846nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=439|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016611|bicd-1|856nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016611|bicd-1|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016612|C43G2.3a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016612|C43G2.3a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016612|C43G2.3a|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=400|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016612|C43G2.3a|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016613|best-9|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016613|best-9|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016614|trpp-12|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016614|trpp-12|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1162|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016614|trpp-12|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=828|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016614|trpp-12|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=697|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016614|trpp-12|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016614|trpp-12|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7214|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6062|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=654|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016616|C43H6.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016617|C43H6.4|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016617|C43H6.4|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1210|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016617|C43H6.4|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016619|C43H6.6|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016619|C43H6.6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00016619|C43H6.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016619|C43H6.6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016619|C43H6.6|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|140nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=169|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|145nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=541|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|150nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|152nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|182nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016620|dhhc-9|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016621|arch-1|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016621|arch-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016621|arch-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1673|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00016621|arch-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016621|arch-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016621|arch-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016621|arch-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2547|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016622|mafr-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=923|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=730|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016623|psmd-9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=958|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=878|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016624|C44B7.2a.3|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016625|aff-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016625|aff-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016625|aff-1|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016626|clhm-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016626|clhm-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1255|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00016626|clhm-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016626|clhm-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016626|clhm-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016626|clhm-1|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016626|clhm-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|1392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11107|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18492|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016627|C44B7.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|991nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016628|slc-36.5|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1484|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016629|C44B7.7|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12333|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016630|acer-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|1019nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016631|C44B7.11|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016632|C44B7.12|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016632|C44B7.12|376nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016632|C44B7.12|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016632|C44B7.12|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016632|C44B7.12|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1584|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016632|C44B7.12|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016632|C44B7.12|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016633|C44B11.1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11959|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3362|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016634|C44B11.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016635|C44B11.6|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016635|C44B11.6|1310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016635|C44B11.6|1316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016635|C44B11.6|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016635|C44B11.6|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14920|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016635|C44B11.6|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1552|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3713|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112797|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00016636|perm-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5868|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016637|C44B12.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016637|C44B12.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016637|C44B12.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016637|C44B12.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1440|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=544|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=315|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141235|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016638|perm-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016639|C44B12.6b|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=354|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016639|C44B12.6b|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016639|C44B12.6b|354nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016639|C44B12.6b|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016639|C44B12.6b|366nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016639|C44B12.6b|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016639|C44B12.6b|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016641|C44C1.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=915|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=753|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016642|chil-10|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=966|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=922|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1235|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016643|vps-45|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016644|abhd-3.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016644|abhd-3.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016644|abhd-3.2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016644|abhd-3.2|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=740|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016644|abhd-3.2|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016644|abhd-3.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016644|abhd-3.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3411|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016645|C44C1.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016648|fbxc-2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016648|fbxc-2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=707|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016648|fbxc-2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00016648|fbxc-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016648|fbxc-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016648|fbxc-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016649|fbxc-1|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016649|fbxc-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=777|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016649|fbxc-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016649|fbxc-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016649|fbxc-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016649|fbxc-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016650|C44E4.1b|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016650|C44E4.1b|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00016650|C44E4.1b|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00016650|C44E4.1b|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=941|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016650|C44E4.1b|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2755|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016652|got-2.1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2428|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016652|got-2.1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016652|got-2.1|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1651|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=664|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13245|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1139|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|229nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|232nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|384nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016653|C44E4.4|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016654|C44E4.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016654|C44E4.5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016654|C44E4.5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016654|C44E4.5|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1447|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016654|C44E4.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=677|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|377nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16051|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=506|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016655|acbp-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016657|C44E12.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00016657|C44E12.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5261|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11356|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=569|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016658|C45B2.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3202|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016659|C45B2.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016660|C45B2.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=992|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016661|C45B2.6.2|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2129|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|710nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|715nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|719nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|723nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|727nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|892nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=226|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|901nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|948nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|956nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=346|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016662|C45B2.8|977nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|115nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|382nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|397nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1922|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|405nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|407nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016663|C45E1.4|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016664|C45E5.1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016664|C45E5.1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016664|C45E5.1|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=374|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016664|C45E5.1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016664|C45E5.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016665|chil-11|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|1150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|1153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2081|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|93nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016667|C45E5.4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016669|ilys-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=762|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016669|ilys-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016670|ilys-3|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016670|ilys-3|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=687|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016670|ilys-3|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016670|ilys-3|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016671|C45G7.4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=862|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016674|C45G9.2|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016675|C45G9.4|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016675|C45G9.4|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=966|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016675|C45G9.4|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016675|C45G9.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=483|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1997|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|579nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016676|C45G9.5|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6a|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6a|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6a|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|1283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=940|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1143|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=620|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016677|C45G9.6b|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016678|C45G9.7|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1332|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016678|C45G9.7|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016678|C45G9.7|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016678|C45G9.7|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016678|C45G9.7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1798|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016679|C45G9.8|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1880|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=286|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016680|C45G9.9|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016681|C45G9.10b|1153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016681|C45G9.10b|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016682|C45G9.11|15nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016682|C45G9.11|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016682|C45G9.11|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016682|C45G9.11|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016682|C45G9.11|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|1378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016683|C45G9.12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=352|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=388|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12728|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=736|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=500|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|452nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016684|C45G9.13|457nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016686|cyp-33C1|188nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016686|cyp-33C1|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016686|cyp-33C1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016686|cyp-33C1|971nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00016687|srbc-17|1525nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016687|srbc-17|1600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016688|srbc-18|1365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00016688|srbc-18|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00016689|srbc-21|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016692|srbc-24|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016695|C45H4.14b|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016697|cyp-33C2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016697|cyp-33C2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016698|C46A5.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016698|C46A5.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016698|C46A5.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016698|C46A5.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016698|C46A5.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016699|del-7|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016699|del-7|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016700|C46A5.4|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00016700|C46A5.4|1079nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016700|C46A5.4|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016700|C46A5.4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016700|C46A5.4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016700|C46A5.4|1331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016701|C46A5.5b|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=824|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00016701|C46A5.5b|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016701|C46A5.5b|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016701|C46A5.5b|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016701|C46A5.5b|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016702|C46A5.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016702|C46A5.6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=358|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016702|C46A5.6|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=837|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016702|C46A5.6|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016702|C46A5.6|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016702|C46A5.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|13nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|1475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|1481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|1483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|1485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=331|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016703|rdl-1|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|361nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|368nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|374nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|378nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=577|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|384nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=239|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016704|hosl-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2a|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2a|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2b|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2b|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016705|C46C11.2b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|1267nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|1502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1022|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3847|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016706|C46C11.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016707|C46E10.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=666|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016710|fbxc-52|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016710|fbxc-52|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016710|fbxc-52|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016710|fbxc-52|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016710|fbxc-52|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016711|fbxc-53|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016711|fbxc-53|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016711|fbxc-53|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016712|C46E10.8|779nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016712|C46E10.8|786nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016712|C46E10.8|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016713|C46E10.9|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=395|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016714|C46F2.1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016716|acs-17|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1605|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016716|acs-17|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016717|math-22|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016717|math-22|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016717|math-22|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016718|math-23|1481nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016718|math-23|1484nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00016718|math-23|1487nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016719|math-24|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016719|math-24|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016719|math-24|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016720|math-25|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016721|C46G7.1|120nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4513|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00016721|C46G7.1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016721|C46G7.1|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016721|C46G7.1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016721|C46G7.1|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016721|C46G7.1|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=344|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5554|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016722|C46G7.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016724|C46H3.1|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=174|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016724|C46H3.1|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016724|C46H3.1|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016724|C46H3.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016724|C46H3.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016725|C46H3.2b.2|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016725|C46H3.2b.2|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=524|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016725|C46H3.2b.2|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016728|C46H11.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016728|C46H11.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016728|C46H11.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016728|C46H11.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016728|C46H11.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016728|C46H11.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016729|C46H11.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016730|C46H11.6|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016730|C46H11.6|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016731|C46H11.7|1066nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016731|C46H11.7|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016731|C46H11.7|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016731|C46H11.7|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016731|C46H11.7|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016731|C46H11.7|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=441|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016731|C46H11.7|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016732|phat-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016732|phat-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016732|phat-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016732|phat-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016732|phat-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016733|phat-2|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016733|phat-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016733|phat-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016733|phat-2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016733|phat-2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6517|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016733|phat-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016733|phat-2|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016734|C46H11.10b.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016734|C46H11.10b.1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016734|C46H11.10b.1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=825|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016734|C46H11.10b.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016735|fhod-1|365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=462|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016735|fhod-1|370nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=647|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016735|fhod-1|373nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2403|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016738|C47D2.1|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|830nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8751|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|835nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|849nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=709|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|851nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|853nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|857nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=551|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|863nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016739|pitr-1|867nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2809|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016740|C48B6.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|624nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|633nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3245|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|636nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|639nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|641nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016741|C48B6.3|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016742|C48B6.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016742|C48B6.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016743|srb-15|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016743|srb-15|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016743|srb-15|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016743|srb-15|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016744|bbs-9|1482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016744|bbs-9|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016744|bbs-9|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=446|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016744|bbs-9|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=491|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=572|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016745|C48B6.9|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|1272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|1285nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|1390nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8992|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=835|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016746|C48B6.10|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=831|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|329nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016747|nmur-1|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016748|aexr-3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016748|aexr-3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016748|aexr-3|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016748|aexr-3|281nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016748|aexr-3|285nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=516|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3473|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016749|C48E7.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1550|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|225nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=167|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016750|let-611|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016751|C48E7.6|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6456|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016752|C48E7.7|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016753|oac-9|1369nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016753|oac-9|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016753|oac-9|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016753|oac-9|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016753|oac-9|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5771|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|1302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|1314nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|721nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016754|cebp-2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016755|C49A9.1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016755|C49A9.1|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|206nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|211nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016756|C49A9.2|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016757|C49A9.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016757|C49A9.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016757|C49A9.3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016757|C49A9.3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|361nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|494nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|496nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016758|C49A9.4.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016759|C49A9.5|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016759|C49A9.5|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016759|C49A9.5|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016760|C49A9.6|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016760|C49A9.6|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016760|C49A9.6|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016760|C49A9.6|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016760|C49A9.6|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016761|tkr-2|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=401|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016761|tkr-2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016761|tkr-2|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1100|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2942|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|450nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|526nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|72nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016762|ugt-24|977nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=329|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|356nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|365nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016763|C49A9.9a.1|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=541|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016764|C49A9.10|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016765|C49C8.1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016765|C49C8.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016766|C49C8.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016766|C49C8.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016767|C49C8.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00016767|C49C8.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016768|cyp-33E1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016768|cyp-33E1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016768|cyp-33E1|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016768|cyp-33E1|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016768|cyp-33E1|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2530|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016769|C49C8.5.1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016770|C49C8.6|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016770|C49C8.6|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016772|nhr-166|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1651|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016773|oac-10|19nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016773|oac-10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016777|nhr-261|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016778|nep-3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016779|sdz-7|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016780|C49G7.1|1033nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016780|C49G7.1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016780|C49G7.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016780|C49G7.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016780|C49G7.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23368|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016781|C49G7.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016782|phat-3|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1643|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016782|phat-3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016782|phat-3|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016782|phat-3|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016782|phat-3|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12205|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=288|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016783|irg-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=894|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00016784|C49G7.6|1055nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016784|C49G7.6|1277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1055nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=350|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5492|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016785|C49G7.7|992nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016786|cyp-35A4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016786|cyp-35A4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=963|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|1118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|1122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|1373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|1542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|1544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|1565nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23786|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52090|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1549|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|552nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|555nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|563nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|569nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|572nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|577nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016788|C49G7.10|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016789|djr-1.2|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016789|djr-1.2|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1027nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|1417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|29nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|524nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=353|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10328|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1066|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016790|C49H3.3.2|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=487|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|593nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016791|C49H3.4|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=436|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|1068nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2994|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=384|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|281nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|674nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016792|C49H3.6b|678nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1168|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1441|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016793|arp-11|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|431nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|518nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=422|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|526nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|537nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2064|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|542nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|545nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|607nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|611nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|615nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|618nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016794|C49H3.9|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|1094nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|1362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016795|C49H3.12b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|1098nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1408|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|1101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|1104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|1282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|389nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016796|cec-2|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016797|C50A2.3c|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016797|C50A2.3c|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016797|C50A2.3c|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016797|C50A2.3c|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016798|ets-8|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1233|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016799|C50C3.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016800|C50C3.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016800|C50C3.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016800|C50C3.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=180|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1640|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=625|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4740|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=757|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=287|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|527nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|624nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016801|C50C3.5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|1275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|413nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6151|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|426nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016803|bath-42|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016804|C50C3.12|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016805|C50D2.1b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016806|C50D2.2|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016806|C50D2.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016806|C50D2.2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=890|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016806|C50D2.2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016806|C50D2.2|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016806|C50D2.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016806|C50D2.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=412|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00016807|C50D2.3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6813|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016808|C50D2.5|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2225|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016809|C50D2.6c.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016810|C50D2.7|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016810|C50D2.7|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=372|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016810|C50D2.7|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016810|C50D2.7|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016810|C50D2.7|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1504|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016810|C50D2.7|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016811|C50D2.8b|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016811|C50D2.8b|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2285|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016811|C50D2.8b|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016811|C50D2.8b|888nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=518|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=390|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|121nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|126nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016812|C50D2.9|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016813|clec-214|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016816|C50E3.5|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016816|C50E3.5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=867|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00016816|C50E3.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016816|C50E3.5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016817|C50E3.6|13nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016817|C50E3.6|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=953|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016817|C50E3.6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=905|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016817|C50E3.6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00016817|C50E3.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016817|C50E3.6|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016818|C50E3.7|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016820|C50E3.9|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016820|C50E3.9|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016820|C50E3.9|343nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=342|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016821|scl-26|1154nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016822|C50E3.11|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016822|C50E3.11|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016822|C50E3.11|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016823|C50E3.12|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016823|C50E3.12|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016823|C50E3.12|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016823|C50E3.12|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016823|C50E3.12|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016824|C50E3.13|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016825|C50E10.1|1003nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016825|C50E10.1|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016825|C50E10.1|120nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016825|C50E10.1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2378|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016825|C50E10.1|816nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016825|C50E10.1|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016826|C50E10.2a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016826|C50E10.2a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016827|sre-53|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016828|sre-52|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016828|sre-52|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016829|sre-54|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00016829|sre-54|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016829|sre-54|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016830|sre-55|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016831|sre-56|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016832|sre-49|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016833|sre-51|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016833|sre-51|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016834|sre-50|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016834|sre-50|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016834|sre-50|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016836|C50F2.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016836|C50F2.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016836|C50F2.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1436|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1111|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=821|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016837|C50F2.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|877nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|882nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|888nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|891nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016838|C50F2.4.2|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016839|C50F2.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016839|C50F2.5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016839|C50F2.5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016839|C50F2.5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016839|C50F2.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016839|C50F2.5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=687|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016839|C50F2.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016840|C50F2.7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016840|C50F2.7|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016840|C50F2.7|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016840|C50F2.7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016841|magu-3|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1676|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016841|magu-3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016841|magu-3|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016842|npr-35|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016843|C50F7.3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016843|C50F7.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|1440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=564|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=516|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1259|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016844|sucg-1|934nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016845|C50F7.5|1600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016845|C50F7.5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016845|C50F7.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016845|C50F7.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=569|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016845|C50F7.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016845|C50F7.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016845|C50F7.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016846|C50F7.6b|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=309|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016846|C50F7.6b|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016847|C50F7.9|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016847|C50F7.9|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016847|C50F7.9|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016848|klo-1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016848|klo-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016848|klo-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016848|klo-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016848|klo-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016848|klo-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016848|klo-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016849|acs-21|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016849|acs-21|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00016851|srt-71|423nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00016851|srt-71|948nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00016852|srt-7|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016852|srt-7|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016852|srt-7|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016852|srt-7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|405nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|586nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=783|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|588nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016855|C50H11.8|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016856|srt-15|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016856|srt-15|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016856|srt-15|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016857|srt-16|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016857|srt-16|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016858|C50H11.13|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016858|C50H11.13|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016858|C50H11.13|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016858|C50H11.13|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016858|C50H11.13|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016860|cyp-33C9|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016860|cyp-33C9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016860|cyp-33C9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016860|cyp-33C9|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00016860|cyp-33C9|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016860|cyp-33C9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016860|cyp-33C9|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016862|C52A10.1|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016862|C52A10.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016862|C52A10.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1601|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016862|C52A10.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00016862|C52A10.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016862|C52A10.1|777nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016863|C52A10.2|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016863|C52A10.2|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016863|C52A10.2|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016863|C52A10.2|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016863|C52A10.2|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016864|C52A10.3|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016864|C52A10.3|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016864|C52A10.3|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016864|C52A10.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016865|ets-9|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016865|ets-9|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016865|ets-9|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016865|ets-9|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016865|ets-9|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016865|ets-9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016865|ets-9|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=773|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00016866|coel-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1159|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=206|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016867|C52B9.4|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016868|C52B9.8|223nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016868|C52B9.8|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016868|C52B9.8|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=953|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016868|C52B9.8|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016868|C52B9.8|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016869|C52B9.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016869|C52B9.10|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016869|C52B9.10|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016869|C52B9.10|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016870|ets-10|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016870|ets-10|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016870|ets-10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|499nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|504nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1564|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|508nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|510nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|512nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016871|inso-1|514nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016872|dop-4|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016872|dop-4|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016872|dop-4|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=348|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016872|dop-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016872|dop-4|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1269|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|320nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|329nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|331nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016874|C52B11.5|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016877|C52D10.3b|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016877|C52D10.3b|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016877|C52D10.3b|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016877|C52D10.3b|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016879|C52D10.12.2|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1221|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016880|fbxb-95|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016880|fbxb-95|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016880|fbxb-95|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016880|fbxb-95|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016881|C52E2.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016883|C52E2.4|1290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016883|C52E2.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016884|C52E2.5|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016884|C52E2.5|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016885|fbxb-97|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016885|fbxb-97|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016886|fbxb-96|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016886|fbxb-96|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|260nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|273nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1892|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|278nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2206|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|283nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016888|C52E12.1|286nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016889|lst-6|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016889|lst-6|416nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016889|lst-6|424nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1260|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016889|lst-6|426nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1083|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016889|lst-6|428nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=718|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016889|lst-6|431nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016890|lst-5|1576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016890|lst-5|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016890|lst-5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1484|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016891|C53A3.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016891|C53A3.1|240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016891|C53A3.1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016891|C53A3.1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5169|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=892|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016892|C53A3.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1898|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1966|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016893|C53B7.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5933|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3b|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016894|C53B7.3c|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016895|C53B7.6|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016896|nep-4|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016898|C53C9.2|1211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016898|C53C9.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016898|C53C9.2|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016898|C53C9.2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016898|C53C9.2|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3973|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016898|C53C9.2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2888|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016898|C53C9.2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016899|C53C11.1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016899|C53C11.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=127|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016900|C53C11.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016901|C53C11.4|1119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016901|C53C11.4|1144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016902|C53D5.1c|299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016902|C53D5.1c|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=810|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00016902|C53D5.1c|784nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=903|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|412nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016903|marc-4|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=840|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=685|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016905|ztf-3|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016906|C53D5.5b.2|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016906|C53D5.5b.2|733nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016906|C53D5.5b.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1486|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016906|C53D5.5b.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5573|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2a|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2d|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2d|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2d|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2d|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016907|C53H9.2d|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016911|drn-1|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4356|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016912|clec-86|32nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016912|clec-86|35nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016912|clec-86|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016912|clec-86|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016912|clec-86|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1074nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1077nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1083nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2717|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1090nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016913|lam-2|966nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016914|C54D1.7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016914|C54D1.7|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016914|C54D1.7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016914|C54D1.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016915|C54D2.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=774|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016915|C54D2.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016916|C54D2.2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1977|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016916|C54D2.2|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016916|C54D2.2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016916|C54D2.2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016917|C54E4.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016917|C54E4.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016917|C54E4.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016917|C54E4.1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016917|C54E4.1|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016917|C54E4.1|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016917|C54E4.1|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4146|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016918|test-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|1197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|1199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1226|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016919|C54E4.4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016920|C54E4.5|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016920|C54E4.5|295nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016920|C54E4.5|389nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016920|C54E4.5|393nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016920|C54E4.5|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=410|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016920|C54E4.5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016920|C54E4.5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016921|C54F6.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016921|C54F6.3|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016921|C54F6.3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016922|swt-2|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016923|C54F6.5|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016923|C54F6.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=648|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016923|C54F6.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016923|C54F6.5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016924|C54F6.6|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016924|C54F6.6|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016924|C54F6.6|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=222|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016925|srb-18|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=347|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016925|srb-18|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016925|srb-18|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016925|srb-18|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016925|srb-18|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00016925|srb-18|934nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016926|nhr-171|1344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016926|nhr-171|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016928|srb-19|1583nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016928|srb-19|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016928|srb-19|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016928|srb-19|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=593|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016928|srb-19|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016929|C54F6.12|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016929|C54F6.12|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016929|C54F6.12|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016930|madf-6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016931|C54G6.2|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016931|C54G6.2|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016931|C54G6.2|693nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016931|C54G6.2|696nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016931|C54G6.2|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016932|C54G6.3|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=480|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016932|C54G6.3|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016933|C54G7.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=459|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016933|C54G7.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=747|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=420|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016934|mboa-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016935|ifta-1|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016935|ifta-1|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016935|ifta-1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=427|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016935|ifta-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00016935|ifta-1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=392|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=636|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016937|tag-294|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016938|C54H2.4|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016938|C54H2.4|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016938|C54H2.4|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016939|C55B6.1a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016939|C55B6.1a|1330nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016939|C55B6.1a|1385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016939|C55B6.1a|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=404|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016939|C55B6.1a|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016939|C55B6.1a|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016939|C55B6.1a|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016940|C55B6.4|399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016941|C55B6.5|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016942|C55B7.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=442|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016942|C55B7.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016942|C55B7.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016942|C55B7.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|240nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=835|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|511nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|513nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|519nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|526nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=393|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7575|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6430|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2031|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2205|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016943|acdh-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1027|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016944|uri-1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2032|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016944|uri-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016944|uri-1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016945|sulp-1|1161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016945|sulp-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016945|sulp-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016945|sulp-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016945|sulp-1|983nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016946|C55B7.10|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016946|C55B7.10|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|126nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=616|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016947|C55B7.11|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016948|scrt-1|1101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00016948|scrt-1|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00016949|C55C2.3|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016950|C55C2.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016951|C55C3.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016951|C55C3.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016951|C55C3.1|1509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016951|C55C3.1|1511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016951|C55C3.1|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016953|C55C3.3|11nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016953|C55C3.3|18nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=676|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016953|C55C3.3|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016953|C55C3.3|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016953|C55C3.3|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016953|C55C3.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016954|C55C3.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016954|C55C3.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016954|C55C3.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016955|perm-5|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016955|perm-5|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016955|perm-5|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2014|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016955|perm-5|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016956|C55C3.6a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016956|C55C3.6a|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5525|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=838|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016957|atic-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|1010nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|1014nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|1017nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|1020nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6363|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1936|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|523nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79523|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16143|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2188|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|973nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016958|ilys-4|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016960|vps-33.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016960|vps-33.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1274|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016960|vps-33.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016960|vps-33.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|320nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20854|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|324nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=660|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|329nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=316|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016961|vps-32.1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016962|C56C10.4|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016962|C56C10.4|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00016962|C56C10.4|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016962|C56C10.4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016962|C56C10.4|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016962|C56C10.4|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00016963|C56C10.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016963|C56C10.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016963|C56C10.6|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016963|C56C10.6|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1740|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|154nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=576|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=406|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016964|C56C10.7c.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1300|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016965|C56C10.9|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|1041nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|1043nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|1133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1839|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=871|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016966|C56C10.10|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016967|C56C10.11|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016967|C56C10.11|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2003|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016967|C56C10.11|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016967|C56C10.11|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016967|C56C10.11|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016968|epg-5|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016970|C56E6.2|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016970|C56E6.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016970|C56E6.2|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00016971|toe-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016971|toe-2|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=699|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016971|toe-2|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2128|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016971|toe-2|227nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016971|toe-2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016972|C56E6.4|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016972|C56E6.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016973|abch-1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016973|abch-1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016973|abch-1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016974|lron-15|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=268|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016974|lron-15|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016975|nhr-173|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016975|nhr-173|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016975|nhr-173|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016975|nhr-173|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016975|nhr-173|765nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|1153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016976|C56E10.3a|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1162nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1166nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8565|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1655|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=837|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016977|akap-1|756nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016978|C56G2.3|358nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=391|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016978|C56G2.3|361nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016978|C56G2.3|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2591|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=435|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016979|C56G2.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016980|C56G2.5|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|1483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6479|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11467|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016981|C56G2.7|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016982|C56G2.9|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016982|C56G2.9|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016982|C56G2.9|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=706|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016982|C56G2.9|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016982|C56G2.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016982|C56G2.9|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|133nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|324nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|401nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|404nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|600nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|778nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016983|C56G2.15|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|177nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=245|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00016984|npr-8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016985|C56G3.2|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016985|C56G3.2|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016985|C56G3.2|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016985|C56G3.2|939nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016985|C56G3.2|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1500|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016987|CC8.2a|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5635|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=574|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|53nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|55nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=424|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1509|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016988|CD4.1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|1044nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|1057nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|1062nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5460|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=328|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016989|CD4.3.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5554|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00016990|vps-37|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016991|CD4.5|1522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=722|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016992|zhit-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00016993|CD4.8|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=506|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016993|CD4.8|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016993|CD4.8|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3641|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2242|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016995|acly-1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016996|D1005.2|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016996|D1005.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016996|D1005.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11816|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|606nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00016997|cebp-1|674nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00016998|D1005.4|608nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00016999|D1005.5a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00016999|D1005.5a|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00016999|D1005.5a|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017000|D1005.6|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017000|D1005.6|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017000|D1005.6|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017000|D1005.6|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017000|D1005.6|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00017000|D1005.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017001|D1007.3|692nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017001|D1007.3|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017001|D1007.3|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017001|D1007.3|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017002|D1007.4|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017002|D1007.4|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017002|D1007.4|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017002|D1007.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017002|D1007.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017002|D1007.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1708|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=957|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017003|D1007.5a|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017004|nrd-1|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017004|nrd-1|379nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017004|nrd-1|382nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2314|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017004|nrd-1|384nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1236|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00017004|nrd-1|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017004|nrd-1|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017004|nrd-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017005|D1007.8|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017005|D1007.8|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1197|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017005|D1007.8|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017005|D1007.8|1475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017005|D1007.8|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017007|D1007.10b.1|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017007|D1007.10b.1|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017007|D1007.10b.1|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=933|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017007|D1007.10b.1|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017007|D1007.10b.1|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017009|D1007.13b|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017009|D1007.13b|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017009|D1007.13b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017009|D1007.13b|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=350|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017009|D1007.13b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017009|D1007.13b|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017010|D1007.15|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017010|D1007.15|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017010|D1007.15|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=826|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017010|D1007.15|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017010|D1007.15|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017010|D1007.15|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017011|eaf-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017011|eaf-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2707|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017011|eaf-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017011|eaf-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=391|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|350nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1528|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|353nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017012|acs-22|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017013|ensh-1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017013|ensh-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017013|ensh-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017013|ensh-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017014|dylt-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=955|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|582nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|588nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|590nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|630nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017015|D1014.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|1021nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|1025nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=774|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=308|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10307|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=128|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|449nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|458nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|525nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017016|snap-1|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017017|D1014.4|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017017|D1014.4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3532|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017017|D1014.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|188nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|190nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017018|D1014.5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=342|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1029nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1066nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1429nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=28|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1433nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=60|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|1571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017019|D1014.6|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017020|D1014.7a|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00017020|D1014.7a|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017021|D1022.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017021|D1022.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017021|D1022.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017021|D1022.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017022|D1022.3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017022|D1022.3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017022|D1022.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017022|D1022.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00017022|D1022.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=517|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1868|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00017023|D1022.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017024|D1022.5|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017024|D1022.5|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017024|D1022.5|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=616|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017025|D1037.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017026|ipla-4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017026|ipla-4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017027|D1044.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017027|D1044.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017027|D1044.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017027|D1044.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017028|dex-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017028|dex-1|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017028|dex-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017028|dex-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017028|dex-1|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017028|dex-1|960nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017031|D1044.6|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017031|D1044.6|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017031|D1044.6|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017031|D1044.6|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017031|D1044.6|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2996|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017031|D1044.6|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017032|D1044.7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017032|D1044.7|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017032|D1044.7|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017032|D1044.7|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017032|D1044.7|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017032|D1044.7|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=172|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|450nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|453nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017033|nekl-4|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017034|otpl-2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017034|otpl-2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017036|D1069.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017037|D1069.3c|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017037|D1069.3c|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00017037|D1069.3c|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017037|D1069.3c|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017038|dmsr-4|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017038|dmsr-4|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017038|dmsr-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017038|dmsr-4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017038|dmsr-4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1157|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017038|dmsr-4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017039|trk-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017039|trk-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017039|trk-1|558nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1207|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017039|trk-1|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017040|D1079.1|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=929|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|664nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017041|D2007.1|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017042|D2007.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1001|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=289|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|779nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017044|mrpl-18|784nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1431|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=579|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017045|atg-13|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017046|utx-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017046|utx-1|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017046|utx-1|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=875|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017048|D2021.4a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017048|D2021.4a|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017048|D2021.4a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017048|D2021.4a|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017050|D2024.1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017050|D2024.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017051|afmd-1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017051|afmd-1|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017051|afmd-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017051|afmd-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017051|afmd-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017052|D2024.4b|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017052|D2024.4b|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017052|D2024.4b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1421|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017052|D2024.4b|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017052|D2024.4b|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=152|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5184|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3362|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017053|D2024.5a|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|338nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|360nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|366nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017054|gstk-2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017055|D2062.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017056|D2062.4a|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=681|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017056|D2062.4a|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017057|D2062.5|289nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00017057|D2062.5|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017057|D2062.5|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1927|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=288|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=466|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=761|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00017058|D2062.6|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017059|D2062.7|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2117|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017059|D2062.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017059|D2062.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=738|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=295|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=581|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|287nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=337|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|290nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|295nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|297nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=454|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017060|D2063.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017061|oac-12|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017061|oac-12|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=573|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=689|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4816|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017062|glrx-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=915|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017063|mctp-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017064|ppfr-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017064|ppfr-2|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017064|ppfr-2|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00017064|ppfr-2|350nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017064|ppfr-2|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017064|ppfr-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017065|D2092.4|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2504|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00017065|D2092.4|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=821|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017065|D2092.4|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017065|D2092.4|300nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017065|D2092.4|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017065|D2092.4|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017065|D2092.4|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|1001nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3442|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|1007nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|1017nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|963nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|968nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|973nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017066|maco-1|996nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017067|D2092.6|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017067|D2092.6|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017067|D2092.6|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017067|D2092.6|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=245|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017067|D2092.6|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017067|D2092.6|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017067|D2092.6|913nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017068|D2092.8|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=972|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017068|D2092.8|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017069|D2096.1a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017069|D2096.1a|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017069|D2096.1a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017069|D2096.1a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1556|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7313|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2088|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=747|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017070|praf-3|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017071|aagr-1|1221nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017071|aagr-1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=740|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017071|aagr-1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017072|D2096.5|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017072|D2096.5|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017072|D2096.5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=514|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017072|D2096.5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017072|D2096.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017072|D2096.5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1300|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017073|D2096.6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017074|D2096.7a|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017074|D2096.7a|639nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017074|D2096.7d.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2449|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017074|D2096.7d.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017074|D2096.7d.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017074|D2096.7d.1|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3689|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=546|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=903|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15479|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2016|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|315nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14112|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=742|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=346|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017075|nap-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|1530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8586|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|58nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017076|D2096.9|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017077|D2096.10|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017077|D2096.10|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017077|D2096.10|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=866|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017077|D2096.10|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017077|D2096.10|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017078|D2096.11|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017078|D2096.11|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017078|D2096.11|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017078|D2096.11|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017078|D2096.11|676nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017079|D2096.12|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017079|D2096.12|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1282|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017079|D2096.12|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2525|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4445|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|609nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017080|lec-12|832nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017082|DC2.5a|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017082|DC2.5a|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017082|DC2.5a|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017082|DC2.5a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017082|DC2.5a|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017082|DC2.5a|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1128|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017082|DC2.5a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017083|kin-33|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017083|kin-33|1338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017083|kin-33|805nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1174|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1316|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017084|E01A2.1b|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=889|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5423|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|238nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|244nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017085|E01A2.2a.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017087|E01A2.5|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017087|E01A2.5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017087|E01A2.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017087|E01A2.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=773|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017087|E01A2.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=547|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017087|E01A2.5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=857|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2289|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9034|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017088|akir-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017089|poml-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017089|poml-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017089|poml-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00017089|poml-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017089|poml-2|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017090|E01A2.8|685nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017091|ttr-40|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=323|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017091|ttr-40|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=303|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017091|ttr-40|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017091|ttr-40|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017092|E02C12.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017092|E02C12.6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8b|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8b|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8c|1016nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=565|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8c|1127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8c|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8c|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8c|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8c|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017093|E02C12.8c|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017096|E02C12.11|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5834|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1b|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1d|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017098|E02D9.1d|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1702|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017099|E02H9.1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017100|E02H9.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017100|E02H9.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017100|E02H9.2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017100|E02H9.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1889|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=195|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017101|E02H9.3a|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017102|E02H9.4.2|1125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017102|E02H9.4.2|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017102|E02H9.4.2|924nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017102|E02H9.4.2|927nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017103|klo-2|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017103|klo-2|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017103|klo-2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017103|klo-2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017103|klo-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017105|E02H9.7.1|1344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017105|E02H9.7.1|1348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017105|E02H9.7.1|1351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017105|E02H9.7.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=780|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017105|E02H9.7.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017105|E02H9.7.1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017106|E02H9.9|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017106|E02H9.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017107|srt-12|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00017107|srt-12|1253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017107|srt-12|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017107|srt-12|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017107|srt-12|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017107|srt-12|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=597|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017108|cyp-43A1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017109|clec-177|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017110|clec-176|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017111|E03H12.4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017111|E03H12.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|117nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|123nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|126nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|1426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=294|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2163|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017112|E03H12.5|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017113|srz-24|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017113|srz-24|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017113|srz-24|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017113|srz-24|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017114|E03H12.7|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017114|E03H12.7|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017114|E03H12.7|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=812|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017116|fbxb-78|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5667|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=529|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=506|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017119|E04A4.5|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017120|tctn-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017120|tctn-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017120|tctn-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017120|tctn-1|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017120|tctn-1|533nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|1300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|1330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75072|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1176|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017121|cyc-2.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017122|E04F6.2|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017122|E04F6.2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017122|E04F6.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017122|E04F6.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017123|maoc-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4493|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017123|maoc-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017124|E04F6.4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017124|E04F6.4|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017124|E04F6.4|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017124|E04F6.4|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017124|E04F6.4|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017124|E04F6.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017124|E04F6.4|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4752|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017125|acdh-12|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|1217nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|1221nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|1225nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=479|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017126|E04F6.6|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017127|E04F6.8.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017127|E04F6.8.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017127|E04F6.8.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2049|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017127|E04F6.8.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017127|E04F6.8.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017127|E04F6.8.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2051|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017127|E04F6.8.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1002|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00017128|E04F6.9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017128|E04F6.9|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017128|E04F6.9|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017128|E04F6.9|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017128|E04F6.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4888|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017128|E04F6.9|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017128|E04F6.9|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|685nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=454|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1731|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|854nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017129|E04F6.10|888nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017131|E04F6.15|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017131|E04F6.15|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017131|E04F6.15|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017131|E04F6.15|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=713|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017132|tofu-6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017132|tofu-6|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017132|tofu-6|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=383|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017132|tofu-6|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2601|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017133|EEED8.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017133|EEED8.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017134|EEED8.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4917|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017134|EEED8.3|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017135|EEED8.4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=675|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017135|EEED8.4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017136|ccpp-6|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017136|ccpp-6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017136|ccpp-6|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017136|ccpp-6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017136|ccpp-6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1582|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017137|pink-1|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017138|EEED8.10a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017138|EEED8.10a|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017138|EEED8.10a|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2763|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017138|EEED8.10a|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=257|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017138|EEED8.10a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017138|EEED8.10a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017139|clec-141|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017140|EEED8.12|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1156|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017141|EEED8.13|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017141|EEED8.13|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017141|EEED8.13|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017141|EEED8.13|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017142|EEED8.14|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017142|EEED8.14|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017142|EEED8.14|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=553|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017142|EEED8.14|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017143|EEED8.15|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017143|EEED8.15|1010nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017143|EEED8.15|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017143|EEED8.15|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017143|EEED8.15|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=438|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017144|brap-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017144|brap-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017144|brap-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017144|brap-2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017144|brap-2|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2901|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017144|brap-2|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1365|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017144|brap-2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017146|EGAP1.1|1531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017146|EGAP1.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017146|EGAP1.1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017146|EGAP1.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017147|EGAP2.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017147|EGAP2.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=631|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017147|EGAP2.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017148|EGAP2.2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00017148|EGAP2.2|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|1508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|1575nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017149|EGAP4.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=648|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017150|EGAP5.1|580nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017151|EGAP9.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017151|EGAP9.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017153|E_BE45912.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017153|E_BE45912.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017153|E_BE45912.2|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017154|ugt-57|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017154|ugt-57|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017154|ugt-57|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017154|ugt-57|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017154|ugt-57|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017154|ugt-57|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017156|F01E11.3|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017156|F01E11.3|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1654|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017157|tyra-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|1079nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3422|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017158|hpo-10|750nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=754|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2154|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017159|F01F1.2|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=549|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|1113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=362|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017160|F01F1.3|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2225|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=605|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1002|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=622|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017161|rabn-5|799nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017162|ddx-23|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017162|ddx-23|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3078|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017162|ddx-23|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017162|ddx-23|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017162|ddx-23|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4656|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017163|dnpp-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017164|eng-1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017164|eng-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017164|eng-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00017164|eng-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=721|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017164|eng-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017164|eng-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017165|F01F1.11|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2064|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017165|F01F1.11|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017165|F01F1.11|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=539|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=187|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017166|aldo-2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84643|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017168|F01F1.14|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017168|F01F1.14|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2246|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017169|F01F1.15.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017170|F01G12.1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017170|F01G12.1|1430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017172|F02C9.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017172|F02C9.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017172|F02C9.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017172|F02C9.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017172|F02C9.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017173|F02C9.2|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017174|tat-6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017174|tat-6|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017174|tat-6|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017175|irld-3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017175|irld-3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017175|irld-3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017175|irld-3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1085|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=480|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|941nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017176|nmur-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|1298nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|1311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=228|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|345nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1858|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=147|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017177|F02E8.4|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|321nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017178|atg-16.1|334nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017179|wht-4|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017179|wht-4|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017179|wht-4|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017179|wht-4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017180|F02E11.2a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1804|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017180|F02E11.2a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00017180|F02E11.2a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017180|F02E11.2a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017182|F02E11.4|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017183|scl-15|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017183|scl-15|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4584|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017184|ncam-1|513nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017188|F07B7.7|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017189|F07B7.8b|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017190|F07B7.12|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017190|F07B7.12|30nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017190|F07B7.12|34nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017192|F07B7.14|1163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1850|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=736|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=872|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|651nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|890nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017193|F07C3.2|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017195|glo-4|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017195|glo-4|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017195|glo-4|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1314|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017195|glo-4|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017195|glo-4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017197|F07C3.9|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=438|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00017197|F07C3.9|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017197|F07C3.9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017197|F07C3.9|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017197|F07C3.9|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017197|F07C3.9|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017199|clec-45|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017199|clec-45|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017199|clec-45|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017200|F07C4.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017200|F07C4.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017200|F07C4.6|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017200|F07C4.6|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017200|F07C4.6|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017200|F07C4.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017200|F07C4.6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017201|grsp-4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1324|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017201|grsp-4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017201|grsp-4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017201|grsp-4|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017204|F07C4.11|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017205|F07C4.12a|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017205|F07C4.12a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017207|fbxb-6|784nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017208|fbxb-35|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017208|fbxb-35|1293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017208|fbxb-35|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017208|fbxb-35|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017210|F07E5.5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017210|F07E5.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017210|F07E5.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017210|F07E5.5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1265|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017210|F07E5.5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|1255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017211|fbxb-36|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017212|F07E5.7|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017212|F07E5.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017213|F07E5.8|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017213|F07E5.8|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017213|F07E5.8|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017213|F07E5.8|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017214|F07E5.9.2|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017215|F07F6.1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017215|F07F6.1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017215|F07F6.1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017215|F07F6.1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017215|F07F6.1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017215|F07F6.1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017216|F07F6.2|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017216|F07F6.2|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017216|F07F6.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1013nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1089nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|1463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017217|F07F6.4|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017218|dct-5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017218|dct-5|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1891|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017218|dct-5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017218|dct-5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017219|F07F6.7|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=501|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017219|F07F6.7|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017219|F07F6.7|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3929|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=709|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017220|F07F6.8|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017225|fbxa-52|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017226|fbxa-53|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017226|fbxa-53|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017227|F07G6.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017228|F07G11.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00017228|F07G11.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017228|F07G11.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017229|F07G11.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017229|F07G11.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017231|F07G11.4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017231|F07G11.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017233|lmd-4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017233|lmd-4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017236|F08B4.4|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017236|F08B4.4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017236|F08B4.4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017236|F08B4.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017237|pole-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017237|pole-2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017237|pole-2|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1123|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017237|pole-2|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|136nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|145nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3430|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|942nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017238|F08B4.7|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|400nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|406nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1267|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=898|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017239|F08B6.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|1402nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2018|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=390|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017240|calu-2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|148nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|163nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|277nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2360|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|330nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017241|pcyt-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017243|F08C6.5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017244|apy-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017244|apy-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017244|apy-1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017244|apy-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1467|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017244|apy-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017244|apy-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=343|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|743nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3329|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|747nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|751nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|758nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017245|srpa-72|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017246|F08D12.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017246|F08D12.2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017246|F08D12.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017246|F08D12.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=634|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017246|F08D12.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017246|F08D12.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017246|F08D12.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017247|F08D12.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017247|F08D12.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017247|F08D12.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017249|fbxb-108|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017250|F08D12.7|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017250|F08D12.7|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017251|fbxb-105|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00017251|fbxb-105|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00017252|sdz-10|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017252|sdz-10|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017252|sdz-10|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017253|sdz-9|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017253|sdz-9|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017254|fbxb-111|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017254|fbxb-111|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017255|F08D12.12|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017255|F08D12.12|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017255|F08D12.12|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1522|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017255|F08D12.12|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017255|F08D12.12|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017257|F08F1.3|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017257|F08F1.3|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017257|F08F1.3|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00017257|F08F1.3|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017257|F08F1.3|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=252|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1597|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=218|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=426|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=455|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017258|F08F1.4a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017259|F08F1.9|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017260|F08F3.1|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1209|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017260|F08F3.1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017260|F08F3.1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017260|F08F3.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017261|acl-6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017261|acl-6|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1646|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017261|acl-6|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3574|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=478|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017262|F08F3.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=552|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017263|F08F3.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017264|F08F3.8|903nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017264|F08F3.8|906nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017264|F08F3.8|922nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017265|snpc-1.3|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017266|F08F3.10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017267|numr-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|273nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017268|hmgr-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|1596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1809|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|235nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017269|F08F8.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017270|numr-1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00017271|F08F8.6|1474nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017271|F08F8.6|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017271|F08F8.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017271|F08F8.6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017272|F08F8.7.2|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017272|F08F8.7.2|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017272|F08F8.7.2|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017272|F08F8.7.2|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017272|F08F8.7.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017272|F08F8.7.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3017|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=994|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017273|gos-28|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=267|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3754|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=588|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|1267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=224|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|1332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|1472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|1483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017274|F08F8.9a.1|1592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017275|F08F8.10a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017275|F08F8.10a|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017275|F08F8.10a|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017275|F08F8.10a|1590nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017275|F08F8.10a|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017275|F08F8.10a|965nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017275|F08F8.10a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1894|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017277|F09C12.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017277|F09C12.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017278|F09C12.6|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017278|F09C12.6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017278|F09C12.6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2095|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017278|F09C12.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017278|F09C12.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017279|F09C12.8|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017279|F09C12.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017279|F09C12.8|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017279|F09C12.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017280|usp-39|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1676|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017280|usp-39|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017281|F09D12.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1475|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=684|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017282|algn-2|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|1410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1813|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4070|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017283|F09E5.3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=885|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=842|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|458nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017284|sec-6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|273nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2862|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=531|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017285|F09E5.7.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|56nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|60nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3436|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|68nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017286|F09E5.8|776nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017288|F09E5.10|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017288|F09E5.10|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017288|F09E5.10|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017289|F09E5.11|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017289|F09E5.11|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017289|F09E5.11|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017289|F09E5.11|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1056|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017289|F09E5.11|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1442|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017289|F09E5.11|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017290|F09E5.12|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017290|F09E5.12|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=490|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017291|F09E5.14|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017291|F09E5.14|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017291|F09E5.14|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017291|F09E5.14|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2951|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017291|F09E5.14|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=696|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1199|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=464|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=708|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|461nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|463nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|470nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=307|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|472nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|474nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|502nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|511nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|519nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=549|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|522nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1271|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4919|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017292|F09E5.16|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017293|bmy-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017293|bmy-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2127|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017293|bmy-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017293|bmy-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1058nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1066nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1089nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1092nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1099nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=210|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1324|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|965nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|973nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017294|F09E10.1|981nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017295|F09E10.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017295|F09E10.5|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017295|F09E10.5|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017295|F09E10.5|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017295|F09E10.5|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017295|F09E10.5|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017296|F09E10.6|188nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017296|F09E10.6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017296|F09E10.6|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|1053nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1779|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26054|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|784nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017297|F09E10.7a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|589nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3119|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|591nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|595nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|597nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|624nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017298|toca-1|633nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017299|molo-1|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1864|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017299|molo-1|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017299|molo-1|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017300|rpc-2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017300|rpc-2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017300|rpc-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017300|rpc-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017300|rpc-2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3072|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017300|rpc-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017300|rpc-2|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017301|F09F7.4a.2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017301|F09F7.4a.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017301|F09F7.4a.2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017301|F09F7.4a.2|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6769|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017301|F09F7.4a.2|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017301|F09F7.4a.2|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017301|F09F7.4a.2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017302|F09F7.5a.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017303|F09F7.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017303|F09F7.6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017303|F09F7.6|68nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017303|F09F7.6|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017303|F09F7.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017303|F09F7.6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1908|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017304|F09F7.7a|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017304|F09F7.7a|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017304|F09F7.7a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017304|F09F7.7a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2219|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017304|F09F7.7a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1015nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1018nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1022nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1026nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14815|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1067nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1073nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1078nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|1558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|967nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|979nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|993nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017305|nspb-12|999nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017306|F09F9.1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=967|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2056|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017307|F09F9.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017308|F09F9.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017308|F09F9.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017308|F09F9.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017308|F09F9.3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017309|F09F9.4|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017309|F09F9.4|807nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017310|F09G2.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017310|F09G2.1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1207|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017310|F09G2.1|149nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017310|F09G2.1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017310|F09G2.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=863|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=921|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2261|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|771nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017311|F09G2.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017312|pitr-5|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017313|cpsf-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017313|cpsf-2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017313|cpsf-2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1823|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017313|cpsf-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=458|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1333|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017314|lgc-39|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017315|ugt-36|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017315|ugt-36|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1380|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=303|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017316|F09G2.8b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12506|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017317|attf-2|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017319|mrps-9|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017319|mrps-9|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1412|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017319|mrps-9|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=484|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017319|mrps-9|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017319|mrps-9|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5247|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017320|F09G8.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017321|F09G8.7|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017321|F09G8.7|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017321|F09G8.7|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017321|F09G8.7|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017321|F09G8.7|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017322|clec-160|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017322|clec-160|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017322|clec-160|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017323|mps-4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017325|F10C1.3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017325|F10C1.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2918|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017325|F10C1.3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017325|F10C1.3|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017325|F10C1.3|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2492|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|378nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017326|dmd-5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017327|F10C1.8a|97nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3142|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017328|F10C5.2.1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=551|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017329|ugt-39|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017331|ugt-40|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017331|ugt-40|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017331|ugt-40|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017331|ugt-40|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017332|ugt-37|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017332|ugt-37|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017332|ugt-37|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017334|F10D2.8|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017334|F10D2.8|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017334|F10D2.8|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017335|F10D2.10|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017335|F10D2.10|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017335|F10D2.10|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017335|F10D2.10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017335|F10D2.10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017336|ugt-41|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017336|ugt-41|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017336|ugt-41|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017336|ugt-41|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=597|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017336|ugt-41|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017336|ugt-41|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017336|ugt-41|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017338|F10D7.1|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017338|F10D7.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017338|F10D7.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017338|F10D7.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=403|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017339|F10D7.2|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017340|F10D7.3|1192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017340|F10D7.3|261nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017340|F10D7.3|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017340|F10D7.3|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=317|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017340|F10D7.3|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017341|F10D7.4|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017341|F10D7.4|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017342|F10D7.5c|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017342|F10D7.5c|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017342|F10D7.5c|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017342|F10D7.5c|480nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017342|F10D7.5c|489nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1203|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017342|F10D7.5c|492nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017343|F10E7.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017344|F10E7.2|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017344|F10E7.2|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017344|F10E7.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3264|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017344|F10E7.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017344|F10E7.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017344|F10E7.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017347|F10E7.5|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5289|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00017347|F10E7.5|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017347|F10E7.5|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017347|F10E7.5|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017347|F10E7.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017348|F10E7.6|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017348|F10E7.6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017348|F10E7.6|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017348|F10E7.6|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017348|F10E7.6|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017348|F10E7.6|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017348|F10E7.6|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1570|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7018|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1876|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|275nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017349|farl-11|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=416|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|1461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|1463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=919|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1947|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|913nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017350|F10E7.9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017351|cutl-5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017351|cutl-5|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017351|cutl-5|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|1160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2227|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|752nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017352|F10E7.11|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2722|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=773|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017353|F10E9.1|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017354|F10E9.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017355|F10E9.3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017356|F10E9.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017356|F10E9.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=824|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017356|F10E9.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=684|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017356|F10E9.4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017356|F10E9.4|1509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|1081nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|1101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|1211nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2876|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017357|F10E9.5|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1025|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017358|F10E9.7.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|560nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017359|F10E9.10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017360|F10E9.11|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017360|F10E9.11|1517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017360|F10E9.11|1543nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017360|F10E9.11|1576nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017360|F10E9.11|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017360|F10E9.11|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2115|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1097nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=816|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|1215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=552|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00017361|F10E9.12|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=824|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=821|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1955|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017362|F10G2.1|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017363|F10G2.2|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017363|F10G2.2|1449nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|183nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|186nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|188nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017364|clec-7|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017365|F10G2.4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017365|F10G2.4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017365|F10G2.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017365|F10G2.4|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017365|F10G2.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017366|F10G2.7|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017366|F10G2.7|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017366|F10G2.7|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017366|F10G2.7|925nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017367|nhr-263|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017367|nhr-263|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017367|nhr-263|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017367|nhr-263|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3680|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|241nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|249nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|277nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|382nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|473nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=70|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|546nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017369|F10G7.5b|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017371|sre-39|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00017371|sre-39|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2921|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|414nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=263|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017372|F10G7.9b|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1511|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017373|F10G7.10a|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017374|ttr-41|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017374|ttr-41|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1633|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017374|ttr-41|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3004|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017374|ttr-41|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=852|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017374|ttr-41|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017374|ttr-41|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=208|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017374|ttr-41|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017375|pbo-6|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017375|pbo-6|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017375|pbo-6|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017376|F11C7.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=505|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017376|F11C7.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017378|F11C7.6a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017378|F11C7.6a|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017378|F11C7.6a|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017378|F11C7.6a|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017378|F11C7.6a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017379|F11C7.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1828|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|295nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017380|F11D5.1a|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=611|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017381|ddr-2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017382|F11D5.5|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017383|F11D5.6|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017384|F11G11.4|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017384|F11G11.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017384|F11G11.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1032|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00017384|F11G11.4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6622|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017385|F11G11.5.2|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017386|nspd-5|1282nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017386|nspd-5|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017386|nspd-5|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017386|nspd-5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8923|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017386|nspd-5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017387|mpst-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017388|F11G11.13|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017388|F11G11.13|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017388|F11G11.13|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6001|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=555|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|870nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|875nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017389|lgc-38|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3168|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1821|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017390|F12A10.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017393|nep-5|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017393|nep-5|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=813|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=597|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017394|cal-8|843nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017395|F12A10.6|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017395|F12A10.6|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017395|F12A10.6|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017396|F12A10.7|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017396|F12A10.7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|109nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1377|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|91nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017397|F12A10.8|96nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017398|slc-17.6|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=874|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00017398|slc-17.6|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017398|slc-17.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017398|slc-17.6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017398|slc-17.6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017399|lgc-51|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017399|lgc-51|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017399|lgc-51|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017400|stg-2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017400|stg-2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017400|stg-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017400|stg-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017400|stg-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1452|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017400|stg-2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017400|stg-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017402|F12E12.1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=800|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017402|F12E12.1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017402|F12E12.1|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017402|F12E12.1|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017402|F12E12.1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017403|F12E12.2|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017404|F12E12.3|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017405|bath-31|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00017405|bath-31|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00017406|sdz-12|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00017406|sdz-12|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00017407|F12E12.6|1402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017407|F12E12.6|1404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017407|F12E12.6|1573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017407|F12E12.6|1576nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00017408|sdz-11|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017410|F13A2.1|1254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017410|F13A2.1|1256nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017411|F13A2.2|1294nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017411|F13A2.2|410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017413|F13A2.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017415|F13A2.6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017416|F13B6.1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017416|F13B6.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|20nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|25nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=499|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017417|F13B6.2|99nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017418|F13B6.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017418|F13B6.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017418|F13B6.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017418|F13B6.3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017418|F13B6.3|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017418|F13B6.3|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1006|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017419|F13B9.1a|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017419|F13B9.1a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017419|F13B9.1a|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017419|F13B9.1a|393nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017419|F13B9.1a|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2091|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017419|F13B9.1a|403nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|1134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=967|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|1373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017420|F13B9.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017421|cutl-29|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017421|cutl-29|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=260|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017421|cutl-29|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|453nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=241|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|457nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|460nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=363|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=815|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017423|F13C5.2|68nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017424|F13C5.3a|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017424|F13C5.3a|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017424|F13C5.3a|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017424|F13C5.3b|1480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=461|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017426|F13C5.5|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=232|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017427|acp-5|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017427|acp-5|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=386|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017427|acp-5|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017427|acp-5|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017428|F13D11.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=722|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017428|F13D11.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017428|F13D11.3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017429|F13D11.4.1|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1313|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|1316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|968nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|970nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017430|bcl-11|972nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|597nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017431|F13H6.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00017433|F13H6.5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017433|F13H6.5|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=479|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017433|F13H6.5|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017433|F13H6.5|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017433|F13H6.5|327nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017434|F13H8.1b|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017434|F13H8.1b|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017434|F13H8.1b|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|1167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|1438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|1459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|1597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2356|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017435|F13H8.2|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017436|F13H8.3.2|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017436|F13H8.3.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=781|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017436|F13H8.3.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017437|nmgp-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017437|nmgp-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1169|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017437|nmgp-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017437|nmgp-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=585|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|280nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|355nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017438|F13H8.5a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017439|F13H8.6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017439|F13H8.6|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017439|F13H8.6|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017439|F13H8.6|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017439|F13H8.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017439|F13H8.6|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017440|upb-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017440|upb-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017440|upb-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017440|upb-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017440|upb-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3943|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017441|F13H8.8|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00017441|F13H8.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017442|F13H8.9|1501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017442|F13H8.9|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017442|F13H8.9|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017442|F13H8.9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017442|F13H8.9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3984|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00017442|F13H8.9|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017442|F13H8.9|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017443|F13H8.11|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017443|F13H8.11|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017443|F13H8.11|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017443|F13H8.11|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017443|F13H8.11|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017444|F13H8.12b|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017444|F13H8.12b|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017445|sid-5|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017445|sid-5|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1591|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017445|sid-5|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4198|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017445|sid-5|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017445|sid-5|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017445|sid-5|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017446|F14B8.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=460|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017446|F14B8.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017446|F14B8.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00017446|F14B8.4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1854|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017447|F14B8.5c.4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017448|F14B8.6|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017448|F14B8.6|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1415|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017448|F14B8.6|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017449|otpl-3|721nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017449|otpl-3|730nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017449|otpl-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017449|otpl-3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017449|otpl-3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017449|otpl-3|845nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017449|otpl-3|861nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017450|bath-27|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=601|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017450|bath-27|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=350|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017451|F14D2.2.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017452|bath-29|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017452|bath-29|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017452|bath-29|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017452|bath-29|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=574|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017452|bath-29|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017453|F14D2.5|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017453|F14D2.5|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=140|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017454|irld-5|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017459|F14D2.11|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017459|F14D2.11|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017459|F14D2.11|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017459|F14D2.11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017460|bath-30|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017460|bath-30|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017460|bath-30|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1519|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017460|bath-30|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017460|bath-30|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017461|bath-28|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=671|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017461|bath-28|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017461|bath-28|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017462|F14D2.14|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=572|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017462|F14D2.14|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017462|F14D2.14|949nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017462|F14D2.14|951nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017463|F14D12.1b|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017463|F14D12.1b|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017463|F14D12.1b|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017463|F14D12.1b|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017464|sulp-2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017464|sulp-2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00017464|sulp-2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017464|sulp-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017464|sulp-2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017464|sulp-2|348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017465|F14F9.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017465|F14F9.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017466|F14F9.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017466|F14F9.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017466|F14F9.3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00017466|F14F9.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017467|F14F9.4|194nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017467|F14F9.4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017467|F14F9.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2469|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017467|F14F9.4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1200|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017467|F14F9.4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017468|F14F9.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017468|F14F9.5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017468|F14F9.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017468|F14F9.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=672|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017469|F14F9.6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017470|F14H12.2|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017471|F14H12.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00017471|F14H12.3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1425|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017471|F14H12.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=703|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2637|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017472|cst-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017473|F14H12.6|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=430|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017474|F14H12.7|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017474|F14H12.7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017474|F14H12.7|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017474|F14H12.7|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=242|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00017474|F14H12.7|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00017474|F14H12.7|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=879|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017475|F14H12.8|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=400|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017476|F15A8.1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017476|F15A8.1|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017477|F15A8.4|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017477|F15A8.4|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=498|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017477|F15A8.4|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017477|F15A8.4|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=572|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1486|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1223|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017478|F15A8.6|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017480|nstp-2|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017480|nstp-2|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1248|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017480|nstp-2|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4016|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017480|nstp-2|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017480|nstp-2|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017480|nstp-2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=596|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=531|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017481|F15B10.3a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017482|set-9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017482|set-9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017482|set-9|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017482|set-9|627nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017482|set-9|663nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017483|lgc-22|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017483|lgc-22|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017483|lgc-22|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017483|lgc-22|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017483|lgc-22|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017483|lgc-22|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017484|F15E6.3|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1063|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017484|F15E6.3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017484|F15E6.3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017484|F15E6.3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017484|F15E6.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017484|F15E6.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017484|F15E6.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017485|F15E6.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017485|F15E6.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1740|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017485|F15E6.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1393|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017485|F15E6.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017485|F15E6.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017485|F15E6.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017486|F15E6.5|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00017486|F15E6.5|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00017487|F15E6.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017487|F15E6.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017487|F15E6.6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017487|F15E6.6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017487|F15E6.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017487|F15E6.6|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017487|F15E6.6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=335|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017488|dct-7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017489|F15E6.9a|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017489|F15E6.9a|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017489|F15E6.9a|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017489|F15E6.9a|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017489|F15E6.9a|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28421|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5118|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017490|pud-2.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017491|irld-28|1275nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017493|irld-30|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017493|irld-30|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017494|irld-31|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|1584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3792|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|900nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1495|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017496|srbc-15|906nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017497|irld-32|1275nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017497|irld-32|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017498|pud-4|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017498|pud-4|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017498|pud-4|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=551|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017498|pud-4|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1269|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017498|pud-4|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017498|pud-4|88nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017498|pud-4|91nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22684|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7533|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1176|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1471|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017499|pud-1.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017500|pud-2.2|775nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00017500|pud-2.2|835nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017500|pud-2.2|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|1073nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|1077nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|1084nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3519|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=294|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|136nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|139nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017501|pud-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017502|F16B3.2|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017502|F16B3.2|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017503|nhr-177|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017503|nhr-177|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017503|nhr-177|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017504|F16B4.2a.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017504|F16B4.2a.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=400|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017504|F16B4.2a.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017504|F16B4.2a.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017504|F16B4.2a.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=853|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1185|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11818|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1535|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017506|F16B4.4|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017507|F16B4.5b|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017507|F16B4.5b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1078|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017507|F16B4.5b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017508|F16B4.6a|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017508|F16B4.6a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017508|F16B4.6a|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017508|F16B4.6a|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017508|F16B4.6a|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017508|F16B4.6a|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017509|F16B4.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017509|F16B4.7|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017509|F16B4.7|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017510|nhr-178|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017510|nhr-178|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017510|nhr-178|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017510|nhr-178|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017510|nhr-178|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017510|nhr-178|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017511|srbc-41|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017511|srbc-41|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017511|srbc-41|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017512|nhr-179|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017512|nhr-179|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017513|F16F9.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017513|F16F9.1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017513|F16F9.1|493nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017513|F16F9.1|496nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017513|F16F9.1|500nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=359|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017513|F16F9.1|503nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017514|F16F9.3b|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017514|F16F9.3b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017514|F16F9.3b|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017514|F16F9.3b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017515|F16F9.4|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017515|F16F9.4|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=743|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00017515|F16F9.4|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017520|F16G10.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017520|F16G10.5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017524|F16G10.9|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017525|F16G10.10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017529|F16G10.15|1563nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00017529|F16G10.15|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00017529|F16G10.15|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1496|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|520nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017530|F16H11.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017532|ent-5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017532|ent-5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1216|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|208nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=371|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017534|F17A9.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|1293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1997|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|1523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|1544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017535|atf-8|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017536|F17A9.4|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017536|F17A9.4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017536|F17A9.4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017536|F17A9.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2341|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017536|F17A9.4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00017536|F17A9.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017537|F17A9.5|324nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=491|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017537|F17A9.5|330nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=576|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017537|F17A9.5|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017537|F17A9.5|420nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017538|ceh-49|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017538|ceh-49|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017538|ceh-49|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00017538|ceh-49|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017538|ceh-49|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017539|F17E9.2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017539|F17E9.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017540|F17E9.3|1054nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017540|F17E9.3|1059nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017540|F17E9.3|1062nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017540|F17E9.3|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017540|F17E9.3|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017540|F17E9.3|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017540|F17E9.3|952nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22496|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5814|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1117|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017541|F17E9.4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017542|F17E9.5|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017542|F17E9.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9829|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017543|lgc-5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00017543|lgc-5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00017544|lgc-6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017544|lgc-6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00017544|lgc-6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017544|lgc-6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017545|F18A1.1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017545|F18A1.1|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00017545|F18A1.1|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12864|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=405|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017546|rpa-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017547|alfa-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017547|alfa-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2198|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017547|alfa-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017547|alfa-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017548|F18A1.7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9227|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017548|F18A1.7|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017548|F18A1.7|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017548|F18A1.7|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017548|F18A1.7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017548|F18A1.7|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3617|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017549|pid-1|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017550|nep-6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017550|nep-6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017550|nep-6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017550|nep-6|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017551|F18A12.2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017551|F18A12.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017552|nep-7|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017552|nep-7|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017553|nep-8|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00017553|nep-8|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00017554|nep-9|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017554|nep-9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017555|nep-10|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017556|F18A12.7|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|289nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1902|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00017557|nep-11|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017559|mpz-3|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017559|mpz-3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=688|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017560|F18C5.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017560|F18C5.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017560|F18C5.5|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017560|F18C5.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017560|F18C5.5|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017560|F18C5.5|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017562|F18C5.9|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017562|F18C5.9|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017562|F18C5.9|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|430nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|438nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9321|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=457|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017563|F18C5.10.1|899nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|1349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|1355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|309nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2449|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=464|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=593|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=288|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017565|ddo-2|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017567|F18E3.11|1341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017567|F18E3.11|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017567|F18E3.11|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017567|F18E3.11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1186|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017567|F18E3.11|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11894|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017567|F18E3.11|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017568|F18E9.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017568|F18E9.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017568|F18E9.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017568|F18E9.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017569|F18E9.3|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017569|F18E9.3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017569|F18E9.3|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017569|F18E9.3|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017569|F18E9.3|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017570|F18E9.4|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017570|F18E9.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017570|F18E9.4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017570|F18E9.4|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017570|F18E9.4|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017570|F18E9.4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|1549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|1553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=879|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017571|jmjd-3.1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017573|F18E9.7b|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017574|F18F11.1|36nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017574|F18F11.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=972|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017576|cdh-8|658nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017577|F18F11.4|539nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017577|F18F11.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017577|F18F11.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017577|F18F11.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017578|drl-1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017578|drl-1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017578|drl-1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017578|drl-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017578|drl-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017578|drl-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00017579|F18G5.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017579|F18G5.1|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|1354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|1466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=642|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1403|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=127|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|854nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017580|lgc-4|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017581|F18G5.5|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1354|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|512nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017582|F18G5.6|936nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|1396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|1399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=758|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017583|F19B10.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017584|F19B10.2|1007nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017584|F19B10.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017584|F19B10.2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017584|F19B10.2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017584|F19B10.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017584|F19B10.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017586|F19B10.4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017586|F19B10.4|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017586|F19B10.4|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017587|F19B10.5|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017589|F19B10.10.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=766|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1841|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=727|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=392|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10359|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017591|F19C7.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017592|F19C7.2|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017592|F19C7.2|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00017593|F19C7.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017593|F19C7.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017594|F19C7.4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017594|F19C7.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017595|F19C7.5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017595|F19C7.5|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017595|F19C7.5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017595|F19C7.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017595|F19C7.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017595|F19C7.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3390|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017597|F19C7.8c|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017598|F19F10.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017598|F19F10.1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017598|F19F10.1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017599|F19F10.3|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017600|ttr-10|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017601|ets-7|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017601|ets-7|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017601|ets-7|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00017601|ets-7|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017601|ets-7|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017601|ets-7|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00017603|clec-212|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1526|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2243|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|1500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017605|F19F10.9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017606|ets-6|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017606|ets-6|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017606|ets-6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=534|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017606|ets-6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017606|ets-6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017606|ets-6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017606|ets-6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017607|F19F10.11a|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017607|F19F10.11a|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017607|F19F10.11a|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017607|F19F10.11a|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=459|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017607|F19F10.11b|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017607|F19F10.11b|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017608|F19F10.12|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017608|F19F10.12|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017608|F19F10.12|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4015|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017608|F19F10.12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017608|F19F10.12|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017608|F19F10.12|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017609|F19G12.1|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017609|F19G12.1|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017611|F19G12.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017611|F19G12.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017611|F19G12.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017613|F20A1.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017613|F20A1.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017613|F20A1.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017613|F20A1.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9145|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017613|F20A1.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017613|F20A1.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017613|F20A1.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017614|F20A1.2|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017614|F20A1.2|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=114|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017615|srsx-32|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017615|srsx-32|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017615|srsx-32|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017616|F20A1.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017616|F20A1.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=292|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00017618|F20A1.6a|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017618|F20A1.6a|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017618|F20A1.6a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017618|F20A1.6a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017618|F20A1.6c|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017619|F20A1.8|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017619|F20A1.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017620|tofu-2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017620|tofu-2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4534|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017620|tofu-2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017620|tofu-2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017620|tofu-2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4839|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017621|F20A1.10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017625|cgt-2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017625|cgt-2|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017625|cgt-2|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017625|cgt-2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017625|cgt-2|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017625|cgt-2|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=516|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|1030nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|1105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|1111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|1338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=469|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4811|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=308|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017628|F20B6.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017629|F20B6.5|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017630|F20B6.6|1561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017632|F20B6.9|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017632|F20B6.9|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017632|F20B6.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017632|F20B6.9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00017632|F20B6.9|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017632|F20B6.9|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017633|F20D6.1|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=190|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017633|F20D6.1|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017633|F20D6.1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017633|F20D6.1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017634|F20D6.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017634|F20D6.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017634|F20D6.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017634|F20D6.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017634|F20D6.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017635|F20D6.5|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017635|F20D6.5|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=517|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017635|F20D6.5|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017635|F20D6.5|180nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017636|F20D6.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017636|F20D6.6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|1095nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2801|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017637|F20D6.8|543nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017638|F20D6.9|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017639|F20D6.10|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017639|F20D6.10|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=384|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017640|F20D6.11|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|415nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=388|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|418nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4686|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|421nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|427nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=816|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|597nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017641|csr-1|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1610|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=382|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017642|F20D12.2|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4260|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017643|czw-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=441|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2706|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017644|exc-9|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017645|F20D12.7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00017645|F20D12.7|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1329|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017646|F20H11.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017647|F20H11.4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017647|F20H11.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017647|F20H11.4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017647|F20H11.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017648|ddo-3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017648|ddo-3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2633|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017648|ddo-3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017648|ddo-3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017648|ddo-3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6107|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017648|ddo-3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=861|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017648|ddo-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017650|F21A9.1|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00017650|F21A9.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00017651|F21A9.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017651|F21A9.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017651|F21A9.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017652|F21C10.1|1548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017652|F21C10.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=160|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|926nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2174|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|930nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|939nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|946nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3a|952nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18631|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=350|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017653|F21C10.3b|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017654|F21C10.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017654|F21C10.4|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017654|F21C10.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017654|F21C10.4|305nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017656|F21C10.6|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017656|F21C10.6|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017656|F21C10.6|356nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017656|F21C10.6|360nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017657|F21C10.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=778|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017658|F21C10.9.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017658|F21C10.9.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017658|F21C10.9.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=963|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017658|F21C10.9.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017658|F21C10.9.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4328|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017659|F21C10.10.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3221|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|23nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=715|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1735|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017660|F21C10.11a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017661|frpr-6|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017661|frpr-6|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017661|frpr-6|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2061|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017661|frpr-6|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017661|frpr-6|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017662|F21D12.2|385nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017662|F21D12.2|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2024|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=583|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1109|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00017663|F21D12.3|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|1069nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|1488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=549|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|959nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017664|npax-1|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017666|F21E9.2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017666|F21E9.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017666|F21E9.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017666|F21E9.2|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017667|ttr-37|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017667|ttr-37|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017668|ins-39|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017668|ins-39|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=348|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=667|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=572|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2564|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=120594|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8478|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017671|pgal-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017672|F21F3.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017672|F21F3.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017672|F21F3.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017673|icmt-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017673|icmt-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017673|icmt-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3749|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017673|icmt-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017674|F21F3.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=316|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017674|F21F3.4|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017674|F21F3.4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017674|F21F3.4|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017674|F21F3.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017674|F21F3.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|382nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|394nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|397nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10111|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1034|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|438nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|456nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|460nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4718|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=261|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|888nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|890nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|893nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|928nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017675|F21F3.6|933nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|1001nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|1010nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|388nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=468|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|393nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=517|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|395nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|748nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|770nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|815nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017676|F21F3.7|820nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017678|asp-12|1533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017678|asp-12|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=211|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017678|asp-12|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=370|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017678|asp-12|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=291|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017679|F21F8.5|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=189|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|237nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=938|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|247nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017681|slc-17.5|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017683|rbbp-5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=860|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017683|rbbp-5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=547|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00017683|rbbp-5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017683|rbbp-5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017683|rbbp-5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017683|rbbp-5|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017684|F21H12.2|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017686|tpp-2|115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2545|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017686|tpp-2|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1671|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017686|tpp-2|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017686|tpp-2|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017686|tpp-2|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1244|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017686|tpp-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|580nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|582nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|661nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|735nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|743nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=887|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|748nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=663|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|750nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1462|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017687|ets-4|764nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=681|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=949|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=169|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017688|ttr-35|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017690|ceh-60|660nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=526|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=653|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=529|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11527|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83587|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3163|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=775|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017691|ilys-5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017692|F22B7.1|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=418|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017692|F22B7.1|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017692|F22B7.1|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017695|fip-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017695|fip-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017696|polk-1|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017696|polk-1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017696|polk-1|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017696|polk-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017696|polk-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1093|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017698|F22B7.9|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017698|F22B7.9|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017698|F22B7.9|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2809|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017698|F22B7.9|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017698|F22B7.9|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|954nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6761|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|957nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017699|flcn-1|960nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017700|F22D3.4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017700|F22D3.4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017700|F22D3.4|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017701|F22D3.5|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017701|F22D3.5|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=574|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017701|F22D3.5|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|671nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017702|F22D3.6|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017703|F22E5.1|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017703|F22E5.1|24nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017703|F22E5.1|36nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017703|F22E5.1|38nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017703|F22E5.1|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017703|F22E5.1|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=375|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017703|F22E5.1|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017704|F22E5.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017705|F22E5.6|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017705|F22E5.6|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017705|F22E5.6|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017705|F22E5.6|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017705|F22E5.6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017705|F22E5.6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017705|F22E5.6|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00017706|F22E5.7|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017706|F22E5.7|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017707|F22E5.8|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017707|F22E5.8|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017708|F22E5.9|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=812|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017708|F22E5.9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017708|F22E5.9|374nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017708|F22E5.9|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017708|F22E5.9|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017708|F22E5.9|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017710|F22E5.12|1233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00017710|F22E5.12|1237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017710|F22E5.12|1239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017711|F22E5.13.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017711|F22E5.13.1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017711|F22E5.13.1|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=280|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017711|F22E5.13.1|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1130|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017711|F22E5.13.1|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017711|F22E5.13.1|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017711|F22E5.13.1|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017712|F22E5.17|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017712|F22E5.17|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017712|F22E5.17|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017713|F22E5.20|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017713|F22E5.20|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017713|F22E5.20|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017713|F22E5.20|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017714|F22F1.2|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=512|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=605|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017715|F22F1.3|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017716|F22F4.1|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2026|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4a.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4b|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4b|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=567|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4b|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4b|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=568|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017717|F22F4.4b|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1551|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1353|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=461|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017718|F22F4.5|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8559|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017719|ldp-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017720|F22F7.2.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017720|F22F7.2.1|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017720|F22F7.2.1|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017720|F22F7.2.1|426nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017720|F22F7.2.1|511nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017720|F22F7.2.1|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017721|F22F7.3|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017722|F22F7.4c|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017723|F22F7.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017723|F22F7.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|609nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|615nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4405|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017724|F22F7.7c|621nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=461|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017725|F22H10.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=213|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=398|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1946|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017726|F22H10.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017727|F22H10.3.2|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017727|F22H10.3.2|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017727|F22H10.3.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017727|F22H10.3.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1158|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017727|F22H10.3.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11578|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017727|F22H10.3.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=673|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=519|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=166|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|259nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=462|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017730|F22H10.6|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017732|F23C8.3a|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017732|F23C8.3b|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017732|F23C8.3b|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017732|F23C8.3b|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017732|F23C8.3b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017732|F23C8.3b|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3777|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1649|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=291|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017733|ubxn-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1332|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5786|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1118|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=906|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017734|F23C8.5b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12155|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|390nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017735|did-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017736|F23C8.7|1228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017736|F23C8.7|1230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017736|F23C8.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017736|F23C8.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017736|F23C8.7|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017737|F23C8.8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017737|F23C8.8|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017738|F23C8.9|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017738|F23C8.9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017738|F23C8.9|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=792|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017738|F23C8.9|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=549|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017741|F23C8.13a|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=963|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8099|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3544|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=388|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017742|nfyc-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017743|F23F1.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017743|F23F1.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|1580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|458nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1645|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017744|fbxc-54|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=423|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|564nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017745|F23F1.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017746|F23F1.5|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017746|F23F1.5|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017746|F23F1.5|171nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017746|F23F1.5|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3039|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017747|F23F1.6|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017747|F23F1.6|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017747|F23F1.6|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017747|F23F1.6|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=389|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00017747|F23F1.6|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1617|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6700|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2481|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|928nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|930nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017748|F23F1.7|932nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1308|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017749|rpoa-49|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017750|F23F1.10|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017750|F23F1.10|542nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017750|F23F1.10|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3239|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017750|F23F1.10|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017750|F23F1.10|713nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017751|F23F12.3|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017751|F23F12.3|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017751|F23F12.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017752|sdz-15|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017754|F23F12.8|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017754|F23F12.8|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=311|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017755|zip-8|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=182|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7919|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|204nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|210nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017756|F23F12.12|718nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2741|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017757|bra-2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|164nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|178nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=696|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017758|F23H11.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017759|sucl-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017759|sucl-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017759|sucl-2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017759|sucl-2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7092|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017759|sucl-2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017759|sucl-2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|1011nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=523|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=369|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=246|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|716nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017760|F23H11.4b|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017761|F23H11.6|1044nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017761|F23H11.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017761|F23H11.6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017761|F23H11.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017761|F23H11.6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017762|F23H11.7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017762|F23H11.7|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017762|F23H11.7|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=173|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017762|F23H11.7|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017762|F23H11.7|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017763|crls-1|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017763|crls-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017763|crls-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1396|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00017763|crls-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5194|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017764|F25A2.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=625|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=860|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017765|gcst-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|1505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=504|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=989|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|769nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|797nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017766|peli-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017767|F25B4.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1115|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5027|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=647|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017768|F25B4.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1671|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|959nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|963nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|966nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|973nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017769|hmgs-1|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|1038nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|1051nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|1053nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|152nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2004|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|156nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|159nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017770|F25B4.7|650nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017771|F25B4.8a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017771|F25B4.8a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=432|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017771|F25B4.8a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|169nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4616|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3560|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9013|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|437nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017772|clec-1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017773|dct-6|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1455|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00017773|dct-6|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017773|dct-6|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017773|dct-6|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017773|dct-6|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017774|nop-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017774|nop-1|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2262|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017774|nop-1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=903|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00017774|nop-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017774|nop-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017774|nop-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8785|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|344nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|353nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|355nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017775|F25B5.3b|366nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|767nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=761|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=888|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|973nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017776|F25B5.5|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017777|F25B5.6c.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017777|F25B5.6c.1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5395|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017777|F25B5.6c.1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017777|F25B5.6c.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017777|F25B5.6c.1|590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017778|nono-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017778|nono-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017778|nono-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5563|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017778|nono-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017778|nono-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017778|nono-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017779|gtr-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00017779|gtr-1|1564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=252|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=405|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2b|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2b|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2b|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2b|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=549|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2b|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1831|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2b|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=500|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017780|F25E2.2b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017781|F25E2.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017781|F25E2.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017781|F25E2.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=387|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017781|F25E2.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|347nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|353nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=795|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|355nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|358nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|427nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017782|F25E5.1|432nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017783|F25E5.2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017783|F25E5.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017784|F25E5.3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017785|F25E5.4|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017785|F25E5.4|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017785|F25E5.4|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00017785|F25E5.4|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017785|F25E5.4|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017786|F25E5.5|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017786|F25E5.5|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017786|F25E5.5|217nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017786|F25E5.5|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017786|F25E5.5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017786|F25E5.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017787|nhr-141|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017787|nhr-141|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017788|F25E5.7|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017788|F25E5.7|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=854|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017788|F25E5.7|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017788|F25E5.7|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017788|F25E5.7|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017788|F25E5.7|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017789|F25E5.8a.2|1253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017789|F25E5.8a.2|1410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017789|F25E5.8a.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017789|F25E5.8a.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1935|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017789|F25E5.8a.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|1061nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|889nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|891nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00017790|F25E5.9|897nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00017791|try-8|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=967|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16b|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017792|F25E5.16b|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017794|mltn-13|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017794|mltn-13|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017794|mltn-13|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017795|F25F8.1|1526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017795|F25F8.1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1360|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017795|F25F8.1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017796|F25G6.1|1379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017796|F25G6.1|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017796|F25G6.1|1398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017796|F25G6.1|1400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017796|F25G6.1|1504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|202nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1317|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|215nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017797|symk-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017798|slc-17.8|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00017798|slc-17.8|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6193|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|277nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017799|F25G6.8|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3488|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017800|F25G6.9|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017801|F26A1.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017801|F26A1.1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3822|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017801|F26A1.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017801|F26A1.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017802|F26A1.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00017802|F26A1.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017802|F26A1.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017802|F26A1.3|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017803|F26A1.4|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017803|F26A1.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017803|F26A1.4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017803|F26A1.4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017803|F26A1.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017804|F26A1.6|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017804|F26A1.6|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017804|F26A1.6|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017804|F26A1.6|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017804|F26A1.6|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017805|F26A1.7|1589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017806|F26A1.8|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017806|F26A1.8|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017806|F26A1.8|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017807|F26A1.9|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017807|F26A1.9|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017807|F26A1.9|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017807|F26A1.9|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017807|F26A1.9|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017808|nspd-9|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017808|nspd-9|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017808|nspd-9|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017808|nspd-9|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1343|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017810|clec-157|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00017810|clec-157|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00017811|F26A1.13|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017811|F26A1.13|483nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=260|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017811|F26A1.13|487nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1348|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|386nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2847|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|388nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|418nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=350|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|423nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|590nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017813|F26A10.1|592nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|1544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|1548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|1561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2548|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|1571nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017814|F26A10.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017815|F26B1.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00017815|F26B1.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=732|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017815|F26B1.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|482nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14151|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|704nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|706nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2a|720nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017816|F26B1.2e|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017817|F26B1.5|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017817|F26B1.5|1556nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00017817|F26B1.5|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017817|F26B1.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017818|F26D11.1.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017819|F26D11.2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017819|F26D11.2|262nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017819|F26D11.2|265nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017819|F26D11.2|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017819|F26D11.2|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017819|F26D11.2|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017822|clec-216|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017822|clec-216|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017822|clec-216|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017823|F26D11.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017823|F26D11.6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3026|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017823|F26D11.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017823|F26D11.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017824|clec-217|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017824|clec-217|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017825|cee-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017825|cee-1|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017825|cee-1|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2399|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017825|cee-1|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=402|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017825|cee-1|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017825|cee-1|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017825|cee-1|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4451|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017826|tag-340|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017827|F26F4.5.1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2306|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017827|F26F4.5.1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017827|F26F4.5.1|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017827|F26F4.5.1|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017827|F26F4.5.1|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017827|F26F4.5.1|294nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=355|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2316|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|873nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017828|F26F4.6|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8013|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|1130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|1393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017829|F26F4.9b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017830|rpb-8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=594|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017830|rpb-8|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4519|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017830|rpb-8|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017830|rpb-8|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017830|rpb-8|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017830|rpb-8|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1946|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017831|F26F4.12|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017832|kbp-2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1523|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017832|kbp-2|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017833|F26F12.2|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017833|F26F12.2|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017833|F26F12.2|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017833|F26F12.2|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017833|F26F12.2|1362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017833|F26F12.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017833|F26F12.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|252nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|331nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|335nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|638nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|640nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|647nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|866nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5495|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017834|F26F12.3c|883nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017835|F26F12.4|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017835|F26F12.4|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=464|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017835|F26F12.4|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017836|F26F12.5a|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00017836|F26F12.5a|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017836|F26F12.5a|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017836|F26F12.5a|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00017836|F26F12.5a|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=509|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1278|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017837|F26G1.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017838|F26G1.2b|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017838|F26G1.2b|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017838|F26G1.2b|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017838|F26G1.2b|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1402|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017838|F26G1.2b|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017839|F26G1.3|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017840|ttm-2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017840|ttm-2|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017840|ttm-2|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017840|ttm-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017841|F26G1.5|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017841|F26G1.5|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=348|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017841|F26G1.5|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017841|F26G1.5|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017841|F26G1.5|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017842|nep-12|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00017842|nep-12|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00017843|F26G5.1b|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017843|F26G5.1b|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017843|F26G5.1b|71nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017843|F26G5.1b|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=641|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017843|F26G5.1b|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017843|F26G5.1b|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017848|F27B3.6|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017848|F27B3.6|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017848|F27B3.6|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017848|F27B3.6|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|1200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|1206nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=73|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|1376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|188nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=366|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|193nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33990|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|201nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017850|F27B10.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017851|F27C1.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017851|F27C1.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017851|F27C1.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2503|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017851|F27C1.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017851|F27C1.1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|1034nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|295nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6510|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=482|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|303nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017852|F27C1.2a|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1409nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|1462nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=136|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017853|F27C1.3|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017854|F27C1.4|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017854|F27C1.4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=842|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017854|F27C1.4|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1421|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=306|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017855|F27C1.6.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=133|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|707nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017858|F27C1.11|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017860|F27C1.13|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017861|F27D9.2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1572|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017861|F27D9.2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017861|F27D9.2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017863|F27D9.4|978nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5169|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5981|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|306nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017864|pcca-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017865|F27D9.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017865|F27D9.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017865|F27D9.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1854|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017866|stn-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017867|slc-28.1|1308nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017867|slc-28.1|1386nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017867|slc-28.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017868|slc-28.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017868|slc-28.2|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017869|F28A10.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00017869|F28A10.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017870|F28A10.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017871|F28A10.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017872|F28A10.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017872|F28A10.4|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017872|F28A10.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017873|F28A10.5|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017874|acdh-9|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017874|acdh-9|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3782|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017874|acdh-9|145nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017874|acdh-9|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017874|acdh-9|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017875|F28A10.7|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017876|F28A10.8|1180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017876|F28A10.8|1183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017877|F28A10.9|1217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017877|F28A10.9|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017878|F28A10.10|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017878|F28A10.10|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017878|F28A10.10|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017879|acd-4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017879|acd-4|1505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017879|acd-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017879|acd-4|744nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017879|acd-4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017879|acd-4|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=239|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=686|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=740|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017880|F28A12.3|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=586|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3477|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|134nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=64|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|137nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|140nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=449|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3725|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1681|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|411nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017881|asp-13|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2846|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|399nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|405nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017885|dip-2|410nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|155nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1449|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|645nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017886|F28B3.5a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|159nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|168nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|171nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4025|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017887|F28B3.6|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=523|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017888|acl-11|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017889|F28B3.10|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4718|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017889|F28B3.10|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017889|F28B3.10|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017889|F28B3.10|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017889|F28B3.10|481nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017890|F28B4.1|1078nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017891|rgl-1|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017891|rgl-1|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017891|rgl-1|499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017891|rgl-1|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=995|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017892|F28B4.3.2|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017892|F28B4.3.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5887|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017892|F28B4.3.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017892|F28B4.3.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=177|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017893|F28B4.4|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017894|F28B12.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017894|F28B12.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017894|F28B12.1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017894|F28B12.1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017894|F28B12.1|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017894|F28B12.1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017894|F28B12.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017895|vrk-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017895|vrk-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017895|vrk-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017895|vrk-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017895|vrk-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3348|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017895|vrk-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017895|vrk-1|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017898|F28C10.3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017898|F28C10.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017898|F28C10.3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017898|F28C10.3|400nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017898|F28C10.3|405nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017898|F28C10.3|411nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1022|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017898|F28C10.3|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017899|F28C10.4|1547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017899|F28C10.4|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017899|F28C10.4|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1178|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13457|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017900|F28E10.1j|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017901|igeg-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017901|igeg-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=894|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00017902|F28E10.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017902|F28E10.4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|346nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=209|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|355nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1402|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|357nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|361nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017904|lim-8|368nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017905|F28F5.6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017905|F28F5.6|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017906|F28F9.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017906|F28F9.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=505|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017907|F28F9.3|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017907|F28F9.3|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2133|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017907|F28F9.3|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017907|F28F9.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|530nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|533nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=575|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|564nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|567nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|570nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017908|F28H1.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017909|F28H1.4b.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017909|F28H1.4b.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=724|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017909|F28H1.4b.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017912|fbxb-107|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|1108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017914|F29A7.4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=517|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017916|F29A7.6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|1019nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|1022nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|1060nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|1063nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=358|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017919|F29B9.1|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017920|jmjd-1.2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017920|jmjd-1.2|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3331|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017920|jmjd-1.2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017921|F29B9.5|1313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017921|F29B9.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017921|F29B9.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017921|F29B9.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1583|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017921|F29B9.5|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017922|F29B9.7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017922|F29B9.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017922|F29B9.7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|189nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2195|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017923|F29B9.8.2|571nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017924|mrps-21|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017924|mrps-21|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017924|mrps-21|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1603|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017924|mrps-21|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017924|mrps-21|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017924|mrps-21|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=673|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10862|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017925|F29B9.11.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25522|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017926|F29C4.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017926|F29C4.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017926|F29C4.2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017926|F29C4.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38212|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017926|F29C4.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6596|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017926|F29C4.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017926|F29C4.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017927|F29C4.4.2|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1070|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=385|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017928|tut-1|25nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1596|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017929|grld-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=567|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017930|F29G9.1|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017930|F29G9.1|840nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2156|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017931|picc-1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017933|F29G9.7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017933|F29G9.7|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017933|F29G9.7|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=360|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00017933|F29G9.7|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|170nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|174nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=600|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|176nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=163|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017934|F30B5.4b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017936|F30B5.7|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017936|F30B5.7|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017936|F30B5.7|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=261|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017937|F30H5.3|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017937|F30H5.3|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1274|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|291nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=306|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017938|F31A3.3|441nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017939|F31A3.5|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017939|F31A3.5|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017939|F31A3.5|487nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=579|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00017939|F31A3.5|489nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017939|F31A3.5|491nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017941|F31A9.2|1220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017941|F31A9.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017942|fbxc-37|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017942|fbxc-37|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017944|F31D5.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017945|F31D5.2.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017945|F31D5.2.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017945|F31D5.2.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017947|mth-2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017948|mth-1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017948|mth-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017949|F31D5.6|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017949|F31D5.6|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00017949|F31D5.6|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017950|F31E3.2b|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017950|F31E3.2b|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017950|F31E3.2b|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1061|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017950|F31E3.2b|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017950|F31E3.2b|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|1487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|1546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1326|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017951|panl-2|348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017954|F31E8.4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017954|F31E8.4|1549nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017954|F31E8.4|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017954|F31E8.4|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017954|F31E8.4|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1347|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017954|F31E8.4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017955|F31E8.5|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017955|F31E8.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017955|F31E8.5|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017955|F31E8.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=315|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017957|F31F4.1a|1046nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017957|F31F4.1a|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017957|F31F4.1a|1050nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00017957|F31F4.1a|1136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017957|F31F4.1a|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017959|ugt-42|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017960|F31F4.11a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017961|nhr-180|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017961|nhr-180|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=390|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017961|nhr-180|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017962|fbxa-72|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017962|fbxa-72|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=740|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017962|fbxa-72|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00017963|F31F4.17|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017963|F31F4.17|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=818|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=219|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4207|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=284|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017964|F31F7.1c|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017965|F31F7.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017965|F31F7.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1198|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017965|F31F7.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017965|F31F7.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017966|F31F7.3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017966|F31F7.3|564nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017967|ada-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017967|ada-2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1518|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00017967|ada-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017967|ada-2|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017968|skpo-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017968|skpo-3|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017968|skpo-3|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017968|skpo-3|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017968|skpo-3|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=909|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|1037nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1022|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017969|F32A5.3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=846|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1853|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=913|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1782|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017970|F32A5.4a.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|713nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1022|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|726nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017971|F32A5.8|737nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=646|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017973|ift-81|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017974|vps-41|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017974|vps-41|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017974|vps-41|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017974|vps-41|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017974|vps-41|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017974|vps-41|707nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017975|F32B5.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017975|F32B5.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017975|F32B5.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017975|F32B5.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017975|F32B5.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2246|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017975|F32B5.1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017975|F32B5.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017976|F32B5.2|1300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017976|F32B5.2|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017976|F32B5.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017976|F32B5.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017976|F32B5.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017977|F32B5.3|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00017978|F32B5.4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017978|F32B5.4|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=346|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017978|F32B5.4|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3758|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017978|F32B5.4|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017978|F32B5.4|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=337|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017978|F32B5.4|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6b|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|424nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5907|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|429nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|431nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017979|F32B5.6d.4|996nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|1080nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5840|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017980|F32B5.7b.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1182|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017981|figl-1|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017982|hpo-18|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017982|hpo-18|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12503|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00017982|hpo-18|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9634|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017982|hpo-18|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1223|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017983|F32D1.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16134|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017984|F32D1.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1540|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=395|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017985|neg-1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2832|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1361|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017986|F32D1.7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017987|F32D1.8|1210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017987|F32D1.8|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017987|F32D1.8|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|107nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=926|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|118nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=597|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=460|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|1433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|1437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=381|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=826|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017988|fipp-1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017989|nol-10|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017989|nol-10|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1387|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017989|nol-10|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|1403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|1550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|1559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1259|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017990|cec-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017991|clec-180|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017991|clec-180|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017991|clec-180|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017991|clec-180|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017991|clec-180|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017992|F32E10.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017992|F32E10.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017992|F32E10.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017992|F32E10.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1012|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017992|F32E10.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017992|F32E10.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017992|F32E10.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|1162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|1171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7805|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=679|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017993|cec-5|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|124nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|126nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|135nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|142nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|156nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15368|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15489|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017995|F32E10.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017996|F33D4.4.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017996|F33D4.4.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017996|F33D4.4.1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9137|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017996|F33D4.4.1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1767|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017997|mrpl-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6a|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6a|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6a|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6a|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6b|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6b|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=760|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6b|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6b|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017998|F33D4.6b|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4026|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1350nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|1356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00017999|emc-6|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018000|F33D11.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018000|F33D11.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018001|F33D11.2.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018002|twk-47|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018002|twk-47|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018002|twk-47|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018002|twk-47|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018003|F33D11.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018004|F33D11.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1959|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1190|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018005|F33D11.8|455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|192nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3107|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|196nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=399|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018006|hpo-3|670nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3726|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3218|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018007|F33D11.10|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|552nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1167|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7624|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018008|vpr-1|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|1547nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|1589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3146|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018009|dhhc-3|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018010|F33E11.2b|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018010|F33E11.2b|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018010|F33E11.2b|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1614|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018010|F33E11.2b|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018010|F33E11.2b|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018011|F33E11.3|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018011|F33E11.3|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018011|F33E11.3|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2749|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018011|F33E11.3|346nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018011|F33E11.3|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018011|F33E11.3|366nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|1196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=843|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|1243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|1250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|177nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018013|phf-10|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018014|F33G12.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018014|F33G12.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018014|F33G12.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=953|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00018014|F33G12.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018014|F33G12.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018014|F33G12.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018015|F33G12.3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018015|F33G12.3|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018015|F33G12.3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1757|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018015|F33G12.3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018015|F33G12.3|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018016|lrr-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2397|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018016|lrr-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018016|lrr-1|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|1433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|1437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2977|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018017|golg-2|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|1077nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2372|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018018|F33G12.6a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018020|F33H12.6|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018020|F33H12.6|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018021|F34D6.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018021|F34D6.1|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018022|ceh-87|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018022|ceh-87|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018023|set-11|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018023|set-11|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018023|set-11|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=967|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018023|set-11|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=445|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018023|set-11|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|1182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|1238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=821|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|676nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|685nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018024|F35A5.1|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018025|F35A5.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1131|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018025|F35A5.2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018025|F35A5.2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|1439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|1447nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|1497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|1546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018026|F35A5.4|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018027|F35A5.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018027|F35A5.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018027|F35A5.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018028|F35B3.1|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00018028|F35B3.1|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1207|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=271|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|1297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018031|F35B3.4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018033|F35B3.7|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018033|F35B3.7|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00018033|F35B3.7|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018035|sek-4|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018036|F35C8.5|1432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018036|F35C8.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1890|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018037|chtl-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018037|chtl-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018037|chtl-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018037|chtl-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00018037|chtl-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018037|chtl-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=182|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018037|chtl-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018039|F35D2.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018039|F35D2.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018039|F35D2.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018040|F35D2.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018040|F35D2.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018040|F35D2.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018040|F35D2.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018041|F35D2.3|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018041|F35D2.3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018041|F35D2.3|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018041|F35D2.3|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018041|F35D2.3|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=553|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|54nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|57nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=262|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018042|mks-3|69nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018043|F35D11.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018043|F35D11.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018043|F35D11.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018043|F35D11.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018043|F35D11.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018043|F35D11.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018043|F35D11.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=692|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018044|F35D11.3.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1560|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018045|F35D11.4.2|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018045|F35D11.4.2|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018045|F35D11.4.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018045|F35D11.4.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1596|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018045|F35D11.4.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=566|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1163|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=390|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00018046|F35D11.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018047|clec-136|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018048|clec-137|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018049|clec-138|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018050|clec-139|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018050|clec-139|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018050|clec-139|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018050|clec-139|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018051|che-10|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018051|che-10|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018051|che-10|578nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018051|che-10|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018054|F35F10.4|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018054|F35F10.4|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018054|F35F10.4|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018054|F35F10.4|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018056|F35F10.6.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=701|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018056|F35F10.6.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018056|F35F10.6.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018057|F35F10.7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018057|F35F10.7|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018059|F35F10.10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018060|arrd-18|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1228|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018060|arrd-18|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018061|arrd-19|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018061|arrd-19|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018061|arrd-19|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018061|arrd-19|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018061|arrd-19|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018061|arrd-19|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018061|arrd-19|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018062|F35F10.13|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018062|F35F10.13|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018063|F35F10.14|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018063|F35F10.14|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018064|cdc-73|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018064|cdc-73|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018064|cdc-73|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018064|cdc-73|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018064|cdc-73|588nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018064|cdc-73|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2898|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018064|cdc-73|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018065|F35F11.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018065|F35F11.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018065|F35F11.2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018067|npr-7|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018067|npr-7|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018067|npr-7|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2201|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018068|F35H10.2|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018069|F35H10.3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018069|F35H10.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018069|F35H10.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018070|F35H10.5|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018070|F35H10.5|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1869|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018070|F35H10.5|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018070|F35H10.5|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018070|F35H10.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018070|F35H10.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018070|F35H10.5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018071|F35H10.6|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2781|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018072|nprl-3|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018072|nprl-3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018072|nprl-3|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018072|nprl-3|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1348|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018072|nprl-3|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=662|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018072|nprl-3|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018072|nprl-3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018073|F35H10.10|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018074|F35H12.1|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018074|F35H12.1|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018074|F35H12.1|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018074|F35H12.1|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=521|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018074|F35H12.1|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018074|F35H12.1|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018075|tbc-11|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018075|tbc-11|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=737|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018075|tbc-11|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=214|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018076|pifk-1|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018076|pifk-1|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=666|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018076|pifk-1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018076|pifk-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018077|F35H12.5a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018078|F35H12.6|705nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018078|F35H12.6|707nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018078|F35H12.6|742nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018078|F35H12.6|744nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018078|F35H12.6|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=720|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018078|F35H12.6|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018078|F35H12.6|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018079|F35H12.7|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018080|F36A4.1|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018080|F36A4.1|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018081|F36A4.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018081|F36A4.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018081|F36A4.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018081|F36A4.2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018081|F36A4.2|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=552|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018082|F36A4.3|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018082|F36A4.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=923|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018083|F36A4.4|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2404|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018084|F36A4.5a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018084|F36A4.5a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018084|F36A4.5a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00018084|F36A4.5a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018084|F36A4.5a|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018084|F36A4.5a|1591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018085|ttr-20|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018085|ttr-20|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018085|ttr-20|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00018085|ttr-20|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018087|F36D4.1|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018087|F36D4.1|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018087|F36D4.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018087|F36D4.1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018087|F36D4.1|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018087|F36D4.1|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1109|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018087|F36D4.1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|103nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=157|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|107nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=243|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|110nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|1378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018088|trpp-4|96nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1668|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=499|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=544|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=481|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018089|F36D4.4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4211|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1021nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1030nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1174|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=399|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|1336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|651nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|700nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|708nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|854nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018090|F36D4.5b.1|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018091|F36D4.6|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018092|F36F12.1b|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018096|clec-207|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018097|clec-208|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018098|F36F12.7|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018098|F36F12.7|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018098|F36F12.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018098|F36F12.7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018099|ztf-28|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018099|ztf-28|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=587|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018099|ztf-28|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018100|math-26|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018100|math-26|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018100|math-26|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018100|math-26|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018100|math-26|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018100|math-26|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018100|math-26|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|1086nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|1397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|1479nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|314nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018101|math-27|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018102|math-28|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018103|F36H5.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018104|fbxb-53|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018106|F36H5.8|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018108|F36H5.10.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018110|F36H9.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018111|F36H9.2a|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018111|F36H9.2a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018112|F36H9.4c|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018112|F36H9.4c|650nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018112|F36H9.4c|652nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018112|F36H9.4c|654nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018112|F36H9.4c|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018112|F36H9.4c|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1142|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018113|F36H9.5|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018113|F36H9.5|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018114|srt-41|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018114|srt-41|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018115|F36H9.7|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018115|F36H9.7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1155|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018115|F36H9.7|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=716|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|330nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5930|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3915|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018117|nlp-47|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018118|F36H12.2b|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018118|F36H12.2b|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018118|F36H12.2b|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018119|F36H12.3|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018119|F36H12.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=486|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018120|F36H12.4|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018121|F36H12.5|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018121|F36H12.5|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018121|F36H12.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=715|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1073nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1076nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1083nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1088nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21733|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1095nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1099nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|1438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018122|ttbk-2|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018123|F36H12.9|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018123|F36H12.9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=740|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018123|F36H12.9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018124|F36H12.10|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018124|F36H12.10|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018130|F36H12.17|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|153nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=540|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|163nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=4253|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|167nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1311|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|214nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|216nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018131|F37A4.1.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|1075nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6564|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018132|F37A4.2.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018133|F37A4.3|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018134|F37A4.4|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018134|F37A4.4|1461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018134|F37A4.4|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00018134|F37A4.4|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=293|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018134|F37A4.4|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018134|F37A4.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|1270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=941|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018135|F37A4.5.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018136|F37A4.6|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018136|F37A4.6|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018136|F37A4.6|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018136|F37A4.6|200nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=351|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018136|F37A4.6|205nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3029|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018137|bath-41|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=493|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7655|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5098|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=562|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|64nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|68nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=106|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|74nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=1963|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018138|folt-2|80nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=589|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018140|F37B4.10|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018140|F37B4.10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018140|F37B4.10|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018140|F37B4.10|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018140|F37B4.10|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2024|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00018140|F37B4.10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018140|F37B4.10|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018142|oac-22|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018142|oac-22|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018142|oac-22|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018142|oac-22|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018143|oac-23|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018143|oac-23|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018144|F37C4.4b.2|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018144|F37C4.4b.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018144|F37C4.4b.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018144|F37C4.4b.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018144|F37C4.4b.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14223|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=798|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=557|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018145|F37C4.5b|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1675|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018146|F37C4.6b|1517nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018146|F37C4.6b|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018146|F37C4.6b|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=485|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018146|F37C4.6b|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=504|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018146|F37C4.6b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=592|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00018146|F37C4.6b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018148|F37C4.8b|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018148|F37C4.8b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=392|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2100|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=553|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018149|F37C12.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018150|epg-4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018150|epg-4|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018150|epg-4|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2918|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018150|epg-4|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018150|epg-4|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018150|epg-4|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018150|epg-4|924nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|1467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10820|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=893|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=360|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|986nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018151|F37C12.3.2|992nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|392nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|394nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|397nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=468|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|426nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10387|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|643nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8885|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|652nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1744|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|656nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018152|acs-4|940nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018153|F37C12.10|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=344|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018153|F37C12.10|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018153|F37C12.10|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018153|F37C12.10|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018153|F37C12.10|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018153|F37C12.10|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3148|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|981nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018154|exos-9|987nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|1173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|1179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018155|F37C12.14|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018156|ncbp-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018156|ncbp-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018156|ncbp-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018156|ncbp-1|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2906|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018156|ncbp-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018157|lron-6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1377|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018157|lron-6|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018158|comp-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018158|comp-1|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018158|comp-1|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=234|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018158|comp-1|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|1170nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|1306nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018159|F37F2.2.2|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3509|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018160|odr-8|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|407nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3395|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|410nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|413nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018161|F38A5.2a|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=634|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=374|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018162|nspb-3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018163|F38A5.6|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5001|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018164|sup-36|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018165|F38A5.8|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018165|F38A5.8|1189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018165|F38A5.8|1389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018165|F38A5.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018166|nspb-5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018167|nspb-4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018167|nspb-4|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1667|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018167|nspb-4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018167|nspb-4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018168|irld-7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018169|nspb-2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018169|nspb-2|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018169|nspb-2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018169|nspb-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018169|nspb-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2455|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018169|nspb-2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018170|nspb-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018170|nspb-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1612|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018170|nspb-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018170|nspb-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1025|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2168|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018172|F38B6.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2160|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00018173|F38B6.3|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018173|F38B6.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018173|F38B6.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018173|F38B6.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018174|F38B6.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1063|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018174|F38B6.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018174|F38B6.4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018174|F38B6.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018175|F38B6.6.1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018175|F38B6.6.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018175|F38B6.6.1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018175|F38B6.6.1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018176|F38B6.7|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018178|F38E1.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018178|F38E1.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018178|F38E1.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018179|F38E1.6|753nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018179|F38E1.6|755nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018179|F38E1.6|942nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018179|F38E1.6|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018180|srsx-22|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018181|F38E1.9|396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018181|F38E1.9|402nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018181|F38E1.9|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018181|F38E1.9|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4506|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018181|F38E1.9|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=315|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018181|F38E1.9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018181|F38E1.9|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018182|F38E1.10|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|358nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|562nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|571nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=460|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018184|F38E9.1|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=190|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|400nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3083|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4016|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|541nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018187|F38E9.5.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|102nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1465|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=997|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018188|F38E9.6|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018189|nhr-181|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018189|nhr-181|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018189|nhr-181|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018190|F38H12.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018191|frpr-7|1335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=893|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018191|frpr-7|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018191|frpr-7|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018191|frpr-7|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018191|frpr-7|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018191|frpr-7|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018192|F39B3.3|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=663|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=294|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018193|F39C12.1|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=217|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=434|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018195|btb-16|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018196|nep-13|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018196|nep-13|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018196|nep-13|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1390nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1393nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=610|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1395nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6869|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1400nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=234|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1404nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1406|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|1549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018198|F39E9.6|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018200|btb-17|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018200|btb-17|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018201|btb-18|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018202|F39F10.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|1041nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|1092nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|1396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|1465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018203|F39F10.3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018204|F39F10.4|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018204|F39F10.4|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018206|ugt-61|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018206|ugt-61|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=480|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00018207|F39G3.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018207|F39G3.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018207|F39G3.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018207|F39G3.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018208|F39G3.3|1040nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=927|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018208|F39G3.3|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018208|F39G3.3|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018208|F39G3.3|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018209|F39G3.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018209|F39G3.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018210|F39G3.5a|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018210|F39G3.5a|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018210|F39G3.5a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018210|F39G3.5a|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018210|F39G3.5a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=517|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00018211|oac-24|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018212|F39H12.1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=741|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018212|F39H12.1|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018212|F39H12.1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018212|F39H12.1|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|1527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|304nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=683|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|307nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018213|F39H12.2|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2252|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1869|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018214|F39H12.3|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018215|igcm-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018215|igcm-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018215|igcm-1|1412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018215|igcm-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=299|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018215|igcm-1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018215|igcm-1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018216|F40A3.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018216|F40A3.1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1316|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018216|F40A3.1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018216|F40A3.1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018217|F40A3.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018217|F40A3.2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018217|F40A3.2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00018217|F40A3.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018217|F40A3.2|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1036|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2092|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2490|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018218|F40A3.3c|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|1464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3550|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|911nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018219|F40A3.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2248|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=410|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018221|F40A3.6|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018222|F40A3.7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018222|F40A3.7|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=749|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018222|F40A3.7|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018222|F40A3.7|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018222|F40A3.7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018223|bath-13|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018223|bath-13|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018223|bath-13|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00018223|bath-13|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018223|bath-13|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1113|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018226|F40B5.2a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|1580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|1595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018227|nep-15|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018229|F40C5.2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=491|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018229|F40C5.2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018230|mage-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018230|mage-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018230|mage-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4459|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018230|mage-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=568|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018231|F40E3.3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018232|F40E3.5.1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018232|F40E3.5.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018232|F40E3.5.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018232|F40E3.5.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018233|F40E3.6a|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018235|F40E12.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018235|F40E12.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018236|fbxb-71|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|1472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|1474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9231|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1867|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018237|drd-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018238|F40F4.7|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018238|F40F4.7|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3397|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00018238|F40F4.7|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018238|F40F4.7|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018239|sec-20|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018239|sec-20|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1158|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018239|sec-20|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018240|cox-17|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2611|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018240|cox-17|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018241|F40G9.5|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018241|F40G9.5|1598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018241|F40G9.5|1601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018241|F40G9.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018241|F40G9.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018241|F40G9.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018241|F40G9.5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018242|F40G9.6|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018242|F40G9.6|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018243|F40G9.7.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018245|F40G9.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018245|F40G9.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018246|clec-148|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018247|F40G9.12|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018248|F40G9.14|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018249|F40H3.1a|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018249|F40H3.1a|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018249|F40H3.1a|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=948|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018249|F40H3.1a|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1146|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|431nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|450nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=258|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018250|F40H3.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018251|F40H3.3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018251|F40H3.3|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018251|F40H3.3|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00018251|F40H3.3|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018251|F40H3.3|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018251|F40H3.3|303nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018252|F40H3.6|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018252|F40H3.6|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018252|F40H3.6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=553|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00018252|F40H3.6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018253|F40H6.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018253|F40H6.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018253|F40H6.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2954|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018253|F40H6.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00018254|F40H6.2|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018256|cutl-28|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018256|cutl-28|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018256|cutl-28|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018257|F41B4.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018257|F41B4.1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018257|F41B4.1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018257|F41B4.1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018258|F41B4.2b|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16561|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018258|F41B4.2b|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=641|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018258|F41B4.2b|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018258|F41B4.2b|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018258|F41B4.2b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018258|F41B4.2b|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018259|F41B4.3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018259|F41B4.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018259|F41B4.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018259|F41B4.3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4230|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018259|F41B4.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018259|F41B4.3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018260|cyp-33C7|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=300|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018260|cyp-33C7|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018261|cyp-33C5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018261|cyp-33C5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018261|cyp-33C5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018261|cyp-33C5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018261|cyp-33C5|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018262|cyp-33C3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018262|cyp-33C3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018262|cyp-33C3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018262|cyp-33C3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018262|cyp-33C3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018264|cyp-33C6|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018265|nhr-182|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018265|nhr-182|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018265|nhr-182|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018265|nhr-182|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018266|nhr-183|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018266|nhr-183|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018266|nhr-183|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1065|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018266|nhr-183|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018266|nhr-183|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018267|F41C3.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018267|F41C3.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018267|F41C3.1|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018268|F41C3.2|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018268|F41C3.2|220nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018268|F41C3.2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018268|F41C3.2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018268|F41C3.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018268|F41C3.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=429|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1852|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018269|acs-11|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=487|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|378nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2311|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018270|F41C3.4|780nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=174|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018271|F41C3.5.2|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21224|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018272|F41C3.6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018272|F41C3.6|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018272|F41C3.6|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018272|F41C3.6|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018274|F41C3.8b|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018274|F41C3.8b|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018274|F41C3.8b|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018274|F41C3.8b|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018274|F41C3.8b|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018274|F41C3.8b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018275|F41C3.11|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018275|F41C3.11|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018275|F41C3.11|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018275|F41C3.11|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018275|F41C3.11|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018279|F41C6.6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018279|F41C6.6|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018279|F41C6.6|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018279|F41C6.6|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018280|F41C6.7|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018280|F41C6.7|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018280|F41C6.7|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018280|F41C6.7|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018280|F41C6.7|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1724|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1884|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018281|tbc-18|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018282|F41D9.2a|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=957|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018282|F41D9.2a|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=772|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018283|sulp-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018283|sulp-3|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018283|sulp-3|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018283|sulp-3|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018284|F41E6.1|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018284|F41E6.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00018284|F41E6.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|1163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|1413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|588nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|763nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3944|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|770nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1402|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018285|smk-1|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=256|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=330|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|417nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018286|F41E6.5b|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018288|F41E6.7|347nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018288|F41E6.7|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018288|F41E6.7|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018289|F41E6.8|1290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|101nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1915|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7191|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018290|vps-60|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018291|fip-4|1344nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1195|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|331nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018292|F41E6.11|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018293|F41E6.12|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018293|F41E6.12|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018293|F41E6.12|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018293|F41E6.12|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018293|F41E6.12|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=769|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7955|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=831|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018294|atg-18|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018295|oac-29|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018295|oac-29|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018295|oac-29|19nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018295|oac-29|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018295|oac-29|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018295|oac-29|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00018296|F41F3.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00018296|F41F3.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9438|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=859|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13681|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=291|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018297|F41F3.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=834|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=540|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2235|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=569|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=823|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37893|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=262|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=337|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39394|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3213|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018298|F41G3.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018299|F41G3.2|267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018300|F41G3.3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018301|F41G3.5|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018301|F41G3.5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018301|F41G3.5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018302|F41G3.6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018302|F41G3.6|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2955|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018302|F41G3.6|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=412|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018302|F41G3.6|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018303|F41G3.10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018303|F41G3.10|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018303|F41G3.10|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=929|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018303|F41G3.10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=442|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018303|F41G3.10|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018304|agr-1|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018305|exos-8|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5035|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018305|exos-8|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018305|exos-8|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018307|dyla-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018307|dyla-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018307|dyla-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018307|dyla-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018307|dyla-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018310|F41G4.7|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1246|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3213|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018311|F41G4.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018312|F41H8.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018312|F41H8.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018313|F41H8.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018314|F41H10.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018314|F41H10.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3685|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018314|F41H10.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018314|F41H10.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018314|F41H10.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018314|F41H10.1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018315|F41H10.2|1471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018315|F41H10.2|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1892|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018316|F41H10.3a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018317|F41H10.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018317|F41H10.4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1032|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018317|F41H10.4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=522|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018317|F41H10.4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018317|F41H10.4|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018317|F41H10.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018318|F41H10.5|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018318|F41H10.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018318|F41H10.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|173nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2489|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=846|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1769|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018319|hda-6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2796|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|553nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|865nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018321|sand-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018322|F41H10.12|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018322|F41H10.12|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018322|F41H10.12|622nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018323|F42A6.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018324|F42A6.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018327|F42A6.5|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018327|F42A6.5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018327|F42A6.5|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018327|F42A6.5|293nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018327|F42A6.5|296nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018327|F42A6.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018328|F42A6.6a|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018328|F42A6.6a|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018328|F42A6.6b|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018328|F42A6.6b|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=977|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018330|elks-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018330|elks-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018330|elks-1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1412|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018330|elks-1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018332|F42A9.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018332|F42A9.3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018333|cyp-33E3|1232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018333|cyp-33E3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018333|cyp-33E3|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00018333|cyp-33E3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018333|cyp-33E3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018334|cyp-33E2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=296|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=617|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2383|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018335|F42A9.6b|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018336|F42A9.7|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018336|F42A9.7|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00018336|F42A9.7|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=233|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018337|F42A9.8b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018337|F42A9.8b|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1106|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018337|F42A9.8b|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018337|F42A9.8b|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018338|F42A9.9|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=773|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3336|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=338|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=478|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018339|abcf-3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018340|anmt-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018340|anmt-2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018340|anmt-2|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018340|anmt-2|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018340|anmt-2|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1793|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018340|anmt-2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018340|anmt-2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018341|F42A10.5|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018341|F42A10.5|581nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9226|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018341|F42A10.5|587nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018341|F42A10.5|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018342|F42A10.6|1114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018342|F42A10.6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018342|F42A10.6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=714|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018342|F42A10.6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1307|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018342|F42A10.6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018342|F42A10.6|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018343|F42A10.7.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1442|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018343|F42A10.7.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018343|F42A10.7.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018344|npr-27|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=617|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018344|npr-27|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018344|npr-27|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018344|npr-27|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018344|npr-27|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=222|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00018344|npr-27|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018345|F42C5.3b|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018346|F42C5.4b|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018346|F42C5.4b|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018346|F42C5.4b|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018346|F42C5.4b|730nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018346|F42C5.4b|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018347|F42C5.5b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018347|F42C5.5b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=723|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=519|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=964|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=462|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5426|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1377|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|484nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018348|F42C5.6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=424|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=315|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|1594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2482|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018349|F42C5.9.1|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=979|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|1401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2881|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=791|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|26nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018350|ifo-1|33nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018351|F42G2.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018351|F42G2.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018351|F42G2.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018351|F42G2.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018352|fbxc-20|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018352|fbxc-20|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|1313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|1315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|1319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=392|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|1328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|1331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|1337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|1354nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018353|fbxa-182|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018354|F42G2.5|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018354|F42G2.5|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018354|F42G2.5|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018354|F42G2.5|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018355|ceh-86|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018355|ceh-86|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018355|ceh-86|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018356|islo-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018356|islo-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018356|islo-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018356|islo-1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2003|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018356|islo-1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018356|islo-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1225|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018357|moc-3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018358|F42G8.7|1534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018358|F42G8.7|1547nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018358|F42G8.7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018359|F42G8.8|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018359|F42G8.8|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018359|F42G8.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018360|irld-8|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018360|irld-8|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5442|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3285|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2988|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=523|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=554|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=607|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=432|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018361|F42G8.10.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=392|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1939|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018362|F42G9.1b|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6632|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3376|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|268nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018363|F42G9.4|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|1499nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=334|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|438nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=879|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|443nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=489|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=563|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018364|dagl-2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018365|tpst-2|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00018365|tpst-2|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018365|tpst-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018366|F42H10.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018366|F42H10.2|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1663|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018366|F42H10.2|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018367|F42H10.3a|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018367|F42H10.3a|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018367|F42H10.3a|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018367|F42H10.3a|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1273|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018367|F42H10.3a|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018367|F42H10.3a|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018369|mig-39|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018369|mig-39|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018369|mig-39|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018369|mig-39|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018369|mig-39|646nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=619|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018369|mig-39|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018369|mig-39|651nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018370|F42H10.6.2|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018370|F42H10.6.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018370|F42H10.6.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018370|F42H10.6.2|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1490|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018370|F42H10.6.2|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018370|F42H10.6.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018371|ess-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018371|ess-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1109|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018371|ess-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018371|ess-2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018374|tag-343|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018374|tag-343|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018374|tag-343|22nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018374|tag-343|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018374|tag-343|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018375|F43C9.1|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38287|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3053|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=518|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018376|F43C9.2|361nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018377|hum-10|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018378|F43C11.1b|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018379|F43C11.2|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018380|decr-1.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018380|decr-1.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1014|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00018380|decr-1.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018380|decr-1.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018380|decr-1.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018383|F43C11.6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018384|F43C11.7|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=845|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018384|F43C11.7|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018384|F43C11.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018385|F43C11.8|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018385|F43C11.8|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018385|F43C11.8|1386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018385|F43C11.8|1401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1910|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018385|F43C11.8|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018385|F43C11.8|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018386|F43C11.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=737|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00018386|F43C11.9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018389|F43C11.12|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018390|F43E2.1.2|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1923|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018390|F43E2.1.2|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3160|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3176|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018391|rpb-4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018392|insc-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018392|insc-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=711|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018392|insc-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018392|insc-1|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018392|insc-1|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018392|insc-1|96nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=463|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6894|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4292|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018393|msra-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018394|F43E2.6b.1|1000nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018394|F43E2.6b.1|1019nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018394|F43E2.6b.1|1170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018394|F43E2.6b.1|960nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3531|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12512|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2125|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018395|mtch-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018396|F43E2.9|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018397|F43E2.11|736nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018397|F43E2.11|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1177|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018398|sptl-2|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018399|F43H9.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=587|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018399|F43H9.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018399|F43H9.3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018399|F43H9.3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018399|F43H9.3|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018399|F43H9.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2256|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|791nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|794nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|798nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018400|F43H9.4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|464nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=219|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|472nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018402|kvs-3|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018403|F44A2.3|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018403|F44A2.3|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018403|F44A2.3|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018403|F44A2.3|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018403|F44A2.3|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018404|nhr-39|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018405|F44A2.5a|1515nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018405|F44A2.5b|350nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=244|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018405|F44A2.5b|359nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=548|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018405|F44A2.5b|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018405|F44A2.5b|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018405|F44A2.5b|693nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018405|F44A2.5b|771nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018406|F44A2.7|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018406|F44A2.7|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018406|F44A2.7|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018406|F44A2.7|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018406|F44A2.7|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018406|F44A2.7|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018406|F44A2.7|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018407|F44B9.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018407|F44B9.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1549|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=665|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=177|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=463|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=283|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|394nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|505nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|512nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018408|F44B9.5|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3641|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|74nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=101|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|77nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018409|F44B9.8|79nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018410|F44B9.9|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018410|F44B9.9|1315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018410|F44B9.9|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018410|F44B9.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018411|F44B9.10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018411|F44B9.10|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018412|nhr-37|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018412|nhr-37|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018412|nhr-37|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=725|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018412|nhr-37|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018412|nhr-37|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|1245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|334nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=799|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018413|cyp-33C4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018414|nstp-8|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018415|nhr-184|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018415|nhr-184|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018415|nhr-184|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018415|nhr-184|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018415|nhr-184|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018415|nhr-184|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018415|nhr-184|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=217|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1330|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|1160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|1171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|1178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1426|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018417|F44E2.3|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018418|F44E2.4|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018418|F44E2.4|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018418|F44E2.4|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018419|F44E2.6b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018419|F44E2.6b|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018419|F44E2.6b|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3078|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018419|F44E2.6b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018420|F44E2.7b.2|1510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018420|F44E2.7b.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018420|F44E2.7b.2|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=590|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018420|F44E2.7b.2|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2647|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018420|F44E2.7b.2|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018420|F44E2.7b.2|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|1474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|1591nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|1595nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|198nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|200nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|203nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1730|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2183|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=400|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018421|F44E2.8|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018422|F44E2.9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018422|F44E2.9|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018422|F44E2.9|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1114|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018422|F44E2.9|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018422|F44E2.9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2338|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=197|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018423|F44E2.10|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9925|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018424|F44E7.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018425|F44E7.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00018425|F44E7.3|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018425|F44E7.3|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018425|F44E7.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4830|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6316|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2050|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4c.1|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4d|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018426|F44E7.4d|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=940|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018427|F44E7.5a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018428|fbxa-183|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018429|F44E7.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00018429|F44E7.7|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00018430|nhr-142|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018430|nhr-142|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=464|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018430|nhr-142|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018430|nhr-142|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018430|nhr-142|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018430|nhr-142|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2312|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018431|F44E7.9|802nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018432|irld-33|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018433|ceh-82|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018433|ceh-82|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018435|btb-9|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018435|btb-9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018435|btb-9|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018436|fbxb-11|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018436|fbxb-11|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018436|fbxb-11|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018437|btb-8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018437|btb-8|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018438|btb-6|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018438|btb-6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018438|btb-6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018438|btb-6|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018438|btb-6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018439|fbxa-184|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00018439|fbxa-184|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00018439|fbxa-184|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00018441|math-29|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018442|sdz-18|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018442|sdz-18|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018443|btb-7|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018443|btb-7|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018443|btb-7|1424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018443|btb-7|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018443|btb-7|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018443|btb-7|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00018443|btb-7|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018444|fbxb-48|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018446|ceh-83|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018446|ceh-83|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00018446|ceh-83|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018446|ceh-83|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018446|ceh-83|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018446|ceh-83|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018446|ceh-83|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018447|irld-9|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018448|F45D11.1.1|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018452|F45D11.5|1008nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018452|F45D11.5|1014nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=586|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018452|F45D11.5|1016nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018452|F45D11.5|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018452|F45D11.5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018455|fbxc-42|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018455|fbxc-42|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018456|fbxc-39|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018456|fbxc-39|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018458|fbxb-30|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018459|F45D11.14|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018459|F45D11.14|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4628|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018459|F45D11.14|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018459|F45D11.14|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018459|F45D11.14|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018459|F45D11.14|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018460|F45D11.15|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018460|F45D11.15|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018460|F45D11.15|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4652|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018460|F45D11.15|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018460|F45D11.15|386nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|497nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=770|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|525nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1241|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018462|F45E1.1|527nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018465|F45E1.4|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|1126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|1202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|1204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018466|F45E1.5|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018467|sdpn-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018467|sdpn-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018467|sdpn-1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1048|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018467|sdpn-1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018467|sdpn-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018467|sdpn-1|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1281|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1953|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=269|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018468|tag-80|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=302|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2711|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018470|F45E4.5c|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=478|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018471|F45E4.6|1086nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018471|F45E4.6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018471|F45E4.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018471|F45E4.6|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=227|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|1496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018472|nep-16|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018473|cima-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018473|cima-1|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018473|cima-1|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018473|cima-1|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=405|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00018473|cima-1|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018473|cima-1|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|537nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1277|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|539nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1377|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|542nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|545nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|548nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|616nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|622nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|628nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018474|cnep-1|989nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018476|F45E12.6|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018477|otpl-4|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|1348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|1391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|1394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|1401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|1457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018478|otpl-5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018479|otpl-6|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018480|otpl-7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00018480|otpl-7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018480|otpl-7|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4453|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=209|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1472|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018481|F45F2.9a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|776nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|783nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1858|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|785nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=835|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|788nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018482|F45F2.10|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|1041nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|1061nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|1310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1100|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018483|F45F2.11a|430nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=508|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018484|F46C8.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018484|F46C8.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018484|F46C8.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018484|F46C8.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018484|F46C8.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018484|F46C8.1|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018485|F46C8.3|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018485|F46C8.3|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018485|F46C8.3|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018485|F46C8.3|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=689|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018485|F46C8.3|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018485|F46C8.3|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018486|glb-16|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018486|glb-16|316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018486|glb-16|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=227|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018486|glb-16|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018487|F46C8.8|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018487|F46C8.8|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018487|F46C8.8|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018487|F46C8.8|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13017|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018488|acs-1|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018489|F46E10.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018489|F46E10.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018489|F46E10.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018489|F46E10.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00018490|F46E10.3|1559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018490|F46E10.3|669nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=205|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31012|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1220|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=355|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018491|mdh-1|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|18nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=981|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=963|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018492|hpo-26|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018493|F46F5.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018497|F46F5.6|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018497|F46F5.6|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018497|F46F5.6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018497|F46F5.6|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018497|F46F5.6|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018497|F46F5.6|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=678|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018497|F46F5.6|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=215|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018498|F46F5.7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018498|F46F5.7|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018498|F46F5.7|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018500|F46F5.9|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018500|F46F5.9|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018500|F46F5.9|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018500|F46F5.9|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018500|F46F5.9|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018500|F46F5.9|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=580|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018501|F46F5.10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018502|F46F5.11|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018502|F46F5.11|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018502|F46F5.11|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018504|F46F5.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018505|F46F5.14|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018505|F46F5.14|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018506|F46F5.15|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018507|F46F5.16|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018508|F46F11.1a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018508|F46F11.1a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018508|F46F11.1a|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018508|F46F11.1a|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2687|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018508|F46F11.1a|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=381|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018508|F46F11.1a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018508|F46F11.1a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1937|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9170|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018509|F46F11.6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018510|F46F11.7|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018510|F46F11.7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018510|F46F11.7|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018510|F46F11.7|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=311|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018510|F46F11.7|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018510|F46F11.7|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4250|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018511|F46F11.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=275|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2945|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018512|trpp-8|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018513|F46F11.10|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018514|F46G11.1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018514|F46G11.1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00018514|F46G11.1|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018514|F46G11.1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018514|F46G11.1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018514|F46G11.1|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018514|F46G11.1|469nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018515|F46G11.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018516|tag-257|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018516|tag-257|166nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018516|tag-257|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018516|tag-257|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018516|tag-257|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018516|tag-257|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018517|F46G11.4|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018517|F46G11.4|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1198|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018517|F46G11.4|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018517|F46G11.4|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018517|F46G11.4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=689|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2985|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018518|F46H5.2a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6544|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3725|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373661|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5979|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|702nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018519|F46H5.3b.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=909|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|352nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|354nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018520|F46H5.4|371nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|103nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=286|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018521|F46H5.5|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=247|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1613|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1209|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1358|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7b.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7c|1499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018522|F46H5.7c|1582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=765|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018523|lact-1|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018525|F47B3.1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=499|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018526|F47B3.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018526|F47B3.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018526|F47B3.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018526|F47B3.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00018527|F47B3.3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018527|F47B3.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018527|F47B3.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018528|F47B3.4|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018528|F47B3.4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018528|F47B3.4|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00018528|F47B3.4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018528|F47B3.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018529|F47B3.5|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018529|F47B3.5|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018529|F47B3.5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018529|F47B3.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018529|F47B3.5|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018531|F47B3.7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018531|F47B3.7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018531|F47B3.7|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018531|F47B3.7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=668|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=721|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1385|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1296|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3163|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018532|F47B7.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2a|667nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2a|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=633|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2b|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2b|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2b|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2b|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2b|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2844|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2b|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018533|F47B7.2b|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018535|F47B7.4|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018537|F47B7.6|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7a|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7a|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7a|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7a|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7a|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7a|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7b|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=323|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018538|F47B7.7b|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018539|nhr-185|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018539|nhr-185|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018541|nhr-186|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018541|nhr-186|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018542|nhr-187|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018542|nhr-187|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018542|nhr-187|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018543|ugt-32|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018543|ugt-32|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018543|ugt-32|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018543|ugt-32|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018544|nhr-188|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018544|nhr-188|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018544|nhr-188|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018544|nhr-188|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018545|nhr-189|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018545|nhr-189|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=275|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018545|nhr-189|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018545|nhr-189|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018545|nhr-189|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018545|nhr-189|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|1151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|1245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|1519nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|1524nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|1527nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018547|clec-78|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018548|clec-79|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018548|clec-79|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018548|clec-79|54nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018548|clec-79|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=490|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018548|clec-79|63nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018551|F47C12.8|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018551|F47C12.8|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018551|F47C12.8|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018552|srt-19|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018552|srt-19|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018552|srt-19|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018552|srt-19|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018555|srt-35|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018556|srt-36|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018558|srt-20|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018558|srt-20|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018559|srt-37|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00018559|srt-37|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|161nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2383|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018560|F47D12.3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|1192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|1200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018561|gadr-3|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=143|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00018562|F47D12.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018562|F47D12.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1199|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018562|F47D12.6|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018562|F47D12.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018563|F47D12.7|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=446|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018563|F47D12.7|961nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6886|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018564|F47D12.9b.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018565|F47E1.1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018565|F47E1.1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1149|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018565|F47E1.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018565|F47E1.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018565|F47E1.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018565|F47E1.1|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018567|F47E1.3|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=382|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018567|F47E1.3|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018567|F47E1.3|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=236|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018567|F47E1.3|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018567|F47E1.3|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018567|F47E1.3|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=673|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018568|F47E1.4|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018568|F47E1.4|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018568|F47E1.4|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018568|F47E1.4|222nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018568|F47E1.4|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|214nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|221nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|227nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|234nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1552|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018569|F47F2.1b|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018571|F47F2.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018571|F47F2.3|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|500nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|937nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|943nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11226|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|949nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=680|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|976nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|978nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018572|lin-42|986nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018573|oac-30|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018573|oac-30|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018574|F47F6.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018575|clec-119|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018575|clec-119|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018576|F47G3.1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018576|F47G3.1|115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00018576|F47G3.1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018576|F47G3.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018576|F47G3.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018577|asna-2|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00018577|asna-2|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018577|asna-2|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018577|asna-2|518nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018578|F47G3.3|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018578|F47G3.3|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018578|F47G3.3|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00018578|F47G3.3|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018579|acs-16|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018579|acs-16|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018579|acs-16|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=761|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018580|F47G6.3|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=236|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018580|F47G6.3|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|55nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|884nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018581|F48A9.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018582|F48A9.2|1192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018582|F48A9.2|1198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018582|F48A9.2|1201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00018582|F48A9.2|1455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018582|F48A9.2|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|419nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1402|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|427nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00018585|F48A11.4b.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018586|ubxn-3|410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5573|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018586|ubxn-3|414nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018586|ubxn-3|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018586|ubxn-3|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=711|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018586|ubxn-3|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018587|F48B9.1|1506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018589|F48B9.3|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018589|F48B9.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018589|F48B9.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018589|F48B9.3|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018589|F48B9.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4010|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8700|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00018590|nlp-37|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018591|npax-2|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018591|npax-2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018593|F48B9.8|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=387|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018593|F48B9.8|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018593|F48B9.8|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018593|F48B9.8|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018593|F48B9.8|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018594|aman-3|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018594|aman-3|1343nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018595|fbxa-145|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018595|fbxa-145|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00018595|fbxa-145|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018596|F48C1.3|968nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018598|F48C1.5|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018598|F48C1.5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018598|F48C1.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018598|F48C1.5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2065|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018599|F48C1.6|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018599|F48C1.6|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3695|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018599|F48C1.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018600|F48C1.8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|1402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|1433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=742|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|653nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018601|F48C1.9|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31418|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|278nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|284nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|287nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018602|F48D6.4b|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018603|F48E3.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018603|F48E3.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=935|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018603|F48E3.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018603|F48E3.2|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018604|uggt-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018604|uggt-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018604|uggt-1|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3735|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018604|uggt-1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=928|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|317nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8262|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4178|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2103|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00018605|F48E3.4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|714nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018606|F48E3.6|973nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018607|F48E3.8c|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018607|F48E3.8c|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018607|F48E3.8c|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018607|F48E3.8c|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018608|F48E3.9|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018608|F48E3.9|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018608|F48E3.9|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018608|F48E3.9|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018608|F48E3.9|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018609|F48E8.2|434nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018609|F48E8.2|440nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018609|F48E8.2|443nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=395|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018609|F48E8.2|447nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1257|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00018609|F48E8.2|453nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018609|F48E8.2|458nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=244|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018609|F48E8.2|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=870|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3054|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018610|F48E8.3.1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|311nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018611|F48E8.4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1656|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=614|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018612|disl-2|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2239|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018613|skpt-1|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018614|F48G7.2b|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018614|F48G7.2b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018615|F48G7.4|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018615|F48G7.4|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018615|F48G7.4|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018616|F48G7.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=723|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018616|F48G7.5|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018616|F48G7.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018616|F48G7.5|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018616|F48G7.5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018616|F48G7.5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018618|F48G7.7|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018619|F48G7.8|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018619|F48G7.8|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018619|F48G7.8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018619|F48G7.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018619|F48G7.8|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018620|F48G7.9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018620|F48G7.9|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00018620|F48G7.9|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=166|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018621|F48G7.10|263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=593|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018622|nhr-190|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018623|F48G7.12b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018623|F48G7.12b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018623|F48G7.12b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018623|F48G7.12b|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018624|F48G7.13|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018624|F48G7.13|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018625|prp-17|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018625|prp-17|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018625|prp-17|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018625|prp-17|265nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2397|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00018625|prp-17|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018626|F49D11.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018626|F49D11.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018626|F49D11.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018626|F49D11.2|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018626|F49D11.2|853nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018626|F49D11.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018627|F49D11.3a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018627|F49D11.3a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018630|F49D11.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018630|F49D11.6|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018631|F49D11.7|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018631|F49D11.7|70nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018631|F49D11.7|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=402|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|1360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|1571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3085|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018632|tag-296|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018634|F49E7.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018634|F49E7.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2766|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018634|F49E7.2|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018634|F49E7.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018634|F49E7.2|26nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018634|F49E7.2|35nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018634|F49E7.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|177nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|182nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|620nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|630nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=750|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018635|nprl-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=955|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018636|F49E8.2a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018636|F49E8.2a|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6010|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|1434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=946|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|478nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=391|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5022|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018637|F49E8.6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1004|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018638|F49E8.7a.1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2268|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|801nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018639|tbc-16|805nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018640|F49E10.2b|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018640|F49E10.2b|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018641|F49E10.4a|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018641|F49E10.4a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018641|F49E10.4a|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018643|drd-50|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018643|drd-50|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=599|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018643|drd-50|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018643|drd-50|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018643|drd-50|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018645|F49F1.5a|414nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018645|F49F1.5a|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=879|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018645|F49F1.5a|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018645|F49F1.5b|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018645|F49F1.5b|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018645|F49F1.5b|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018646|mul-1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018646|mul-1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018647|F49F1.7b|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018647|F49F1.7b|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018648|F49F1.8|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018652|F49F1.12|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018652|F49F1.12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018653|F49H12.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018653|F49H12.2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018653|F49H12.2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=916|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018653|F49H12.2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018653|F49H12.2|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018653|F49H12.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018653|F49H12.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018654|F49H12.3|1297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018654|F49H12.3|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018654|F49H12.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018654|F49H12.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2657|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018655|F49H12.4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018655|F49H12.4|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=422|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018655|F49H12.4|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=569|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018655|F49H12.4|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018656|F49H12.5|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018656|F49H12.5|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4106|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018656|F49H12.5|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018657|acl-4|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018657|acl-4|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018657|acl-4|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018657|acl-4|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3324|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018659|F52C6.2|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018659|F52C6.2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018659|F52C6.2|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=659|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018659|F52C6.2|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018660|F52C6.3|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018660|F52C6.3|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018661|F52C6.4|504nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018661|F52C6.4|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018665|bath-4|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018665|bath-4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018665|bath-4|938nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018667|bath-7|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018667|bath-7|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=266|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018668|bath-2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018668|bath-2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018668|bath-2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018668|bath-2|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018668|bath-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018668|bath-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018669|F52C6.12.1|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018672|F52C9.1.2|1383nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018672|F52C9.1.2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018672|F52C9.1.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018672|F52C9.1.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018672|F52C9.1.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1506|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018672|F52C9.1.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018672|F52C9.1.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018674|F52C9.3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1184|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018674|F52C9.3|1180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018674|F52C9.3|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018674|F52C9.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018674|F52C9.3|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018674|F52C9.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018675|F52C9.5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018675|F52C9.5|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018675|F52C9.5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018678|F52C12.1a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1440|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018678|F52C12.1a|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018678|F52C12.1a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018679|F52C12.2.2|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018679|F52C12.2.2|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018679|F52C12.2.2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018679|F52C12.2.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1108|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018680|tsen-54|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1741|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018680|tsen-54|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018680|tsen-54|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|658nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|665nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|670nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=548|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018681|denn-4|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1598|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018682|aagr-4|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018682|aagr-4|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=783|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018682|aagr-4|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018682|aagr-4|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018682|aagr-4|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018682|aagr-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018683|F52D1.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018683|F52D1.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018683|F52D1.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018683|F52D1.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018684|fbxa-41|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018687|F52D2.5|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018687|F52D2.5|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018688|F52D2.6|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018688|F52D2.6|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018689|F52D2.7|476nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018689|F52D2.7|485nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018689|F52D2.7|515nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018689|F52D2.7|522nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=783|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018689|F52D2.7|527nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018690|fbxa-46|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018690|fbxa-46|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018692|F52E1.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018693|F52E1.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018693|F52E1.3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018694|F52E1.5|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018694|F52E1.5|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018694|F52E1.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018694|F52E1.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018694|F52E1.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018694|F52E1.5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018696|pho-6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018696|pho-6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018696|pho-6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018696|pho-6|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|437nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|445nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|451nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=392|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|523nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018697|F52E1.9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018698|vha-18|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2559|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018698|vha-18|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018698|vha-18|1235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018698|vha-18|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|1106nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|1112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|1122nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|1423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|476nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1136|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3488|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5880|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|514nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|527nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|531nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|533nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|536nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018700|lmd-3|543nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16854|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=359|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|239nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018701|pccb-1|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1461|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018702|F52E4.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018703|sec-3|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018703|sec-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018703|sec-3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018703|sec-3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=642|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018703|sec-3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00018704|ztf-13|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018704|ztf-13|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1450|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018704|ztf-13|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|43nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018706|F52F10.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018707|oac-31|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018707|oac-31|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018708|oac-32|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018708|oac-32|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018708|oac-32|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018708|oac-32|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=317|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018708|oac-32|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018709|srsx-8|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018709|srsx-8|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018709|srsx-8|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3367|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018710|F52G3.1|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018711|F52G3.3|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018713|F52G3.5|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018713|F52G3.5|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018713|F52G3.5|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018714|F52H2.1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018714|F52H2.1|344nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018714|F52H2.1|351nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018715|F52H2.3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018715|F52H2.3|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=593|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018715|F52H2.3|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018715|F52H2.3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018715|F52H2.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018716|F52H2.4|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=811|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018716|F52H2.4|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018716|F52H2.4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018716|F52H2.4|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1208|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018716|F52H2.4|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018716|F52H2.4|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018716|F52H2.4|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018717|F52H2.5.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018717|F52H2.5.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018717|F52H2.5.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=971|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00018717|F52H2.5.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=509|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018717|F52H2.5.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018718|F52H2.6|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018718|F52H2.6|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018718|F52H2.6|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018718|F52H2.6|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018718|F52H2.6|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018718|F52H2.6|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018718|F52H2.6|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018719|F52H2.7|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018719|F52H2.7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=977|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018719|F52H2.7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018720|F53A3.1|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018720|F53A3.1|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018720|F53A3.1|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018720|F53A3.1|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=311|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018720|F53A3.1|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018720|F53A3.1|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018721|polh-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018721|polh-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018721|polh-1|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1497|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018721|polh-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018723|F53A3.7.2|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018723|F53A3.7.2|13nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018723|F53A3.7.2|15nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018723|F53A3.7.2|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=782|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018723|F53A3.7.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018723|F53A3.7.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018724|F53A9.1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018724|F53A9.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018724|F53A9.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018724|F53A9.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018724|F53A9.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018724|F53A9.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2968|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018724|F53A9.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018725|kreg-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018725|kreg-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018725|kreg-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018725|kreg-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00018725|kreg-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018725|kreg-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018725|kreg-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018726|F53A9.3|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018726|F53A9.3|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018726|F53A9.3|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018727|jbts-14|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018727|jbts-14|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018727|jbts-14|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00018727|jbts-14|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018727|jbts-14|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00018727|jbts-14|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|523nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|525nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018728|frpr-8|550nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018729|F53A9.6|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018729|F53A9.6|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018729|F53A9.6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1450|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00018729|F53A9.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|1222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=983|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018730|F53A9.7|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=423|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7265|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018731|F53A9.8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018732|F53A9.9|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018732|F53A9.9|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018732|F53A9.9|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=699|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018734|F53A10.2a|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018735|F53B1.2|376nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=769|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|512nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018736|F53B1.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1424|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018737|F53B1.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018738|swip-10|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018738|swip-10|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018738|swip-10|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018738|swip-10|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018738|swip-10|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018738|swip-10|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018739|F53B1.8b|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018739|F53B1.8b|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018739|F53B1.8b|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018739|F53B1.8b|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1550|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018739|F53B1.8b|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018739|F53B1.8b|736nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018739|F53B1.8b|739nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018740|tra-4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018740|tra-4|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018740|tra-4|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=650|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018740|tra-4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018740|tra-4|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018741|comt-1|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018741|comt-1|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018742|F53B3.3|457nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|500nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|505nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|507nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|512nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|514nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=648|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018743|F53B3.5|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=464|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=888|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018744|F53B3.6|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018745|F53C3.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018745|F53C3.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018745|F53C3.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018746|fbxb-103|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=853|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018747|F53C3.3|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|1209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|1213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=471|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=809|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1324|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=483|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6506|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|337nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018748|F53C3.4|345nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=160|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|1536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=705|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1281|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1795|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018749|F53C3.5|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1771|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1309|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|253nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018750|F53C3.6a|255nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1058nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018751|F53C3.7|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018752|F53C3.8|1016nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018754|F53C3.11|361nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018755|bcmo-2|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=428|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018755|bcmo-2|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|11nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1716|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|15nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|17nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=815|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1025nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2782|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1035nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1063nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1082nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1096nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|1434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|171nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|174nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=120|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=447|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13b.1|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13c|123nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13c|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13c|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13c|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018756|F53C3.13c|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018757|tag-304|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018757|tag-304|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018757|tag-304|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1259|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00018757|tag-304|1505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018757|tag-304|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018758|F53E10.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018758|F53E10.1|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=335|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018758|F53E10.1|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=494|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018758|F53E10.1|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018758|F53E10.1|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018760|irg-3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018760|irg-3|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018760|irg-3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018760|irg-3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018761|F53E10.5|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018761|F53E10.5|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018762|F53E10.6|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018762|F53E10.6|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1204|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018762|F53E10.6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|286nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018763|F53F10.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16517|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018764|F53F10.2a.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3564|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3578|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018765|F53F10.3.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018766|F53G2.1|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018767|F53G2.2|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018767|F53G2.2|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018769|mnat-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018769|mnat-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2465|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018769|mnat-1|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=942|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018772|F53G12.4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018772|F53G12.4|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00018772|F53G12.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00018773|F53G12.8|24nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=342|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018773|F53G12.8|27nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=405|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018773|F53G12.8|30nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018773|F53G12.8|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018774|F53G12.9b|1020nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018774|F53G12.9b|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018774|F53G12.9b|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=838|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2051|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=493|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|1329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|1425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|1482nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|1577nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=337|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018776|F53H1.1e|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018777|F53H1.3a|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1033|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|385nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2037|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|597nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018778|F53H1.4a|607nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018779|F53H8.3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018779|F53H8.3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018779|F53H8.3|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018779|F53H8.3|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=249|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018779|F53H8.3|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1530|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018781|F54A3.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|1013nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|964nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6587|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018782|cct-3|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018783|cbs-2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018783|cbs-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018783|cbs-2|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018783|cbs-2|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018783|cbs-2|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1106|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6406|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6929|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1763|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018784|F54A3.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018785|F54A3.6|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018785|F54A3.6|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018785|F54A3.6|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018785|F54A3.6|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018785|F54A3.6|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1493|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018785|F54A3.6|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=493|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018786|hmbx-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018786|hmbx-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018786|hmbx-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018786|hmbx-1|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018786|hmbx-1|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00018787|cutl-20|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00018787|cutl-20|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=691|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018787|cutl-20|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=417|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018787|cutl-20|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018788|shc-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018788|shc-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018788|shc-1|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018788|shc-1|585nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018788|shc-1|587nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018788|shc-1|592nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4408|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00018788|shc-1|595nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018789|F54C1.1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018789|F54C1.1|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018789|F54C1.1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018789|F54C1.1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018791|F54C1.6|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018791|F54C1.6|808nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018791|F54C1.6|834nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018792|F54C1.8|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018792|F54C1.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018792|F54C1.8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00018793|mrpl-40|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018793|mrpl-40|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018793|mrpl-40|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2602|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018793|mrpl-40|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018794|attf-3|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018794|attf-3|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1052|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018794|attf-3|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018794|attf-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018795|F54C4.4|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4923|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00018795|F54C4.4|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018795|F54C4.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018795|F54C4.4|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018795|F54C4.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6394|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018797|F54D7.2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018798|gnrr-1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018798|gnrr-1|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=491|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018798|gnrr-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018802|F54D8.6|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1003|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018802|F54D8.6|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018802|F54D8.6|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018802|F54D8.6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018802|F54D8.6|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=811|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=428|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6121|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=538|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|90nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018803|fbxa-24|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=314|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018804|F54D10.3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018805|F54D10.4.2|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018805|F54D10.4.2|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018805|F54D10.4.2|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00018805|F54D10.4.2|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=245|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|139nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=295|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|148nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=60|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018806|F54D10.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018808|F54D10.7|71nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=552|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018809|F54D10.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018811|pmt-2|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018811|pmt-2|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31475|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018811|pmt-2|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=424|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018811|pmt-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|938nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|941nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=821|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|943nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3123|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|950nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|957nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=396|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=573|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|970nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018812|sumv-2|973nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018813|F54D11.3|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018813|F54D11.3|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018813|F54D11.3|622nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00018813|F54D11.3|624nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018813|F54D11.3|724nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|455nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018814|F54D11.4|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018819|rog-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018819|rog-1|937nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018819|rog-1|944nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1763|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018819|rog-1|946nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018819|rog-1|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018821|F54D12.8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018822|F54D12.9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5687|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=253|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018823|F54E2.1|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018824|F54E2.2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018824|F54E2.2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|1545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018825|F54E2.5|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2036|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=883|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018827|pst-2|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018828|sdz-21|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018828|sdz-21|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(76.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018828|sdz-21|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018829|F54E7.6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018829|F54E7.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=477|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1382|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018830|ska-3|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=258|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|24nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=215|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|39nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=291|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=565|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=371|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018831|F54E7.9|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018833|ztf-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=733|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018833|ztf-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1025|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018833|ztf-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018833|ztf-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018834|F54F2.6|396nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018834|F54F2.6|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018834|F54F2.6|839nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018834|F54F2.6|849nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018834|F54F2.6|851nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018835|F54F2.7|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=508|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018835|F54F2.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018835|F54F2.7|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018835|F54F2.7|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018835|F54F2.7|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018835|F54F2.7|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018836|F54F2.9|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018836|F54F2.9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018836|F54F2.9|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018836|F54F2.9|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018836|F54F2.9|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018836|F54F2.9|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|466nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|478nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6609|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|481nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|70nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|81nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=70|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018837|F54G2.1c|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018838|F54G2.2|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018838|F54G2.2|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018838|F54G2.2|689nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=639|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018838|F54G2.2|691nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1466|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018838|F54G2.2|835nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018839|F54H5.2a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018839|F54H5.2a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00018839|F54H5.2a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00018840|F54H5.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018840|F54H5.3|46nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018840|F54H5.3|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018840|F54H5.3|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018841|F54H5.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=841|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|541nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|767nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018842|F54H12.2|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018845|F54H12.5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018845|F54H12.5|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018845|F54H12.5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|1597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2412|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1427|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45345|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105517|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018846|eef-1B.1|97nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1073nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1214nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1217nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1330nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|504nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=340|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|508nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=486|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|528nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|536nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|538nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|543nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1252|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018847|marc-6|547nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018848|F55A3.2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=576|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018848|F55A3.2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018848|F55A3.2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=298|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4422|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1565|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018849|F55A3.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018850|gpx-8|1054nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018850|gpx-8|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018850|gpx-8|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018850|gpx-8|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018852|F55A3.7|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018852|F55A3.7|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018852|F55A3.7|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=463|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|423nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018853|sec-22|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|318nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|329nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|336nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|417nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|421nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|423nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3266|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|427nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1949|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|860nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018854|nlf-1|946nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018855|F55A4.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=750|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|1069nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|465nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1890|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018857|stau-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018859|F55A4.7|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018859|F55A4.7|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018859|F55A4.7|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018859|F55A4.7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018860|F55A4.8c|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018860|F55A4.8c|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018860|F55A4.8c|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=638|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018860|F55A4.8c|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018860|F55A4.8c|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018860|F55A4.8c|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018861|cutl-21|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|164nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|166nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2175|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=484|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|178nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018862|wago-2|803nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018863|F55A12.2c|173nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018863|F55A12.2c|717nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018863|F55A12.2c|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018863|F55A12.2c|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00018863|F55A12.2c|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=933|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1784|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=528|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018864|F55A12.5|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=862|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018865|F55A12.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018865|F55A12.6|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018865|F55A12.6|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018865|F55A12.6|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=181|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1216|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1208|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|185nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018866|nath-10|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018867|F55A12.10|1463nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018867|F55A12.10|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018867|F55A12.10|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018867|F55A12.10|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=857|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018867|F55A12.10|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018868|F55C7.2|302nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|1040nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|426nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|429nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=158|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4265|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018869|rfip-1|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018870|F55C12.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018870|F55C12.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1304|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1699|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018871|F55C12.4|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2266|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=492|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1875|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5a|430nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5c|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5c|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5c|772nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5c|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018872|F55C12.5c|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018873|F55C12.6|331nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018873|F55C12.6|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018873|F55C12.6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018873|F55C12.6|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018873|F55C12.6|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018873|F55C12.6|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018873|F55C12.6|68nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|204nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1206|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018874|tag-234|613nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018875|F55D1.1|1403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=426|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1096|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=813|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018877|aman-1|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39115|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018878|glit-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018878|glit-1|223nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=424|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018878|glit-1|226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018878|glit-1|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=853|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|819nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|826nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|834nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018879|F55D10.4|843nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018880|acc-3|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018880|acc-3|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018880|acc-3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018881|F55E10.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018881|F55E10.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018882|F55E10.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018882|F55E10.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018883|F55E10.4|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018884|F55E10.5|1186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018884|F55E10.5|1190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00018884|F55E10.5|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018885|drd-5|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018885|drd-5|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1790|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018885|drd-5|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018885|drd-5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018885|drd-5|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018885|drd-5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018885|drd-5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018886|npr-28|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018886|npr-28|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018886|npr-28|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018886|npr-28|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00018886|npr-28|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018886|npr-28|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018890|F55F8.2b|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018890|F55F8.2b|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1713|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018890|F55F8.2b|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018890|F55F8.2b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018890|F55F8.2b|142nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018890|F55F8.2b|152nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018890|F55F8.2b|156nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018891|F55F8.3|205nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1095|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018891|F55F8.3|213nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=287|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018891|F55F8.3|652nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018891|F55F8.3|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018891|F55F8.3|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018891|F55F8.3|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018891|F55F8.3|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|1420nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1017|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1145|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018892|cir-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|1028nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|1048nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2091|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|1180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|1547nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018893|wdr-12|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|1360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|1368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|1397nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=518|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2682|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018894|mff-2|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018895|F55F8.7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018895|F55F8.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018895|F55F8.7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018896|F55F8.8|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018897|F55F8.9a|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018897|F55F8.9a|501nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018897|F55F8.9a|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018897|F55F8.9a|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018897|F55F8.9a|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1956|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018897|F55F8.9a|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018897|F55F8.9a|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018898|F55F10.1b|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018898|F55F10.1b|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018898|F55F10.1b|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2189|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018898|F55F10.1b|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018898|F55F10.1b|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018898|F55F10.1b|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018899|F55G1.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018899|F55G1.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018899|F55G1.1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018899|F55G1.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3093|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1422|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018900|rod-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018901|F55G1.5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018901|F55G1.5|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=715|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018901|F55G1.5|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018902|F55G1.6|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018902|F55G1.6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018902|F55G1.6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2487|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018902|F55G1.6|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018902|F55G1.6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018902|F55G1.6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018902|F55G1.6|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018903|F55G1.7b|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018903|F55G1.7b|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018903|F55G1.7b|216nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=252|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00018904|F55G1.9|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018904|F55G1.9|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018904|F55G1.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018904|F55G1.9|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018904|F55G1.9|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018904|F55G1.9|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=618|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018906|egas-4|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018906|egas-4|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=213|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018906|egas-4|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018907|F55G1.15|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018907|F55G1.15|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018908|fncm-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018908|fncm-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=709|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018908|fncm-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018908|fncm-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018908|fncm-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018909|slx-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018909|slx-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1925|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4134|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|955nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1889|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|959nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|961nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018911|F56A4.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018912|F56A4.4|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018913|F56A4.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00018913|F56A4.5|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00018914|F56A4.6|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018914|F56A4.6|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018915|str-267|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018915|str-267|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018915|str-267|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018915|str-267|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018915|str-267|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018917|irld-35|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018917|irld-35|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018917|irld-35|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018918|F56A4.10|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018918|F56A4.10|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=416|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00018918|F56A4.10|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018918|F56A4.10|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018920|F56A4.12|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018920|F56A4.12|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018921|sago-2|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018921|sago-2|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018921|sago-2|150nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2134|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018921|sago-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018923|eme-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018923|eme-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1104|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018923|eme-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018923|eme-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018924|F56A11.4b|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018924|F56A11.4b|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=499|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018925|F56A11.5a|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3642|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018925|F56A11.5a|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018925|F56A11.5a|624nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018925|F56A11.5a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018925|F56A11.5a|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018926|F56A11.6|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018926|F56A11.6|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=441|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018926|F56A11.6|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018926|F56A11.6|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018926|F56A11.6|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018926|F56A11.6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018928|F56B3.2|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=876|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018928|F56B3.2|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018928|F56B3.2|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018929|F56B3.3|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018929|F56B3.3|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018929|F56B3.3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018929|F56B3.3|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018929|F56B3.3|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018930|F56B3.6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018931|ugt-52|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00018931|ugt-52|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018931|ugt-52|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018931|ugt-52|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018932|mrpl-2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1826|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018932|mrpl-2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018932|mrpl-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018934|F56B3.11a|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018934|F56B3.11a|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018934|F56B3.11a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018934|F56B3.11a|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2158|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018934|F56B3.11a|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018934|F56B3.11a|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018935|skr-18|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3785|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018935|skr-18|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018937|F56B6.6|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018937|F56B6.6|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018937|F56B6.6|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018940|F56C3.3|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018941|F56C3.4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018941|F56C3.4|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018941|F56C3.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00018943|dgn-2|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018945|F56C3.8|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018945|F56C3.8|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018945|F56C3.8|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018946|F56C3.9|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018946|F56C3.9|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1786|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|303nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=277|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018948|F56C9.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018949|acbp-4|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018949|acbp-4|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018949|acbp-4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018949|acbp-4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018949|acbp-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018949|acbp-4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018950|F56C9.6a|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018950|F56C9.6a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00018950|F56C9.6a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018950|F56C9.6a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018950|F56C9.6a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3382|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018950|F56C9.6a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018951|F56C9.7.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018951|F56C9.7.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018951|F56C9.7.1|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018951|F56C9.7.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6174|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018951|F56C9.7.1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=709|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018951|F56C9.7.1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=324|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018952|F56C9.8|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018952|F56C9.8|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018952|F56C9.8|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018952|F56C9.8|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018952|F56C9.8|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|503nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|508nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5721|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|513nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018953|F56C9.10b|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018954|F56C9.11|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018954|F56C9.11|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2814|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018954|F56C9.11|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018954|F56C9.11|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018954|F56C9.11|903nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018954|F56C9.11|99nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018955|F56C11.3|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018955|F56C11.3|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018955|F56C11.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018955|F56C11.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=651|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018955|F56C11.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1014|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018957|F56C11.5a|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018958|F56C11.6a|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018958|F56C11.6a|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018958|F56C11.6a|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=741|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018958|F56C11.6a|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018958|F56C11.6a|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018959|F56D1.1|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1379|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018959|F56D1.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018959|F56D1.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018960|F56D1.2|1603nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018960|F56D1.2|312nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1531|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018960|F56D1.2|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018960|F56D1.2|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018960|F56D1.2|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018960|F56D1.2|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018961|mrps-16|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018961|mrps-16|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2450|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018961|mrps-16|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00018961|mrps-16|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018961|mrps-16|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|1199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=635|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1001|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2690|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8719|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=563|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=844|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018963|ucr-1|921nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018964|F56D2.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018964|F56D2.2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018964|F56D2.2|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018964|F56D2.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018964|F56D2.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018964|F56D2.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018965|F56D2.3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018965|F56D2.3|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018965|F56D2.3|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=828|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018965|F56D2.3|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018965|F56D2.3|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018965|F56D2.3|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018965|F56D2.3|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|1089nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|1091nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=364|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1132|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018966|F56D2.5|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3577|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=740|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1409|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018967|ddx-15|239nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018968|F56D2.8|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018968|F56D2.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018968|F56D2.8|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=802|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018968|F56D2.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018969|F56D3.1.2|282nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018969|F56D3.1.2|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1393|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018969|F56D3.1.2|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018969|F56D3.1.2|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018970|clec-68|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018970|clec-68|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|624nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|627nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=283|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1003|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018971|clec-67|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018972|srz-19|556nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018973|srz-20|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=451|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|1129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3218|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018974|fcho-1|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018975|F56E10.1b|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018975|F56E10.1b|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3430|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018976|daam-1|1066nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018976|daam-1|1077nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=219|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018978|ttr-58|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018978|ttr-58|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018980|F56F4.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018980|F56F4.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00018980|F56F4.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018981|F56F4.4|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018981|F56F4.4|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018981|F56F4.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018984|F56F10.1.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=608|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018984|F56F10.1.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018984|F56F10.1.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018984|F56F10.1.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2098|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018984|F56F10.1.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=779|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2489|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7070|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|328nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00018985|F56F10.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018986|cdo-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018986|cdo-1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=240|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018986|cdo-1|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2772|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018986|cdo-1|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018986|cdo-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018986|cdo-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=555|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018987|lgl-1|993nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018988|F56F11.1|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=438|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018989|F56F11.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00018990|klf-1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018990|klf-1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018991|F56F11.4b|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00018991|F56F11.4b|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018991|F56F11.4b|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=213|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018991|F56F11.4b|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=578|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018991|F56F11.4b|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=400|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018991|F56F11.4b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018993|nhr-266|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018993|nhr-266|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018993|nhr-266|1358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018993|nhr-266|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018993|nhr-266|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018993|nhr-266|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018994|F56H1.3|1288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00018994|F56H1.3|1300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00018994|F56H1.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00018995|ccpp-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018995|ccpp-1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1331|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018995|ccpp-1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1581|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=597|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=924|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018996|F57B9.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00018997|F57B9.3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018997|F57B9.3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018997|F57B9.3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|280nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2125|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|284nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|286nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018998|flap-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018999|F57B9.8|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00018999|F57B9.8|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00018999|F57B9.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00018999|F57B9.8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10500|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5375|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019001|ipgm-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019002|F57B10.4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019002|F57B10.4|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1761|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019002|F57B10.4|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019002|F57B10.4|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=652|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4258|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1701|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|1561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|1564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=319|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=719|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019003|F57B10.5|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|1235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=831|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019004|xpg-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=579|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019005|F57B10.8|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1846|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13338|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|478nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019006|F57B10.9|773nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30072|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|1594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|771nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|777nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|795nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019007|F57B10.14|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=610|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|168nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|170nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|174nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|178nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|180nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=347|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019008|F57C9.1b|187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1023|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019009|clec-90|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4a|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4a|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1128|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4b|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4b|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=859|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019011|F57C9.4b|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019012|F57C9.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=512|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019012|F57C9.6|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019012|F57C9.6|781nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019012|F57C9.6|784nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019012|F57C9.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019012|F57C9.6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019012|F57C9.6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019013|tofu-4|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019013|tofu-4|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019014|F57C12.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019014|F57C12.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019015|F57F4.1|73nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019015|F57F4.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019015|F57F4.1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=513|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1827|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15644|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019017|F57F4.4|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|1077nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|1080nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=921|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|327nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1717|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019018|abts-3|830nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=451|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019019|frpr-10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019020|F57H12.5a|1258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019020|F57H12.5a|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019020|F57H12.5a|1316nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019020|F57H12.5a|1319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019020|F57H12.5a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019020|F57H12.5a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1640|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2675|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019021|F57H12.6|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019022|F58A6.1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019022|F58A6.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019022|F58A6.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019022|F58A6.1|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019022|F58A6.1|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=581|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019022|F58A6.1|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019022|F58A6.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019023|F58A6.2|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019023|F58A6.2|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=846|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019024|F58A6.5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019024|F58A6.5|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019024|F58A6.5|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019025|srb-16|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019025|srb-16|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019027|srb-12|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019027|srb-12|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019027|srb-12|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=357|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019027|srb-12|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019027|srb-12|345nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019027|srb-12|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019027|srb-12|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019028|srb-13|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019029|F58B6.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019030|exc-6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019030|exc-6|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=855|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019032|srsx-17|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019032|srsx-17|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019032|srsx-17|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019032|srsx-17|1329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019032|srsx-17|1602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019032|srsx-17|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019034|fbxb-25|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019034|fbxb-25|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019035|fbxb-26|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019035|fbxb-26|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00019035|fbxb-26|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019037|fbxb-17|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019037|fbxb-17|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019038|irld-37|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019039|fbxb-18|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019040|fbxb-19|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019040|fbxb-19|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019041|fbxc-22|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019042|fbxc-21|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019043|fbxc-26|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019044|F58E1.13|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019045|fbxb-47|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019045|fbxb-47|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019046|F58E2.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019047|F58E2.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019047|F58E2.3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019047|F58E2.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019047|F58E2.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019047|F58E2.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019048|F58E2.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019048|F58E2.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019048|F58E2.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019048|F58E2.4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019048|F58E2.4|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019048|F58E2.4|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019048|F58E2.4|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019049|F58E2.5|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019049|F58E2.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019051|srz-23|1220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019051|srz-23|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019054|F58F6.6|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019054|F58F6.6|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|1169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|1189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10423|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=566|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|898nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|905nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019055|F58F9.1a|975nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019057|F58F9.3b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019058|F58F9.4|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019058|F58F9.4|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019058|F58F9.4|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00019058|F58F9.4|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019059|F58F9.6b|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019060|F58F9.7.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=851|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019060|F58F9.7.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019060|F58F9.7.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019060|F58F9.7.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019060|F58F9.7.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=587|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019060|F58F9.7.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019060|F58F9.7.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19814|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1713|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7335|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019061|F58F12.1|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|59nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=820|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019062|F58F12.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019063|F58F12.3|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019063|F58F12.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019064|myo-5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019064|myo-5|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019064|myo-5|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1916|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019064|myo-5|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019065|F58G4.3|855nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019066|sdz-23|1434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019066|sdz-23|1438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019066|sdz-23|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019067|F58H7.1|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019067|F58H7.1|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019067|F58H7.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019067|F58H7.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019067|F58H7.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019067|F58H7.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019068|faah-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019068|faah-3|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=868|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019068|faah-3|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019068|faah-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019069|lgc-30|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019069|lgc-30|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019069|lgc-30|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019069|lgc-30|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019069|lgc-30|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019070|F58H7.5|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019070|F58H7.5|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019072|fbxc-8|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019074|cpd-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019074|cpd-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019074|cpd-1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019074|cpd-1|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019074|cpd-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019075|F59A3.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=793|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019075|F59A3.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1783|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019076|mrpl-24|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019077|F59A3.4|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5454|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|1021nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|982nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|987nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6588|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019079|rpa-4|991nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019080|F59A3.7|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019080|F59A3.7|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019080|F59A3.7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019081|F59A3.8|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019081|F59A3.8|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019082|pup-3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019082|pup-3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019084|F59A6.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2624|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00019084|F59A6.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019086|F59A6.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019086|F59A6.4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019086|F59A6.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019087|F59A6.5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019087|F59A6.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019087|F59A6.5|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019087|F59A6.5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019087|F59A6.5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1318|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019087|F59A6.5|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019087|F59A6.5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019089|clec-206|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019090|F59A7.2|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019090|F59A7.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019090|F59A7.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019090|F59A7.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=661|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019090|F59A7.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019090|F59A7.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|291nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=498|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=495|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019092|F59A7.5c|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019094|F59A7.7|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019094|F59A7.7|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019094|F59A7.7|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019094|F59A7.7|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019094|F59A7.7|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019096|cysl-4|1466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019096|cysl-4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019096|cysl-4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019096|cysl-4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019096|cysl-4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019096|cysl-4|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00019096|cysl-4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3518|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1699|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019097|F59B1.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019098|F59B1.4|657nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019098|F59B1.4|660nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019100|F59B1.8|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019101|F59B1.10|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019101|F59B1.10|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019101|F59B1.10|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=282|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019102|F59C12.3|339nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019103|F59D6.1|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019103|F59D6.1|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=423|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019103|F59D6.1|168nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019103|F59D6.1|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019103|F59D6.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019103|F59D6.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019103|F59D6.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019104|asp-7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019105|asp-8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019105|asp-8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019105|asp-8|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|16nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=302|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|21nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|26nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019106|irld-38|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019107|irld-10|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019107|irld-10|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019108|chpf-2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019108|chpf-2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00019108|chpf-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019109|F59E11.2|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019109|F59E11.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019109|F59E11.2|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=149|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019109|F59E11.2|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019111|F59E11.5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019111|F59E11.5|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019111|F59E11.5|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019111|F59E11.5|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019111|F59E11.5|216nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=623|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019112|F59E11.6|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019112|F59E11.6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019112|F59E11.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019113|F59E11.7a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2532|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019114|nhr-194|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019114|nhr-194|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019114|nhr-194|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019115|nhr-195|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019115|nhr-195|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019115|nhr-195|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019116|nhr-143|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019116|nhr-143|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019116|nhr-143|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019116|nhr-143|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=909|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1469|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|507nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=275|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|945nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019118|F59E12.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019119|F59E12.3|899nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|1212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=251|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|1214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=197|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|1217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|696nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3264|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2512|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=364|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019120|npl-4.1|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3332|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2158|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=392|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|264nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019121|npl-4.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019122|F59E12.6b|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019124|F59E12.9|287nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019124|F59E12.9|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019124|F59E12.9|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1545|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019124|F59E12.9|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019124|F59E12.9|414nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019124|F59E12.9|416nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019124|F59E12.9|479nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=887|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|671nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|675nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|711nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|713nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|723nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019125|ddl-1|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2661|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019126|sam-4|331nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6574|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019127|cgt-3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019128|F59G1.4a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019128|F59G1.4a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019128|F59G1.4a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019128|F59G1.4a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1409|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00019128|F59G1.4a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1032|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019129|F59G1.8a|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019130|gbas-1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019130|gbas-1|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=733|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019132|bath-19|1370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019132|bath-19|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00019132|bath-19|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019135|math-32|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019135|math-32|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019135|math-32|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019136|F59H6.5|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019136|F59H6.5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019139|bath-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019139|bath-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019139|bath-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019140|bath-3|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=504|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019141|bath-5|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1084|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2780|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019142|btb-4|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019143|H01M10.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019143|H01M10.1|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019143|H01M10.1|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019143|H01M10.1|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1144|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019144|H01M10.2|1312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019144|H01M10.2|1317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019144|H01M10.2|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019145|H02F09.2|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019146|H02F09.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019146|H02F09.3|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019146|H02F09.3|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019148|H03E18.1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019148|H03E18.1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019148|H03E18.1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019148|H03E18.1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019149|H03E18.2a|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=718|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019149|H03E18.2a|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019149|H03E18.2a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019149|H03E18.2a|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019149|H03E18.2a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019149|H03E18.2a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019149|H03E18.2a|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019150|H04J21.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019150|H04J21.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019150|H04J21.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019150|H04J21.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019151|pck-3|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019151|pck-3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019151|pck-3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019152|nspb-6|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019152|nspb-6|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019152|nspb-6|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019152|nspb-6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3972|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019152|nspb-6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1584|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019152|nspb-6|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019153|H04M03.3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019153|H04M03.3|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=935|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019153|H04M03.3|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019153|H04M03.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019153|H04M03.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019153|H04M03.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019154|glf-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019154|glf-1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019154|glf-1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00019154|glf-1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019155|H04M03.11|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019155|H04M03.11|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019155|H04M03.11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019156|H04M03.12a|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=598|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019156|H04M03.12a|571nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019156|H04M03.12a|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1714|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019156|H04M03.12a|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=928|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019156|H04M03.12a|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1b|1578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1c|1040nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1c|1101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1c|1104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1c|1109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2344|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1c|1112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1c|1115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019157|H05C05.1c|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|1348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2824|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019158|H05C05.2b|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019159|H05C05.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=313|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|256nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=271|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82539|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13368|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2658|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1421|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=385|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019160|H05L03.3.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019162|eif-1.A|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019162|eif-1.A|304nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16711|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019162|eif-1.A|312nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8377|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019162|eif-1.A|460nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019162|eif-1.A|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=590|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5015|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019163|ubxn-6|772nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1675|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019164|H06H21.8a|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019165|mpz-4|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=608|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019165|mpz-4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=652|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00019166|tat-2|600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019167|H06I04.1a|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019167|H06I04.1a|1472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019167|H06I04.1a|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=972|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019167|H06I04.1a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019167|H06I04.1a|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019167|H06I04.1a|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3515|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=307|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3a|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3c|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3c|1266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019168|H06I04.3c|1272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019169|H06I04.5|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019169|H06I04.5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|739nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|743nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=456|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|751nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|779nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|788nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1265|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|792nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|858nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1206|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019170|H06I04.6b|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019171|fipr-29|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019174|H09G03.1|990nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019174|H09G03.1|997nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019177|H10D18.1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019177|H10D18.1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019177|H10D18.1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019177|H10D18.1|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4120|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019177|H10D18.1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019177|H10D18.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019177|H10D18.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019178|scl-12|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00019178|scl-12|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019178|scl-12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019178|scl-12|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019179|scl-13|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019179|scl-13|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=174|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1251|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=681|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3309|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019180|H10D18.5|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019182|H10E21.1b|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019182|H10E21.1b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019182|H10E21.1b|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019183|npr-30|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=285|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019184|H10E21.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|225nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4588|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019185|H10E21.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019187|H11E01.2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019187|H11E01.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6347|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=446|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019188|H11E01.3|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019189|H11L12.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019189|H11L12.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2840|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019189|H11L12.1|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019189|H11L12.1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019190|H12I13.1|1250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019194|H12I13.6|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=219|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019194|H12I13.6|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3313|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3415|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019196|H14A12.3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019197|H14A12.5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019197|H14A12.5|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019197|H14A12.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019197|H14A12.5|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019197|H14A12.5|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019197|H14A12.5|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019197|H14A12.5|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019198|H14E04.1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|1091nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3507|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019199|H14E04.2a|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019200|H14E04.3|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019200|H14E04.3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019200|H14E04.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1979|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019200|H14E04.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019200|H14E04.3|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019202|H14N18.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1512|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=309|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019203|ttr-47|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=316|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|722nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|733nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019204|H14N18.4b|736nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|267nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|514nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|516nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|525nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=465|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5443|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019205|kcc-2|701nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019207|fgt-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11167|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019207|fgt-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019208|lips-14|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019208|lips-14|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|1121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=263|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1081|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|203nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3618|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019209|emc-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1084nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2462|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|1164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|695nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|700nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019211|H18N23.2a|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019212|H19M22.3a|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019212|H19M22.3a|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019213|H20E11.1a|79nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019214|H20E11.2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019214|H20E11.2|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019214|H20E11.2|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019215|H20E11.3b|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019216|H20J04.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=552|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019216|H20J04.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|425nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|432nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2015|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|439nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019217|athp-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019218|madf-3|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=680|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00019218|madf-3|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=358|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019218|madf-3|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019218|madf-3|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019218|madf-3|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019218|madf-3|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019218|madf-3|845nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019219|H20J04.4b|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019219|H20J04.4b|912nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=720|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019220|pfd-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019220|pfd-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019220|pfd-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019220|pfd-2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=796|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019220|pfd-2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9812|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019220|pfd-2|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019220|pfd-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=962|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019221|H20J04.6|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019222|H20J04.7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019224|gnrr-5|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019224|gnrr-5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019224|gnrr-5|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019224|gnrr-5|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019224|gnrr-5|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019224|gnrr-5|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019225|bgal-2|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019225|bgal-2|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019225|bgal-2|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=634|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019225|bgal-2|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=445|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019225|bgal-2|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019225|bgal-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019226|H22K11.3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019226|H22K11.3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019226|H22K11.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019227|sgca-1|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019227|sgca-1|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019227|sgca-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019227|sgca-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019227|sgca-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=684|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=444|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2573|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019228|H23L24.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019229|ipla-5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019229|ipla-5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019229|ipla-5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019230|ttll-11|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019230|ttll-11|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019230|ttll-11|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019230|ttll-11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019230|ttll-11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019231|H23L24.4|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=400|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019231|H23L24.4|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019232|ugt-13|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=814|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00019232|ugt-13|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019232|ugt-13|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019232|ugt-13|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019232|ugt-13|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019232|ugt-13|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019232|ugt-13|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019233|ugt-14|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019234|ugt-8|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019234|ugt-8|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019234|ugt-8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019234|ugt-8|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=278|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019234|ugt-8|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=436|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019234|ugt-8|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019235|H23N18.4|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019236|H23N18.5|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019236|H23N18.5|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019236|H23N18.5|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=857|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019236|H23N18.5|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=692|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019236|H23N18.5|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|345nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|382nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019237|H24G06.1a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019239|H24K24.2a|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019240|H24K24.3a.1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019240|H24K24.3a.1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2550|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019240|H24K24.3a.1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019240|H24K24.3a.1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019240|H24K24.3a.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019240|H24K24.3a.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|329nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|607nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=311|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|610nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|618nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=455|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019241|H24K24.4a.2|623nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019242|srbc-40|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019242|srbc-40|1148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019242|srbc-40|1154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019242|srbc-40|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1104|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019242|srbc-40|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019242|srbc-40|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019243|fbxb-72|1005nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019243|fbxb-72|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019243|fbxb-72|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00019243|fbxb-72|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019243|fbxb-72|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019243|fbxb-72|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|1376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|1383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|1552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=301|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2404|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019245|sacy-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4430|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=886|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|520nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|524nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019246|rpb-5|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019247|syp-4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019247|syp-4|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2525|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019247|syp-4|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019247|syp-4|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019247|syp-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019247|syp-4|96nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019248|H27M09.5|707nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019248|H27M09.5|710nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019248|H27M09.5|712nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019248|H27M09.5|768nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019248|H27M09.5|772nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|1031nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|1037nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=481|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|1088nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|1095nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3261|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019249|H28G03.1c|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019250|H28G03.2a|540nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019250|H28G03.2a|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019250|H28G03.2a|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019250|H28G03.2a|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2716|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019250|H28G03.2a|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019250|H28G03.2a|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019250|H28G03.2a|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019251|H28G03.3|1338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019251|H28G03.3|1458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019251|H28G03.3|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019251|H28G03.3|1541nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019251|H28G03.3|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019253|H31G24.1|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019253|H31G24.1|1438nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019253|H31G24.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019253|H31G24.1|975nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019254|H31G24.3|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019254|H31G24.3|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019254|H31G24.3|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=952|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019254|H31G24.3|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019254|H31G24.3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019255|H32C10.1a.2|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019257|dhhc-13|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019257|dhhc-13|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019257|dhhc-13|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019257|dhhc-13|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019257|dhhc-13|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6856|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|878nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019259|H34C03.2b|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019260|H34I24.1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00019260|H34I24.1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00019261|H34I24.2|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019261|H34I24.2|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=323|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019261|H34I24.2|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1532|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00019261|H34I24.2|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2727|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019261|H34I24.2|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2005|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019261|H34I24.2|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019261|H34I24.2|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019262|dmsr-12|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=519|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019263|H35B03.1|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019264|H35B03.2d|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019264|H35B03.2d|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019264|H35B03.2d|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019264|H35B03.2d|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1330|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019264|H35B03.2d|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019264|H35B03.2d|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019264|H35B03.2d|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019265|H35N09.1|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019265|H35N09.1|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1195|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019265|H35N09.1|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019265|H35N09.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019266|H35N09.2|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019266|H35N09.2|736nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019266|H35N09.2|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019267|H39E20.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019267|H39E20.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019268|H41C03.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019268|H41C03.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019268|H41C03.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019268|H41C03.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019269|H41C03.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=573|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019269|H41C03.2|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019270|H41C03.3.3|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019270|H41C03.3.3|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019270|H41C03.3.3|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019270|H41C03.3.3|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019270|H41C03.3.3|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=421|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00019270|H41C03.3.3|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019272|H42K12.3.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019272|H42K12.3.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019272|H42K12.3.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019272|H42K12.3.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019273|H43E16.1|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019273|H43E16.1|1572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019273|H43E16.1|1589nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019273|H43E16.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019273|H43E16.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=586|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019273|H43E16.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019274|H43I07.1|1384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019274|H43I07.1|1390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=841|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019274|H43I07.1|1403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019274|H43I07.1|603nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019275|rpac-40|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2760|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019275|rpac-40|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019275|rpac-40|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019276|H43I07.3|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019276|H43I07.3|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019276|H43I07.3|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1407|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019276|H43I07.3|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00019276|H43I07.3|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019276|H43I07.3|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019277|sgcb-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019277|sgcb-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019279|K01A2.4a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019279|K01A2.4a|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019279|K01A2.4a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019279|K01A2.4a|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019279|K01A2.4a|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019279|K01A2.4a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019280|K01A2.5a|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019280|K01A2.5a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019280|K01A2.5a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019280|K01A2.5a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=200|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019280|K01A2.5a|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1225|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019281|K01A2.6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019281|K01A2.6|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019281|K01A2.6|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00019281|K01A2.6|626nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=797|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1774|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|827nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1000|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=901|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019282|mps-2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019283|K01A2.9|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019284|K01A2.10b.2|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019284|K01A2.10b.2|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1273|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019284|K01A2.10b.2|522nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=662|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=635|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019285|cbn-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=746|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1406|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019286|K01A12.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019287|K01A12.3|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019287|K01A12.3|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019287|K01A12.3|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019287|K01A12.3|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019288|K02A2.1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019288|K02A2.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019289|kcc-3|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019289|kcc-3|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019289|kcc-3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019290|K02A2.5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019290|K02A2.5|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019290|K02A2.5|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019290|K02A2.5|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019290|K02A2.5|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019290|K02A2.5|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=847|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|1547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|652nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11203|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4088|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019293|K02A6.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=209|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9970|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019294|K02A6.3b.2|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019295|pfkb-1.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019295|pfkb-1.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019295|pfkb-1.2|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019295|pfkb-1.2|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2415|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019295|pfkb-1.2|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019295|pfkb-1.2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=554|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2743|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019296|mcu-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3677|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2238|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019298|K02D7.1a.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019299|snai-1|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019299|snai-1|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00019299|snai-1|588nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019300|swt-1|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019300|swt-1|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=873|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019300|swt-1|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=645|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019300|swt-1|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019300|swt-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1053|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019300|swt-1|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019300|swt-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1b.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1b.2|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1b.2|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1b.2|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1b.2|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7486|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1b.2|260nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1495|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1b.2|263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1c|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1c|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1420|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1c|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019301|K02D10.1c|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019302|K02D10.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019302|K02D10.2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019302|K02D10.2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019303|K02D10.3|563nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|1043nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|1051nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|701nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|708nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|712nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=895|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|716nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|719nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019304|K02D10.4|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11136|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019305|snap-29|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019306|K02E7.1a|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019309|K02E7.4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00019309|K02E7.4|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00019311|K02E7.6.2|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019311|K02E7.6.2|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019313|btb-10|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019313|btb-10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019314|K02E7.10|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11774|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2834|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019315|K02E7.11|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019316|K02E7.12.1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019316|K02E7.12.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019316|K02E7.12.1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|345nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|352nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1862|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|356nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=430|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|360nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|403nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=412|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019317|K02E10.1|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019318|K02E10.4a|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019318|K02E10.4a|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019318|K02E10.4a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019318|K02E10.4a|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019318|K02E10.4a|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019318|K02E10.4a|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019319|K02E10.5|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019319|K02E10.5|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019319|K02E10.5|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=536|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019319|K02E10.5|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00019319|K02E10.5|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00019319|K02E10.5|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|1041nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|1128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|1133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|1517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=619|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=201|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019320|K02E10.6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019321|K02E10.7|170nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019321|K02E10.7|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019321|K02E10.7|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019321|K02E10.7|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=529|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019321|K02E10.7|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019321|K02E10.7|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4887|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5727|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=557|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19077|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55664|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2085|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|362nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019322|ahcy-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|1135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|1141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|1480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|1491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=997|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|1501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|1505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|1508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|278nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|283nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|286nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|288nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|290nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|296nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2216|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019323|teg-4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|1176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1341|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1156|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132378|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|985nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019324|K02F2.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1020nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1069nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3607|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|1400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019326|K02F3.2b|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|1143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|1331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|1333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1489|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29434|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5422|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=519|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|674nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11757|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019327|zip-2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=386|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019328|clec-149|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019328|clec-149|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019328|clec-149|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019328|clec-149|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019328|clec-149|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019328|clec-149|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019328|clec-149|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019329|ceeh-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1077|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00019329|ceeh-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019329|ceeh-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019329|ceeh-1|80nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019331|dos-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=453|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=538|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1953|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=797|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019332|K02F3.9|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6586|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|188nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019333|moma-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019334|K02F3.12a|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2196|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019334|K02F3.12a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=540|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019335|K02F6.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019337|K02F6.3|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019337|K02F6.3|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019339|K02F6.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019339|K02F6.5|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019339|K02F6.5|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019339|K02F6.5|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019339|K02F6.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=692|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019339|K02F6.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=711|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019340|K02F6.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019341|K02F6.7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019341|K02F6.7|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=589|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019342|K02F6.8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019342|K02F6.8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019342|K02F6.8|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019342|K02F6.8|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019342|K02F6.8|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=734|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019342|K02F6.8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=700|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019343|nep-18|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00019343|nep-18|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|177nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=783|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|180nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|633nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019344|dhhc-10|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019345|tmem-135|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019346|K02G10.5b|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019346|K02G10.5b|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=460|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00019346|K02G10.5b|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019346|K02G10.5b|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|1504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|1524nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019347|mbl-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019348|K02H11.4|550nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019348|K02H11.4|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019349|trx-5|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019350|K02H11.9|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019351|lron-7|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019351|lron-7|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3534|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019351|lron-7|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1306|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019351|lron-7|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019351|lron-7|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019351|lron-7|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019351|lron-7|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2123|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019352|K03A1.4b|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019353|K03B4.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019353|K03B4.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019353|K03B4.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1669|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019353|K03B4.1|502nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019353|K03B4.1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=714|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019353|K03B4.1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019353|K03B4.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7569|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019354|K03B4.2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019355|K03B4.4b|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13379|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019355|K03B4.4b|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14124|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019355|K03B4.4b|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019355|K03B4.4b|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019355|K03B4.4b|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019356|K03B4.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019356|K03B4.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019356|K03B4.6|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4529|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=580|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019357|cpg-8|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1703|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019360|neto-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1204|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8045|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019361|K03E5.2a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1490|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019362|cdk-2|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019364|mksr-1|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019364|mksr-1|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019364|mksr-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019364|mksr-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019364|mksr-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019364|mksr-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019364|mksr-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=557|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=575|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019365|K03E6.7|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019367|K03H6.1|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=567|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019368|K03H6.2a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019369|K03H6.4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1390|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019370|K03H6.5b|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=477|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019370|K03H6.5b|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019370|K03H6.5b|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019370|K03H6.5b|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019370|K03H6.5b|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019372|K03H9.3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|19nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019373|K04A8.1.2|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019374|K04A8.2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019374|K04A8.2|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019376|lipl-4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00019376|lipl-4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019376|lipl-4|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019379|K04A8.10|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019379|K04A8.10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019379|K04A8.10|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019379|K04A8.10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2927|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|195nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|205nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019380|K04C2.2|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|1078nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5928|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1252|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019381|K04C2.3a|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019382|K04C2.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019382|K04C2.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019382|K04C2.5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019383|K04E7.1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019386|irld-42|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019387|K04F1.8a|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1042|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019388|K04F1.9b|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019389|irld-40|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019389|irld-40|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019391|irld-11|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019391|irld-11|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019391|irld-11|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019391|irld-11|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019392|irld-44|323nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019392|irld-44|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019393|irld-45|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019393|irld-45|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|1238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|1240nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1160|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019394|K04F10.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019395|K04F10.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=612|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019395|K04F10.2|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019395|K04F10.2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019395|K04F10.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019395|K04F10.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019395|K04F10.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|1595nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6409|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2527|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019396|K04F10.3a|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=278|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=585|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4810|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019399|K04F10.7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1667|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019400|K04G7.1.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1761|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10716|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|322nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=306|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019401|nuo-4|327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019402|K04G7.11|1067nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019402|K04G7.11|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019402|K04G7.11|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019402|K04G7.11|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019402|K04G7.11|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2796|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019402|K04G7.11|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=794|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019403|K05B2.2a|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019404|K05B2.4|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019404|K05B2.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019404|K05B2.4|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019404|K05B2.4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019404|K05B2.4|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019404|K05B2.4|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019405|K05F1.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019405|K05F1.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019406|acdh-8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019406|acdh-8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1631|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019406|acdh-8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019406|acdh-8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019407|K05F1.5|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019407|K05F1.5|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019407|K05F1.5|1130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019407|K05F1.5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=590|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019407|K05F1.5|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|1542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1278|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019408|K05F1.6a.1|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019409|K05F1.8|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019409|K05F1.8|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019409|K05F1.8|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019410|K05F1.9|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019410|K05F1.9|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019410|K05F1.9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019410|K05F1.9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019410|K05F1.9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019411|K05F1.10|1033nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019411|K05F1.10|1043nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=729|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019411|K05F1.10|1047nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=434|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019411|K05F1.10|1049nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019411|K05F1.10|1055nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019411|K05F1.10|979nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019412|fbxb-49|1109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019412|fbxb-49|1132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019412|fbxb-49|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019413|fbxb-50|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019414|fbxb-51|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019415|K05F6.4|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019415|K05F6.4|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019415|K05F6.4|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019415|K05F6.4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019416|fbxb-44|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00019416|fbxb-44|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019416|fbxb-44|910nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019418|fbxb-54|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019418|fbxb-54|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019420|fbxb-46|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019420|fbxb-46|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019421|K05F6.10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019421|K05F6.10|67nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019423|K05G3.2|703nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019424|aptf-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019424|aptf-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1641|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019424|aptf-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00019424|aptf-1|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019424|aptf-1|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019424|aptf-1|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019424|aptf-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019425|K06A1.2a|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019425|K06A1.2a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019426|cutl-16|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019426|cutl-16|320nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019426|cutl-16|326nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019426|cutl-16|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=297|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019427|atg-16.2|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=237|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019428|dgk-5|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019428|dgk-5|335nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=904|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019428|dgk-5|341nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=687|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019428|dgk-5|346nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019428|dgk-5|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019429|K06A5.1b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019429|K06A5.1b|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2218|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019429|K06A5.1b|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=651|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=587|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=658|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|385nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|391nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|408nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=377|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|431nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|65nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019430|K06A5.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019431|K06A5.3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00019431|K06A5.3|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=772|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019431|K06A5.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=987|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=429|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019432|knl-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019433|acdh-3|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4021|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00019433|acdh-3|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=765|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019433|acdh-3|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019433|acdh-3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019433|acdh-3|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019433|acdh-3|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019434|nmtn-1|609nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019434|nmtn-1|613nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019434|nmtn-1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019434|nmtn-1|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2050|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019434|nmtn-1|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019434|nmtn-1|635nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019434|nmtn-1|675nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019435|K06A9.1a|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019435|K06A9.1a|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019435|K06A9.1a|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019435|K06A9.1a|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019435|K06A9.1a|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019435|K06A9.1a|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019436|K06A9.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019436|K06A9.2|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|1311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|381nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=710|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019444|frpr-11|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019445|frpr-12|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019445|frpr-12|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019445|frpr-12|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019445|frpr-12|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019445|frpr-12|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=509|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1602|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019448|frpr-13|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019449|K06H6.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019449|K06H6.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019450|K06H6.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019450|K06H6.2|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019450|K06H6.2|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019451|nstp-7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019451|nstp-7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019453|K06H6.5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019455|K06H7.1|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019455|K06H7.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019455|K06H7.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019455|K06H7.1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|102nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019456|K06H7.2|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|1078nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|1162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|1165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10269|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019457|vms-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=826|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|663nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1151|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019458|K06H7.7|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5454|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019459|K06H7.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019459|K06H7.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019459|K06H7.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019460|idi-1|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019460|idi-1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7431|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019460|idi-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019460|idi-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019460|idi-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019461|K07A3.3b|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019461|K07A3.3b|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=177|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00019461|K07A3.3b|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019461|K07A3.3b|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019462|K07A9.3|988nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019462|K07A9.3|990nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1003|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019464|K07B1.4a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2345|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=369|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|208nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|211nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=128|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|215nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|220nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=372|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|225nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=1122|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=718|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=921|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019465|acl-14|651nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2243|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|1131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|221nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=698|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15968|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26467|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|890nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2670|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|908nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|918nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|921nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019466|tos-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|1383nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2581|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7a|998nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7b|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019467|K07B1.7b|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019470|cyp-35B3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019471|cyp-35B2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019472|cyp-35B1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019472|cyp-35B1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00019472|cyp-35B1|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019473|cyp-35A5|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019473|cyp-35A5|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019473|cyp-35A5|174nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019473|cyp-35A5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019473|cyp-35A5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1270|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|178nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019476|K07C11.3.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=591|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019477|K07C11.4|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019477|K07C11.4|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=619|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019477|K07C11.4|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019477|K07C11.4|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019477|K07C11.4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=961|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019478|cri-2|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=271|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1396|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13201|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|316nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019479|K07C11.7b.2|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|1576nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7221|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=381|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019480|K07C11.8.2|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019481|cogc-6|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019481|cogc-6|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019481|cogc-6|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2740|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019481|cogc-6|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1760|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019481|cogc-6|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019481|cogc-6|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2075|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019482|K07C11.10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019483|K07D4.2|1326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=410|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|343nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019484|K07D4.4|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019485|K07D4.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019485|K07D4.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019485|K07D4.5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019485|K07D4.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019485|K07D4.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00019485|K07D4.5|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019486|K07D4.6|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019486|K07D4.6|946nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019486|K07D4.6|957nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019487|ephx-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019487|ephx-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019487|ephx-1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019487|ephx-1|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=734|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019487|ephx-1|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019487|ephx-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019487|ephx-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12459|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|1251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|1255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|1258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|248nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=851|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019488|K07D4.9.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019489|K07E1.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019489|K07E1.1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019489|K07E1.1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1895|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019489|K07E1.1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019489|K07E1.1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019489|K07E1.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|1182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|827nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|831nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=900|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|836nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|839nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|845nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019490|K07E3.1|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019491|K07E3.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019491|K07E3.2|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019491|K07E3.2|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019491|K07E3.2|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=124|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019491|K07E3.2|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019491|K07E3.2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019491|K07E3.2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1396|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5177|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=619|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3783|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1362|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|158nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|845nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019492|K07E3.4a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|124nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|574nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|577nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|579nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|582nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019493|catp-5|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|162nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|167nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=832|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=474|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2261|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019495|sdz-24|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=365|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019496|frpr-14|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019497|K07E8.6a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019497|K07E8.6a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019497|K07E8.6a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019497|K07E8.6a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019497|K07E8.6a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019498|K07E8.7|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=732|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019501|K07E12.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019501|K07E12.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019501|K07E12.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1733|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019503|tbce-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4625|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019504|K07H8.2b.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019506|K07H8.5|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019506|K07H8.5|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=627|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019506|K07H8.5|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=113|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019507|K07H8.7|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019507|K07H8.7|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1037nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1046nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1092nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1310nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|1585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|330nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=103|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|346nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|688nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|982nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019508|K07H8.8|997nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019509|K07H8.9|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4407|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00019509|K07H8.9|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019509|K07H8.9|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019509|K07H8.9|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=706|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4509|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40186|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=315|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019510|K07H8.10|417nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1380|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019511|K08A2.1.2|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019512|K08A2.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00019512|K08A2.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019512|K08A2.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019512|K08A2.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019512|K08A2.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019513|K08A2.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019514|K08B4.2|1003nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00019514|K08B4.2|1278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019514|K08B4.2|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00019514|K08B4.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00019514|K08B4.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019515|ugt-19|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019515|ugt-19|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019516|ugt-20|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019516|ugt-20|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00019518|K08B5.1|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019518|K08B5.1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019518|K08B5.1|277nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019519|K08B5.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019520|K08B12.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019520|K08B12.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=675|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|635nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|640nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|642nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|722nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|727nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1039|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019521|dmd-7|731nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019522|K08B12.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=325|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00019522|K08B12.3|199nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019522|K08B12.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019522|K08B12.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019524|K08D9.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019524|K08D9.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|1316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019525|K08D9.4|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019526|K08D9.5|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019526|K08D9.5|521nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00019526|K08D9.5|551nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019526|K08D9.5|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019527|K08D9.6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019527|K08D9.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019527|K08D9.6|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019527|K08D9.6|601nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019527|K08D9.6|667nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019529|K08D10.5|740nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00019529|K08D10.5|743nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019529|K08D10.5|745nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019530|scrm-8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019530|scrm-8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019530|scrm-8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019530|scrm-8|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019530|scrm-8|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019531|scrm-5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019533|K08D10.10|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019533|K08D10.10|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019534|K08D10.11|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019534|K08D10.11|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019534|K08D10.11|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019534|K08D10.11|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019534|K08D10.11|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019535|tsen-34|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019535|tsen-34|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00019535|tsen-34|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=584|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019535|tsen-34|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019536|rpi-2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019536|rpi-2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019536|rpi-2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019536|rpi-2|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019536|rpi-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|195nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24118|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=599|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=558|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3b.1|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019537|K08D12.3b.1|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|1053nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1451|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019538|K08D12.4|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=355|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=754|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12249|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2316|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3952|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019540|K08D12.6|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019541|K08F11.1a|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=234|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019541|K08F11.1a|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019541|K08F11.1a|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7279|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=563|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=517|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1079|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|182nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019543|cif-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019544|miro-1|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2436|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019544|miro-1|256nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019544|miro-1|258nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019545|K09B3.1a|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019545|K09B3.1a|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019545|K09B3.1a|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019545|K09B3.1a|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019545|K09B3.1a|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019546|glct-6|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019546|glct-6|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1094|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00019546|glct-6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019546|glct-6|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019546|glct-6|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019546|glct-6|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019547|K09C4.1a|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019547|K09C4.1a|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019547|K09C4.1a|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=165|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019547|K09C4.1a|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019547|K09C4.1a|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019547|K09C4.1a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019547|K09C4.1a|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019548|K09C4.2|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019550|K09C4.5|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00019550|K09C4.5|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019550|K09C4.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019551|K09C4.6|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019551|K09C4.6|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00019551|K09C4.6|160nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019551|K09C4.6|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019551|K09C4.6|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019551|K09C4.6|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00019553|K09C4.9|159nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019553|K09C4.9|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019554|K09C4.10|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019554|K09C4.10|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=690|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019554|K09C4.10|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019554|K09C4.10|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019554|K09C4.10|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019556|K09C6.2e|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019556|K09C6.2e|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019556|K09C6.2e|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019557|K09C6.3a|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019561|K09C6.7a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019561|K09C6.7a|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019562|K09C6.8a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019562|K09C6.8a|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019563|K09C6.9|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019563|K09C6.9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019563|K09C6.9|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019563|K09C6.9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=414|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019563|K09C6.9|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019563|K09C6.9|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019564|K09D9.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019564|K09D9.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019564|K09D9.1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019564|K09D9.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34335|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019564|K09D9.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6691|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019564|K09D9.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1027nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1386nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1392nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1395nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1397nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|1563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|975nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019565|cyp-35A3|977nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019566|K09D9.3|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019566|K09D9.3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019566|K09D9.3|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019566|K09D9.3|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019566|K09D9.3|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019566|K09D9.3|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019566|K09D9.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019567|K09D9.9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019567|K09D9.9|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019567|K09D9.9|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019568|K09D9.11|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019568|K09D9.11|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019570|K09E2.1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00019570|K09E2.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019570|K09E2.1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019570|K09E2.1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019570|K09E2.1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019571|K09E2.2|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019571|K09E2.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1865|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=830|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019572|K09E2.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019576|K09E3.5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019576|K09E3.5|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019576|K09E3.5|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019577|K09E3.6|1031nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019577|K09E3.6|1162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019578|K09E3.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=592|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=212|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019579|oac-57|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019580|oac-58|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019580|oac-58|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019580|oac-58|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019580|oac-58|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019580|oac-58|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019584|set-12|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019584|set-12|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019584|set-12|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019584|set-12|638nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=349|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019584|set-12|647nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019586|K09F6.3|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=277|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019586|K09F6.3|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019587|K09F6.4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019588|K09F6.5|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019588|K09F6.5|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019588|K09F6.5|729nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019588|K09F6.5|828nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019588|K09F6.5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019589|K09F6.6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2715|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019589|K09F6.6|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019589|K09F6.6|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019590|K09F6.7|1160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019590|K09F6.7|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019590|K09F6.7|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019590|K09F6.7|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019591|fbxc-25|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019591|fbxc-25|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019591|fbxc-25|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019591|fbxc-25|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5302|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|826nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019592|K09F6.9|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|1253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1164|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=413|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|631nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1262|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|633nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1837|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|641nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=479|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019593|K09F6.10|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=746|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019595|K09H9.2.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019597|K09H9.5|18nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019597|K09H9.5|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=274|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019597|K09H9.5|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1717|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00019597|K09H9.5|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1292|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019598|K09H9.7|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019599|K09H11.1|1192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019599|K09H11.1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019599|K09H11.1|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019599|K09H11.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019599|K09H11.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=688|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019599|K09H11.1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019599|K09H11.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|491nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|507nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=2693|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00019600|rga-3|512nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=131|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019601|K09H11.4|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00019601|K09H11.4|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019603|K09H11.6|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019603|K09H11.6|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019603|K09H11.6|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019603|K09H11.6|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=764|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019603|K09H11.6|294nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019605|ctsa-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=274|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9363|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=597|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|261nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|442nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|444nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=244|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|448nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|451nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|513nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|516nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019606|clec-88|519nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34361|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=715|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|88nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019607|K10B2.4|90nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|428nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|430nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|432nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1219|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|435nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1931|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|440nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=270|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|442nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|444nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019608|ani-2|508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1b|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1b|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1b|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1b|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1b|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019609|K10B3.1b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1240|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019611|K10B3.5|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019611|K10B3.5|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=767|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019611|K10B3.5|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019611|K10B3.5|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019611|K10B3.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1992|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019612|gpcp-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019614|srt-54|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019615|K10B4.3|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019615|K10B4.3|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=334|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019615|K10B4.3|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019616|nmur-2|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019616|nmur-2|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019616|nmur-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|729nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|776nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2859|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019617|K10C2.1|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019618|K10C2.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019618|K10C2.2|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=839|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7708|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019619|asp-14|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|1345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3497|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5908|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019620|fah-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019622|K10C2.7|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019622|K10C2.7|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00019622|K10C2.7|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019622|K10C2.7|446nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019622|K10C2.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=959|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18042|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1537|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|285nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=191|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|288nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|343nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=236|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=692|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2727|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1269|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=573|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019623|K10C9.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019624|K10C9.3|327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019624|K10C9.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019624|K10C9.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019624|K10C9.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=638|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00019624|K10C9.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019625|K10C9.4a|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019625|K10C9.4a|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019626|K10C9.7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019626|K10C9.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=332|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00019626|K10C9.7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=588|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019626|K10C9.7|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019626|K10C9.7|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019627|K10D2.1a|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1548|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019627|K10D2.1a|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|433nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|451nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|760nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|762nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1255|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|767nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|788nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019628|pup-2|847nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|452nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|455nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2579|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|460nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=644|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019629|cid-1|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019630|emb-1|1096nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019630|emb-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019630|emb-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3190|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019630|emb-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019630|emb-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019631|K10D2.5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6197|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019631|K10D2.5|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=642|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019631|K10D2.5|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019631|K10D2.5|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=360|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00019633|K10D2.7|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=780|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019636|gsto-3|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1088|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019636|gsto-3|704nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019640|dos-2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019640|dos-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019640|dos-2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019641|K10G6.4|1108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019641|K10G6.4|1266nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019641|K10G6.4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019641|K10G6.4|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019641|K10G6.4|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019641|K10G6.4|910nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019641|K10G6.4|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019642|K11C4.1|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019642|K11C4.1|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=639|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019642|K11C4.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019642|K11C4.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019642|K11C4.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019643|K11C4.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019643|K11C4.2|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019643|K11C4.2|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019643|K11C4.2|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019644|cpt-4|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019644|cpt-4|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019645|swt-7|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019645|swt-7|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2705|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019645|swt-7|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019645|swt-7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019645|swt-7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019646|K11D12.6|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00019646|K11D12.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019646|K11D12.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019646|K11D12.6|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00019647|K11D12.7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019647|K11D12.7|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019647|K11D12.7|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1488|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019647|K11D12.7|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019647|K11D12.7|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019647|K11D12.7|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019647|K11D12.7|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019648|K11D12.8|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019648|K11D12.8|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019649|K11D12.9|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019649|K11D12.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019650|K11D12.11|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019650|K11D12.11|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019650|K11D12.11|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019650|K11D12.11|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019650|K11D12.11|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=694|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019651|K11D12.12|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019651|K11D12.12|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019651|K11D12.12|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1124|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019651|K11D12.12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019652|K11G9.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019653|K11G9.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00019653|K11G9.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019653|K11G9.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019654|K11G9.3|1046nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019654|K11G9.3|1085nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019654|K11G9.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019654|K11G9.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019655|K11G9.5|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=423|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00019655|K11G9.5|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019655|K11G9.5|833nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4159|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1011|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|291nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019656|K11G12.5|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019657|K11G12.6a|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019657|K11G12.6a|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1605|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019657|K11G12.6a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00019658|K11H12.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019659|K11H12.3|1210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019659|K11H12.3|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019659|K11H12.3|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019659|K11H12.3|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019659|K11H12.3|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019659|K11H12.3|766nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019660|K11H12.4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=785|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019660|K11H12.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019660|K11H12.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019661|K11H12.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019662|K11H12.6a|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019662|K11H12.6a|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019662|K11H12.6a|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019662|K11H12.6a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019662|K11H12.6a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019662|K11H12.6a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|315nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3348|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019663|K11H12.7|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11281|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8b|1193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8b|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019664|K11H12.8b|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019665|K11H12.9a|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=857|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=743|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019666|sago-1|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019667|K12B6.2|464nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=170|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019667|K12B6.2|476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019668|fil-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1070|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=359|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2962|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019669|K12B6.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019670|K12B6.6|1498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019672|K12B6.8.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019672|K12B6.8.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019672|K12B6.8.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019673|K12C11.1b|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=353|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00019673|K12C11.1b|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019673|K12C11.1b|203nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019673|K12C11.1b|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019673|K12C11.1b|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019673|K12C11.1b|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019673|K12C11.1b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2748|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00019674|K12C11.3b|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019674|K12C11.3b|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00019674|K12C11.3b|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=403|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019674|K12C11.3b|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019674|K12C11.3b|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019675|K12D9.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019675|K12D9.1|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00019675|K12D9.1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019675|K12D9.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019676|irld-46|1326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00019676|irld-46|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00019677|K12H4.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019677|K12H4.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019677|K12H4.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019677|K12H4.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1282|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019677|K12H4.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019677|K12H4.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019677|K12H4.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019678|K12H4.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019678|K12H4.3|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019678|K12H4.3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4728|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019678|K12H4.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019678|K12H4.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019678|K12H4.3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=654|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12461|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=626|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|732nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019679|K12H4.4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019680|K12H4.5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019680|K12H4.5|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8508|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019680|K12H4.5|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019680|K12H4.5|831nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019680|K12H4.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019681|K12H4.6|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019681|K12H4.6|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019681|K12H4.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7699|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4872|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019682|K12H4.7a|973nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019683|K12H6.2|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019683|K12H6.2|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019683|K12H6.2|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019683|K12H6.2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019684|K12H6.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019685|K12H6.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2908|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019686|K12H6.6b|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019687|K12H6.7|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019688|K12H6.8|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019688|K12H6.8|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019689|K12H6.9|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019689|K12H6.9|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019690|set-13|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019691|K12H6.12|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019691|K12H6.12|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019691|K12H6.12|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019692|M01A10.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019692|M01A10.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1438|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019692|M01A10.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=859|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4885|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3261|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019693|ostd-1|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019697|M01B12.4c|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019697|M01B12.4c|1022nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019697|M01B12.4c|1264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019697|M01B12.4c|1267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2727|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019697|M01B12.4c|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019697|M01B12.4c|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019697|M01B12.4c|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019699|math-34|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019700|btb-11|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019700|btb-11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019703|fbxb-41|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019703|fbxb-41|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019703|fbxb-41|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019703|fbxb-41|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019704|fbxb-40|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019704|fbxb-40|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019704|fbxb-40|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019705|fbxb-45|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019705|fbxb-45|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1727|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=357|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019710|M01E11.1|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1206|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=861|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=579|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019711|M01E11.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019712|M01E11.3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019712|M01E11.3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019712|M01E11.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019712|M01E11.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1196|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27318|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019713|pqn-52|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|732nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|775nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|784nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019715|M01G5.1|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=615|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=289|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019716|M01G5.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019717|trx-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019717|trx-3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019717|trx-3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019717|trx-3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019717|trx-3|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=315|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019717|trx-3|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019717|trx-3|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019718|M01H9.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019718|M01H9.2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019718|M01H9.2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|1230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|280nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=811|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=586|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1172|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3029|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24320|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|666nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019719|M01H9.3d.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019720|M01H9.4g|226nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019720|M01H9.4g|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00019720|M01H9.4g|233nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019720|M01H9.4g|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019720|M01H9.4g|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019720|M01H9.4h|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1078|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019721|M01H9.5|1417nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=163|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019721|M01H9.5|1420nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019721|M01H9.5|1505nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019721|M01H9.5|1509nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019721|M01H9.5|1515nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019721|M01H9.5|1527nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019722|M02A10.1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019722|M02A10.1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=405|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019723|fbxc-47|1212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019723|fbxc-47|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=567|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019723|fbxc-47|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019723|fbxc-47|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019723|fbxc-47|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019724|M02B7.2a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019724|M02B7.2a|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019724|M02B7.2a|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019724|M02B7.2a|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=644|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019724|M02B7.2a|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1622|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019724|M02B7.2a|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019724|M02B7.2a|75nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=318|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=372|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|1499nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019725|algn-14|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019726|bris-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019726|bris-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019726|bris-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019726|bris-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019726|bris-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1893|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019726|bris-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=228|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019726|bris-1|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=756|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2087|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4166|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=685|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1102|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|23nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|245nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=485|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019727|M02D8.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019728|M02D8.2|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019728|M02D8.2|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019728|M02D8.2|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019728|M02D8.2|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019728|M02D8.2|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019728|M02D8.2|598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019728|M02D8.2|609nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019729|M02D8.3|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019729|M02D8.3|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019729|M02D8.3|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019730|asns-2|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019730|asns-2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3722|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019730|asns-2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019730|asns-2|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019730|asns-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019731|M02D8.5|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019731|M02D8.5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019731|M02D8.5|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00019731|M02D8.5|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019731|M02D8.5|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019731|M02D8.5|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=960|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1880|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11293|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=737|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=335|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3538|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=900|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2764|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|466nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|468nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=261|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|679nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|750nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=224|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|86nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=753|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|92nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=819|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019732|M02D8.6|996nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|726nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|738nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|743nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|750nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|910nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=949|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|939nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|943nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|948nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019733|M02E1.1a|950nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=490761|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6304|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=543|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=259|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|769nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|771nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=647|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019734|M02E1.2|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019735|M02F4.1|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019736|M02F4.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019736|M02F4.2|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019736|M02F4.2|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1369|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|458nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|503nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=617|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019737|M02F4.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=473|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2322|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019738|clec-265|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019741|nhr-201|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019741|nhr-201|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019741|nhr-201|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019741|nhr-201|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019741|nhr-201|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019741|nhr-201|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019742|nhr-202|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019743|nhr-203|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019743|nhr-203|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019743|nhr-203|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019743|nhr-203|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019743|nhr-203|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019744|M02H5.8b.2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019744|M02H5.8b.2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019744|M02H5.8b.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019744|M02H5.8b.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019744|M02H5.8b.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3959|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019744|M02H5.8b.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019746|M03A1.3|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019746|M03A1.3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=600|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019746|M03A1.3|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|419nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|421nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|489nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|492nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|498nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|502nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1906|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|629nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019747|ipla-1|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019748|atg-2|518nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2316|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019748|atg-2|526nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019748|atg-2|530nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|294nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|297nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1156|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|304nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=615|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019749|M03A8.3|508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|123nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|419nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2625|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019750|M03D4.3|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019751|M03D4.4b|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019751|M03D4.4b|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019751|M03D4.4b|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019753|M03E7.1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019753|M03E7.1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2156|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019753|M03E7.1|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019753|M03E7.1|1183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019753|M03E7.1|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019753|M03E7.1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019753|M03E7.1|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019754|M03E7.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019754|M03E7.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019754|M03E7.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1274|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019755|M03E7.3|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019755|M03E7.3|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019756|M03E7.4|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019756|M03E7.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019756|M03E7.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019756|M03E7.4|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019756|M03E7.4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|1022nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|1501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|1506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4803|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1216|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|52nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019757|memb-2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|144nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|148nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|182nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|437nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5934|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1303|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|524nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|526nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|537nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019759|M03F4.6|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=624|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11957|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|740nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019760|calu-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=756|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019761|M03F8.1|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019761|M03F8.1|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019761|M03F8.1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019761|M03F8.1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019761|M03F8.1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019761|M03F8.1|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019762|M03F8.3a|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019762|M03F8.3a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2606|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019762|M03F8.3a|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019762|M03F8.3a|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019762|M03F8.3a|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019762|M03F8.3a|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019762|M03F8.3a|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019763|galt-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1886|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00019763|galt-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019764|M03F8.5|1337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019764|M03F8.5|1340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019764|M03F8.5|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=607|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=328|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019765|M03F8.6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|726nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|729nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|732nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|868nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1722|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|872nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=202|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019766|M4.1a|874nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019767|rpa-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019767|rpa-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019767|rpa-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019767|rpa-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6581|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019767|rpa-2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019768|M04F3.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=478|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019768|M04F3.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019768|M04F3.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019768|M04F3.2|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019768|M04F3.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019769|M04F3.3|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019769|M04F3.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1531|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5430|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14670|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=780|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019770|M04F3.4b|853nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|1179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|232nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|244nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1881|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019771|M04F3.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=322|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019772|M04G7.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019773|M04G7.2a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00019773|M04G7.2a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00019774|M04G7.3b|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1355|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019774|M04G7.3b|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019774|M04G7.3b|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019774|M04G7.3b|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019774|M04G7.3b|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019776|M6.4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019776|M6.4|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019776|M6.4|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=658|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019776|M6.4|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019776|M6.4|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019776|M6.4|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019776|M6.4|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019777|M57.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019777|M57.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019777|M57.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=435|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019778|M57.2a.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019778|M57.2a.2|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4679|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019778|M57.2a.2|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019778|M57.2a.2|294nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019778|M57.2a.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019778|M57.2a.2|765nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1491|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1255|total_reads(33.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=591|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019779|M60.2.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|1046nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7107|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019780|M60.4b.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|285nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|290nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|293nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3248|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=780|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019781|M60.6|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019782|M60.7|1484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019782|M60.7|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019782|M60.7|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019782|M60.7|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019782|M60.7|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019782|M60.7|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019782|M60.7|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1015|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019783|M70.1a|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019783|M70.1a|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019783|M70.1a|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019783|M70.1a|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019783|M70.1b|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019783|M70.1b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|1108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=789|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=263|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019785|M70.3b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019786|M70.4b|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1582|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019786|M70.4b|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019786|M70.4b|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019787|M70.5|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019787|M70.5|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019787|M70.5|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019787|M70.5|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019787|M70.5|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019787|M70.5|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019787|M70.5|669nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019788|M116.1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019788|M116.1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=731|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019792|M116.5|491nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019793|M151.1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019795|M151.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019795|M151.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019795|M151.3|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019795|M151.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019796|M151.4|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019796|M151.4|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=70|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019797|fbxb-31|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019797|fbxb-31|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019798|fbxb-32|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019798|fbxb-32|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019799|M151.7|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019799|M151.7|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019799|M151.7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019799|M151.7|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019799|M151.7|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019799|M151.7|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019799|M151.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1769|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|120nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|669nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019800|mtss-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=653|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1283|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|254nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|258nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019801|aak-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019803|PDB1.1c|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019803|PDB1.1c|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019803|PDB1.1c|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019803|PDB1.1c|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019803|PDB1.1c|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1825|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019803|PDB1.1c|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019803|PDB1.1c|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019804|R01B10.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1818|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019805|R01B10.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019806|R01B10.4|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019806|R01B10.4|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1239|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019806|R01B10.4|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019806|R01B10.4|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019806|R01B10.4|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019806|R01B10.4|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019806|R01B10.4|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=404|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1769|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1902|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019807|jamp-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=499|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4079|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=815|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019808|R01B10.6|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019810|R01H2.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019810|R01H2.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019810|R01H2.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019810|R01H2.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019810|R01H2.2|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019811|egg-2|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2968|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019811|egg-2|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=569|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019811|egg-2|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019811|egg-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019811|egg-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019812|R01H2.4b|1274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019812|R01H2.4b|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019812|R01H2.4b|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019812|R01H2.4b|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019812|R01H2.4b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019813|ger-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019813|ger-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019813|ger-1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2155|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019813|ger-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019814|R02C2.1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019814|R02C2.1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019815|kin-34|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019815|kin-34|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019815|kin-34|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019816|nhr-204|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019816|nhr-204|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019817|R02C2.6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019818|R02C2.7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019818|R02C2.7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019818|R02C2.7|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019818|R02C2.7|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019818|R02C2.7|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019819|R02D3.1b|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2154|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019819|R02D3.1b|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=776|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019819|R02D3.1b|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1950|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019820|cogc-8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019821|R02D3.3b|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019821|R02D3.3b|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019821|R02D3.3b|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2281|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019821|R02D3.3b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019821|R02D3.3b|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019822|R02D3.4c|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019822|R02D3.4c|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1607|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019822|R02D3.4c|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019822|R02D3.4c|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2048|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=249|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019823|fnta-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=843|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019824|R02D3.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3351|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1813|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019825|R02D3.8|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019826|R02E4.1|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019826|R02E4.1|792nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|739nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|745nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3141|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|748nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=702|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=618|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|755nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019827|mop-25.1|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019828|R02E12.4|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019828|R02E12.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=388|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019828|R02E12.4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|751nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|757nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|781nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|830nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|834nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=968|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|837nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|840nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019829|R02E12.5|844nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019830|hrg-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019830|hrg-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019830|hrg-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3931|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019830|hrg-1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019830|hrg-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019830|hrg-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|133nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=570|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|638nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3400|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|641nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18971|total_reads(65.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|662nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4739|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|741nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1b.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019831|R02F2.1c.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019832|osg-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019832|osg-1|817nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019832|osg-1|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019832|osg-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019832|osg-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019833|R02F2.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019833|R02F2.4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019833|R02F2.4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019833|R02F2.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019834|R02F2.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019834|R02F2.5|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019836|R02F2.7.1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019836|R02F2.7.1|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019836|R02F2.7.1|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019836|R02F2.7.1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1523|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019837|R02F2.8.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019837|R02F2.8.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019838|R02F2.9|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2417|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00019838|R02F2.9|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019838|R02F2.9|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=673|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|166nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|198nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|265nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1421|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|473nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019839|R02F11.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6350|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019840|R02F11.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019841|R02F11.3a|490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2342|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019842|R02F11.4|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019843|R03E9.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019843|R03E9.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019843|R03E9.2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019843|R03E9.2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019844|abts-4|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019844|abts-4|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019844|abts-4|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=848|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019844|abts-4|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019844|abts-4|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019845|irld-13|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019845|irld-13|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019846|gpx-7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019846|gpx-7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019846|gpx-7|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019847|R03G5.6a|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1411|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019847|R03G5.6a|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019847|R03G5.6a|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019847|R03G5.6a|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019847|R03G5.6a|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019847|R03G5.6b|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019847|R03G5.6b|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019849|oac-40|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019849|oac-40|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019849|oac-40|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019849|oac-40|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00019849|oac-40|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019849|oac-40|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00019851|oac-41|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019854|R03H10.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019854|R03H10.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019854|R03H10.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019855|R03H10.2|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019855|R03H10.2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019855|R03H10.2|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019856|R03H10.4|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019858|R03H10.6|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019858|R03H10.6|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019858|R03H10.6|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019858|R03H10.6|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00019858|R03H10.6|549nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019858|R03H10.6|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019859|R03H10.7|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019859|R03H10.7|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019859|R03H10.7|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019859|R03H10.7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019861|R04A9.1|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019861|R04A9.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7963|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019861|R04A9.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019862|nrde-3|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=264|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019863|R04A9.3|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019864|ceh-93|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019864|ceh-93|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019864|ceh-93|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019865|R04A9.6|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019865|R04A9.6|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019865|R04A9.6|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019865|R04A9.6|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019865|R04A9.6|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019865|R04A9.6|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019866|R04B3.1|377nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019866|R04B3.1|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019866|R04B3.1|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019866|R04B3.1|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019867|R04B3.2|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019867|R04B3.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019867|R04B3.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019867|R04B3.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=569|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=575|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019868|R04B3.3|990nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019869|R04E5.2|181nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019869|R04E5.2|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019869|R04E5.2|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019869|R04E5.2|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019869|R04E5.2|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019869|R04E5.2|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00019869|R04E5.2|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|1072nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=507|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2084|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019870|R04E5.7|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1045nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1048nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1087|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=488|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1057nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=386|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1062nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1066nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1071nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1079nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019871|R04E5.8b|1105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019872|R04E5.9|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019872|R04E5.9|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1125|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019872|R04E5.9|759nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3018|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019872|R04E5.9|761nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019872|R04E5.9|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019872|R04E5.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019872|R04E5.9|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=749|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2589|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=891|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019873|arrd-26|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019874|R05C11.2|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019874|R05C11.2|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019874|R05C11.2|513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019874|R05C11.2|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00019875|mca-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019875|mca-2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019875|mca-2|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019875|mca-2|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019875|mca-2|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019875|mca-2|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=607|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00019875|mca-2|516nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=700|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1544|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019877|R05D3.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=584|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019878|R05D3.3.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019879|R05D3.5|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=505|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019879|R05D3.5|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019879|R05D3.5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3517|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|1444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|679nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|728nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019881|R05D3.8|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1110|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019882|R05D3.9|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1963|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019883|met-2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12a|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12a|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=707|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12a|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12a|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12b|1328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12b|1551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12b|1568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12b|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12b|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12d|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12d|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12d|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019884|R05D3.12d|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019885|R05D8.7|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019885|R05D8.7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019885|R05D8.7|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00019885|R05D8.7|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019885|R05D8.7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019886|R05D8.9|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019886|R05D8.9|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019887|R05D8.11|163nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00019887|R05D8.11|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|1600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|167nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=688|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|169nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|172nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|604nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019888|btbd-10|867nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|112nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3953|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1423|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=279|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019890|R05F9.6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019891|R05F9.7|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019891|R05F9.7|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019891|R05F9.7|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00019892|R05F9.9|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019892|R05F9.9|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019892|R05F9.9|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2060|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00019892|R05F9.9|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019892|R05F9.9|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019892|R05F9.9|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|269nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5558|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7223|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019893|sgt-1|790nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019894|R05F9.11|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019894|R05F9.11|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019894|R05F9.11|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019894|R05F9.11|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019894|R05F9.11|1564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=872|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3516|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2076|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019895|aagr-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=232|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019896|R05G6.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019898|R05G6.4|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019898|R05G6.4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019898|R05G6.4|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019898|R05G6.4|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019898|R05G6.4|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=630|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019898|R05G6.4|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019899|R05G6.5|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019899|R05G6.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019899|R05G6.5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00019899|R05G6.5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019899|R05G6.5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019899|R05G6.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019899|R05G6.5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=753|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13929|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1136|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|134nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42924|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2860|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019900|vdac-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019901|R05G6.9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2461|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019902|R05G6.10b|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=803|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|1116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|1120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|132nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|1368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1879|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|1413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24792|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|147nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8778|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|1509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|1515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|151nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|374nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|382nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=649|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019904|twk-49|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|1268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|191nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|195nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=453|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00019905|R05G9.3|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019906|R05G9R.1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019906|R05G9R.1|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019906|R05G9R.1|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019906|R05G9R.1|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019907|R05H11.1|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019907|R05H11.1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019907|R05H11.1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019908|R05H11.2.1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019908|R05H11.2.1|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2231|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019908|R05H11.2.1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1173|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019908|R05H11.2.1|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019908|R05H11.2.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019909|R06A10.1|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019909|R06A10.1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019909|R06A10.1|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019909|R06A10.1|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019909|R06A10.1|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019911|R06A10.4|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019911|R06A10.4|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019911|R06A10.4|425nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=204|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019911|R06A10.4|428nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=222|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00019911|R06A10.4|431nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019913|R06B10.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019913|R06B10.2|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4310|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1873|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2286|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1236|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|897nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|900nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|917nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3956|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019914|clec-150|922nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=322|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019915|tbc-10|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019915|tbc-10|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019915|tbc-10|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=599|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019915|tbc-10|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019915|tbc-10|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019917|clec-43|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019917|clec-43|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019918|fbxc-36|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019918|fbxc-36|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019918|fbxc-36|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019920|acs-15|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019920|acs-15|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00019920|acs-15|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00019920|acs-15|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00019921|fbxc-34|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=574|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019922|fbxc-28|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019923|fbxc-29|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019924|fbxc-33|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019925|fbxc-31|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019927|fbxc-24|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019927|fbxc-24|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019928|clec-44|1318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019928|clec-44|1323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019928|clec-44|1325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019928|clec-44|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019929|R07C3.13|1111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019929|R07C3.13|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1048|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019930|fbxc-35|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019930|fbxc-35|861nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019931|R07C12.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019933|R07C12.3|1059nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019933|R07C12.3|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|1043nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|1331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|875nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|880nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019935|R07E4.1a|948nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019937|R07E4.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019937|R07E4.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019937|R07E4.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019937|R07E4.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019937|R07E4.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2666|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019937|R07E4.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019937|R07E4.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019938|R07E4.5|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=347|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019938|R07E4.5|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=216|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019938|R07E4.5|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|24nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019939|lips-17|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019940|npp-21|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019940|npp-21|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019940|npp-21|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019940|npp-21|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3758|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019940|npp-21|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=980|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019940|npp-21|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019941|pgam-5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019941|pgam-5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019941|pgam-5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6079|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019941|pgam-5|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019941|pgam-5|661nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019941|pgam-5|666nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019941|pgam-5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019943|R07G3.7b.2|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019943|R07G3.7b.2|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2742|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019943|R07G3.7b.2|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019943|R07G3.7b.2|596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|1148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|448nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|452nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|461nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|467nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|629nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|634nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|984nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019944|R07G3.8|990nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019945|R08C7.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019945|R08C7.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|22nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6053|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019946|chat-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=991|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25967|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1493|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019947|htz-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019948|R08C7.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019948|R08C7.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019949|R08C7.5a|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019949|R08C7.5a|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019949|R08C7.5a|363nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019950|clec-175|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019950|clec-175|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00019950|clec-175|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019951|R08C7.8|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019951|R08C7.8|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019952|fbxb-74|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|228nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3565|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|232nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|236nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|264nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|268nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019953|wapl-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=964|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019955|R08C7.12b|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019956|fbxb-75|1207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019956|fbxb-75|1210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019956|fbxb-75|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019956|fbxb-75|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019956|fbxb-75|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4448|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1a|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1a|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1a|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1a|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1b|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019957|R08E3.1b|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019959|R08E3.3b|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019959|R08E3.3b|271nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019959|R08E3.3b|274nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019959|R08E3.3b|276nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019959|R08E3.3b|279nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019959|R08E3.3b|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=702|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019960|ztf-16|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019960|ztf-16|697nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019960|ztf-16|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019960|ztf-16|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019960|ztf-16|709nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019961|R08E5.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019961|R08E5.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019961|R08E5.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019961|R08E5.1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019962|cysl-3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1044|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019962|cysl-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=865|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019962|cysl-3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019962|cysl-3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019962|cysl-3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2513|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=425|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=373|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|323nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1034|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019963|R08E5.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019964|R08E5.4|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019964|R08E5.4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019964|R08E5.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019964|R08E5.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019964|R08E5.4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019965|R08F11.1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019965|R08F11.1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019965|R08F11.1|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019965|R08F11.1|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019965|R08F11.1|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019966|srt-30|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019966|srt-30|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019966|srt-30|705nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019966|srt-30|73nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=895|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4673|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019967|cyp-33C8|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019968|R08F11.4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019969|fpn-1.3|877nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019970|R08F11.7|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019970|R08F11.7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7483|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019971|ergo-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019972|R09A1.2c|1367nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=72|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019972|R09A1.2c|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019972|R09A1.2c|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019972|R09A1.2c|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019972|R09A1.2c|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=560|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019972|R09A1.2c|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019972|R09A1.2c|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019973|R09A1.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019973|R09A1.3|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019973|R09A1.3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019973|R09A1.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019973|R09A1.3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|1042nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019975|flp-34|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11238|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019977|fpn-1.2|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019977|fpn-1.2|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00019977|fpn-1.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019977|fpn-1.2|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019977|fpn-1.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019977|fpn-1.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019978|hacd-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5792|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019978|hacd-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00019978|hacd-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019978|hacd-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019979|R09B5.11|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00019980|chil-14|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019980|chil-14|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019980|chil-14|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00019980|chil-14|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|734nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019983|sti-1|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2369|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019986|R09F10.1|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=749|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=870|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019987|R09F10.3|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|234nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=558|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019988|R09F10.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2790|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019989|R09F10.8|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019991|R09H3.3.2|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019991|R09H3.3.2|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2782|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=706|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5633|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2112|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019993|rbx-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019994|cdh-1|1447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=718|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019994|cdh-1|1454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019994|cdh-1|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019995|R10F2.4|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019996|R10F2.5|1445nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019996|R10F2.5|1536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019997|R10F2.6|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019997|R10F2.6|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019997|R10F2.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00019998|R10H1.1|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019998|R10H1.1|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019998|R10H1.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019998|R10H1.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019998|R10H1.1|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1458|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019998|R10H1.1|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=963|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00019999|srab-14|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020003|R11E3.1|1294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020003|R11E3.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020003|R11E3.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020004|R11E3.2|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020004|R11E3.2|162nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020004|R11E3.2|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00020004|R11E3.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020004|R11E3.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020006|set-15|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=914|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020006|set-15|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020007|R11F4.1.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020007|R11F4.1.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020007|R11F4.1.2|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1993|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020007|R11F4.1.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020008|R11F4.2b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020008|R11F4.2b|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020008|R11F4.2b|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=475|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020008|R11F4.2b|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020009|R11F4.3|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020009|R11F4.3|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020009|R11F4.3|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00020010|R11G1.1|1400nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020010|R11G1.1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00020010|R11G1.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=454|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020012|R11G1.6c|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020014|R11G11.6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020014|R11G11.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020014|R11G11.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020014|R11G11.6|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020015|nhr-210|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020015|nhr-210|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020015|nhr-210|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=355|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020015|nhr-210|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020015|nhr-210|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020015|nhr-210|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020016|lipl-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020016|lipl-3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020016|lipl-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020017|R12A1.3b|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020017|R12A1.3b|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020017|R12A1.3b|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020017|R12A1.3b|303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020017|R12A1.3b|319nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020017|R12A1.3b|322nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=422|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020017|R12A1.3b|332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|116nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1101|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|227nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|233nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020018|R12B2.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=616|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|812nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|845nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020019|R12B2.3|961nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020020|R12B2.6|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00020020|R12B2.6|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020020|R12B2.6|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020021|R12B2.7|1222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020022|R12C12.1a.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020022|R12C12.1a.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020022|R12C12.1a.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3471|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020022|R12C12.1a.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020022|R12C12.1a.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020022|R12C12.1a.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=53|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|1153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|1155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=436|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|1367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|1417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020023|frpr-16|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020025|R12C12.5|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020025|R12C12.5|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020025|R12C12.5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3038|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020025|R12C12.5|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020025|R12C12.5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020025|R12C12.5|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020025|R12C12.5|226nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=305|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1863|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5982|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=355|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|1486nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|1514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|1516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020026|R12C12.6b.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020027|R12C12.7|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020027|R12C12.7|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020027|R12C12.7|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020027|R12C12.7|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020027|R12C12.7|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020027|R12C12.7|877nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00020027|R12C12.7|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020028|R12C12.8b|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=836|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020028|R12C12.8b|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020028|R12C12.8b|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020028|R12C12.8b|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020029|R12C12.9a.1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1699|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020029|R12C12.9a.1|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020029|R12C12.9a.1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020029|R12C12.9a.1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020029|R12C12.9a.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020029|R12C12.9a.1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00020029|R12C12.9a.1|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=800|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020030|R12E2.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020031|suco-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020031|suco-1|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020031|suco-1|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7747|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020031|suco-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020031|suco-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020031|suco-1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020031|suco-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020032|R12E2.6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020032|R12E2.6|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15517|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2851|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=124|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020033|R12E2.7.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020034|R12E2.8|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020034|R12E2.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020034|R12E2.8|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020034|R12E2.8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020034|R12E2.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020035|egg-5|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2703|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020035|egg-5|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020035|egg-5|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020035|egg-5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020035|egg-5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020035|egg-5|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1780|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=921|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1262|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=788|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020036|R12E2.11|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020037|mrps-6|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020037|mrps-6|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=998|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020037|mrps-6|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=594|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020037|mrps-6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020037|mrps-6|321nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5241|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020038|R12E2.13|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020039|R12E2.14|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020039|R12E2.14|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11395|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020039|R12E2.14|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020040|R12E2.15.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020040|R12E2.15.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020040|R12E2.15.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=545|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020040|R12E2.15.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9947|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020040|R12E2.15.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020040|R12E2.15.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020040|R12E2.15.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020041|R13A1.1|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00020041|R13A1.1|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00020042|R13A1.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00020042|R13A1.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020043|R13A1.5|916nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=545|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=299|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|362nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=957|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=207|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020045|glb-23|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020046|best-16|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2067|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020047|ttr-32|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020048|lgc-12|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020048|lgc-12|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=619|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020048|lgc-12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020048|lgc-12|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020049|ttr-8|1066nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020049|ttr-8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020049|ttr-8|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020049|ttr-8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020049|ttr-8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=843|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020049|ttr-8|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|1206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|344nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=559|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020050|R13A5.7|399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5621|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5995|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|290nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|295nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|504nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020051|R13A5.9|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=209|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=809|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020052|R13A5.10|9nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020053|R13A5.11a|1449nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020053|R13A5.11a|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020053|R13A5.11a|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020053|R13A5.11a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020053|R13A5.11a|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020053|R13A5.11a|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020053|R13A5.11a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020054|R13D7.2|1559nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020054|R13D7.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020054|R13D7.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020057|R13D11.3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020058|R13D11.4a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020058|R13D11.4a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020058|R13D11.4a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020058|R13D11.4a|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020058|R13D11.4a|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020058|R13D11.4a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2061|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020058|R13D11.4a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020060|srab-16|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020060|srab-16|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020062|nhr-270|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020062|nhr-270|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020063|R13D11.10|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020063|R13D11.10|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00020063|R13D11.10|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00020064|kbp-1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020064|kbp-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1378|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020064|kbp-1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020064|kbp-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020064|kbp-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020066|dhhc-5|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020066|dhhc-5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020066|dhhc-5|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020067|clec-158|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=357|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020067|clec-158|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020067|clec-158|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020068|cra-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020068|cra-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5929|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00020069|R13H7.2c|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020069|R13H7.2c|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020069|R13H7.2c|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020069|R13H7.2c|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=465|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020069|R13H7.2c|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1288|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020069|R13H7.2c|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020069|R13H7.2c|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020070|rmd-6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=565|total_reads(75.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020070|rmd-6|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1095nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1098nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22041|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|1233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=897|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020071|R13H9.5|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020072|R13H9.6|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020072|R13H9.6|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=707|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020072|R13H9.6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020073|sdz-28|1194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020073|sdz-28|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020073|sdz-28|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020073|sdz-28|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020075|math-35|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=406|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020077|R52.5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020078|R52.6|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020078|R52.6|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020080|math-37|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020080|math-37|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020080|math-37|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020080|math-37|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020080|math-37|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020080|math-37|72nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020082|gcp-2.1|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020082|gcp-2.1|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=234|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020082|gcp-2.1|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1263|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020082|gcp-2.1|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020082|gcp-2.1|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020082|gcp-2.1|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020082|gcp-2.1|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020083|R57.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020083|R57.2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020083|R57.2|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=187|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1378|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020084|R105.1|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020085|R106.1|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|1401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|262nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=557|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020086|npr-24|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|509nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|517nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=326|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|616nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|667nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|669nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|672nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020088|R119.2|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020089|R119.3.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020089|R119.3.1|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2409|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00020089|R119.3.1|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020089|R119.3.1|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|248nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=48|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|251nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=56|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|258nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=105|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|318nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020090|R119.5a|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|336nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|639nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020091|rnp-8|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=910|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=826|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020092|pcf-11|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1434|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=432|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020093|R144.3a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3270|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|405nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020094|wip-1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020095|R144.5|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020095|R144.5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020095|R144.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020095|R144.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020095|R144.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020095|R144.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1689|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=276|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020096|R144.6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|1165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|1167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|1173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6984|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|1186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4334|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|1189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|1505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020097|larp-1|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020098|R144.10|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020098|R144.10|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1645|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00020098|R144.10|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020099|R144.11|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020099|R144.11|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1240|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00020099|R144.11|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020099|R144.11|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4406|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4967|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15294|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=431|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020100|mks-1|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020101|lmtr-5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020101|lmtr-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020101|lmtr-5|608nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020101|lmtr-5|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4256|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020101|lmtr-5|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020101|lmtr-5|632nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3a|528nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3a|532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=351|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=434|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|566nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=1990|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|571nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|644nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|648nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=404|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|696nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020102|R148.3b|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020103|R148.4a.2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020103|R148.4a.2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2371|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020103|R148.4a.2|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020103|R148.4a.2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020103|R148.4a.2|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020103|R148.4b|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|1187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|1190nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=469|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=627|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020104|R148.5a|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020105|R148.7|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1124|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020105|R148.7|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020105|R148.7|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020106|R151.1a|1303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020106|R151.1a|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020106|R151.1a|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|322nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=215|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|326nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=133|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|329nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=2021|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1655|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6285|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|584nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020107|R151.2d.2|587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=355|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1658|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|340nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|464nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|626nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|907nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|910nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020109|R151.6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=331|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00020110|hsp-75|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4966|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020110|hsp-75|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020110|hsp-75|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020111|R151.8|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020111|R151.8|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020111|R151.8|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1582|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020111|R151.8|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020111|R151.8|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020112|pfd-5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020112|pfd-5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8120|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020112|pfd-5|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020112|pfd-5|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020112|pfd-5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020112|pfd-5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020113|R151.10.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020113|R151.10.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020113|R151.10.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1448|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00020113|R151.10.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020113|R151.10.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020113|R151.10.1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020113|R151.10.1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|787nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|791nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|794nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|797nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|805nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|808nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=889|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|815nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8089|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1694|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|820nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|823nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020114|pde-4|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|1061nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=285|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=367|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3498|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|1428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|755nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|757nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020115|mboa-6|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020116|moa-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020116|moa-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020117|R155.3|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020117|R155.3|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020118|R155.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020118|R155.4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020120|R160.3|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=166|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020120|R160.3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020120|R160.3|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020120|R160.3|311nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020121|R160.4|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020121|R160.4|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020121|R160.4|174nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020121|R160.4|502nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020121|R160.4|929nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020122|R160.5b|1043nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020122|R160.5b|1045nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020123|R160.6|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020123|R160.6|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020123|R160.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|330nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|500nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|503nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=466|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|506nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|520nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020125|R173.3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7351|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=868|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020126|flp-26|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020127|R193.1|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00020127|R193.1|475nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00020128|R193.2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=502|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020128|R193.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=337|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020128|R193.2|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020128|R193.2|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020130|igcm-2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020130|igcm-2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020130|igcm-2|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020130|igcm-2|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020130|igcm-2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020130|igcm-2|205nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|729nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|736nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7283|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|738nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|774nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020131|gcy-28|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020134|T01B6.1|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=95|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020134|T01B6.1|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020134|T01B6.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020134|T01B6.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020134|T01B6.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020135|aakg-4|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020135|aakg-4|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020135|aakg-4|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020135|aakg-4|411nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020135|aakg-4|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020135|aakg-4|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=758|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020135|aakg-4|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10732|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9884|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|203nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020136|T01B6.4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020137|T01B10.5|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=199|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020137|T01B10.5|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=238|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020137|T01B10.5|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020137|T01B10.5|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=332|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=252|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020138|T01B11.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|75nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|79nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2043|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020139|T01B11.2a.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020140|ant-1.4|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020140|ant-1.4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020140|ant-1.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1963|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020140|ant-1.4|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020140|ant-1.4|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020141|lmd-5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020141|lmd-5|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1030|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|544nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|546nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|550nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|556nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020142|aak-2|776nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020143|T01C8.2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020143|T01C8.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1487|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020143|T01C8.2|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=609|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020143|T01C8.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020143|T01C8.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020143|T01C8.2|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020144|T01C8.3|872nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1024|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020144|T01C8.3|877nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020145|got-1.1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020145|got-1.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020146|got-1.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020146|got-1.2|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=93|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020146|got-1.2|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=609|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020146|got-1.2|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5151|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020146|got-1.2|184nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020146|got-1.2|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020146|got-1.2|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020148|T01D1.3|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020148|T01D1.3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020148|T01D1.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020148|T01D1.3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020148|T01D1.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020148|T01D1.3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3019|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|260nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020149|T01D1.4b|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020151|T01G6.1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020151|T01G6.1|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020151|T01G6.1|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020151|T01G6.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020152|nhr-211|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020152|nhr-211|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020153|nhr-212|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020153|nhr-212|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020153|nhr-212|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=389|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020153|nhr-212|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020154|T01G6.10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020154|T01G6.10|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020155|T02B11.3a|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020155|T02B11.3a|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020155|T02B11.3a|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020155|T02B11.3a|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=705|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00020155|T02B11.3a|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020155|T02B11.3a|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1709|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020155|T02B11.3a|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1471|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020156|T02B11.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=589|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00020156|T02B11.4|935nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020157|T02B11.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00020157|T02B11.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1877|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|180nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=311|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2367|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=637|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020158|T02C5.1a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|726nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|828nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|834nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|842nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020160|igcm-3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020163|T02G5.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020163|T02G5.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020163|T02G5.3|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020163|T02G5.3|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1367|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020163|T02G5.3|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1529|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6155|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020166|T02G5.7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020168|mct-5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020168|mct-5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020168|mct-5|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=183|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020168|mct-5|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=522|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020168|mct-5|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020168|mct-5|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020168|mct-5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|197nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1443|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1801|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020169|mmaa-1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020170|T02G5.14|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020170|T02G5.14|448nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020170|T02G5.14|459nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020170|T02G5.14|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020171|T02H6.1a|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020171|T02H6.1a|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=388|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020171|T02H6.1a|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1319|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020171|T02H6.1a|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020171|T02H6.1a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020171|T02H6.1a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=570|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020172|thoc-1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020172|thoc-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020172|thoc-1|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020172|thoc-1|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020173|T02H6.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020175|T02H6.5|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020175|T02H6.5|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020177|T02H6.7|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=206|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020177|T02H6.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020179|T02H6.9|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020179|T02H6.9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020179|T02H6.9|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020179|T02H6.9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1026|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40979|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7053|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1341|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020181|T02H6.11.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020182|ugt-53|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020182|ugt-53|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020182|ugt-53|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020183|T03D3.5|301nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=537|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020184|uba-5|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020184|uba-5|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2559|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020184|uba-5|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3600|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2956|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2283|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020185|pgk-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020187|gsp-4|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1219|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020187|gsp-4|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020187|gsp-4|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020187|gsp-4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020187|gsp-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020187|gsp-4|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020187|gsp-4|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1053|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020188|T03F1.6a|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020188|T03F1.6a|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020188|T03F1.6a|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020189|tfbm-1|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020189|tfbm-1|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020189|tfbm-1|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020189|tfbm-1|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020189|tfbm-1|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=630|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020189|tfbm-1|87nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1221|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1648|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5897|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|322nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020190|guk-1|329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020191|clec-53|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020191|clec-53|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=463|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020191|clec-53|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020191|clec-53|862nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1736|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4996|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=617|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020192|T03F1.11|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1022|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|177nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020193|T03F1.12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|1014nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=866|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020194|T03G6.1|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020195|T03G6.3|1377nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020195|T03G6.3|148nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020195|T03G6.3|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020195|T03G6.3|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020195|T03G6.3|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=986|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020195|T03G6.3|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2674|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020196|T03G11.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|245nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|249nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=232|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=885|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020197|mans-3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020199|T03G11.6|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020199|T03G11.6|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020199|T03G11.6|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2479|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020199|T03G11.6|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020199|T03G11.6|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|1344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2558|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=953|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020200|T04A6.1a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020201|T04A6.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020202|T04A6.3a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020202|T04A6.3b|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020202|T04A6.3b|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020203|T04B8.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020204|T04B8.2|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020204|T04B8.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020205|arrd-1|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020207|T04B8.5d|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020207|T04B8.5d|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2885|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020207|T04B8.5d|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|1320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|1323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|1327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2207|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|1330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=524|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|190nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|195nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|198nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|702nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1a|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1c|1070nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020208|T04C4.1c|1312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2047|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3764|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|669nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020209|T04C9.1a|685nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020211|T04C9.3|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020212|T04D1.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020212|T04D1.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020212|T04D1.2|1539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020212|T04D1.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020214|attf-5|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020214|attf-5|853nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020214|attf-5|856nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=371|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00020214|attf-5|861nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020214|attf-5|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|102nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|107nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1916|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020215|T04G9.4|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5474|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6572|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=851|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|254nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=272|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=657|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020216|trap-2|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|299nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8392|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13432|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5290|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|62nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=2111|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|65nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=245|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020218|T04G9.7|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020219|T05A7.1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00020219|T05A7.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020219|T05A7.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020219|T05A7.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020219|T05A7.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020221|T05A7.3|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020222|fut-6|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020222|fut-6|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020222|fut-6|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020222|fut-6|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020222|fut-6|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020222|fut-6|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020223|T05A7.6|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020223|T05A7.6|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020223|T05A7.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=394|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020224|T05A7.7|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=729|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020225|sre-40|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00020225|sre-40|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020225|sre-40|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020227|T05A8.1.1|485nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020228|T05A8.2.1|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=523|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=431|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=886|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6430|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96261|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=401|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020229|T05A8.3|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020230|nep-2|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020230|nep-2|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1998|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020230|nep-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020230|nep-2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020231|T05A8.5|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020231|T05A8.5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020231|T05A8.5|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020231|T05A8.5|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020232|T05A8.6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020233|T05A8.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1250|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020234|T05A12.3.1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|255nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020235|T05A12.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020236|lgc-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020236|lgc-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020237|phat-4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020237|phat-4|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15321|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020237|phat-4|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020237|phat-4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020237|phat-4|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020238|T05B4.4|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020239|T05B4.8|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020239|T05B4.8|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020240|T05B4.9|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020242|phat-5|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020242|phat-5|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020242|phat-5|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020242|phat-5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020243|T05B4.12|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020244|T05B4.13|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020244|T05B4.13|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00020244|T05B4.13|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020245|T05B11.1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|290nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=725|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1874|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8051|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3483|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|739nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020246|clic-1|742nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=313|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020247|T05B11.4|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020248|T05C1.1|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020248|T05C1.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020248|T05C1.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020248|T05C1.1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020248|T05C1.1|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020249|T05C1.2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020249|T05C1.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020249|T05C1.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020249|T05C1.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020249|T05C1.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=460|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020249|T05C1.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1029|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020249|T05C1.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020250|T05C1.3|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020250|T05C1.3|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=204|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020250|T05C1.3|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|229nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|231nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=528|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=883|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020251|camt-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=309|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00020252|T05C1.5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020254|T05C3.2|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020254|T05C3.2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020256|T05C3.6a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=947|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020256|T05C3.6a|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020256|T05C3.6a|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020258|T05E7.1|123nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020258|T05E7.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020258|T05E7.1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020258|T05E7.1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020258|T05E7.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=938|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020258|T05E7.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020258|T05E7.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020259|T05E7.3|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020259|T05E7.3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1175|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020259|T05E7.3|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=211|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=753|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020260|T05E7.4|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020261|vet-1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020261|vet-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020261|vet-1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020261|vet-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|1291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5984|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|302nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|307nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|309nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=225|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|312nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|322nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020263|let-355|324nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|861nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|863nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|869nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=507|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|871nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|884nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=809|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|890nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1132|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020264|acl-8|894nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020265|fbxa-196|1108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020265|fbxa-196|1410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020265|fbxa-196|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020265|fbxa-196|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020266|T05H4.3|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020266|T05H4.3|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00020266|T05H4.3|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020267|T05H4.4|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=170|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1011|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11368|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020268|hpo-19|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=895|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=479|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|158nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1176|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5592|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3851|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020269|erfa-1|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020270|T05H4.7|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=243|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1910|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|91nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|95nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020273|T05H4.10|97nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|1004nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|1012nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6085|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020274|T05H4.11.2|466nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|1425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|1450nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|186nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|189nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1184|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|193nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=598|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32075|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020275|atp-4|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1586|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020276|T05H4.15b|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020276|T05H4.15b|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020276|T05H4.15b|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00020276|T05H4.15b|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020276|T05H4.15b|401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020277|T06A1.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=368|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1310|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020279|glb-25|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|1075nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|1084nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=676|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020280|T06A1.5|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020281|T06A4.1a|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020281|T06A4.1a|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=448|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020282|mps-3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020283|T06A4.3a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020283|T06A4.3a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020283|T06A4.3a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020283|T06A4.3a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020283|T06A4.3b|129nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020283|T06A4.3b|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020283|T06A4.3b|135nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1060|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=798|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020284|mel-46|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020285|T06A10.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020285|T06A10.2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020285|T06A10.2|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|24nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|42nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=646|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|50nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=1061|total_reads(56.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020286|T06A10.3a|53nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=47|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|1126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=82|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1824|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=580|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2656|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020287|lsy-13|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020288|srt-73|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020288|srt-73|967nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020289|T06C10.3|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020289|T06C10.3|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020289|T06C10.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020289|T06C10.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020289|T06C10.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|121nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|128nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=129|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|132nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|231nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=391|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|238nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020290|T06D4.1a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020291|T06D4.2|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020292|nep-19|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|695nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|708nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=511|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|733nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4341|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|737nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020294|T06F4.1b|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020295|pqbp-1.2|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020295|pqbp-1.2|176nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020295|pqbp-1.2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=799|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020295|pqbp-1.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020295|pqbp-1.2|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020295|pqbp-1.2|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020295|pqbp-1.2|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1624|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=339|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020296|T07A9.8|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8438|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1739|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|545nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020297|nog-1|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2061|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|1204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3573|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|1491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020298|T07A9.10|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1122|total_reads(74.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020299|T07A9.12a|89nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4352|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020300|tag-261|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|235nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2088|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020301|T07D1.2.2|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020302|T07D1.3|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020302|T07D1.3|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020302|T07D1.3|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020302|T07D1.3|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020302|T07D1.3|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020302|T07D1.3|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020302|T07D1.3|633nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020307|T07D3.4|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020307|T07D3.4|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=402|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020307|T07D3.4|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020307|T07D3.4|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020311|T07D3.9b.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00020311|T07D3.9b.1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020311|T07D3.9b.1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020311|T07D3.9b.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020311|T07D3.9b.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020311|T07D3.9b.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020313|T07E3.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020313|T07E3.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4287|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|381nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|385nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|389nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|392nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020314|T07E3.3|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020315|T07E3.4a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020315|T07E3.4a|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020315|T07E3.4a|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=328|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020315|T07E3.4a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1222|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020315|T07E3.4a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020315|T07E3.4a|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020315|T07E3.4a|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=475|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=568|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020316|brc-2|257nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|1043nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|1049nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|1094nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|1100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|1102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|1157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171346|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10617|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|319nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=429|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|326nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16821|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5307|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1023|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=630|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|417nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1892|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2627|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10550|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190534|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=901|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=279|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=984|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4702|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5357|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=206|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=466|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|691nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=846|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|695nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=302|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|701nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|704nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|736nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=462|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=322|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020317|pdf-1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020318|T07F8.1|892nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020319|npr-31|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00020319|npr-31|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020320|T07F8.4|1033nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020320|T07F8.4|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020320|T07F8.4|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020320|T07F8.4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2590|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020320|T07F8.4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020320|T07F8.4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020320|T07F8.4|874nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020321|T07F12.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020321|T07F12.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020321|T07F12.1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020321|T07F12.1|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020321|T07F12.1|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|333nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|336nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2789|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020322|T07F12.2|348nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020323|arrd-23|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020323|arrd-23|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020323|arrd-23|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020323|arrd-23|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2346|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|250nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020324|T07F12.4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020325|bath-46|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020325|bath-46|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020326|math-38|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020326|math-38|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020326|math-38|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00020326|math-38|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020327|clec-21|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020328|clec-20|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020329|bath-26|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020329|bath-26|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020330|T07H6.1a|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020330|T07H6.1a|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020331|T07H6.4|1043nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020331|T07H6.4|1048nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020331|T07H6.4|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020331|T07H6.4|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020331|T07H6.4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020331|T07H6.4|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020331|T07H6.4|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020333|sre-12|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020333|sre-12|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|290nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=620|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=345|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|295nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|300nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=374|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020334|atg-11|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020335|ttr-30|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=480|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020335|ttr-30|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020335|ttr-30|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020339|ttr-59|103nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020339|ttr-59|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1224|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020339|ttr-59|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020339|ttr-59|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020339|ttr-59|99nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1331|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020340|T08B1.1c|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020341|T08B1.4b|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020341|T08B1.4b|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020341|T08B1.4b|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=378|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020341|T08B1.4b|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020341|T08B1.4b|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020341|T08B1.4b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020341|T08B1.4b|209nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020342|fbxa-201|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020342|fbxa-201|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020342|fbxa-201|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00020343|acs-3|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020343|acs-3|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020343|acs-3|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020345|T08B2.4|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020345|T08B2.4|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=743|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1621|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1124|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|821nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|898nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5c|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5e|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020346|T08B2.5e|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10214|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=271|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|568nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=784|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020347|ech-1.2|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020348|mrpl-23|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020348|mrpl-23|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020348|mrpl-23|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6299|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020348|mrpl-23|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|1056nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|1118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1044|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020349|T08B2.11|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7620|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1154|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020350|T08B2.12|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020351|T08B6.1|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020351|T08B6.1|1513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020351|T08B6.1|1522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00020351|T08B6.1|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00020353|T08B6.4|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=216|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020353|T08B6.4|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00020353|T08B6.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020354|T08B6.5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020354|T08B6.5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020354|T08B6.5|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020356|T08B6.9|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020356|T08B6.9|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=321|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020356|T08B6.9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020356|T08B6.9|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020358|math-39|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020359|math-40|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00020359|math-40|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00020360|math-41|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020360|math-41|599nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020360|math-41|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020360|math-41|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020361|fbxc-19|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020361|fbxc-19|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020361|fbxc-19|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020362|fbxb-10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00020362|fbxb-10|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00020363|fbxa-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7774|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020363|fbxa-3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020363|fbxa-3|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020363|fbxa-3|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020364|T08E11.8|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020365|T08G2.2|1099nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020365|T08G2.2|1102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020365|T08G2.2|675nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020365|T08G2.2|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1641|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3100|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=314|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020366|acdh-10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1127|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3704|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1034|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|267nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=523|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|274nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020368|ast-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=178|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=250|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2536|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020369|T08H10.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020370|T08H10.3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020371|T08H10.4|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020371|T08H10.4|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020372|T09A12.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020372|T09A12.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00020372|T09A12.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020372|T09A12.1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020372|T09A12.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020372|T09A12.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020373|gpx-6|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=819|total_reads(98.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020373|gpx-6|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2435|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|368nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2350|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2294|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020374|T09A12.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|1358nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=803|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=652|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=774|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020375|pigv-1|386nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1863|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020376|T09B4.2.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020377|T09B4.3b|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020377|T09B4.3b|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020377|T09B4.3b|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020377|T09B4.3b|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020377|T09B4.3b|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020377|T09B4.3b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020378|T09B4.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020378|T09B4.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020378|T09B4.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020378|T09B4.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|620nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|623nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=296|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|654nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|658nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020379|T09B4.5a|662nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00020380|T09B4.6|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020380|T09B4.6|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020380|T09B4.6|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020380|T09B4.6|322nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020380|T09B4.6|438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020380|T09B4.6|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020381|T09B4.7|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020381|T09B4.7|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|1117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1559|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|382nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020382|T09B4.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=444|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2994|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020383|tin-44|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020384|T09D3.3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020385|nhr-216|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020385|nhr-216|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=658|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020385|nhr-216|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=94|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020386|cyp-34A4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|1121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2079|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|476nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|479nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|481nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|670nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020389|T10B5.3b|838nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4b|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4b|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4b|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12007|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1002|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020390|T10B5.4c|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=858|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4472|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1721|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2171|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|332nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=4078|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|356nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=480|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|360nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|364nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|366nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|625nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020391|cct-7|878nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|1129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|1374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|1379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|1386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=899|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=364|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=337|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020392|knl-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1090|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=551|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1074|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020393|T10B5.7a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|658nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|664nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020394|T10B5.8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020396|T10B5.10b|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=393|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020396|T10B5.10b|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020396|T10B5.10b|330nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020396|T10B5.10b|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8949|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=842|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=314|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020397|pcbd-1|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020398|T10B11.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3263|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020398|T10B11.2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1392|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1296|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|257nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020399|ztf-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020400|T10B11.4|1050nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020400|T10B11.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020401|T10B11.5|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020402|T10B11.6.1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020402|T10B11.6.1|11nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020402|T10B11.6.1|14nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=66|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020402|T10B11.6.1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2723|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020402|T10B11.6.1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020402|T10B11.6.1|21nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020402|T10B11.6.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020403|T10B11.7b|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020403|T10B11.7b|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020403|T10B11.7b|760nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2230|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1262|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020404|T10B11.8b|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020406|T10D4.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020407|chil-24|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020407|chil-24|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020407|chil-24|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020407|chil-24|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020407|chil-24|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00020408|T10D4.6a|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020408|T10D4.6a|312nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020408|T10D4.6a|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020408|T10D4.6a|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=552|total_reads(72%)
- ID=WBGene00020408|T10D4.6a|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020408|T10D4.6a|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020408|T10D4.6a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020409|T10D4.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020411|T10E9.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=432|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020411|T10E9.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020411|T10E9.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020411|T10E9.1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=828|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020412|T10E9.2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020412|T10E9.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020412|T10E9.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020412|T10E9.2|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020412|T10E9.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1395|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020412|T10E9.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020412|T10E9.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020413|T10E9.3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020413|T10E9.3|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020413|T10E9.3|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020413|T10E9.3|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|1521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|1582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1670|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020414|T10E9.4.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1225|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020415|T10E9.5|987nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020416|T10E9.6|14nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020416|T10E9.6|18nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=19|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020416|T10E9.6|20nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020416|T10E9.6|25nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020416|T10E9.6|409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020416|T10E9.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=250|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020416|T10E9.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|1018nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|1021nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2410|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=486|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3157|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020417|nuo-2|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020418|T10E9.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020418|T10E9.8|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020418|T10E9.8|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=600|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020419|acdh-4|232nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020421|T10E10.4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020421|T10E10.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020421|T10E10.4|1318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020421|T10E10.4|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|1162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|1172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|1324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2795|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|259nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|266nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020422|T10F2.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5372|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1431|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=189|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020423|prp-19|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020424|T10H9.1|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=420|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020424|T10H9.1|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020424|T10H9.1|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1097|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2440|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020425|syx-18|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020426|T10H10.2|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020426|T10H10.2|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020426|T10H10.2|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020427|sav-1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=736|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020427|sav-1|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020433|T11F8.1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020433|T11F8.1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020433|T11F8.1|19nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020433|T11F8.1|45nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020433|T11F8.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020435|T11F8.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020436|T12A2.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020436|T12A2.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020436|T12A2.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020437|stt-3|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020437|stt-3|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020437|stt-3|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020437|stt-3|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020437|stt-3|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8342|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020437|stt-3|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=673|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020437|stt-3|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020438|T12A2.3|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020438|T12A2.3|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020440|T12A2.6|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020441|T12A2.7.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020441|T12A2.7.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020441|T12A2.7.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020441|T12A2.7.1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020441|T12A2.7.1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4589|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020441|T12A2.7.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|1161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|1172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|1235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|1237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|1292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|230nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=314|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3149|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1296|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=379|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020442|gen-1|856nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020443|esyt-2|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=789|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020443|esyt-2|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=450|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020444|T12B3.1|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020445|T12B3.2|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020445|T12B3.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020445|T12B3.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020445|T12B3.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020445|T12B3.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020446|T12B3.3|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020446|T12B3.3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020446|T12B3.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020446|T12B3.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020446|T12B3.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020446|T12B3.3|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1425|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00020446|T12B3.3|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1683|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1852|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=342|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|339nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|368nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|375nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1669|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020447|T12B3.4b.2|380nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020448|fbxa-51|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020449|fbxa-54|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020449|fbxa-54|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020449|fbxa-54|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020449|fbxa-54|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020449|fbxa-54|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020449|fbxa-54|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020449|fbxa-54|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020450|fbxa-10|1420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020450|fbxa-10|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020450|fbxa-10|259nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020450|fbxa-10|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020450|fbxa-10|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020450|fbxa-10|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020450|fbxa-10|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020451|fbxa-11|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020451|fbxa-11|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=383|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020452|fbxa-22|1405nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020453|fbxa-55|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|821nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|915nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|920nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|923nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|928nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|940nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020455|fbxa-59|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=475|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=679|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=244|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00020456|fbxa-60|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=425|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|867nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|875nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020457|fbxa-67|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020459|fbxa-23|779nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00020459|fbxa-23|781nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00020460|nhr-273|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020460|nhr-273|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020460|nhr-273|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00020461|T12C9.7a|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2523|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020461|T12C9.7a|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=309|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020461|T12C9.7a|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020461|T12C9.7a|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020461|T12C9.7c|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020461|T12C9.7c|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1031|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|736nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020462|T12E12.1|764nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020463|cec-6|1434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020463|cec-6|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020463|cec-6|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020463|cec-6|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1776|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020463|cec-6|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020463|cec-6|480nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020463|cec-6|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|1296nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|330nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|336nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1121|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020464|T12E12.3|906nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020465|T12E12.6|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020465|T12E12.6|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020466|sld-2|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=796|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020467|T12F5.2|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020467|T12F5.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=646|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020467|T12F5.2|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020467|T12F5.2|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020467|T12F5.2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020467|T12F5.2|376nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020467|T12F5.2|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020468|T13A10.1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020468|T13A10.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020469|T13A10.2|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1307|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020469|T13A10.2|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020469|T13A10.2|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020471|pho-14|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020471|pho-14|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020471|pho-14|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3179|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020471|pho-14|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020471|pho-14|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020471|pho-14|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020472|lips-11|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020472|lips-11|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020473|lips-12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020474|lips-13|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020474|lips-13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020474|lips-13|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=272|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=636|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1170|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020475|sut-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020476|T13B5.9|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020476|T13B5.9|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020478|T13C2.2|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020479|T13C2.3b|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020479|T13C2.3b|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020479|T13C2.3b|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020479|T13C2.3b|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020479|T13C2.3b|878nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1221|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020480|ssup-72|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6952|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020481|T13C2.6a|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=516|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|127nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=358|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|133nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020482|T13C2.7|901nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020483|T13C5.2|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020483|T13C5.2|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020483|T13C5.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020483|T13C5.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020484|T13C5.3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020484|T13C5.3|152nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00020484|T13C5.3|155nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020484|T13C5.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020484|T13C5.3|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020484|T13C5.3|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|11nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|16nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|21nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|23nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020485|ceh-54|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18818|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=793|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|112nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|1323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|228nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=149|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|249nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|291nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1844|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2613|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|970nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|972nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020486|T13C5.6|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1322|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020487|T13C5.7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020487|T13C5.7|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020487|T13C5.7|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020487|T13C5.7|1483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020487|T13C5.7|1541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00020487|T13C5.7|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020487|T13C5.7|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020489|hot-8|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020489|hot-8|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=812|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020489|hot-8|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1456|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|442nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020490|tmc-1|446nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020491|T13G4.4.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020491|T13G4.4.2|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020491|T13G4.4.2|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020491|T13G4.4.2|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020491|T13G4.4.2|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020491|T13G4.4.2|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020494|T13G4.7|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020494|T13G4.7|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020496|spat-3|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1135|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00020496|spat-3|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=881|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020496|spat-3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020496|spat-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020497|T14A8.2b|1598nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020497|T14A8.2b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020497|T14A8.2b|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020497|T14A8.2b|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1458|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020497|T14A8.2b|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020497|T14A8.2b|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=885|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020498|T14B4.1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020499|T14B4.2|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020499|T14B4.2|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020499|T14B4.2|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3027|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020499|T14B4.2|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020500|T14B4.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3975|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00020500|T14B4.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020500|T14B4.3|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020500|T14B4.3|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020501|T14B4.5|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020501|T14B4.5|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00020501|T14B4.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020501|T14B4.5|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020501|T14B4.5|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020501|T14B4.5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|226nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=731|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=765|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020502|T14B4.8a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020503|T14B4.9|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020503|T14B4.9|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020503|T14B4.9|1187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020503|T14B4.9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020503|T14B4.9|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020503|T14B4.9|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020503|T14B4.9|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=421|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2100|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|377nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020504|svh-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020505|T14E8.2|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=663|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020506|dop-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=271|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7746|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020507|vha-15|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020508|T14F9.2|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020508|T14F9.2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=415|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020508|T14F9.2|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020508|T14F9.2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020508|T14F9.2|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5300|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|79nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020509|hex-1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020510|T14G11.1|407nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020510|T14G11.1|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020510|T14G11.1|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2346|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020510|T14G11.1|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020510|T14G11.1|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1875|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1159|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020511|immt-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|309nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=283|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1515|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=351|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=449|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020516|T15B7.1|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8233|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020517|hpo-8|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020523|dmsr-14|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020523|dmsr-14|335nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00020523|dmsr-14|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020524|dmsr-13|1001nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020524|dmsr-13|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020524|dmsr-13|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020524|dmsr-13|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020524|dmsr-13|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020524|dmsr-13|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020524|dmsr-13|997nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020526|T15B7.14|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020526|T15B7.14|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020526|T15B7.14|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020527|T15B7.15|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020527|T15B7.15|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020527|T15B7.15|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020528|lgc-54|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020528|lgc-54|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020528|lgc-54|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020528|lgc-54|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020529|T15B7.17|157nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020529|T15B7.17|161nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2470|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|846nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020530|T15B12.1b|978nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020531|T15B12.2|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020531|T15B12.2|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=312|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00020531|T15B12.2|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020532|math-42|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020532|math-42|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020532|math-42|753nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020533|T16A1.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020533|T16A1.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020533|T16A1.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020534|fbxc-49|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020534|fbxc-49|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=195|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020534|fbxc-49|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020534|fbxc-49|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020535|T16A1.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020536|T16A1.5|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020537|fbxb-37|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020537|fbxb-37|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020537|fbxb-37|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020537|fbxb-37|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00020539|T16D1.1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020540|T17A3.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020540|T17A3.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=765|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020540|T17A3.2|1590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020541|fbxb-81|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020542|fbxb-82|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020543|fbxb-83|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020544|fbxb-84|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020544|fbxb-84|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020545|T17A3.9|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020546|T17A3.10|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020548|T17A3.12|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020548|T17A3.12|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6266|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=383|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2755|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2101|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=955|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020549|nmt-1|364nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020550|T17H7.1.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020550|T17H7.1.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020550|T17H7.1.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020550|T17H7.1.2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020550|T17H7.1.2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|130nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020551|T17H7.7|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1478|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|177nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1187|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=319|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020553|T19A5.1|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020554|T19A5.3b|389nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020554|T19A5.3b|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020554|T19A5.3b|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020554|T19A5.3b|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020554|T19A5.3b|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020555|nhr-219|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020555|nhr-219|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020556|pamn-1|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020556|pamn-1|1302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020556|pamn-1|1314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4049|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020556|pamn-1|1348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020556|pamn-1|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020556|pamn-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=876|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2668|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1190|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020557|T19B4.3|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020558|T19B4.5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020558|T19B4.5|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020558|T19B4.5|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020558|T19B4.5|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1216|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020558|T19B4.5|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020558|T19B4.5|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020558|T19B4.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020559|best-17|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020559|best-17|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00020559|best-17|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020559|best-17|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020559|best-17|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020560|T19C3.2|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1267|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|1259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8345|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|138nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020561|T19C3.3|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020562|T19C3.4|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020562|T19C3.4|453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020562|T19C3.4|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020562|T19C3.4|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2747|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020562|T19C3.4|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020562|T19C3.4|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=494|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=206|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|1286nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=457|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|160nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|466nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1649|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=713|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41195|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020563|T19C3.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020564|T19C3.6|513nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020564|T19C3.6|995nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020565|T19C3.7|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020565|T19C3.7|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020565|T19C3.7|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020566|ttr-7|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020566|ttr-7|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020566|ttr-7|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020566|ttr-7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=816|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020566|ttr-7|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020566|ttr-7|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020566|ttr-7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020567|T19D2.1|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=709|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020568|T19D2.3|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020569|lgc-32|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020569|lgc-32|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020569|lgc-32|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020571|lpr-7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020571|lpr-7|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=845|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=496|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020572|rund-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|148nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=230|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=969|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1076|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=432|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020573|T19D7.5|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020574|T19D7.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020574|T19D7.6|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=567|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020575|T19D7.7|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020575|T19D7.7|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020575|T19D7.7|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020575|T19D7.7|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020576|T19D12.1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2a.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2b.2|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=215|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2b.2|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2b.2|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2b.2|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2b.2|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020577|T19D12.2c.3|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020578|T19D12.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020579|T19D12.4a|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020579|T19D12.4a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020579|T19D12.4a|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020579|T19D12.4a|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020580|T19D12.5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020580|T19D12.5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1927|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2341|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020581|T19D12.6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1395|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|487nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|492nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020582|oig-8|495nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020583|T19D12.9|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020583|T19D12.9|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020584|T19D12.10|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=441|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020585|clec-178|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69756|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00020586|frpr-18|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020586|frpr-18|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=700|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020586|frpr-18|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=371|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020586|frpr-18|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020586|frpr-18|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020587|ugt-9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020587|ugt-9|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020587|ugt-9|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020588|T19H12.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020588|T19H12.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020588|T19H12.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020588|T19H12.2|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020588|T19H12.2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32068|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020588|T19H12.2|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020588|T19H12.2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020589|T19H12.3|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020589|T19H12.3|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020589|T19H12.3|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020589|T19H12.3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020589|T19H12.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=620|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020589|T19H12.3|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020590|T19H12.6|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|1521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=925|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=564|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020592|ugt-12|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020593|ugt-11|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020593|ugt-11|1332nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020593|ugt-11|1338nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020593|ugt-11|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020593|ugt-11|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020594|ugt-10|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020594|ugt-10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020595|T20B5.2|1216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020595|T20B5.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020595|T20B5.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020595|T20B5.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020595|T20B5.2|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=773|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00020595|T20B5.2|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020595|T20B5.2|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|1092nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|214nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=575|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|216nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=71|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|220nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|368nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|395nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020596|oga-1|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020597|T20B6.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020599|T20B6.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020599|T20B6.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020599|T20B6.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2276|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00020599|T20B6.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=511|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=351|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020600|trd-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020601|T20B12.3|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020601|T20B12.3|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020601|T20B12.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020601|T20B12.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1039|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020601|T20B12.3|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=379|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020601|T20B12.3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020603|T20B12.5|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9224|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020604|T20B12.7|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|1311nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|469nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|662nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|667nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|671nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020605|lgc-50|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020606|nhr-284|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020606|nhr-284|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=177|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020609|T20D4.3|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020609|T20D4.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020609|T20D4.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020610|T20D4.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020610|T20D4.4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020610|T20D4.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020612|arrd-22|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1070|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020612|arrd-22|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020612|arrd-22|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020612|arrd-22|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020612|arrd-22|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020612|arrd-22|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020612|arrd-22|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020613|T20D4.7|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020613|T20D4.7|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020614|T20D4.8|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020615|T20D4.9|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020616|T20D4.10|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=271|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020616|T20D4.10|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020616|T20D4.10|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020616|T20D4.10|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020617|T20D4.11|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020617|T20D4.11|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020617|T20D4.11|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020618|T20D4.12|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020618|T20D4.12|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020619|T20D4.13|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020619|T20D4.13|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020620|T20D4.15|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020620|T20D4.15|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020622|T20D4.17|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020622|T20D4.17|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020624|T20D4.19|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020625|mrrf-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020626|T20F5.4|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020626|T20F5.4|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020626|T20F5.4|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00020626|T20F5.4|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020626|T20F5.4|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020627|T20F5.5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020627|T20F5.5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=640|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|279nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=210|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|306nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1309|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|415nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020628|T20F5.6|419nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|1378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|1391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|394nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2328|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|412nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=693|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|530nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020629|T20F5.7|533nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020630|T20F7.1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020630|T20F7.1|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020630|T20F7.1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020630|T20F7.1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020630|T20F7.1|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020630|T20F7.1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020631|T20F7.3|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020631|T20F7.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020631|T20F7.3|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=992|total_reads(89%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020632|T20F7.5|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|1015nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|302nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|562nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020633|aakg-2|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=436|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|505nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1953|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=404|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020634|acs-9|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020635|T20H4.2|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020635|T20H4.2|1159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020635|T20H4.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=626|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1092|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=529|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2621|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1053|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=924|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|39nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020636|T20H4.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020638|fbxa-43|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020638|fbxa-43|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020638|fbxa-43|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020640|fbxa-73|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020642|T20H9.6|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020645|T21D9.2|423nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020645|T21D9.2|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020645|T21D9.2|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1789|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020645|T21D9.2|541nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020645|T21D9.2|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020646|T21D11.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020646|T21D11.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020646|T21D11.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020646|T21D11.1|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020646|T21D11.1|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=209|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1815|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=680|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020647|pqbp-1.1|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020648|T21D12.7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020649|sma-10|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020649|sma-10|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=318|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020649|sma-10|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020649|sma-10|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020650|T21D12.11|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020651|T21D12.12|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020651|T21D12.12|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020651|T21D12.12|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020651|T21D12.12|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020651|T21D12.12|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1075|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020651|T21D12.12|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020651|T21D12.12|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020652|egg-4|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020652|egg-4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020652|egg-4|629nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020652|egg-4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020652|egg-4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020652|egg-4|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020652|egg-4|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2445|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020653|T21E3.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020655|T21E12.3|17nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020655|T21E12.3|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020656|T21E12.5|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020656|T21E12.5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020656|T21E12.5|82nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|1457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=983|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020657|lgc-53|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020659|T21G5.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020659|T21G5.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020659|T21G5.1|262nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020659|T21G5.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020659|T21G5.1|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020659|T21G5.1|591nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020660|T21G5.2|1175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020660|T21G5.2|1196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020660|T21G5.2|1200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020660|T21G5.2|1376nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020661|smz-2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020661|smz-2|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020661|smz-2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020661|smz-2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=884|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020661|smz-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020662|T21H3.1a.1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020662|T21H3.1a.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020662|T21H3.1a.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26698|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00020662|T21H3.1a.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020662|T21H3.1a.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020663|cutl-22|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020663|cutl-22|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|1002nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|1007nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|523nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|780nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|784nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|802nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|813nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|823nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|831nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|868nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|878nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|890nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|895nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|982nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020664|T21H3.5a|991nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020665|T22B2.1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020665|T22B2.1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020666|T22B2.2|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020669|T22B2.5|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020669|T22B2.5|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020669|T22B2.5|628nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020670|T22B2.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020670|T22B2.6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020670|T22B2.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020670|T22B2.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020672|T22B7.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020672|T22B7.3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020673|T22B7.4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00020673|T22B7.4|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020673|T22B7.4|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020673|T22B7.4|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020673|T22B7.4|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020673|T22B7.4|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=139|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13017|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19014|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020674|T22B7.7|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=452|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|360nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|366nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|427nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|466nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|469nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=202|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|478nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020675|T22B11.1|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020677|T22B11.3|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020677|T22B11.3|622nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00020677|T22B11.3|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|280nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|286nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|289nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1223|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020678|T22B11.4a|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18651|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020679|ogdh-1|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020682|T22D1.3e.4|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8129|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00020682|T22D1.3e.4|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=496|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020682|T22D1.3e.4|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020682|T22D1.3e.4|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020682|T22D1.3e.4|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020682|T22D1.3e.4|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020682|T22D1.3e.4|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|1028nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|1378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18832|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2281|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|371nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|387nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|391nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|394nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020683|ribo-1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4188|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020684|T22D1.5|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020686|T22D1.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1048|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=741|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1465|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1480|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1833|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020687|ruvb-2|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020688|T22D1.11|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020688|T22D1.11|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020688|T22D1.11|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020689|npr-12|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1668|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020689|npr-12|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=127|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020689|npr-12|157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=391|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020689|npr-12|313nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=192|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=386|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84706|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8599|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020690|T22E5.1a|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020691|igdb-3|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00020691|igdb-3|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|416nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|690nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|916nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|924nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020692|T22E5.6|964nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020693|lron-8|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020693|lron-8|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020693|lron-8|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=735|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020693|lron-8|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00020693|lron-8|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|1243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|1245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=351|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=359|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|223nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|257nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=379|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|263nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020694|dhhc-11|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1753|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020695|T22F3.2b|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|1041nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|1467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|242nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|246nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2005|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|251nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21626|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10517|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1329|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=426|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020696|T22F3.3a|969nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020697|T22F3.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020697|T22F3.7|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020697|T22F3.7|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020698|T22F3.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020698|T22F3.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020699|T22F3.10|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020699|T22F3.10|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020700|T22F3.11a|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020700|T22F3.11a|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020700|T22F3.11a|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020700|T22F3.11a|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020700|T22F3.11a|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=433|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020700|T22F3.11a|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020700|T22F3.11a|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020701|T22F7.1|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020701|T22F7.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00020701|T22F7.1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020702|T22F7.3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1078|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=765|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020703|T22F7.4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020704|T22F7.5|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020704|T22F7.5|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020705|T22H9.1b.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1200|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020705|T22H9.1b.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020705|T22H9.1b.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|827nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1468|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|926nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020706|atg-9|929nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020707|wago-10|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020707|wago-10|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00020707|wago-10|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020708|dmd-8|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00020708|dmd-8|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020708|dmd-8|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|1087nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1725|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|247nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=472|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020709|T23B3.1a|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8689|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020710|T23B3.2|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020712|ckr-1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020712|ckr-1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00020712|ckr-1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020712|ckr-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|112nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|114nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|120nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|123nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1972|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020713|T23B3.5|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|1024nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|1059nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|1069nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|1071nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8434|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|865nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|940nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|943nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020714|T23B3.6|987nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020715|nspd-4|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|1081nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=889|total_reads(49%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=575|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|1490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020716|phf-30|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020717|mrpl-4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020717|mrpl-4|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1427|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020717|mrpl-4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020717|mrpl-4|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020717|mrpl-4|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=464|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020718|mrps-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020718|mrps-2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020718|mrps-2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020718|mrps-2|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020718|mrps-2|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=438|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020718|mrps-2|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2055|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020718|mrps-2|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|1332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=325|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3289|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020719|natc-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020720|T23B12.5|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020720|T23B12.5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1601|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|249nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020721|T23B12.6|714nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|1192nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|1225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22064|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35028|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020722|T23B12.8a.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020725|cnp-3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1159|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=490|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020726|T23C6.4|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020727|npr-21|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020727|npr-21|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020727|npr-21|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020727|npr-21|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=471|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020728|T23E1.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(67.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020728|T23E1.1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020730|T23E1.3a|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020730|T23E1.3a|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020730|T23E1.3a|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00020732|T23E7.2a|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020732|T23E7.2a|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3509|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020732|T23E7.2a|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020732|T23E7.2a|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020732|T23E7.2f|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|773nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|776nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|836nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|838nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|841nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|845nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|861nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020735|T23F2.2a|864nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9008|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020736|T23F2.3|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020737|T23F2.4|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020737|T23F2.4|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=674|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020737|T23F2.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10130|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|268nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020738|T23F2.5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020740|T23F4.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020740|T23F4.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020740|T23F4.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020740|T23F4.2|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020740|T23F4.2|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020740|T23F4.2|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=496|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00020740|T23F4.2|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020741|dlhd-1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020741|dlhd-1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020741|dlhd-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020741|dlhd-1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=336|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2518|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|276nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|289nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|291nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|293nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020742|T23H2.3|949nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020743|mam-8|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020743|mam-8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020743|mam-8|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020743|mam-8|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020743|mam-8|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=284|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00020744|T24A6.1|1047nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=885|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00020744|T24A6.1|1050nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020744|T24A6.1|1052nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020744|T24A6.1|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020744|T24A6.1|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020744|T24A6.1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020746|srbc-66|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020746|srbc-66|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=358|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00020746|srbc-66|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020746|srbc-66|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00020746|srbc-66|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|160nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=532|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=407|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|420nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|482nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020747|T24A6.7|979nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020748|nhr-221|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00020748|nhr-221|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(68%)
- ID=WBGene00020749|srbc-67|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020749|srbc-67|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020750|nhr-222|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020750|nhr-222|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020750|nhr-222|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020755|grl-31|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020756|T24A6.20|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1109|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00020756|T24A6.20|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020756|T24A6.20|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020756|T24A6.20|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=628|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=380|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|456nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2838|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=246|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=221|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020757|ucr-2.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1633|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020758|T24C4.2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020758|T24C4.2|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020758|T24C4.2|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020758|T24C4.2|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1077|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020758|T24C4.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020759|T24C4.3|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020759|T24C4.3|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=402|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020759|T24C4.3|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020760|T24C4.4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020760|T24C4.4|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020760|T24C4.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3483|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00020760|T24C4.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020760|T24C4.4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020760|T24C4.4|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|922nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|929nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=888|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|935nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020761|T24C4.5|992nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|294nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=335|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|297nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|301nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|698nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5933|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|718nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020762|zer-1|729nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=303|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=294|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|221nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020763|ztf-18|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=301|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020764|T24C12.1|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020764|T24C12.1|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020764|T24C12.1|896nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020765|T24C12.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020765|T24C12.3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=662|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020765|T24C12.3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020765|T24C12.3|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020765|T24C12.3|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020766|T24C12.4|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020766|T24C12.4|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020766|T24C12.4|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=708|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020766|T24C12.4|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020767|lgc-40|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020767|lgc-40|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=604|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020767|lgc-40|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=524|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020767|lgc-40|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020767|lgc-40|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020769|T24D8.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|719nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|726nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2717|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|733nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|735nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|777nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|779nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020770|eat-17|813nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020771|T24E12.1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020771|T24E12.1|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020772|T24E12.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020774|T24E12.5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020774|T24E12.5|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020774|T24E12.5|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=149|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020775|T24E12.6a|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020775|T24E12.6a|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00020775|T24E12.6a|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020775|T24E12.6a|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020777|T24E12.10|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020777|T24E12.10|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020778|T24E12.11|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020778|T24E12.11|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020778|T24E12.11|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020778|T24E12.11|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020779|T24G10.2|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020779|T24G10.2|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020779|T24G10.2|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020779|T24G10.2|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020779|T24G10.2|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3034|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020779|T24G10.2|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020779|T24G10.2|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3556|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020781|T24H7.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020782|T24H7.3.2|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020782|T24H7.3.2|1594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020782|T24H7.3.2|1596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020782|T24H7.3.2|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2016|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020782|T24H7.3.2|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4851|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020783|blos-4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020783|blos-4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020783|blos-4|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020783|blos-4|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1690|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020783|blos-4|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020783|blos-4|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8213|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|1501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020784|tat-4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020785|T25B2.1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=741|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=468|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=289|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020786|T25B2.2a|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020788|nep-22|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020788|nep-22|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1564|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020788|nep-22|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020788|nep-22|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020788|nep-22|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020788|nep-22|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020789|T25B6.3|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|135nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=89|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=499|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|144nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|148nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|219nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1078|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020790|T25B6.4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020791|T25B6.5|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020791|T25B6.5|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00020791|T25B6.5|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=99|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020791|T25B6.5|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020791|T25B6.5|417nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020791|T25B6.5|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020791|T25B6.5|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020792|T25B6.6|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=520|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020793|T25D1.1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020793|T25D1.1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020796|mrpl-28|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020796|mrpl-28|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020796|mrpl-28|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=775|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020796|mrpl-28|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020796|mrpl-28|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=594|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020796|mrpl-28|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=474|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020796|mrpl-28|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020797|T25D3.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00020797|T25D3.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020797|T25D3.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2234|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|930nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020798|T25D3.4c|938nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020799|T25D10.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020799|T25D10.1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020799|T25D10.1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=948|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020799|T25D10.1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020800|zig-10|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020800|zig-10|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020800|zig-10|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00020800|zig-10|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020800|zig-10|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020801|T25D10.4|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020801|T25D10.4|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020801|T25D10.4|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020801|T25D10.4|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020802|btb-2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020802|btb-2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1299|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020803|T25E4.1|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020804|T25E4.2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020804|T25E4.2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020806|T25F10.3.2|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020806|T25F10.3.2|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020806|T25F10.3.2|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020807|T25F10.4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020807|T25F10.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020807|T25F10.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020807|T25F10.4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020807|T25F10.4|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65988|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9606|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=429|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020808|clik-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020809|T25G12.1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020811|T25G12.3|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020811|T25G12.3|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1997|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2636|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=160|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020812|acdh-7|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=616|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020813|T25G12.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020813|T25G12.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=293|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020813|T25G12.6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020813|T25G12.6|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020813|T25G12.6|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020813|T25G12.6|714nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020813|T25G12.6|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020817|T25G12.11|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020817|T25G12.11|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020817|T25G12.11|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020817|T25G12.11|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020817|T25G12.11|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|319nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|349nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|352nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|357nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020819|T26A5.2a|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|1117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|1545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|1565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1816|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020820|algn-1|902nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|1300nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|1396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1051|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|609nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2720|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|619nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|709nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|812nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|894nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|897nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|903nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|912nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|916nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020821|jhdm-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=996|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|939nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020822|T26A5.6|947nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2385|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2804|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=144|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020823|T26A5.8|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020824|T26A8.1.3|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020824|T26A8.1.3|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020824|T26A8.1.3|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020824|T26A8.1.3|435nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3846|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020824|T26A8.1.3|438nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020824|T26A8.1.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=321|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020825|T26A8.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020826|T26A8.3|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020826|T26A8.3|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020826|T26A8.3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020826|T26A8.3|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|460nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2427|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|466nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|469nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|808nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|817nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020827|T26A8.4|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020830|T26C11.4a|1315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020830|T26C11.4a|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=524|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020830|T26C11.4a|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020830|T26C11.4a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020830|T26C11.4a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020830|T26C11.4a|644nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=933|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1672|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1774|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020831|T26C12.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020832|T26C12.2|465nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020832|T26C12.2|531nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020832|T26C12.2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020832|T26C12.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020833|T26C12.3b|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020833|T26C12.3b|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020834|T27A1.2|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020835|T27A1.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=482|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=374|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020836|lgc-34|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020837|slc-36.2|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|161nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|164nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4239|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1030|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|332nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|339nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|341nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020838|trak-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3809|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020839|usp-5|765nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020840|spch-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020840|spch-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020840|spch-3|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020840|spch-3|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020840|spch-3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11007|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020840|spch-3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6852|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020840|spch-3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020841|T27A3.5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020841|T27A3.5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020841|T27A3.5|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020842|T27A3.6|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1419|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020842|T27A3.6|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020842|T27A3.6|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|323nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=286|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|330nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=99|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|475nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|486nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1001|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|488nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020843|T27A3.7|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020844|T27A10.2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020844|T27A10.2|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020844|T27A10.2|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19216|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020844|T27A10.2|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020844|T27A10.2|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020844|T27A10.2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020844|T27A10.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020845|T27A10.5|1105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020845|T27A10.5|1237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020845|T27A10.5|1244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020845|T27A10.5|1351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020845|T27A10.5|662nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020845|T27A10.5|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020845|T27A10.5|777nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020846|T27A10.6.1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020846|T27A10.6.1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=848|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020846|T27A10.6.1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020846|T27A10.6.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020847|cgr-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020847|cgr-1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020847|cgr-1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020847|cgr-1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=547|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020849|nhr-225|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020849|nhr-225|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020849|nhr-225|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020849|nhr-225|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020849|nhr-225|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020850|nhr-226|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020850|nhr-226|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020851|nhr-227|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020852|nhr-228|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020852|nhr-228|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020852|nhr-228|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020852|nhr-228|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020852|nhr-228|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2363|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020852|nhr-228|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=804|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020852|nhr-228|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020853|fbxa-137|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020853|fbxa-137|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020853|fbxa-137|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=468|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1836|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|359nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2248|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36132|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3853|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=424|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|442nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=155|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|483nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|487nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|490nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|492nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=604|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|498nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|504nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|586nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|602nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|638nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|647nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|651nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020854|T27C4.1.2|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020855|hpo-36|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020855|hpo-36|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020856|srt-61|1208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020856|srt-61|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020856|srt-61|275nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020857|srt-62|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00020857|srt-62|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00020857|srt-62|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020857|srt-62|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020857|srt-62|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020858|mop-25.3|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=673|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020858|mop-25.3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020858|mop-25.3|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020860|nspd-10|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020860|nspd-10|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020860|nspd-10|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020860|nspd-10|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020860|nspd-10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8621|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|1099nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|1390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|1521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5301|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=881|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020861|T27E4.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1747|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4283|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|94nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020862|fip-2|98nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020863|T27E4.5|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020863|T27E4.5|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020863|T27E4.5|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020864|oac-50|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020864|oac-50|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020864|oac-50|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|1053nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|307nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=899|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=533|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|314nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|579nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|582nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020865|T27E4.7|642nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=168|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8594|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020866|vps-24|680nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020867|shc-2|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020867|shc-2|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020867|shc-2|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=689|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020867|shc-2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020867|shc-2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020869|T28A11.2a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00020869|T28A11.2a|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020869|T28A11.2a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020869|T28A11.2b|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020869|T28A11.2b|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1230|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020869|T28A11.2b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020870|T28A11.3|150nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00020870|T28A11.3|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00020870|T28A11.3|973nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020871|T28A11.4|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020871|T28A11.4|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020872|T28A11.5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|380nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|382nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|471nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|480nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020873|T28A11.6|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020875|T28A11.13|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020877|srt-63|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020878|T28A11.16|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020878|T28A11.16|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020878|T28A11.16|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020878|T28A11.16|205nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020878|T28A11.16|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020878|T28A11.16|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020878|T28A11.16|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020879|T28A11.17|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00020879|T28A11.17|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00020881|T28A11.19|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020881|T28A11.19|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020882|T28A11.20|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020883|fbxa-64|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=439|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020883|fbxa-64|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=391|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020883|fbxa-64|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020883|fbxa-64|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=134|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020883|fbxa-64|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020884|T28B4.1c|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=596|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00020884|T28B4.1c|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020884|T28B4.1c|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=399|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|132nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|138nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|140nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|1437nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|146nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=87|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3134|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2090|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020886|ttr-6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=372|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1217|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10307|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1277|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020887|T28B4.4.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020888|T28C12.1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020889|T28C12.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020889|T28C12.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020890|fbxa-202|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00020890|fbxa-202|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=590|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020891|T28C12.4b|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020893|T28C12.6|236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=920|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|325nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13835|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13153|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|371nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020894|T28D9.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020895|T28D9.3d|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020895|T28D9.3d|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020895|T28D9.3d|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020895|T28D9.3d|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1243|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00020895|T28D9.3d|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=178|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020896|T28D9.4a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020896|T28D9.4a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020896|T28D9.4a|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=895|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020896|T28D9.4a|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1364|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020896|T28D9.4a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020896|T28D9.4a|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020897|del-10|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020897|del-10|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020897|del-10|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=314|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020898|T28D9.9|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020899|T28D9.11|1187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020899|T28D9.11|1502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020900|T28F2.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020900|T28F2.1|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1818|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020901|T28F2.2b|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020902|jmjc-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020902|jmjc-1|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020902|jmjc-1|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=226|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020902|jmjc-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=107|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020902|jmjc-1|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020902|jmjc-1|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020902|jmjc-1|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020903|acd-5|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020903|acd-5|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020903|acd-5|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=225|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020904|T28F12.1|110nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020904|T28F12.1|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020905|T28H11.7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020905|T28H11.7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020905|T28H11.7|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1239|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020905|T28H11.7|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020906|T28H11.8.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020906|T28H11.8.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020907|VC5.1|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020907|VC5.1|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020907|VC5.1|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00020907|VC5.1|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020908|VC5.2|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020908|VC5.2|1284nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020908|VC5.2|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=751|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020908|VC5.2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|47nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|50nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3308|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=471|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020909|W01A11.1a|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1101|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020910|dgtr-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020911|cpt-6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020911|cpt-6|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=596|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020911|cpt-6|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00020911|cpt-6|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00020911|cpt-6|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020912|W01A11.7.2|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020912|W01A11.7.2|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=172|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020912|W01A11.7.2|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=429|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020912|W01A11.7.2|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020912|W01A11.7.2|151nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020912|W01A11.7.2|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020913|W01B11.1|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020913|W01B11.1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020913|W01B11.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020914|sulp-6|1183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00020914|sulp-6|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00020914|sulp-6|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020914|sulp-6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020914|sulp-6|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|1188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=870|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8213|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|318nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|321nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=229|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020915|nol-5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=402|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1004|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4733|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020917|W01B11.6a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020918|W01C8.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020918|W01C8.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020918|W01C8.1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020918|W01C8.1|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020919|set-19|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020919|set-19|1206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020919|set-19|703nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020919|set-19|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020919|set-19|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020919|set-19|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020919|set-19|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1537|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|820nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020920|set-20|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020921|W01C8.5b|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020921|W01C8.5b|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020921|W01C8.5b|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020921|W01C8.5b|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1289|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020921|W01C8.5b|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020921|W01C8.5b|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020921|W01C8.5b|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020923|W02B3.3|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020924|W02B3.4|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020924|W02B3.4|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020924|W02B3.4|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020924|W02B3.4|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020924|W02B3.4|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2a|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3634|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47537|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020929|W02C12.2b|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|1001nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|1008nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|1011nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|322nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=838|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|665nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|677nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|699nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|701nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|773nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|913nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|921nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|924nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|960nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2812|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|964nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1557|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|966nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=481|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020930|hlh-30|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7143|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2610|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=426|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020931|cytb-5.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020932|dhod-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4397|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020932|dhod-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=696|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020932|dhod-1|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020932|dhod-1|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020932|dhod-1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020932|dhod-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020932|dhod-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|227nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|231nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|238nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=128|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|255nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2238|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020933|W02D3.4.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|1023nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|1027nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|1236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1193|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020935|fnci-1|495nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|1342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|460nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1228|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=744|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|674nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020936|hrpf-1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020937|W02D3.12|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020937|W02D3.12|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=388|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020937|W02D3.12|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020937|W02D3.12|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1695|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020937|W02D3.12|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=807|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020937|W02D3.12|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020937|W02D3.12|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=796|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=474|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1161|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020938|clec-218|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020939|W02D7.3|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020939|W02D7.3|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020939|W02D7.3|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00020939|W02D7.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020939|W02D7.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020940|W02D7.4|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020940|W02D7.4|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020940|W02D7.4|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020940|W02D7.4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1415|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00020940|W02D7.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020940|W02D7.4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020940|W02D7.4|93nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020941|W02D7.5|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020941|W02D7.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020941|W02D7.5|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020941|W02D7.5|960nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|1547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2160|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020942|W02D7.6|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020943|W02D7.8|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020945|clec-219|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020946|W02D7.11|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020946|W02D7.11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020946|W02D7.11|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|257nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=133|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|259nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|261nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=506|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020947|W02F12.2|961nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2652|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1423|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=261|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=700|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020948|era-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4c|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=404|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=731|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1106|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020949|W02F12.4d|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16699|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2394|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020950|dlst-1|706nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020951|sna-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020951|sna-1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1027|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020951|sna-1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8438|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020951|sna-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020951|sna-1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020951|sna-1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020951|sna-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=300|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020952|kel-8|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020953|W02G9.3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020953|W02G9.3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020953|W02G9.3|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=947|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020954|W02G9.4|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1233|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020954|W02G9.4|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020954|W02G9.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|599nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=632|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|607nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020957|W02H5.2|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020961|sknr-1|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020962|W02H5.8|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020962|W02H5.8|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020962|W02H5.8|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020962|W02H5.8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00020962|W02H5.8|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020962|W02H5.8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020964|polq-1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00020964|polq-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020964|polq-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020964|polq-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1223|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020964|polq-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020964|polq-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020966|W03A5.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00020966|W03A5.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020966|W03A5.1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020966|W03A5.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020966|W03A5.1|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020967|W03A5.2|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020967|W03A5.2|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=276|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020967|W03A5.2|49nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|592nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|597nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2131|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|600nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020968|W03A5.4.1|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020972|trpl-2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00020972|trpl-2|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020972|trpl-2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020973|W03B1.3.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020973|W03B1.3.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020974|W03B1.5|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020974|W03B1.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020976|oac-51|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020976|oac-51|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020976|oac-51|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020976|oac-51|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020977|oac-52|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020977|oac-52|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020978|W03B1.9|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020978|W03B1.9|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020982|ilys-6|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00020983|W03D2.9|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020983|W03D2.9|239nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020983|W03D2.9|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020983|W03D2.9|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00020983|W03D2.9|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020983|W03D2.9|931nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020984|W03D8.1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020984|W03D8.1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020985|W03D8.2a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020985|W03D8.2a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020986|W03D8.3|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020986|W03D8.3|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020986|W03D8.3|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020987|W03D8.5|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020987|W03D8.5|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020988|W03D8.7|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020988|W03D8.7|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020988|W03D8.7|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020989|W03D8.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020989|W03D8.8|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020989|W03D8.8|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020989|W03D8.8|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020990|W03D8.9.2|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020990|W03D8.9.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020990|W03D8.9.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020990|W03D8.9.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020990|W03D8.9.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1825|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020990|W03D8.9.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020990|W03D8.9.2|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020993|W03F8.3a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=550|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00020993|W03F8.3a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020993|W03F8.3a|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020993|W03F8.3a|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=205|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020993|W03F8.3a|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020993|W03F8.3a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020993|W03F8.3a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|298nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3788|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00020994|W03F8.4|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3045|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|585nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|805nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020995|W03F8.6c|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020997|gpa-18|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020997|gpa-18|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020997|gpa-18|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=312|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020997|gpa-18|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020997|gpa-18|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|1307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3189|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|384nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|387nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00020999|W03F9.1b|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|1162nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021000|W03F9.2a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021002|W03F9.4b|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021002|W03F9.4b|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021002|W03F9.4b|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021003|W03F9.9|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021003|W03F9.9|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3267|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=719|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021004|W03F9.10|875nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2063|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3608|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3404|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=369|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021005|W03F11.1b|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021006|dct-9|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021006|dct-9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=669|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021006|dct-9|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021006|dct-9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021007|W03F11.4|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021007|W03F11.4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021008|W03F11.5|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021008|W03F11.5|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00021008|W03F11.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021009|afd-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021009|afd-1|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021009|afd-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021009|afd-1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021009|afd-1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1131|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021009|afd-1|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2354|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021009|afd-1|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021010|W03G1.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021010|W03G1.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021010|W03G1.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021010|W03G1.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021011|W03G1.5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021011|W03G1.5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021011|W03G1.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021011|W03G1.5|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=645|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021011|W03G1.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=487|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021011|W03G1.5|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|1184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|1190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|1194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2480|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00021012|pig-1|650nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021014|W03G9.2|1173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021014|W03G9.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=958|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021014|W03G9.2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021014|W03G9.2|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021014|W03G9.2|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021015|enu-3.3|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2667|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021015|enu-3.3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021015|enu-3.3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021015|enu-3.3|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021016|W03G9.5|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021016|W03G9.5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00021016|W03G9.5|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021017|W03G9.7|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021017|W03G9.7|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021017|W03G9.7|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=302|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021017|W03G9.7|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=342|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021017|W03G9.7|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=642|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3564|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|382nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|385nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|389nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021019|W04B5.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021020|W04B5.3b|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021020|W04B5.3b|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021020|W04B5.3b|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=544|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021020|W04B5.3b|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2883|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021020|W04B5.3b|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1209|total_reads(53.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=359|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021021|mrpl-30|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=165|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021022|W04B5.5|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021022|W04B5.5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=585|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021022|W04B5.5|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021022|W04B5.5|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021022|W04B5.5|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021022|W04B5.5|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1289|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5284|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=649|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|493nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021024|W04C9.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021025|cutl-13|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021025|cutl-13|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021025|cutl-13|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021026|W04C9.4|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021026|W04C9.4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021026|W04C9.4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021026|W04C9.4|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3196|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021026|W04C9.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021027|W04C9.5|1280nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021027|W04C9.5|1287nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021027|W04C9.5|1357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021027|W04C9.5|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021027|W04C9.5|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00021027|W04C9.5|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021028|W04C9.6|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021028|W04C9.6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021030|W04H10.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021030|W04H10.1|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021031|W04H10.2|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021031|W04H10.2|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021031|W04H10.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021032|clec-118|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021032|clec-118|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021032|clec-118|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021034|enu-3.4|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=806|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021034|enu-3.4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021034|enu-3.4|609nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021034|enu-3.4|615nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=705|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|1053nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8860|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6847|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|790nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|795nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021035|W05F2.3|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=962|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=743|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021036|W05F2.4b|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021038|W05F2.6a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021038|W05F2.6a|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1081|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021038|W05F2.6a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1558|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021039|W05F2.7|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=606|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021039|W05F2.7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=380|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021039|W05F2.7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021039|W05F2.7|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021040|W05G11.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=418|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021040|W05G11.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021041|W05G11.4|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021041|W05G11.4|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021042|btb-5|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021042|btb-5|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39108|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=679|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|1284nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=936|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021043|pck-1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=302|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021044|W05H7.1|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021045|W05H7.2|1105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021045|W05H7.2|1108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021045|W05H7.2|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021045|W05H7.2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021046|sedl-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021046|sedl-1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021046|sedl-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021046|sedl-1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021046|sedl-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1653|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1421|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021047|zfp-3|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021048|W05H9.1a.2|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021048|W05H9.1a.2|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=531|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021048|W05H9.1a.2|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3663|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021048|W05H9.1a.2|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021048|W05H9.1a.2|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=809|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021049|W05H9.2|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021051|W05H9.4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021051|W05H9.4|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021051|W05H9.4|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3423|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021051|W05H9.4|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021051|W05H9.4|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021053|gadr-4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021053|gadr-4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=673|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021053|gadr-4|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021055|W06A11.4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021055|W06A11.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021055|W06A11.4|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=267|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|215nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|221nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1249|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=870|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021056|W06B4.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021057|W06B4.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021058|vps-18|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021058|vps-18|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00021058|vps-18|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=474|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1841|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=186|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021059|atat-2|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1376|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=857|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021060|dct-11|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1379|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021061|W06E11.1|813nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1130|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5188|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021063|sbds-1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021066|W06H8.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021066|W06H8.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021066|W06H8.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(71.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021067|W06H8.4|1270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021067|W06H8.4|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|1004nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|1032nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|112nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|1155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|1299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|129nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|1426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|51nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021068|W06H8.6|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021070|cpr-8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=989|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021070|cpr-8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021070|cpr-8|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021072|W07B8.4b|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021072|W07B8.4b|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00021072|W07B8.4b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021073|nol-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021073|nol-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021073|nol-1|226nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2023|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021073|nol-1|235nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=808|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021074|W07E6.2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1144|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021074|W07E6.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021075|W07E6.3a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021075|W07E6.3a|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00021075|W07E6.3a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021076|W07E6.5a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021076|W07E6.5a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1226|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00021076|W07E6.5a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|434nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=588|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|438nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=152|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|440nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1544|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|447nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|464nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2849|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|468nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|565nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021078|unc-132|598nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021079|W08A12.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021079|W08A12.2|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1815|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021079|W08A12.2|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=405|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021079|W08A12.2|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021080|W08A12.3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021080|W08A12.3|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021080|W08A12.3|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021080|W08A12.3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(59.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021080|W08A12.3|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021080|W08A12.3|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021081|W08A12.4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021081|W08A12.4|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00021081|W08A12.4|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021082|zip-11|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021082|zip-11|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021082|zip-11|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021082|zip-11|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021083|W08E12.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021083|W08E12.2|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021083|W08E12.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021083|W08E12.2|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021083|W08E12.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021083|W08E12.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021083|W08E12.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12979|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021084|W08E12.3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021084|W08E12.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021084|W08E12.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5338|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021084|W08E12.3|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2381|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021084|W08E12.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11579|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=515|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1735|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021086|W08E12.5|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021087|W08E12.6|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021087|W08E12.6|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|424nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|426nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|428nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|496nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5534|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11670|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=701|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|653nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|657nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|663nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|974nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021088|W08E12.7.1|979nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=640|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021089|W08E12.8b.2|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021090|W08E12.9|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1300|total_reads(98.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021090|W08E12.9|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021092|fbxb-34|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4779|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3733|total_reads(40.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021093|W08F4.3|721nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021094|W08F4.5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021095|mlt-8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021095|mlt-8|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1307|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021096|W08F4.7|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=922|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5161|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=775|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|359nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021097|cdc-37|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021098|fbxb-14|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021098|fbxb-14|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021098|fbxb-14|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021098|fbxb-14|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021098|fbxb-14|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021098|fbxb-14|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021099|W08F4.10|61nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021100|W08F4.11|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=395|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021100|W08F4.11|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021101|W08F4.12|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021103|eri-3|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=255|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021103|eri-3|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=778|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00021103|eri-3|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021104|W09B6.4b.1|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=938|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021104|W09B6.4b.1|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=301|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021104|W09B6.4b.1|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021104|W09B6.4b.1|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021106|W09B7.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021106|W09B7.1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021107|W09B7.2|1408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021107|W09B7.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021107|W09B7.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021107|W09B7.2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=304|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00021107|W09B7.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021107|W09B7.2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021107|W09B7.2|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021109|W09C3.1|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021109|W09C3.1|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021110|W09C3.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021110|W09C3.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021110|W09C3.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=199|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021111|W09C3.3|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021111|W09C3.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021111|W09C3.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021111|W09C3.3|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|1140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=825|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021112|W09C3.4|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=148|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021113|gsp-3|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4413|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021114|W09C3.7|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021114|W09C3.7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021114|W09C3.7|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5036|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021114|W09C3.7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021114|W09C3.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021114|W09C3.7|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021116|ncs-6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1452|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021116|ncs-6|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021117|clec-126|241nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00021117|clec-126|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021117|clec-126|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021117|clec-126|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021117|clec-126|309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021117|clec-126|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021118|clec-125|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021118|clec-125|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021120|W09G12.6|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021120|W09G12.6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021121|W09G12.7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021121|W09G12.7|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021121|W09G12.7|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021121|W09G12.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021121|W09G12.7|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021122|W09G12.8|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|1071nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1538|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021123|W09G12.9|306nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021124|W10C4.1|1070nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00021124|W10C4.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021124|W10C4.1|180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=616|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|1164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|1167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=556|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021125|ccb-2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021126|W10C8.3|297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021127|W10C8.4d|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021127|W10C8.4d|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021127|W10C8.4d|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7323|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1478|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021128|W10C8.5.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021129|W10D9.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021129|W10D9.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021129|W10D9.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021130|W10D9.2|1152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021130|W10D9.2|1158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021131|W10D9.3|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021131|W10D9.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1634|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021131|W10D9.3|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021132|nfyb-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021132|nfyb-1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021132|nfyb-1|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1645|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021132|nfyb-1|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021133|tomm-22|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021133|tomm-22|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7345|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021133|tomm-22|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021133|tomm-22|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021133|tomm-22|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021133|tomm-22|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021134|W10G11.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021135|W10G11.2|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021135|W10G11.2|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021135|W10G11.2|197nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021135|W10G11.2|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021135|W10G11.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021136|W10G11.3|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=441|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021136|W10G11.3|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021137|W10G11.4|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021138|clec-127|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021139|clec-128|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021143|clec-132|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021144|clec-130|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021145|clec-129|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021146|lgc-45|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021148|W10G11.19|1094nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021148|W10G11.19|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021148|W10G11.19|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021148|W10G11.19|961nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|213nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3382|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1397|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021149|dnc-3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021152|mgl-3|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=645|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021152|mgl-3|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021152|mgl-3|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021152|mgl-3|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021153|Y4C6A.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021153|Y4C6A.3|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021153|Y4C6A.3|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1476|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021153|Y4C6A.3|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021153|Y4C6A.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021154|Y4C6A.4|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021154|Y4C6A.4|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021154|Y4C6A.4|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=248|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021155|Y4C6B.1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021155|Y4C6B.1|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1466|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021155|Y4C6B.1|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021155|Y4C6B.1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021155|Y4C6B.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021156|Y4C6B.2a|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021156|Y4C6B.2a|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021156|Y4C6B.2a|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=230|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021156|Y4C6B.2a|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021156|Y4C6B.2a|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021156|Y4C6B.2a|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021156|Y4C6B.2a|732nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021157|Y4C6B.3a|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021157|Y4C6B.3a|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021157|Y4C6B.3a|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021158|Y4C6B.4a|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021158|Y4C6B.4a|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021159|Y4C6B.5|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021159|Y4C6B.5|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021159|Y4C6B.5|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021159|Y4C6B.5|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=519|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021159|Y4C6B.5|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2148|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=876|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021160|gba-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|590nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|592nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=290|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021161|Y4C6B.7a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2092|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021163|nhr-275|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021163|nhr-275|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021163|nhr-275|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021164|Y5H2B.1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021164|Y5H2B.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021165|Y5H2B.3|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021167|cyp-32B1|1287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021167|cyp-32B1|25nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021167|cyp-32B1|33nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=366|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021167|cyp-32B1|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021167|cyp-32B1|83nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021168|cyp-33C12|738nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021168|cyp-33C12|740nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021168|cyp-33C12|747nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2957|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021170|arx-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021171|Y8A9A.2|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021171|Y8A9A.2|1444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021171|Y8A9A.2|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021171|Y8A9A.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021172|Y8A9A.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021175|math-46|1344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021175|math-46|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021175|math-46|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021176|Y9C9A.1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021176|Y9C9A.1|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021176|Y9C9A.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00021177|Y9C9A.5|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021178|Y9C9A.8|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021180|Y9C9A.13|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021180|Y9C9A.13|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021180|Y9C9A.13|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021182|srz-28|1339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021182|srz-28|1393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021182|srz-28|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021182|srz-28|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021182|srz-28|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021182|srz-28|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00021182|srz-28|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021183|Y9C9A.16a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021183|Y9C9A.16a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021183|Y9C9A.16a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021183|Y9C9A.16a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021183|Y9C9A.16a|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=558|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=756|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021185|Y9C12A.1|748nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021186|Y9D1A.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=698|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021187|Y9D1A.2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=715|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021188|Y13C8A.1|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021189|Y13C8A.2|629nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021190|Y14H12A.1|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021190|Y14H12A.1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021190|Y14H12A.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1244|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021190|Y14H12A.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021191|Y14H12B.1a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021191|Y14H12B.1a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021191|Y14H12B.1a|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021191|Y14H12B.1a|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021191|Y14H12B.1a|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2208|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021191|Y14H12B.1a|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2473|total_reads(51.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021191|Y14H12B.1a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021192|Y14H12B.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1723|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021193|math-44|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021195|Y17G9A.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021195|Y17G9A.2|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021195|Y17G9A.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021196|Y17G9A.3|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021196|Y17G9A.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021196|Y17G9A.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021196|Y17G9A.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021197|Y17G9A.4|1192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021197|Y17G9A.4|1196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021197|Y17G9A.4|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021197|Y17G9A.4|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021197|Y17G9A.4|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021197|Y17G9A.4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021198|Y17G9B.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021198|Y17G9B.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021198|Y17G9B.1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021198|Y17G9B.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021199|Y17G9B.2|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=331|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021200|cyp-31A3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021200|cyp-31A3|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021200|cyp-31A3|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=263|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021200|cyp-31A3|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1352|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00021200|cyp-31A3|74nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021201|Y17G9B.4a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1275|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00021201|Y17G9B.4a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021201|Y17G9B.4a|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021201|Y17G9B.4a|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021201|Y17G9B.4a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021201|Y17G9B.4a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021202|Y17G9B.5|1309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021202|Y17G9B.5|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021202|Y17G9B.5|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021202|Y17G9B.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021202|Y17G9B.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021202|Y17G9B.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1558|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021202|Y17G9B.5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021204|fbxb-77|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021204|fbxb-77|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021204|fbxb-77|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021205|Y17G9B.8|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=746|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021205|Y17G9B.8|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021205|Y17G9B.8|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1132|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021205|Y17G9B.8|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2066|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021205|Y17G9B.8|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021205|Y17G9B.8|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=743|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=941|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021206|Y17G9B.9|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021207|Y18H1A.1|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021207|Y18H1A.1|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021207|Y18H1A.1|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021208|Y18H1A.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021208|Y18H1A.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2186|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021208|Y18H1A.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=661|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1177|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00021209|hgap-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021210|Y18H1A.4.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021210|Y18H1A.4.1|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1818|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00021210|Y18H1A.4.1|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021210|Y18H1A.4.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021210|Y18H1A.4.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021210|Y18H1A.4.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021210|Y18H1A.4.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021211|Y18H1A.7b|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021211|Y18H1A.7b|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021211|Y18H1A.7b|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021212|Y18H1A.8a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021212|Y18H1A.8a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021213|Y18H1A.9|247nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021213|Y18H1A.9|251nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021213|Y18H1A.9|257nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=360|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021213|Y18H1A.9|261nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021213|Y18H1A.9|263nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021213|Y18H1A.9|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021214|hasp-2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021214|hasp-2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021214|hasp-2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021215|Y18H1A.11a.2|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=625|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00021215|Y18H1A.11a.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021217|Y19D10A.2|1075nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021217|Y19D10A.2|683nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021217|Y19D10A.2|686nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00021219|Y19D10A.4|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021220|Y19D10A.5|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021220|Y19D10A.5|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021222|irld-53|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021222|irld-53|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00021222|irld-53|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021223|Y19D10A.8|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021223|Y19D10A.8|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021223|Y19D10A.8|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021223|Y19D10A.8|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=396|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021223|Y19D10A.8|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021223|Y19D10A.8|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021224|clec-209|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021224|clec-209|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021224|clec-209|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14093|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021224|clec-209|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021226|Y19D10A.11|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021226|Y19D10A.11|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=111|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|410nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|412nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|414nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1577|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021227|mct-1|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021232|irld-15|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021232|irld-15|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021232|irld-15|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00021235|Y19D10B.6|1458nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021235|Y19D10B.6|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021235|Y19D10B.6|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021235|Y19D10B.6|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021236|pud-1.2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021236|pud-1.2|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|1017nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|282nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|356nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|771nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|809nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021237|crtc-1|950nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021239|Y20F4.4b|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1120|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021239|Y20F4.4b|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021239|Y20F4.4b|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021241|Y22D7AL.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021243|Y22D7AL.3|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021243|Y22D7AL.3|594nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00021243|Y22D7AL.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021245|Y22D7AL.6b|15nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021245|Y22D7AL.6b|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021245|Y22D7AL.6b|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021245|Y22D7AL.6b|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021246|Y22D7AL.7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=284|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021246|Y22D7AL.7|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=714|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021247|Y22D7AL.9|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=235|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021247|Y22D7AL.9|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=651|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4337|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11733|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8193|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021248|Y22D7AL.10.1|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021249|Y22D7AL.11|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021249|Y22D7AL.11|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021249|Y22D7AL.11|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021249|Y22D7AL.11|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021251|Y22D7AL.13|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00021251|Y22D7AL.13|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00021252|cht-4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021253|Y22D7AL.15|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021253|Y22D7AL.15|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021253|Y22D7AL.15|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2251|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021253|Y22D7AL.15|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021253|Y22D7AL.15|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021253|Y22D7AL.15|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021254|Y22D7AL.16|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1681|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021254|Y22D7AL.16|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|1023nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|1392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021257|Y22D7AR.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021259|glb-30|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00021259|glb-30|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021259|glb-30|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021259|glb-30|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021259|glb-30|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021260|Y22D7AR.6.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021260|Y22D7AR.6.2|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021260|Y22D7AR.6.2|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021260|Y22D7AR.6.2|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021261|Y22D7AR.7|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|1530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|583nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|621nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=357|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|626nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|794nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021262|fbxa-74|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021263|Y22D7AR.10|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8814|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021263|Y22D7AR.10|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021263|Y22D7AR.10|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021263|Y22D7AR.10|72nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4094|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021263|Y22D7AR.10|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021264|fbxa-13|1047nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021264|fbxa-13|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021264|fbxa-13|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021264|fbxa-13|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1187|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021264|fbxa-13|663nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021264|fbxa-13|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00021264|fbxa-13|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021266|Y22D7AR.14|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=330|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021267|Y23B4A.1|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1072|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=488|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5032|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35587|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8640|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021268|capa-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=862|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021269|Y23H5A.2a|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021270|Y23H5A.3|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021270|Y23H5A.3|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2353|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021270|Y23H5A.3|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021271|spe-47|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021271|spe-47|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021271|spe-47|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021271|spe-47|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=440|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021271|spe-47|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021271|spe-47|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=408|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=787|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4137|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021272|Y23H5B.1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021274|Y23H5B.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021274|Y23H5B.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021274|Y23H5B.3|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021274|Y23H5B.3|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021275|dmsr-2|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2304|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021275|dmsr-2|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021275|dmsr-2|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021276|Y23H5B.5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021276|Y23H5B.5|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021276|Y23H5B.5|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021276|Y23H5B.5|578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2169|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021276|Y23H5B.5|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021276|Y23H5B.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021277|Y23H5B.6a|115nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021277|Y23H5B.6a|120nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1077|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021277|Y23H5B.6a|125nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=515|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021277|Y23H5B.6a|130nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021277|Y23H5B.6a|1514nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021279|Y23H5B.8|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021279|Y23H5B.8|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021279|Y23H5B.8|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021279|Y23H5B.8|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021279|Y23H5B.8|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|1036nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6099|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|1040nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=888|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|359nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|666nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021281|ell-1|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021282|set-21|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021282|set-21|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021282|set-21|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=880|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19435|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|1243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021286|Y24D9A.8a.2|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|105nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=822|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|117nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021287|Y24D9B.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021288|clec-123|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021288|clec-123|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=360|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021288|clec-123|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021288|clec-123|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021289|Y25C1A.2|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021289|Y25C1A.2|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021292|copb-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021292|copb-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021292|copb-1|293nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5675|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021292|copb-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=623|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021293|Y25C1A.6|499nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021293|Y25C1A.6|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00021293|Y25C1A.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021293|Y25C1A.6|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7b|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7b|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7b|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7b|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7b|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7c.1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7c.1|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7c.1|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3540|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021294|Y25C1A.7c.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=321|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021295|Y25C1A.8b|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=688|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=635|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021296|Y25C1A.13|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021298|Y27F2A.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021298|Y27F2A.6|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021299|Y27F2A.8|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021299|Y27F2A.8|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021299|Y27F2A.8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021300|Y27F2A.9|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021300|Y27F2A.9|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021301|Y32G9A.2b|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021301|Y32G9A.2b|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021301|Y32G9A.2b|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021302|Y32G9A.3a|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021302|Y32G9A.3a|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021303|Y32G9A.5|1295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021303|Y32G9A.5|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021304|nphp-2|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021304|nphp-2|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021304|nphp-2|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021304|nphp-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|378nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|692nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2332|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1855|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|820nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|822nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|831nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|905nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|928nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|941nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021305|oig-6|947nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021309|Y32G9B.1e|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=709|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021309|Y32G9B.1e|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021310|Y32H12A.1|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021310|Y32H12A.1|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021310|Y32H12A.1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00021310|Y32H12A.1|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|370nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021311|Y32H12A.2a.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1174|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4280|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2788|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=322|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021312|szy-2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021313|paqr-2|260nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021313|paqr-2|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021313|paqr-2|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021313|paqr-2|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2208|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021313|paqr-2|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021314|Y32H12A.6|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1920|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00021314|Y32H12A.6|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021314|Y32H12A.6|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021314|Y32H12A.6|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2473|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021315|Y32H12A.7.1|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021316|Y32H12A.8|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021316|Y32H12A.8|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021316|Y32H12A.8|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021316|Y32H12A.8|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1139|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021316|Y32H12A.8|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00021316|Y32H12A.8|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=172|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021317|Y32H12A.9|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021319|Y34B4A.2|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021319|Y34B4A.2|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021319|Y34B4A.2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021319|Y34B4A.2|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=880|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021319|Y34B4A.2|99nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021320|Y34B4A.4a|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021320|Y34B4A.4a|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=280|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021320|Y34B4A.4a|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=241|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021320|Y34B4A.4a|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021320|Y34B4A.4a|224nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021320|Y34B4A.4a|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021321|Y34B4A.5|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021321|Y34B4A.5|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021321|Y34B4A.5|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14395|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021322|Y34B4A.6|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=997|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=215|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=935|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021323|Y34B4A.7.1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|424nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|536nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=289|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|538nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|541nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=485|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|547nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=385|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021324|Y34B4A.8a|550nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021325|Y34B4A.9|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021325|Y34B4A.9|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2925|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021325|Y34B4A.9|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4101|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021325|Y34B4A.9|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021325|Y34B4A.9|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021325|Y34B4A.9|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021326|Y34B4A.10.2|133nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021326|Y34B4A.10.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1458|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021326|Y34B4A.10.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021326|Y34B4A.10.2|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021326|Y34B4A.10.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3569|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021327|mrpl-38|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=611|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021328|npr-23|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021328|npr-23|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021328|npr-23|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021328|npr-23|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=841|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021328|npr-23|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021328|npr-23|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021328|npr-23|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=519|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=738|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=225|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021329|Y34D9A.3a|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=157|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=273|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=736|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8542|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021331|glrx-10|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|1410nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00021332|Y34D9A.7a|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|1399nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|1401nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5591|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=460|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021333|Y34D9A.8c|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1174|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00021334|vps-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021335|spp-23|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021335|spp-23|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021335|spp-23|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=862|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021336|Y34F4.1b|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=660|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021337|Y34F4.2a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021337|Y34F4.2a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021337|Y34F4.2a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021337|Y34F4.2a|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021337|Y34F4.2a|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021337|Y34F4.2a|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021337|Y34F4.2a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021339|Y34F4.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(66%)
- ID=WBGene00021339|Y34F4.4|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00021339|Y34F4.4|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021340|Y34F4.5a|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021340|Y34F4.5a|21nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021340|Y34F4.5a|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3616|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021340|Y34F4.5a|32nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021340|Y34F4.5a|47nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021340|Y34F4.5a|51nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021340|Y34F4.5a|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021343|cutl-23|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1494|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00021343|cutl-23|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021343|cutl-23|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021344|Y37B11A.2b|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021344|Y37B11A.2b|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021344|Y37B11A.2b|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=282|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021345|Y37B11A.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021345|Y37B11A.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2999|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00021345|Y37B11A.3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021345|Y37B11A.3|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021346|Y37E3.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021346|Y37E3.1|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5197|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5932|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=323|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021347|rpb-10|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8118|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|488nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1495|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=338|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021348|moag-4|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1064nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1079nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1081nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1091nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1099nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|1516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|403nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|463nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2208|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|747nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021349|arl-13|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28948|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110474|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5727|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021350|Y37E3.8b.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|245nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|255nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|517nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6170|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|852nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021351|Y37E3.10a|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1117|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=603|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2640|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11a|763nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11g.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021352|Y37E3.11g.2|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=228|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=764|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021353|iglr-3|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021354|fpn-1.1|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021354|fpn-1.1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021354|fpn-1.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021354|fpn-1.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021354|fpn-1.1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021354|fpn-1.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021354|fpn-1.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021355|Y37E3.17a|1111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021355|Y37E3.17a|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021355|Y37E3.17a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10576|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00021355|Y37E3.17a|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021355|Y37E3.17a|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=612|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|536nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|708nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|791nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|923nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021357|Y37E11AL.1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021358|Y37E11AL.2a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021358|Y37E11AL.2a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1298|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021358|Y37E11AL.2a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|1370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3722|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3a.2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3b|1334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3b|1431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3b|1435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3b|1445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3b|1455nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021359|Y37E11AL.3b|1530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021362|Y37E11AL.6c|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021362|Y37E11AL.6c|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021362|Y37E11AL.6c|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021362|Y37E11AL.6c|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00021363|taf-6.2|1179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021363|taf-6.2|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=477|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021363|taf-6.2|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021363|taf-6.2|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021363|taf-6.2|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=708|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021363|taf-6.2|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=384|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021363|taf-6.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021364|Y37E11AL.9|1506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021364|Y37E11AL.9|1518nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021364|Y37E11AL.9|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021365|smgl-2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021365|smgl-2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021365|smgl-2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1137|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021365|smgl-2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=280|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1585|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021366|Y37E11AM.2a.1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2090|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|818nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021367|Y37E11AM.3c|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021368|best-20|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021368|best-20|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00021368|best-20|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021368|best-20|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021369|siah-1|342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021369|siah-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021369|siah-1|511nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3131|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021369|siah-1|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021369|siah-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021369|siah-1|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021370|nape-2|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021370|nape-2|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1709|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021371|nape-1|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021371|nape-1|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=621|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021371|nape-1|88nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021371|nape-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|679nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|773nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021372|ugt-45|937nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021373|Y37E11AR.7|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021374|Y37E11B.1b|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021374|Y37E11B.1b|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021374|Y37E11B.1b|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021374|Y37E11B.1b|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1576|total_reads(57.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021374|Y37E11B.1b|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=927|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021374|Y37E11B.1b|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|241nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=541|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021375|Y37E11B.2.2|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=316|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|1562nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021376|Y37E11B.3b|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1023|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021377|Y37E11B.5|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021377|Y37E11B.5|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021377|Y37E11B.5|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021377|Y37E11B.5|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021377|Y37E11B.5|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=677|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021377|Y37E11B.5|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021377|Y37E11B.5|310nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021378|Y37E11B.6|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021378|Y37E11B.6|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3641|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021379|Y37E11B.7b|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021379|Y37E11B.7b|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021379|Y37E11B.7b|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021379|Y37E11B.7b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021381|Y37E11B.10a|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=934|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021381|Y37E11B.10a|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021381|Y37E11B.10a|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4013|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021382|Y37F4.1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1006nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1066nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1068nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1093nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|1551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|547nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11107|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|551nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|703nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|900nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=493|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|905nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=186|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|932nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|945nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|953nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|968nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021383|Y37F4.2|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021384|Y37F4.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021386|Y37F4.5.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021386|Y37F4.5.1|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021387|Y37F4.6a|1221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021387|Y37F4.6a|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021387|Y37F4.6a|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=631|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021387|Y37F4.6a|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021387|Y37F4.6a|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021388|Y37F4.7|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=916|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021388|Y37F4.7|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021389|Y38A10A.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021389|Y38A10A.2|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021390|fbxa-214|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=764|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=230|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=166|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|758nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021391|smut-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=503|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1081|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|1081nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=477|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|195nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|200nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021392|Y38A10A.7|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|364nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|366nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|373nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|392nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=826|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=847|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021394|Y38C1AA.1d|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|1466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|397nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|654nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4972|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021395|pnc-1|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021396|cutl-24|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021396|cutl-24|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=340|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00021396|cutl-24|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021397|Y38C1AA.6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021397|Y38C1AA.6|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021397|Y38C1AA.6|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021397|Y38C1AA.6|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021397|Y38C1AA.6|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021397|Y38C1AA.6|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1831|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10697|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3831|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021398|Y38C1AA.7|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021400|Y38C1AA.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021400|Y38C1AA.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021400|Y38C1AA.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=911|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021400|Y38C1AA.9|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021400|Y38C1AA.9|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021401|prdx-6|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021401|prdx-6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021401|prdx-6|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021401|prdx-6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021401|prdx-6|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3619|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00021401|prdx-6|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021401|prdx-6|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021402|Y38C1AA.12a|669nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021402|Y38C1AA.12a|679nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=185|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021402|Y38C1AA.12a|681nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1286|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021402|Y38C1AA.12a|683nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021403|Y38C1AB.1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021403|Y38C1AB.1|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021403|Y38C1AB.1|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021403|Y38C1AB.1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021404|trpl-3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021404|trpl-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|424nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|429nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021406|frm-5.2|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021409|Y38C1AB.7|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021412|cyp-29A3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021412|cyp-29A3|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021412|cyp-29A3|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021412|cyp-29A3|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021412|cyp-29A3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|112nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|220nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=219|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021415|nsy-4|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021416|mksr-2|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021416|mksr-2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021416|mksr-2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00021416|mksr-2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021416|mksr-2|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021417|nhr-236|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00021417|nhr-236|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=423|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021417|nhr-236|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021417|nhr-236|645nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|1395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021419|eri-5|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=533|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13959|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1055|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|332nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|334nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021420|trap-3|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1960|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|1409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|355nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021421|Y38F2AR.3a|401nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021423|tftc-1|1097nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1598|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021423|tftc-1|1106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021423|tftc-1|1501nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021423|tftc-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021423|tftc-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021425|ppgn-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021425|ppgn-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021425|ppgn-1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1316|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|1545nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1007|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17123|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3970|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021427|Y38F2AR.9|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021428|Y38F2AR.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021428|Y38F2AR.10|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021428|Y38F2AR.10|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021430|Y38F2AR.12b|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021430|Y38F2AR.12b|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021433|Y39A3A.2|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021434|Y39A3A.3|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021434|Y39A3A.3|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021435|Y39A3A.4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021435|Y39A3A.4|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021435|Y39A3A.4|774nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021436|Y39A3B.1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021436|Y39A3B.1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021436|Y39A3B.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(86.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021437|lgc-42|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021437|lgc-42|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021437|lgc-42|831nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021437|lgc-42|836nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=456|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021437|lgc-42|838nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021438|Y39A3B.3|981nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021438|Y39A3B.3|984nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021438|Y39A3B.3|987nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021438|Y39A3B.3|992nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021439|ckr-2|1398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1368|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021439|ckr-2|1405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021439|ckr-2|1410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021439|ckr-2|1461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021439|ckr-2|1463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021439|ckr-2|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021440|Y39A3CL.1|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021440|Y39A3CL.1|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021440|Y39A3CL.1|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1499|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021440|Y39A3CL.1|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021441|Y39A3CL.3|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021441|Y39A3CL.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021441|Y39A3CL.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2701|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021441|Y39A3CL.3|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3727|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00021442|Y39A3CL.4c|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1735|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021442|Y39A3CL.4c|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021442|Y39A3CL.4c|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021443|Y39A3CL.7a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021443|Y39A3CL.7a|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021443|Y39A3CL.7a|497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1719|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021443|Y39A3CL.7a|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021443|Y39A3CL.7a|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|1019nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|131nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|874nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|881nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|885nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=345|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|889nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021444|ttc-7|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021445|Y39A3CR.5|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021445|Y39A3CR.5|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021445|Y39A3CR.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021445|Y39A3CR.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021446|hlh-33|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021447|Y39A3CR.8b|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021447|Y39A3CR.8b|583nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021448|Y39D8A.1d|336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021448|Y39D8A.1d|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021448|Y39D8A.1d|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(69.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021448|Y39D8A.1d|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021448|Y39D8A.1d|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021449|mltn-7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021450|mltn-6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021452|Y39F10A.1|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021452|Y39F10A.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=889|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021452|Y39F10A.1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00021454|Y39F10A.3|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021454|Y39F10A.3|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|1320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2676|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=371|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|725nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021456|Y39F10B.1a|757nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021458|Y39G10AL.1a|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00021458|Y39G10AL.1a|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021458|Y39G10AL.1a|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021458|Y39G10AL.1a|720nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021458|Y39G10AL.1a|722nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021458|Y39G10AL.1a|727nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021460|zwl-1|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2123|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021460|zwl-1|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1204|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021460|zwl-1|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021460|zwl-1|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021460|zwl-1|409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021460|zwl-1|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021461|nekl-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021461|nekl-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021463|zeel-1|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021463|zeel-1|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021464|ugt-31|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=381|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021464|ugt-31|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021464|ugt-31|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021464|ugt-31|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021464|ugt-31|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021464|ugt-31|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=987|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00021465|ekl-7|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021465|ekl-7|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021465|ekl-7|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021465|ekl-7|365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2006|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021465|ekl-7|424nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|227nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|232nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9846|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|235nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2764|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=254|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021466|Y39G10AR.8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|201nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2615|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021467|Y39G10AR.9a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021468|epg-2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021468|epg-2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021468|epg-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021468|epg-2|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1361|total_reads(67.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021468|epg-2|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|1084nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|1109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|720nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1732|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|725nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1083|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|729nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|732nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021469|Y39G10AR.11.2|903nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|296nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|302nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=130|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|431nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=155|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|433nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1111|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|44nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|553nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|558nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|561nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021470|tpxl-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021471|Y39G10AR.15|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021471|Y39G10AR.15|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021471|Y39G10AR.15|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021472|Y39G10AR.16|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021472|Y39G10AR.16|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=184|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00021472|Y39G10AR.16|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021472|Y39G10AR.16|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021474|dot-1.1|1196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021474|dot-1.1|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021474|dot-1.1|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021474|dot-1.1|1362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021474|dot-1.1|1584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00021474|dot-1.1|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=868|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1465|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=560|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1782|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=322|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=484|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021475|tbca-1|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021476|nsun-4|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021476|nsun-4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021476|nsun-4|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021476|nsun-4|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1108|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00021476|nsun-4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021476|nsun-4|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021477|srbc-64|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021477|srbc-64|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021478|Y39H10A.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021478|Y39H10A.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021478|Y39H10A.1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021479|oac-55|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00021479|oac-55|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|799nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=400|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=289|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021482|Y39H10A.6|897nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44716|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13144|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3556|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021486|lbp-9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021487|comt-3|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021487|comt-3|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021490|Y40B10A.5c|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021490|Y40B10A.5c|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021490|Y40B10A.5c|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021491|comt-4|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021491|comt-4|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021491|comt-4|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021492|comt-5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021492|comt-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021492|comt-5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021492|comt-5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|124nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|1549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=685|total_reads(78.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021493|Y40B10A.9b|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021494|Y40B10B.1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00021494|Y40B10B.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021494|Y40B10B.1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|771nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|776nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021495|sqst-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021496|Y40C5A.3i|295nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021497|Y40C5A.4b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1762|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021497|Y40C5A.4d|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021500|Y40C7B.4|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021500|Y40C7B.4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021500|Y40C7B.4|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021500|Y40C7B.4|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021502|Y40D12A.1a|194nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021502|Y40D12A.1a|197nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=742|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021502|Y40D12A.1a|201nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021502|Y40D12A.1a|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021502|Y40D12A.1a|300nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1280|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021503|ctsa-2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00021504|Y41D4A.1|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021504|Y41D4A.1|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021504|Y41D4A.1|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=119|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021505|Y41D4A.3|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021505|Y41D4A.3|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021505|Y41D4A.3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021505|Y41D4A.3|194nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021505|Y41D4A.3|202nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=130|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00021505|Y41D4A.3|204nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021505|Y41D4A.3|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|204nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=658|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3954|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2315|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|395nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|399nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|653nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4c.2|662nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4e|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4e|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021506|Y41D4A.4e|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|298nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|300nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1586|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|637nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|639nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|645nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021508|Y41D4A.6f|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|1011nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|1032nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|1038nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|1057nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|1113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|747nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|751nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|753nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|757nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|759nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=269|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|761nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|763nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|879nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|884nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|888nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021509|Y41D4A.7b|892nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021510|frpr-19|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021510|frpr-19|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021510|frpr-19|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=539|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021511|Y41D4B.1|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021511|Y41D4B.1|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021512|Y41D4B.4a|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021512|Y41D4B.4a|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=525|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021512|Y41D4B.4a|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021512|Y41D4B.4a|819nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=711|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021513|Y41D4B.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021513|Y41D4B.6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021514|Y41D4B.11a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021514|Y41D4B.11a|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021514|Y41D4B.11a|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021514|Y41D4B.11a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021514|Y41D4B.11a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021514|Y41D4B.11a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1121|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021514|Y41D4B.11a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=963|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|1424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|1426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=923|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021515|set-23|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021516|Y41D4B.14|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021516|Y41D4B.14|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021517|Y41D4B.15|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00021517|Y41D4B.15|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021517|Y41D4B.15|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00021517|Y41D4B.15|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021517|Y41D4B.15|515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021517|Y41D4B.15|550nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021517|Y41D4B.15|583nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00021518|hpo-6|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021518|hpo-6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021518|hpo-6|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2050|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00021519|Y41D4B.17|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021519|Y41D4B.17|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021519|Y41D4B.17|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021519|Y41D4B.17|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021521|nhr-287|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021521|nhr-287|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021521|nhr-287|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=373|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021521|nhr-287|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021521|nhr-287|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|1431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|1437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=785|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|784nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|795nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|809nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021522|nhr-274|812nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021524|Y41D4B.24|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021524|Y41D4B.24|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021524|Y41D4B.24|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021525|Y41D4B.26|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021525|Y41D4B.26|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00021525|Y41D4B.26|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021526|Y41G9A.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021526|Y41G9A.2|1241nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021526|Y41G9A.2|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=335|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021526|Y41G9A.2|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021527|aakg-3|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021527|aakg-3|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=461|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021527|aakg-3|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021527|aakg-3|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021527|aakg-3|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021528|gbb-1|1327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021528|gbb-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021528|gbb-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021528|gbb-1|486nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=183|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021528|gbb-1|499nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1493|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021528|gbb-1|692nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021529|Y41G9A.5a|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021529|Y41G9A.5a|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021529|Y41G9A.5a|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021529|Y41G9A.5a|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021529|Y41G9A.5a|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021529|Y41G9A.5a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021529|Y41G9A.5a|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021530|Y41G9A.6|968nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021531|Y42G9A.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021532|Y42G9A.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021532|Y42G9A.2|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=813|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021532|Y42G9A.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021533|Y42G9A.3a|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021533|Y42G9A.3a|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021533|Y42G9A.3a|1054nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021533|Y42G9A.3a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=664|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021533|Y42G9A.3a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021533|Y42G9A.3a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021533|Y42G9A.3a|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|1164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|1170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|1258nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=370|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|522nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|532nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1997|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|543nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2293|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|757nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|787nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|806nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|808nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=672|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021534|mvk-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021535|wht-7|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021535|wht-7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021535|wht-7|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=832|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021535|wht-7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021535|wht-7|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021535|wht-7|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021535|wht-7|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2030|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021536|Y42H9AR.1.3|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021537|Y42H9AR.2|1355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021537|Y42H9AR.2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021537|Y42H9AR.2|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021537|Y42H9AR.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021537|Y42H9AR.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021537|Y42H9AR.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1523|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021538|rabs-5|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|438nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=985|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=525|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|535nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=594|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021539|Y42H9AR.4|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021540|Y42H9AR.5|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021540|Y42H9AR.5|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=653|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021540|Y42H9AR.5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021540|Y42H9AR.5|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021540|Y42H9AR.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021540|Y42H9AR.5|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3637|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021541|Y42H9B.3|379nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021542|Y43B11AL.1|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021542|Y43B11AL.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021542|Y43B11AL.1|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6965|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=340|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021543|Y43B11AR.1|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|197nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=667|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021544|Y43B11AR.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021545|Y43H11AL.1e.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021545|Y43H11AL.1e.2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021545|Y43H11AL.1e.2|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3154|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021545|Y43H11AL.1e.2|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021545|Y43H11AL.1e.2|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021545|Y43H11AL.1e.2|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021545|Y43H11AL.1e.2|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|1205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|1486nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|517nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|522nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|543nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|549nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|561nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1921|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021546|laat-1|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2597|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|355nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021547|Y44E3A.1a|428nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021548|trx-4|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021548|trx-4|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021548|trx-4|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021548|trx-4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8210|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021548|trx-4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1257|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00021548|trx-4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021548|trx-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|1017nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=968|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|1030nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|1058nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|579nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|669nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|972nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021549|Y44E3A.4|978nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=378|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|310nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=299|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2053|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=150|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2099|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=116|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|620nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021551|Y44E3A.6b|663nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2600|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|301nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021552|zip-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021553|tyr-5|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021553|tyr-5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021553|tyr-5|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021553|tyr-5|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=270|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2822|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|314nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021554|Y45G5AL.1a|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021555|Y45G5AM.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=502|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021555|Y45G5AM.2|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021555|Y45G5AM.2|386nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021556|Y45G5AM.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021556|Y45G5AM.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021556|Y45G5AM.3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9007|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021556|Y45G5AM.3|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021556|Y45G5AM.3|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021556|Y45G5AM.3|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021557|Y45G5AM.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1246|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021558|Y45G5AM.6|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=603|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1248|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021559|Y45G5AM.7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|1269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|1301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=685|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|309nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|694nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|858nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021560|coh-4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021561|Y45G5AM.9c|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021561|Y45G5AM.9c|252nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1514|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021561|Y45G5AM.9c|258nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021561|Y45G5AM.9c|261nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021561|Y45G5AM.9c|328nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021561|Y45G5AM.9c|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|1184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|243nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=606|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1576|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2932|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2988|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021562|nuo-5|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1531|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=368|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021563|Y45G12B.2a|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021564|Y45G12B.3|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=279|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021564|Y45G12B.3|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021564|Y45G12B.3|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021565|Y45G12C.1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=201|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00021565|Y45G12C.1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021565|Y45G12C.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021565|Y45G12C.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021567|Y45G12C.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021567|Y45G12C.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021573|Y45G12C.10|1379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021573|Y45G12C.10|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021573|Y45G12C.10|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021574|Y45G12C.11|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021576|fbxc-51|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(72.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021576|fbxc-51|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021576|fbxc-51|1318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021576|fbxc-51|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021577|Y46B2A.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021577|Y46B2A.2|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|55nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00021579|clec-73|67nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=382|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021580|clec-174|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021580|clec-174|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021581|clec-70|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021581|clec-70|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021581|clec-70|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021582|clec-71|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021583|clec-72|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021583|clec-72|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021585|clec-74|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(36.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021585|clec-74|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021586|clec-75|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021586|clec-75|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021586|clec-75|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021586|clec-75|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021586|clec-75|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021586|clec-75|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021586|clec-75|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021587|clec-76|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021587|clec-76|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021589|Y46D2A.1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021589|Y46D2A.1|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=124|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021589|Y46D2A.1|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021589|Y46D2A.1|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021590|Y46D2A.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021590|Y46D2A.2|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021590|Y46D2A.2|156nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021590|Y46D2A.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021590|Y46D2A.2|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021590|Y46D2A.2|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1077|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021594|tig-3|1056nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021594|tig-3|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021594|tig-3|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021594|tig-3|456nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021595|Y46E12BL.2a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021595|Y46E12BL.2a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021595|Y46E12BL.2a|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1108|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021595|Y46E12BL.2a|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021595|Y46E12BL.2a|200nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021595|Y46E12BL.2a|209nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021595|Y46E12BL.2a|54nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3329|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021596|spsb-2|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|1277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|1299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|1305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6792|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|1309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|1325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=344|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|1351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021597|spsb-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021598|Y46E12BR.1|443nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=416|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=850|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=391|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021599|srt-42|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=383|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021600|Y46H3A.4b|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021601|Y46H3A.5b.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|456nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021602|clec-205|522nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021603|clec-204|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021603|clec-204|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021603|clec-204|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021603|clec-204|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021605|Y46H3C.5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021605|Y46H3C.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021605|Y46H3C.5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021605|Y46H3C.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1158|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=483|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|184nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021608|Y46H3D.1|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021609|irld-17|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021610|nhr-237|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00021610|nhr-237|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021610|nhr-237|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021610|nhr-237|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021611|nhr-238|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021611|nhr-238|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=665|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021612|Y46H3D.8|586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021613|Y47A7.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021613|Y47A7.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021613|Y47A7.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021613|Y47A7.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=441|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021613|Y47A7.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021613|Y47A7.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021613|Y47A7.1|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021614|Y47A7.2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021614|Y47A7.2|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021614|Y47A7.2|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1455|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021614|Y47A7.2|827nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021614|Y47A7.2|833nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021614|Y47A7.2|836nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021614|Y47A7.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021616|Y47D7A.2|355nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021616|Y47D7A.2|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021619|Y47D7A.6|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021619|Y47D7A.6|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021620|Y47D7A.7|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021620|Y47D7A.7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021620|Y47D7A.7|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021621|Y47D7A.9|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021623|Y47D7A.11|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021623|Y47D7A.11|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021623|Y47D7A.11|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021624|Y47D7A.12|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021624|Y47D7A.12|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021624|Y47D7A.12|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021625|Y47D7A.13|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7192|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021625|Y47D7A.13|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=545|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00021625|Y47D7A.13|272nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021625|Y47D7A.13|91nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=71|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021625|Y47D7A.13|95nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=861|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=602|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021626|rft-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021627|Y47D7A.15|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021627|Y47D7A.15|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021627|Y47D7A.15|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2043|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021627|Y47D7A.15|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021627|Y47D7A.15|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=768|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3833|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|286nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021628|Y47D9A.1a|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021629|scpl-3|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021629|scpl-3|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2031|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021629|scpl-3|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021629|scpl-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021629|scpl-3|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021630|Y47D9A.3|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021630|Y47D9A.3|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021630|Y47D9A.3|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021630|Y47D9A.3|537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021631|Y47D9A.4|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021631|Y47D9A.4|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021631|Y47D9A.4|650nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021631|Y47D9A.4|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021632|Y47D9A.5.2|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021632|Y47D9A.5.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021632|Y47D9A.5.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021633|Y47G6A.3|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021633|Y47G6A.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021633|Y47G6A.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021634|rde-10|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021634|rde-10|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021634|rde-10|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1470|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021634|rde-10|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021634|rde-10|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021634|rde-10|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|669nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|671nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=165|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|673nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021635|Y47G6A.5a|677nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=398|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=627|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021636|pcaf-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|108nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1940|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|262nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|352nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|424nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|431nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021637|Y47G6A.7a.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021638|Y47G6A.9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021638|Y47G6A.9|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021638|Y47G6A.9|365nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021638|Y47G6A.9|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021638|Y47G6A.9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021638|Y47G6A.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=383|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021638|Y47G6A.9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1370|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021639|Y47G6A.13|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021639|Y47G6A.13|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021639|Y47G6A.13|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021639|Y47G6A.13|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021639|Y47G6A.13|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=397|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|58nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|67nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=30|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|71nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021640|Y47G6A.14|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19990|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=993|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1897|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|519nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=911|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|749nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|762nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021641|Y47G6A.15|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021643|ccep-290|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021643|ccep-290|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021643|ccep-290|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021643|ccep-290|60nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1047nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=86|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1205nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2664|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1297nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1299nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2460|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1320nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|1349nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|940nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021644|Y47G6A.18|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1345|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=246|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021646|Y47G6A.21|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021647|Y47G6A.22|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021647|Y47G6A.22|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021647|Y47G6A.22|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021647|Y47G6A.22|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021647|Y47G6A.22|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4060|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021647|Y47G6A.22|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1127|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021648|mis-12|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021648|mis-12|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021648|mis-12|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021648|mis-12|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021648|mis-12|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1228|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021648|mis-12|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|1316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=645|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=372|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021649|Y47G6A.25|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021650|Y47G6A.26|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00021650|Y47G6A.26|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021650|Y47G6A.26|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021650|Y47G6A.26|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021650|Y47G6A.26|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021650|Y47G6A.26|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|687nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|694nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|696nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|720nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=614|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|730nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|766nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|771nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|781nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|813nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021653|Y47G6A.30|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021654|Y47G7B.2|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021654|Y47G7B.2|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021654|Y47G7B.2|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=154|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021654|Y47G7B.2|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|111nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|113nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=114|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=896|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021655|Y48A5A.1.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021656|Y48D7A.1|1553nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021657|Y48G1A.1|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021657|Y48G1A.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021657|Y48G1A.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021657|Y48G1A.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021657|Y48G1A.1|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021657|Y48G1A.1|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021658|Y48G1A.2|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021658|Y48G1A.2|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021658|Y48G1A.2|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=574|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021658|Y48G1A.2|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2458|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021658|Y48G1A.2|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021658|Y48G1A.2|233nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021658|Y48G1A.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021660|Y48G1A.4|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1041|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021660|Y48G1A.4|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=131|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021660|Y48G1A.4|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021660|Y48G1A.4|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021660|Y48G1A.4|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=265|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021661|mbtr-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021662|snpc-3.3|1413nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021662|snpc-3.3|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021662|snpc-3.3|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=227|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00021662|snpc-3.3|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00021662|snpc-3.3|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021666|Y48G1BL.7|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00021666|Y48G1BL.7|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00021666|Y48G1BL.7|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00021667|snpc-3.2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=493|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021667|snpc-3.2|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021671|Y48G1BM.6|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021672|Y48G1BM.7|1018nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021672|Y48G1BM.7|1021nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021675|Y48G1BR.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021675|Y48G1BR.1|436nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021675|Y48G1BR.1|440nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=311|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021675|Y48G1BR.1|470nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021675|Y48G1BR.1|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=897|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021676|Y48G1C.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021677|pgs-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021677|pgs-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021677|pgs-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1246|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021677|pgs-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021678|Y48G1C.5|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(71.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021678|Y48G1C.5|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021678|Y48G1C.5|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021679|Y48G1C.6|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021679|Y48G1C.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=355|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021679|Y48G1C.6|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021679|Y48G1C.6|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021681|Y48G1C.8a|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021681|Y48G1C.8a|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2338|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00021681|Y48G1C.8a|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021681|Y48G1C.8a|359nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021681|Y48G1C.8a|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021682|Y48G1C.9.1|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021682|Y48G1C.9.1|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4107|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021682|Y48G1C.9.1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|616nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|683nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|694nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=473|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021683|Y48G1C.10c|698nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1747|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|216nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021685|herc-1|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|378nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1596|total_reads(76.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021686|Y48G8AL.5a|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021687|Y48G8AL.7|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021687|Y48G8AL.7|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021689|Y48G8AL.10e|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021689|Y48G8AL.10e|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021689|Y48G8AL.10e|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=773|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=760|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23739|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021690|Y48G8AL.12|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6163|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=806|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=315|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021691|Y48G8AL.13b.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|105nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=260|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=828|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021692|Y48G8AL.15|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021693|Y48G8AR.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021693|Y48G8AR.2|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021693|Y48G8AR.2|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=823|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021694|Y48G8AR.3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021694|Y48G8AR.3|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=647|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3057|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021697|gcn-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021698|frl-1|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1113|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021698|frl-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021700|Y48G9A.6|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021701|Y48G9A.7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021701|Y48G9A.7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021701|Y48G9A.7|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021702|Y48G9A.9a|240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021702|Y48G9A.9a|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2791|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021702|Y48G9A.9a|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021702|Y48G9A.9a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021702|Y48G9A.9a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021703|cpt-3|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021703|cpt-3|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021704|Y48G9A.11|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021704|Y48G9A.11|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=553|total_reads(79.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021704|Y48G9A.11|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021706|srbc-39|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021709|ugt-29|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021709|ugt-29|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1441|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021709|ugt-29|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021710|cyp-33C11|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=84|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021710|cyp-33C11|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021711|wago-11|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021713|Y49F6A.5|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=499|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1270nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1276nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021714|cyh-1|628nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021715|Y49F6B.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021715|Y49F6B.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1064|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021715|Y49F6B.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021715|Y49F6B.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021716|fbxb-112|1029nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021716|fbxb-112|1033nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021716|fbxb-112|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00021717|sdz-32|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021717|sdz-32|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021718|Y49F6B.6|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021719|fbxb-104|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021720|Y49F6B.8|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|105nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=348|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021721|Y49F6B.9b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021725|bath-9|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021725|bath-9|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021725|bath-9|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021726|bath-10|107nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021726|bath-10|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021726|bath-10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021726|bath-10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021727|bath-23|1090nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00021727|bath-23|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021727|bath-23|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00021727|bath-23|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021728|Y49F6C.6|540nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=334|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021730|Y49F6C.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021731|Y49G5A.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021731|Y49G5A.1|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021731|Y49G5A.1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021731|Y49G5A.1|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021731|Y49G5A.1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021731|Y49G5A.1|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021731|Y49G5A.1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021732|Y49G5B.1.2|718nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021732|Y49G5B.1.2|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021732|Y49G5B.1.2|788nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021732|Y49G5B.1.2|798nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1745|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021732|Y49G5B.1.2|801nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021732|Y49G5B.1.2|805nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021733|otub-2|351nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021733|otub-2|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021733|otub-2|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021733|otub-2|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021733|otub-2|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1319|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021733|otub-2|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021733|otub-2|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|308nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021734|Y50C1A.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=322|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=464|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021735|Y50D4A.1a|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021736|wrb-1|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021736|wrb-1|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021736|wrb-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=663|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021736|wrb-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=570|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021738|Y50D4A.4b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021738|Y50D4A.4b|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1324|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021738|Y50D4A.4b|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021738|Y50D4A.4b|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021739|Y50D4A.5|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021739|Y50D4A.5|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1286|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021739|Y50D4A.5|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021739|Y50D4A.5|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021739|Y50D4A.5|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021740|Y50D4B.1a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021740|Y50D4B.1a|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021740|Y50D4B.1a|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1695|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021740|Y50D4B.1a|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021741|Y50D4B.2b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021741|Y50D4B.2b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021743|Y50D4B.4a|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021745|Y50D4B.6|1046nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021745|Y50D4B.6|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00021745|Y50D4B.6|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021745|Y50D4B.6|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=303|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021748|Y50D4C.3b|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|1498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=276|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|1501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|1557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1094|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|1560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=361|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|1563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021749|Y50D4C.5b|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021750|Y50D4C.6a|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1187|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021750|Y50D4C.6a|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021751|Y50D7A.1|1588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021751|Y50D7A.1|610nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(70.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021752|xpd-1|1125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021752|xpd-1|1127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=884|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021752|xpd-1|1136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021752|xpd-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021753|Y50D7A.3a|493nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1442|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021753|Y50D7A.3a|497nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=306|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00021753|Y50D7A.3a|505nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1283|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021753|Y50D7A.3a|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021753|Y50D7A.3b|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021753|Y50D7A.3b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|1002nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3731|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|1118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|1366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|922nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=131|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|924nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021754|hpo-29|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021755|hpo-38|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021755|hpo-38|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021755|hpo-38|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021755|hpo-38|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021755|hpo-38|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021757|taco-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021757|taco-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021757|taco-1|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00021757|taco-1|260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00021757|taco-1|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021757|taco-1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021758|Y50D7A.10|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3610|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021758|Y50D7A.10|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021758|Y50D7A.10|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6728|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021763|Y51F10.2a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|554nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|562nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|570nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|572nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=642|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|660nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=687|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=457|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021764|Y51F10.3a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1002|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021765|Y51F10.4a|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021766|hex-4|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021766|hex-4|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021766|hex-4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021766|hex-4|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1613|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021766|hex-4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021766|hex-4|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5710|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9386|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1394|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|508nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021768|Y51F10.7|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|1106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5540|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=267|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021771|Y51F10.10e|33nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021772|math-45|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021772|math-45|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021772|math-45|581nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021772|math-45|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021773|fbxb-42|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021773|fbxb-42|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021773|fbxb-42|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021774|fbxb-43|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021774|fbxb-43|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021776|Y51H7BR.4a|821nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2502|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021776|Y51H7BR.4a|830nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021778|Y51H7BR.7|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021778|Y51H7BR.7|1427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021778|Y51H7BR.7|1432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021778|Y51H7BR.7|1435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021778|Y51H7BR.7|1450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021779|Y51H7C.1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021779|Y51H7C.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021779|Y51H7C.1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=851|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021779|Y51H7C.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021780|scl-17|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1005|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=505|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021781|Y51H7C.3|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1217|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1042|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021783|Y51H7C.5.1|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2309|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021784|cogc-4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=398|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=438|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1349|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=159|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021785|Y51H7C.7|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021786|Y51H7C.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021787|Y51H7C.9|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00021787|Y51H7C.9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021787|Y51H7C.9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021787|Y51H7C.9|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021787|Y51H7C.9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021787|Y51H7C.9|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021788|Y51H7C.10|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021789|nol-6|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021789|nol-6|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1014|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021789|nol-6|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021789|nol-6|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021789|nol-6|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021790|Y51H7C.12a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021790|Y51H7C.12a|445nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021790|Y51H7C.12a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021791|Y51H7C.13|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021791|Y51H7C.13|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1311|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021791|Y51H7C.13|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021791|Y51H7C.13|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021793|Y52D5A.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021793|Y52D5A.2|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021794|Y52E8A.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021794|Y52E8A.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021794|Y52E8A.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021795|Y52E8A.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021795|Y52E8A.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021795|Y52E8A.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=418|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021795|Y52E8A.2|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=347|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021795|Y52E8A.2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021796|Y52E8A.3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021796|Y52E8A.3|99nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=849|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021797|plep-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021797|plep-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021797|plep-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021799|Y53G8AL.1|534nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021799|Y53G8AL.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021799|Y53G8AL.1|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021799|Y53G8AL.1|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1663|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2338|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|515nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2856|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021800|Y53G8AL.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021801|Y53G8AL.3|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021801|Y53G8AL.3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021804|Y53G8AM.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021804|Y53G8AM.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00021804|Y53G8AM.4|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00021804|Y53G8AM.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021805|Y53G8AM.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021805|Y53G8AM.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021806|Y53G8AM.6|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021806|Y53G8AM.6|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021806|Y53G8AM.6|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021808|Y53G8AM.8.2|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021808|Y53G8AM.8.2|1029nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021808|Y53G8AM.8.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=427|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021808|Y53G8AM.8.2|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=701|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021808|Y53G8AM.8.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021808|Y53G8AM.8.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021808|Y53G8AM.8.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021809|Y53G8AR.1|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2163|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021810|phf-15|1569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3729|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=231|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|327nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|410nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|464nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021811|ral-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021812|Y53G8AR.5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021812|Y53G8AR.5|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=112|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021812|Y53G8AR.5|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=360|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021812|Y53G8AR.5|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=261|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|544nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=607|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=616|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|668nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=170|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|678nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021813|Y53G8AR.6|769nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021814|Y53G8AR.7a|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021814|Y53G8AR.7a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021814|Y53G8AR.7a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00021815|Y53G8AR.8|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021815|Y53G8AR.8|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021815|Y53G8AR.8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021815|Y53G8AR.8|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021815|Y53G8AR.8|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021815|Y53G8AR.8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1008nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1010nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1012nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1075nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2564|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1085nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1170nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1174nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|1278nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|840nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021816|Y53G8AR.9|871nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|443nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|451nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|454nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=492|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|460nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|476nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|665nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7455|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=591|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|793nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021817|Y53G8B.1|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021818|Y53G8B.2|1032nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021818|Y53G8B.2|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=264|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021818|Y53G8B.2|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=821|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021818|Y53G8B.2|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021818|Y53G8B.2|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021820|nipa-1|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021820|nipa-1|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1991|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021820|nipa-1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021820|nipa-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021820|nipa-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021820|nipa-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021820|nipa-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021826|txl-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4041|total_reads(89.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021826|txl-1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=411|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021826|txl-1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021826|txl-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021826|txl-1|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021826|txl-1|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=585|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2243|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|90nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021827|dnc-6|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|32nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|634nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2153|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021828|Y54E10A.6|713nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=81|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|101nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|110nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|118nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|1552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=683|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=682|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021829|mrpl-17|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021830|Y54E10A.10|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021830|Y54E10A.10|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021830|Y54E10A.10|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021830|Y54E10A.10|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3276|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=446|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021831|Y54E10A.11|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1736|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=365|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|1353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|372nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021832|Y54E10A.12|983nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021833|Y54E10A.13|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021833|Y54E10A.13|1038nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021833|Y54E10A.13|1057nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021833|Y54E10A.13|1219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|291nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=349|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=782|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021834|mab-31|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|1062nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|1065nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2874|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021835|Y54E10A.17.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=620|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9878|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1368|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|39nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021838|Y54E10BL.3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=858|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021839|nduf-5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1149|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021840|Y54E10BR.1a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|890nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|894nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2929|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00021841|Y54E10BR.2.1|947nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2065|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021842|Y54E10BR.3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021843|Y54E10BR.4|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=950|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00021843|Y54E10BR.4|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=556|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021843|Y54E10BR.4|1218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021843|Y54E10BR.4|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021843|Y54E10BR.4|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021843|Y54E10BR.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=298|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9885|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1960|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=609|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021844|Y54E10BR.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021845|rpb-7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021845|rpb-7|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021845|rpb-7|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021845|rpb-7|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3660|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021845|rpb-7|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=585|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021846|ztf-23|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021846|ztf-23|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=783|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00021846|ztf-23|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=964|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|327nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1152|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=535|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|498nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|505nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|792nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|795nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1a|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1b|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021847|Y54F10AL.1b|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021848|nhr-239|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021848|nhr-239|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021848|nhr-239|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021848|nhr-239|930nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6803|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021849|Y54F10AM.5|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|129nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|432nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021850|Y54F10AM.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1616|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=782|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=237|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021852|Y54F10AM.8|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021853|Y54F10AM.11|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021853|Y54F10AM.11|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=605|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021853|Y54F10AM.11|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021853|Y54F10AM.11|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|1007nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|1115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|1153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1310|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|1162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|1166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|917nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|920nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|951nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|965nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|969nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021854|Y54F10AR.1|995nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021855|Y54F10AR.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021855|Y54F10AR.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3092|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021855|Y54F10AR.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=865|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021855|Y54F10AR.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021856|Y54F10BM.1|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021856|Y54F10BM.1|1208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021856|Y54F10BM.1|1211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021856|Y54F10BM.1|1217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1415|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021856|Y54F10BM.1|1219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021856|Y54F10BM.1|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021857|iffb-1|393nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2971|total_reads(53.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021857|iffb-1|398nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2475|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021857|iffb-1|400nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=108|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021858|Y54F10BM.3|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021858|Y54F10BM.3|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=416|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00021858|Y54F10BM.3|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00021859|fbxa-39|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021860|fbxa-9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00021860|fbxa-9|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00021861|Y54F10BM.6|492nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021861|Y54F10BM.6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021861|Y54F10BM.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021862|fbxa-48|368nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021863|Y54F10BM.9|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021863|Y54F10BM.9|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1361|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021863|Y54F10BM.9|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021863|Y54F10BM.9|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021863|Y54F10BM.9|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021863|Y54F10BM.9|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021864|fbxa-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021864|fbxa-1|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021864|fbxa-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021865|fbxa-66|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021865|fbxa-66|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021865|fbxa-66|817nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2350|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|287nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|381nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|389nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|430nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021866|Y54F10BM.12|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021867|Y54F10BM.13|1553nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021867|Y54F10BM.13|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1090|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021868|atln-1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021868|atln-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021868|atln-1|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021868|atln-1|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5305|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021868|atln-1|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2772|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021868|atln-1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7846|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1356|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021869|Y54G2A.3a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|155nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=264|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1398|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=397|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021870|samt-1|59nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021871|dml-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=652|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021871|dml-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|209nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|219nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|221nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7380|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021872|clec-85|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021873|clec-82|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021875|Y54G2A.10a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00021875|Y54G2A.10a|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021875|Y54G2A.10a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2026|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021876|Y54G2A.11b|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021877|Y54G2A.12|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021877|Y54G2A.12|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=143|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021877|Y54G2A.12|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021877|Y54G2A.12|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=104|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021877|Y54G2A.12|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021877|Y54G2A.12|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021877|Y54G2A.12|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021878|Y54G2A.13|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021878|Y54G2A.13|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=454|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3007|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1281|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021879|clec-83|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021880|Y54G2A.15|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=891|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00021880|Y54G2A.15|76nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021880|Y54G2A.15|79nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021881|Y54G2A.16c|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2632|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021882|Y54G2A.17a.1|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15318|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021883|Y54G2A.18|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021884|Y54G2A.19|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021884|Y54G2A.19|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021884|Y54G2A.19|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=532|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021884|Y54G2A.19|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021887|fbxc-45|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021887|fbxc-45|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1015|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021887|fbxc-45|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3210|total_reads(67.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1304|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021888|Y54G2A.23|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|519nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7209|total_reads(71.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=607|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|633nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1929|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|664nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021890|Y54G2A.26c|667nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021892|Y54G2A.28c|1189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021892|Y54G2A.28c|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021892|Y54G2A.28c|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021892|Y54G2A.28c|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021893|ndnf-1|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=356|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021893|ndnf-1|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021894|Y54G2A.32.3|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021894|Y54G2A.32.3|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021894|Y54G2A.32.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021894|Y54G2A.32.3|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00021894|Y54G2A.32.3|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=404|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021894|Y54G2A.32.3|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021894|Y54G2A.32.3|945nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021895|clec-84|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=922|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021897|ser-6|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021897|ser-6|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021897|ser-6|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021897|ser-6|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021897|ser-6|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021898|Y54G2A.36|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021898|Y54G2A.36|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1509|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021898|Y54G2A.36|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021898|Y54G2A.36|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1976|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1203|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|1576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|1589nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|1594nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|1596nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=672|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021899|Y54H5A.1.2|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=313|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=674|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2419|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021900|Y54H5A.2|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021901|tag-262|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021901|tag-262|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021901|tag-262|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=424|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021901|tag-262|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3577|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021901|tag-262|135nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=425|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021901|tag-262|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021901|tag-262|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021902|oxy-4|1515nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021902|oxy-4|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021902|oxy-4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1287|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021902|oxy-4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021903|Y55B1AL.1|1558nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021903|Y55B1AL.1|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021903|Y55B1AL.1|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021903|Y55B1AL.1|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021903|Y55B1AL.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021903|Y55B1AL.1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021904|Y55B1AL.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021904|Y55B1AL.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021904|Y55B1AL.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021904|Y55B1AL.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021904|Y55B1AL.2|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5030|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021904|Y55B1AL.2|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021904|Y55B1AL.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021905|helq-1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=712|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021905|helq-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|1054nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1490|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|1058nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|1087nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|1092nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021906|Y55B1AR.2a|885nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021907|Y55B1AR.3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00021907|Y55B1AR.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00021908|Y55B1AR.4|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=253|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021908|Y55B1AR.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021909|Y55B1BL.1b.1|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021909|Y55B1BL.1b.1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021909|Y55B1BL.1b.1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021909|Y55B1BL.1b.1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021909|Y55B1BL.1b.1|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1024|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021909|Y55B1BL.1b.1|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=844|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021909|Y55B1BL.1b.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=785|total_reads(33.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=942|total_reads(39.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=442|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021910|stim-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021911|Y55B1BR.1|775nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021911|Y55B1BR.1|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021912|Y55B1BR.2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021912|Y55B1BR.2|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021912|Y55B1BR.2|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=467|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021912|Y55B1BR.2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021912|Y55B1BR.2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00021913|cec-8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021913|cec-8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021913|cec-8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021913|cec-8|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00021913|cec-8|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021913|cec-8|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021914|magu-1|812nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021914|magu-1|935nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021914|magu-1|938nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021914|magu-1|942nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021915|Y55D5A.1a|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021915|Y55D5A.1a|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=504|total_reads(75.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021915|Y55D5A.1a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021915|Y55D5A.1a|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021916|Y55D5A.2|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021916|Y55D5A.2|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021916|Y55D5A.2|400nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021917|Y55D5A.3|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021917|Y55D5A.3|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021917|Y55D5A.3|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021917|Y55D5A.3|418nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021917|Y55D5A.3|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021917|Y55D5A.3|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021918|Y55D5A.4|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00021918|Y55D5A.4|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021918|Y55D5A.4|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021918|Y55D5A.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00021918|Y55D5A.4|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00021918|Y55D5A.4|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021919|cutl-25|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021919|cutl-25|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021920|mrps-25|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1338|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021920|mrps-25|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021920|mrps-25|794nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3a|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3a|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3a|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4805|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3a|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3a|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3b|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3b|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3b|638nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3b|642nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021921|Y55F3AM.3b|778nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021922|atg-3|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021922|atg-3|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=679|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021922|atg-3|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3944|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021923|Y55F3AM.5|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021923|Y55F3AM.5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021923|Y55F3AM.5|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2192|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021923|Y55F3AM.5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|652nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|795nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|799nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=661|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|802nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|808nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6a|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021924|Y55F3AM.6b|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021925|immp-2|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021925|immp-2|1416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021925|immp-2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021925|immp-2|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021925|immp-2|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=456|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021925|immp-2|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00021925|immp-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021926|Y55F3AM.9b|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021926|Y55F3AM.9b|231nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=236|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021926|Y55F3AM.9b|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2197|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021926|Y55F3AM.9b|239nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1583|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021926|Y55F3AM.9b|243nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=142|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021926|Y55F3AM.9b|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021927|abhd-14|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00021927|abhd-14|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=950|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00021927|abhd-14|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021927|abhd-14|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021928|Y55F3AM.11|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00021928|Y55F3AM.11|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021928|Y55F3AM.11|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021928|Y55F3AM.11|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=888|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021928|Y55F3AM.11|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021928|Y55F3AM.11|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3891|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021929|dcap-1|968nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021930|Y55F3AM.13|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021930|Y55F3AM.13|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021930|Y55F3AM.13|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5391|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021930|Y55F3AM.13|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|1250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|755nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|757nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|760nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|767nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1210|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|769nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021931|Y55F3AM.14|772nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021932|Y55F3AR.1.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1034|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021932|Y55F3AR.1.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021932|Y55F3AR.1.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021932|Y55F3AR.1.1|1527nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021932|Y55F3AR.1.1|1532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021932|Y55F3AR.1.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|841nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1042|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021933|Y55F3AR.2|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|1254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|325nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|649nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|699nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|701nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2239|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|709nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|711nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|718nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|722nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021934|cct-8|742nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021935|mrpl-46|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021935|mrpl-46|490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021935|mrpl-46|498nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021935|mrpl-46|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021935|mrpl-46|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021935|mrpl-46|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021935|mrpl-46|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|1229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=376|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|1236nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|1252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1917|total_reads(75.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|1283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|1292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|621nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021936|Y55F3BL.2b|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021938|Y55F3BR.1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021938|Y55F3BR.1|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021938|Y55F3BR.1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1853|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021938|Y55F3BR.1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021939|Y55F3BR.2a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=454|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021939|Y55F3BR.2a|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021941|lgc-33|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=683|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021941|lgc-33|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1248|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021941|lgc-33|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021942|madf-1|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=589|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021942|madf-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00021942|madf-1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|130nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|687nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|702nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|705nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|740nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|745nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1995|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|750nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=311|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|754nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|768nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021943|Y55F3BR.6|806nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021944|Y55F3BR.7|1234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1842|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=900|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021945|lem-4|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021947|srt-23|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021947|srt-23|53nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021948|kvs-5|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021948|kvs-5|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021948|kvs-5|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=108|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021948|kvs-5|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=94|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021948|kvs-5|317nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021948|kvs-5|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021949|clec-164|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021949|clec-164|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021949|clec-164|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021950|cutl-26|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=801|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021950|cutl-26|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021950|cutl-26|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021951|srt-24|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021951|srt-24|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|14nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|381nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|392nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1156|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|397nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4985|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3643|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=322|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021952|vha-19|572nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021953|Y55H10A.2|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=416|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021953|Y55H10A.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021953|Y55H10A.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2935|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11571|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021956|Y57E12AL.1a|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021957|Y57E12AL.2|1273nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021957|Y57E12AL.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021958|Y57E12AL.4|1534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=317|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|1075nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|1095nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|1098nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|1117nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|161nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|908nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021959|Y57E12AL.6.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12347|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16135|total_reads(96.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=338|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|905nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021960|Y57E12AM.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021961|Y57E12B.1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00021963|lipl-6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021963|lipl-6|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021963|lipl-6|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021963|lipl-6|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021964|Y57E12B.4|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021964|Y57E12B.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021965|Y57G7A.1|1326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021965|Y57G7A.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=521|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021966|Y57G7A.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021966|Y57G7A.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021967|Y57G7A.3a|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=166|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00021967|Y57G7A.3a|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=470|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021967|Y57G7A.3a|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021968|Y57G7A.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021968|Y57G7A.5|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=480|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021969|Y57G7A.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021969|Y57G7A.6|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021969|Y57G7A.6|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=471|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021970|srz-64|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021970|srz-64|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3577|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=831|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021972|glb-31|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=444|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4164|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021973|emc-2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021974|Y57G7A.11|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021974|Y57G7A.11|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00021974|Y57G7A.11|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021974|Y57G7A.11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=584|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=506|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|441nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021975|Y58A7A.1a|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021976|Y58A7A.2|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1320|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021976|Y58A7A.2|200nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00021976|Y58A7A.2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021976|Y58A7A.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021977|Y58A7A.3|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021977|Y58A7A.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021977|Y58A7A.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5364|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021977|Y58A7A.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021978|Y58A7A.4|1202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021978|Y58A7A.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021978|Y58A7A.4|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021978|Y58A7A.4|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=419|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021978|Y58A7A.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=850|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021978|Y58A7A.4|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=822|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|1494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|175nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|180nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|202nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=280|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|258nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|76nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=3610|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|824nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021979|Y58A7A.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|1210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|1326nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|1450nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|1482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|194nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4208|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021980|glb-32|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1362|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11005|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=127|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1795|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1204|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=551|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2629|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=340|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=241|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1091|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=786|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1353|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021981|lgc-26|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00021983|npr-5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021983|npr-5|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021983|npr-5|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1216|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021983|npr-5|294nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021983|npr-5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021983|npr-5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021983|npr-5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1252|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021984|Y59C2A.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021986|Y59C2A.3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021986|Y59C2A.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2723|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021986|Y59C2A.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021986|Y59C2A.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021988|rgs-8.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021988|rgs-8.2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=381|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021988|rgs-8.2|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021988|rgs-8.2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021988|rgs-8.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021988|rgs-8.2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=562|total_reads(50.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021988|rgs-8.2|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021993|Y59E9AL.3|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021993|Y59E9AL.3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00021993|Y59E9AL.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2489|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021993|Y59E9AL.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021993|Y59E9AL.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|1289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|1301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021994|Y59E9AL.4|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00021996|Y59E9AL.6|1240nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00021996|Y59E9AL.6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2504|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021996|Y59E9AL.6|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00021997|Y59E9AR.1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021997|Y59E9AR.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021997|Y59E9AR.1|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021997|Y59E9AR.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00021997|Y59E9AR.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15546|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00021997|Y59E9AR.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=431|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00021997|Y59E9AR.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1504|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022002|Y59E9AR.7|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022003|Y59E9AR.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022003|Y59E9AR.8|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022004|npr-22|152nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022004|npr-22|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022004|npr-22|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022004|npr-22|317nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022004|npr-22|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022005|Y59H11AM.1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022006|mpst-5|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022006|mpst-5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022006|mpst-5|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=180|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022006|mpst-5|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022006|mpst-5|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022006|mpst-5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022006|mpst-5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022008|Y59H11AM.4|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022008|Y59H11AM.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022008|Y59H11AM.4|571nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022008|Y59H11AM.4|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|1140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|1381nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|352nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|354nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=725|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|363nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|367nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=777|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=602|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|374nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022010|catp-7|376nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022011|Y59H11AR.3|320nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022011|Y59H11AR.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022011|Y59H11AR.3|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|1109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|1118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|1123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|224nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|404nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|406nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022012|Y59H11AR.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022013|Y60C6A.1|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022013|Y60C6A.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022013|Y60C6A.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022013|Y60C6A.1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022013|Y60C6A.1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022013|Y60C6A.1|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022014|Y61A9LA.1|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022014|Y61A9LA.1|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022014|Y61A9LA.1|413nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022014|Y61A9LA.1|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5752|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022014|Y61A9LA.1|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022015|Y61A9LA.3a|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1862|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022015|Y61A9LA.3a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022015|Y61A9LA.3a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022015|Y61A9LA.3a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022015|Y61A9LA.3b|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022015|Y61A9LA.3b|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1622|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022015|Y61A9LA.3b|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022016|Y61A9LA.4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022016|Y61A9LA.4|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022016|Y61A9LA.4|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022016|Y61A9LA.4|837nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022018|Y61A9LA.7b|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022018|Y61A9LA.7b|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022018|Y61A9LA.7b|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2760|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022018|Y61A9LA.7b|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|476nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|552nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|591nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=669|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|596nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022019|sut-2|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022020|hpo-39|664nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022021|Y61A9LA.10|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022021|Y61A9LA.10|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022021|Y61A9LA.10|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=374|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022021|Y61A9LA.10|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1320|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022021|Y61A9LA.10|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022021|Y61A9LA.10|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022021|Y61A9LA.10|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022022|Y61A9LA.11b|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1184|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022022|Y61A9LA.11b|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022024|Y64H9A.2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022024|Y64H9A.2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022024|Y64H9A.2|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022024|Y64H9A.2|159nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=191|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022024|Y64H9A.2|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00022024|Y64H9A.2|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=592|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022024|Y64H9A.2|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1149|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|935nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|944nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|957nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|978nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022025|Y65B4A.1|982nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|1294nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=962|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|429nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|822nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|837nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|846nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|849nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|859nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|876nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022026|Y65B4A.2a|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2626|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2059|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5336|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1900|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022027|vps-20|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022028|Y65B4A.4|943nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|1002nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|1024nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|1513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|1535nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|1539nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=80|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|774nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022029|Y65B4A.6b|999nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022030|Y65B4A.7b|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022030|Y65B4A.7b|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022031|Y65B4A.8.1|436nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022031|Y65B4A.8.1|441nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=344|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022031|Y65B4A.8.1|446nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=106|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022031|Y65B4A.8.1|449nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=195|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022031|Y65B4A.8.1|451nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022031|Y65B4A.8.1|453nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022031|Y65B4A.8.1|471nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022032|Y65B4A.9a|1406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022032|Y65B4A.9a|1409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00022032|Y65B4A.9a|1417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022032|Y65B4A.9a|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(56.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022032|Y65B4A.9a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022032|Y65B4A.9a|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022032|Y65B4A.9b|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022033|Y65B4BL.1a|207nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022033|Y65B4BL.1a|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022033|Y65B4BL.1b|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022033|Y65B4BL.1b|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022033|Y65B4BL.1b|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022033|Y65B4BL.1b|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022033|Y65B4BL.1b|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1678|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022034|deps-1|181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6778|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022034|deps-1|186nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=324|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022034|deps-1|190nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022034|deps-1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022034|deps-1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022034|deps-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022034|deps-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022035|Y65B4BL.3b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022035|Y65B4BL.3b|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=131|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022035|Y65B4BL.3b|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=113|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022035|Y65B4BL.3b|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=706|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022036|Y65B4BL.4|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1259|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022036|Y65B4BL.4|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1377|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8543|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022037|acs-13|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1787|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|169nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1068|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022038|Y65B4BL.6b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022039|Y65B4BL.7b|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022039|Y65B4BL.7b|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022039|Y65B4BL.7b|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022039|Y65B4BL.7b|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022040|Y65B4BR.1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022040|Y65B4BR.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2561|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=104|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022042|icd-2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47389|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|1077nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=600|total_reads(39.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022043|psf-3|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022044|dpm-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022044|dpm-1|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022044|dpm-1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022044|dpm-1|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=496|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022044|dpm-1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3229|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022044|dpm-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022045|mrpl-55|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022045|mrpl-55|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022045|mrpl-55|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022045|mrpl-55|372nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022045|mrpl-55|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1584|total_reads(48.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022045|mrpl-55|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1608|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=833|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1553|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=681|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1318|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1362|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=359|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=781|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022046|Y66H1A.4.1|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1226nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1236nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1260nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|1265nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1187|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|163nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=540|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022047|Y66H1A.5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=267|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|326nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|329nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=246|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|335nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=509|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|338nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3266|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|346nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9322|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=571|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|363nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022048|fln-1|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=173|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=533|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=656|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022051|rep-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022052|Y67D2.2|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022052|Y67D2.2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022052|Y67D2.2|281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2321|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022053|cisd-3.2|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022053|cisd-3.2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022053|cisd-3.2|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8013|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022053|cisd-3.2|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022053|cisd-3.2|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022053|cisd-3.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022054|Y67D2.4a|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022054|Y67D2.4a|71nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=931|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022054|Y67D2.4a|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022055|Y67D2.5|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=382|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022055|Y67D2.5|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022056|ddx-35|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022056|ddx-35|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022056|ddx-35|85nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=257|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022056|ddx-35|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|1270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1012|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|425nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|461nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=333|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022057|Y67D2.7|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022059|Y67D8A.2a.2|448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022059|Y67D8A.2a.2|617nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022059|Y67D8A.2a.2|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2100|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022059|Y67D8A.2c|773nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022060|dmd-9|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=770|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022060|dmd-9|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1212|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022060|dmd-9|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00022060|dmd-9|989nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022062|Y67D8B.2|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=262|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|156nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|163nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1781|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022063|Y67D8B.4a|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022064|Y67D8B.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022064|Y67D8B.5|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022067|Y67D8C.3c|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022067|Y67D8C.3c|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022067|Y67D8C.3c|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022067|Y67D8C.3c|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022067|Y67D8C.3c|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022067|Y67D8C.3c|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1358|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022067|Y67D8C.3c|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|1013nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2726|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|423nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|430nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=2739|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|432nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10382|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|434nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=891|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|437nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|474nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|478nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|480nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=221|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|522nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022069|eel-1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022071|Y67D8C.7|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9830|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2523|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=142|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=590|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022072|cpg-9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022073|Y67D8C.9b|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022073|Y67D8C.9b|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1621|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022073|Y67D8C.9b|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022074|Y69A2AR.1b|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022074|Y69A2AR.1b|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022074|Y69A2AR.1b|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2694|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022074|Y69A2AR.1b|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022075|Y69A2AR.3|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022075|Y69A2AR.3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022075|Y69A2AR.3|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022075|Y69A2AR.3|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3033|total_reads(57.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022075|Y69A2AR.3|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1682|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022075|Y69A2AR.3|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=505|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022075|Y69A2AR.3|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022076|daao-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022076|daao-1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022076|daao-1|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022077|vamp-7|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1751|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022077|vamp-7|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1712|total_reads(49.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|592nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=817|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|596nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|604nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=422|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|677nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022078|epg-9|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022083|Y69A2AR.12|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022083|Y69A2AR.12|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(52.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022083|Y69A2AR.12|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022083|Y69A2AR.12|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022083|Y69A2AR.12|255nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022086|sprr-3|1214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022086|sprr-3|1222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022086|sprr-3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022087|Y69A2AR.16a|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022087|Y69A2AR.16a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022087|Y69A2AR.16a|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2051|total_reads(69.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022087|Y69A2AR.16a|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18a|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=637|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2222|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7726|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=683|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022089|Y69A2AR.18b|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022090|Y69A2AR.19a|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=471|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022090|Y69A2AR.19a|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022092|Y69A2AR.21|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022092|Y69A2AR.21|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022092|Y69A2AR.21|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3674|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022092|Y69A2AR.21|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022093|Y69A2AR.22|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022093|Y69A2AR.22|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022093|Y69A2AR.22|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=983|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022094|Y69A2AR.23|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00022094|Y69A2AR.23|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022095|Y69A2AR.24a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022095|Y69A2AR.24a|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022096|Y69A2AR.25|1498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022096|Y69A2AR.25|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022096|Y69A2AR.25|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00022096|Y69A2AR.25|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022096|Y69A2AR.25|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022096|Y69A2AR.25|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022099|Y69A2AR.28|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022099|Y69A2AR.28|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2792|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00022099|Y69A2AR.28|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=395|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022099|Y69A2AR.28|1329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022099|Y69A2AR.28|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022100|Y69A2AR.31|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022100|Y69A2AR.31|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022100|Y69A2AR.31|901nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022100|Y69A2AR.31|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022100|Y69A2AR.31|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022101|Y69A2AR.32a|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022101|Y69A2AR.32a|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=590|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022101|Y69A2AR.32a|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=740|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022101|Y69A2AR.32a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022101|Y69A2AR.32a|168nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022102|Y69F12A.1|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(71.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022102|Y69F12A.1|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022103|cdh-12|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022103|cdh-12|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022103|cdh-12|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022104|Y71D11A.3a|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=751|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022104|Y71D11A.3a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022104|Y71D11A.3a|903nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022104|Y71D11A.3a|971nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|170nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|175nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(50.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022106|lgc-46|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1192|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|1320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022107|Y71F9AL.1|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022108|Y71F9AL.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00022108|Y71F9AL.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022108|Y71F9AL.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022110|Y71F9AL.4|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022110|Y71F9AL.4|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022110|Y71F9AL.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=787|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022110|Y71F9AL.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022111|Y71F9AL.6|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022111|Y71F9AL.6|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022112|Y71F9AL.7|1041nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022112|Y71F9AL.7|1322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022112|Y71F9AL.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022112|Y71F9AL.7|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022112|Y71F9AL.7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00022112|Y71F9AL.7|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022113|Y71F9AL.8|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022113|Y71F9AL.8|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022113|Y71F9AL.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1308|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022113|Y71F9AL.8|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00022113|Y71F9AL.8|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1365|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11430|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2831|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022114|Y71F9AL.9|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|1328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|18nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=143|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|709nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|755nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|874nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|878nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|914nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2846|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022115|Y71F9AL.10.2|995nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022116|Y71F9AL.11|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|1228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|1291nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|1330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|1336nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=108|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2253|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|511nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022117|Y71F9AL.12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022118|dnc-5|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022118|dnc-5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022118|dnc-5|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022118|dnc-5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1387|total_reads(44.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022118|dnc-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1388|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022119|copa-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022119|copa-1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7760|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022119|copa-1|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022121|cogc-3|159nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022121|cogc-3|165nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022121|cogc-3|176nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2244|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022121|cogc-3|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022121|cogc-3|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|1206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|1208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|1210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|1213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|268nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|271nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=475|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17990|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1313|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=437|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022122|trap-1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022123|Y71F9AR.2|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=367|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022123|Y71F9AR.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022123|Y71F9AR.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022124|supr-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022124|supr-1|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022124|supr-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022124|supr-1|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022125|Y71F9B.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=669|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022125|Y71F9B.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022125|Y71F9B.1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022126|Y71F9B.2a|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=146|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=144|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22459|total_reads(88.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1714|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=357|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022127|yop-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022128|Y71F9B.6e|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022128|Y71F9B.6e|933nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1818|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00022128|Y71F9B.6e|937nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022129|lron-11|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022129|lron-11|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1038|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022129|lron-11|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022129|lron-11|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022130|Y71F9B.9a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022130|Y71F9B.9a|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022130|Y71F9B.9a|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=564|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022130|Y71F9B.9a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022130|Y71F9B.9a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022131|Y71F9B.13c|1064nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022131|Y71F9B.13c|1072nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022131|Y71F9B.13c|1079nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022131|Y71F9B.13c|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022131|Y71F9B.13c|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022131|Y71F9B.13c|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1462|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022131|Y71F9B.13c|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022133|Y71F9B.15|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022133|Y71F9B.15|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|1004nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1867|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|1007nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=804|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|1010nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|1103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|1111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|717nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|984nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|994nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022134|Y71G10AL.1b|996nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=478|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|1505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|741nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022138|trpp-10|749nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022139|tub-2|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022139|tub-2|182nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022139|tub-2|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022139|tub-2|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022139|tub-2|726nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2040|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022140|Y71G12A.4|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022140|Y71G12A.4|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022140|Y71G12A.4|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022140|Y71G12A.4|46nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022140|Y71G12A.4|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022141|chaf-2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022141|chaf-2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2610|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022142|Y71G12B.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00022142|Y71G12B.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(65%)
- ID=WBGene00022143|Y71G12B.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=800|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022143|Y71G12B.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022143|Y71G12B.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=110097|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6239|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|187nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|26nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=302|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=135|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2141|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1712|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|95nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=186|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022144|pghm-1|99nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022145|Y71G12B.5a|1542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(42.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022145|Y71G12B.5a|1545nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022146|Y71G12B.6a|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022146|Y71G12B.6a|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022146|Y71G12B.6a|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=822|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=982|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1084|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|1541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|1582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|1587nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|1590nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022148|ddx-27|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=796|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=727|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=635|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|506nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|657nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022149|lin-65|661nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=284|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|23nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022150|Y71G12B.10|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2314|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=168|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=298|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=441|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=590|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022152|atg-5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022153|Y71G12B.13|669nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022153|Y71G12B.13|696nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1175|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022153|Y71G12B.13|699nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022153|Y71G12B.13|703nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022153|Y71G12B.13|780nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022153|Y71G12B.13|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022153|Y71G12B.13|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022154|drag-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022154|drag-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00022154|drag-1|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022155|Y71G12B.17|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=165|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022155|Y71G12B.17|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022155|Y71G12B.17|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022155|Y71G12B.17|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=429|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022156|Y71G12B.18a|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022156|Y71G12B.18a|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022156|Y71G12B.18a|63nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022156|Y71G12B.18a|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022156|Y71G12B.18a|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022157|Y71G12B.22|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022157|Y71G12B.22|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022158|Y71G12B.23b|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022158|Y71G12B.23b|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1160|total_reads(89.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022158|Y71G12B.23b|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022158|Y71G12B.23b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022158|Y71G12B.23b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022158|Y71G12B.23b|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=801|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022159|mppa-1|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022160|Y71G12B.25b|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=986|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022160|Y71G12B.25b|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022161|Y71G12B.26b|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=315|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022161|Y71G12B.26b|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022162|Y71G12B.27|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=776|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022162|Y71G12B.27|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=846|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022165|Y71H2AL.2|1241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022165|Y71H2AL.2|1323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022165|Y71H2AL.2|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022165|Y71H2AL.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022165|Y71H2AL.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022165|Y71H2AL.2|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022165|Y71H2AL.2|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1868|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|719nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|940nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|947nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4289|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022166|Y71H2AM.1.1|956nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022167|Y71H2AM.2|1158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|1234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|1240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|57nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|776nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=621|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|779nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022168|Y71H2AM.3|781nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00022169|Y71H2AM.4|1340nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022169|Y71H2AM.4|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022169|Y71H2AM.4|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022169|Y71H2AM.4|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13634|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022169|Y71H2AM.4|985nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=696|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6959|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|67nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30021|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=277|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=613|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022170|Y71H2AM.5.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022171|Y71H2AM.6a|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022171|Y71H2AM.6a|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022171|Y71H2AM.6a|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022171|Y71H2AM.6a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022171|Y71H2AM.6a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1107|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022171|Y71H2AM.6a|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022171|Y71H2AM.6a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022172|cosa-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1013|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00022172|cosa-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=368|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022172|cosa-1|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|682nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|775nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|780nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|785nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|789nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022173|set-27|791nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|1580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2246|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|532nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|539nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|542nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022174|Y71H2AM.9|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022175|Y71H2AM.10|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022175|Y71H2AM.10|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022175|Y71H2AM.10|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022175|Y71H2AM.10|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022175|Y71H2AM.10|768nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022175|Y71H2AM.10|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022175|Y71H2AM.10|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=650|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1456|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=533|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=823|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022176|Y71H2AM.11|754nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022177|Y71H2AM.12|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022177|Y71H2AM.12|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(60.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022177|Y71H2AM.12|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022177|Y71H2AM.12|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022177|Y71H2AM.12|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022178|Y71H2AM.13|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2024|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022178|Y71H2AM.13|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022179|Y71H2AM.14a.1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022179|Y71H2AM.14a.1|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022179|Y71H2AM.14a.1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022179|Y71H2AM.14a.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022179|Y71H2AM.14a.1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022180|Y71H2AM.15a|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022180|Y71H2AM.15a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022180|Y71H2AM.15a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022180|Y71H2AM.15a|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00022180|Y71H2AM.15a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022181|pho-9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022181|pho-9|36nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022181|pho-9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022181|pho-9|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022181|pho-9|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|1127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|1129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|1456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|627nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|652nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022182|swsn-3|849nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022185|Y71H2AM.20b|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022185|Y71H2AM.20b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022185|Y71H2AM.20b|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3500|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022185|Y71H2AM.20b|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=898|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022185|Y71H2AM.20b|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|139nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4508|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=411|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022188|Y71H2AR.1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022189|Y71H2AR.2|399nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022190|josd-1|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=720|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022190|josd-1|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022190|josd-1|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022190|josd-1|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022190|josd-1|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022190|josd-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6441|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=549|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022191|Y71H2B.1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|1287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|1290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|1292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|1294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|1297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=814|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|1300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=224|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=740|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=466|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|649nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|651nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|655nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022192|Y71H2B.2|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022193|ppfr-4|720nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=466|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022193|ppfr-4|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=631|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022193|ppfr-4|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022193|ppfr-4|730nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022193|ppfr-4|735nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1625|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4287|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12533|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022194|Y71H2B.4|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|58nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022195|Y71H2B.5|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022196|gpa-17|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022196|gpa-17|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=615|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022196|gpa-17|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022198|Y71H2B.11|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022198|Y71H2B.11|1138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022198|Y71H2B.11|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022198|Y71H2B.11|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022198|Y71H2B.11|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=886|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022198|Y71H2B.11|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2818|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1269|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1626|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022199|pfk-1.1|341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|669nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|707nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1008|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|712nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1553|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|716nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022200|fard-1|729nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|372nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2003|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1635|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022201|Y71H10B.1c.1|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022202|Y72A10A.1|198nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022202|Y72A10A.1|200nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022202|Y72A10A.1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022202|Y72A10A.1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022202|Y72A10A.1|386nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4610|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022202|Y72A10A.1|389nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022203|Y73B3A.1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022203|Y73B3A.1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022203|Y73B3A.1|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=674|total_reads(88.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022203|Y73B3A.1|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022203|Y73B3A.1|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022203|Y73B3A.1|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022205|Y73B3A.3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00022205|Y73B3A.3|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022206|Y73B3A.4|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022206|Y73B3A.4|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022206|Y73B3A.4|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022206|Y73B3A.4|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022206|Y73B3A.4|721nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(82.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022206|Y73B3A.4|733nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022210|Y73B3A.8|48nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022211|Y73B3A.9|1251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022211|Y73B3A.9|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022211|Y73B3A.9|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1052|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022212|Y73B3A.10|1347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022212|Y73B3A.10|1469nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022212|Y73B3A.10|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022213|Y73B3A.11|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022213|Y73B3A.11|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022214|cal-6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022214|cal-6|174nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=323|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022214|cal-6|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2570|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022214|cal-6|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022214|cal-6|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022214|cal-6|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022215|Y73B3A.13|348nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022215|Y73B3A.13|350nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022216|fbxa-16|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022217|fbxa-221|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022219|Y73B3A.18a|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022219|Y73B3A.18a|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022219|Y73B3A.18a|484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022219|Y73B3A.18a|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123314|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022219|Y73B3A.18a|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1551|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022219|Y73B3A.18a|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022219|Y73B3A.18a|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022223|Y73B3B.1|1329nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022223|Y73B3B.1|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022223|Y73B3B.1|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022223|Y73B3B.1|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1521|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022223|Y73B3B.1|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022223|Y73B3B.1|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022224|set-28|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022225|Y73B3B.3|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022228|Y73B6A.1b|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022228|Y73B6A.1b|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022228|Y73B6A.1b|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022230|Y73B6A.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022230|Y73B6A.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022230|Y73B6A.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00022230|Y73B6A.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022231|tyr-6|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022231|tyr-6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022231|tyr-6|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022231|tyr-6|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022232|exos-2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1213|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022232|exos-2|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022232|exos-2|428nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022232|exos-2|555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022232|exos-2|774nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022232|exos-2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022233|ipla-6|293nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2458|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022233|ipla-6|296nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022233|ipla-6|302nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|1005nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|1008nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|1022nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=248|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|715nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|770nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|784nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|817nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|829nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|923nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=192|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=379|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|954nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|963nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|966nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=158|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|969nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13924|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|975nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1585|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|979nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|981nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=186|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|984nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=738|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022235|sqd-1|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022236|Y73B6BL.12|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022236|Y73B6BL.12|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022237|Y73B6BL.14|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022237|Y73B6BL.14|932nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|402nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|408nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=109|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|416nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=141|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|422nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|473nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|476nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=292|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|753nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|912nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|936nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|963nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022240|shl-1|987nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022242|sfrp-1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022242|sfrp-1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022242|sfrp-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=313|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022242|sfrp-1|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022243|Y73B6BL.22|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(44.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022243|Y73B6BL.22|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=181|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022243|Y73B6BL.22|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=101|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022243|Y73B6BL.22|60nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|506nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3434|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|514nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022244|Y73B6BL.23|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=150|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=123|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18499|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=414|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022245|acp-6|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022246|acp-7|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=322|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022246|acp-7|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022246|acp-7|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022246|acp-7|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022247|lgc-10|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022247|lgc-10|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=693|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022247|lgc-10|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022247|lgc-10|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022247|lgc-10|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5603|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|192nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=346|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022248|Y73B6BL.27|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022250|Y73B6BL.29a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022250|Y73B6BL.29a|1492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022250|Y73B6BL.29a|1578nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022250|Y73B6BL.29a|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022250|Y73B6BL.29a|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022250|Y73B6BL.29a|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=173|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022250|Y73B6BL.29a|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=634|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1327|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5029|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|209nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1326|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=825|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022251|blos-2|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|1287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|1289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|18nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=763|total_reads(60.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022252|Y73B6BL.31a|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|1050nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|1056nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|274nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|400nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=66|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|402nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=341|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|406nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=1836|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|409nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=152|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|411nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=69|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|415nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=89|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022253|hrpf-2|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|151nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|158nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=3189|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|161nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=565|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=217|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4805|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9539|total_reads(43.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|213nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=462|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1137|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|469nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|612nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|62nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1057|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022254|Y73B6BL.35b|719nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022255|Y73B6BL.36|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022255|Y73B6BL.36|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(59.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022255|Y73B6BL.36|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022255|Y73B6BL.36|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022255|Y73B6BL.36|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022256|Y73B6BL.37|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022256|Y73B6BL.37|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|1316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|1535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=124|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4860|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2759|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022257|puf-11|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022258|Y73C8B.1|19nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022258|Y73C8B.1|27nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=177|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022258|Y73C8B.1|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022258|Y73C8B.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022258|Y73C8B.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022258|Y73C8B.1|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022259|Y73C8B.2|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=291|total_reads(49.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022259|Y73C8B.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022259|Y73C8B.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022259|Y73C8B.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022259|Y73C8B.2|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|26nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=916|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=804|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|61nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022260|Y73C8B.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022261|clec-210|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022261|clec-210|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022261|clec-210|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022261|clec-210|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022262|Y73C8C.3|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00022262|Y73C8C.3|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00022263|Y73C8C.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022265|Y73C8C.8|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022267|Y73C8C.10|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022268|Y73E7A.1a|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022268|Y73E7A.1a|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022268|Y73E7A.1a|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022268|Y73E7A.1a|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022268|Y73E7A.1a|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2825|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022268|Y73E7A.1a|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022268|Y73E7A.1a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|1056nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|1117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|450nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022269|Y73E7A.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=309|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3a|1382nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3a|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=310|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3a|405nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=274|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3a|594nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=316|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3a|783nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=300|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3b.1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022270|Y73E7A.3b.1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|316nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15832|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|332nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|746nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022271|cpx-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|178nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|181nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|214nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=821|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|258nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|263nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022273|Y73E7A.6.2|708nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022274|Y73E7A.8|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022275|Y74C9A.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|1056nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|1068nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|199nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=246|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|204nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=2739|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|209nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|212nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36803|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4877|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022276|nlp-40|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4747|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=838|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022277|homt-1|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|1166nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|1175nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|1180nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|1187nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|1257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|1260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|415nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|425nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=2687|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|584nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|747nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022278|rcor-1|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|261nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|293nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1730|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022279|sesn-1|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7105|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022280|Y74C10AL.2.1|674nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|1099nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|379nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=729|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022281|abtm-1|782nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022282|Y74C10AR.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00022282|Y74C10AR.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022282|Y74C10AR.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=946|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022283|lgc-27|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022284|glb-33|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022284|glb-33|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2615|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00022284|glb-33|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022285|Y75B7AL.2b|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1082|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022285|Y75B7AL.2b|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022285|Y75B7AL.2b|233nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022285|Y75B7AL.2b|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|730nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2428|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022286|rga-4|733nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|50nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|54nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022287|Y75B7AR.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7433|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022288|Y75B7B.1|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=200|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022288|Y75B7B.1|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022288|Y75B7B.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00022288|Y75B7B.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|353nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|356nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=542|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|359nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|361nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|365nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|471nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022292|Y75D11A.3|474nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022295|cng-2|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=337|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022295|cng-2|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022295|cng-2|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022295|cng-2|179nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022296|xpc-1|1134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2278|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022296|xpc-1|1137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=309|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022296|xpc-1|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022296|xpc-1|938nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022296|xpc-1|942nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022296|xpc-1|985nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3891|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3007|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022297|Y76B12C.3a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022298|Y76B12C.4b|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022298|Y76B12C.4b|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022298|Y76B12C.4b|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=291|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022298|Y76B12C.4b|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022298|Y76B12C.4b|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|1540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|1564nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|1572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=379|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2533|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|750nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=490|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|838nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022300|Y76B12C.6a|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022301|cpsf-1|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022301|cpsf-1|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1323|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00022301|cpsf-1|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022301|cpsf-1|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|70nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022302|Y76B12C.8|84nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022303|Y76B12C.9|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00022303|Y76B12C.9|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00022303|Y76B12C.9|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00022303|Y76B12C.9|307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(55.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022303|Y76B12C.9|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2115|total_reads(82.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022306|hxk-3|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|1000nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|1124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1474|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=212|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|824nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|860nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|934nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|950nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022307|Y77E11A.2|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022309|rpc-11|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1472|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022309|rpc-11|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022309|rpc-11|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022309|rpc-11|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022309|rpc-11|161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022309|rpc-11|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022309|rpc-11|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022310|Y77E11A.7c|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022310|Y77E11A.7c|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022310|Y77E11A.7c|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1181|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022310|Y77E11A.7c|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=600|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022310|Y77E11A.7c|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022311|Y77E11A.8|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022313|Y77E11A.12c|1479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022313|Y77E11A.12c|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=463|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022314|Y77E11A.14a.2|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=223|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022314|Y77E11A.14a.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022316|Y81B9A.2|1424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022316|Y81B9A.2|1557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00022316|Y81B9A.2|984nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022320|Y82E9BL.3|1382nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022320|Y82E9BL.3|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(63.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022321|fbxa-25|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022322|Y82E9BL.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022322|Y82E9BL.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022323|Y82E9BL.6|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022324|fbxa-26|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00022324|fbxa-26|20nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022324|fbxa-26|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022325|fbxa-5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022325|fbxa-5|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022325|fbxa-5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00022326|fbxa-14|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022326|fbxa-14|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=325|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022326|fbxa-14|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022326|fbxa-14|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022326|fbxa-14|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022327|fbxa-15|131nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022327|fbxa-15|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022327|fbxa-15|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022327|fbxa-15|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022327|fbxa-15|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022328|Y82E9BL.12|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022328|Y82E9BL.12|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022329|fbxa-79|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1254|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022329|fbxa-79|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022329|fbxa-79|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022330|fbxa-80|1326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022330|fbxa-80|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=207|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022332|fbxa-20|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022333|fbxa-27|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022333|fbxa-27|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022334|Y82E9BR.1|282nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(73.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022334|Y82E9BR.1|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022334|Y82E9BR.1|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|194nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1100|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022335|Y82E9BR.2|248nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3276|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=827|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=451329|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=559|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5385|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=809|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=232|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|217nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|221nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23270|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=733|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|281nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=350|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1213|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022336|Y82E9BR.3.2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022337|Y82E9BR.4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|418nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|548nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022338|Y82E9BR.5|614nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022339|Y82E9BR.6|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022339|Y82E9BR.6|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022344|Y82E9BR.11|811nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022345|fbxa-138|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022345|fbxa-138|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022346|Y82E9BR.13|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022346|Y82E9BR.13|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4731|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|185nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|192nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=182|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=691|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022347|Y82E9BR.14b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2424|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|312nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=712|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|330nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|332nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|350nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|475nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|508nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|517nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|643nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|776nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022348|Y82E9BR.16b|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022349|Y82E9BR.17b.1|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022349|Y82E9BR.17b.1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022349|Y82E9BR.17b.1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022349|Y82E9BR.17b.1|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022349|Y82E9BR.17b.1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022349|Y82E9BR.17b.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022350|Y82E9BR.18|189nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1224|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022350|Y82E9BR.18|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022350|Y82E9BR.18|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022351|Y82E9BR.19|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022351|Y82E9BR.19|1328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022351|Y82E9BR.19|1347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1980|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022351|Y82E9BR.19|1354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=415|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022351|Y82E9BR.19|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022351|Y82E9BR.19|943nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022353|Y82E9BR.21|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022354|Y82E9BR.22|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2314|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00022354|Y82E9BR.22|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=410|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022354|Y82E9BR.22|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022354|Y82E9BR.22|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022354|Y82E9BR.22|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022354|Y82E9BR.22|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1570|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022356|eak-3|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00022356|eak-3|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00022357|kbp-4|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1832|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022357|kbp-4|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022357|kbp-4|825nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022358|Y92H12A.2a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022358|Y92H12A.2a|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022358|Y92H12A.2a|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022358|Y92H12A.2a|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022358|Y92H12A.2a|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2731|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022358|Y92H12A.2a|592nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022360|Y92H12A.4a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|159nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|434nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|888nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|892nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=941|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022361|Y92H12A.5a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022363|Y92H12BL.1a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022363|Y92H12BL.1a|1227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=793|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00022363|Y92H12BL.1a|1232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=171|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022363|Y92H12BL.1a|1235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022363|Y92H12BL.1a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022365|Y92H12BL.4|1198nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022366|Y92H12BL.5|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022366|Y92H12BL.5|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022366|Y92H12BL.5|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=125|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022366|Y92H12BL.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00022367|Y92H12BM.1|1072nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022367|Y92H12BM.1|1078nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=612|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022367|Y92H12BM.1|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022367|Y92H12BM.1|723nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022367|Y92H12BM.1|728nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022367|Y92H12BM.1|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022367|Y92H12BM.1|949nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2744|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022368|Y92H12BR.2|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|574nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1355|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|667nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022369|Y92H12BR.3b|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022371|set-29|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022371|set-29|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022371|set-29|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=672|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022371|set-29|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=311|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022371|set-29|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022371|set-29|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=277|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1056nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=238|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|1303nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022373|mrpl-15|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=253|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022374|nhr-277|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=452|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022374|nhr-277|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022374|nhr-277|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022375|Y94H6A.2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|1388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|175nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=244|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022376|Y94H6A.3|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2877|total_reads(78.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022377|gpx-4|494nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(80.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022377|gpx-4|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022377|gpx-4|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022377|gpx-4|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022378|Y94H6A.5b|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022378|Y94H6A.5b|43nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022378|Y94H6A.5b|47nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=991|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022378|Y94H6A.5b|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=349|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022379|Y94H6A.7|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022379|Y94H6A.7|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=455|total_reads(83.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022379|Y94H6A.7|867nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=907|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=638|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|232nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022380|Y94H6A.8.2|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10304|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2356|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=448|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022381|ubxn-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=867|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4284|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=391|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2737|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1136|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=502|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=156|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|207nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=547|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|215nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=258|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|222nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1321|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|224nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=557|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|230nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022382|Y94H6A.10|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022383|Y95B8A.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022383|Y95B8A.2|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022383|Y95B8A.2|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1043|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022383|Y95B8A.2|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022383|Y95B8A.2|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022385|Y95B8A.4|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022386|Y95B8A.6c|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|1005nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2421|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|1128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|1150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|1240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|916nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|995nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022388|Y95B8A.8|998nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|1197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|1259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|1526nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|1593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|671nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|710nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|713nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|718nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=672|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|721nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|723nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=1124|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|729nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|731nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022389|pde-6|738nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022390|him-19|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022390|him-19|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1075|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022390|him-19|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022390|him-19|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=227|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022390|him-19|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1875|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=252|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=399|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022391|Y95B8A.12b|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022392|Y97E10AL.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022392|Y97E10AL.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022392|Y97E10AL.1|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022392|Y97E10AL.1|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022392|Y97E10AL.1|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022392|Y97E10AL.1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=364|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022392|Y97E10AL.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022393|abhd-12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022393|abhd-12|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022393|abhd-12|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022393|abhd-12|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022393|abhd-12|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=275|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022393|abhd-12|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4783|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022393|abhd-12|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=295|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022394|Y97E10AL.3|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1979|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022395|ceh-76|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022396|Y97E10AR.1.2|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=523|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022396|Y97E10AR.1.2|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022397|Y97E10AR.2b|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022397|Y97E10AR.2b|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022398|Y97E10AR.3|1020nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022398|Y97E10AR.3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022398|Y97E10AR.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022398|Y97E10AR.3|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1920|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022398|Y97E10AR.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022398|Y97E10AR.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022398|Y97E10AR.3|92nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022399|Y97E10AR.4|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022399|Y97E10AR.4|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=471|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022399|Y97E10AR.4|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=280|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022399|Y97E10AR.4|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022399|Y97E10AR.4|870nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=659|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6625|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022400|rpb-9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3171|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=837|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022401|Y97E10AR.6|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1737|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|150nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1868|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|153nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022402|lmtr-2|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1013|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022403|Y97E10B.1|251nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022403|Y97E10B.1|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022403|Y97E10B.1|479nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022404|srsx-5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022404|srsx-5|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022404|srsx-5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022404|srsx-5|151nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022404|srsx-5|155nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022405|srsx-6|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022405|srsx-6|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022405|srsx-6|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022405|srsx-6|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022405|srsx-6|83nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022405|srsx-6|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022408|srsx-3|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022408|srsx-3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022408|srsx-3|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022408|srsx-3|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=446|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022408|srsx-3|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022408|srsx-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022409|srt-53|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|423nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|823nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|857nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|859nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|861nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|865nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=601|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|868nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7288|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3665|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|893nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022410|Y97E10C.1.2|935nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022411|Y102A11A.1|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022411|Y102A11A.1|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022412|Y102A11A.2b|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022412|Y102A11A.2b|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=478|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022412|Y102A11A.2b|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00022413|Y102A11A.3|508nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022413|Y102A11A.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022413|Y102A11A.3|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1056|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022413|Y102A11A.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022413|Y102A11A.3|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=108|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6619|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=830|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022415|Y102A11A.5|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022416|Y102A11A.6|1001nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022416|Y102A11A.6|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(51.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022416|Y102A11A.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022417|Y102A11A.7|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022417|Y102A11A.7|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022417|Y102A11A.7|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=868|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022417|Y102A11A.7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022417|Y102A11A.7|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022417|Y102A11A.7|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022418|igcm-4|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=837|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022418|igcm-4|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022418|igcm-4|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|252nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1663|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022419|Y102A11A.9a|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4605|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=528|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022420|Y102E9.2a|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022423|nhr-41|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022423|nhr-41|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022423|nhr-41|1273nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022423|nhr-41|1288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=754|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00022423|nhr-41|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022423|nhr-41|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=583|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|1124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1592|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|1172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|1188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|821nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022425|plst-1|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022426|Y104H12D.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022426|Y104H12D.2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=644|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022426|Y104H12D.2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022427|Y104H12D.3a|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022427|Y104H12D.3a|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022427|Y104H12D.3a|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1551|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022428|Y104H12D.4|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=875|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022433|Y108F1.5|1301nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022433|Y108F1.5|1329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00022433|Y108F1.5|1331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=806|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022433|Y108F1.5|1340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022433|Y108F1.5|1346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022435|Y108G3AL.3b|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022435|Y108G3AL.3b|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=234|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022435|Y108G3AL.3b|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022435|Y108G3AL.3b|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022438|Y110A2AL.1|1032nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00022438|Y110A2AL.1|1258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00022438|Y110A2AL.1|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00022439|Y110A2AL.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022439|Y110A2AL.2|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022440|Y110A2AL.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022440|Y110A2AL.3|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022441|Y110A2AL.4a|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022441|Y110A2AL.4a|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022441|Y110A2AL.4a|267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022441|Y110A2AL.4b|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022441|Y110A2AL.4b|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1612|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00022441|Y110A2AL.4b|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022442|Y110A2AL.5|1482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=155|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022442|Y110A2AL.5|1487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022442|Y110A2AL.5|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022442|Y110A2AL.5|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022444|Y110A2AL.7|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=255|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022445|Y110A2AL.9|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022446|Y110A2AL.10|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(39.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022446|Y110A2AL.10|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022447|hpo-20|1443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022447|hpo-20|1488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022447|hpo-20|1490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022447|hpo-20|1492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00022447|hpo-20|1495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022447|hpo-20|1510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=236|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|844nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|847nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|854nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|862nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=719|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|869nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=366|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|883nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=239|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022448|pinn-1|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022449|Y110A2AM.1|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00022449|Y110A2AM.1|1523nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022449|Y110A2AM.1|1526nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022449|Y110A2AM.1|1528nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2133|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=907|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=640|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1182|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022452|Y110A2AR.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1295|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2550|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8629|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|438nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|1441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|1446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|1453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|1458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022453|Y110A2AR.3b|622nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022454|Y110A7A.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022454|Y110A7A.2|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022454|Y110A7A.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022455|tyms-1|443nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022455|tyms-1|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022455|tyms-1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1894|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022455|tyms-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022455|tyms-1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|179nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=661|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4596|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|291nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022456|pfkb-1.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022457|Y110A7A.7|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1302|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022457|Y110A7A.7|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1039|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022457|Y110A7A.7|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022457|Y110A7A.7|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022457|Y110A7A.7|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022457|Y110A7A.7|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022457|Y110A7A.7|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|1095nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|1512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=514|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3042|total_reads(63.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=894|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022458|prp-31|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=80|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|134nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1588|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=571|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|1477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022459|Y110A7A.9a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1249|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3885|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|752nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022460|use-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|456nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|459nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=239|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|461nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=438|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|463nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=249|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|465nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=162|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|467nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022462|Y110A7A.15b|469nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|1332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1839|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|921nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022463|elpc-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=814|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2670|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022465|ift-20|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022466|Y119C1A.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022466|Y119C1A.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022466|Y119C1A.1|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022466|Y119C1A.1|405nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=662|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022466|Y119C1A.1|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022466|Y119C1A.1|411nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=291|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022466|Y119C1A.1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022467|Y119C1B.1|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022467|Y119C1B.1|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022467|Y119C1B.1|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022469|Y119C1B.3|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022469|Y119C1B.3|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022469|Y119C1B.3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022469|Y119C1B.3|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022469|Y119C1B.3|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022469|Y119C1B.3|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1569|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00022469|Y119C1B.3|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=455|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|140nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|180nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|214nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|363nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|665nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|674nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|775nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1395|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|90nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022470|mrpl-19|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022471|Y119C1B.5|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022471|Y119C1B.5|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022471|Y119C1B.5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=324|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022471|Y119C1B.5|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=859|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3783|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|36nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=209|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|51nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|628nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|794nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|880nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|882nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022472|Y119C1B.6|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|315nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=660|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1725|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|618nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022473|bet-1|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=393|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=79|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|390nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022474|zig-9|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=399|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=561|total_reads(40.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10b|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022475|Y119C1B.10b|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022477|fbxa-28|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022478|fbxa-35|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022478|fbxa-35|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00022478|fbxa-35|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022479|fbxa-36|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022479|fbxa-36|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022479|fbxa-36|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022479|fbxa-36|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022479|fbxa-36|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022482|fbxa-208|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00022482|fbxa-208|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=233|total_reads(42.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022482|fbxa-208|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022482|fbxa-208|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022482|fbxa-208|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022484|fbxa-77|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=337|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00022484|fbxa-77|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022484|fbxa-77|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00022484|fbxa-77|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022485|fbxa-63|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022485|fbxa-63|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022485|fbxa-63|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1044|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022485|fbxa-63|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022486|fbxa-61|1137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022486|fbxa-61|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00022487|fbxa-21|187nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00022487|fbxa-21|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022487|fbxa-21|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022487|fbxa-21|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022488|orc-3|1570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022488|orc-3|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=248|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00022488|orc-3|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=813|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022488|orc-3|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022489|Y119D3B.12b|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022489|Y119D3B.12b|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022489|Y119D3B.12b|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022489|Y119D3B.12b|421nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022490|Y119D3B.13|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022490|Y119D3B.13|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022490|Y119D3B.13|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022490|Y119D3B.13|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=883|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022490|Y119D3B.13|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022490|Y119D3B.13|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022491|Y119D3B.14|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022491|Y119D3B.14|402nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=379|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022491|Y119D3B.14|405nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022491|Y119D3B.14|408nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022491|Y119D3B.14|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022491|Y119D3B.14|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022491|Y119D3B.14|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|252nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=145|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|263nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13444|total_reads(83.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=872|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=367|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|288nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=857|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022492|dss-1|354nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022493|mrpl-45|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022493|mrpl-45|1056nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022493|mrpl-45|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1372|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022493|mrpl-45|1073nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022493|mrpl-45|1420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022494|fbxa-91|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022494|fbxa-91|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022494|fbxa-91|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022494|fbxa-91|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022494|fbxa-91|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022495|fbxa-78|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022495|fbxa-78|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022496|fbxa-92|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022496|fbxa-92|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022496|fbxa-92|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(48.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022496|fbxa-92|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022496|fbxa-92|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|141nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|1439nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|143nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|273nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=518|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18919|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23851|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022497|Y119D3B.21|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022498|hsd-2|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022498|hsd-2|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022499|set-30|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022499|set-30|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022499|set-30|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022499|set-30|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|264nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2478|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12554|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=900|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022500|lfi-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022501|ZC8.6|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022501|ZC8.6|338nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=51|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022501|ZC8.6|347nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=81|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022501|ZC8.6|349nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1100|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022501|ZC8.6|356nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022501|ZC8.6|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022501|ZC8.6|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022502|ZC13.1b|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022502|ZC13.1b|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022502|ZC13.1b|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022502|ZC13.1b|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1603|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022502|ZC13.1b|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022502|ZC13.1b|282nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|351nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|354nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|452nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|469nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|472nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|478nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022503|ZC13.2|783nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022504|mam-1|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022504|mam-1|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3b|896nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3b|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3b|915nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3b|918nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3b|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1264nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=970|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1277nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1307nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|1323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|273nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022505|ZC21.3c|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022506|ZC21.6a|629nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=381|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022506|ZC21.6a|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022506|ZC21.6a|672nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022507|ZC21.8|179nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022507|ZC21.8|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022507|ZC21.8|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022507|ZC21.8|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=353|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022507|ZC21.8|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022508|ZC53.1|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022508|ZC53.1|459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022512|dot-1.5|683nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022512|dot-1.5|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=856|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1305|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022515|ttr-48|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=601|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1283|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2326|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|1158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022516|mtx-2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=724|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=506|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022517|ZC123.1|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|391nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|393nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|397nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|540nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|610nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|615nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|621nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022518|zfh-2|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3925|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022519|ZC123.4c|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022519|ZC123.4c|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022519|ZC123.4c|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1148|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022519|ZC123.4c|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=355|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022521|ZC132.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022521|ZC132.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=142|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|1157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=902|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=339|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7615|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022522|ZC132.3|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022523|ZC132.4|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022523|ZC132.4|597nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022526|ZC132.8|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022526|ZC132.8|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022526|ZC132.8|198nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022526|ZC132.8|249nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022526|ZC132.8|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022526|ZC132.8|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022526|ZC132.8|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|318nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1502|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=823|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|471nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022527|ZC132.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022528|srt-13|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022529|srt-14|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022530|ZC155.2|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022530|ZC155.2|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=859|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022530|ZC155.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022530|ZC155.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022531|morc-1|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=419|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022531|morc-1|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022531|morc-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022531|morc-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=737|total_reads(61.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022531|morc-1|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022531|morc-1|338nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|1261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1873|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=121|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|807nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|833nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|843nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022532|ZC155.4|882nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022533|cutl-19|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022533|cutl-19|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00022533|cutl-19|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00022533|cutl-19|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022533|cutl-19|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|205nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=691|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3168|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|91nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022534|syx-16|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022537|ZC190.2|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022537|ZC190.2|172nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022537|ZC190.2|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022537|ZC190.2|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022537|ZC190.2|965nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022538|ZC190.4|1060nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022538|ZC190.4|1069nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022538|ZC190.4|1074nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022538|ZC190.4|967nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022538|ZC190.4|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022540|ZC190.6|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022540|ZC190.6|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00022540|ZC190.6|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022540|ZC190.6|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022540|ZC190.6|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022540|ZC190.6|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=304|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022541|ZC190.7|441nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022541|ZC190.7|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022541|ZC190.7|452nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022541|ZC190.7|456nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022541|ZC190.7|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(77.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022542|ZC190.8|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022542|ZC190.8|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022542|ZC190.8|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022542|ZC190.8|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022544|ZC190.10a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022546|ZC196.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022547|ZC196.3a|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022548|ZC196.4|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022548|ZC196.4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022548|ZC196.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00022549|ZC196.5|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=546|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022549|ZC196.5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022549|ZC196.5|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022550|droe-8|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022551|ZC196.8|1181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00022551|ZC196.8|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022551|ZC196.8|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022551|ZC196.8|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022551|ZC196.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022551|ZC196.8|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022552|ZC196.9a|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022552|ZC196.9a|193nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022552|ZC196.9a|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022552|ZC196.9a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022552|ZC196.9a|420nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022554|duxl-1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3020|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022554|duxl-1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022555|btb-12|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022555|btb-12|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00022555|btb-12|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022555|btb-12|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022557|fbxb-15|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(67.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022557|fbxb-15|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022557|fbxb-15|678nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022558|fbxb-21|1375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022558|fbxb-21|1378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022558|fbxb-21|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00022559|fbxb-20|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(86.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022559|fbxb-20|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022560|fbxb-16|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022561|btb-13|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022561|btb-13|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022562|ZC204.12|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022562|ZC204.12|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022562|ZC204.12|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=432|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022562|ZC204.12|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=289|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022562|ZC204.12|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=212|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022564|ZC204.14|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022564|ZC204.14|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022564|ZC204.14|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022564|ZC204.14|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022565|ZC239.2|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022566|ZC239.3|714nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022566|ZC239.3|800nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022566|ZC239.3|803nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022566|ZC239.3|806nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022567|ZC239.4|146nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022567|ZC239.4|148nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022567|ZC239.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|1269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|449nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|454nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022568|ZC239.5|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=92|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=945|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|257nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=289|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|260nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=160|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|262nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|264nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=403|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|769nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|804nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2400|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1176|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|821nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022569|ZC239.6.3|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022570|sdz-35|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022571|ZC239.13a|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022572|ZC239.14|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022572|ZC239.14|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022572|ZC239.14|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022573|ZC239.15|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022573|ZC239.15|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022573|ZC239.15|67nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022574|ZC239.16|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022575|ZC239.17|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022575|ZC239.17|711nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022576|ZC250.2|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00022576|ZC250.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022577|nstp-3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022578|ZC262.1|1304nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022578|ZC262.1|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=462|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022578|ZC262.1|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022578|ZC262.1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2165|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=655|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=137|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1037|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|207nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2a|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2b|553nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2b|561nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022579|ZC262.2b|711nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|1234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|1239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4694|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1024|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=191|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=317|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022580|iglr-2|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022581|ZC262.4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022581|ZC262.4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=126|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022581|ZC262.4|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022581|ZC262.4|60nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00022582|ZC262.5|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4210|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022582|ZC262.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022582|ZC262.5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022583|mrps-18A|1054nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022583|mrps-18A|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022583|mrps-18A|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022583|mrps-18A|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022583|mrps-18A|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2777|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022583|mrps-18A|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=716|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022583|mrps-18A|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022584|ZC266.1|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022584|ZC266.1|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=216|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022584|ZC266.1|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1125|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022584|ZC266.1|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022586|ZC308.4a|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2207|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00022586|ZC308.4a|104nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022586|ZC308.4a|153nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022586|ZC308.4a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022586|ZC308.4a|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022586|ZC308.4a|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022588|ZC317.2|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022588|ZC317.2|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=55|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022588|ZC317.2|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022589|ZC317.6|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022589|ZC317.6|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022589|ZC317.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022589|ZC317.6|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=362|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|139nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022590|ZC317.7|490nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022591|cuti-1|101nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022591|cuti-1|103nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022591|cuti-1|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022591|cuti-1|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=555|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|1075nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|1089nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=882|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=640|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022592|klu-2|956nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=365|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1228|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|50nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022593|ZC328.3b|887nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022594|ZC328.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022594|ZC328.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022596|ZC395.4|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022596|ZC395.4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022597|ZC395.5|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022597|ZC395.5|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022597|ZC395.5|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022597|ZC395.5|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022597|ZC395.5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6133|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022597|ZC395.5|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|1122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|1152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|1173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|1182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|118nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|126nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1281|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|306nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=99|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|311nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=179|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022598|ztf-8|446nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|1267nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|1272nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|1282nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25611|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3971|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=279|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022599|ZC395.10.1|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|506nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|600nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022601|ZC404.1|643nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|303nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|310nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|313nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|319nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|440nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1472|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|444nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=251|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|450nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=255|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022603|gck-2|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022604|dmsr-10|341nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022605|dmsr-11|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|1269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|581nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022606|dmsr-9|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|1301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|363nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|416nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|636nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|640nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=551|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|645nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=803|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022608|madf-9|648nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022609|ZC416.2|1078nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022609|ZC416.2|1080nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022609|ZC416.2|1082nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022609|ZC416.2|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1228|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022609|ZC416.2|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022610|ZC416.6b|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3169|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022610|ZC416.6b|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|1495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|177nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022611|ZC449.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022612|ZC449.2|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022612|ZC449.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022612|ZC449.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022612|ZC449.2|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|295nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=452|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=506|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=688|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|426nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|432nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=640|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|438nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|441nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|444nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022613|sek-3|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=761|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|272nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=938|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3528|total_reads(55.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|289nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=601|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|361nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022614|ZC449.4|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|445nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=693|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=139|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022615|ZC449.5|500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022616|hsd-3|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022617|ZC477.2|1585nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022617|ZC477.2|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022617|ZC477.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2613|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1540|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1789|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=295|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3a|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022618|ZC477.3c|443nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022620|rde-8|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022620|rde-8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1833|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00022620|rde-8|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022620|rde-8|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022621|ZC477.7a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022621|ZC477.7a|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022621|ZC477.7a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1036|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022621|ZC477.7a|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022621|ZC477.7a|558nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022621|ZC477.7a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=148|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=794|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022623|ZC487.1a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022624|ZC487.2|1490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022624|ZC487.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022625|ZC487.3|1180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022626|ZC513.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022628|ZC513.3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022628|ZC513.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022628|ZC513.3|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022628|ZC513.3|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|1088nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1266|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=125|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|446nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|451nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|533nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022629|ZC513.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022630|fbxa-223|278nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022631|nekl-2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022631|nekl-2|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022631|nekl-2|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022631|nekl-2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00022631|nekl-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=152|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00022631|nekl-2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=450|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022632|ZC581.2|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022632|ZC581.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022632|ZC581.2|1153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022632|ZC581.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022633|ZC581.3|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022633|ZC581.3|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022633|ZC581.3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1130|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022633|ZC581.3|1505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022634|ZC581.7|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=946|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022634|ZC581.7|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=39|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022634|ZC581.7|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|106nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1291|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|128nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|133nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|136nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|140nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=699|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|288nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|295nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022635|ZC581.9|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022638|scl-27|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022638|scl-27|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022639|nhr-253|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022639|nhr-253|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00022639|nhr-253|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022640|nhr-254|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022640|nhr-254|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022640|nhr-254|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022641|ZK6.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022641|ZK6.6|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022641|ZK6.6|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022641|ZK6.6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|118nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=630|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3223|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|416nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|419nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|424nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12031|total_reads(69.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=460|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|503nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022642|lipl-5|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022643|ZK6.8|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022643|ZK6.8|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=157|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022643|ZK6.8|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|1329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|133nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1524|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=220|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=533|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3645|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1808|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022644|dod-19|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=838|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022645|ZK6.11a|111nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022645|ZK6.11a|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1488|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022645|ZK6.11a|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13594|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022645|ZK6.11a|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3752|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00022645|ZK6.11a|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=863|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022645|ZK6.11a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022645|ZK6.11a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022646|acl-9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022646|acl-9|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|1390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|1402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|1409nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3900|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=538|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|323nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|325nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|375nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=204|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|381nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|406nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022647|slc-17.1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|699nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|756nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12622|total_reads(50.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12246|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022648|ZK54.3|802nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022649|ZK84.1|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2063|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022649|ZK84.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022649|ZK84.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022649|ZK84.1|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=159|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=831|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1067|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022650|ZK84.2|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022652|ZK84.5|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=472|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=297|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3795|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022653|ZK105.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022654|ZK105.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022655|srsx-40|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022655|srsx-40|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022656|ZK105.5|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022660|ZK112.4|699nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1097nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1239nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1489nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|1536nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=389|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=946|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|520nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|525nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|528nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=530|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|611nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|615nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|654nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|65nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3886|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|841nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|898nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022661|ZK112.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022662|ZK112.6|1369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022662|ZK112.6|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022662|ZK112.6|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022662|ZK112.6|256nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022662|ZK112.6|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022662|ZK112.6|459nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022663|glrx-21|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022663|glrx-21|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022663|glrx-21|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022663|glrx-21|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2586|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022663|glrx-21|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022663|glrx-21|37nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022663|glrx-21|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022664|ZK121.2|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022664|ZK121.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022664|ZK121.2|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022664|ZK121.2|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2772|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022664|ZK121.2|276nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022665|ZK154.1|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022665|ZK154.1|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022665|ZK154.1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=817|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00022665|ZK154.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|1251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|1260nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|1262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|1438nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3073|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|86nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022666|ZK154.4|936nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022667|ZK154.5|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022667|ZK154.5|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022667|ZK154.5|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2711|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022667|ZK154.5|707nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|1468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=258|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9155|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|279nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7541|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|282nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1172|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=763|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|287nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=169|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|609nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022668|ZK154.6b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022669|ZK177.1|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022670|ZK177.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022671|ZK177.3|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022672|ZK177.4.2|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2778|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022672|ZK177.4.2|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=192|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022672|ZK177.4.2|988nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|144nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2670|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022673|ZK177.8b.1|937nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022674|ZK177.9|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022674|ZK177.9|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022674|ZK177.9|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2724|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1105|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022675|gbb-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022677|ZK180.3c|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022677|ZK180.3c|116nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022677|ZK180.3c|122nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1290|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022677|ZK180.3c|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=189|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00022677|ZK180.3c|131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022677|ZK180.3c|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022677|ZK180.3c|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|251nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|263nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|283nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|286nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|457nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1859|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|465nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1257|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|471nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=774|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7236|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|488nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=362|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|530nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|532nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|534nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022678|sar-1|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=334|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5157|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1120|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022679|ZK180.5a|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022680|ZK180.6b|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1325|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022680|ZK180.6b|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022681|ZK185.1a|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022681|ZK185.1a|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022681|ZK185.1a|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022681|ZK185.1a|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022681|ZK185.1a|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022681|ZK185.1a|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022681|ZK185.1a|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00022682|ZK185.2|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022682|ZK185.2|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=429|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=430|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022683|ZK185.3|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022685|ZK250.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022689|math-48|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022690|math-49|89nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022691|math-50|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022692|ZK250.9|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1215|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|742nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022694|ZK328.4|773nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022695|ZK328.6|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022695|ZK328.6|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00022695|ZK328.6|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022695|ZK328.6|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022695|ZK328.6|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022696|ZK328.7a|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00022696|ZK328.7a|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022696|ZK328.7a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022696|ZK328.7a|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022696|ZK328.7b|1019nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|392nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|396nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|541nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|544nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|563nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4179|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022697|cyy-1|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022698|ZK353.2|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(43%)
- ID=WBGene00022698|ZK353.2|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022698|ZK353.2|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022698|ZK353.2|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022698|ZK353.2|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022698|ZK353.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022699|ZK353.3|1063nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022699|ZK353.3|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022699|ZK353.3|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00022699|ZK353.3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022699|ZK353.3|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00022700|ZK353.4|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022700|ZK353.4|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022700|ZK353.4|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022700|ZK353.4|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022700|ZK353.4|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022700|ZK353.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022700|ZK353.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=759|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|472nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=722|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|475nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3118|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|478nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022702|cutc-1|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022703|ubxn-4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022703|ubxn-4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2778|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022703|ubxn-4|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=898|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00022703|ubxn-4|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022703|ubxn-4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022703|ubxn-4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2725|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=969|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|353nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|359nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022704|ZK353.9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022705|ZK354.2a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=998|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022705|ZK354.2a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022705|ZK354.2b|1411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022705|ZK354.2b|1426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9508|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022705|ZK354.2b|1430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022705|ZK354.2b|1436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022705|ZK354.2b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022706|ZK354.3|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022706|ZK354.3|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=223|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022707|ZK354.6|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022707|ZK354.6|1051nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4204|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022707|ZK354.6|1055nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022707|ZK354.6|1059nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022707|ZK354.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022707|ZK354.6|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022708|ZK354.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022708|ZK354.7|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022708|ZK354.7|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022708|ZK354.7|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022709|ZK354.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022709|ZK354.8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022709|ZK354.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022709|ZK354.8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022710|ZK354.9|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022710|ZK354.9|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022710|ZK354.9|535nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022710|ZK354.9|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022710|ZK354.9|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022712|ZK355.2a|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022712|ZK355.2a|253nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022712|ZK355.2a|257nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022712|ZK355.2a|265nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2552|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022712|ZK355.2a|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022713|ZK355.3|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022713|ZK355.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022714|irld-64|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022715|irld-65|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022715|irld-65|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|307nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|313nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4648|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022717|hipr-1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|254nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1319|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4644|total_reads(70.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022718|ZK370.4a|522nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|162nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=430|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|168nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|358nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2819|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2196|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022719|pdhk-2|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022720|ZK370.6a|564nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=595|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022720|ZK370.6a|570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2558|total_reads(79%)
- ID=WBGene00022720|ZK370.6a|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022720|ZK370.6a|577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022720|ZK370.6a|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022720|ZK370.6b|1572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|1121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|213nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|222nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=397|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022721|ugtp-1|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=916|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022722|ZK370.8|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022722|ZK370.8|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3318|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022722|ZK370.8|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022722|ZK370.8|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022722|ZK370.8|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022723|ZK380.2|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022724|ZK380.4|1086nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022724|ZK380.4|1092nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022725|ZK381.2|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022725|ZK381.2|393nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022725|ZK381.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022725|ZK381.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022726|nhr-249|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=384|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=382|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022727|prkl-1|462nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022728|ZK402.1|1051nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022728|ZK402.1|1143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022728|ZK402.1|1267nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(53.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022728|ZK402.1|1270nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022729|ZK402.2|1101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022730|ZK402.3|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=258|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00022730|ZK402.3|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022730|ZK402.3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022732|ZK418.2a|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022732|ZK418.2a|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=792|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022732|ZK418.2a|84nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=211|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022732|ZK418.2a|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022733|ZK418.3|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022733|ZK418.3|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022733|ZK418.3|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=505|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022733|ZK418.3|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022733|ZK418.3|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022733|ZK418.3|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022733|ZK418.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=462|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3790|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022734|ZK418.5|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022735|ZK418.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022735|ZK418.6|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022735|ZK418.6|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022735|ZK418.6|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022736|ZK418.7|136nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022736|ZK418.7|139nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022736|ZK418.7|142nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=222|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022736|ZK418.7|145nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022736|ZK418.7|216nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022736|ZK418.7|219nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022736|ZK418.7|222nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022737|tofu-7|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022737|tofu-7|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2552|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022737|tofu-7|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022737|tofu-7|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022738|ZK418.9b.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022738|ZK418.9b.2|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1568|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022738|ZK418.9b.2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5752|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022738|ZK418.9b.2|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=413|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022738|ZK418.9b.2|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022739|toe-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022739|toe-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022739|toe-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022739|toe-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1603|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00022739|toe-1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022741|ZK430.5|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022741|ZK430.5|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022741|ZK430.5|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=785|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|310nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|317nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|347nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|386nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|395nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022742|ZK430.7|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022743|mlt-7|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022743|mlt-7|303nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022743|mlt-7|306nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022743|mlt-7|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=974|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022743|mlt-7|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=496|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00022744|ZK470.1|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|1058nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|1584nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|194nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|198nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|201nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|205nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|599nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=160|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|613nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13808|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|622nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|628nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|756nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|764nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|772nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022745|ZK470.2c|926nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022747|ZK470.6|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022747|ZK470.6|206nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=332|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00022747|ZK470.6|210nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022747|ZK470.6|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022747|ZK470.6|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=564|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=434|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|402nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|420nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35989|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3826|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|439nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=329|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|441nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|443nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|683nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022748|oaz-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|453nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|458nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2469|total_reads(60.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=850|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|468nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022749|ZK484.3|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|1125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|1573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|400nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3635|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022750|ZK484.4b|968nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022751|ZK484.5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022751|ZK484.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=488|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022751|ZK484.5|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12556|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022751|ZK484.5|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022751|ZK484.5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022751|ZK484.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022752|ZK484.6|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=794|total_reads(89.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022752|ZK484.6|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022752|ZK484.6|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1057nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=521|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1080nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1115nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1120nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=407|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|1285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|741nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|796nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|804nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=242|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|813nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|815nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|910nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|914nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|942nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022753|ZK484.7|946nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022754|nspd-1|142nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022754|nspd-1|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022754|nspd-1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022754|nspd-1|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022754|nspd-1|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11331|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022754|nspd-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022756|nhr-251|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022757|ZK488.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022758|ZK488.6|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022758|ZK488.6|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|115nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5569|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|122nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=174|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022759|ZK546.2a|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022761|ZK546.4|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022761|ZK546.4|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=666|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022761|ZK546.4|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=221|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022762|ZK546.5|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022762|ZK546.5|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=203|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022762|ZK546.5|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022762|ZK546.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022762|ZK546.5|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022765|ZK546.14b.1|1053nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022765|ZK546.14b.1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022765|ZK546.14b.1|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3334|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022765|ZK546.14b.1|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=888|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022765|ZK546.14b.1|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022765|ZK546.14b.1|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022765|ZK546.14b.1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|1129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2958|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022766|cblc-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022767|ZK563.2|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022767|ZK563.2|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1444|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022769|ZK563.5|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022770|acp-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022770|acp-1|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022770|acp-1|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(80.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|1394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=294|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=306|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022771|ZK616.1.1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022772|ZK616.2|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022772|ZK616.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=584|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022773|ZK616.3a|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=974|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2371|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|691nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022774|swsn-6|693nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022775|ZK616.5|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022775|ZK616.5|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022775|ZK616.5|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2816|total_reads(90.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022775|ZK616.5|538nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022775|ZK616.5|543nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022775|ZK616.5|865nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|1311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8085|total_reads(63.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4310|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=177|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|656nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022776|perm-3|925nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022778|ZK616.8|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022778|ZK616.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022778|ZK616.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022778|ZK616.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022780|ZK622.1|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022781|pmt-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022781|pmt-1|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11737|total_reads(81.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022781|pmt-1|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2332|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022781|pmt-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022781|pmt-1|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022781|pmt-1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022781|pmt-1|391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022782|ZK622.4|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=883|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022782|ZK622.4|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022782|ZK622.4|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022782|ZK622.4|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022783|tomm-7|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12502|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022783|tomm-7|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2418|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022783|tomm-7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022783|tomm-7|503nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022785|ZK652.6a|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022785|ZK652.6a|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022785|ZK652.6a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1389|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022785|ZK652.6a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=778|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022785|ZK652.6a|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022786|ZK652.8|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022786|ZK652.8|619nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022786|ZK652.8|629nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022786|ZK652.8|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022786|ZK652.8|665nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3118|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022786|ZK652.8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|168nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2731|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|575nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|655nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022787|tag-307|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022788|slc-17.7|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022788|slc-17.7|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1871|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022788|slc-17.7|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022788|slc-17.7|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022789|lron-2|290nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=367|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00022789|lron-2|292nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022789|lron-2|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(49.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022790|ZK682.7|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1779|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2580|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2291|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022791|ZK686.1.1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022792|ZK686.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=608|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022792|ZK686.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022792|ZK686.2|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022792|ZK686.2|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022792|ZK686.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=502|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022792|ZK686.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022792|ZK686.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|238nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|242nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1977|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|245nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6848|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|247nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=288|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|250nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|800nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|808nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|851nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|876nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|884nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|886nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022793|ZK686.3.2|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022794|snu-23|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022794|snu-23|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022794|snu-23|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4152|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022794|snu-23|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022795|ZK686.5|1202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022795|ZK686.5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022795|ZK686.5|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022795|ZK686.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=926|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022796|ZK688.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022796|ZK688.1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022796|ZK688.1|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022797|best-24|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022797|best-24|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=669|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00022797|best-24|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022797|best-24|250nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022797|best-24|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022797|best-24|739nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022797|best-24|748nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=920|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1577|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=196|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022798|fahd-1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022799|ZK688.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022799|ZK688.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022799|ZK688.4|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022799|ZK688.4|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022799|ZK688.4|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00022799|ZK688.4|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022800|ZK688.5a|1149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022800|ZK688.5a|1163nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022800|ZK688.5a|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022800|ZK688.5a|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022800|ZK688.5a|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3255|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022800|ZK688.5a|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=195|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022801|pcp-5|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022801|pcp-5|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3497|total_reads(97.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022801|pcp-5|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022801|pcp-5|654nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022802|ZK688.7|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022802|ZK688.7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=701|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022802|ZK688.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022803|ZK688.9|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2636|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022804|ZK697.1|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022804|ZK697.1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022804|ZK697.1|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(42.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022804|ZK697.1|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022805|nhr-256|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022805|nhr-256|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=886|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022805|nhr-256|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022807|srab-25|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00022807|srab-25|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00022808|ZK697.8|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022808|ZK697.8|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022808|ZK697.8|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022809|ZK697.14|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022809|ZK697.14|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(41.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|1201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|219nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|221nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=758|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|405nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|443nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022810|ZK721.3|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022811|ZK721.4.2|747nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022812|ZK742.2|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022812|ZK742.2|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022812|ZK742.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00022812|ZK742.2|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00022812|ZK742.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022813|ZK742.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022813|ZK742.3|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022813|ZK742.3|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022814|ZK742.4|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022814|ZK742.4|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022814|ZK742.4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022814|ZK742.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022814|ZK742.4|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022815|asic-1|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022815|asic-1|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022815|asic-1|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022815|asic-1|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022815|asic-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|441nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|444nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|485nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|494nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|498nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|518nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022816|fbn-1|520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=162|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|170nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|174nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=583|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7886|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|218nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022817|upp-1|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022819|ZK783.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022819|ZK783.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022819|ZK783.5|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=203|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37697|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2275|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022820|ZK813.1.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1557|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|58nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=290|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3502|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|767nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8582|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|850nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|864nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|887nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|895nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|972nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|984nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022821|ZK813.2|999nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|28nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|30nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3165|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=23618|total_reads(54.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|84nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=326|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14967|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022822|ZK813.3|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1316|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|321nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|368nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|371nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|445nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=386|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|562nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1038|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022823|ZK813.4a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=303|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|1181nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|59nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|63nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2158|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=228|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022824|ZK813.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022825|ZK816.1|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022825|ZK816.1|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022825|ZK816.1|407nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022825|ZK816.1|410nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022825|ZK816.1|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1266|total_reads(82.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022825|ZK816.1|428nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022825|ZK816.1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022827|ZK816.4|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022829|ZK867.2|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022829|ZK867.2|819nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022829|ZK867.2|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022830|ZK973.1|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=907|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022830|ZK973.1|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1376|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022830|ZK973.1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022830|ZK973.1|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022830|ZK973.1|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022830|ZK973.1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022831|cec-10|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=112|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022831|cec-10|176nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=484|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022831|cec-10|180nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022831|cec-10|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022831|cec-10|211nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=591|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022831|cec-10|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=199|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|230nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=338|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=323|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022832|pdp-1|295nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022833|ZK973.4|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=122|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022833|ZK973.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(33.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022834|ZK973.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=576|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022834|ZK973.8|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=517|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|140nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|144nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|148nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=343|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|154nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=443|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|157nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|160nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022835|ZK973.9|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5305|total_reads(73.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1307|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|206nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|217nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022836|ZK973.11|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022837|ceh-45|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022837|ceh-45|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022837|ceh-45|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022838|ZK993.2a|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022840|ZK994.1|1180nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022840|ZK994.1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=564|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|345nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022842|ZK994.6|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1610|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022843|ZK1055.2|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022843|ZK1055.2|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022843|ZK1055.2|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022843|ZK1055.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022843|ZK1055.2|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(37.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022845|ZK1055.4|350nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022845|ZK1055.4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00022845|ZK1055.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022845|ZK1055.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00022846|ZK1055.5|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022846|ZK1055.5|465nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6a|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6a|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6a|1413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6a|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1173|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6a|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6a|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6a|73nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6c|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6c|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022847|ZK1055.6c|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022848|ZK1055.7|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1711|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022848|ZK1055.7|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=560|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022848|ZK1055.7|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=303|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022849|acs-6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022849|acs-6|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022849|acs-6|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022849|acs-6|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=450|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022849|acs-6|62nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1028|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2583|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=308|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022850|ZK1127.3|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022851|ZK1127.4.1|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022851|ZK1127.4.1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022851|ZK1127.4.1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022851|ZK1127.4.1|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022851|ZK1127.4.1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022851|ZK1127.4.1|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2237|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=645|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|82nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=534|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022852|ZK1127.5|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|252nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|255nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=76|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|258nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=254|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|260nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5881|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|263nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1208|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|265nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=217|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=516|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022853|ZK1127.6.2|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|1257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|587nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=664|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|591nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|593nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|971nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|975nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022854|cin-4|979nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1016nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1038nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1108nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1263nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1273nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022855|tcer-1|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=312|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25774|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=659|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=218|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022856|cth-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022857|ZK1127.12.2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1465|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022857|ZK1127.12.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022858|ZK1193.2|1549nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022858|ZK1193.2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022858|ZK1193.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022858|ZK1193.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=500|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022858|ZK1193.2|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022858|ZK1193.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|115nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|234nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|246nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|505nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|523nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|538nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|631nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022860|ZK1193.4|659nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022861|dve-1|1577nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022861|dve-1|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022861|dve-1|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022861|dve-1|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022862|ZK1236.1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=766|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022862|ZK1236.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022862|ZK1236.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022862|ZK1236.1|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022862|ZK1236.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022864|ZK1236.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=235|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2921|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1050|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|197nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022865|ufbp-1|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022866|ZK1240.1|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022866|ZK1240.1|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022867|ZK1240.2|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022867|ZK1240.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=499|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022867|ZK1240.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022867|ZK1240.2|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022868|ZK1240.3a|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022868|ZK1240.3a|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022868|ZK1240.3a|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022868|ZK1240.3a|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022868|ZK1240.3a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022868|ZK1240.3a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022869|ZK1240.4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022870|ZK1240.5|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(56.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022870|ZK1240.5|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022870|ZK1240.5|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022873|ZK1240.9|1158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022873|ZK1240.9|1161nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022873|ZK1240.9|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022873|ZK1240.9|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00022873|ZK1240.9|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022873|ZK1240.9|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022874|nep-25|1099nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022874|nep-25|397nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022874|nep-25|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022874|nep-25|442nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022874|nep-25|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022874|nep-25|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022875|ZK1248.4|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022876|ZK1248.5|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022876|ZK1248.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022877|wago-5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2064|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=387|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022880|tbc-2|408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022881|ZK1248.11|1003nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022881|ZK1248.11|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022881|ZK1248.11|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022881|ZK1248.11|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3561|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022881|ZK1248.11|1555nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022881|ZK1248.11|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022881|ZK1248.11|994nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022882|ZK1248.13|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1219|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022882|ZK1248.13|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022882|ZK1248.13|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022882|ZK1248.13|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022882|ZK1248.13|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022882|ZK1248.13|904nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022882|ZK1248.13|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022883|ZK1248.15|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1365|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022884|ZK1248.17|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022884|ZK1248.17|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|1089nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|1092nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2331|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022885|ZK1248.19|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022886|ZK1290.1|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=211|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4474|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=98|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022887|ZK1290.5|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022888|rnh-1.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022888|rnh-1.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(39%)
- ID=WBGene00022888|rnh-1.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022888|rnh-1.1|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022889|ZK1290.7|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022889|ZK1290.7|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022889|ZK1290.7|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022889|ZK1290.7|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022889|ZK1290.7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00022890|fbxa-224|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00022890|fbxa-224|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022891|ZK1290.10|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022891|ZK1290.10|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022891|ZK1290.10|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00022892|ZK1290.11|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|339nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|344nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|777nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00022893|ZK1290.13|786nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023172|Y23H5A.8a.2|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023186|Y67D8B.3|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023284|F41B5.1|427nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023284|F41B5.1|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023284|F41B5.1|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=476|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023284|F41B5.1|446nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023284|F41B5.1|448nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023404|plr-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023404|plr-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023404|plr-1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023404|plr-1|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023404|plr-1|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023404|plr-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1409|total_reads(75.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=424|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023405|sor-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|1059nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|1064nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7794|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4155|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1503|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=428|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=795|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19232|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|1515nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|1586nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=789|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|182nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|185nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=152|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|187nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=394|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|191nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1477|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=514|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|198nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|202nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=387|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=269|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=945|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1485|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11450|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2727|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1915|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|293nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=991|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|430nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=135|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|493nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1616|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|497nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=506|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|500nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|502nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|505nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=388|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1844|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8342|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023407|cex-1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1039|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1267|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023408|cex-2|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023409|mbd-2|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=222|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023409|mbd-2|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=55|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023409|mbd-2|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=974|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023409|mbd-2|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023409|mbd-2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023409|mbd-2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023409|mbd-2|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023411|srz-3|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023411|srz-3|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023411|srz-3|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023411|srz-3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=333|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023413|H31B20.2|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|204nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3541|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|311nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|313nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023414|R01H2.7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023415|F16C3.3|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023415|F16C3.3|394nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023416|spi-1|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3760|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|164nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|168nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=427|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=159|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=318|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|501nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12914|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023417|swm-1|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=149|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|146nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|1502nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=193|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023418|R06F6.12|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1060|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=310|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3335|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023419|F53F4.16|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023420|C26D10.7|504nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023420|C26D10.7|510nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(54.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|154nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=194|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2450|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|320nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023421|rde-11|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|1015nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|1044nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|1063nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|1066nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1513|total_reads(39.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|1211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=205|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|1217nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|1220nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=733|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1088|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|915nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|926nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|930nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|936nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023422|mrpl-21|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|1513nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|1518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=227|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14917|total_reads(56%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10955|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|381nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|394nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|50nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023423|F43C1.7|822nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023424|C53D6.10|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=716|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023424|C53D6.10|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00023424|C53D6.10|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023424|C53D6.10|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023424|C53D6.10|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023424|C53D6.10|738nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023425|try-9|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(58.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023425|try-9|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023427|F14D2.15|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023427|F14D2.15|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=633|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00023427|F14D2.15|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=402|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023427|F14D2.15|648nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023427|F14D2.15|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023431|C25E10.13|108nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023431|C25E10.13|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023431|C25E10.13|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023431|C25E10.13|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(78.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=951|total_reads(66.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|1399nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|1467nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|1477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|1479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023432|K12B6.9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023450|T12D8.10|1043nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023450|T12D8.10|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023450|T12D8.10|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4478|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023450|T12D8.10|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023450|T12D8.10|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12665|total_reads(92.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023451|mlc-7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023458|M02E1.3|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023458|M02E1.3|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=890|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023458|M02E1.3|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=732|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023458|M02E1.3|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023460|F46H6.5|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023460|F46H6.5|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023460|F46H6.5|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023460|F46H6.5|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023462|srz-83|1183nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023462|srz-83|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00023462|srz-83|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023462|srz-83|374nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023462|srz-83|380nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023462|srz-83|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023462|srz-83|464nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023463|srz-82|1295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023474|srz-37|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023475|srz-69|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023477|nspc-1|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023477|nspc-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023477|nspc-1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023477|nspc-1|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=650|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00023477|nspc-1|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3248|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023477|nspc-1|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023477|nspc-1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023479|srz-67|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023479|srz-67|1123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023479|srz-67|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023479|srz-67|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=214|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023479|srz-67|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023479|srz-67|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023483|Y75B8A.39|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023484|Y54G2A.37|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|140nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=200|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|187nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|310nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=588|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023485|ttr-49|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|119nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|321nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=789|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=602|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023486|K08B4.7|385nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023487|mrps-24|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2931|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023487|mrps-24|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023487|mrps-24|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023487|mrps-24|1287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023487|mrps-24|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023487|mrps-24|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|144nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=834|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|589nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|620nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023489|F42A10.9|666nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023490|F36A2.14|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023490|F36A2.14|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=383|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023490|F36A2.14|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|146nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|149nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1583|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023491|tsp-21|225nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023492|T24D3.2.3|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=988|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023492|T24D3.2.3|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|240nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5855|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|251nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2157|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|256nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1160|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023497|lin-15B|430nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5374|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=577|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|113nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|327nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023498|lin-15A|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023499|srz-63|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023499|srz-63|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=332|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|212nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|221nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023500|C11H1.9a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023501|F11E6.11b.1|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00023501|F11E6.11b.1|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023501|F11E6.11b.1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023502|clec-184|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023502|clec-184|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023502|clec-184|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023503|F17C11.13b|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023503|F17C11.13b|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=308|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023503|F17C11.13b|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023503|F17C11.13b|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023503|F17C11.13b|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023504|F26F2.8|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023504|F26F2.8|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=461|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023505|srz-102|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023505|srz-102|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(85.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023506|srz-11|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023506|srz-11|274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023506|srz-11|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023506|srz-11|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023506|srz-11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=270|total_reads(35.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023506|srz-11|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023506|srz-11|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023515|srz-97|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023515|srz-97|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00023515|srz-97|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023515|srz-97|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023515|srz-97|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023517|srz-75|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00023517|srz-75|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023519|Y60A3A.24|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023519|Y60A3A.24|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00023519|Y60A3A.24|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023519|Y60A3A.24|282nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|318nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8623|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|333nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00023520|oig-5|832nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043049|F32H2.11|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043049|F32H2.11|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043049|F32H2.11|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043050|oig-4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043050|oig-4|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=347|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043050|oig-4|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1891|total_reads(79.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043050|oig-4|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043050|oig-4|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043051|C29E4.13c.5|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043051|C29E4.13c.5|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043051|C29E4.13c.5|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043051|C29E4.13c.5|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1815|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00043051|C29E4.13c.5|60nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043051|C29E4.13c.5|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043052|srz-104|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=65|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043052|srz-104|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043052|srz-104|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=280|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=129|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043054|T21B4.15|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043056|nfya-2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=971|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043056|nfya-2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043057|M142.8a|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043057|M142.8a|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1048|total_reads(72.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043057|M142.8a|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=308|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043057|M142.8a|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043057|M142.8a|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043057|M142.8a|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043057|M142.8a|544nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043058|sre-34|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00043059|srab-26|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043059|srab-26|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043059|srab-26|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00043060|R144.12|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043060|R144.12|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=357|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043060|R144.12|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2643|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043060|R144.12|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043060|R144.12|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043061|Y54G2A.38|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=433|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=748|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043062|clec-80|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21157|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3060|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=506|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=578|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|324nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=558|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|330nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=69|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|334nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043064|nbet-1|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043065|C55C3.7|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043065|C55C3.7|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043066|acr-25|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00043066|acr-25|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00043067|dlc-5|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043067|dlc-5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043067|dlc-5|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00043068|F32E10.9|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=857|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043068|F32E10.9|907nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043068|F32E10.9|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043069|F20D6.12|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00043097|C02D5.4|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043097|C02D5.4|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2097|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00043097|C02D5.4|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3344|total_reads(55.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043097|C02D5.4|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00043097|C02D5.4|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043120|C09H10.4|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043120|C09H10.4|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043120|C09H10.4|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=100|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043120|C09H10.4|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3702|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=330|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043156|C27F2.9|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043279|F22D6.8.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043279|F22D6.8.2|1327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043279|F22D6.8.2|16nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043279|F22D6.8.2|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=510|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043279|F22D6.8.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=955|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043279|F22D6.8.2|866nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|280nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|435nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=256|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2151|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|554nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|618nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|652nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=184|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|804nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=240|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043297|F28F5.4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=417|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=429|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=313|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043302|F32D8.11.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=225|total_reads(50.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|201nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043308|F39B2.9|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043466|R05G6.3|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00043469|R09H3.2|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00043534|W02B12.13a|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043534|W02B12.13a|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043534|W02B12.13a|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=251|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043666|Y45G5AM.4|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=291|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00043702|Y54G2A.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|307nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=258|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|315nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|317nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|326nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043705|egrh-2|362nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|1038nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=192|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|754nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|779nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3619|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|782nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|797nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|805nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3510|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043948|ZC262.7|809nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043952|ZC404.2|1335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043952|ZC404.2|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043952|ZC404.2|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043952|ZC404.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=377|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043952|ZC404.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00043952|ZC404.2|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043980|F11D5.7|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00043981|T14E8.4|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043981|T14E8.4|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043982|B0403.6|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043982|B0403.6|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=400|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=281|total_reads(40.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|258nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=140|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|260nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|263nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|306nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|308nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|310nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043983|C39D10.11|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043984|C56E6.7|338nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043984|C56E6.7|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043985|C44C10.11.1|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043985|C44C10.11.1|371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(64.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043985|C44C10.11.1|374nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043985|C44C10.11.1|378nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043985|C44C10.11.1|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043985|C44C10.11.1|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043986|fut-5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043986|fut-5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043990|AC8.12|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=264|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00043990|AC8.12|577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043990|AC8.12|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|182nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|191nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043992|bbs-4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=376|total_reads(45.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043994|C07A9.12|257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043994|C07A9.12|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043995|F40F12.9a.1|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043995|F40F12.9a.1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043995|F40F12.9a.1|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=251|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00043995|F40F12.9a.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00043995|F40F12.9b|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00043995|F40F12.9b|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(62.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043996|fbxb-87|518nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00043996|fbxb-87|526nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(35.2%)
- ID=WBGene00043996|fbxb-87|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00043997|Y79H2A.12|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043997|Y79H2A.12|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00043997|Y79H2A.12|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00043997|Y79H2A.12|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00043998|T21C12.8b|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00043998|T21C12.8b|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=617|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00043998|T21C12.8b|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044001|C09G4.4|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=716|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044001|C09G4.4|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4025|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044001|C09G4.4|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044001|C09G4.4|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044003|Y41E3.18|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044003|Y41E3.18|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044003|Y41E3.18|758nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044003|Y41E3.18|761nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044004|C24A8.6|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=223|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044004|C24A8.6|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044004|C24A8.6|148nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044004|C24A8.6|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044004|C24A8.6|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2518|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044004|C24A8.6|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044005|F37C12.18|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044005|F37C12.18|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=578|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044005|F37C12.18|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044005|F37C12.18|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044005|F37C12.18|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044005|F37C12.18|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044006|H32K21.1|224nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044006|H32K21.1|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044006|H32K21.1|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044006|H32K21.1|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1075|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044006|H32K21.1|253nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044006|H32K21.1|266nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044006|H32K21.1|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|1076nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|1083nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|1105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1879|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=757|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044007|ZK1320.13|952nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044008|gip-2|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044008|gip-2|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1934|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044008|gip-2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044008|gip-2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044009|ZK822.6|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044009|ZK822.6|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2222|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044009|ZK822.6|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044009|ZK822.6|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=336|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2218|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5657|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044011|T06E4.12.2|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=328|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044012|srxa-19|284nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00044012|srxa-19|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00044012|srxa-19|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00044012|srxa-19|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00044012|srxa-19|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00044016|C35A5.10|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=273|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044016|C35A5.10|790nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044016|C35A5.10|835nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044018|T04B2.8|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044018|T04B2.8|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044018|T04B2.8|359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044018|T04B2.8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044019|C55A6.12b|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1155|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044019|C55A6.12b|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1155|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044019|C55A6.12b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044019|C55A6.12b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=289|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|435nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2745|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=727|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|686nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|783nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|785nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044020|ZK856.14a|791nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044021|R02E4.2|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(34%)
- ID=WBGene00044021|R02E4.2|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044021|R02E4.2|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044021|R02E4.2|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044021|R02E4.2|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11a|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11a|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11a|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=102|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11a|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2701|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11a|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11b|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044024|C35A5.11b|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044025|T01G1.4|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=407|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044025|T01G1.4|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2294|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=580|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|126nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2522|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=151|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2985|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1989|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044026|cisd-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044027|F27E5.8|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044027|F27E5.8|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044027|F27E5.8|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044027|F27E5.8|780nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(57%)
- ID=WBGene00044028|F33H1.6|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1639|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044028|F33H1.6|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044028|F33H1.6|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=253|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|251nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|254nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|335nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|355nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2459|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|363nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044029|C05D12.7|529nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044030|Y17G7B.23a|247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044030|Y17G7B.23a|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044030|Y17G7B.23a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044030|Y17G7B.23a|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00044031|F49C5.9|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044031|F49C5.9|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044032|ceh-99|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044032|ceh-99|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044035|F27E5.7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=552|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044035|F27E5.7|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044043|Y46G5A.38|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00044043|Y46G5A.38|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00044043|Y46G5A.38|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00044043|Y46G5A.38|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00044045|R11G10.3|13nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044045|R11G10.3|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044045|R11G10.3|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=651|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044045|R11G10.3|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044045|R11G10.3|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044047|Y57A10C.11|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044048|F57G9.7|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1366|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044049|sfxn-5|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044058|F17B5.6|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044061|tbc-12|298nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044061|tbc-12|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044061|tbc-12|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00044061|tbc-12|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044061|tbc-12|529nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044061|tbc-12|534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=972|total_reads(78.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044061|tbc-12|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044062|snb-6|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(29.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044062|snb-6|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=611|total_reads(70.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|105nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2050|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044063|tag-231|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044065|tag-229|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3157|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044065|tag-229|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044065|tag-229|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044065|tag-229|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044065|tag-229|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044066|fbxb-66|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(85.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044066|fbxb-66|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044066|fbxb-66|675nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044066|fbxb-66|837nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|1404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|1409nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=167|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=219|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|328nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=936|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1327|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|339nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=448|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|661nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|818nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|824nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=753|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|829nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|850nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|926nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|935nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|948nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044067|hke-4.1|954nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|442nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|445nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|642nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|646nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|771nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|775nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|778nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|781nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3530|total_reads(85%)
- ID=WBGene00044068|syd-9|785nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|470nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=829|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|482nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|530nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|567nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1744|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044069|hat-1|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044070|set-18|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044070|set-18|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1578|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044070|set-18|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044070|set-18|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044070|set-18|138nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044070|set-18|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3575|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|461nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044071|dhhc-14|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|201nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2142|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|212nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044072|ham-3|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=251|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=117|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044073|tag-244|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044074|mltn-5|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044074|mltn-5|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|369nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2071|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|375nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2584|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=218|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|399nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044077|tag-232|402nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044078|tag-243|124nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044078|tag-243|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044078|tag-243|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044078|tag-243|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1170|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044078|tag-243|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044079|tag-241|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044079|tag-241|246nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=808|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044079|tag-241|254nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00044079|tag-241|295nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044079|tag-241|297nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044079|tag-241|299nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1067|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|120nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|125nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=207|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|136nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|1593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2330|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2864|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=272|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044080|D1086.10a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52479|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=840|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8452|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1821|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=656|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1349|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044081|D1086.11b|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|110nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|168nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=260|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1103|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1187|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=203|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044082|D1086.12b|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044083|tin-9.2|642nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044083|tin-9.2|644nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044084|sre-46|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044086|clec-228|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044086|clec-228|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044087|C45H4.18|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044087|C45H4.18|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044090|srbc-33|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(49.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044090|srbc-33|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044090|srbc-33|1591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044090|srbc-33|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044090|srbc-33|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044091|srbc-60|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044091|srbc-60|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044092|srbc-71|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00044092|srbc-71|834nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|184nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|186nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=421|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|188nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3429|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044094|fitm-2|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044099|srd-75|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044099|srd-75|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044099|srd-75|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044099|srd-75|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044106|srbc-84|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1871|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044107|F58G6.9b.2|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044109|K02E11.10|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044109|K02E11.10|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=176|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044109|K02E11.10|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044109|K02E11.10|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044109|K02E11.10|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044109|K02E11.10|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044109|K02E11.10|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044113|C54F6.15|1242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044113|C54F6.15|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044113|C54F6.15|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044113|C54F6.15|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044115|srxa-12|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00044115|srxa-12|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00044116|srxa-13|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044116|srxa-13|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044117|srsx-10|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044117|srsx-10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044117|srsx-10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044117|srsx-10|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044117|srsx-10|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044120|C36B1.13|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044120|C36B1.13|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044121|gcp-2.3|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00044121|gcp-2.3|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00044121|gcp-2.3|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00044122|T28B8.6|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044122|T28B8.6|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=785|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00044122|T28B8.6|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044125|srsx-16|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044125|srsx-16|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044125|srsx-16|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044125|srsx-16|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044125|srsx-16|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044125|srsx-16|879nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044125|srsx-16|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044127|BE10.5.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044127|BE10.5.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044131|Y45G12C.16|379nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044131|Y45G12C.16|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2245|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044131|Y45G12C.16|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044131|Y45G12C.16|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044131|Y45G12C.16|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044132|C23H4.8|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044132|C23H4.8|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044132|C23H4.8|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044132|C23H4.8|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044132|C23H4.8|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044134|D1025.10|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044134|D1025.10|1576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044134|D1025.10|1588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=793|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044134|D1025.10|1595nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044134|D1025.10|1597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044134|D1025.10|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044135|F08G12.11|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044137|F28H6.8|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044137|F28H6.8|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044137|F28H6.8|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044137|F28H6.8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044138|sssh-1|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044138|sssh-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=478|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00044138|sssh-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044138|sssh-1|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044139|F42D1.4|1292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044139|F42D1.4|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044139|F42D1.4|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044140|F42F12.11|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044141|H03G16.6|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00044141|H03G16.6|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(59%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044142|H13N06.7|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|629nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|634nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=979|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|641nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=249|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|647nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|684nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044143|K09E9.4|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|416nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=949|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|430nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4203|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1679|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|465nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|470nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=497|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044144|M153.4|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=103|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044145|M163.9|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044145|M163.9|112nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044146|M163.10|187nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044146|M163.10|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044146|M163.10|255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044146|M163.10|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044147|M163.11|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044147|M163.11|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(52.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|593nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|599nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044150|VB0395L.1|91nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044151|W04G3.12|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044152|W04G3.10|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044152|W04G3.10|881nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044152|W04G3.10|884nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044152|W04G3.10|887nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044152|W04G3.10|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044152|W04G3.10|895nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044152|W04G3.10|899nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044153|W04G3.11|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044153|W04G3.11|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044153|W04G3.11|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044153|W04G3.11|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=101|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044154|Y7A5A.10|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044154|Y7A5A.10|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044156|Y66C5A.1|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044156|Y66C5A.1|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044156|Y66C5A.1|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044156|Y66C5A.1|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044156|Y66C5A.1|243nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=766|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044158|Y53C12A.8|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044158|Y53C12A.8|130nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044160|W10C6.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044161|C47G2.8|195nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044161|C47G2.8|197nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00044161|C47G2.8|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=215|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044163|F49C5.11a|74nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044164|Y46G5A.39|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044166|C54C6.7|180nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044166|C54C6.7|183nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=153|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044166|C54C6.7|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044166|C54C6.7|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044166|C54C6.7|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044167|C36A4.11.2|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=319|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044167|C36A4.11.2|333nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044167|C36A4.11.2|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044167|C36A4.11.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044167|C36A4.11.2|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044167|C36A4.11.2|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=110|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=272|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=99|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|198nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044169|C06C3.10|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|133nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|143nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|147nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|149nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=710|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1483|total_reads(60.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044174|fipr-5|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044175|fipr-9|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044175|fipr-9|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2204|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00044175|fipr-9|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|1070nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=315|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|422nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|426nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2097|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044176|C30G7.2a|434nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044177|C30G7.3|1494nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044177|C30G7.3|1498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044177|C30G7.3|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044177|C30G7.3|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1109|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044177|C30G7.3|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044177|C30G7.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044177|C30G7.3|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|1025nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|1196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|1200nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|230nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=503|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044178|C30G7.4.1|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044179|C30G7.5|409nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(68.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044179|C30G7.5|489nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|1116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|1502nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2296|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044180|C47E8.11|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044181|F09C6.11b|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044182|F09C6.12|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044182|F09C6.12|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=117|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044183|F09C6.13|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044187|ttll-9|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044187|ttll-9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044188|F28F8.9a|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044188|F28F8.9a|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044188|F28F8.9a|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044188|F28F8.9a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1622|total_reads(97.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044188|F28F8.9a|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044189|F36D3.14|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(44%)
- ID=WBGene00044189|F36D3.14|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00044189|F36D3.14|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=557|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|396nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|437nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1399|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|439nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|441nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044191|F43D2.6|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044192|F46B6.13|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00044192|F46B6.13|387nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00044193|F47B8.13|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=610|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044193|F47B8.13|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044194|F47B8.14|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044194|F47B8.14|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044194|F47B8.14|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044194|F47B8.14|1594nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=325|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|193nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|195nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=134|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044195|F49A5.10|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044197|fbxb-63|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044198|F56H9.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044198|F56H9.6|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044199|F57B1.8b|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044200|H37A05.4a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044200|H37A05.4b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044200|H37A05.4b|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044200|H37A05.4b|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044200|H37A05.4b|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=650|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044201|H39E23.3|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=362|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044201|H39E23.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044201|H39E23.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044202|K10G4.10|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044203|T02E9.6|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044203|T02E9.6|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=497|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=164|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|197nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=239|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=88|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|712nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044204|suds-3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044205|T13F3.8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044205|T13F3.8|186nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044205|T13F3.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044205|T13F3.8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044205|T13F3.8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=401|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044205|T13F3.8|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2050|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044206|T26H5.9a|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044207|Y6G8.5a|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044207|Y6G8.5a|582nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044207|Y6G8.5a|611nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00044207|Y6G8.5a|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044207|Y6G8.5a|800nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044210|Y51A2D.21|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044210|Y51A2D.21|128nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044210|Y51A2D.21|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044210|Y51A2D.21|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044210|Y51A2D.21|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044210|Y51A2D.21|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044211|Y60A3A.25|407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044211|Y60A3A.25|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044211|Y60A3A.25|542nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00044211|Y60A3A.25|554nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3954|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=652|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=760|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=193|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044212|Y68A4A.13|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044213|Y102A5C.36.1|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(32.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044213|Y102A5C.36.1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=581|total_reads(65.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044213|Y102A5C.36.1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044213|Y102A5C.36.1|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=905|total_reads(64%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|330nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|483nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=144|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044221|F41G3.18.2|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044222|T16G12.10|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044227|C07A9.13|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044227|C07A9.13|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044227|C07A9.13|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044228|T03F6.7|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(77.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044228|T03F6.7|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044230|C36E8.6|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044232|C18D11.7|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=83|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044233|Y56A3A.36|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044235|C06A1.7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044235|C06A1.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00044235|C06A1.7|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044235|C06A1.7|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044236|C17E4.11|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044236|C17E4.11|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=961|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044236|C17E4.11|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044236|C17E4.11|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044236|C17E4.11|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044238|C30H6.12b|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00044238|C30H6.12b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044238|C30H6.12b|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044238|C30H6.12b|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=170|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044239|C33D9.10|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044240|C47E12.14|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044241|C53D6.11|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=130|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044241|C53D6.11|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=106|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044241|C53D6.11|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00044241|C53D6.11|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044242|C54C8.12|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044242|C54C8.12|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=180|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044243|F16C3.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044244|F26D10.13|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044244|F26D10.13|614nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=542|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|1269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|1365nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|1369nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=92|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044245|F32A7.8|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044246|F36D1.10|65nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044247|F36H2.4|1571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044247|F36H2.4|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044247|F36H2.4|584nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044247|F36H2.4|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044247|F36H2.4|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044249|F55B11.6.1|459nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044249|F55B11.6.1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044249|F55B11.6.1|478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044249|F55B11.6.1|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044250|F56G4.7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00044250|F56G4.7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044250|F56G4.7|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044250|F56G4.7|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00044251|F59C6.12|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044251|F59C6.12|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=477|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044251|F59C6.12|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044251|F59C6.12|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044253|M117.6|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=460|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00044253|M117.6|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044253|M117.6|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044256|Y45F10C.6|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00044256|Y45F10C.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|1063nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|1134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|1391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|1493nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|1551nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|38nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044257|Y45F10D.16.1|41nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044258|Y57G11C.51.2|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044258|Y57G11C.51.2|120nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044258|Y57G11C.51.2|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2711|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044258|Y57G11C.51.2|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044259|Y73F8A.36|165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044260|Y87G2A.19|145nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044260|Y87G2A.19|152nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1918|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044260|Y87G2A.19|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044261|Y87G2A.20|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044271|nspa-2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044271|nspa-2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044274|nspa-7|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1569|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044275|nspa-10|1459nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044278|F09C6.14|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044278|F09C6.14|328nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044278|F09C6.14|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|303nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=580|total_reads(41.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|562nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=67|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=483|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044280|W02A2.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044281|R04A9.7|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044281|R04A9.7|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044281|R04A9.7|182nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044281|R04A9.7|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044282|T19H12.12|1319nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044282|T19H12.12|1384nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044282|T19H12.12|1387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044282|T19H12.12|1408nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044282|T19H12.12|634nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(36.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044283|spp-22|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044283|spp-22|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044283|spp-22|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=998|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00044283|spp-22|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044283|spp-22|90nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(78.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|649nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|656nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044284|spp-21|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044286|ugt-35|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044287|F21H12.7|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044288|F30H5.5|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044288|F30H5.5|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044289|Y37F4.8|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=290|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044289|Y37F4.8|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044289|Y37F4.8|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044289|Y37F4.8|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=158|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044289|Y37F4.8|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044289|Y37F4.8|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044289|Y37F4.8|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044290|B0035.18|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044290|B0035.18|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1327|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044290|B0035.18|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=160|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044290|B0035.18|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044291|C25F9.10a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044291|C25F9.10a|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=641|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044291|C25F9.10a|614nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044291|C25F9.10a|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044292|F56D6.8|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1037|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044292|F56D6.8|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=526|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044292|F56D6.8|74nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=667|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044292|F56D6.8|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044292|F56D6.8|827nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044292|F56D6.8|82nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044292|F56D6.8|836nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044293|K08D12.7|51nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044293|K08D12.7|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=219|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044294|C01B10.11|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044294|C01B10.11|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1991|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044294|C01B10.11|197nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044294|C01B10.11|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044295|C09E7.10|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044295|C09E7.10|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044295|C09E7.10|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044295|C09E7.10|386nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044295|C09E7.10|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00044296|F10C1.9a|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=354|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044296|F10C1.9a|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044296|F10C1.9a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=256|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044296|F10C1.9a|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=106|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044297|C25B8.8|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044297|C25B8.8|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044297|C25B8.8|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044297|C25B8.8|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044297|C25B8.8|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044297|C25B8.8|380nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044298|T23B7.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=421|total_reads(64.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044298|T23B7.2|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=233|total_reads(35.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1018nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1026nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|1539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|355nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|390nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|414nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|565nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|603nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|670nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|686nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|707nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|723nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|839nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|872nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044299|C42D8.9|996nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044300|D1022.9a|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=371|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044300|D1022.9a|123nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044300|D1022.9a|126nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=553|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15766|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=562|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=906|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044301|lgc-28|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044303|hst-3.2|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044303|hst-3.2|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(29.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044303|hst-3.2|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00044303|hst-3.2|905nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4273|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=392|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044304|F52B10.3c|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044305|rad-8|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2444|total_reads(97.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044305|rad-8|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044305|rad-8|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044305|rad-8|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044305|rad-8|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044307|F58F9.9a|1600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044310|H20J04.9|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044310|H20J04.9|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=691|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=747|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|173nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|212nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044311|K04C2.7|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044312|K04C2.8|498nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044312|K04C2.8|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044312|K04C2.8|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044312|K04C2.8|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044313|M02D8.7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044313|M02D8.7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044313|M02D8.7|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044313|M02D8.7|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044314|fbxb-33|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044314|fbxb-33|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044314|fbxb-33|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044315|F41G3.20|1173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044316|F41G3.21|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1376|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044316|F41G3.21|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044316|F41G3.21|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044316|F41G3.21|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044316|F41G3.21|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044317|F41G3.19|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044318|tag-267|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044318|tag-267|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1013|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044318|tag-267|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|1059nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|1478nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|1583nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|599nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|609nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|624nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|627nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3087|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044319|tag-266|633nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044321|mrps-30|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044321|mrps-30|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=981|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044321|mrps-30|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3215|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00044321|mrps-30|1182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044321|mrps-30|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044322|tag-280|108nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044322|tag-280|1583nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044322|tag-280|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044322|tag-280|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=911|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044322|tag-280|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=419|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044322|tag-280|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044323|tag-281|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=174|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044323|tag-281|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=367|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6333|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044324|ufm-1|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|1237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|1316nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|1454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|1492nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|201nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|203nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|208nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2715|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|210nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=662|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|218nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044325|tag-321|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|1004nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2972|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=289|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|1231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|128nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=901|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|835nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|953nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044326|tag-322|958nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|470nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|559nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|775nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|780nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|810nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|919nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2798|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|940nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|942nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|953nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=489|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|990nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044329|cpsf-4|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|1492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|677nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|711nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|720nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|725nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=819|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|733nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|757nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|764nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|766nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044330|alr-1|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044331|clec-25|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044331|clec-25|665nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044332|clec-36|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044332|clec-36|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044333|C01G12.13|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044338|nspc-3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1994|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044338|nspc-3|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(17.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044338|nspc-3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5275|total_reads(94.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=91|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044339|nspc-4|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044341|ave-1|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044341|ave-1|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044341|ave-1|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044341|ave-1|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044341|ave-1|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2086|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044341|ave-1|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044341|ave-1|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=282|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=330|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1561nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|1571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=733|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044342|T05B11.7|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044344|mrpl-39|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044344|mrpl-39|111nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=935|total_reads(95.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044344|mrpl-39|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044344|mrpl-39|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044345|Y48G1C.12|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044345|Y48G1C.12|358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044345|Y48G1C.12|364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044345|Y48G1C.12|367nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044345|Y48G1C.12|385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044345|Y48G1C.12|407nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1121|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044345|Y48G1C.12|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|1453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|1498nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|1557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|1561nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|1590nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044346|Y59E9AL.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044347|Y71G12B.30c|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044347|Y71G12B.30c|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044347|Y71G12B.30c|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00044347|Y71G12B.30c|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=147|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044347|Y71G12B.30c|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044347|Y71G12B.30c|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044347|Y71G12B.30c|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00044348|Y71G12B.31b|820nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044348|Y71G12B.31b|914nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=408|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044349|Y71G12B.32|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044349|Y71G12B.32|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044350|Y73B6BL.44|202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=383|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044350|Y73B6BL.44|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044350|Y73B6BL.44|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044350|Y73B6BL.44|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044350|Y73B6BL.44|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044350|Y73B6BL.44|55nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044350|Y73B6BL.44|66nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044352|ZK381.8|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|188nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=214|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1148|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=120|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|816nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044353|ZK418.10|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|1256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|1375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|1513nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=172|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|638nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|726nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044354|ZK418.11|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044355|ZK563.7|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=430|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044355|ZK563.7|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044356|W02D7.12|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00044356|W02D7.12|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4882|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044357|nspc-6|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044358|Y71G12B.33a|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044358|Y71G12B.33a|118nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044358|Y71G12B.33a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044358|Y71G12B.33a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044359|C16C4.17b|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044359|C16C4.17b|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044361|K09F6.11|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044363|F22E5.21.1|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044363|F22E5.21.1|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044363|F22E5.21.1|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044363|F22E5.21.1|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044364|F34D6.7|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044365|F34D6.8|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044366|F34D6.9|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00044366|F34D6.9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044366|F34D6.9|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044366|F34D6.9|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00044367|T05A8.8|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044367|T05A8.8|161nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044367|T05A8.8|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044368|K12H6.10|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00044368|K12H6.10|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00044370|C41H7.9|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=887|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00044370|C41H7.9|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044371|ZC239.20|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044372|ZC239.21|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044373|C17F4.11|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044374|C17F4.12|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044374|C17F4.12|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00044374|C17F4.12|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044376|Y49F6B.12|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044376|Y49F6B.12|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044376|Y49F6B.12|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(71.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044376|Y49F6B.12|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044376|Y49F6B.12|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044376|Y49F6B.12|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044379|F40H7.12|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044380|T24E12.12|223nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=184|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044380|T24E12.12|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044380|T24E12.12|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=301|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044380|T24E12.12|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=207|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044380|T24E12.12|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044381|K10G6.5|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044382|Y14H12A.2|242nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044382|Y14H12A.2|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044382|Y14H12A.2|329nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044383|T05A7.11|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044384|F11G11.14|1258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044384|F11G11.14|1512nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00044384|F11G11.14|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00044384|F11G11.14|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044384|F11G11.14|788nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044384|F11G11.14|796nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044384|F11G11.14|809nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=801|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3283|total_reads(73.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044385|F59A6.10|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044386|C27A2.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044386|C27A2.7|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00044386|C27A2.7|235nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044386|C27A2.7|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(59.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|1396nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=647|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=969|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044387|C27A2.8|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|1184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|1188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|1190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4096|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|1198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|1200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|1240nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|1244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=389|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044388|C27D6.11|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044389|C27D6.12b|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=957|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044389|C27D6.12b|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=48|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044391|C25H3.15|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=171|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|685nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|688nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|690nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=162|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|71nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=204|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|763nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044392|C25H3.16|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=428|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044393|ZK1248.20|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044393|ZK1248.20|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044393|ZK1248.20|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044394|B0034.7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044394|B0034.7|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044394|B0034.7|811nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044395|R12C12.10|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=419|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044395|R12C12.10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044396|ZK1290.14|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044396|ZK1290.14|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044396|ZK1290.14|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1121|total_reads(85.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044396|ZK1290.14|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044396|ZK1290.14|257nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=917|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=529|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|253nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=3720|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|270nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=386|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|326nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044401|Y55B1BR.6c|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=100|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044402|Y82E9BL.18|100nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=184|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044402|Y82E9BL.18|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044402|Y82E9BL.18|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044402|Y82E9BL.18|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044402|Y82E9BL.18|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1202nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=746|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1274nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=341|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|1281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044403|fbxa-219|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044404|F36H2.5|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044404|F36H2.5|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00044404|F36H2.5|237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044404|F36H2.5|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044404|F36H2.5|244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044404|F36H2.5|249nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044404|F36H2.5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|11nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=804|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|238nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1697|total_reads(52%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044406|F02A9.7|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044409|C45G9.14|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044409|C45G9.14|441nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044409|C45G9.14|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044410|F48E8.8c|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044410|F48E8.8c|172nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044410|F48E8.8c|384nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044410|F48E8.8c|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=470|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044410|F48E8.8c|766nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|1099nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|1118nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|196nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|200nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|216nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1534|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|384nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|393nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|617nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044411|R12B2.8|771nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044412|F40H6.6|166nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044412|F40H6.6|170nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044412|F40H6.6|172nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=26|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044412|F40H6.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|296nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|371nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|439nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=665|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1326|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044413|B0205.12|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044414|C06A5.12|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044417|C08F1.11|1484nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044417|C08F1.11|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(84.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044417|C08F1.11|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4557|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|223nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044418|C08G5.7c|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044419|fbxc-17|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044419|fbxc-17|217nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044419|fbxc-17|223nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|740nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|745nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=190|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|762nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=468|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|769nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|965nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=762|total_reads(50.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044420|C50D2.10a.2|968nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=171|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=85|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4592|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=746|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|134nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1001|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|211nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|220nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|60nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2745|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=286|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|78nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044421|D1007.18|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044422|F46F11.11|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|468nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|484nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|493nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|495nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=505|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|534nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=273|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|579nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=475|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|642nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=467|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|645nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044423|F53F10.8.1|648nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044424|F54D12.10|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044427|F56A6.5|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044428|T01D1.7|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|1131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|1407nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|1539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|1559nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|1561nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|725nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2531|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1460|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|878nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=541|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044431|W03G9.8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044432|W03G9.9|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=286|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044432|W03G9.9|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044433|W10C8.6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044433|W10C8.6|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044433|W10C8.6|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=549|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044434|Y18H1A.15|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(45.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044434|Y18H1A.15|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(43.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044434|Y18H1A.15|636nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044434|Y18H1A.15|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044435|Y20F4.8|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044435|Y20F4.8|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=189|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044435|Y20F4.8|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044435|Y20F4.8|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044436|Y47G6A.31|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=195|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044436|Y47G6A.31|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00044436|Y47G6A.31|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044436|Y47G6A.31|206nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044436|Y47G6A.31|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044437|Y47G6A.32|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044437|Y47G6A.32|482nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=366|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044438|Y51F10.11|1351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044438|Y51F10.11|1354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044438|Y51F10.11|1356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044438|Y51F10.11|1489nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=992|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044438|Y51F10.11|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044438|Y51F10.11|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044438|Y51F10.11|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044439|Y51H7C.15|173nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044439|Y51H7C.15|202nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044439|Y51H7C.15|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=752|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00044440|adpr-1|1406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=865|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044441|Y119C1B.11|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044441|Y119C1B.11|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044442|T08A9.13|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044442|T08A9.13|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00044442|T08A9.13|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044442|T08A9.13|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044442|T08A9.13|763nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044442|T08A9.13|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|215nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2212|total_reads(86.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044443|ZC21.10.2|239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=799|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=58|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3357|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044445|C02F5.14|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2857|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(76.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|172nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|175nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|951nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044446|C06G4.6|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|1236nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|131nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|135nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(40.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(24.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00044447|ZK688.10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044448|ZK783.6|155nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044448|ZK783.6|158nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044448|ZK783.6|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=587|total_reads(90.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044448|ZK783.6|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044448|ZK783.6|83nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044449|fipr-20|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044450|fipr-18|49nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=116|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044451|fipr-19|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|147nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|151nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|156nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=439|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=222|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|286nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044452|Y102E9.5|296nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044453|Y102E9.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044453|Y102E9.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044453|Y102E9.6|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044455|F23F12.13|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044455|F23F12.13|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044455|F23F12.13|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(26.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044455|F23F12.13|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044457|C18H7.11|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(19.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044457|C18H7.11|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044457|C18H7.11|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=123|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044457|C18H7.11|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044457|C18H7.11|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044457|C18H7.11|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044459|Y55F3C.9a|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044459|Y55F3C.9a|48nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044459|Y55F3C.9a|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044459|Y55F3C.9a|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044459|Y55F3C.9b|1343nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044459|Y55F3C.9b|512nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044460|Y55F3C.10|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044461|Y18H1A.14|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044462|C44B12.9|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=138|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044462|C44B12.9|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044463|W09G12.10|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1174|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044463|W09G12.10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044464|Y77E11A.16|1000nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044464|Y77E11A.16|1065nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044464|Y77E11A.16|1069nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044464|Y77E11A.16|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044464|Y77E11A.16|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044466|Y48A5A.3a|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044466|Y48A5A.3a|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2076|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044466|Y48A5A.3a|61nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=95|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|365nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2099|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|560nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|679nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044467|R05C11.4a|682nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|107nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1470|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|111nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=74|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=283|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044468|Y69A2AL.2|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044469|clec-173|272nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044470|C09G12.17|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044471|F56D6.9|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044471|F56D6.9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5566|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044471|F56D6.9|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=219|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044471|F56D6.9|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044472|dct-8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044472|dct-8|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1783|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044472|dct-8|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044472|dct-8|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044472|dct-8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044474|F56D6.12|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=179|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044474|F56D6.12|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044475|F56D6.13|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1109|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044475|F56D6.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044475|F56D6.13|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044476|F56D6.14|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044476|F56D6.14|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=597|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044476|F56D6.14|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044477|F49F1.14|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044478|K06B9.6|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=233|total_reads(72.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044478|K06B9.6|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044479|F15E6.10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=286|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044480|ZK185.4b|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044480|ZK185.4b|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044480|ZK185.4b|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044480|ZK185.4b|734nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044481|ZK185.5|105nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044481|ZK185.5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=623|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044481|ZK185.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044482|F29B9.12|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1120|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044482|F29B9.12|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044482|F29B9.12|89nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044482|F29B9.12|93nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044482|F29B9.12|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=121|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2995|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2145|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|910nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|95nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044483|H06H21.11|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|138nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1108|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=629|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|204nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=230|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|206nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044484|hot-9|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|869nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|871nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044485|Y54G2A.41.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044487|Y54G2A.44|1171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044487|Y54G2A.44|1382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044487|Y54G2A.44|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044487|Y54G2A.44|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|24nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=187|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=745|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044488|Y54G2A.45a|73nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044489|pudl-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044490|pudl-2|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044490|pudl-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044491|Y54G2A.48|132nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00044491|Y54G2A.48|134nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00044492|Y54G2A.49a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044492|Y54G2A.49a|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=480|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044492|Y54G2A.49a|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044492|Y54G2A.49a|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044493|Y54G2A.50|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044493|Y54G2A.50|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=722|total_reads(54.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044493|Y54G2A.50|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044493|Y54G2A.50|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044493|Y54G2A.50|401nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044495|Y54G2A.40|429nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044499|T11F8.5|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044499|T11F8.5|438nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044499|T11F8.5|442nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044499|T11F8.5|548nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|1181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=404|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=797|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|129nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|529nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|625nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|630nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|636nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044500|T19E7.6.1|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044501|C55C3.8|1398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044501|C55C3.8|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044501|C55C3.8|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044502|C46G7.5|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(88.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044502|C46G7.5|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044504|R13A1.10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00044504|R13A1.10|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1021|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|108nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|571nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|575nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|832nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|856nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044508|nsy-7|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|357nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|397nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=265|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1158|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|402nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|407nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044509|K07H8.12|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044510|K07H8.11|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044511|clec-181|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044511|clec-181|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00044511|clec-181|1498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044511|clec-181|1503nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044511|clec-181|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044511|clec-181|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044511|clec-181|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044512|W03F9.11|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00044512|W03F9.11|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044512|W03F9.11|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044512|W03F9.11|565nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(39.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044513|Y58G8A.5|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044513|Y58G8A.5|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044513|Y58G8A.5|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044513|Y58G8A.5|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1404|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044513|Y58G8A.5|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044513|Y58G8A.5|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044513|Y58G8A.5|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044514|R09E12.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3576|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044514|R09E12.9|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044520|F59A7.12|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044521|Y5H2A.4|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044521|Y5H2A.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044523|F37B4.14|398nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044523|F37B4.14|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044523|F37B4.14|580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044523|F37B4.14|585nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044525|Y73C8B.5b|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044525|Y73C8B.5b|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(77.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044526|T28A11.22|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044526|T28A11.22|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(37.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|287nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044527|Y39H10B.2a|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=88|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044528|lgc-29|131nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044528|lgc-29|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044528|lgc-29|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00044529|irld-1|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044529|irld-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044529|irld-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044529|irld-1|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044530|F32D1.11|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044530|F32D1.11|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044530|F32D1.11|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044530|F32D1.11|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044531|F13A2.9|1436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044531|F13A2.9|704nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00044531|F13A2.9|709nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044531|F13A2.9|713nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044531|F13A2.9|715nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044533|F41F3.8|109nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00044533|F41F3.8|1190nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044533|F41F3.8|1217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044533|F41F3.8|1225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044533|F41F3.8|232nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044533|F41F3.8|923nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|437nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=253|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|441nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|509nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=362|total_reads(30.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=452|total_reads(38.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044534|H23N18.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=524|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=534|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|38nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|451nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=162|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1609|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|652nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044535|K11D12.13|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044536|F14F9.8|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=599|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044536|F14F9.8|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044536|F14F9.8|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044537|B0238.15|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044537|B0238.15|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044537|B0238.15|206nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044538|T09D3.8|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044538|T09D3.8|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044538|T09D3.8|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044538|T09D3.8|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044539|K09H11.9|57nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044539|K09H11.9|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044539|K09H11.9|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(33.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044541|K09H11.11|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044541|K09H11.11|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044541|K09H11.11|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=78|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044542|CD4.11|922nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4483|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044544|F26F12.8.2|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=795|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044545|EGAP9.4|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044546|T01C4.8|1465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3080|total_reads(87.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|1227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|1229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|1236nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|284nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|531nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044547|C13A2.12|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044548|cnc-9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044548|cnc-9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044548|cnc-9|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044548|cnc-9|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044548|cnc-9|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044548|cnc-9|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044548|cnc-9|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044551|ZK105.8|1181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044551|ZK105.8|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044551|ZK105.8|351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00044551|ZK105.8|814nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044552|Y97E10AR.8|203nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044552|Y97E10AR.8|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044552|Y97E10AR.8|393nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044552|Y97E10AR.8|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044552|Y97E10AR.8|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044552|Y97E10AR.8|653nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=656|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|405nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|411nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3480|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|416nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=230|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|419nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044553|T23B12.11.1|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044554|F41E6.15|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1627|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044554|F41E6.15|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044555|F36D4.7|1560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044555|F36D4.7|1566nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044555|F36D4.7|1570nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(37.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044555|F36D4.7|616nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|288nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|294nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|297nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=381|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00044556|F38G1.3|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044557|ZC13.10|1014nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044557|ZC13.10|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044557|ZC13.10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044557|ZC13.10|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044557|ZC13.10|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044557|ZC13.10|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1620|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044559|ZK380.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044559|ZK380.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(50.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044560|C36C9.6|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044560|C36C9.6|876nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044560|C36C9.6|891nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044562|C14E2.7|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=528|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044562|C14E2.7|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044562|C14E2.7|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=116|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044562|C14E2.7|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044562|C14E2.7|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044562|C14E2.7|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044562|C14E2.7|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044564|ZK813.6|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044564|ZK813.6|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044564|ZK813.6|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044565|F53B1.9|1093nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044566|T06F4.3|417nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044566|T06F4.3|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(73.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044567|C46C11.4|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044567|C46C11.4|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(64.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044568|ntc-1|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044568|ntc-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7602|total_reads(98.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044568|ntc-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044568|ntc-1|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044569|C25F6.8|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044569|C25F6.8|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044569|C25F6.8|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044570|T22B7.8|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=278|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044570|T22B7.8|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044571|C46F4.3|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044571|C46F4.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044571|C46F4.3|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044571|C46F4.3|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044573|C15B12.9|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044575|F38B6.8|1070nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044575|F38B6.8|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(82.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044579|C06E2.9|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|104nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|106nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|109nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|113nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044582|B0222.11|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044584|T03G11.9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044584|T03G11.9|68nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=91|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044587|srz-105|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=670|total_reads(83.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044588|ZK1236.9a|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044589|C29F5.8|307nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044589|C29F5.8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044589|C29F5.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(24.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044602|C31B8.16|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044603|acbp-7|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044603|acbp-7|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044603|acbp-7|42nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044603|acbp-7|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044603|acbp-7|45nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044603|acbp-7|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=460|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044603|acbp-7|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044604|T10F2.5|1330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044604|T10F2.5|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044604|T10F2.5|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044604|T10F2.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4833|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044604|T10F2.5|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044604|T10F2.5|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044604|T10F2.5|991nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044605|ttr-36|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044605|ttr-36|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044605|ttr-36|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2577|total_reads(99.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|1033nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|1346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|1352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|569nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1037|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044607|K02A11.4|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|1005nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|123nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=540|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5572|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044608|glrx-22|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044609|tbcc-1|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=196|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044609|tbcc-1|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1074|total_reads(57.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044609|tbcc-1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=598|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00044610|D2092.10|1537nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044610|D2092.10|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044610|D2092.10|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(69.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044611|T27A3.8|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00044611|T27A3.8|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044611|T27A3.8|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044612|Y57E12AR.1|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=738|total_reads(98.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044612|Y57E12AR.1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044614|C36B1.14|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044614|C36B1.14|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044614|C36B1.14|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4214|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044614|C36B1.14|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044614|C36B1.14|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|121nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|131nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|1547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30351|total_reads(80.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6927|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044615|B0252.8|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044616|M01A12.4|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044617|bus-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044617|bus-1|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00044617|bus-1|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044617|bus-1|162nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044617|bus-1|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044618|bus-2|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(74.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044618|bus-2|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044618|bus-2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044620|bus-4|106nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044620|bus-4|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044620|bus-4|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=372|total_reads(56.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044620|bus-4|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=183|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044620|bus-4|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|423nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|447nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|449nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=204|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|451nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=298|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|456nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|463nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|468nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=661|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|497nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|499nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|514nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044623|bus-8|517nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044630|bus-17|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044630|bus-17|201nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044630|bus-17|209nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=327|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044630|bus-17|211nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=89|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00044630|bus-17|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044630|bus-17|218nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044631|bus-18|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044631|bus-18|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00044631|bus-18|147nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044631|bus-18|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044633|F54H12.7|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044633|F54H12.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=815|total_reads(65.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044633|F54H12.7|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044633|F54H12.7|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044634|C29E4.14|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044634|C29E4.14|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=137|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044634|C29E4.14|54nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044634|C29E4.14|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=378|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044634|C29E4.14|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044634|C29E4.14|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044634|C29E4.14|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|1460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=163|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|43nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=186|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=70|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=82|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=4289|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=307|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044636|B0393.9a|91nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11307|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044637|rft-1|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044637|rft-1|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044637|rft-1|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044637|rft-1|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044637|rft-1|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044637|rft-1|231nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=154|total_reads(27.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044638|F23A7.8|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=1638|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=161|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|234nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|237nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|244nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|247nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|454nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044640|B0432.14a|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044641|T01D1.8a.2|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00044641|T01D1.8a.2|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044641|T01D1.8a.2|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044641|T01D1.8a.2|501nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044641|T01D1.8a.2|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=173|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=370|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|306nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044643|H17B01.5|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|261nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=82|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6586|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48565|total_reads(83.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2594|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044644|B0205.13|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044645|Y51H7BR.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9386|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044646|B0205.14|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|1024nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|1102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|1114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1727|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|1120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=561|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|1126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=275|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|1128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1467|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044648|R144.13|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044649|C23H5.11b|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044649|C23H5.11b|27nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044649|C23H5.11b|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=62|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044649|C23H5.11b|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=524|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00044649|C23H5.11b|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1146|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044649|C23H5.11b|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044649|C23H5.11b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044650|Y71G10AR.4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044650|Y71G10AR.4|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044650|Y71G10AR.4|702nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044650|Y71G10AR.4|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044650|Y71G10AR.4|822nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3215|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044650|Y71G10AR.4|825nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044650|Y71G10AR.4|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044651|egrh-3|623nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044651|egrh-3|630nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044651|egrh-3|677nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044651|egrh-3|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044651|egrh-3|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044651|egrh-3|931nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044651|egrh-3|942nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044654|fbxa-85|20nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044654|fbxa-85|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044654|fbxa-85|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044655|fbxa-194|932nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044658|C01G10.17|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(32.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044658|C01G10.17|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=174|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044659|fbxa-142|1441nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044659|fbxa-142|1447nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044659|fbxa-142|1449nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044659|fbxa-142|1453nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044659|fbxa-142|1458nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044659|fbxa-142|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044661|fbxa-143|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044661|fbxa-143|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044662|F26G1.9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1255|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044662|F26G1.9|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044662|F26G1.9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044663|F26G1.10|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(16.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044663|F26G1.10|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044663|F26G1.10|265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(73%)
- ID=WBGene00044665|F59A6.12|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1177|total_reads(84.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044665|F59A6.12|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044665|F59A6.12|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044665|F59A6.12|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044666|F33G12.7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2136|total_reads(99.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044666|F33G12.7|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|113nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6714|total_reads(86%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|373nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|485nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|487nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|490nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|528nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|558nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044667|ZK622.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044668|C18A3.11|1141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044672|fbxa-4|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044672|fbxa-4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044672|fbxa-4|126nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044672|fbxa-4|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=530|total_reads(74.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044672|fbxa-4|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044672|fbxa-4|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044672|fbxa-4|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|1077nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|1252nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|283nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=591|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1158|total_reads(38.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=443|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|74nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|78nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|82nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044674|B0280.17|84nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044675|fbxa-76|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=229|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044675|fbxa-76|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044675|fbxa-76|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044676|fbxa-42|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044676|fbxa-42|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044676|fbxa-42|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=861|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=4404|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|109nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|1474nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|362nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044677|ZK353.10a|94nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044678|B0303.16|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044678|B0303.16|447nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044678|B0303.16|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044678|B0303.16|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044678|B0303.16|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|18nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|25nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1429|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42636|total_reads(84.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6005|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00044679|K02B12.9|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044680|F30A10.13b|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044680|F30A10.13b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=145|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044680|F30A10.13b|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044680|F30A10.13b|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=267|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044680|F30A10.13b|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(41.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044681|T24C4.8|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044681|T24C4.8|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(82.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044681|T24C4.8|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044681|T24C4.8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=194|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=306|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=136|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7188|total_reads(66.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044683|C36E6.8.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2805|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044684|T08G11.2|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044684|T08G11.2|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044684|T08G11.2|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044684|T08G11.2|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=428|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044684|T08G11.2|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=891|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|207nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=337|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|280nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=201|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|286nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=49677|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|291nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3485|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|295nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|301nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=60|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|319nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1366|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|327nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|342nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|641nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|644nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044686|flp-28|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044687|B0563.9|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044687|B0563.9|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|1057nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|747nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|759nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|767nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|785nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|788nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|794nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|858nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044689|arid-1|865nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1653|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044690|M02B7.7|1267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044690|M02B7.7|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044690|M02B7.7|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=307|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044690|M02B7.7|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=522|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044690|M02B7.7|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044690|M02B7.7|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044690|M02B7.7|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044692|fbxb-91|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044692|fbxb-91|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044692|fbxb-91|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=129|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044692|fbxb-91|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044693|fbxb-92|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00044693|fbxb-92|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00044694|fbxb-90|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(58.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044694|fbxb-90|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044694|fbxb-90|59nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=923|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13037|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3429|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044696|F52E1.14|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044697|poml-4|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044697|poml-4|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044697|poml-4|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=279|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044697|poml-4|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044697|poml-4|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00044697|poml-4|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|1083nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|556nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|560nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|563nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|567nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|573nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=335|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|579nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044698|K09F5.6|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=124|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044699|nhr-286|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6435|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044701|AH9.6|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1201|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1643|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044705|T22F3.12|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044707|F22G12.7|859nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044708|C17H1.13a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044712|F22G12.8|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044712|F22G12.8|41nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044712|F22G12.8|46nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044712|F22G12.8|54nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044712|F22G12.8|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044712|F22G12.8|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044718|T20D4.20|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044719|clec-172|309nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044719|clec-172|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044719|clec-172|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044719|clec-172|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044720|Y53F4B.42|745nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=720|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044723|K11H12.11|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044723|K11H12.11|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=88|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044724|R02E4.3|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044724|R02E4.3|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044724|R02E4.3|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044724|R02E4.3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00044724|R02E4.3|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044725|R11G1.7|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044725|R11G1.7|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044725|R11G1.7|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044725|R11G1.7|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044725|R11G1.7|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=198|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044725|R11G1.7|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044732|T03G11.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=541|total_reads(95.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044732|T03G11.10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044732|T03G11.10|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044732|T03G11.10|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044733|W08F4.13|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00044733|W08F4.13|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00044734|Y19D10A.16|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044734|Y19D10A.16|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044734|Y19D10A.16|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044734|Y19D10A.16|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044736|gfrp-1|46nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00044736|gfrp-1|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044736|gfrp-1|65nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=606|total_reads(55.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044736|gfrp-1|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=233|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044736|gfrp-1|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5600|total_reads(69.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2165|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044737|ttr-45|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044738|folt-3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044741|Y57G11C.52|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=952|total_reads(97.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044741|Y57G11C.52|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044741|Y57G11C.52|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044742|Y55F3BR.10|479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044742|Y55F3BR.10|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=352|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044743|crb-3|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044743|crb-3|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044743|crb-3|164nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044743|crb-3|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1702|total_reads(91.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044743|crb-3|191nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044743|crb-3|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044744|F10G7.12|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044744|F10G7.12|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=283|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044745|Y62E10A.20|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(22.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044745|Y62E10A.20|1325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044745|Y62E10A.20|1333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044745|Y62E10A.20|1359nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044745|Y62E10A.20|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044745|Y62E10A.20|646nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044746|C53H9.3|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044746|C53H9.3|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044746|C53H9.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=326|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044746|C53H9.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1092|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044746|C53H9.3|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1523|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044746|C53H9.3|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044753|F49H12.7|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044753|F49H12.7|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044753|F49H12.7|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(29.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044753|F49H12.7|759nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044754|Y119C1B.12|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(42.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=289|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044756|F58F12.4|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044758|Y37H2A.12a|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044758|Y37H2A.12a|119nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=382|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00044758|Y37H2A.12a|121nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044760|Y71H2AM.25|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=47|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044760|Y71H2AM.25|46nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044761|Y82E9BR.23|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=180|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|1045nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3833|total_reads(60.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2265|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|340nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|354nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|39nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|423nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044762|ZK688.11|835nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044763|ZK688.12|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00044763|ZK688.12|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=359|total_reads(82%)
- ID=WBGene00044763|ZK688.12|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=175|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=87|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|296nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|303nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=226|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|306nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1339|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|314nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|337nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|341nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|344nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|352nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|366nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=593|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044767|T23B7.3a|611nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|1270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|588nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|591nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=443|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=86|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|745nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|752nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044770|C53C11.5|755nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=164|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(27.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=947|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=78|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044771|T23E7.5|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|133nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|137nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=175|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|1389nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|141nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=235|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|277nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|289nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|298nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|315nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|321nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|334nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|487nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=132|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=153|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00044772|T23E7.6|96nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1618|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044773|C08A9.10|73nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044774|F16B3.3b|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044774|F16B3.3b|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044774|F16B3.3b|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044774|F16B3.3b|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044774|F16B3.3b|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1500|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044774|F16B3.3b|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044776|T02B11.8a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044776|T02B11.8a|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044776|T02B11.8a|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044776|T02B11.8a|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=522|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00044777|T02B11.9|37nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=23|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044777|T02B11.9|40nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=148|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00044777|T02B11.9|44nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=103|total_reads(37.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044778|K09C6.10|248nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00044778|K09C6.10|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00044779|T10H9.8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044779|T10H9.8|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044779|T10H9.8|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=609|total_reads(65.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044779|T10H9.8|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044783|T26H5.10|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044783|T26H5.10|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044783|T26H5.10|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044783|T26H5.10|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=646|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=132|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=572|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=805|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|190nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=669|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2344|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1636|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=305|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|320nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|344nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|381nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=278|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044784|F13H10.8a|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044787|C54D10.12|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044787|C54D10.12|128nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044788|ttr-38|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00044788|ttr-38|109nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00044788|ttr-38|111nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044788|ttr-38|113nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=565|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|194nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|243nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|323nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|338nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|346nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3454|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|348nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044789|T07A9.14|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044790|clec-224|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044790|clec-224|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044790|clec-224|85nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|172nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|49nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|52nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=151|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1008|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|84nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044791|bnc-1|88nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044792|F59C6.14a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044792|F59C6.14a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=481|total_reads(72.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044792|F59C6.14a|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044794|Y59A8B.25|1156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044794|Y59A8B.25|1228nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044794|Y59A8B.25|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1031|total_reads(47%)
- ID=WBGene00044794|Y59A8B.25|144nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1138|total_reads(51.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044795|C06H5.8a|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00044795|C06H5.8a|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044795|C06H5.8a|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044795|C06H5.8a|633nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044796|W03D8.11|114nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044796|W03D8.11|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=105|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044796|W03D8.11|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044796|W03D8.11|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00044797|F13E9.13|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044797|F13E9.13|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044797|F13E9.13|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00044797|F13E9.13|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044798|tbx-43|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044798|tbx-43|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044799|ZK686.6|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044801|ZC262.9|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=115|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044801|ZC262.9|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044801|ZC262.9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044801|ZC262.9|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044801|ZC262.9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=287|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044803|C02G6.3|92nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044805|Y53C10A.15|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(14.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044805|Y53C10A.15|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044805|Y53C10A.15|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044807|T19H5.6|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044807|T19H5.6|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(10.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044807|T19H5.6|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=45|total_reads(57.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044810|Y37E3.19|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044811|F12E12.11|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044811|F12E12.11|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00044811|F12E12.11|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=494|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044811|F12E12.11|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044891|T07C4.12|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044891|T07C4.12|544nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044891|T07C4.12|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044891|T07C4.12|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2158|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044891|T07C4.12|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|154nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=924|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044894|Y71F9AR.4|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044895|R06A10.5b|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044895|R06A10.5b|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044895|R06A10.5b|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00044895|R06A10.5b|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044895|R06A10.5b|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044896|K12C11.5|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(70.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044896|K12C11.5|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044897|M01D7.9|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044897|M01D7.9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044897|M01D7.9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044898|let-383|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044898|let-383|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044898|let-383|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044898|let-383|558nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=662|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00044898|let-383|562nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=194|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044898|let-383|602nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044898|let-383|607nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044900|cnc-11|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1613|total_reads(99.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044900|cnc-11|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044901|Y41G9A.10|491nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044901|Y41G9A.10|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044901|Y41G9A.10|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1138|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044901|Y41G9A.10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044903|K03H1.13a|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=233|total_reads(46.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044903|K03H1.13a|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=246|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044903|K03H1.13a|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044903|K03H1.13a|926nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044906|Y67A10A.11a|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00044906|Y67A10A.11a|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00044908|F38A1.15|1253nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(61.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044908|F38A1.15|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044911|H38K22.6|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044911|H38K22.6|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044911|H38K22.6|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1450nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1453nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1457nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3454|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1228|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1492nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|1498nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044912|H38K22.7|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|102nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=133|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|159nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1419|total_reads(57.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|88nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=52|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044916|F40F8.11b.1|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=529|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044917|F40F8.12|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044917|F40F8.12|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=345|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044917|F40F8.12|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16864|total_reads(94.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=138|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=178|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=124|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044921|F53C11.9|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044922|Y43C5A.7|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2184|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044922|Y43C5A.7|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044922|Y43C5A.7|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044922|Y43C5A.7|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044922|Y43C5A.7|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00044924|M106.7|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2846|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044949|Y49A10A.2|146nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044949|Y49A10A.2|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044949|Y49A10A.2|153nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044949|Y49A10A.2|477nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=829|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044949|Y49A10A.2|483nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044949|Y49A10A.2|487nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044949|Y49A10A.2|490nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044953|D2096.13|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=282|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=545|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|228nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|231nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|233nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=68|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|240nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|252nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|259nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=700|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|25nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|262nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|303nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|309nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|311nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|338nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6006|total_reads(56.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|539nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1277|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|542nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=589|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|546nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|552nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|554nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|559nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=214|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044977|F56C4.4b|908nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044978|F58D2.3|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00044978|F58D2.3|178nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00044978|F58D2.3|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00044979|Y41E3.19|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044979|Y41E3.19|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044979|Y41E3.19|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044979|Y41E3.19|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00044987|K07A1.17|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044987|K07A1.17|1570nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044987|K07A1.17|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044987|K07A1.17|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2659|total_reads(96.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|1241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3434|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2079|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044988|W01A8.8b|89nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|426nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=90|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|429nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|436nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|455nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|457nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|477nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|480nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2724|total_reads(83.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=110|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044989|Y37A1B.17d|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00044990|T25B9.11a|110nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(80.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044990|T25B9.11a|117nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044991|T25B9.12|230nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00044991|T25B9.12|236nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=179|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00044991|T25B9.12|239nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00044991|T25B9.12|256nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044998|M199.9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00044998|M199.9|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(82.6%)
- ID=WBGene00044998|M199.9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00044998|M199.9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1a|1580nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1a|1584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=366|total_reads(29.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1a|17nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1a|19nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=84|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1a|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1c|758nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1c|768nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045013|F08A7.1c|774nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=675|total_reads(54.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045024|C43F9.11a|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045036|K08E4.7|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045036|K08E4.7|295nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045036|K08E4.7|301nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045036|K08E4.7|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045036|K08E4.7|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=422|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045036|K08E4.7|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=579|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|221nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=585|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4780|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1421|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1719|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3160|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=211|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045038|F13G11.3|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|200nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=157|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|222nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1785|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045048|D1007.19|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045050|ZC15.10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(32.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045050|ZC15.10|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045050|ZC15.10|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045052|K12C11.6|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=167|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045052|K12C11.6|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=323|total_reads(65.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045053|K12C11.7a|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045053|K12C11.7a|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=156|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045053|K12C11.7a|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045053|K12C11.7a|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045053|K12C11.7a|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(54.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045053|K12C11.7a|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045053|K12C11.7a|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045056|F13H10.9|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045056|F13H10.9|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=274|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045056|F13H10.9|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045056|F13H10.9|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045056|F13H10.9|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045058|gadr-5|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045058|gadr-5|71nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045058|gadr-5|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=58|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045058|gadr-5|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045060|F55B11.7a|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045060|F55B11.7a|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=194|total_reads(91.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045060|F55B11.7a|45nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045060|F55B11.7a|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045061|Y57G11B.8|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045061|Y57G11B.8|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045061|Y57G11B.8|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045063|Y37A1A.4a|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045063|Y37A1A.4a|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045063|Y37A1A.4a|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045063|Y37A1A.4a|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=185|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045067|F07C6.6|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00045067|F07C6.6|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00045078|C46C2.7|166nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045078|C46C2.7|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=820|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045078|C46C2.7|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045096|K01A6.7|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045096|K01A6.7|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=268|total_reads(51.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045096|K01A6.7|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(44.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045101|C35D6.13a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00045101|C35D6.13a|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00045108|H01G02.4.2|314nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045108|H01G02.4.2|380nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045108|H01G02.4.2|382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(68.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|602nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|608nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|618nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|751nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|797nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045122|F22B3.10a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045128|Y116A8C.49|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00045128|Y116A8C.49|657nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00045144|Y64G10A.10a|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045146|Y41E3.22a|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045146|Y41E3.22a|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045146|Y41E3.22a|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045146|Y41E3.22a|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=568|total_reads(91.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045146|Y41E3.22a|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045146|Y41E3.22a|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045177|T21D12.14|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045177|T21D12.14|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=130|total_reads(58%)
- ID=WBGene00045177|T21D12.14|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045177|T21D12.14|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045178|fipr-27|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045180|K07F5.17|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045183|T28C6.10|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045183|T28C6.10|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045183|T28C6.10|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045183|T28C6.10|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045183|T28C6.10|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045183|T28C6.10|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|163nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|165nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|200nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=275|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=193|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045190|R01H2.8|46nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|525nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|538nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|612nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|635nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|648nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=149|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|654nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|689nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|730nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|737nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4669|total_reads(84%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|740nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045192|aho-3|744nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045195|F53F4.17.1|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045195|F53F4.17.1|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045195|F53F4.17.1|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2714|total_reads(74%)
- ID=WBGene00045195|F53F4.17.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=772|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00045195|F53F4.17.1|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045195|F53F4.17.1|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045198|K10D11.7b|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045207|F13E9.14|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3339|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045208|F13E9.15|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045210|C54D2.6|505nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=123|total_reads(92.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045210|C54D2.6|508nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045211|C18D11.9|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045211|C18D11.9|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|1167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|51nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=118|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=676|total_reads(61.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045212|Y110A7A.21|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045215|ceh-63|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045215|ceh-63|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045215|ceh-63|1248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045234|Y26D4A.17a|759nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045237|mrt-1|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045237|mrt-1|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045237|mrt-1|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(40.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045237|mrt-1|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=426|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045237|mrt-1|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=339|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00045237|mrt-1|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045237|mrt-1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045239|Y49E10.29|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045239|Y49E10.29|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00045239|Y49E10.29|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=255|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045239|Y49E10.29|1592nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045239|Y49E10.29|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045242|C05B5.11|569nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=86|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|103nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|109nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18617|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|1196nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=361|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=341|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|1297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|1301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=354|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4727|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3026|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|190nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=60|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|208nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|211nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=146|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=92|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=107|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=514|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1065|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=99|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045245|ttr-34|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=121|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=241|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=281|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(10.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=331|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045246|C29E4.15|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045247|F54H12.8|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045247|F54H12.8|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=548|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045247|F54H12.8|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045247|F54H12.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|244nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|377nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|382nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|384nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|389nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|410nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045248|ZK180.7|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1569|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045249|T07A9.15|119nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=50|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045249|T07A9.15|121nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045249|T07A9.15|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=938|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045249|T07A9.15|79nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5827|total_reads(81.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045249|T07A9.15|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=343|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045250|Y73B6BL.47|1110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1085nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1089nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1500nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1509nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1516nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1554nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|1572nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=409|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045251|F54F7.9|993nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045252|Y62H9A.15a|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00045252|Y62H9A.15a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=739|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00045253|F46C3.6|115nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045253|F46C3.6|118nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=51|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045253|F46C3.6|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1997|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045253|F46C3.6|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045253|F46C3.6|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045255|nhr-146|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045255|nhr-146|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045255|nhr-146|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=231|total_reads(68.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045255|nhr-146|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=250|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|274nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|276nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|283nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|43nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=111|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|46nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2905|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|76nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=777|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045261|H29C22.1|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045265|K10C2.8|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045265|K10C2.8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(95%)
- ID=WBGene00045265|K10C2.8|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045268|ttr-42|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=482|total_reads(18.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045268|ttr-42|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1511|total_reads(59.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045268|ttr-42|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=353|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045268|ttr-42|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045268|ttr-42|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00045268|ttr-42|85nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|135nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=44|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=828|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|148nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=210|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|224nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|404nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045269|F46G11.6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045270|C04E7.5|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045270|C04E7.5|20nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045270|C04E7.5|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045270|C04E7.5|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00045270|C04E7.5|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045270|C04E7.5|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045270|C04E7.5|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=256|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045271|F07G6.10|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045272|F59C12.4|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045272|F59C12.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045272|F59C12.4|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045272|F59C12.4|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045272|F59C12.4|55nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2056|total_reads(96.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045272|F59C12.4|65nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|100nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|1175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=316|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3683|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1388|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045275|F18E3.12|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=169|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|17nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1410|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|192nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=205|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|240nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|26nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|29nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=984|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5608|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9357|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00045276|F18E3.13|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=373|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1427|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|141nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|209nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|455nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045277|ZK742.6|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045283|K08E4.8|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045283|K08E4.8|635nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045289|fbxa-169|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045289|fbxa-169|293nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045291|F23D12.10|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00045291|F23D12.10|235nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00045291|F23D12.10|251nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=50|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00045291|F23D12.10|350nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00045291|F23D12.10|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00045292|fbxa-179|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(26.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045292|fbxa-179|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045292|fbxa-179|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045292|fbxa-179|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045292|fbxa-179|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045292|fbxa-179|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(30.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045295|fbxa-222|1331nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00045295|fbxa-222|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045295|fbxa-222|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045295|fbxa-222|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045295|fbxa-222|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045295|fbxa-222|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045297|fbxc-43|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(59.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045297|fbxc-43|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045297|fbxc-43|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045297|fbxc-43|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045298|fbxc-12|1432nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00045298|fbxc-12|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00045301|fbxc-9|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045302|fbxc-30|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045304|Y27F2A.11|370nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045304|Y27F2A.11|374nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045305|ZC250.4|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045305|ZC250.4|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045305|ZC250.4|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045305|ZC250.4|417nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2037|total_reads(87.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045305|ZC250.4|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045305|ZC250.4|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045306|ZC250.5|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045306|ZC250.5|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=183|total_reads(63.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045306|ZC250.5|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045306|ZC250.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|169nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|171nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|173nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|234nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=234|total_reads(49.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045308|C37H5.14a|465nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045331|F14D7.12|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045331|F14D7.12|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=356|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045331|F14D7.12|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045331|F14D7.12|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045331|F14D7.12|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7480|total_reads(66.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045331|F14D7.12|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3141|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10895|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|75nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|82nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|84nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045336|R11D1.12b|87nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045337|M01B2.12|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045337|M01B2.12|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045338|M01B2.13|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00045338|M01B2.13|1157nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00045339|T10H4.13|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045339|T10H4.13|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|1021nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|1023nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|1099nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|112nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|114nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=437|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|118nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|124nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2668|total_reads(48.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|129nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1064|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=176|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|1398nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|299nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|828nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=327|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|830nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|834nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045340|T10G3.8|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045344|Y43F8C.23|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045355|D1086.17|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045355|D1086.17|1094nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045355|D1086.17|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045355|D1086.17|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=127|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045355|D1086.17|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1803|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045356|T03E6.9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1201|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|1597nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045357|F13A7.14|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045362|F11D11.12|485nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|1371nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=143|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1957|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|342nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=288|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|699nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|736nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045365|ZC449.7|746nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|1176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|1186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|48nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|56nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045379|C45B11.6|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00045381|F28B1.9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045382|T05E12.8|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(20.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045382|T05E12.8|404nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045385|lgc-24|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2635|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045385|lgc-24|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045385|lgc-24|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045385|lgc-24|235nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045385|lgc-24|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=385|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=208|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1491|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11207|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4049|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|248nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|810nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045386|C02B4.4|812nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045387|K09H9.8|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045387|K09H9.8|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045387|K09H9.8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045387|K09H9.8|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1146|total_reads(51%)
- ID=WBGene00045387|K09H9.8|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1043|total_reads(46.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045387|K09H9.8|697nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045390|C38C3.10|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045390|C38C3.10|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045390|C38C3.10|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(86.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045390|C38C3.10|581nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045392|F26D11.12|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045392|F26D11.12|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7248|total_reads(99.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045392|F26D11.12|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045392|F26D11.12|527nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045392|F26D11.12|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045393|F26D11.13|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045393|F26D11.13|210nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045393|F26D11.13|290nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045393|F26D11.13|304nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=747|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|47nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1577|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|52nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=993|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1732|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1186|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7969|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20050|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7112|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3332|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10916|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=202|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045394|ZK813.7.2|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=102|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|155nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|173nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=115|total_reads(17.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|176nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045395|F09F9.5|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=391|total_reads(59.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045396|ZC334.12|1257nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045396|ZC334.12|1263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00045396|ZC334.12|1266nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=168|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00045396|ZC334.12|1268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00045396|ZC334.12|368nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045396|ZC334.12|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045396|ZC334.12|902nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|152nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1927|total_reads(79.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|154nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=356|total_reads(14.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|157nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|466nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|541nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=49|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|553nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|564nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045397|Y54G2A.52|606nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045398|Y71F9AM.8|1495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045398|Y71F9AM.8|64nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|18nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=98|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|25nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|50nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|53nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1346|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=317|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3291|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5036|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045399|Y47G6A.33|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=213|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045400|C54D10.13|28nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045401|eol-1|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045401|eol-1|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045401|eol-1|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(30.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045401|eol-1|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(30.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045402|Y75B12B.13|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045403|K10H10.12|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045403|K10H10.12|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045403|K10H10.12|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045405|D1086.18|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045405|D1086.18|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045406|D1086.19|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|317nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=343|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|45nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1513|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|49nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1509|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045407|T07D4.5|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=200|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045411|C25F9.11|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045411|C25F9.11|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=237|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045411|C25F9.11|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045411|C25F9.11|292nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1120|total_reads(69.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045411|C25F9.11|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045412|C25F9.12|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045412|C25F9.12|436nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045412|C25F9.12|440nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=115|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045412|C25F9.12|446nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045413|C25F9.13|685nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(62.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045413|C25F9.13|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045414|T19H5.7|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045414|T19H5.7|153nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045414|T19H5.7|160nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045414|T19H5.7|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045414|T19H5.7|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045414|T19H5.7|81nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=527|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045414|T19H5.7|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045415|Y43F8B.15|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1724|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045416|Y37H2A.14|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=86|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|694nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(15.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|712nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|714nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|743nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045417|Y37H2A.13|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2885|total_reads(94.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|293nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00045418|F15B9.10a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|1373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|1386nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|1394nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=985|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|393nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|427nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|436nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|439nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=181|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|441nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1907|total_reads(53.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|446nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=297|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045419|lsy-12|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045433|F49D11.10.1|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045433|F49D11.10.1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1239|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045433|F49D11.10.1|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045433|F49D11.10.1|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045433|F49D11.10.1|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045433|F49D11.10.1|266nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045433|F49D11.10.1|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=42|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1015|total_reads(73.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=249|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|279nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|286nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045434|Y95D11A.3|288nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045455|F26G1.11|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045455|F26G1.11|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00045455|F26G1.11|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045455|F26G1.11|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00045455|F26G1.11|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045455|F26G1.11|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045455|F26G1.11|726nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045456|C10A4.9b|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045456|C10A4.9b|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1930|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045456|C10A4.9b|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=197|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045456|C10A4.9b|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045457|F33H12.7|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=215|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00045457|F33H12.7|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045457|F33H12.7|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045457|F33H12.7|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045457|F33H12.7|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045457|F33H12.7|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1807|total_reads(58.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045457|F33H12.7|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=771|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00045458|F17B5.8|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(62.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045458|F17B5.8|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045458|F17B5.8|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045458|F17B5.8|190nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045458|F17B5.8|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045459|Y59A8B.26|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=477|total_reads(96.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045459|Y59A8B.26|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045460|C15C8.8|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045461|C25F9.14a|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=473|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045461|C25F9.14a|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045461|C25F9.14a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045461|C25F9.14a|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045468|F08A8.8|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045468|F08A8.8|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045468|F08A8.8|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=324|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045468|F08A8.8|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045468|F08A8.8|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045468|F08A8.8|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=220|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=472|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|75nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|83nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045473|F30A10.14|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045474|C49G9.2|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=357|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045474|C49G9.2|275nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045475|T07A5.7|1245nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045475|T07A5.7|1247nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(20.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045475|T07A5.7|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045475|T07A5.7|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045475|T07A5.7|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045480|F14F3.5|383nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00045480|F14F3.5|386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045480|F14F3.5|389nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00045480|F14F3.5|391nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00045481|M153.5|57nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045482|T03F6.9|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045482|T03F6.9|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045482|T03F6.9|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045482|T03F6.9|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045482|T03F6.9|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8975|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00045482|T03F6.9|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=145|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045482|T03F6.9|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045483|oxy-5|131nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10433|total_reads(97%)
- ID=WBGene00045483|oxy-5|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045483|oxy-5|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045483|oxy-5|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045483|oxy-5|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045483|oxy-5|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00045484|F34D10.9|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045484|F34D10.9|73nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=216|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045484|F34D10.9|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045486|K05F6.12|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|143nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|190nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(25.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045488|F57B1.9b|232nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045493|F55G7.4|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045494|ZK662.6|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045494|ZK662.6|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045494|ZK662.6|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045494|ZK662.6|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=305|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|1306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|175nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|178nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|181nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|257nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|262nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3904|total_reads(65.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|265nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1747|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|268nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|270nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045495|F11C1.7b|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045497|K03A11.6|46nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045497|K03A11.6|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045497|K03A11.6|602nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=77|total_reads(52.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045497|K03A11.6|605nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045497|K03A11.6|608nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045497|K03A11.6|640nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045497|K03A11.6|642nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045498|F56F4.8|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045498|F56F4.8|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045506|F57G4.10|1131nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045506|F57G4.10|1238nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|158nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|172nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=872|total_reads(40.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1029|total_reads(48.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|192nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|91nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045507|F10A3.17|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045508|D1081.10|467nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00045508|D1081.10|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00045508|D1081.10|476nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(28.9%)
- ID=WBGene00045510|F11A5.17|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045511|F11A5.18|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045511|F11A5.18|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00045511|F11A5.18|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(42.8%)
- ID=WBGene00045511|F11A5.18|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00045513|F14H3.14|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00045517|R11D1.13|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00045517|R11D1.13|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00045517|R11D1.13|394nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00045517|R11D1.13|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(80.5%)
- ID=WBGene00045517|R11D1.13|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050875|bah-1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050875|bah-1|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050875|bah-1|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(77.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050879|D1081.11|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=104|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050880|F32H2.12|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050881|ZK39.10|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(47.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050881|ZK39.10|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050881|ZK39.10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050881|ZK39.10|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050884|Y69H2.15|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050885|Y94H6A.12b|1421nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050885|Y94H6A.12b|1591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050885|Y94H6A.12b|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1060|total_reads(95.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050885|Y94H6A.12b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00050885|Y94H6A.12b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050889|T04C12.9|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050889|T04C12.9|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050889|T04C12.9|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050889|T04C12.9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050889|T04C12.9|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=786|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050892|ttr-57|735nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050896|ttr-56|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00050896|ttr-56|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050896|ttr-56|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(40.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050896|ttr-56|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(22.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050896|ttr-56|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00050898|T19B10.12|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15b|432nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15b|434nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15b|507nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|1005nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|1007nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=215|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|1011nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=123|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|1206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=320|total_reads(37.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050899|T10C6.15c|997nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050904|Y70C5A.3|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(59.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050904|Y70C5A.3|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050904|Y70C5A.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050906|F20E11.17|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050906|F20E11.17|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050906|F20E11.17|141nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050907|Y51A2B.9|100nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=96|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050907|Y51A2B.9|102nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(23.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050907|Y51A2B.9|98nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050910|Y43F8B.17|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050913|T12B5.14|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050913|T12B5.14|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=832|total_reads(87.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050913|T12B5.14|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050914|T12B5.15|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=986|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050914|T12B5.15|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1181|total_reads(54.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050914|T12B5.15|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00050915|Y6E2A.10|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1040|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050916|F55F10.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=88|total_reads(54%)
- ID=WBGene00050916|F55F10.3|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050916|F55F10.3|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050917|Y53G8AL.4a.2|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050917|Y53G8AL.4a.2|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1091|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050917|Y53G8AL.4a.2|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050919|C45G9.15|271nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00050919|C45G9.15|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=105|total_reads(74.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050919|C45G9.15|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050931|F59B2.14|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(39.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050931|F59B2.14|410nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050931|F59B2.14|412nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050934|T19C9.10a|470nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050934|T19C9.10a|510nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050934|T19C9.10a|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00050936|ZK856.16|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050936|ZK856.16|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050936|ZK856.16|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050936|ZK856.16|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1480|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050936|ZK856.16|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1109|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050936|ZK856.16|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050937|R02D5.8|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=242|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050937|R02D5.8|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=520|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00050937|R02D5.8|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050937|R02D5.8|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050937|R02D5.8|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050937|R02D5.8|305nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00050937|R02D5.8|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=503|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1417|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|40nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|77nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2970|total_reads(33.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|80nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=3724|total_reads(42%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|85nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=67|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050939|C05G5.7|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=357|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050940|C25D7.16|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050941|C33F10.14|114nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050941|C33F10.14|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050941|C33F10.14|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00050941|C33F10.14|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050941|C33F10.14|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2593|total_reads(94.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050943|ZC412.10|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1255|total_reads(60.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050943|ZC412.10|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=776|total_reads(37.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050943|ZC412.10|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050943|ZC412.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050943|ZC412.10|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050943|ZC412.10|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00050944|C14A11.9|1548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050944|C14A11.9|286nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3244|total_reads(93.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050944|C14A11.9|293nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050944|C14A11.9|296nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=165|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050944|C14A11.9|298nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050944|C14A11.9|305nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|1100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|319nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=671|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|789nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=52|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050947|K07C5.13|880nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|31nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=611|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|41nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00050956|C14A6.13|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00050957|C10A4.10|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=209|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050967|C25F9.15|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(23.8%)
- ID=WBGene00050967|C25F9.15|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(76.2%)
- ID=WBGene00050968|R11G10.4|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00050974|Y6G8.9|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00050974|Y6G8.9|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|1456nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|1495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=140|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|1522nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=296|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|1524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|1528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=247|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077439|F55B12.10|214nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=348|total_reads(31%)
- ID=WBGene00077445|Y51A2A.12|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077450|K06B4.15|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=351|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077453|Y62F5A.12|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077453|Y62F5A.12|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2545|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077453|Y62F5A.12|116nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077453|Y62F5A.12|672nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077455|Y69H2.17|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077455|Y69H2.17|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077455|Y69H2.17|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077455|Y69H2.17|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=543|total_reads(64.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077489|C04G6.13|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077490|M03A1.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077490|M03A1.8|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1419|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077490|M03A1.8|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077490|M03A1.8|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077491|K08H10.10|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077491|K08H10.10|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077491|K08H10.10|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=550|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077491|K08H10.10|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077491|K08H10.10|802nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077491|K08H10.10|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077491|K08H10.10|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077495|Y20C6A.4|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077497|K06A4.10|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=87|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077497|K06A4.10|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077500|C27H6.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077500|C27H6.9|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1386|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00077500|C27H6.9|939nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077503|AC3.12|62nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077508|T27F6.10|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00077508|T27F6.10|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077508|T27F6.10|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077514|F07B10.7a|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077514|F07B10.7a|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1128|total_reads(61.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=287|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077519|T27C10.8|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077520|C37A5.11|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077520|C37A5.11|152nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077520|C37A5.11|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=140|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077520|C37A5.11|215nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077520|C37A5.11|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=434|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077521|maf-1|1226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077521|maf-1|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077521|maf-1|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077521|maf-1|353nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077521|maf-1|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077521|maf-1|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1185|total_reads(93.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077521|maf-1|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|1072nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|1098nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|117nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=266|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|271nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|530nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=63|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|603nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|606nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|610nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|670nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|672nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|674nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4657|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|678nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|681nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|710nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|718nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=145|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|723nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=139|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|725nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7440|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|735nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=836|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|739nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077522|T10D4.15|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=854|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077523|C23H5.12|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077523|C23H5.12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(60.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22702|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077526|C25A1.16|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077531|F40G9.15|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(60.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077531|F40G9.15|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077531|F40G9.15|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=135|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=216|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(32.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|900nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=175|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077536|F38B7.10|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077538|T04F3.5|1168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077538|T04F3.5|1415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(23.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077538|T04F3.5|1419nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077538|T04F3.5|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077539|Y52B11A.12|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077539|Y52B11A.12|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077539|Y52B11A.12|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077539|Y52B11A.12|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=176|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077539|Y52B11A.12|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077539|Y52B11A.12|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077543|F27D4.8|1376nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00077543|F27D4.8|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077543|F27D4.8|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077543|F27D4.8|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=892|total_reads(79.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077543|F27D4.8|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077543|F27D4.8|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077546|C01A2.9|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077548|F21C3.7|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(53.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077548|F21C3.7|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077548|F21C3.7|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077548|F21C3.7|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077548|F21C3.7|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077548|F21C3.7|87nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=59|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077548|F21C3.7|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=61|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077553|C26C6.10|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=65|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077553|C26C6.10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077553|C26C6.10|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077558|T06D10.3|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077558|T06D10.3|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077559|R05D7.7|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=557|total_reads(91.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077559|R05D7.7|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077559|R05D7.7|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077562|ZC443.7|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077563|peel-1|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077563|peel-1|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=138|total_reads(69.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077565|W07G4.7|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077565|W07G4.7|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=465|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077565|W07G4.7|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077569|F53F4.18|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=623|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|138nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=1232|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|143nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=150|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|211nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|217nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|85nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077573|T08G5.15|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077576|C15H11.13|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077576|C15H11.13|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=90|total_reads(41.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077576|C15H11.13|860nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(33.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077576|C15H11.13|873nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077576|C15H11.13|879nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077577|R02D5.9|167nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077582|F14H8.8|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=102|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077582|F14H8.8|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=179|total_reads(63.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077583|C01G10.18|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077585|T01G5.8|129nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=440|total_reads(95.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077585|T01G5.8|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077585|T01G5.8|325nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077588|T26H8.5|338nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077588|T26H8.5|341nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=387|total_reads(79.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077588|T26H8.5|345nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077588|T26H8.5|347nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00077592|T25B2.3|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077592|T25B2.3|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077592|T25B2.3|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7752|total_reads(32.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6142|total_reads(25.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9422|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=512|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077593|C49G7.12|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=97|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077599|T20F5.8|62nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=338|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077599|T20F5.8|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=233|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077599|T20F5.8|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077599|T20F5.8|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1375|total_reads(67.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077599|T20F5.8|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00077599|T20F5.8|863nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077599|T20F5.8|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077607|T10C6.16.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(91%)
- ID=WBGene00077607|T10C6.16.1|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00077616|F57E7.4|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077622|T25E12.14|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2156|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|228nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=156|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|311nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|669nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077643|trpp-1|673nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|151nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|204nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|223nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|225nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=314|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=125|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|236nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|313nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077658|M106.8|66nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077663|F55C9.14|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077669|Y38H6A.5b|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077669|Y38H6A.5b|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077669|Y38H6A.5b|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00077669|Y38H6A.5b|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077673|B0563.10|159nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077673|B0563.10|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(43.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077674|K02A6.4|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077674|K02A6.4|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077674|K02A6.4|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077679|K11E4.6|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077680|F54F7.10|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=164|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077680|F54F7.10|124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077680|F54F7.10|1298nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077680|F54F7.10|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=287|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|21nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=117|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|305nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077681|Y44A6D.7a|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077682|F58B4.7|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=407|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077684|Y26D4A.21|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(93.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077684|Y26D4A.21|86nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077685|C04F12.12|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077685|C04F12.12|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(39.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077685|C04F12.12|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077685|C04F12.12|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077690|mtp-18|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=635|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077690|mtp-18|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=604|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077690|mtp-18|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077690|mtp-18|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077690|mtp-18|150nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077690|mtp-18|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077691|T06E4.14|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=87|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077691|T06E4.14|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6455|total_reads(98.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077692|C08E8.10|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=246|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077692|C08E8.10|151nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077692|C08E8.10|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077692|C08E8.10|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|143nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|170nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=74|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|177nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1024|total_reads(41.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1016|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077693|T04C12.11|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=72|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077696|marc-1|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=376|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13a|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13a|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=743|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13a|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13a|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13a|127nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13a|129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13c|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077697|F58E6.13c|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|164nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=101|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|33nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=338|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=385|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=52|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|687nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|690nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077698|lurp-4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077699|C45B11.8|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=295|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077699|C45B11.8|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=81|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2071|total_reads(80.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=329|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077701|poml-3|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077703|K08E5.5|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077704|F12A10.9|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077704|F12A10.9|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=318|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077704|F12A10.9|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00077712|nipi-4|328nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077712|nipi-4|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=311|total_reads(93.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077712|nipi-4|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077714|R102.11b|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077714|R102.11b|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077714|R102.11b|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077714|R102.11b|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=960|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077728|T23G11.11|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2947|total_reads(87.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077728|T23G11.11|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=398|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077728|T23G11.11|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077732|szy-4|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077732|szy-4|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077732|szy-4|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3451|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077751|irld-27|1069nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077752|Y105C5A.508|337nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077756|Y11D7A.19|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00077757|E02H4.7|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077757|E02H4.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=641|total_reads(92.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077758|irld-12|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(84.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077758|irld-12|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077758|irld-12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|1411nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|1414nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|401nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|521nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|524nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1267|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|530nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1181|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|533nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=361|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|537nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|540nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=263|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|571nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|578nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|681nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|726nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|729nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|732nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00077761|zip-9|816nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077762|Y57G11C.499|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077762|Y57G11C.499|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077762|Y57G11C.499|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=277|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1211|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077763|Y57G11B.97b|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2440|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077764|F59C6.16|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5502|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077764|F59C6.16|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077764|F59C6.16|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077764|F59C6.16|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077766|F17B5.9|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077766|F17B5.9|302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077768|K04G2.12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=191|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077768|K04G2.12|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077768|K04G2.12|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077769|F33E2.10|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077769|F33E2.10|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077769|F33E2.10|153nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2670|total_reads(94.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077769|F33E2.10|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077769|F33E2.10|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077770|M04D5.3.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=136|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077770|M04D5.3.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(35.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077770|M04D5.3.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077770|M04D5.3.1|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077770|M04D5.3.1|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077770|M04D5.3.1|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077770|M04D5.3.1|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13064|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=375|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077771|C41G7.9a.1|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00077773|F25H5.10|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077773|F25H5.10|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077773|F25H5.10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077773|F25H5.10|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(31.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077773|F25H5.10|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077773|F25H5.10|980nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|125nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|127nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|325nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8327|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|632nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077775|T07C12.15|748nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077782|T26H10.2|19nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=302|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077782|T26H10.2|221nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077782|T26H10.2|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|112nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6790|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|115nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|238nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|240nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|249nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|27nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|488nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077783|D1054.18b|490nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077784|F35C8.9|1086nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077784|F35C8.9|1090nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00077784|F35C8.9|1096nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1260|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00077784|F35C8.9|1103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077784|F35C8.9|1110nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00077784|F35C8.9|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|101nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|1246nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|1417nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|1464nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|892nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=141|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|896nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=153|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|908nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|922nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=763|total_reads(62.4%)
- ID=WBGene00077786|F53F8.7|928nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077788|W07G4.8|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(39.2%)
- ID=WBGene00077788|W07G4.8|56nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00077788|W07G4.8|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00077788|W07G4.8|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00077788|W07G4.8|72nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=15|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|198nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|262nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|652nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1333|total_reads(87%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|659nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|663nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00086546|cil-1|739nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00086551|D2005.7|1096nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00086551|D2005.7|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086551|D2005.7|1511nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086551|D2005.7|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2677|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00086553|ZC334.13|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00086553|ZC334.13|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086553|ZC334.13|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00086553|ZC334.13|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18407|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00086553|ZC334.13|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086553|ZC334.13|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00086553|ZC334.13|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00086554|D1081.12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00086554|D1081.12|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=172|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00086554|D1081.12|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1009|total_reads(84.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086554|D1081.12|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00086555|F49B2.7|87nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00086556|F36D1.12|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086556|F36D1.12|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00086556|F36D1.12|34nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=54|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086556|F36D1.12|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00086557|K07A12.8b|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=266|total_reads(43.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086557|K07A12.8b|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=181|total_reads(29.4%)
- ID=WBGene00086557|K07A12.8b|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00086557|K07A12.8b|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00086557|K07A12.8b|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00086557|K07A12.8b|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00086558|F12E12.12|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00086559|Y43F8B.20|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=225|total_reads(66.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086559|Y43F8B.20|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=113|total_reads(33.4%)
- ID=WBGene00086560|ZK355.8|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00086560|ZK355.8|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=485|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00086560|ZK355.8|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00086565|W06G6.17|277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00086565|W06G6.17|284nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(88.9%)
- ID=WBGene00086566|C08H9.16|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086566|C08H9.16|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086566|C08H9.16|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=898|total_reads(77.9%)
- ID=WBGene00086566|C08H9.16|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00086566|C08H9.16|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00086567|C05C10.8|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(76%)
- ID=WBGene00086567|C05C10.8|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00086568|Y2H9A.6a|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=118|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00086568|Y2H9A.6a|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|1438nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|180nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=118|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=202|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=69|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00086569|F38A6.5|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|258nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=226|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|674nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1868|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|95nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=684|total_reads(23.2%)
- ID=WBGene00119203|T04A8.18|97nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|1137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|1156nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|1165nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|193nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=483|total_reads(75.4%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|985nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00119204|ZC116.5|989nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|375nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=54|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=363|total_reads(60%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=68|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|445nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00138711|R07B1.13|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00138714|T02D1.9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00138714|T02D1.9|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00138715|Y6G8.14|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00138717|F52C12.6a|229nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00138717|F52C12.6a|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1482|total_reads(98.3%)
- ID=WBGene00138718|E02A10.5|388nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00138719|F26F2.10b|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=197|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00138719|F26F2.10b|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00138719|F26F2.10b|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00138719|F26F2.10b|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00138719|F26F2.10b|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00138719|F26F2.10b|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00138720|F58H1.8|181nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(34.7%)
- ID=WBGene00138720|F58H1.8|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=854|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00138720|F58H1.8|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00138721|C54D10.14b|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(52.9%)
- ID=WBGene00138721|C54D10.14b|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00138724|F15B9.11|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(70.6%)
- ID=WBGene00138724|F15B9.11|463nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00138724|F15B9.11|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(27.1%)
- ID=WBGene00164968|K08H2.10|144nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(35%)
- ID=WBGene00164968|K08H2.10|165nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00164968|K08H2.10|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00164969|K09C8.9|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00164969|K09C8.9|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00164969|K09C8.9|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=237|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00164969|K09C8.9|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00164971|T21E8.6|336nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(48.9%)
- ID=WBGene00164971|T21E8.6|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(51.1%)
- ID=WBGene00164972|T21E8.7|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00164973|C39B10.7|148nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00164973|C39B10.7|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00164973|C39B10.7|156nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00164973|C39B10.7|270nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00164973|C39B10.7|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00164973|C39B10.7|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=442|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00164973|C39B10.7|291nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=236|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00164985|ZK1010.10|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00164985|ZK1010.10|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00164985|ZK1010.10|68nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00164985|ZK1010.10|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=482|total_reads(79.8%)
- ID=WBGene00164985|ZK1010.10|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00164985|ZK1010.10|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00175027|W02F12.8|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2216|total_reads(96.2%)
- ID=WBGene00175027|W02F12.8|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00175027|W02F12.8|150nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00175027|W02F12.8|159nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00175027|W02F12.8|161nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00175027|W02F12.8|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00175028|nspe-8|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|1177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=72|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2334|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|219nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00175030|Y53C12A.10|47nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00175031|C06C3.12|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00175031|C06C3.12|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|132nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|275nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|286nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|301nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=486|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1903|total_reads(77%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|309nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00175034|F54B3.4|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|117nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|228nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|246nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(20.2%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00175035|F54C9.14|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00184956|F49C5.12|211nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00184956|F49C5.12|214nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(16.8%)
- ID=WBGene00184956|F49C5.12|218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00184990|C14B1.12|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00184990|C14B1.12|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1535|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00184990|C14B1.12|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00184990|C14B1.12|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00184990|C14B1.12|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|1230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|1233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|1239nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|1241nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|1243nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|163nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=190|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|170nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=349|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|182nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00185001|F56A8.9|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185002|K11H3.8a|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185002|K11H3.8a|331nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=142|total_reads(19.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185002|K11H3.8a|335nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=558|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185002|K11H3.8a|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00185002|K11H3.8a|373nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00185002|K11H3.8a|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185002|K11H3.8a|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185005|T03F6.10.1|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(96.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185005|T03F6.10.1|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185005|T03F6.10.1|443nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185005|T03F6.10.1|745nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185006|F59B2.15|103nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=12|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185006|F59B2.15|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185006|F59B2.15|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(55.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185014|F17C8.9|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00185014|F17C8.9|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1413|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185014|F17C8.9|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00185014|F17C8.9|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185014|F17C8.9|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00185014|F17C8.9|30nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185014|F17C8.9|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|458nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|524nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|67nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1351|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|70nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=344|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|76nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=90|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|906nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|923nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|927nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185048|urm-1|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185055|Y47D3B.12|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185055|Y47D3B.12|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=440|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185055|Y47D3B.12|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185055|Y47D3B.12|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00185055|Y47D3B.12|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00185067|Y54G11A.17|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=3240|total_reads(99.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185067|Y54G11A.17|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185067|Y54G11A.17|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185067|Y54G11A.17|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185075|C03C10.9|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185075|C03C10.9|188nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(51.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185075|C03C10.9|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(26.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185075|C03C10.9|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185077|F58D2.4|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00185077|F58D2.4|196nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(20.6%)
- ID=WBGene00185077|F58D2.4|278nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(14.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185077|F58D2.4|286nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(47.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|984nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|988nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|990nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=196|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|992nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=147|total_reads(19.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|996nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(25.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185078|F40G9.17|999nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=127|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185079|W10D9.6|122nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185079|W10D9.6|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185079|W10D9.6|135nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185079|W10D9.6|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=889|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185079|W10D9.6|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00185079|W10D9.6|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185086|F59A3.12|196nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00185086|F59A3.12|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2015|total_reads(97.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185086|F59A3.12|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185086|F59A3.12|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185088|Y55F3BL.4|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=345|total_reads(61.6%)
- ID=WBGene00185088|Y55F3BL.4|1476nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185088|Y55F3BL.4|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185088|Y55F3BL.4|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185089|C16A11.10|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185089|C16A11.10|693nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185092|K08D8.7a|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185092|K08D8.7a|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185092|K08D8.7a|94nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=129|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185092|K08D8.7a|97nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00185095|W09C2.7|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00185095|W09C2.7|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=401|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185095|W09C2.7|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(25.6%)
- ID=WBGene00185096|W09C2.9|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00185097|C49C3.20|136nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185097|C49C3.20|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=332|total_reads(83.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185097|C49C3.20|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00185097|C49C3.20|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185097|C49C3.20|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00185098|Y71G12B.35|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=79|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00185098|Y71G12B.35|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=270|total_reads(64.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185098|Y71G12B.35|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185098|Y71G12B.35|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(12.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185098|Y71G12B.35|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185100|T12A7.9|12nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00185102|Y105C5A.1268|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185102|Y105C5A.1268|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1423|total_reads(74.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185102|Y105C5A.1268|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00185102|Y105C5A.1268|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00185102|Y105C5A.1268|403nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185102|Y105C5A.1268|406nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00185102|Y105C5A.1268|565nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185116|W09C2.8|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185116|W09C2.8|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185116|W09C2.8|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185116|W09C2.8|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=73|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00185116|W09C2.8|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185116|W09C2.8|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185117|C45B11.9|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=279|total_reads(81.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185117|C45B11.9|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185117|C45B11.9|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(16%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|121nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|126nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5049|total_reads(64.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1511|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|140nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|143nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=72|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|162nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|177nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1015|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|179nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|888nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00185118|K02E2.11|896nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189930|Y26G10.5|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189930|Y26G10.5|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(48.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189931|Y26G10.6|123nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00189931|Y26G10.6|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00189931|Y26G10.6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189931|Y26G10.6|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=78|total_reads(62.9%)
- ID=WBGene00189932|Y26G10.7|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|1334nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|1431nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=116|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|283nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|320nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=262|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|631nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|633nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=573|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189933|F38B7.11|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00189937|Y6G8.15|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00189937|Y6G8.15|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189943|Y116F11B.17|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189943|Y116F11B.17|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(34.1%)
- ID=WBGene00189943|Y116F11B.17|49nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00189943|Y116F11B.17|562nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189943|Y116F11B.17|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00189947|C06B3.16|400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(14.1%)
- ID=WBGene00189947|C06B3.16|430nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189947|C06B3.16|433nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189947|C06B3.16|701nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00189948|F56H9.8a|107nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=95|total_reads(25.2%)
- ID=WBGene00189948|F56H9.8a|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=260|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00189948|F56H9.8a|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189949|Y48G1C.13|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=375|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00189949|Y48G1C.13|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00189949|Y48G1C.13|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189949|Y48G1C.13|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=139|total_reads(16.1%)
- ID=WBGene00189949|Y48G1C.13|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=71|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00189949|Y48G1C.13|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189949|Y48G1C.13|81nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189950|C39B5.14.1|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00189950|C39B5.14.1|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00189952|K10D2.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1172|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00189953|R155.5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(31.3%)
- ID=WBGene00189953|R155.5|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189953|R155.5|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189953|R155.5|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189953|R155.5|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00189954|F40G9.18|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00189954|F40G9.18|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(77.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189956|Y34F4.6b|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00189956|Y34F4.6b|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189956|Y34F4.6b|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189956|Y34F4.6b|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189957|M03F8.7|1110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00189957|M03F8.7|1131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15%)
- ID=WBGene00189957|M03F8.7|1155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(55%)
- ID=WBGene00189961|Y54G2A.57|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189961|Y54G2A.57|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(73.5%)
- ID=WBGene00189987|C18H7.12|312nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189987|C18H7.12|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=78|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00189993|C49C3.21|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=649|total_reads(73.3%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00189995|C06E7.88|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194642|C25H3.17|1479nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194642|C25H3.17|681nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194642|C25H3.17|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1650|total_reads(96.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194642|C25H3.17|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194643|C48D1.9c|703nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5190|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194643|C48D1.9c|706nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194643|C48D1.9c|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194643|C48D1.9c|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4824|total_reads(43.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194643|C48D1.9c|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=928|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194643|C48D1.9c|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=245|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194645|Y105C5A.1269|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194646|Y105C5A.1270|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194646|Y105C5A.1270|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194647|Y51H4A.935|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=587|total_reads(99%)
- ID=WBGene00194647|Y51H4A.935|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194649|Y57G11C.1130|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194649|Y57G11C.1130|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194649|Y57G11C.1130|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194649|Y57G11C.1130|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=75|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194649|Y57G11C.1130|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=487|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194649|Y57G11C.1130|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194649|Y57G11C.1130|79nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=686|total_reads(85.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|1281nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|149nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|1545nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|1566nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00194651|C33D9.13|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194653|F36H2.6|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=112|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194653|F36H2.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(16.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194654|M05B5.7|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(44.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194654|M05B5.7|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194654|M05B5.7|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=129|total_reads(45.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194654|M05B5.7|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194654|M05B5.7|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15808|total_reads(89.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1033|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|1247nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|1249nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=310|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=242|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|847nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194658|R09E10.13|86nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194660|W09C5.12|348nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194660|W09C5.12|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00194660|W09C5.12|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194661|Y57G11C.1131|95nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|168nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=158|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|176nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|189nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=118|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|195nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2075|total_reads(85.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194663|F38B2.6|204nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194664|K09E9.7|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=193|total_reads(76.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194664|K09E9.7|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(23.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|1172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|1202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|1210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=156|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|1230nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|127nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=248|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|129nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|1587nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|379nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=46|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|382nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194670|K07E3.9|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194672|Y116A8C.463|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(67.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194672|Y116A8C.463|960nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(32.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|23nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20423|total_reads(58.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8407|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=284|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|53nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2372|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=2672|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=338|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194674|F23D12.11|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194677|D1054.19a|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(35.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194677|D1054.19a|76nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(64.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194679|T26C11.9|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=247|total_reads(44.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194679|T26C11.9|109nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194679|T26C11.9|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194679|T26C11.9|92nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194679|T26C11.9|98nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=265|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194680|Y17D7C.6a|144nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(50.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194680|Y17D7C.6a|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194680|Y17D7C.6a|210nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194680|Y17D7C.6a|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194680|Y17D7C.6a|635nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194680|Y17D7C.6a|658nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194680|Y17D7C.6a|836nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194682|F40D4.17|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194682|F40D4.17|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194682|F40D4.17|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194682|F40D4.17|185nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(62.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194682|F40D4.17|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194684|Y48A6B.14|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194687|F57C12.6|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194687|F57C12.6|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00194687|F57C12.6|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194687|F57C12.6|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=97|total_reads(61%)
- ID=WBGene00194687|F57C12.6|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194689|Y38H6C.24|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194689|Y38H6C.24|185nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194689|Y38H6C.24|188nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194689|Y38H6C.24|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=166|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00194689|Y38H6C.24|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7742|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194689|Y38H6C.24|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=238|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194691|ZK1098.12|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=565|total_reads(99.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194691|ZK1098.12|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|1005nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|1015nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=84|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1163|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50175|total_reads(42.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61669|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=628|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=255|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194692|T02C12.5|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=4127|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194695|B0462.5|205nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=149|total_reads(72.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194695|B0462.5|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=57|total_reads(27.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194697|F59A3.13|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=104|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194697|F59A3.13|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=48|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194698|F49D11.11|269nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194698|F49D11.11|271nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(75.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194698|F49D11.11|275nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=13|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194699|Y43F8B.22|1244nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194700|B0025.5|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1912|total_reads(54.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194700|B0025.5|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1572|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194701|Y23H5B.12a|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194701|Y23H5B.12a|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194701|Y23H5B.12a|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(51.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|185nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|188nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=18|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|220nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|40nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|58nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|61nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|64nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(7.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|67nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194702|C32E8.12|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=229|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8008|total_reads(91.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=320|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194703|F26B1.8|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194704|T07H3.8|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194705|Y39F10C.2|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194705|Y39F10C.2|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(41%)
- ID=WBGene00194705|Y39F10C.2|73nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194706|C53A5.16a|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194706|C53A5.16a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194706|C53A5.16a|1520nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194706|C53A5.16a|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194706|C53A5.16a|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194706|C53A5.16a|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=498|total_reads(45.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194706|C53A5.16a|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=511|total_reads(46.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194707|C53A5.17|183nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194707|C53A5.17|185nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194707|C53A5.17|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194707|C53A5.17|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=148|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194707|C53A5.17|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=936|total_reads(79.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194707|C53A5.17|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194708|Y36E3A.2|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=585|total_reads(93.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194708|Y36E3A.2|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194708|Y36E3A.2|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194708|Y36E3A.2|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194708|Y36E3A.2|378nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194710|mks-2|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194710|mks-2|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1679|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194710|mks-2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194711|D2062.13|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194711|D2062.13|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(19.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194712|T11F9.21a|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=289|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|226nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|242nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|367nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6290|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|372nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1328|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|431nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=55|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|68nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|81nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|96nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194713|F19B10.13|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=34|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194714|ZC204.17|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194715|T25E12.16|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194715|T25E12.16|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194717|ZC239.22|136nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=264|total_reads(87.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194717|ZC239.22|141nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194717|ZC239.22|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00194725|T16H12.13|133nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=48|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=535|total_reads(68.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|26nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|329nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194726|R13A5.15|413nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194727|C18D11.10|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194727|C18D11.10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(85.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194727|C18D11.10|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194729|ZK783.7|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194729|ZK783.7|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=60|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194729|ZK783.7|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(16.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194730|C29E4.17|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194730|C29E4.17|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194730|C29E4.17|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194730|C29E4.17|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194731|Y39A1A.27|1109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194731|Y39A1A.27|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=438|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194731|Y39A1A.27|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=417|total_reads(46.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194731|Y39A1A.27|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194731|Y39A1A.27|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194733|Y41C4A.21|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194733|Y41C4A.21|783nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194733|Y41C4A.21|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194733|Y41C4A.21|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(27.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(10.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|161nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194737|Y50D7A.13b|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194738|Y46E12A.5|59nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194738|Y46E12A.5|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=304|total_reads(87.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194738|Y46E12A.5|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194742|F37C12.21|252nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194742|F37C12.21|31nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194742|F37C12.21|35nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=293|total_reads(81.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194742|F37C12.21|376nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194742|F37C12.21|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00194742|F37C12.21|495nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194742|F37C12.21|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194744|Y38H6C.25|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(84.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194744|Y38H6C.25|151nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1321|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|203nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|708nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194747|H05C05.4|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194780|C12D8.20|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194780|C12D8.20|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(76.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194783|K03B8.14|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194784|T11F9.22|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194785|C52E4.12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(30.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194785|C52E4.12|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(21%)
- ID=WBGene00194785|C52E4.12|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194785|C52E4.12|77nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(22.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194787|T16G1.13|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=574|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194788|R02D5.10|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(86.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194788|R02D5.10|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194788|R02D5.10|80nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194793|W04G3.13|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(75.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194793|W04G3.13|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(24.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194795|F42F12.14|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(61.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194795|F42F12.14|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194801|Y6G8.16|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(78.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194801|Y6G8.16|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194803|C25F9.16|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194803|C25F9.16|223nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194803|C25F9.16|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(80.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194813|D1025.11|1336nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194813|D1025.11|1345nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194813|D1025.11|1351nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2573|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194813|D1025.11|1354nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4417|total_reads(62.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194813|D1025.11|1361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194815|Y43F8B.23|783nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194815|Y43F8B.23|787nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(81.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194816|ZK616.61|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194816|ZK616.61|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=384|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194816|ZK616.61|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194816|ZK616.61|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194821|dmsr-16|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(26.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194821|dmsr-16|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194821|dmsr-16|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194821|dmsr-16|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194821|dmsr-16|213nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194821|dmsr-16|314nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(38.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194832|Y73B6BL.270|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194832|Y73B6BL.270|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2059|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00194832|Y73B6BL.270|121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194832|Y73B6BL.270|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194832|Y73B6BL.270|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194833|F17E9.15|1364nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=80|total_reads(83.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194833|F17E9.15|854nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194835|Y17G9B.11a|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194835|Y17G9B.11a|259nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194835|Y17G9B.11a|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194835|Y17G9B.11a|284nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194835|Y17G9B.11a|299nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194835|Y17G9B.11a|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(8.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194839|C01B10.44|3nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(31.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194839|C01B10.44|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194839|C01B10.44|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194839|C01B10.44|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194839|C01B10.44|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(13.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194848|T27D12.6|117nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194848|T27D12.6|127nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=218|total_reads(45.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194848|T27D12.6|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=238|total_reads(49.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194848|T27D12.6|141nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194849|K09A9.8|55nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=308|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194849|K09A9.8|58nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=16|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194849|K09A9.8|904nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194850|F44F4.15|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=457|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194850|F44F4.15|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194850|F44F4.15|39nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194850|F44F4.15|42nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00194850|F44F4.15|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194852|T28A8.8a|122nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194852|T28A8.8a|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194852|T28A8.8a|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=591|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194852|T28A8.8a|186nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194852|T28A8.8a|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194852|T28A8.8a|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194855|Y75B8A.44|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194855|Y75B8A.44|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=103|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194855|Y75B8A.44|106nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=73|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194855|Y75B8A.44|114nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1407|total_reads(84.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194855|Y75B8A.44|90nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194855|Y75B8A.44|99nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194861|H04D03.6b|125nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194861|H04D03.6b|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=260|total_reads(56.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194861|H04D03.6b|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194861|H04D03.6b|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194861|H04D03.6b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194861|H04D03.6b|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194861|H04D03.6b|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194864|Y66A7A.9|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(14.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194864|Y66A7A.9|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=342|total_reads(85.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194866|Y41C4A.22|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194866|Y41C4A.22|30nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=77|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194866|Y41C4A.22|36nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=1107|total_reads(91.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194866|Y41C4A.22|81nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194867|W09C2.10|35nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194869|K01A6.8|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194869|K01A6.8|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=210|total_reads(94.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194870|F53A2.11|216nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194870|F53A2.11|269nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194870|F53A2.11|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194870|F53A2.11|298nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194883|B0496.11|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=616|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194886|C05B5.12|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=24|total_reads(36.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194886|C05B5.12|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194886|C05B5.12|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194888|K10H10.13|104nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(36.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194888|K10H10.13|39nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(20.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194888|K10H10.13|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(43.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194890|C01B9.4|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00194890|C01B9.4|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|139nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|531nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=210|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=393|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=188|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194892|dsb-2|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194894|T05B4.14|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194894|T05B4.14|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=447|total_reads(52.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194894|T05B4.14|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194894|T05B4.14|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194894|T05B4.14|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=136|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194894|T05B4.14|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194894|T05B4.14|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=117|total_reads(13.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194895|ZK105.11|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194902|Y39H10B.3.1|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(65.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194902|Y39H10B.3.1|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(34.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194904|W02H5.12|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194904|W02H5.12|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4859|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8077|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4816|total_reads(19.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6592|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=445|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|134nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|137nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=146|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|142nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=54|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|145nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|171nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|34nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=122|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194905|Y53F4B.51|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194907|E02H4.8|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=816|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|225nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|227nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|229nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=40|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|238nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|242nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|245nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|457nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=217|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194908|F22F7.8|465nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|1509nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|306nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|309nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|374nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|382nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|389nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|395nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|404nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=76|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|414nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=177|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|422nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1396|total_reads(25.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|424nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3682|total_reads(66.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|432nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194909|F41E6.17|440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194910|ZC404.15|145nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194910|ZC404.15|147nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194910|ZC404.15|151nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194910|ZC404.15|359nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194910|ZC404.15|420nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194910|ZC404.15|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00194910|ZC404.15|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=396|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194912|ZK856.18|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194912|ZK856.18|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194912|ZK856.18|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=138|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194912|ZK856.18|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194912|ZK856.18|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194913|Y105C5A.1272|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194913|Y105C5A.1272|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194913|Y105C5A.1272|9nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(41.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194914|F44D12.16|262nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194916|F35D2.6|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194916|F35D2.6|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194916|F35D2.6|35nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194916|F35D2.6|51nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194916|F35D2.6|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194917|Y45F10B.59|1014nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194917|Y45F10B.59|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194917|Y45F10B.59|140nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(35.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194918|K08D8.9|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194919|K08D8.10|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194920|H12I19.115|1237nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194920|H12I19.115|1242nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|1007nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=448|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=449|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6811|total_reads(49.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=680|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=149|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=403|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=570|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=185|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|300nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=297|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=3594|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00194921|ZK742.7.2|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194922|F13E9.19|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194925|K08D8.11|888nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194925|K08D8.11|928nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194925|K08D8.11|940nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=261|total_reads(84.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194925|K08D8.11|944nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00194925|K08D8.11|949nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194926|K08D8.12a|63nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=68|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194926|K08D8.12a|69nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=301|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194926|K08D8.12b|479nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(6.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194926|K08D8.12b|481nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194926|K08D8.12b|486nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194926|K08D8.12b|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194928|ZC513.14|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194928|ZC513.14|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194933|T12A7.10|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194934|ZK809.9a|1065nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00194934|ZK809.9a|164nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194934|ZK809.9a|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=343|total_reads(95.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194935|M02G9.4a|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(50.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194935|M02G9.4a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194935|M02G9.4a|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194940|C34C6.9|368nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00194940|C34C6.9|771nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00194949|Y10G11A.90|1179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194949|Y10G11A.90|1186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194949|Y10G11A.90|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194949|Y10G11A.90|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1738|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00194949|Y10G11A.90|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=105|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194952|ZK666.14|132nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194952|ZK666.14|244nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194952|ZK666.14|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1541|total_reads(99.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194955|F37H8.6|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00194955|F37H8.6|191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194955|F37H8.6|655nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=109|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194955|F37H8.6|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|1027nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|1158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|137nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(38.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|143nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(12.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194956|F37H8.7|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194957|Y116A8C.465|548nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194957|Y116A8C.465|555nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194957|Y116A8C.465|557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194981|Y49E10.30|1379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00194981|Y49E10.30|1382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194981|Y49E10.30|1419nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=127|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00194982|Y17D7B.10|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2348|total_reads(91.7%)
- ID=WBGene00194982|Y17D7B.10|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=212|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194983|T25B2.4|364nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|232nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|245nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=132|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|248nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=98|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|250nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|332nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|36nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|53nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194985|Y25C1A.14|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|100nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=793|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=159|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|120nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|361nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|546nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|557nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|666nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=65|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|761nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29965|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|764nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|783nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|786nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=114|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|816nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|835nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|837nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=785|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|855nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194986|T27F7.4|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00194998|C16C4.18|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00194998|C16C4.18|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=163|total_reads(59.1%)
- ID=WBGene00194998|C16C4.18|82nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=98|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195003|Y46C8AL.11|138nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|219nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|252nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|289nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|342nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|43nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=84|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=151|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|480nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|53nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2759|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00195004|K08D12.8|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195006|C35B1.9|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195006|C35B1.9|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1337nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=361|total_reads(46.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1342nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=164|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1572nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(11.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1575nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1578nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=59|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|1580nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195009|F17E9.16|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00195010|Y37E11AL.12|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=342|total_reads(91.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195010|Y37E11AL.12|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00195010|Y37E11AL.12|37nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195010|Y37E11AL.12|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195011|ZK180.8b|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(74.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195011|ZK180.8b|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195011|ZK180.8b|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195011|ZK180.8b|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195011|ZK180.8b|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195045|W05F2.8a|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195045|W05F2.8a|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195045|W05F2.8a|64nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=75|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00195045|W05F2.8a|67nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00195045|W05F2.8a|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=231|total_reads(55.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195045|W05F2.8a|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195045|W05F2.8a|74nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195046|F42A9.11|405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(26.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195046|F42A9.11|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(73.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195049|CC8.3|1334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195049|CC8.3|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=119|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=168|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|26nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=35|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00195050|T22D1.17a|986nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195051|T22D1.18|219nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195051|T22D1.18|226nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=603|total_reads(88.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195051|T22D1.18|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195051|T22D1.18|280nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195051|T22D1.18|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195056|C45E1.5|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195056|C45E1.5|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195056|C45E1.5|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(70.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195056|C45E1.5|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195057|B0261.9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195057|B0261.9|346nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00195057|B0261.9|663nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195058|C54E10.7|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|103nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|107nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|120nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195063|Y38C1AA.14b|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=2067|total_reads(92.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195067|C04C3.9|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195067|C04C3.9|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195067|C04C3.9|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195067|C04C3.9|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(56.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=85|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|125nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4560|total_reads(95.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195068|Y48G8AL.16|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195069|W03G9.10|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195070|C16C8.20|42nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=83|total_reads(44.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195070|C16C8.20|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(55.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195071|C16C8.21|101nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195071|C16C8.21|104nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(34.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195071|C16C8.21|93nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195072|C16C8.22|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=111|total_reads(78.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195072|C16C8.22|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195072|C16C8.22|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195072|C16C8.22|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195073|F02E11.7c|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195073|F02E11.7c|34nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195073|F02E11.7c|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=459|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195073|F02E11.7c|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2844|total_reads(81.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195073|F02E11.7c|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195077|T24E12.13|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195077|T24E12.13|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195081|C04F6.7|277nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195081|C04F6.7|285nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=521|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195081|C04F6.7|287nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195084|C43C3.4|160nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195084|C43C3.4|166nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=581|total_reads(89.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195084|C43C3.4|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=28|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|173nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|185nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|187nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=636|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|207nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=90|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|215nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|250nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|255nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195086|F21C10.13|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=187|total_reads(17.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|100nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=224|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=216|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1018|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|87nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195093|Y59E9AL.36|94nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195142|M110.10|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195142|M110.10|112nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195142|M110.10|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(36%)
- ID=WBGene00195142|M110.10|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=329|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195143|C16D2.2|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195143|C16D2.2|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6210|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195143|C16D2.2|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1161|total_reads(15.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195143|C16D2.2|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195143|C16D2.2|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195144|C16D2.3|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195144|C16D2.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195145|ZK666.15.1|204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=89|total_reads(64.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195145|ZK666.15.1|206nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195146|F54D5.17|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=128|total_reads(63.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195146|F54D5.17|1573nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00195146|F54D5.17|1586nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195146|F54D5.17|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(12.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195146|F54D5.17|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00195146|F54D5.17|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00195147|F14E5.8|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195147|F14E5.8|31nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(10.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195147|F14E5.8|37nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(46.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195147|F14E5.8|40nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195147|F14E5.8|42nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195147|F14E5.8|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195147|F14E5.8|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195149|F26H11.8|426nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195150|Y81G3A.6|20nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=93|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195154|F13A2.10|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195154|F13A2.10|1256nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195154|F13A2.10|1265nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195154|F13A2.10|1267nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=204|total_reads(73.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195154|F13A2.10|321nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=43|total_reads(15.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195155|W04A8.9|1450nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=6|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195155|W04A8.9|1481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195155|W04A8.9|323nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(20.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195155|W04A8.9|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00195157|C12D8.21b|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195158|F26F2.11a|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195158|F26F2.11a|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(86.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195160|Y47D7A.17|188nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195160|Y47D7A.17|191nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195164|K12B6.11|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195164|K12B6.11|170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195164|K12B6.11|191nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=673|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195164|K12B6.11|193nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00195164|K12B6.11|208nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195164|K12B6.11|212nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195165|F57G4.11|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|189nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|25nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|63nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3966|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|66nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=3273|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|70nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=64|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|721nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|728nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|733nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|735nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=225|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|739nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=876|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00195166|W05B10.6|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=209|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195168|T13C5.9|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195168|T13C5.9|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195168|T13C5.9|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(26.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195168|T13C5.9|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195169|Y50D4A.6b|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=735|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195169|Y50D4A.6b|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195169|Y50D4A.6b|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00195169|Y50D4A.6b|821nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195169|Y50D4A.6b|879nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195171|T09D3.9|275nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=110|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195176|Y43F8B.24|395nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=325|total_reads(92.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195176|Y43F8B.24|398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00195176|Y43F8B.24|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195177|Y43F8B.25|130nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(43.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195177|Y43F8B.25|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(56.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195178|ZC581.10|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=409|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195179|F48C1.11|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(58.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195179|F48C1.11|97nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195180|C41D11.10|588nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00195180|C41D11.10|691nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00195181|F15H10.12|121nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195182|C17G10.10|413nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195182|C17G10.10|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195183|R04A9.9b.1|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=243|total_reads(90.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195183|R04A9.9b.1|61nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195184|F19G12.8|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=154|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195184|F19G12.8|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195184|F19G12.8|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195185|F19G12.9|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195185|F19G12.9|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1473|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195185|F19G12.9|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|116nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=197|total_reads(22.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|311nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=338|total_reads(38.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=213|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|417nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00195189|ZC449.8|50nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195208|W02H3.3|1114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195208|W02H3.3|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195208|W02H3.3|159nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(37.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195208|W02H3.3|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(23.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195209|C07B5.8|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195209|C07B5.8|106nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195209|C07B5.8|125nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195209|C07B5.8|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(20.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195209|C07B5.8|99nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=566|total_reads(76.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195210|Y7A5A.13|1136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=192|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195210|Y7A5A.13|1174nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00195210|Y7A5A.13|1198nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195210|Y7A5A.13|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195210|Y7A5A.13|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195211|C34F6.12|1167nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00195211|C34F6.12|1358nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(45%)
- ID=WBGene00195211|C34F6.12|1367nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(11.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195211|C34F6.12|1522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195212|F09B12.7|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=608|total_reads(96.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195212|F09B12.7|103nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195213|F11C1.9|1199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195214|F11C1.10|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195214|F11C1.10|340nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(21.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195214|F11C1.10|600nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195214|F11C1.10|603nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195214|F11C1.10|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(17.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195214|F11C1.10|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(13.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195215|F55G7.5|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195226|ZC404.16|313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195226|ZC404.16|349nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195226|ZC404.16|356nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(62%)
- ID=WBGene00195226|ZC404.16|360nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195226|ZC404.16|372nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195227|Y71A12B.23|44nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=32|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195227|Y71A12B.23|50nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=115|total_reads(67.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195227|Y71A12B.23|52nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195227|Y71A12B.23|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195232|F36D1.15|26nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|1025nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|103nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|1047nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=776|total_reads(40.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|290nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|748nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|776nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|779nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=56|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|976nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195239|ZK1127.13|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=936|total_reads(48.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195240|Y39B6A.69|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(13.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195240|Y39B6A.69|56nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=69|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195240|Y39B6A.69|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|440nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|532nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|69nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=61|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|72nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=107|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(11%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=435|total_reads(47.3%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=191|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195241|Y113G7B.27b|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195243|F46B3.23|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=64|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00195243|F46B3.23|75nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195244|F30A10.15|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=77|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|1152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=61|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|611nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=41|total_reads(18.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|614nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(6.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|639nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|93nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(29.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00195246|ZK546.19|97nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|1507nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|192nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|197nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=2128|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|199nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(7.8%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|202nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|353nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00195248|emc-5|81nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00202495|T26H5.11.2|177nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00202496|R02F11.9|51nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=41|total_reads(30.1%)
- ID=WBGene00202496|R02F11.9|57nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00202496|R02F11.9|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=59|total_reads(43.4%)
- ID=WBGene00202496|R02F11.9|78nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00202497|R02F11.10|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(57.1%)
- ID=WBGene00202497|R02F11.10|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00202498|Y60C6A.2|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00202501|Y57E12B.10|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=134|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00202511|F07C3.16|564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00202511|F07C3.16|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00202511|F07C3.16|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(35.3%)
- ID=WBGene00202511|F07C3.16|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00202511|F07C3.16|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00202512|C25E10.16|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=45|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00202513|ZK938.10|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00202514|T09F5.20a|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206354|F27E5.9|142nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=119|total_reads(30.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206354|F27E5.9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206354|F27E5.9|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=128|total_reads(33.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206354|F27E5.9|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=132|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206355|C34C6.10|379nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=71|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206356|T08B2.15.2|460nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=450|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206356|T08B2.15.2|462nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=571|total_reads(54.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206356|T08B2.15.2|472nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206356|T08B2.15.2|484nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206356|T08B2.15.2|567nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206356|T08B2.15.2|889nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206357|C09D4.9|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=953|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206358|F46E10.18|75nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=109|total_reads(33%)
- ID=WBGene00206358|F46E10.18|78nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=221|total_reads(67%)
- ID=WBGene00206359|C05E4.15b|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206359|C05E4.15b|726nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206359|C05E4.15b|731nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(42.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206359|C05E4.15b|733nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(34.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206360|T13C5.10|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(67.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206360|T13C5.10|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206360|T13C5.10|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00206361|K02G10.15|415nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=181|total_reads(83%)
- ID=WBGene00206361|K02G10.15|452nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(17%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2892|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1129nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|1564nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206362|B0041.11.2|861nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206363|F56H1.10|11nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(52.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206363|F56H1.10|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(47.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206364|C07A12.18b|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206364|C07A12.18b|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206364|C07A12.18b|166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206364|C07A12.18b|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(15.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206364|C07A12.18b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206364|C07A12.18b|41nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(28.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206365|B0563.18|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206365|B0563.18|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206368|Y39F10C.3|36nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=268|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206370|F02D8.9|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(77.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206370|F02D8.9|155nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=48|total_reads(22.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206371|F28B12.6|220nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=60|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206372|B0454.26|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206372|B0454.26|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=178|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|1095nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|1405nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(21.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|161nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|175nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|324nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|333nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=420|total_reads(56.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|568nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206373|C27A2.12|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206374|K10G6.9|1195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206374|K10G6.9|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206374|K10G6.9|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=390|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206374|K10G6.9|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|1014nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|1018nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|544nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=228|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|596nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|605nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206376|F47E1.17|918nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|207nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|411nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|435nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|462nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|496nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|82nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206377|F44E5.15|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=20|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|1485nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=39|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|251nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=106|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|260nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2305|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|263nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=860|total_reads(24.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|281nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206380|C42D4.18|340nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206381|F52H2.15|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00206381|F52H2.15|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206381|F52H2.15|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=126|total_reads(60.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=63|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|128nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|138nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=491|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|146nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|149nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|156nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|171nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|176nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=62|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|254nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7904|total_reads(90.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|259nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|90nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206382|F01G12.18|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206383|kvs-2|183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206385|T06D4.6|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206385|T06D4.6|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|35nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18922|total_reads(70.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=4906|total_reads(18.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=497|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|47nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206386|K10C2.12|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2203|total_reads(8.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206388|K10C2.14|279nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(35.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206388|K10C2.14|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(57.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206388|K10C2.14|444nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206389|C29F7.10|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=34|total_reads(21.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206389|C29F7.10|104nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=121|total_reads(75.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206389|C29F7.10|96nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206392|F47D2.11|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=150|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206392|F47D2.11|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206392|F47D2.11|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=68|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206392|F47D2.11|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206392|F47D2.11|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1340|total_reads(64.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206392|F47D2.11|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=403|total_reads(19.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206393|W04G5.16|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206412|T24H7.8|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206412|T24H7.8|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(62.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206412|T24H7.8|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206413|ZK1240.11.1|1024nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206413|ZK1240.11.1|1076nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206413|ZK1240.11.1|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=82|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206413|ZK1240.11.1|473nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206414|F31D5.7|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=57|total_reads(91.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206414|F31D5.7|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206415|F59H6.14|836nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(31.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206415|F59H6.14|868nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(68.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206416|W04H10.5|1043nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(88%)
- ID=WBGene00206416|W04H10.5|870nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00206417|W04H10.6|124nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=105|total_reads(95.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206417|W04H10.6|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5a|103nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=63|total_reads(10.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5a|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5a|140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5a|205nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5a|276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5b|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=222|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5b|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(34.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206418|M04C3.5b|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=80|total_reads(13.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|109nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|216nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|219nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|282nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|607nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|611nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|626nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=336|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|628nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7431|total_reads(81%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|637nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|640nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|642nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=71|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|645nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=343|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|650nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|652nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=53|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|656nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=39|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|703nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|727nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=349|total_reads(3.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206419|R106.5|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=73|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206421|T26G10.8|491nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(58.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206421|T26G10.8|529nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(41.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206422|T26G10.9|1302nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(54.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206422|T26G10.9|1340nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(45.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206460|F56H9.9|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=137|total_reads(77.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206460|F56H9.9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206460|F56H9.9|235nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206460|F56H9.9|237nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00206460|F56H9.9|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00206461|Y47D3A.34|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206461|Y47D3A.34|17nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206461|Y47D3A.34|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=560|total_reads(86.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206461|Y47D3A.34|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=73|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206462|B0391.14|234nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206462|B0391.14|241nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206462|B0391.14|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=23|total_reads(45.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=38|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=519|total_reads(26%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1155|total_reads(57.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=161|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=49|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206464|F59C6.18|962nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206466|T08D10.5|246nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206466|T08D10.5|250nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206466|T08D10.5|307nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206468|ZC262.11|35nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00206468|ZC262.11|44nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00206469|F58D2.5|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=166|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206471|Y22F5A.11|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206471|Y22F5A.11|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206473|B0273.115|533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206473|B0273.115|57nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206473|B0273.115|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206473|B0273.115|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(40%)
- ID=WBGene00206474|T22A3.12|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=144|total_reads(90%)
- ID=WBGene00206474|T22A3.12|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00206475|F27D9.12|29nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206475|F27D9.12|31nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(52.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206475|F27D9.12|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206475|F27D9.12|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206478|M6.11|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206479|C44C11.6|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=257|total_reads(93.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206479|C44C11.6|199nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206479|C44C11.6|215nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206479|C44C11.6|225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206481|Y51B9A.14|66nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206482|B0416.10|720nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206482|B0416.10|746nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=123|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206483|B0416.11|113nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206483|B0416.11|116nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=75|total_reads(92.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206484|C31H2.14|105nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=33|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00206484|C31H2.14|110nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206484|C31H2.14|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=437|total_reads(80%)
- ID=WBGene00206484|C31H2.14|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=62|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206485|C10A4.13|1201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206485|C10A4.13|1204nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206487|best-19|154nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206487|best-19|182nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206487|best-19|184nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=754|total_reads(92.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206487|best-19|217nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206487|best-19|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206488|ZK757.10|228nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=21|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206488|ZK757.10|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206488|ZK757.10|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206488|ZK757.10|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(61.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206488|ZK757.10|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206488|ZK757.10|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00206495|F20E11.18a|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206496|Y51A2B.16|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206497|Y52B11A.18|434nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206499|C06H5.11|172nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(8.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206499|C06H5.11|78nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=72|total_reads(85.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206499|C06H5.11|84nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00206500|F55C9.15|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(38.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206500|F55C9.15|834nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(61.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206502|T01B7.13|1564nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00206502|T01B7.13|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=638|total_reads(93.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206502|T01B7.13|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206502|T01B7.13|325nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206504|K10G4.15|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206504|K10G4.15|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(61.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206505|B0250.18b|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=645|total_reads(95.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206505|B0250.18b|227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206507|Y51A2A.16|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206508|ZK262.19|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206508|ZK262.19|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=166|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206510|Y113G7A.22|536nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206510|Y113G7A.22|540nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=44|total_reads(10.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206510|Y113G7A.22|543nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=369|total_reads(87.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206512|Y39A3B.7|158nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(28.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206512|Y39A3B.7|163nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(71.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206514|R05G9.5|1147nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(12%)
- ID=WBGene00206514|R05G9.5|741nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(78%)
- ID=WBGene00206514|R05G9.5|744nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00206517|T27F7.12|237nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=45|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206517|T27F7.12|244nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206517|T27F7.12|365nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(9.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206519|F36H5.13|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206521|T02G5.15|396nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(15.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206521|T02G5.15|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(74.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206521|T02G5.15|651nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206523|C54E10.10|25nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(88.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206523|C54E10.10|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206524|C54E10.11|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=2311|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=77|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|13nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|140nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|148nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|150nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|153nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=37|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=35|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|217nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|224nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|228nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|230nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|233nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=63|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=404|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34529|total_reads(88.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1344|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|65nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206525|R74.10|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206527|T27A8.7|1269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206527|T27A8.7|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206527|T27A8.7|1278nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(24.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206528|Y53H1A.7|383nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|1218nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|227nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|313nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|315nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=17|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=148|total_reads(40.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(17.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206529|C04A2.15|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206530|Y52B11A.19|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00206530|Y52B11A.19|569nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=67|total_reads(80.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206530|Y52B11A.19|571nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206530|Y52B11A.19|574nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00206532|F11A6.15|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00206532|F11A6.15|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=346|total_reads(71.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206532|F11A6.15|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206533|C30A5.16|1351nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206533|C30A5.16|1509nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00206533|C30A5.16|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(83.6%)
- ID=WBGene00206533|C30A5.16|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(12.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206534|C31A11.13|448nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00206535|M162.15|58nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(66.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206535|M162.15|874nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00206537|Y71H9A.10|213nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=32|total_reads(47.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206537|Y71H9A.10|399nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=35|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00206538|C09G5.13|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00206538|C09G5.13|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10267|total_reads(90.7%)
- ID=WBGene00206538|C09G5.13|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=51|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00206538|C09G5.13|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=199|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00206538|C09G5.13|83nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=784|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00206538|C09G5.13|88nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=17|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219205|R03D7.15|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(48%)
- ID=WBGene00219205|R03D7.15|199nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(20%)
- ID=WBGene00219205|R03D7.15|98nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(32%)
- ID=WBGene00219206|W05H12.4|1191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219206|W05H12.4|669nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219206|W05H12.4|671nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(65.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219207|C01F6.14|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=223|total_reads(19%)
- ID=WBGene00219207|C01F6.14|194nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219207|C01F6.14|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=896|total_reads(76.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219207|C01F6.14|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219207|C01F6.14|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219207|C01F6.14|547nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|178nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|270nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|28nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|43nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=100|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|73nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=67|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=928|total_reads(49.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|95nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=694|total_reads(37.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219208|B0365.9|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219209|F29F11.20|175nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219209|F29F11.20|178nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(69%)
- ID=WBGene00219209|F29F11.20|604nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219210|Y37H2A.18|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=357|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219216|K08D10.14.1|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=546|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219216|K08D10.14.1|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=55|total_reads(9%)
- ID=WBGene00219216|K08D10.14.1|89nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219217|C08F8.15|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(11.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219217|C08F8.15|126nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(72.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219217|C08F8.15|135nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(16.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|100nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(3%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|1277nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|1440nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|1509nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|572nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|704nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=29|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|92nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=284|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219218|Y73B6BL.288|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=453|total_reads(53%)
- ID=WBGene00219236|K03B4.9|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219238|M151.9|122nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=58|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|1020nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|1103nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=14|total_reads(13.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|1108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|1183nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|1246nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|1299nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|1576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219244|Y51H4A.938a|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(34.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219271|F36H5.14|106nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219271|F36H5.14|171nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219271|F36H5.14|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219271|F36H5.14|63nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=83|total_reads(76.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219272|C17C3.24.2|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219274|T25G12.13|1382nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219274|T25G12.13|1386nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=205|total_reads(59.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219274|T25G12.13|1388nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(27.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219274|T25G12.13|58nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219275|Y39G10AR.32b|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219275|Y39G10AR.32b|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=462|total_reads(17.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219275|Y39G10AR.32b|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1712|total_reads(66.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219275|Y39G10AR.32b|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219275|Y39G10AR.32b|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219275|Y39G10AR.32b|60nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219278|R09A8.9|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=141|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219280|C05B5.16|1283nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219280|C05B5.16|134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219280|C05B5.16|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(44.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219281|K10D3.8|101nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219281|K10D3.8|86nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=244|total_reads(82.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219281|K10D3.8|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219282|F43G9.21|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=120|total_reads(96%)
- ID=WBGene00219282|F43G9.21|4nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00219283|F55H12.7b|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(69.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219283|F55H12.7b|92nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|155nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=47|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|163nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=318|total_reads(53.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|222nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=94|total_reads(15.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|227nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|237nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=37|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|262nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=11|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|273nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=15|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|279nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219286|C04F12.16|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=31|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219287|F36D1.23|59nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=406|total_reads(97.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219287|F36D1.23|68nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219288|Y87G2A.25|1115nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=262|total_reads(87.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219288|Y87G2A.25|1121nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00219288|Y87G2A.25|119nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219289|T05C12.15|28nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=70|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219289|T05C12.15|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=188|total_reads(42.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219289|T05C12.15|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219289|T05C12.15|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(29.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219289|T05C12.15|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219289|T05C12.15|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219291|F35H8.12|261nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219293|B0334.20|132nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219293|B0334.20|157nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(45.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219293|B0334.20|163nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219294|F43G6.16|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219294|F43G6.16|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=303|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219295|C34C12.12|326nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00219295|C34C12.12|329nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00219296|C54C6.11|32nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(15.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219296|C54C6.11|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(48.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219296|C54C6.11|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219296|C54C6.11|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219297|T23F11.11|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(92.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219297|T23F11.11|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219298|F55H2.8|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=155|total_reads(89.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219298|F55H2.8|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219298|F55H2.8|575nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219299|C01G12.16|145nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=69|total_reads(46%)
- ID=WBGene00219299|C01G12.16|21nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219299|C01G12.16|709nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(50.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219300|W10G6.6|110nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219300|W10G6.6|199nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=109|total_reads(30.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219300|W10G6.6|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219300|W10G6.6|213nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219300|W10G6.6|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=163|total_reads(45.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219300|W10G6.6|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219300|W10G6.6|285nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219302|Y43F8B.28|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219308|W06G6.20.1|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(29.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219308|W06G6.20.1|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=59|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219308|W06G6.20.1|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(18.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|165nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|189nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=30|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=399|total_reads(27%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|201nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=728|total_reads(49.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|203nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(5.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|218nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|224nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|232nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|275nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=65|total_reads(4.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|701nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=40|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|718nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219313|C17E4.20|744nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219314|C05B5.17|1533nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219314|C05B5.17|55nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219314|C05B5.17|64nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=97|total_reads(89.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219315|F07E5.12|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(18.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219315|F07E5.12|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(13.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219315|F07E5.12|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(68.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219316|F21A3.11|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219316|F21A3.11|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=495|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219316|F21A3.11|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219316|F21A3.11|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(16.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1009nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|100nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1027nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|102nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1031nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1036nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1061nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|106nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1070nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1074nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1086nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1092nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1097nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1140nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1156nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1166nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1179nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1191nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1209nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1214nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1245nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1356nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1370nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1377nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1381nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1385nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1387nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1391nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1408nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1424nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1433nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1437nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1448nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1459nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1571nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|1577nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|193nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|208nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|210nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|220nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|231nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|234nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|248nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|264nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|289nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|292nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|298nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|305nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|315nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|318nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|31nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|334nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|343nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|347nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|349nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|360nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|375nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|481nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|487nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|492nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|499nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|514nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|521nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|539nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|550nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|556nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|562nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|573nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|576nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|582nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|585nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|591nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|595nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|598nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|601nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|604nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|609nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|615nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|617nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|626nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|632nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|637nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|650nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=30|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|657nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|664nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|676nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|680nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|685nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|690nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|695nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|700nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|713nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|718nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|727nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|734nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|743nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|749nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|760nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|785nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|792nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|798nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|801nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|803nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|805nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|810nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|820nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|827nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|842nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|846nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|853nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|861nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|866nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|868nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|881nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|891nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|911nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|921nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|929nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|933nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|938nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|94nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=28|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|955nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|959nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|966nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|974nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|989nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219317|F31E3.12|992nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219318|R08A2.9|357nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219322|C33C12.12|108nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219322|C33C12.12|110nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219322|C33C12.12|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219322|C33C12.12|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(36.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219322|C33C12.12|118nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00219324|F47B8.18|105nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=319|total_reads(51.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219324|F47B8.18|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=298|total_reads(48.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=43|total_reads(10%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=96|total_reads(22.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|1369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=49|total_reads(11.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|1412nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|1542nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|1600nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|268nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|300nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(21.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|673nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|716nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|732nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|817nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|827nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|873nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219325|F17C11.22|957nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219326|F36D3.16|124nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00219326|F36D3.16|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=276|total_reads(67.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219326|F36D3.16|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219326|F36D3.16|68nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219326|F36D3.16|70nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=95|total_reads(23.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219326|F36D3.16|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219327|ZK822.9a|1134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00219327|ZK822.9a|1137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(70%)
- ID=WBGene00219329|K02D10.8|137nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219329|K02D10.8|13nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=507|total_reads(84.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219329|K02D10.8|442nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219329|K02D10.8|50nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00219329|K02D10.8|55nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219329|K02D10.8|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=36|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00219329|K02D10.8|9nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=7|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219330|F18E2.15|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=165|total_reads(97.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219330|F18E2.15|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219337|T16G1.18|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219342|Y57G11C.1143a|61nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=189|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219351|Y7A5A.20|1534nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219351|Y7A5A.20|23nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(27.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219362|ZK470.14|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219362|ZK470.14|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=385|total_reads(89.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219368|F14H12.17|174nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(28.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219368|F14H12.17|176nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(71.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219369|R160.10|144nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(8.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219369|R160.10|158nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=44|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219369|R160.10|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=42|total_reads(33.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219369|R160.10|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=29|total_reads(23%)
- ID=WBGene00219371|C03G5.14|333nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=553|total_reads(70.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|169nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|69nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=46|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|795nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|797nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|813nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=58|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=43|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219372|F01E11.17|87nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=25|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|167nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|189nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|195nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|340nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=947|total_reads(53.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|344nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=74|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|351nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|362nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=683|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219373|F01E11.18|398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219374|C25A11.10|470nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219374|C25A11.10|473nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219375|C02B8.12|95nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=197|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219375|C02B8.12|98nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|107nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|134nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|165nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|97nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=96|total_reads(34.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219376|C28G1.10|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(14.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219378|F43G6.17a|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219378|F43G6.17a|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=182|total_reads(97.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219381|C47A10.16|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219383|Y61B8A.6|190nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219394|Y48A6C.8|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219394|Y48A6C.8|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219394|Y48A6C.8|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=745|total_reads(87.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219394|Y48A6C.8|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219394|Y48A6C.8|54nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219395|M199.134|86nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219399|Y55F3AM.21a|73nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=101|total_reads(46.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219399|Y55F3AM.21a|78nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=112|total_reads(51.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219399|Y55F3AM.21a|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219410|C04C3.14|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(36.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219410|C04C3.14|65nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219412|ZK381.62|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00219412|ZK381.62|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=625|total_reads(98%)
- ID=WBGene00219413|Y38F2AL.12|678nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=12|total_reads(10.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219413|Y38F2AL.12|681nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219413|Y38F2AL.12|685nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219413|Y38F2AL.12|718nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=85|total_reads(75.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219414|F14H3.15|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(88.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219414|F14H3.15|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(11.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219418|F44D12.19|40nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219420|T19C4.24|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=66|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00219420|T19C4.24|43nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=20|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219420|T19C4.24|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219421|Y66D12A.30|150nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00219421|Y66D12A.30|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219421|Y66D12A.30|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(55.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219421|Y66D12A.30|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(9.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219422|Y52B11A.20a|108nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(10.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219422|Y52B11A.20a|187nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(58.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219422|Y52B11A.20a|195nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(31.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219423|C23H5.15|160nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219423|C23H5.15|162nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00219423|C23H5.15|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219423|C23H5.15|87nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=756|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219423|C23H5.15|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=28|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00219423|C23H5.15|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219424|Y54G2A.72|31nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=47|total_reads(46.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219424|Y54G2A.72|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(32.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219424|Y54G2A.72|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219434|F54D5.23|292nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219436|C49H3.16|96nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=271|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219443|Y57G11C.1144|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=40|total_reads(85.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219443|Y57G11C.1144|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(14.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219445|C06H5.12|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219447|C06H5.14|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219447|C06H5.14|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=239|total_reads(94.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219449|Y38A10A.11|154nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219449|Y38A10A.11|157nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(63.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219449|Y38A10A.11|160nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(18.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219449|Y38A10A.11|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219450|F53B6.13|115nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(37%)
- ID=WBGene00219450|F53B6.13|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(63%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|397nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=35|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|400nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=226|total_reads(34.9%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|411nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|415nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(22.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|423nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(22.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|425nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|428nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00219451|F52D2.12|431nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00219452|F21D9.11a|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219454|C26H9A.3|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(21.7%)
- ID=WBGene00219454|C26H9A.3|914nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(26.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219454|C26H9A.3|919nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(52.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219455|Y43F8B.29|1398nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219456|ZK822.10|38nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=14|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219460|K09H9.9|40nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=143|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219476|D1046.16|212nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219478|Y105C5B.1418|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219491|Y53F4B.62b|17nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(19.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219491|Y53F4B.62b|24nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00219491|Y53F4B.62b|5nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(30.8%)
- ID=WBGene00219493|C18D4.12|347nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=637|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219544|C17G1.14|888nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219547|T06A10.106|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=208|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219750|Y38C1AA.19|344nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00219796|C03D6.9|1495nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(24%)
- ID=WBGene00219796|C03D6.9|1501nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00219796|C03D6.9|1504nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=64|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00219796|C03D6.9|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=328|total_reads(62.6%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1225nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1247nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1265nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1276nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=81|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1279nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(9.4%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1291nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1302nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1322nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(12.9%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1341nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|1365nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00220249|R144.19|203nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00220250|C09B9.85|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00220250|C09B9.85|241nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=79|total_reads(94%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|1528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=53|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1041|total_reads(57.6%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=46|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=108|total_reads(6%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=504|total_reads(27.9%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|864nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00220257|C02H6.3|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00220258|C50C3.19|1597nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00220258|C50C3.19|1600nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=230|total_reads(41.7%)
- ID=WBGene00220258|C50C3.19|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00220258|C50C3.19|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=119|total_reads(21.6%)
- ID=WBGene00220258|C50C3.19|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=157|total_reads(28.5%)
- ID=WBGene00220258|C50C3.19|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00220259|ZK418.13|133nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00220259|ZK418.13|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00220259|ZK418.13|32nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=220|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|1170nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|1180nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|1313nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|1350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|1358nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|44nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|48nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(2%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|51nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=226|total_reads(63.5%)
- ID=WBGene00220261|ZC434.10|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(5.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235090|C38D9.13|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=153|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235092|C54F6.17|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235092|C54F6.17|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(47.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235092|C54F6.17|59nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=99|total_reads(42.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235092|C54F6.17|86nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(5.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|49nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|528nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=22|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|548nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|689nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|694nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=39|total_reads(8.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|696nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|699nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235093|C54F6.18|970nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=288|total_reads(66.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|194nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|197nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=47|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|200nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=111|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|202nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=18|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=611|total_reads(18%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|44nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=2477|total_reads(72.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|48nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=38|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|78nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235094|K08D9.9|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235095|B0035.21|116nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235095|B0035.21|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(24.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235095|B0035.21|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=147|total_reads(68.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235095|B0035.21|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(3.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|1049nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|119nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|139nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|1400nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|149nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|52nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1299|total_reads(14.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|56nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=412|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|67nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1643|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|72nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=4036|total_reads(44.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=382|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=41|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=496|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=636|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00235102|Y54G2A.75|98nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235110|T14G12.12|79nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=19|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235113|ZK105.12|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235114|ZK105.13|1541nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(18.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235114|ZK105.13|1557nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(20.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235114|ZK105.13|28nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00235114|ZK105.13|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(11.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235118|K04A8.18|1065nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(36.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235118|K04A8.18|1152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235129|ZC518.8a|212nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00235129|ZC518.8a|90nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(26.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235129|ZC518.8a|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235132|ZK792.12|1345nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(30%)
- ID=WBGene00235132|ZK792.12|1584nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(43.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235132|ZK792.12|856nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(26.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235133|T26H5.14|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=501|total_reads(79.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235133|T26H5.14|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(12.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235133|T26H5.14|62nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=50|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00235158|Y37E3.30|377nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=285|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|128nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|133nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=50|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|137nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|142nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|144nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|148nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|152nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=17|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|157nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1533|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|29nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|337nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=245|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|45nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=100|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|483nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6349|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=556216|total_reads(98.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|69nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=596|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|72nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|7nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|80nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235164|K09F6.13|85nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=42|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235254|F49D11.14|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=259|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235254|F49D11.14|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235254|F49D11.14|819nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|1227nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|1531nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=66|total_reads(11.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|22nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|2nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|30nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=56|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|35nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=383|total_reads(66.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|481nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=16|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235256|Y54G11A.19|489nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235257|T05C7.4|253nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235257|T05C7.4|322nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=92|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235257|T05C7.4|324nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|1104nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|1594nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|677nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|704nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|719nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=15|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|724nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=710|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|728nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=93|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|730nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=125|total_reads(12.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|735nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235260|T05C7.7|742nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00235263|Y66H1A.8a|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(5.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235263|Y66H1A.8a|136nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=152|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235264|M04G7.5|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(71.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235264|M04G7.5|74nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(28.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235267|Y77E11A.23|271nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=64|total_reads(83.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235267|Y77E11A.23|81nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=13|total_reads(16.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235268|Y54G2A.76|101nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=158|total_reads(13.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235268|Y54G2A.76|109nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=963|total_reads(82.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235268|Y54G2A.76|89nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=29|total_reads(2.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235268|Y54G2A.76|94nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00235269|F59E12.15|111nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=70|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235269|F59E12.15|114nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=52|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235269|F59E12.15|117nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2740|total_reads(72.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235269|F59E12.15|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=869|total_reads(23.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235269|F59E12.15|124nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235269|F59E12.15|60nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235269|F59E12.15|64nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235271|C49C8.8|101nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00235271|C49C8.8|88nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=11|total_reads(27.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235271|C49C8.8|93nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(47.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235273|T11F8.12|1001nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=28|total_reads(12.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235273|T11F8.12|123nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235273|T11F8.12|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(3.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235273|T11F8.12|47nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=187|total_reads(81.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235274|C54E4.12a|1312nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(5.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235274|C54E4.12a|303nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=96|total_reads(69.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235274|C54E4.12a|308nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(24.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235275|T09A12.8|396nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235277|T04C4.3|75nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(38.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235277|T04C4.3|80nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=11|total_reads(35.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235277|T04C4.3|87nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(25.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235279|Y67D8C.22b|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=111|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235280|F42A9.17|33nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235280|F42A9.17|38nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=79|total_reads(36.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235280|F42A9.17|40nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=91|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235280|F42A9.17|45nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=38|total_reads(17.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235280|F42A9.17|55nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235283|Y55F3BL.6|6nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=57|total_reads(31.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235283|Y55F3BL.6|8nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=122|total_reads(68.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|1369nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(15.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|1380nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|1392nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|1398nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|1429nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=7|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|1434nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|653nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(7.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|673nt|PAS=aacgaa|coverage=18|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235284|T12G3.11|77nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(11.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235285|F56D6.18|50nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=102|total_reads(77.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235285|F56D6.18|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(15.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235285|F56D6.18|92nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(7.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235288|Y69A2AR.46|102nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235288|Y69A2AR.46|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235288|Y69A2AR.46|98nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235290|Y59H11AR.10|37nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=250|total_reads(82.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235290|Y59H11AR.10|65nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(6.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235290|Y59H11AR.10|680nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(8.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235290|Y59H11AR.10|688nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|10nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=13|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|111nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|1127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|1136nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|1230nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=38|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|1405nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|145nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=51|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|251nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|254nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|269nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=955|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|272nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|281nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|288nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17218|total_reads(90.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|294nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=682|total_reads(3.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|330nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|64nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|79nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235291|C01G5.25|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0%)
- ID=WBGene00235293|F56D6.19|81nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=624|total_reads(96.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235293|F56D6.19|85nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(3.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235294|Y69A2AR.47|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=424|total_reads(72.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235294|Y69A2AR.47|132nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235294|Y69A2AR.47|34nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235294|Y69A2AR.47|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235294|Y69A2AR.47|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=114|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235294|Y69A2AR.47|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(3.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235295|C42D4.19|1134nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235295|C42D4.19|362nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00235295|C42D4.19|495nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(24.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235295|C42D4.19|498nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235296|C07G1.15|803nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235296|C07G1.15|83nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=327|total_reads(95.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235296|C07G1.15|89nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235297|F56D6.20|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=845|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235298|F19B6.10|119nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=31|total_reads(86.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235298|F19B6.10|123nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(13.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235300|T06A10.107|67nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235300|T06A10.107|72nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=413|total_reads(90.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235300|T06A10.107|75nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235300|T06A10.107|77nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(4.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235301|B0513.90|1335nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00235301|B0513.90|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(22%)
- ID=WBGene00235301|B0513.90|88nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00235302|C07C7.3|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(21.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235302|C07C7.3|21nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=66|total_reads(78.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235303|T13A10.64|285nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235303|T13A10.64|46nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=668|total_reads(98.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235304|Y116A8C.468|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=332|total_reads(94.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235304|Y116A8C.468|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(5.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235305|Y116A8C.469|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=240|total_reads(80.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235305|Y116A8C.469|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=16|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235305|Y116A8C.469|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=43|total_reads(14.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235306|W03D2.13a|350nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235306|W03D2.13a|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=846|total_reads(92.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235306|W03D2.13a|69nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(2.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235306|W03D2.13a|71nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=37|total_reads(4%)
- ID=WBGene00235308|C37C3.17|49nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=188|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235309|F21C10.17|1469nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235309|F21C10.17|1532nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235309|F21C10.17|169nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(16.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235309|F21C10.17|848nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00235309|F21C10.17|857nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=16|total_reads(22.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235309|F21C10.17|882nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235309|F21C10.17|893nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(9.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|126nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|202nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|258nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(8.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|61nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=222|total_reads(53.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|71nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=74|total_reads(17.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|74nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(7.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|77nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235310|R02D1.2|79nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=23|total_reads(5.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235311|Y57E12B.11|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00235311|Y57E12B.11|47nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=133|total_reads(93%)
- ID=WBGene00235312|F28A12.10|44nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1066|total_reads(97.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235312|F28A12.10|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235312|F28A12.10|85nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=18|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235313|C25E10.17b|22nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00235313|C25E10.17b|27nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=707|total_reads(90.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235313|C25E10.17b|326nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235313|C25E10.17b|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(2.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235313|C25E10.17b|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235315|Y50D4A.10|125nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=379|total_reads(47.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235315|Y50D4A.10|128nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=33|total_reads(4.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235315|Y50D4A.10|139nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235315|Y50D4A.10|142nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=56|total_reads(7%)
- ID=WBGene00235315|Y50D4A.10|146nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=54|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235315|Y50D4A.10|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=257|total_reads(32.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235315|Y50D4A.10|152nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235316|B0222.15|93nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=198|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235320|R02F11.11|66nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=407|total_reads(93.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235320|R02F11.11|69nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=27|total_reads(6.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235321|Y73C8B.9|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=24|total_reads(58.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235321|Y73C8B.9|53nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(17.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235321|Y73C8B.9|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235322|F32F2.4|34nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|113nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=8|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|121nt|PAS=aaugag|coverage=9|total_reads(1.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|164nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|169nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=254|total_reads(38%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|171nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=131|total_reads(19.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|179nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=12|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|181nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|183nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=29|total_reads(4.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|186nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|188nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|220nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|229nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=87|total_reads(13%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|624nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|928nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(6.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235325|C08D8.7|99nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=15|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235326|F22F7.11|295nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=53|total_reads(29.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235326|F22F7.11|297nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=107|total_reads(58.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235326|F22F7.11|304nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235326|F22F7.11|683nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235326|F22F7.11|849nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(6.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235328|T06E4.21.1|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=33|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235330|F21C10.18|1543nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235330|F21C10.18|29nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=310|total_reads(88.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235330|F21C10.18|32nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235330|F21C10.18|352nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235330|F21C10.18|36nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(2.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235330|F21C10.18|778nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235330|F21C10.18|814nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235332|K04A8.20|127nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235332|K04A8.20|16nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(6.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235332|K04A8.20|19nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(19.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235332|K04A8.20|39nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=34|total_reads(28.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235332|K04A8.20|42nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=45|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235339|F14F8.15|269nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=18|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235340|C45G7.13|167nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=85|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235342|Y69A2AR.50|113nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=243|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235343|Y69A2AR.51|22nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235343|Y69A2AR.51|24nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(9.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235343|Y69A2AR.51|56nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(31.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235343|Y69A2AR.51|64nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=12|total_reads(12.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235343|Y69A2AR.51|84nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(7.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235343|Y69A2AR.51|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=27|total_reads(28.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235350|Y54G2A.77|135nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00235350|Y54G2A.77|175nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(50%)
- ID=WBGene00235351|C32B5.18|186nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(47.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235351|C32B5.18|191nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=25|total_reads(52.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235352|ZK250.13.1|54nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=34|total_reads(44.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235352|ZK250.13.1|60nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235352|ZK250.13.1|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(6.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235352|ZK250.13.1|77nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=24|total_reads(31.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235354|ZK250.14|189nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=9|total_reads(29%)
- ID=WBGene00235354|ZK250.14|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=22|total_reads(71%)
- ID=WBGene00235359|F56D6.22|18nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=504|total_reads(92%)
- ID=WBGene00235359|F56D6.22|22nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=44|total_reads(8%)
- ID=WBGene00235361|F56D6.23|27nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=19|total_reads(31.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235361|F56D6.23|947nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=41|total_reads(68.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235363|F49F1.2|50nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(9.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235363|F49F1.2|55nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=91|total_reads(90.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235364|F49F1.4|66nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(74.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235364|F49F1.4|68nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(25.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235365|F49F1.15|51nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=169|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235367|F49F1.17|205nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=26|total_reads(81.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235367|F49F1.17|209nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(18.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235368|F49F1.18|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235371|F30B5.11|57nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=17|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235374|R11E3.19|30nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=10|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|1124nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|130nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|138nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|141nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|183nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|214nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=128|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|224nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=93|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|226nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=30|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|233nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=24|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|33nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|37nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=207|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|39nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=584|total_reads(14%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|41nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1187|total_reads(28.4%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|52nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=1612|total_reads(38.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|54nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=97|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|59nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|71nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|75nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=21|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|82nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=32|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=40|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00235380|C24D10.49|95nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235383|ZK616.65b|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00235383|ZK616.65b|38nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00235383|ZK616.65b|42nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=293|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00235383|ZK616.65b|45nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(3.2%)
- ID=WBGene00235391|F38A5.22|28nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=9|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00235391|F38A5.22|48nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=36|total_reads(4.5%)
- ID=WBGene00235391|F38A5.22|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=755|total_reads(94.4%)
- ID=WBGene00236786|C17H12.37|1366nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(10.5%)
- ID=WBGene00236786|C17H12.37|1408nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=5|total_reads(5.3%)
- ID=WBGene00236786|C17H12.37|52nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=60|total_reads(63.2%)
- ID=WBGene00236786|C17H12.37|56nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=20|total_reads(21.1%)
- ID=WBGene00236789|Y18H1A.18|14nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=49|total_reads(9.2%)
- ID=WBGene00236789|Y18H1A.18|16nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=126|total_reads(23.7%)
- ID=WBGene00236789|Y18H1A.18|23nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=347|total_reads(65.2%)
- ID=WBGene00236789|Y18H1A.18|53nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=10|total_reads(1.9%)
- ID=WBGene00236806|D2024.18|268nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(53.8%)
- ID=WBGene00236806|D2024.18|522nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=6|total_reads(46.2%)
- ID=WBGene00236808|C54G6.8|14nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=161|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|104nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1071|total_reads(39.9%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|1201nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=26|total_reads(1%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|123nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=56|total_reads(2.1%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|1308nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|80nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=12|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|83nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00249815|F20D12.12|97nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1492|total_reads(55.6%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|116nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|122nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=31|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|130nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=27|total_reads(1.2%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|137nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|184nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|207nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(0.5%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|62nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=18|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|66nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=14|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|74nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|88nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=268|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|91nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=1787|total_reads(79.3%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|93nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00249817|F42G8.19|96nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=61|total_reads(2.7%)
- ID=WBGene00255375|F08B4.8|24nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=19|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00255375|F08B4.8|27nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00255375|F08B4.8|30nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.1%)
- ID=WBGene00255375|F08B4.8|57nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11907|total_reads(99.7%)
- ID=WBGene00255420|Y51F10.15|623nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(25.9%)
- ID=WBGene00255420|Y51F10.15|722nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(74.1%)
- ID=WBGene00255457|F23C8.14b|76nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=344|total_reads(78.5%)
- ID=WBGene00255457|F23C8.14b|80nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=94|total_reads(21.5%)
- ID=WBGene00255469|C25G4.17|174nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=21|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00255522|Y57G11B.223|37nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=21|total_reads(75%)
- ID=WBGene00255522|Y57G11B.223|460nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(25%)
- ID=WBGene00255550|W03D8.14|29nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00255594|Y48G1BL.8|149nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=356|total_reads(98.6%)
- ID=WBGene00255594|Y48G1BL.8|166nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(1.4%)
- ID=WBGene00255595|D1046.18.2|14nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=134|total_reads(4.6%)
- ID=WBGene00255595|D1046.18.2|18nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=146|total_reads(5%)
- ID=WBGene00255595|D1046.18.2|21nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=2548|total_reads(86.9%)
- ID=WBGene00255595|D1046.18.2|30nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=76|total_reads(2.6%)
- ID=WBGene00255595|D1046.18.2|33nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(0.4%)
- ID=WBGene00255595|D1046.18.2|924nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00255595|D1046.18.2|968nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00255598|BE0003N10.6e|38nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=187|total_reads(37.5%)
- ID=WBGene00255598|BE0003N10.6e|41nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=122|total_reads(24.4%)
- ID=WBGene00255598|BE0003N10.6e|43nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=190|total_reads(38.1%)
- ID=WBGene00255600|F54H5.14|58nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=14|total_reads(11.9%)
- ID=WBGene00255600|F54H5.14|61nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=83|total_reads(70.3%)
- ID=WBGene00255600|F54H5.14|63nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=11|total_reads(9.3%)
- ID=WBGene00255600|F54H5.14|70nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=10|total_reads(8.5%)
- ID=WBGene00255605|T23B3.8|108nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=11|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00255605|T23B3.8|114nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00255605|T23B3.8|1243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00255605|T23B3.8|1250nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=887|total_reads(89.7%)
- ID=WBGene00255605|T23B3.8|1255nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=7|total_reads(0.7%)
- ID=WBGene00255605|T23B3.8|127nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=23|total_reads(2.3%)
- ID=WBGene00255605|T23B3.8|131nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=31|total_reads(3.1%)
- ID=WBGene00255607|F22H10.11|353nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=5|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00255611|Y116A8C.470|32nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=30|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00255702|C06A12.19|1149nt|PAS=gauaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(18.2%)
- ID=WBGene00255702|C06A12.19|34nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=27|total_reads(81.8%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|105nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=20|total_reads(5.4%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|112nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|199nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=75|total_reads(20.4%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|208nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=103|total_reads(28%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|212nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=135|total_reads(36.7%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|233nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=6|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|84nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=13|total_reads(3.5%)
- ID=WBGene00255704|B0348.10|91nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=8|total_reads(2.2%)
- ID=WBGene00255714|B0511.19|239nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=1415|total_reads(93.3%)
- ID=WBGene00255714|B0511.19|243nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(0.6%)
- ID=WBGene00255714|B0511.19|327nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=71|total_reads(4.7%)
- ID=WBGene00255714|B0511.19|333nt|PAS=aaugaa|coverage=22|total_reads(1.5%)
- ID=WBGene00255731|T02B11.11|54nt|PAS=AAUAAA|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00255733|T02B11.13|15nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=9|total_reads(100%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|102nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=953|total_reads(41.6%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|107nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=754|total_reads(32.9%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|118nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=113|total_reads(4.9%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|1497nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=42|total_reads(1.8%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|1515nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=26|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|1533nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=36|total_reads(1.6%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|1554nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=19|total_reads(0.8%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|1575nt|PAS=aagaaa|coverage=8|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|1585nt|PAS=aaaaaa|coverage=6|total_reads(0.3%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|86nt|PAS=n/a|coverage=5|total_reads(0.2%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|94nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=25|total_reads(1.1%)
- ID=WBGene00268196|F59A7.14|99nt|PAS=uauaaa|coverage=303|total_reads(13.2%)
- Locus
- name
- Name=AC8.13
- Name=AC8.13a
- Name=AC8.8
- Name=AC8.8a
- Name=AH9.5
- Name=AH9.5b
- Name=B0034.6
- Name=B0034.6b
- Name=B0035.17
- Name=B0035.17a
- Name=B0035.17b
- Name=B0286.7
- Name=B0286.7a
- Name=B0286.7b
- Name=B0361.12
- Name=B0361.12a
- Name=B0361.12b
- Name=B0395.4
- Name=B0395.4a
- Name=B0395.4b
- Name=C01B12.11
- Name=C01B12.11a
- Name=C01B12.11b
- Name=C01B12.12
- Name=C01B12.12a
- Name=C01B12.12b
- Name=C04E12.13
- Name=C04E12.13b
- Name=C04F6.6
- Name=C04F6.6a
- Name=C05G5.6
- Name=C05G5.6.1
- Name=C05G5.6.2
- Name=C05G5.6.3
- Name=C05G5.6a
- Name=C05G5.6b
- Name=C06A6.6
- Name=C06A6.6a
- Name=C06A6.6b
- Name=C06H2.8
- Name=C06H2.8a
- Name=C07B3.1
- Name=C07B3.1a
- Name=C09B9.86
- Name=C09B9.86a
- Name=C09B9.86b
- Name=C11D2.102
- Name=C11D2.102b
- Name=C11H1.12
- Name=C11H1.12.1
- Name=C11H1.12a
- Name=C11H1.12b
- Name=C12C8.4
- Name=C12C8.4a
- Name=C12C8.4b
- Name=C13B4.3
- Name=C13B4.3a
- Name=C13B4.3b
- Name=C14A11.8
- Name=C14A11.8b
- Name=C14E2.8
- Name=C14E2.8a
- Name=C16H3.5
- Name=C16H3.5a
- Name=C16H3.5b
- Name=C16H3.8
- Name=C16H3.8a
- Name=C16H3.8b
- Name=C18A11.8
- Name=C18A11.8a
- Name=C18A11.8b
- Name=C18D11.11
- Name=C18D11.11a
- Name=C18D11.11b
- Name=C23G10.13
- Name=C23G10.13a
- Name=C23G10.13b
- Name=C24H12.16
- Name=C24H12.16a
- Name=C24H12.16b
- Name=C24H12.17
- Name=C24H12.17a
- Name=C24H12.17b
- Name=C27A12.13
- Name=C27A12.13a
- Name=C28D4.16
- Name=C28D4.16a
- Name=C28D4.16b
- Name=C29E6.7
- Name=C29E6.7a
- Name=C29E6.7b
- Name=C31B8.17
- Name=C31B8.17a
- Name=C31B8.17b
- Name=C32C4.6
- Name=C32C4.6a
- Name=C32C4.6b
- Name=C32D5.13
- Name=C32D5.13a
- Name=C32D5.13b
- Name=C34E11.5
- Name=C34E11.5a
- Name=C34E11.5b
- Name=C34E11.6
- Name=C34E11.6a
- Name=C34E11.6b
- Name=C39D10.10
- Name=C39D10.10a
- Name=C39D10.10b
- Name=C39D10.12
- Name=C39D10.12a
- Name=C39D10.12b
- Name=C39D10.18
- Name=C39D10.18a
- Name=C39D10.18b
- Name=C39E6.7
- Name=C39E6.7a
- Name=C39E6.7b
- Name=C39E6.8
- Name=C39E6.8a
- Name=C39E6.8b
- Name=C41G7.14
- Name=C41G7.14a
- Name=C44B11.5
- Name=C44B11.5a
- Name=C44B11.5b
- Name=C44C11.7
- Name=C44C11.7a
- Name=C44C11.7b
- Name=C46A5.10
- Name=C46A5.10a
- Name=C46A5.10b
- Name=C46F2.2
- Name=C46F2.2a
- Name=C46F2.2b
- Name=C50H11.19
- Name=C50H11.19a
- Name=C50H11.19b
- Name=C52E12.7
- Name=C52E12.7a
- Name=C52E12.7b
- Name=C54G10.6
- Name=C54G10.6.1
- Name=C54G10.6a
- Name=C54G10.6b
- Name=C55B6.8
- Name=C55B6.8a
- Name=C55B6.8b
- Name=D1007.17
- Name=D1007.17a
- Name=E01F3.2
- Name=E01F3.2b
- Name=E01G4.9
- Name=E01G4.9b
- Name=EGAP1.2
- Name=EGAP1.2a
- Name=EGAP1.2b
- Name=F07A11.16
- Name=F07A11.16a
- Name=F07A11.16b
- Name=F07A11.8
- Name=F07A11.8a
- Name=F07A11.8b
- Name=F08F3.11
- Name=F08F3.11a
- Name=F08F3.11b
- Name=F08G12.12
- Name=F08G12.12a
- Name=F08G12.12b
- Name=F09A5.5
- Name=F09A5.5a
- Name=F09A5.5b
- Name=F09A5.6
- Name=F09A5.6a
- Name=F09A5.6b
- Name=F09A5.8
- Name=F09A5.8a
- Name=F09A5.8b
- Name=F10C2.8
- Name=F10C2.8a
- Name=F10C2.8b
- Name=F13D11.5
- Name=F13D11.5a
- Name=F13D11.5b
- Name=F13H10.7
- Name=F13H10.7a
- Name=F13H10.7b
- Name=F16A11.4
- Name=F16A11.4a
- Name=F16A11.4b
- Name=F18E9.9
- Name=F18E9.9b
- Name=F19C6.6
- Name=F19C6.6a
- Name=F19C6.6b
- Name=F20D1.11
- Name=F20D1.11a
- Name=F20D1.11b
- Name=F21A9.4
- Name=F21A9.4a
- Name=F21A9.4b
- Name=F22D3.9
- Name=F22D3.9.1
- Name=F22D3.9a
- Name=F22D3.9b
- Name=F22F1.4
- Name=F22F1.4a
- Name=F22F1.4b
- Name=F25D1.6
- Name=F25D1.6a
- Name=F25D1.6b
- Name=F25G6.10
- Name=F25G6.10a
- Name=F25G6.10b
- Name=F25G6.11
- Name=F25G6.11a
- Name=F25G6.11b
- Name=F26H11.7
- Name=F26H11.7a
- Name=F26H11.7b
- Name=F31E3.11
- Name=F31E3.11a
- Name=F31E3.11b
- Name=F31E3.7
- Name=F31E3.7a
- Name=F31E3.7b
- Name=F33E2.9
- Name=F33E2.9a
- Name=F33E2.9b
- Name=F35F10.16
- Name=F35F10.16b
- Name=F35G12.13
- Name=F35G12.13a
- Name=F35G12.13b
- Name=F36A4.16
- Name=F36A4.16a
- Name=F36H1.7
- Name=F36H1.7a
- Name=F36H1.7b
- Name=F36H1.8
- Name=F36H1.8a
- Name=F36H1.8b
- Name=F36H12.64
- Name=F36H12.64a
- Name=F36H12.64b
- Name=F37B1.9
- Name=F37B1.9a
- Name=F37B1.9b
- Name=F39B1.2
- Name=F39B1.2a
- Name=F39B1.2b
- Name=F39E9.13
- Name=F39E9.13b
- Name=F41G3.23
- Name=F41G3.23a
- Name=F41G3.23b
- Name=F42G8.17
- Name=F42G8.17a
- Name=F44E7.11
- Name=F44E7.11a
- Name=F44E7.11b
- Name=F46A9.7
- Name=F46A9.7a
- Name=F46A9.7b
- Name=F46F2.8
- Name=F46F2.8a
- Name=F46F2.8b
- Name=F46G11.5
- Name=F46G11.5a
- Name=F46G11.5b
- Name=F49E12.11
- Name=F49E12.11a
- Name=F49E12.11b
- Name=F53G2.11
- Name=F53G2.11a
- Name=F53G2.11b
- Name=F53G2.9
- Name=F53G2.9a
- Name=F53G2.9b
- Name=F54B11.12
- Name=F54B11.12a
- Name=F54B11.12b
- Name=F55A11.12
- Name=F55A11.12a
- Name=F55A11.12b
- Name=F55A11.9
- Name=F55A11.9a
- Name=F55A11.9b
- Name=F55D12.7
- Name=F55D12.7a
- Name=F55D12.7b
- Name=F55F3.10
- Name=F55F3.10a
- Name=F55F3.10b
- Name=F55F3.11
- Name=F55F3.11a
- Name=F55F3.11b
- Name=F56A12.3
- Name=F56A12.3a
- Name=F56A12.3b
- Name=F56A12.4
- Name=F56A12.4a
- Name=F56A12.4b
- Name=F56C3.13
- Name=F56C3.13b
- Name=F59D6.8
- Name=F59D6.8a
- Name=F59D6.8b
- Name=F59D6.9
- Name=F59D6.9a
- Name=F59D6.9b
- Name=F59F3.7
- Name=F59F3.7a
- Name=F59G1.6
- Name=F59G1.6a
- Name=F59G1.6b
- Name=H25K10.142
- Name=H25K10.142a
- Name=K01A6.22
- Name=K01A6.22a
- Name=K01A6.22b
- Name=K01F9.1
- Name=K01F9.1a
- Name=K01F9.1b
- Name=K01F9.3
- Name=K01F9.3a
- Name=K01F9.3b
- Name=K01F9.5
- Name=K01F9.5a
- Name=K01F9.5b
- Name=K02B9.5
- Name=K02B9.5a
- Name=K02B9.5b
- Name=K02E7.13
- Name=K02E7.13a
- Name=K02E7.13b
- Name=K09A9.7
- Name=K09A9.7a
- Name=K09A9.7b
- Name=K09F6.12
- Name=K09F6.12a
- Name=K09F6.12b
- Name=K10C2.9
- Name=K10C2.9a
- Name=K10C2.9b
- Name=K12D12.10
- Name=K12D12.10a
- Name=K12D12.10b
- Name=LLC1.122
- Name=LLC1.122a
- Name=LLC1.122b
- Name=M01F1.11
- Name=M01F1.11a
- Name=M03B6.6
- Name=M03B6.6b
- Name=M04C9.7
- Name=M04C9.7a
- Name=M04C9.7b
- Name=M04C9.8
- Name=M04C9.8a
- Name=M04C9.8b
- Name=M106.9
- Name=M106.9a
- Name=M106.9b
- Name=R04A9.8
- Name=R04A9.8a
- Name=R04A9.8b
- Name=R05C11.6
- Name=R05C11.6a
- Name=R05C11.6b
- Name=R08C7.14
- Name=R08C7.14a
- Name=R08C7.14b
- Name=R11.5
- Name=R11.5a
- Name=R11.5b
- Name=R11.6
- Name=R11.6a
- Name=R11.6b
- Name=R13A5.14
- Name=R13A5.14a
- Name=R13A5.14b
- Name=T01B10.6
- Name=T01B10.6a
- Name=T01B10.6b
- Name=T01B6.12
- Name=T01B6.12.1
- Name=T01B6.12a
- Name=T01B6.12b
- Name=T04D1.5
- Name=T04D1.5a
- Name=T04D1.5b
- Name=T07A9.17
- Name=T07A9.17a
- Name=T07A9.17b
- Name=T07C5.6
- Name=T07C5.6b
- Name=T07D1.6
- Name=T07D1.6a
- Name=T07D1.6b
- Name=T07D1.7
- Name=T07D1.7a
- Name=T07D1.7b
- Name=T07D10.7
- Name=T07D10.7a
- Name=T07D10.7b
- Name=T07D10.9
- Name=T07D10.9a
- Name=T07D10.9b
- Name=T07H8.8
- Name=T07H8.8b
- Name=T09A5.13
- Name=T09A5.13a
- Name=T09A5.13b
- Name=T09B4.11
- Name=T09B4.11a
- Name=T09B4.11b
- Name=T09B4.12
- Name=T09B4.12a
- Name=T09B4.12b
- Name=T09B4.20
- Name=T09B4.20a
- Name=T09B4.20b
- Name=T09F5.21
- Name=T09F5.21a
- Name=T09F5.21b
- Name=T10H9.7
- Name=T10H9.7a
- Name=T10H9.7b
- Name=T11G6.10
- Name=T11G6.10a
- Name=T11G6.12
- Name=T11G6.12a
- Name=T11G6.12b
- Name=T12E12.7
- Name=T12E12.7a
- Name=T12E12.7b
- Name=T12E12.8
- Name=T12E12.8a
- Name=T12E12.8b
- Name=T14G12.7
- Name=T14G12.7a
- Name=T16G12.11
- Name=T16G12.11a
- Name=T16G12.11b
- Name=T19E7.28
- Name=T19E7.28b
- Name=T21B4.13
- Name=T21B4.13a
- Name=T21B4.13b
- Name=T21D12.13
- Name=T21D12.13a
- Name=T22A3.9
- Name=T22A3.9b
- Name=T22C1.13
- Name=T22C1.13.1
- Name=T22C1.13a
- Name=T22C1.13b
- Name=T23F6.6
- Name=T23F6.6b
- Name=T24D8.7
- Name=T24D8.7a
- Name=T24D8.7b
- Name=T24D8.8
- Name=T24D8.8a
- Name=T24D8.8b
- Name=T24D8.9
- Name=T24D8.9a
- Name=T24D8.9b
- Name=T26C12.5
- Name=T26C12.5b
- Name=T27D12.11
- Name=T27D12.11a
- Name=T27D12.11b
- Name=T27D12.5
- Name=T27D12.5a
- Name=T27D12.5b
- Name=T28F3.10
- Name=T28F3.10a
- Name=T28F3.10b
- Name=W02B12.14
- Name=W02B12.14a
- Name=W02B12.14b
- Name=W02B9.4
- Name=W02B9.4a
- Name=W02B9.4b
- Name=W03G11.5
- Name=W03G11.5a
- Name=W03G11.5b
- Name=W06F12.9
- Name=W06F12.9a
- Name=W06F12.9b
- Name=W08D2.14
- Name=W08D2.14b
- Name=W09C5.16
- Name=W09C5.16a
- Name=W09C5.16b
- Name=W09G3.10
- Name=W09G3.10a
- Name=W09G3.10b
- Name=W09G3.11
- Name=W09G3.11a
- Name=W09G3.11b
- Name=W09H1.8
- Name=W09H1.8a
- Name=WBGene00002285
- Name=WBGene00002993
- Name=WBGene00003039
- Name=WBGene00003088
- Name=WBGene00003260
- Name=WBGene00003261
- Name=WBGene00003262
- Name=WBGene00003263
- Name=WBGene00003264
- Name=WBGene00003265
- Name=WBGene00003266
- Name=WBGene00003267
- Name=WBGene00003268
- Name=WBGene00003269
- Name=WBGene00003270
- Name=WBGene00003271
- Name=WBGene00003272
- Name=WBGene00003273
- Name=WBGene00003274
- Name=WBGene00003275
- Name=WBGene00003277
- Name=WBGene00003278
- Name=WBGene00003279
- Name=WBGene00003280
- Name=WBGene00003281
- Name=WBGene00003282
- Name=WBGene00003283
- Name=WBGene00003284
- Name=WBGene00003285
- Name=WBGene00003286
- Name=WBGene00003287
- Name=WBGene00003288
- Name=WBGene00003289
- Name=WBGene00003290
- Name=WBGene00003291
- Name=WBGene00003292
- Name=WBGene00003293
- Name=WBGene00003294
- Name=WBGene00003295
- Name=WBGene00003298
- Name=WBGene00003299
- Name=WBGene00003300
- Name=WBGene00003301
- Name=WBGene00003302
- Name=WBGene00003303
- Name=WBGene00003304
- Name=WBGene00003305
- Name=WBGene00003306
- Name=WBGene00003307
- Name=WBGene00003308
- Name=WBGene00003309
- Name=WBGene00003310
- Name=WBGene00003311
- Name=WBGene00003312
- Name=WBGene00003313
- Name=WBGene00003314
- Name=WBGene00003315
- Name=WBGene00003318
- Name=WBGene00003319
- Name=WBGene00003321
- Name=WBGene00003322
- Name=WBGene00003323
- Name=WBGene00003324
- Name=WBGene00003325
- Name=WBGene00003326
- Name=WBGene00003327
- Name=WBGene00003328
- Name=WBGene00003329
- Name=WBGene00003330
- Name=WBGene00003331
- Name=WBGene00003332
- Name=WBGene00003333
- Name=WBGene00003334
- Name=WBGene00003335
- Name=WBGene00003336
- Name=WBGene00003337
- Name=WBGene00003338
- Name=WBGene00003339
- Name=WBGene00003340
- Name=WBGene00003341
- Name=WBGene00003342
- Name=WBGene00003343
- Name=WBGene00003344
- Name=WBGene00003345
- Name=WBGene00003346
- Name=WBGene00003347
- Name=WBGene00003348
- Name=WBGene00003349
- Name=WBGene00003350
- Name=WBGene00003351
- Name=WBGene00003352
- Name=WBGene00003353
- Name=WBGene00003354
- Name=WBGene00003355
- Name=WBGene00003356
- Name=WBGene00003357
- Name=WBGene00003358
- Name=WBGene00003359
- Name=WBGene00003360
- Name=WBGene00003361
- Name=WBGene00003362
- Name=WBGene00003363
- Name=WBGene00003364
- Name=WBGene00003365
- Name=WBGene00003366
- Name=WBGene00014391
- Name=WBGene00014534
- Name=WBGene00014612
- Name=WBGene00023452
- Name=WBGene00023453
- Name=WBGene00023454
- Name=WBGene00023455
- Name=WBGene00023456
- Name=WBGene00023457
- Name=WBGene00043991
- Name=WBGene00045324
- Name=WBGene00045325
- Name=WBGene00045326
- Name=WBGene00045327
- Name=WBGene00045328
- Name=WBGene00045329
- Name=WBGene00045330
- Name=WBGene00045341
- Name=WBGene00045342
- Name=WBGene00045343
- Name=WBGene00045350
- Name=WBGene00045351
- Name=WBGene00045352
- Name=WBGene00045353
- Name=WBGene00045354
- Name=WBGene00045358
- Name=WBGene00045359
- Name=WBGene00045360
- Name=WBGene00050921
- Name=WBGene00050922
- Name=WBGene00050923
- Name=WBGene00050924
- Name=WBGene00077705
- Name=WBGene00077706
- Name=WBGene00077707
- Name=WBGene00077708
- Name=WBGene00077709
- Name=WBGene00077715
- Name=WBGene00077716
- Name=WBGene00077717
- Name=WBGene00077718
- Name=WBGene00077719
- Name=WBGene00077720
- Name=WBGene00077721
- Name=WBGene00077722
- Name=WBGene00077723
- Name=WBGene00077725
- Name=WBGene00077726
- Name=WBGene00077727
- Name=WBGene00189969
- Name=WBGene00189970
- Name=WBGene00194802
- Name=WBGene00194804
- Name=WBGene00194805
- Name=WBGene00194806
- Name=WBGene00194807
- Name=WBGene00194808
- Name=WBGene00194809
- Name=WBGene00194810
- Name=WBGene00194822
- Name=WBGene00194823
- Name=WBGene00194824
- Name=WBGene00194825
- Name=WBGene00194826
- Name=WBGene00194827
- Name=WBGene00194828
- Name=WBGene00194829
- Name=WBGene00194830
- Name=WBGene00194831
- Name=WBGene00194840
- Name=WBGene00195007
- Name=WBGene00195008
- Name=WBGene00195236
- Name=WBGene00195238
- Name=WBGene00195833
- Name=WBGene00199918
- Name=WBGene00201935
- Name=WBGene00219219
- Name=WBGene00219220
- Name=WBGene00219221
- Name=WBGene00219222
- Name=WBGene00219223
- Name=WBGene00219224
- Name=WBGene00219225
- Name=WBGene00219226
- Name=WBGene00219227
- Name=WBGene00219228
- Name=WBGene00219229
- Name=WBGene00219230
- Name=WBGene00219231
- Name=WBGene00219232
- Name=WBGene00219233
- Name=WBGene00219245
- Name=WBGene00219246
- Name=WBGene00219247
- Name=WBGene00219248
- Name=WBGene00219249
- Name=WBGene00219250
- Name=WBGene00219251
- Name=WBGene00219252
- Name=WBGene00219253
- Name=WBGene00219254
- Name=WBGene00219255
- Name=WBGene00219256
- Name=WBGene00219257
- Name=WBGene00219258
- Name=WBGene00219259
- Name=WBGene00219260
- Name=WBGene00219261
- Name=WBGene00219262
- Name=WBGene00219263
- Name=WBGene00219264
- Name=WBGene00219265
- Name=WBGene00219266
- Name=WBGene00219267
- Name=WBGene00219269
- Name=WBGene00219270
- Name=WBGene00219810
- Name=WBGene00220055
- Name=WBGene00235080
- Name=WBGene00235084
- Name=WBGene00235085
- Name=WBGene00235087
- Name=WBGene00235088
- Name=WBGene00255560
- Name=WBGene00255561
- Name=WBGene00255562
- Name=WBGene00255563
- Name=WBGene00255564
- Name=WBGene00255565
- Name=WBGene00255566
- Name=WBGene00255567
- Name=WBGene00255568
- Name=WBGene00255569
- Name=WBGene00255570
- Name=WBGene00255571
- Name=WBGene00255572
- Name=WBGene00255573
- Name=WBGene00255574
- Name=WBGene00255575
- Name=WBGene00255576
- Name=WBGene00255577
- Name=WBGene00255578
- Name=WBGene00255579
- Name=WBGene00255580
- Name=WBGene00255581
- Name=WBGene00255582
- Name=WBGene00255583
- Name=WBGene00255584
- Name=WBGene00255586
- Name=WBGene00255587
- Name=WBGene00255588
- Name=Y102A5D.4
- Name=Y102A5D.4a
- Name=Y105C5A.1286
- Name=Y105C5A.1286a
- Name=Y105C5A.1286b
- Name=Y105E8A.31
- Name=Y105E8A.31a
- Name=Y105E8A.31b
- Name=Y105E8A.51
- Name=Y105E8A.51a
- Name=Y105E8A.51b
- Name=Y116A8C.464
- Name=Y116A8C.464a
- Name=Y116A8C.464b
- Name=Y23B4A.3
- Name=Y23B4A.3a
- Name=Y23B4A.3b
- Name=Y23H5B.14
- Name=Y23H5B.14a
- Name=Y23H5B.14b
- Name=Y37A1B.16
- Name=Y37A1B.16a
- Name=Y37A1B.16b
- Name=Y37B11A.6
- Name=Y37B11A.6a
- Name=Y37F4.9
- Name=Y37F4.9a
- Name=Y38E10A.27
- Name=Y38E10A.27a
- Name=Y38F2AR.22
- Name=Y38F2AR.22a
- Name=Y40H7A.12
- Name=Y40H7A.12b
- Name=Y41C4A.20
- Name=Y41C4A.20b
- Name=Y41E3.214
- Name=Y41E3.214b
- Name=Y41G9A.11
- Name=Y41G9A.11a
- Name=Y41G9A.11b
- Name=Y41G9A.7
- Name=Y41G9A.7a
- Name=Y41G9A.7b
- Name=Y41G9A.9
- Name=Y41G9A.9b
- Name=Y47H9C.21
- Name=Y47H9C.21a
- Name=Y47H9C.21b
- Name=Y48C3A.21
- Name=Y48C3A.21a
- Name=Y48C3A.21b
- Name=Y48D7A.3
- Name=Y48D7A.3a
- Name=Y48D7A.3b
- Name=Y48G9A.13
- Name=Y48G9A.13a
- Name=Y48G9A.13b
- Name=Y48G9A.14
- Name=Y48G9A.14a
- Name=Y48G9A.14b
- Name=Y48G9A.15
- Name=Y48G9A.15a
- Name=Y48G9A.15b
- Name=Y48G9A.16
- Name=Y48G9A.16a
- Name=Y48G9A.16b
- Name=Y50D4A.11
- Name=Y50D4A.11a
- Name=Y50D4A.11b
- Name=Y51A2D.39
- Name=Y51A2D.39a
- Name=Y51H4A.34
- Name=Y51H4A.34a
- Name=Y51H4A.34b
- Name=Y51H4A.402
- Name=Y51H4A.402a
- Name=Y53G8AL.5
- Name=Y53G8AL.5b
- Name=Y55F3AM.16
- Name=Y55F3AM.16a
- Name=Y55F3AM.16b
- Name=Y55F3AM.17
- Name=Y55F3AM.17a
- Name=Y55F3AM.17b
- Name=Y55F3AM.18
- Name=Y55F3AM.18a
- Name=Y55F3AM.18b
- Name=Y55F3AM.19
- Name=Y55F3AM.19a
- Name=Y55F3AM.19b
- Name=Y55F3AM.20
- Name=Y55F3AM.20a
- Name=Y55F3AM.20b
- Name=Y56A3A.34
- Name=Y56A3A.34a
- Name=Y56A3A.34b
- Name=Y56A3A.40
- Name=Y56A3A.40a
- Name=Y56A3A.40b
- Name=Y57A10A.42
- Name=Y57A10A.42a
- Name=Y57A10A.42b
- Name=Y59A8B.39
- Name=Y59A8B.39a
- Name=Y59A8B.39b
- Name=Y59E1B.10
- Name=Y59E1B.10b
- Name=Y59E1B.11
- Name=Y59E1B.11b
- Name=Y59E1B.12
- Name=Y59E1B.12b
- Name=Y59E1B.13
- Name=Y59E1B.13b
- Name=Y59E1B.15
- Name=Y59E1B.15a
- Name=Y59E1B.15b
- Name=Y59E1B.3
- Name=Y59E1B.3b
- Name=Y59E1B.4
- Name=Y59E1B.4a
- Name=Y59E1B.4b
- Name=Y59E1B.6
- Name=Y59E1B.6b
- Name=Y59E1B.7
- Name=Y59E1B.7a
- Name=Y59E1B.7b
- Name=Y59E1B.8
- Name=Y59E1B.8a
- Name=Y59E1B.8b
- Name=Y59E1B.9
- Name=Y59E1B.9b
- Name=Y62F5A.2
- Name=Y62F5A.2a
- Name=Y62F5A.2b
- Name=Y62F5A.3
- Name=Y62F5A.3a
- Name=Y62F5A.3b
- Name=Y62F5A.4
- Name=Y62F5A.4a
- Name=Y62F5A.4b
- Name=Y62F5A.5
- Name=Y62F5A.5a
- Name=Y62F5A.5b
- Name=Y62F5A.6
- Name=Y62F5A.6a
- Name=Y62F5A.6b
- Name=Y62F5A.7
- Name=Y62F5A.7a
- Name=Y62F5A.7b
- Name=Y62F5A.8
- Name=Y62F5A.8a
- Name=Y62F5A.8b
- Name=Y64G10A.14
- Name=Y64G10A.14b
- Name=Y67D8A.4
- Name=Y67D8A.4a
- Name=Y67D8A.4b
- Name=Y71A12B.20
- Name=Y71A12B.20a
- Name=Y71F9AL.22
- Name=Y71F9AL.22a
- Name=Y71F9AL.22b
- Name=Y71F9AL.23
- Name=Y71F9AL.23b
- Name=Y71G12B.29
- Name=Y71G12B.29a
- Name=Y71G12B.29b
- Name=Y73B6A.7
- Name=Y73B6A.7a
- Name=Y73B6A.7b
- Name=Y73B6BL.290
- Name=Y73B6BL.290a
- Name=Y73B6BL.290b
- Name=Y87G2A.21
- Name=Y87G2A.21a
- Name=Y87G2A.21b
- Name=ZK384.5
- Name=ZK384.5b
- Name=ZK455.9
- Name=ZK455.9a
- Name=ZK455.9b
- Name=ZK525.3
- Name=ZK525.3a
- Name=ZK525.3b
- Name=ZK593.10
- Name=ZK593.10a
- Name=ZK593.10b
- Name=ZK593.12
- Name=ZK593.12a
- Name=ZK593.12b
- Name=ZK652.12
- Name=ZK652.12a
- Name=ZK652.13
- Name=ZK652.13a
- Name=ZK652.13b
- Name=ZK84.8
- Name=ZK84.8a
- Name=ZK84.8b
- Name=ZK930.10
- Name=ZK930.10a
- Name=ZK930.10b
- Name=ZK930.11
- Name=ZK930.11a
- Name=ZK930.11b
- Name=ZK930.8
- Name=ZK930.8a
- Name=ZK930.8b
- Name=ZK930.9
- Name=ZK930.9a
- Name=ZK930.9b
- Operon
- Sequence
- Transcript
Viewing a Precise Region around a Landmark
You can view a precise region around a landmark using the notation
landmark:start..stop, where start and stop are
the start and stop positions of the sequence relative to the landmark.
The beginning of the feature is position 1. In the case of complex
features, such as genes, the "beginning" is defined by the database
administrator. For example, in the C. elegans data set,
position 1 of a predicted gene is the AUG at the beginning of the CDS,
so to view the region that begins 100 base pairs upstream of the AUG
ends 500 bases downstream of it, you would search for
mek-1:-99..500.
This offset notation will work correctly for negative strand features
as well as positive strand features. The coordinates are always
relative to the feature itself.
To offset relative to a qualified feature name, just include the type
name, as in PCR_Product:sjj_K08A8.1:-500..500 (note that this
particular example only works with the C. elegans database).
Searching for Keywords
Anything that you type into the "Landmark or Region" textbox that
isn't recognized as a landmark will be treated as a full text search
across the feature database. This will find comments or other feature
notations that match the typed text. Depending on how the database is
set up, you may find gene names, gene functions, author names, or
bibliographic references.
If successfull, the browser will present you with a list of possible
matching landmarks and their comments. You will then be asked to
select one y to view. To see this in action, try typing "kinase" into
the "Landmark or Region" box.

Once a region is displayed, you can navigate through it in a number of
ways:
- Scroll left or right with the <<, <,
> and >> buttons
- These buttons, which appear in the "Scroll/Zoom" section of the
screen, will scroll the detail panel to the left or right. The
<< and >> buttons scroll an entire
screen's worth, while < and >> scroll a
half screen.
- Zoom in or out using the "Show XXX Kbp" menu.
- Use menu that appears in the center of the "Scroll/Zoom" section
to change the zoom level. The menu item name indicates the
number of base pairs to show in the detail panel. For example,
selecting the item "100 Kbp" will zoom the detail panel so as
to show a region 100 Kbp wide.
- Make fine adjustments on the zoom level using the "-" and
"+" buttons.
- Press the - and + buttons to change the zoom level
by small increments (usually 10-20%, depending on how the
browser is configured).
 Recenter the detail panel by clicking on its scale
Recenter the detail panel by clicking on its scale
- The scale at the top of the detail panel is live. Clicking on
it will recenter the detail panel around the location you
clicked. This is a fast and easy way to make fine adjustments
in the displayed region.
- Get information on a feature by clicking on it
- Clicking on a feature in the detail view will link to a page
that displays more information about it. This could be a page on
the browser's web site, or a page on an external web site.
 Jump to a new region by clicking on the overview panel
Jump to a new region by clicking on the overview panel
- Click on the overview panel to immediately jump
to the corresponding region of the genome.
The detailed view is composed of a number of distinct tracks which
stretch horizontally from one end of the display to another. Each
track corresponds to a different type of genomic feature, and is
distinguished by a distinctive graphical shape and color.
The key to the tracks is shown at the bottom of the detail panel. For
more information on the source and nature of the track, click on the
track label in the "Search Settings" area (discussed below).
Customizing the Detail Panel
You can customize the detailed display in a number of ways:
- Turn tracks on and off using the "Search Settings" area
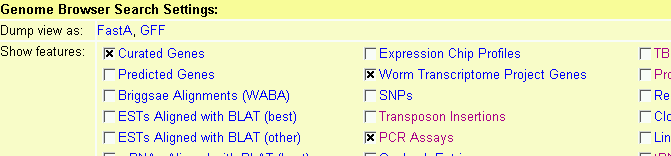
The panel labeled "Search Settings" contains a series of
checkboxes. Each checkbox corresponds to a track type. Selecting
the checkbox activates its type. Select the label to the
right of the checkbox to display a window that provides more
detailed information on the track, such the algorithm used to
generate it, its author, or citations.
- Change the properties of the tracks using the "Set Track Options" button
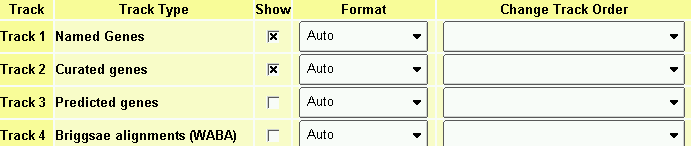
This will bring up a window that has detailed settings for each of the tracks.
Toggle the checkbox in the "Show" column to turn the track on
and off (this is the same as changing the checkbox in the Search
Settings area). Change the popup menu in the "Format" column to
alter the appearance of the corresponding track. Options include:
Compact which forces all items in the track onto a single overlapping line without
labels or descriptions; Expand, which causes items to bump each other so that
they don't collide; and Expand & Label, which causes items to be labeled
with their names and a brief description. The default, Auto will choose compact
mode if there are too many features on the track, or one of the expanded modes if there
is sufficient room. Any changes you make are remembered the next time you visit the browser.
Press Accept Changes and Return... when you are satisfied with the current options.
- Change the order of tracks using the "Set Track Options" button
- The last column of the track options window allows you to change the order of the
tracks. The popup menu lists all possible feature types in alphabetic order. Select
the feature type you wish to assign to the track. The window should refresh with the
adjusted order automatically, but if it doesn't, select the "Refresh" button to see the
new order.
This browser supports third party annotations, both your own private
annotations and published annotations contributed by third parties.
Uploading Your Own Annotations

To view your own annotations on the displayed genome, go to the bottom
of the screen and click on the Browse... button in the file
upload area. This will prompt you for a text file containing your
annotations. See the annotation format help document for information on
how to create this file.
Once loaded, tracks containing these annotations will appear on the
detailed display and you can control them just like any of the
built-in tracks. In addition new Edit, Delete and
Download buttons will appear in the file upload area. As their
names imply, these buttons allow you to edit the uploaded file,
download it, or delete it completely.
The date at which the uploaded file was created or last modified is
printed next to its name. If there are a manageable number of
annotated areas, GBrowse will create links that allow you to jump
directly to them.
You may upload as many files as you wish, but be advised that the
performance of the browser may decrease if there are many large
uploads to process.
Viewing 3d Party Annotations
To view 3d party annotations, the annotations must be published on a
reachable web server and you must know the annotation file's URL.
At the bottom of the browser window is a text box labeled "Enter
Remote Annotation URL". Type in the URL and then press "Update URLs".
The system will attempt to upload the indicated URL. If successful,
the data will appear as one or more new tracks. Otherwise you will
be alerted with an error message.
You may add as many remote URLs as you wish. To delete one, simply
erase it and press "Update URLs" again.
Another way to upload your own features is by adding an "add" argument
to the gbrowse URL. For example, this URL will create a track named
"MyDeletions" containing a feature named "Deletion3". Deletion3
occupies the region on chromosome 3 between 10,050,000 and 10,051,000:
https://tomato.biodesign.asu.edu/cgi-bin/gbrowse/celegans_WS250?add=chr3+MyDeletions+Deletion3+10050000..10051000
You can have as many "add" options as you like:
https://tomato.biodesign.asu.edu/cgi-bin/gbrowse/celegans_WS250?add=chr3+MyDeletions+Deletion3+10050000..10051000;add=chr3+MyDeletions+Deletion4+950000..960000
The format is:
reference+trackName+featureName+start..stop,start..stop,start..stop ...
where "reference" is the name of the landmark that start and stop are
relative to. You can use a chromosome name, a contig name, a gene
name, or anything else that this browser recognizes in the search
box. "trackName" is the name of the track to upload, "featureName" is
the name of the feature you are uploading, and "start..stop" are the
start and end coordinates relative to "reference". For multisegmented
features, specify multiple start..stop pairs separated by commas.
For more control over the way quick upload features appear, specify the "style" option to the URL:
https://tomato.biodesign.asu.edu/cgi-bin/gbrowse/celegans_WS250?style=MyDeletions+glyph=arrow+double=1+fgcolor=blue
This says to configure the "MyDeletions" track with the following options:
glyph=arrow
double=1
fgcolor=blue
See the uploaded annotation help
file for more details
.
As always, this software may contain bugs. Please report any that
you suspect to the author, along with whatever information that you can
provide as to what you were doing when the bug appeared.
Lincoln Stein <lstein@cshl.org>
Note: This page uses cookies to save and restore preference information.
No information is shared.
Generic genome browser version 1.70
 To select a region of the genome to view, enter its name in the text
field labeled "Landmark or Region". Recognized types of names are
under the control of the administrator, but usually the following
names are accepted:
To select a region of the genome to view, enter its name in the text
field labeled "Landmark or Region". Recognized types of names are
under the control of the administrator, but usually the following
names are accepted:
 To select a region of the genome to view, enter its name in the text
field labeled "Landmark or Region". Recognized types of names are
under the control of the administrator, but usually the following
names are accepted:
To select a region of the genome to view, enter its name in the text
field labeled "Landmark or Region". Recognized types of names are
under the control of the administrator, but usually the following
names are accepted:


 Recenter the detail panel by clicking on its scale
Recenter the detail panel by clicking on its scale
 Jump to a new region by clicking on the overview panel
Jump to a new region by clicking on the overview panel





